Optimizing Thermomechanical Processing for Producing Bulk Fine-Grained Aluminum Alloy with Thermal Stability
Abstract
1. Introduction
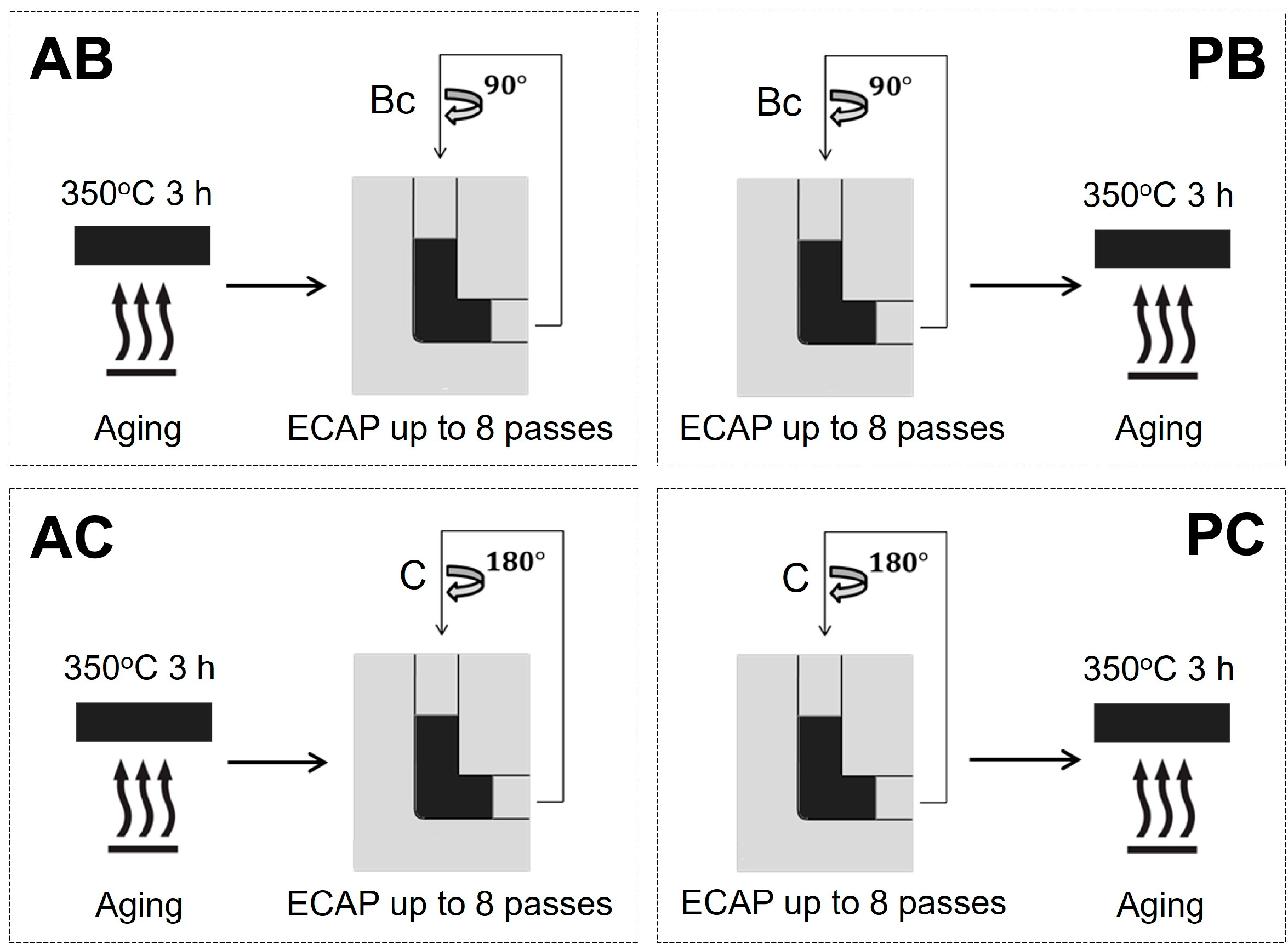
2. Materials and Methods
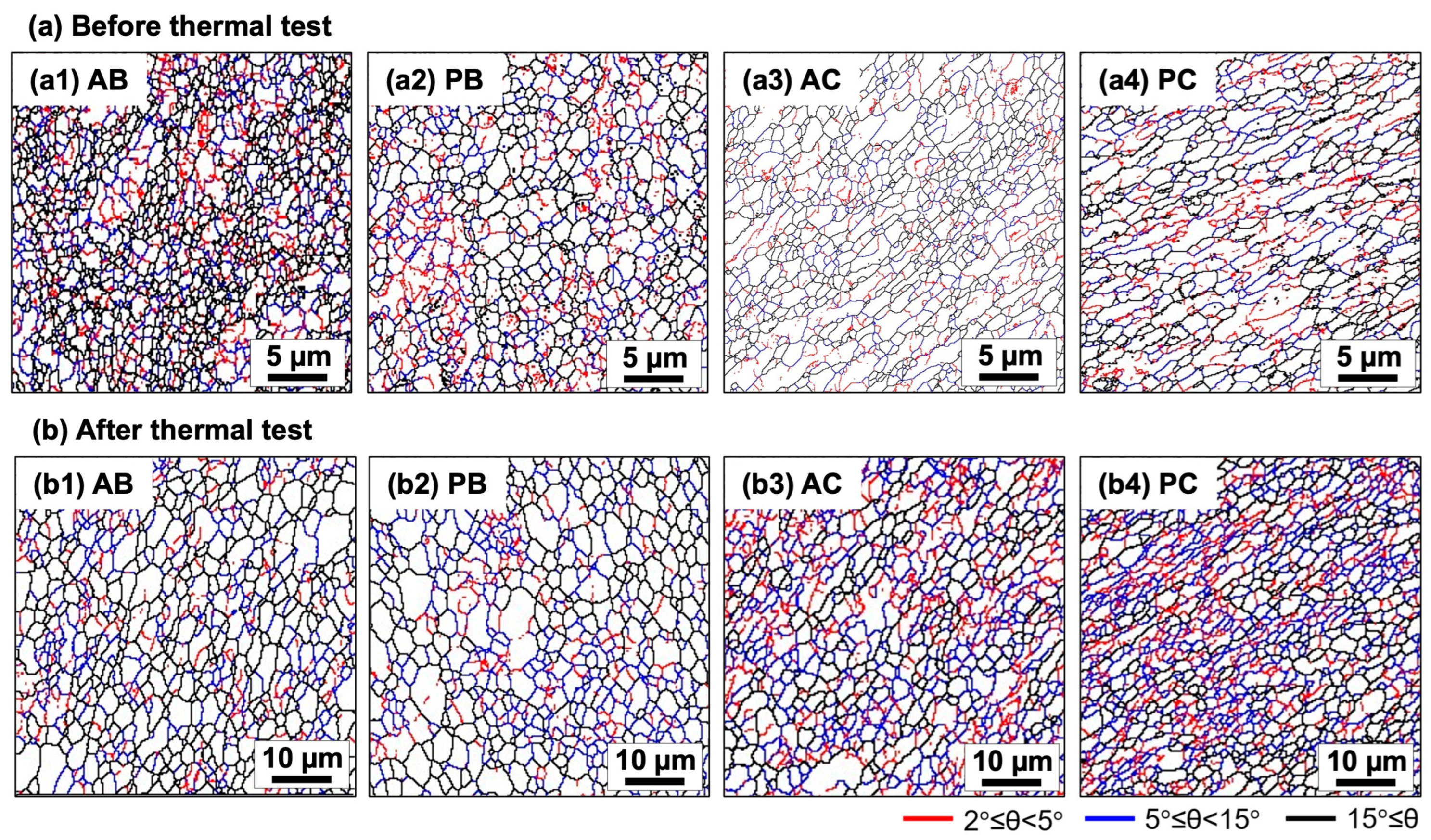
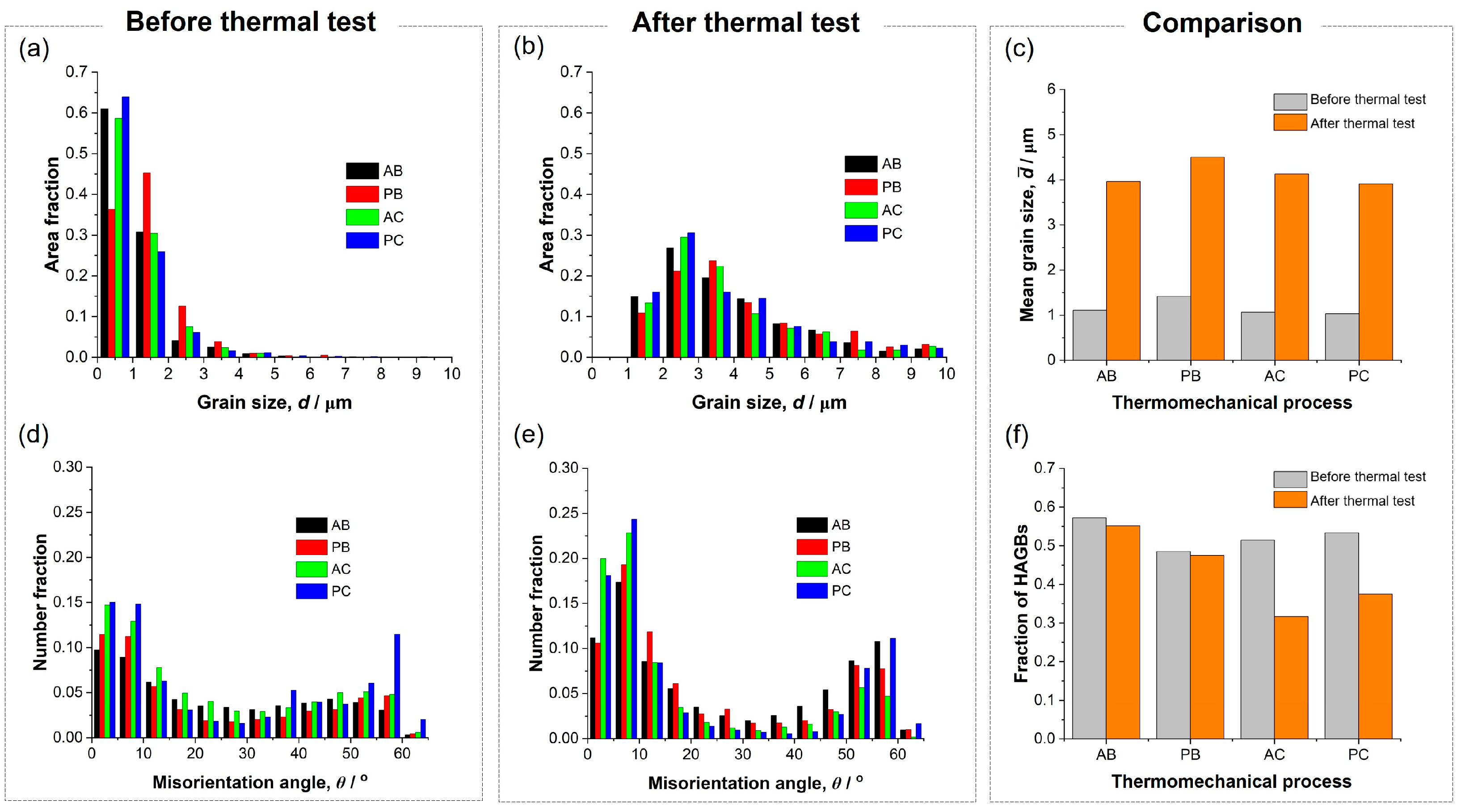
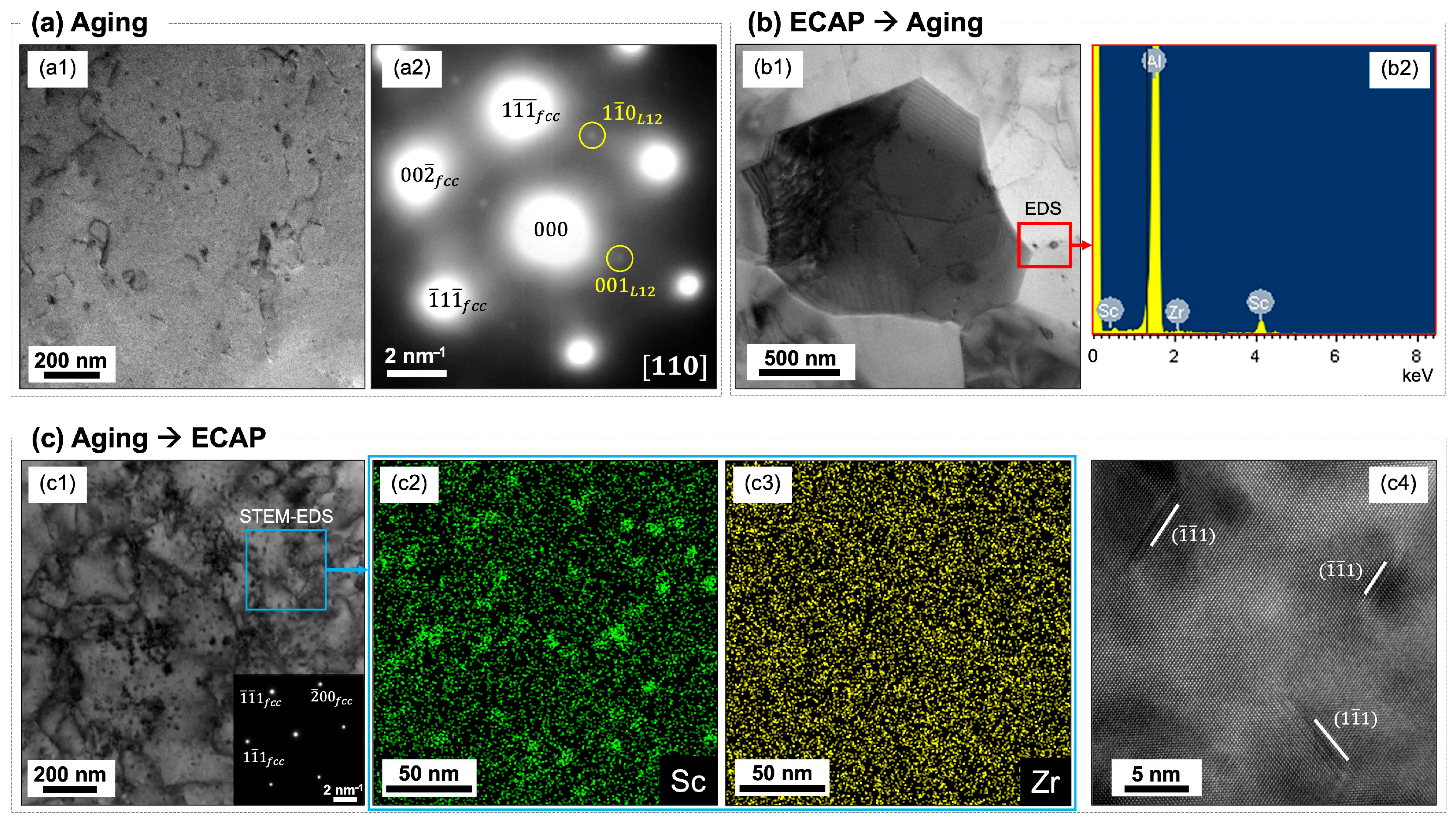
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Valiev, R.Z.; Islamgaliev, R.K.; Alexandrov, I.V. Bulk Nanostructured Materials from Severe Plastic Deformation. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2000, 45, 103–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, N.; Ito, Y.; Saito, Y.; Minamino, Y. Strength and Ductility of Ultrafine Grained Aluminum and Iron Produced by ARB and Annealing. Scr. Mater. 2002, 47, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreau, O.; Gubicza, J.; Zhang, N.X.; Huang, Y.; Jenei, P.; Langdon, T.G. Effect of Short-Term Annealing on the Microstructures and Flow Properties of an Al–1% Mg Alloy Processed by High-Pressure Torsion. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 615, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Utsunomiya, A.; Akamatsu, H.; Neishi, K.; Furukawa, M.; Horita, Z.; Langdon, T.G. Influence of Scandium and Zirconium on Grain Stability and Superplastic Ductilities in Ultrafine-Grained Al–Mg Alloys. Acta Mater. 2002, 50, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frint, S.; Hockauf, M.; Frint, P.; Wagner, M.F.-X. Scaling up Segal’s Principle of Equal-Channel Angular Pressing. Mater. Des. 2016, 97, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banjongprasert, C.; Jak-Ra, A.; Domrong, C.; Patakham, U.; Pongsaksawad, W.; Chairuangsri, T. Characterization of an Equal Channel Angular Pressed Al-Zn-In Alloy. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2015, 60, 887–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shenawy, M.; Ahmed, M.M.Z.; Nassef, A.; El-Hadek, M.; Alzahrani, B.; Zedan, Y.; El-Garaihy, W.H. Effect of ECAP on the Plastic Strain Homogeneity, Microstructural Evolution, Crystallographic Texture and Mechanical Properties of AA2xxx Aluminum Alloy. Metals 2021, 11, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damavandi, E.; Nourouzi, S.; Rabiee, S.M.; Jamaati, R.; Szpunar, J.A. EBSD Study of the Microstructure and Texture Evolution in an Al–Si–Cu Alloy Processed by Route A ECAP. J. Alloy. Compd. 2021, 858, 157651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, H.; Su, Y.; Yang, W.; Hao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Xue, W.; Zhong, Y.; Wu, J. Influence of Mechanical Deformation on the Corrosion Behavior of Pure Aluminum for Al-Air Battery. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 14969–14978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linjee, S.; Moonngam, S.; Klomjit, P.; Pålsson, N.S.; Banjongprasert, C. Corrosion Behaviour Improvement from the Ultrafine-Grained Al–Zn–In Alloys in Al–Air Battery. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 5117–5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiev, R.Z.; Langdon, T.G. Principles of Equal-Channel Angular Pressing as a Processing Tool for Grain Refinement. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2006, 51, 881–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alateyah, A.I.; Alawad, M.O.; Aljohani, T.A.; El-Garaihy, W.H. Effect of ECAP Route Type on the Microstructural Evolution, Crystallographic Texture, Electrochemical Behavior and Mechanical Properties of ZK30 Biodegradable Magnesium Alloy. Materials 2022, 15, 6088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, T.A.; Totik, Y.; Lule Senoz, G.M.; Bostan, B. Microstructure Evolution and Wear Properties of ECAP-Treated Al-Zn-Mg Alloy: Effect of Route, Temperature and Number of Passes. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 33, 104628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwahashi, Y.; Horita, Z.; Nemoto, M.; Langdon, T.G. The Process of Grain Refinement in Equal-Channel Angular Pressing. Acta Mater. 1998, 46, 3317–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabibbo, M. A TEM Kikuchi Pattern Study of ECAP AA1200 via Routes A, C, BC. Mater. Charact. 2010, 61, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, M.; Hamilton, N.E.; Humphreys, F.J. Continuous and Discontinuous Grain Coarsening in a Fine-Grained Particle-Containing Al–Sc Alloy. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 1097–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, M.; Burhan, N. Microstructural Evolution in a Fine-Grained Al–0.3wt.% Sc Alloy Produced by Severe Plastic Deformation. Scr. Mater. 2007, 56, 525–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, M.; Burhan, N. Structural and Kinetic Aspects of Continuous Grain Coarsening in a Fine-Grained Al–0.3Sc Alloy. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 3479–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, N.E.; Ferry, M. Grain Growth in a Nanocrystalline Al-Sc Alloy. Mater. Trans. 2004, 45, 2264–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, H.; Komura, S.; Utsunomiya, A.; Horita, Z.; Furukawa, M.; Nemoto, M.; Langdon, T.G. Thermal Stability of Ultrafine-Grained Aluminum in the Presence of Mg and Zr Additions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1999, 265, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolyarov, V.V.; Zhu, Y.T.; Alexandrov, I.V.; Lowe, T.C.; Valiev, R.Z. Influence of ECAP Routes on the Microstructure and Properties of Pure Ti. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 299, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Jiang, F.; Zhang, M.; Tang, Z.; Tong, M. Recrystallization Behavior of Al-Mg-Mn-Sc-Zr Alloy Based on Two Different Deformation Ways. Mater. Lett. 2020, 265, 127455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A.; Enikeev, N.A.; Murashkin, M.Y.; Arita, M.; Edalati, K. Developing Age-Hardenable Al-Zr Alloy by Ultra-Severe Plastic Deformation: Significance of Supersaturation, Segregation and Precipitation on Hardening and Electrical Conductivity. Acta Mater. 2021, 203, 116503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchaussoy, A.; Sauvage, X.; Edalati, K.; Horita, Z.; Renou, G.; Deschamps, A.; De Geuser, F. Structure and Mechanical Behavior of Ultrafine-Grained Aluminum-Iron Alloy Stabilized by Nanoscaled Intermetallic Particles. Acta Mater. 2019, 167, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, M. Microstructure of Two-Phase Al–1.7 At% Cu Alloy Deformed by Equal-Channel Angular Pressing. Acta Mater. 2001, 49, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhal, A.; Panigrahi, S.K.; Shunmugam, M.S. Insight into the Microstructural Evolution during Cryo-Severe Plastic Deformation and Post-Deformation Annealing of Aluminum and Its Alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 726, 1205–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Punyafu, J.; Domrong, C.; Patakham, U.; Murayama, M.; Banjongprasert, C. Optimizing Thermomechanical Processing for Producing Bulk Fine-Grained Aluminum Alloy with Thermal Stability. Materials 2025, 18, 4180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174180
Punyafu J, Domrong C, Patakham U, Murayama M, Banjongprasert C. Optimizing Thermomechanical Processing for Producing Bulk Fine-Grained Aluminum Alloy with Thermal Stability. Materials. 2025; 18(17):4180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174180
Chicago/Turabian StylePunyafu, Jesada, Chonlada Domrong, Ussadawut Patakham, Mitsuhiro Murayama, and Chaiyasit Banjongprasert. 2025. "Optimizing Thermomechanical Processing for Producing Bulk Fine-Grained Aluminum Alloy with Thermal Stability" Materials 18, no. 17: 4180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174180
APA StylePunyafu, J., Domrong, C., Patakham, U., Murayama, M., & Banjongprasert, C. (2025). Optimizing Thermomechanical Processing for Producing Bulk Fine-Grained Aluminum Alloy with Thermal Stability. Materials, 18(17), 4180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174180





