Mechanical and Thermal Characteristics of Cement Composites Containing PEDOT:PSS and Amorphous Metallic Fibers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
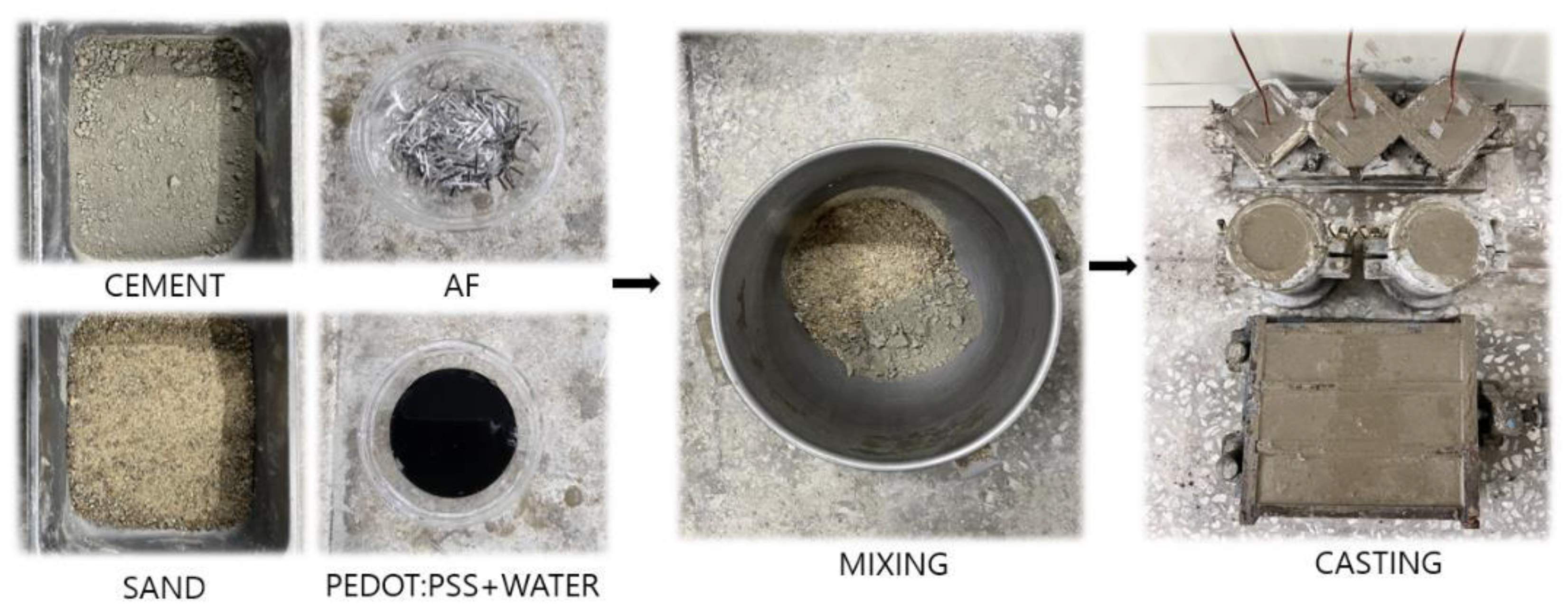
2.2. Mixing Proportions and Specimen Synthesis
3. Results and Discussion
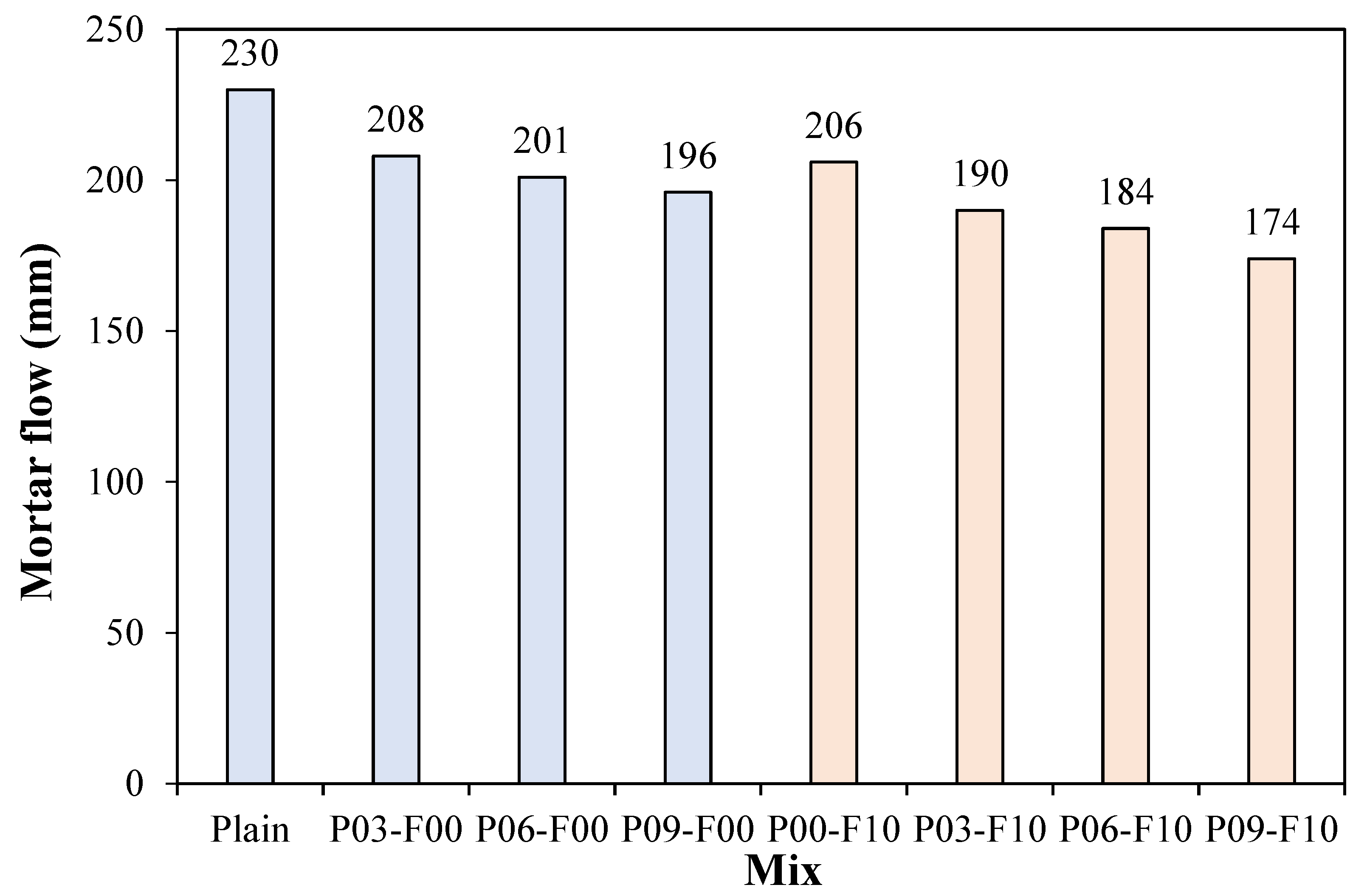
3.1. Mortar Flow
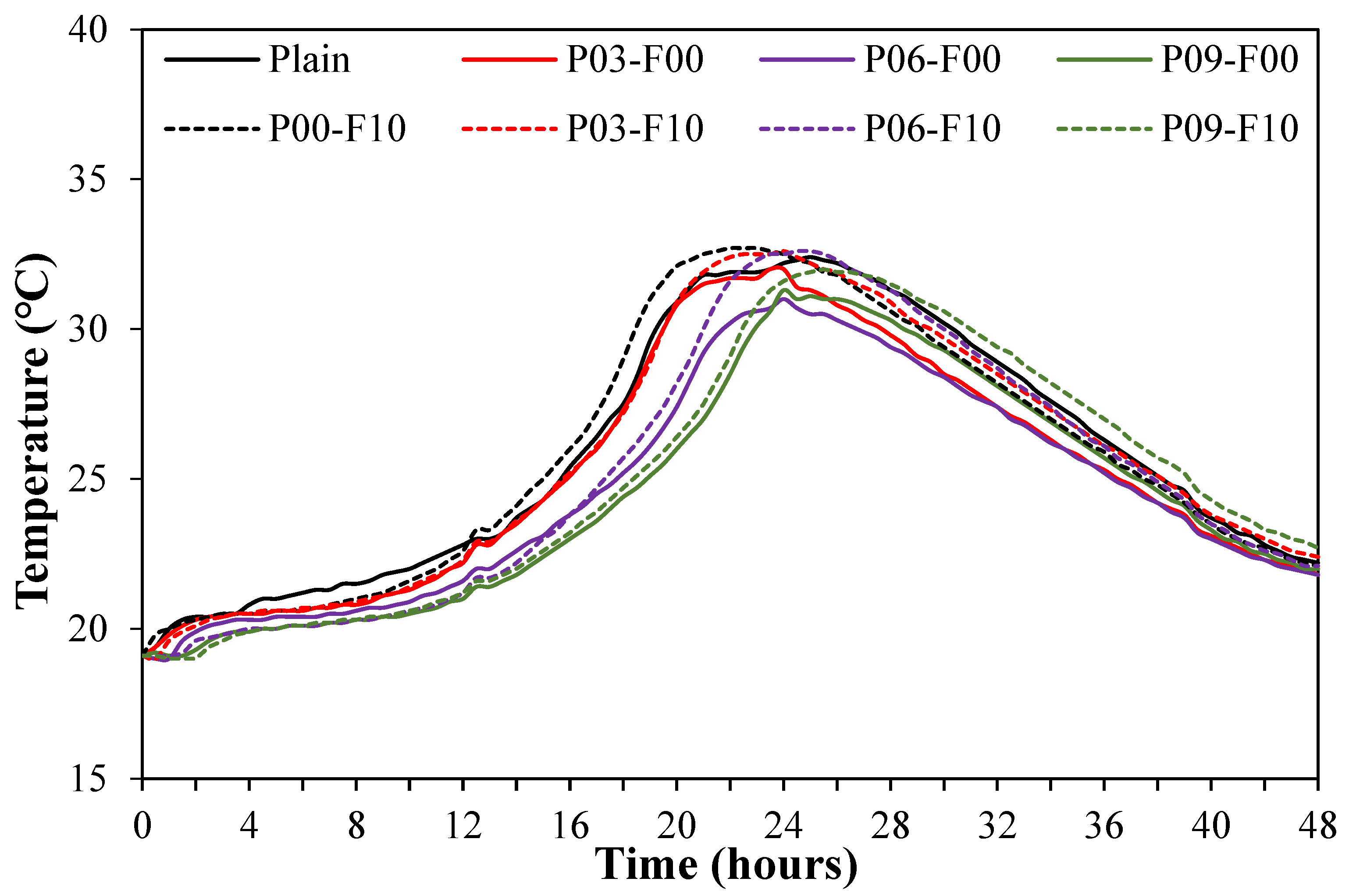
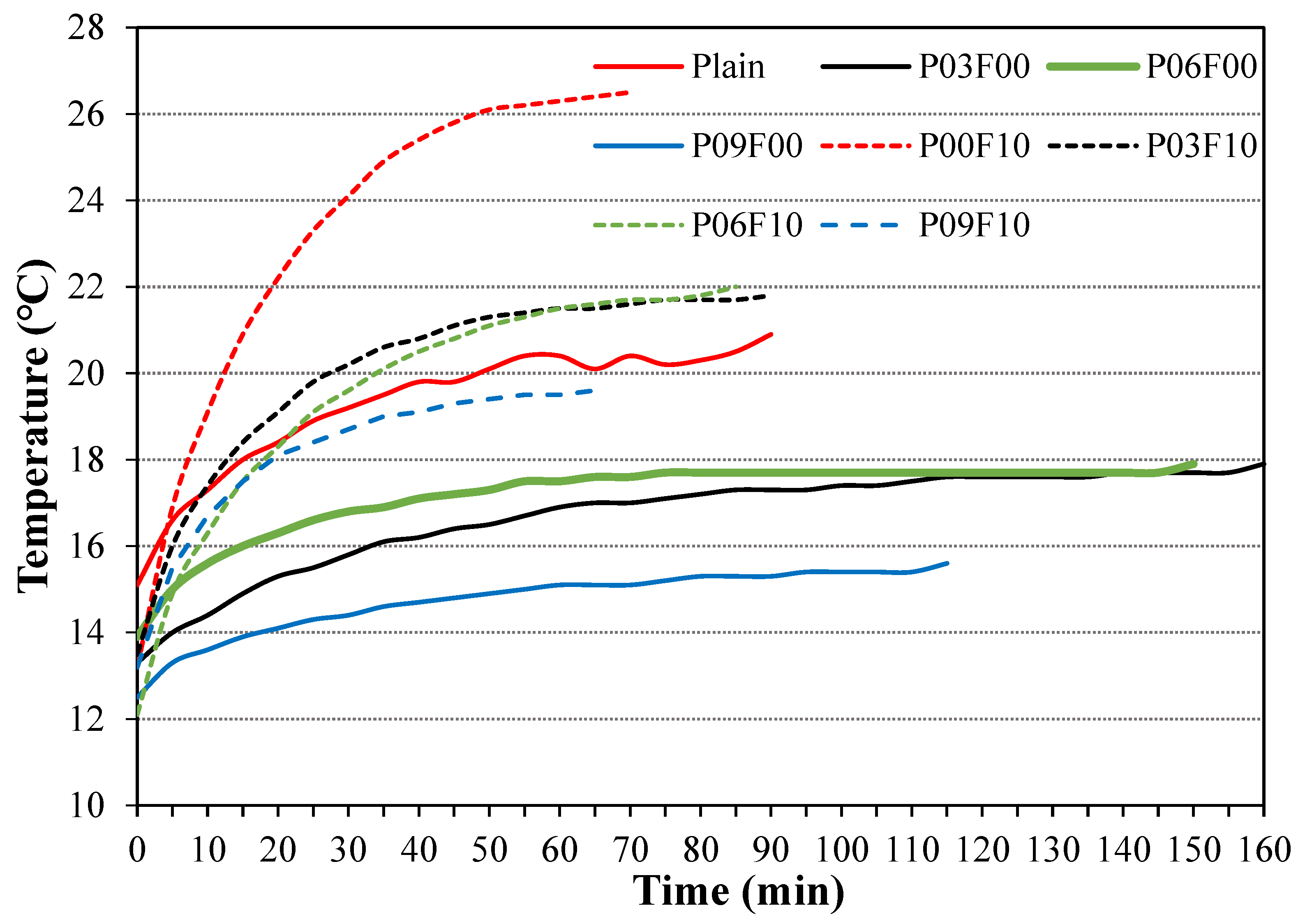
3.2. Heat of Hydration
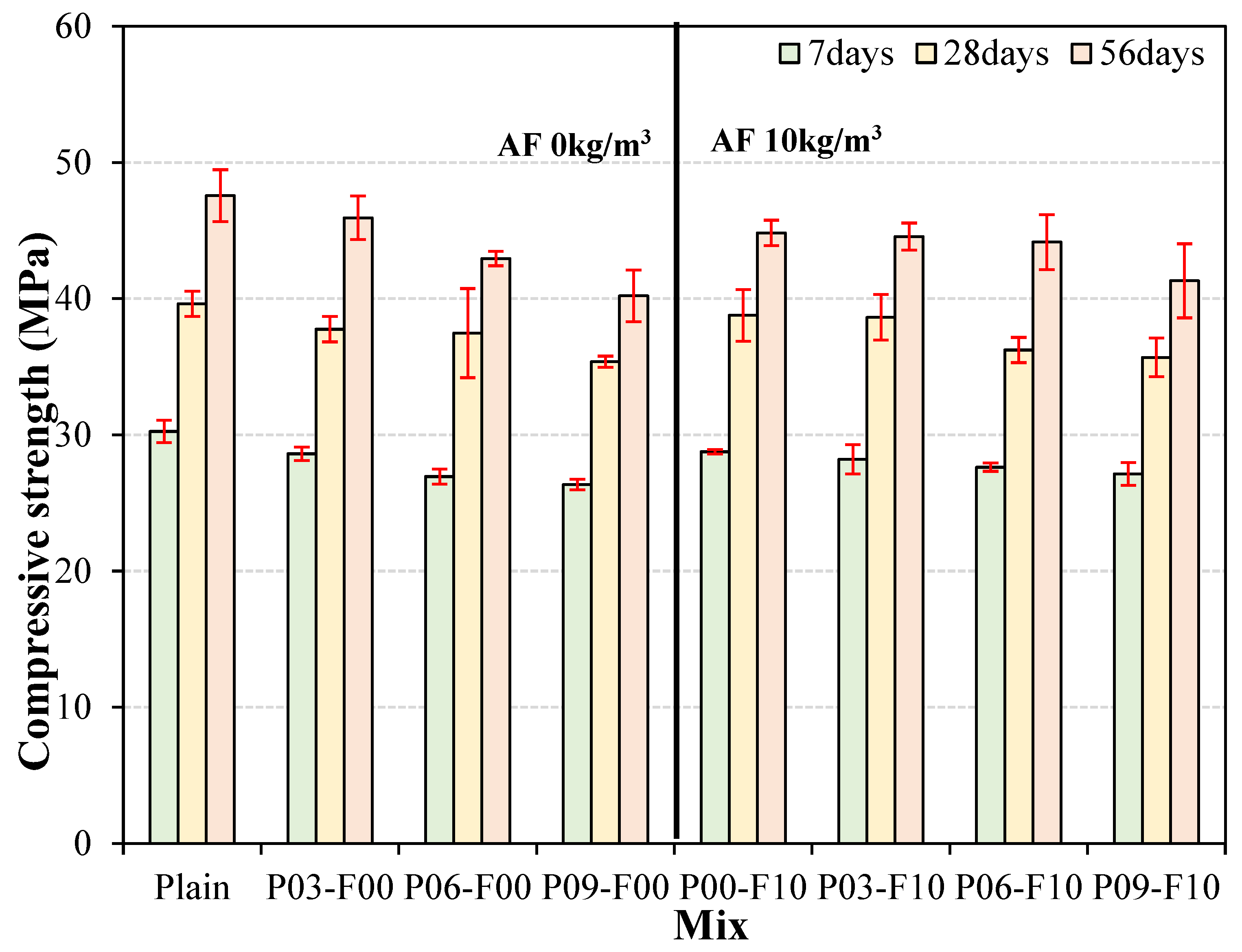
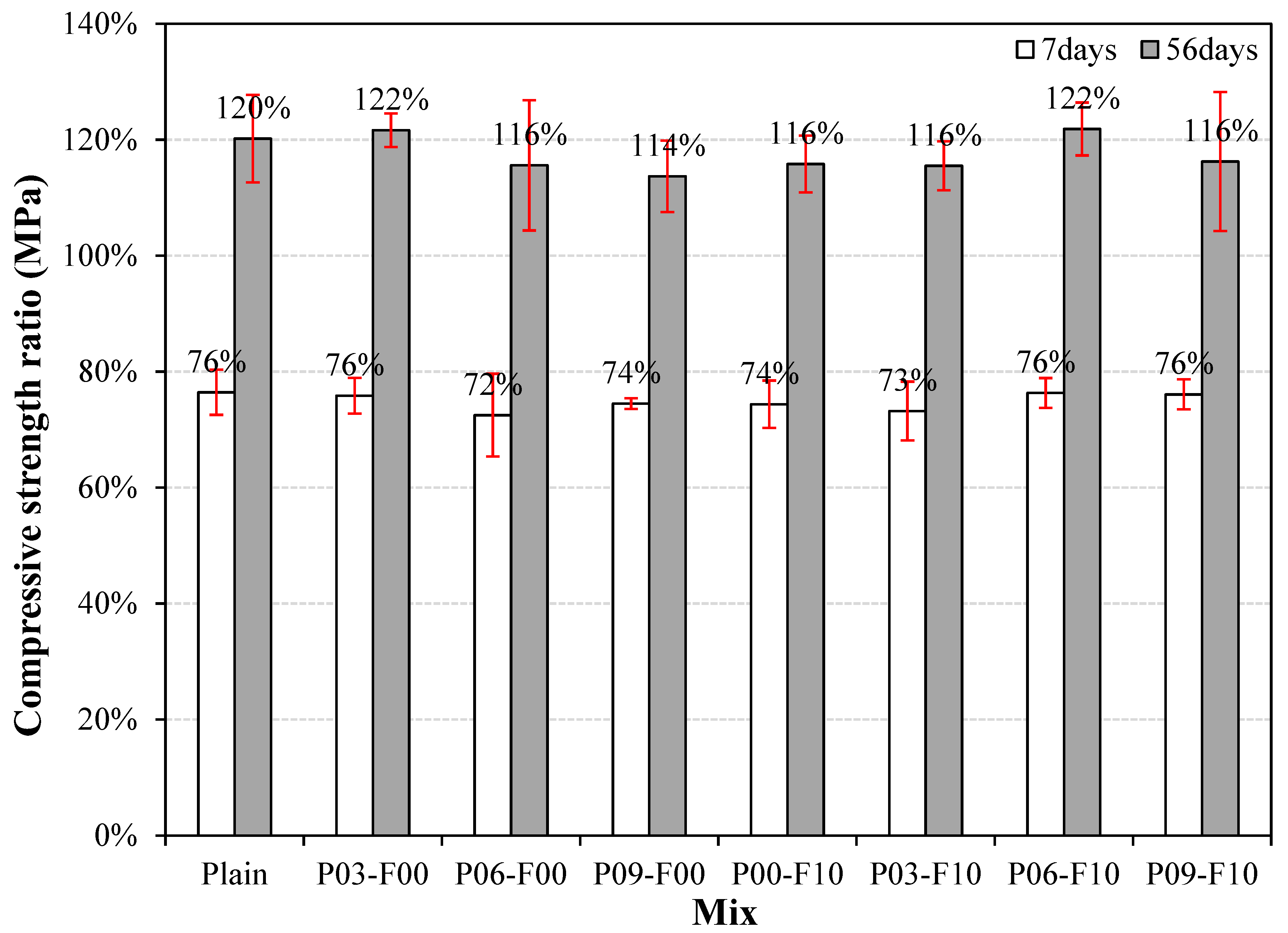
3.3. Compressive Strength
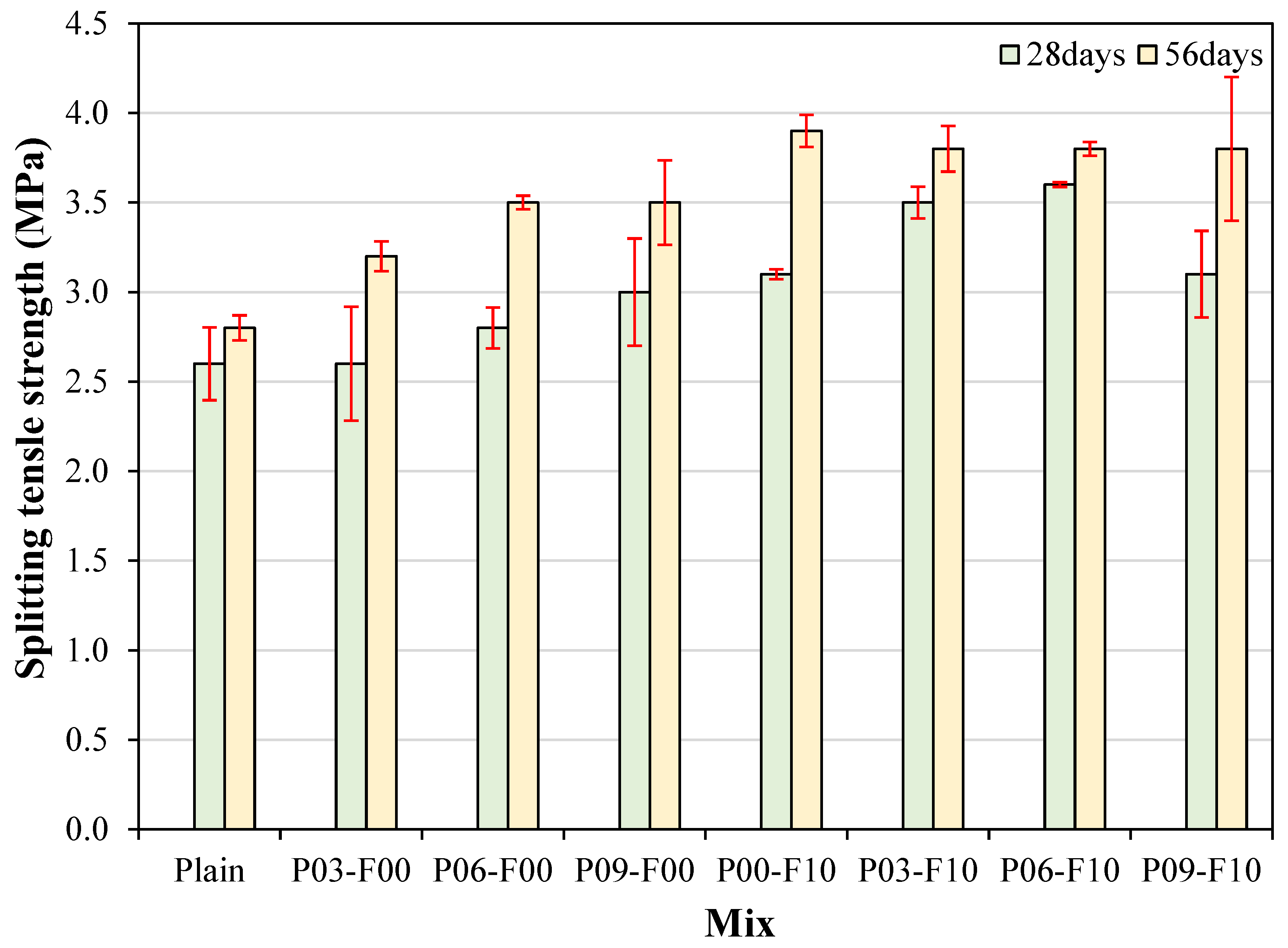
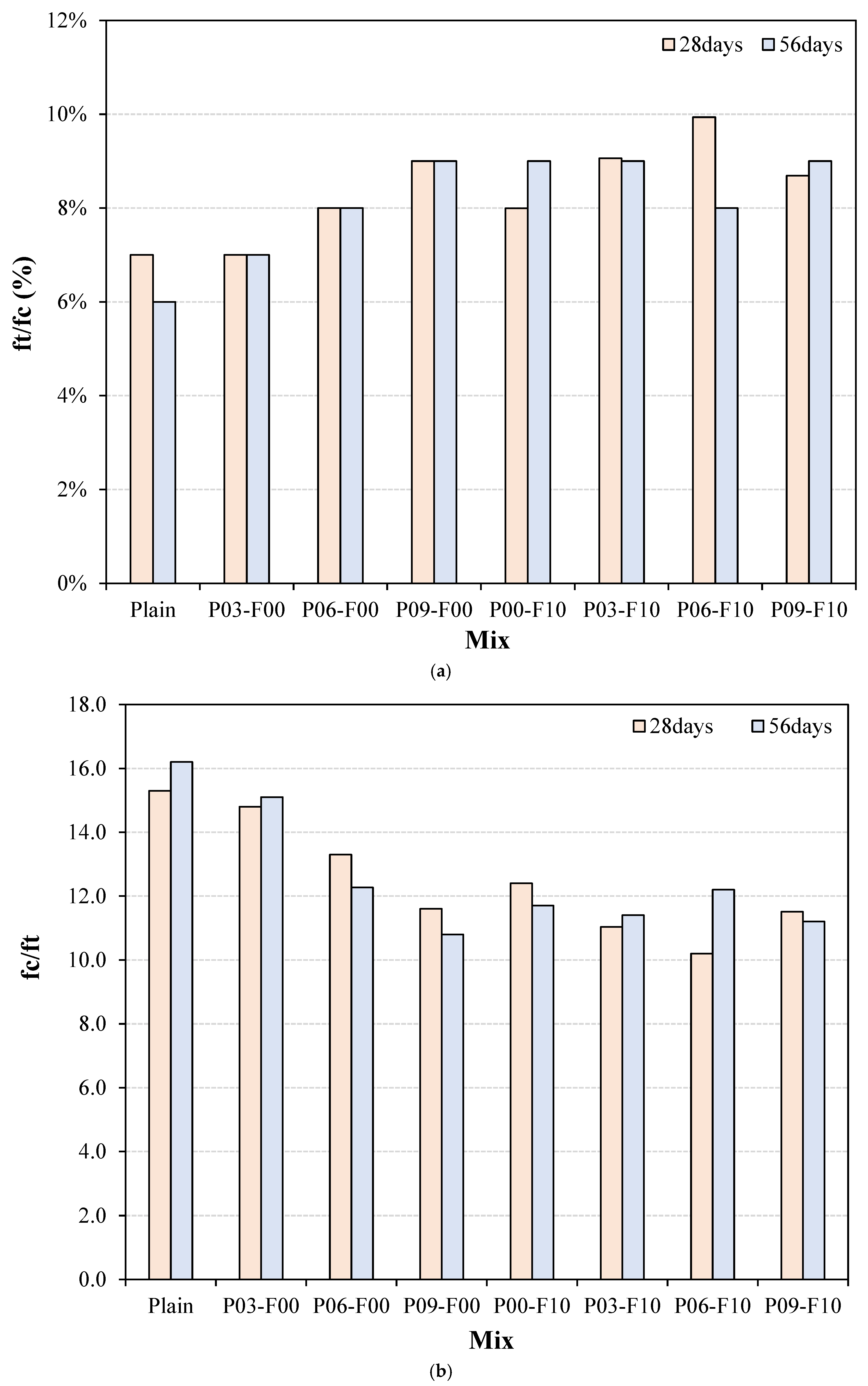
3.4. Splitting Tensile Strength
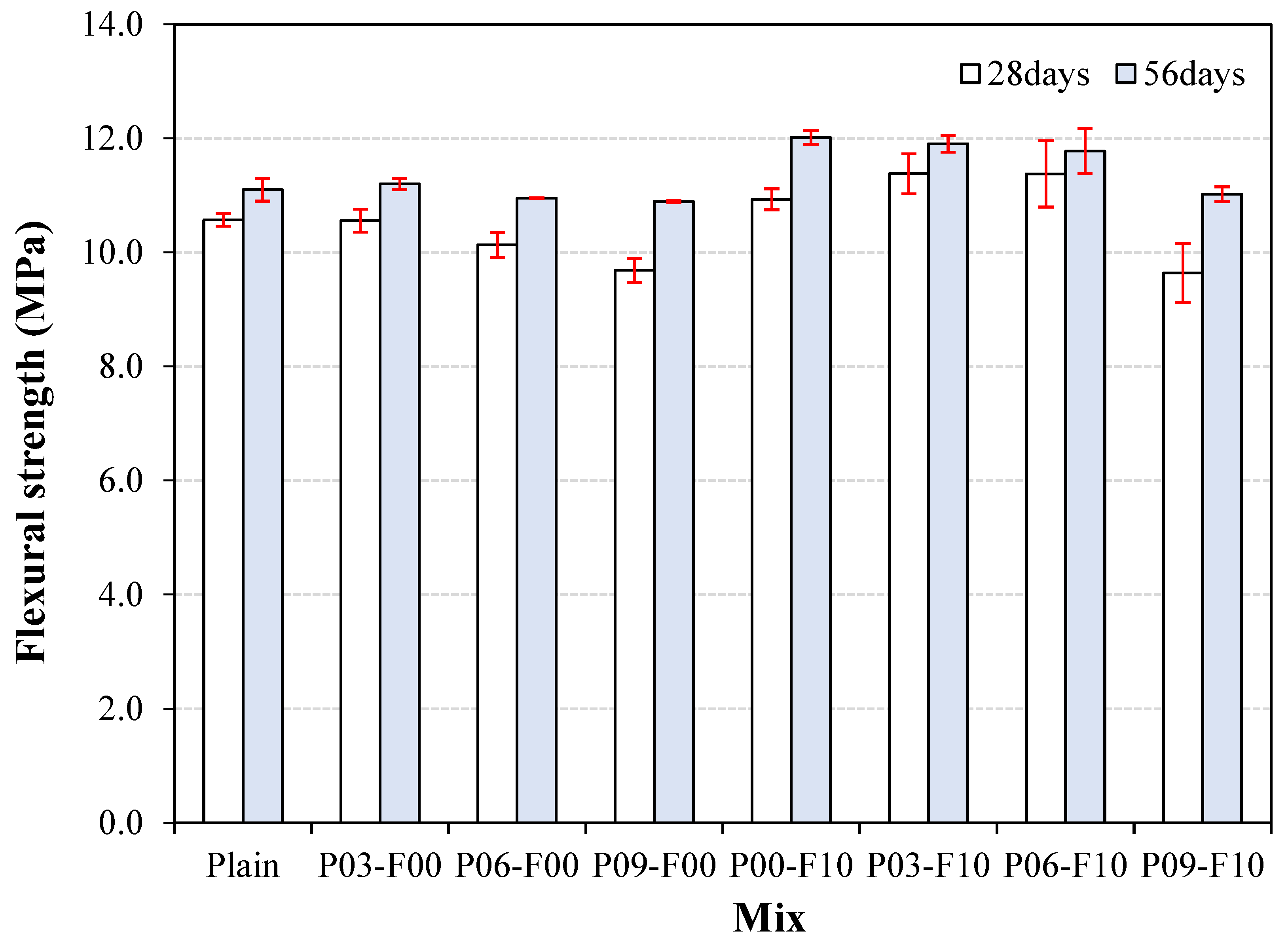
3.5. Flexural Strength
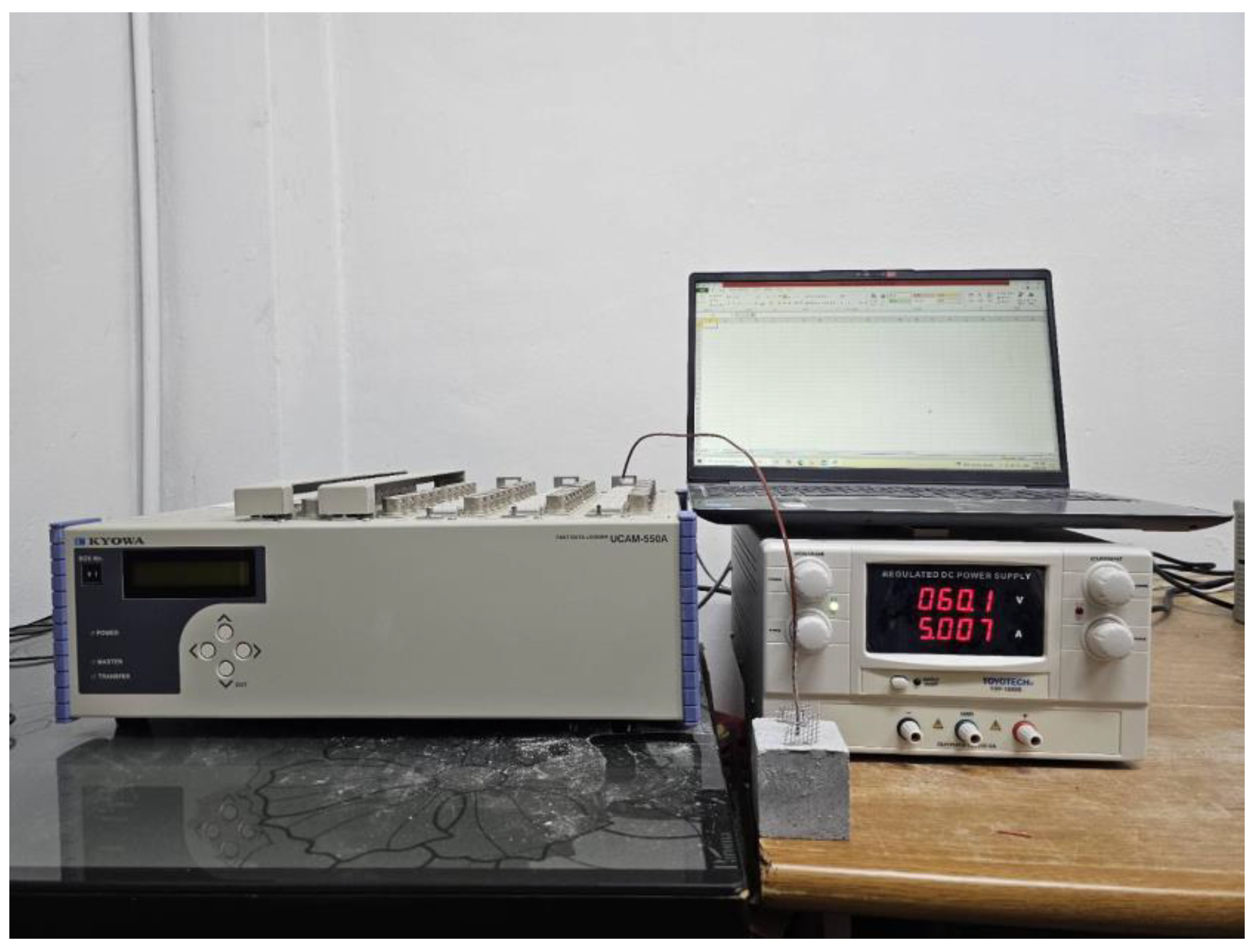
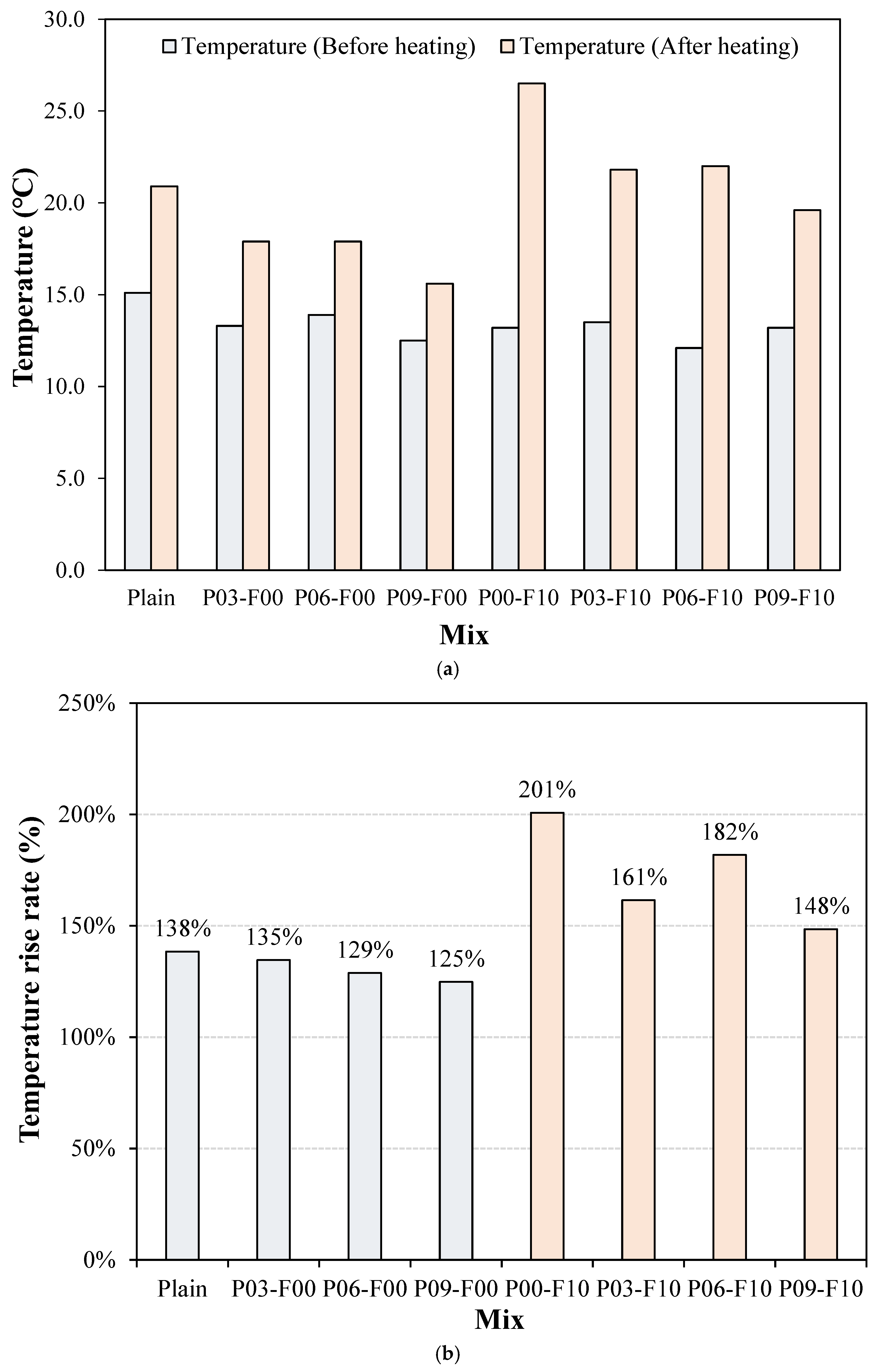
3.6. Thermal Properties
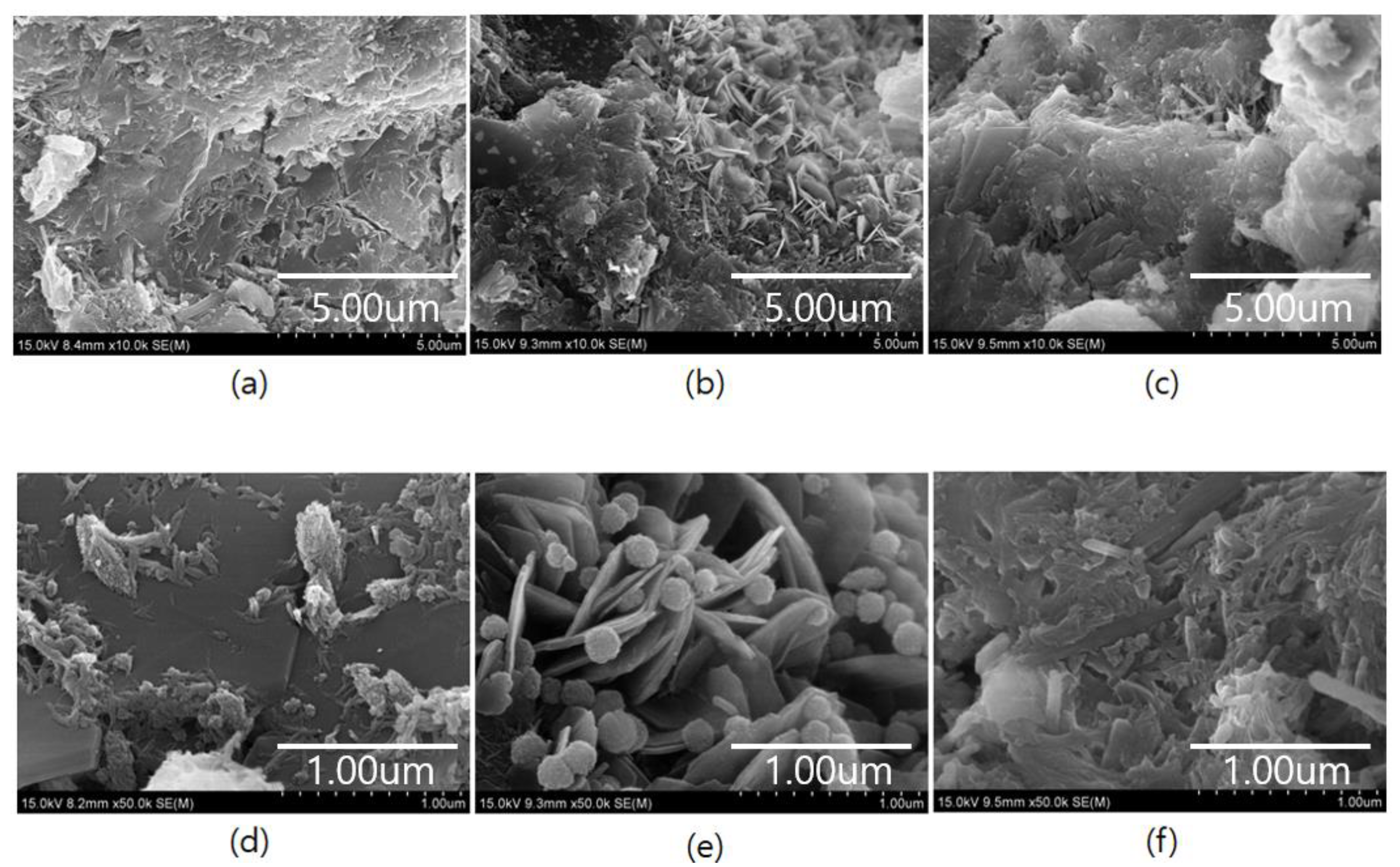
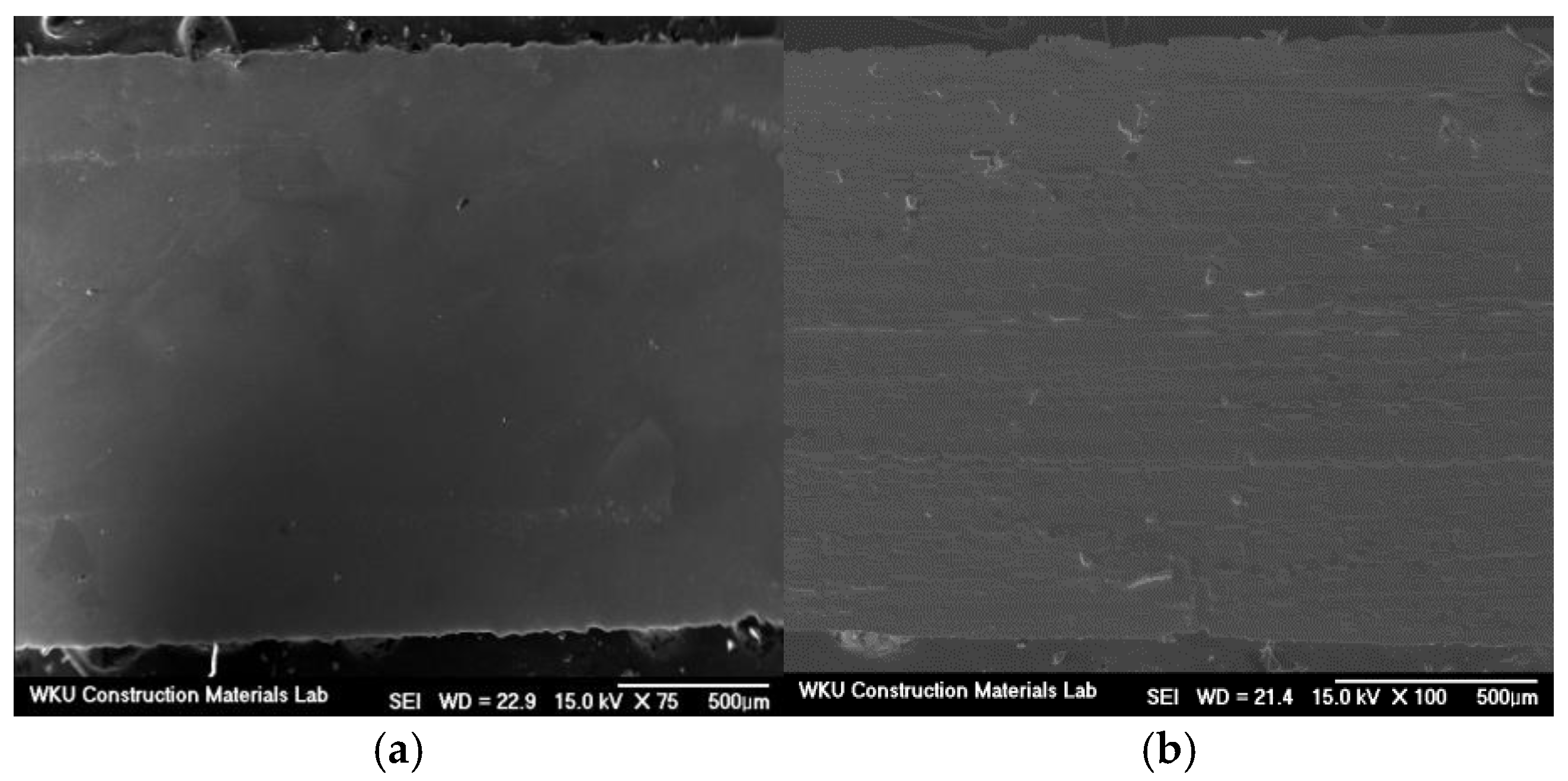
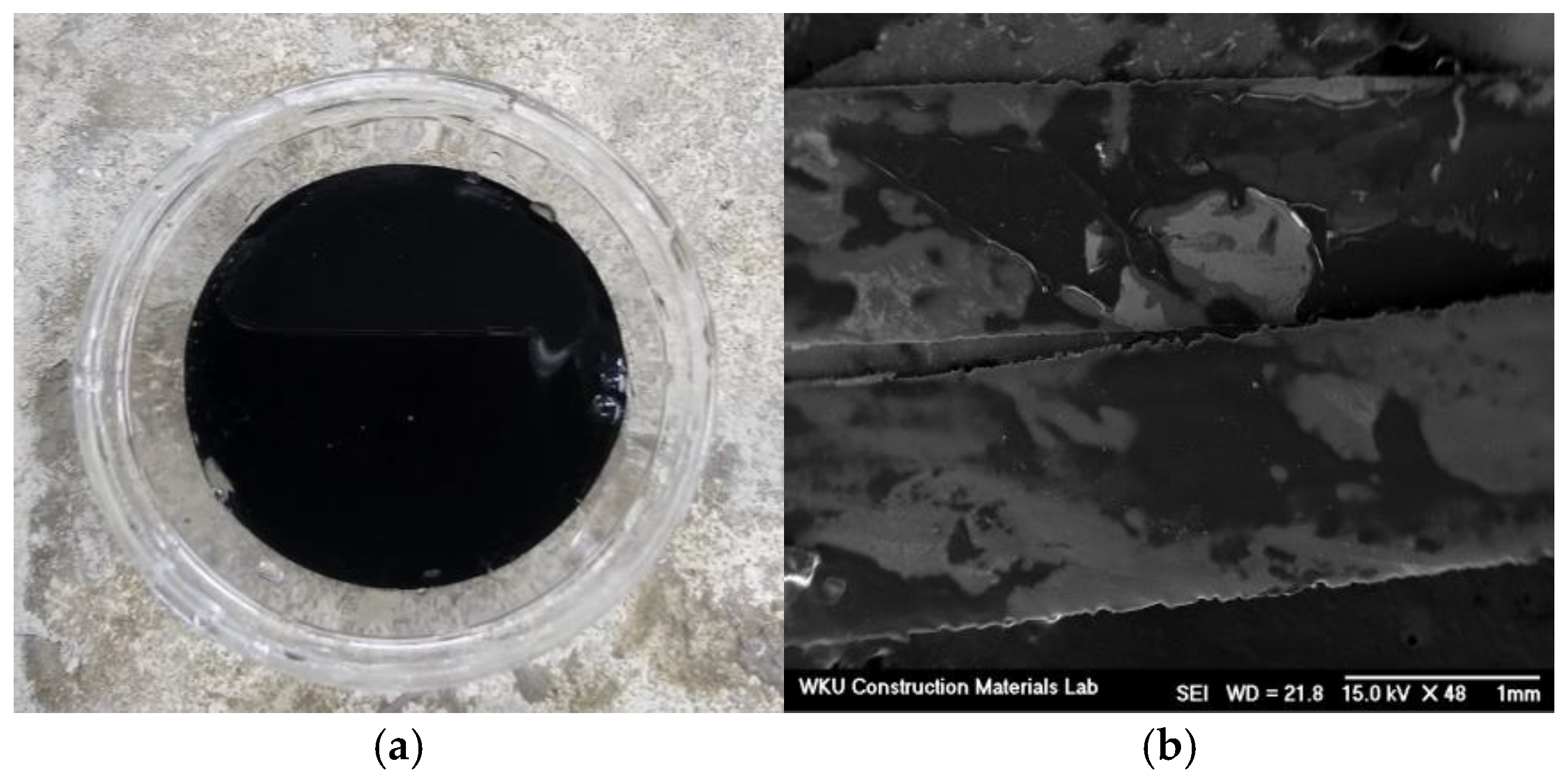
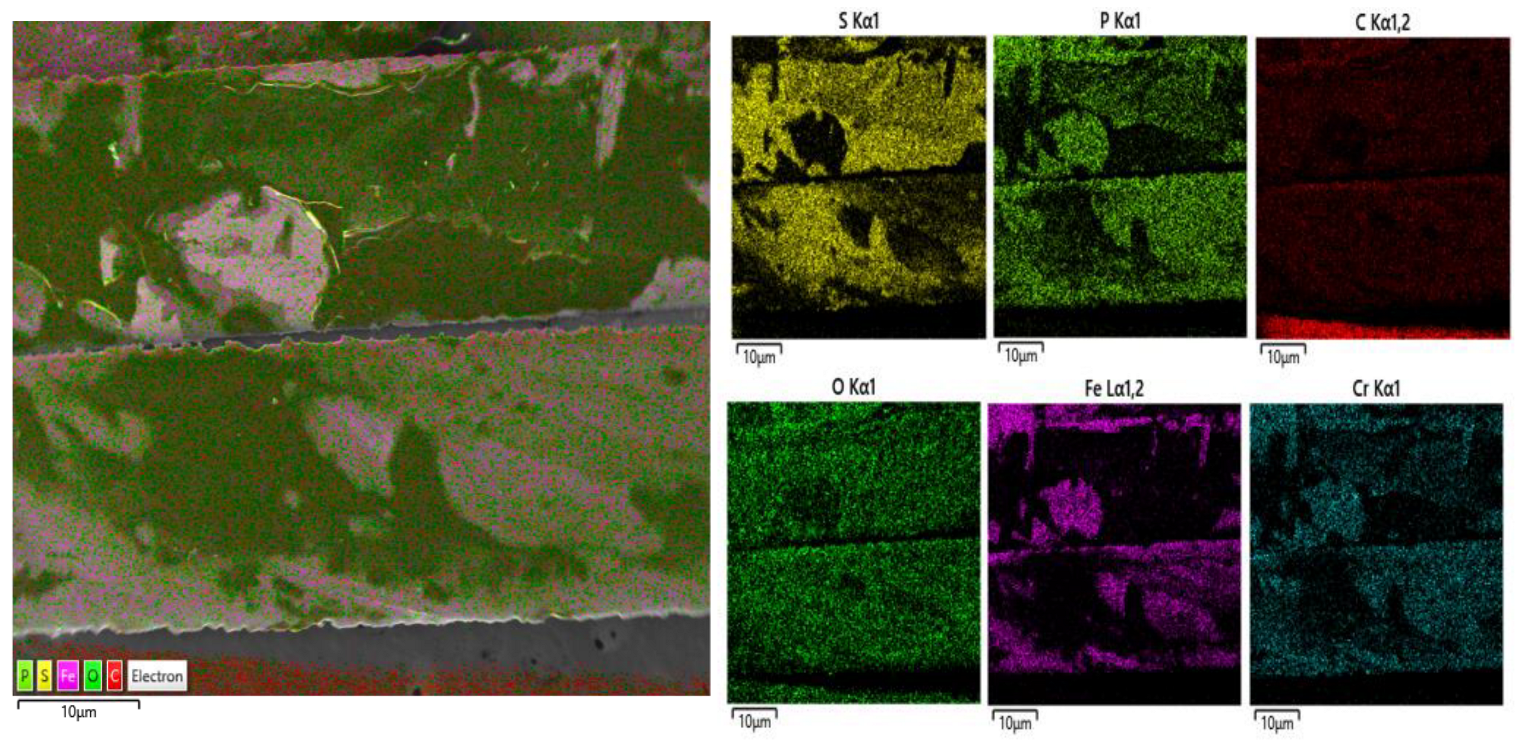
3.7. Microstructural Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AF | Amorphous metallic fiber |
| CNTs | Carbon nanotubes |
| CF | Carbon fiber |
| PEDOT | poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) |
| PSS | poly(styrenesulfonate) |
References
- Eslamlou, A.D.; Ghaderiaram, A.; Schlangen, E.; Fotouhi, M. A review on non-destructive evaluation of construction materials and structures using magnetic sensors. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 397, 132460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarbozagh, A.S.; Rezaifar, O.; Gholhaki, M.; Abavisani, I. Magnetic enhancement of carbon nanotube concrete compressive behavior. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 262, 120772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Jang, C.; Kim, H.G.; Woo, B.H. Snow-melting performance of the thermally conductive concrete pavement-experimental evaluation in field application. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Kang, M.H.; Song, J.I.; Hwang, K.Y. The Detection of Black Ice Accident for Preventative Automated Vehicles Using Convolution Neural Networks. Electronics 2020, 9, 2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilorenzo, T.; Yu, X. Use of ice detection sensors for improving winter road safety. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2023, 191, 107197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Jiang, X.; Leng, Z.; Hou, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhong, J. Electrically conductive asphalt concrete for smart and sustainable pavement construction: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 406, 133433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Su, J.; Guo, J.; Hu, S. Influence of carbon nanotube on properties of concrete: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 369, 130388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, M.T.; Khushnood, R.A. Influence of carbon nano fibers (CNF) on the performance of high strength concrete exposed to elevated temperatures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 268, 121108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Lin, S.; Zhang, G.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, C.; Morsy, A.M.; Wang, X. The effect of graphite and slag on electrical and mechanical properties of electrically conductive cementitious composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 281, 122606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Gao, P.; Li, G.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Xu, X. Fabrication and electrical properties of carbon fiber, graphite and nano carbon black conductive cement-based composites. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2024, 60, 104834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, W.; Sheng, J.G.; Liang, L.B.; Lei, P.; Ying, F.; Ni, G.; Zhi, L.K. Dispersion of carbon fibers and conductivity of carbon fiber-reinforced cement-based composites. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 15122–15132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zhang, W.; Li, B.; Zhu, J.; Wang, C.; Song, G.; Wu, G.; Yang, X.; Huang, Y.; Ma, L. Recent advances of interphase in carbon fiber-reinforced polymer composites: A review. Compos. B Eng. 2022, 233, 109639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Ouyang, J. Thermoelectric Properties of PEDOT:POSS. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2019, 5, 1800769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Liu, C.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, J. Effective Approaches to Improve the Electrical Conductivity of PEODT:PSS A Review. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2015, 1, 1500017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseghai, G.B.; Mengisite, D.A.; Malengire, B.; Fante, K.A.; Langenhove, L.V. PEDOT:PSS-Based Conductive Textiles and Their Applications. Sensors 2020, 20, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naim, A.F.A.; El-Shamy, A.G. Review on recent development on thermoelectric functions of PEDOT:PSS based systems. Mat. Sci. Semicond. Proc. 2022, 152, 107041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, J.; Liang, L.; Deng, L.; Chen, G. A PEDOT:PSS thermoelectric fiber generator. Nano Energy 2022, 102, 107678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.; Min, Y.K.; Chung, W.; Lee, S.E.; Kang, S.E. Effects of dispersants and defoamers on the enhanced electrical performance by carbon nanotube networks embedded in cement-matrix composites. Compos. Struct. 2020, 243, 112193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahyuni, W.T.; Rahman, H.A.; Afifah, S.; Anindya, W.; Hidayat, R.A.; Khalil, M.; Fan, B.; Putra, B.R. Comparison of the analytical performance of two different electrochemical sensors based on a composite of gold nanorods with carbon nanomaterials and PEDOT:PSS for the sensitive detection of nitrite on processed meat products. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 24856–24873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belli, A.; Mobili, A.; Bellezze, T.; Tittarelli, F. Commercial and recycled carbon/steel fibers for fiber-reinforced cement mortars with high electrical conductivity. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2020, 190, 103569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.I.; Kim, C.Y.; Yoon, J.H.; Choi, S.J. Study on the Engineering Properties of Cement Composites using Carbon Nanotubes and Amorphous Metallic Fiber. J. Korea Concr. Inst. 2024, 36, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Niu, D.; Guo, B. Study on the mechanical and electrical conductivity properties of waste short carbon fibers concrete and the establishment of conductivity models. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 95, 110296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, G.; Kim, G.; Kim, H.; Hwang, E.; Lee, S.; Son, M.; Nam, J. Influence of amorphous metallic fibers on spalling properties of high-strength concrete exposed to high temperature. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 263, 120711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, G.; Kim, H.; Son, M.; Choe, G.; Kobayashi, K.; Nam, J. Impact resistance, flexural and tensile properties of amorphous metallic fiber-reinforced cementitious composites according to fiber length. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 271, 121872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.J.; Lee, J.I.; Kim, C.Y.; Yoon, J.H.; Kim, K.H. Effect of Amorphous Metallic Fibers on Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Lightweight Aggregates Cement Mortars Containing Carbon Nanotubes. Materials 2024, 17, 5449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; He, T.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, S.; Tan, J.; Liu, Z.; Su, J. The influence of fiber type and length on the cracking resistance, durability and pore structure of face slab concrete. Contr. Build. Mater. 2021, 282, 122706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, G.; Lee, S.; Choe, G.; Noguchi, T.; Nam, J. Direct tensile behavior of amorphous metallic fiber-reinforced cementitious composites: Effect of fiber length, fiber volume fraction, and strain rate. Compos. B Eng. 2019, 177, 107430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Dagsgård, F.; Turner, A.P.F.; Mak, W.C. Bi-functional sulphonate-coupled reduced graphene oxide as an efficient dopant for a conducting polymer with enhanced electrochemical performance. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 12829–12839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KS L 5111; Flow Table for Use in Tests of Hydraulic Cement. Korea Industrial Standards. Korea Standards & Certification Information Center: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2017.
- KS L 5105; Testing Method for Compressive Strength of Hydraulic Cement Mortars. Korea Industrial Standards. Korea Standards & Certification Information Center: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2017.
- ASTM C 1753; Standard Practice for Evaluation Early Hydration of Hydraulic Cementitious Mixtures Using Thermal Measurements. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021.
- KS F 2423; Standard Test Method for Tensile Splitting Strength of Concrete. Korea Industrial Standards. Korean Standards & Certification Information Center: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2011.
- KS F 2408; Standard Test Method for Flexural Strength of Concrete. Korea Industrial Standards, Seoul (Korea). Korean Standards & Certification Information Center: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2016.
- Zhanshayeva, L.; Favaron, V.; Lubineau, G. Macroscopic Modeling of Water Uptake Behavior of PEDOT:PSS Films. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 21883–21890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tounakyi, C.; Decorse, P.; Kouki, F.; Lang, P. Relationship between enhancement of PEDOT:PSS conductivity by solvent treatment and PSS chain reorganization. J. Polym. Sci. 2023, 61, 582–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dramé, A.; Darmanin, T.; Dieng, S.Y.; Givenchy, E.T.D.; Guittard, F. Superhydrophobic and oleophobic surfaces containing wrinkles and nanoparticles of PEDOT with two short fluorinated chains. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 10935–10943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Nie, W.; Tsai, H.; Wang, N.; Huang, H.; Cheng, Y.; Wen, R.; Ma, L.; Yan, F.; Xia, Y. PEDOT:PSS for Flexible and Stretchable Electronics: Modifications, Strategies, and Applications. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1900813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.M.; Kim, J.K.; Yoo, D.Y. Effects of amorphous metallic fibers on the properties of asphalt concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 125, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, J.; Zhou, Z. Properties of concrete with addition carbon nanotubes: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 393, 132066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chen, B.; Nuti, C. Influence of steel fiber on compressive properties of ultra-high performance fiber-reinforced concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 302, 124104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hari, R.; Mini, K.M. Mechanical and durability properties of basalt-steel wool hybrid fibre reinforced pervious concrete—A Box Behnken approach. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 70, 106307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Guo, M.M.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, C.Y.; Jiang, C.; Dong, Y.; Law, W.C.; Du, F.P. Flexible, stretchable and conductive PVA/PEDOT:PSS composite hydrogels prepared by SIPN strategy. Polym. Test. 2020, 81, 106213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeri, P.; Ruiz, M.F.; Muttoni, A. Tensile response of textile reinforced concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 258, 119517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalal, A.; Hakim, L.; Shafiq, N. Mechanical and Post-Cracking Characteristics of Fiber Reinforced Concrete Containing Copper-Coated Steel and PVA Fibers in 100% Cement and Fly Ash Concrete. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, A.M.; Khan, A.H.; Akhtar, M.N.; Khan, N.A.; Koloor, S.S.R.; Petru, M.; Radwan, N. Strength and flexural behavior of steel fiber and silica fume incorporated self-compacting concrete. J. Mater. Res. Techno 2021, 12, 1380–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Ma, W.; Xu, Z.; Chai, J.; Zhou, H. Effects of nylon fiber and nylon fiber fabric on the permeability of cracked concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 274, 121786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miah, M.J.; Pei, J.; Kim, H.; Jang, J.G. Flexural behavior, porosity, and water absorption of CO2-cured amorphous metallic-fiber-reinforced belite-rich cement composites. Contr. Build. Mater. 2023, 387, 131668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Xu, X.; Li, H.; Ham, Z.; Hao, J.; Yang, G.; Xie, Z.; Chen, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, Q.; et al. Soft liquid-metal/elastomer foam with compression-adjustable thermal conductivity and electromagnetic interference shielding. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 410, 128288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.L.L.P.; Ma, R.N.; Jia, W.L.; Wang, H.S. Electrodeposition of PtNPs on the LBL assembled multilayer films of (PDDA-GS/PEDOT:PSS)n and their electrocatalytic activity toward methanol oxidation. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 16371–16378. [Google Scholar]



| Type | Density (g/cm3) | Tensile Strength (N/mm2) | Length (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amorphous metallic fiber | 7.2 | 1400 | 15 |
| Type | Solid Content (%) | pH (-) | Conductivity (S/cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PEDOT:PSS | 0.8–1.1 | 1.5–2.5 | 230 |
| Type | PEDOT:PSS (C*wt%) | PEDOT:PSS (g) | AF (g) | Water (g) | Cement (g) | Sand (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cubic (50 × 50 × 50 mm) Cylindrical (Ø50 × 100 mm) Prismatic (40 × 40 × 160 mm) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 856 | 1712 | 4476 |
| 0.3 | 5.1 | |||||
| 0.6 | 10.2 | |||||
| 0.9 | 15.3 | |||||
| 0 | 0 | 26.7 | ||||
| 0.3 | 5.1 | |||||
| 0.6 | 10.2 | |||||
| 0.9 | 15.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, S.-J.; Park, J.-Y.; Kim, M.-J.; Lee, J.-I. Mechanical and Thermal Characteristics of Cement Composites Containing PEDOT:PSS and Amorphous Metallic Fibers. Materials 2025, 18, 4486. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194486
Choi S-J, Park J-Y, Kim M-J, Lee J-I. Mechanical and Thermal Characteristics of Cement Composites Containing PEDOT:PSS and Amorphous Metallic Fibers. Materials. 2025; 18(19):4486. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194486
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Se-Jin, Jeong-Yeon Park, Min-Jeong Kim, and Jae-In Lee. 2025. "Mechanical and Thermal Characteristics of Cement Composites Containing PEDOT:PSS and Amorphous Metallic Fibers" Materials 18, no. 19: 4486. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194486
APA StyleChoi, S.-J., Park, J.-Y., Kim, M.-J., & Lee, J.-I. (2025). Mechanical and Thermal Characteristics of Cement Composites Containing PEDOT:PSS and Amorphous Metallic Fibers. Materials, 18(19), 4486. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194486







