Effect of Back-Tempering on the Wear and Corrosion Properties of Multiple-Pass Friction Stir Processed High-Speed Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
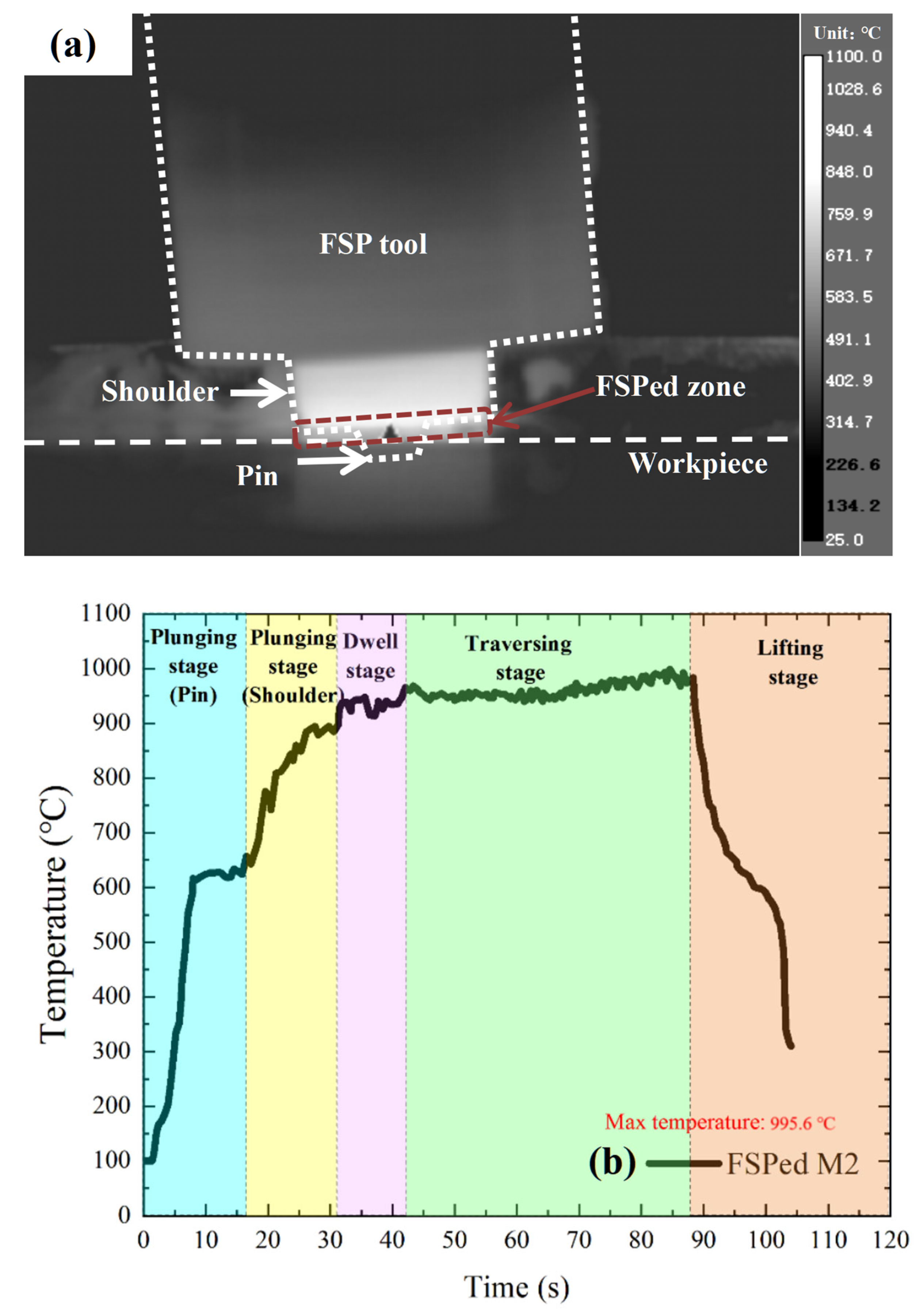
2.2. Friction Stir Processing
2.3. Metallographic and Microstructural Studies
2.4. Hardness Testing
2.5. Wear Testing
2.6. Corrosion Testing
3. Results and Discussion
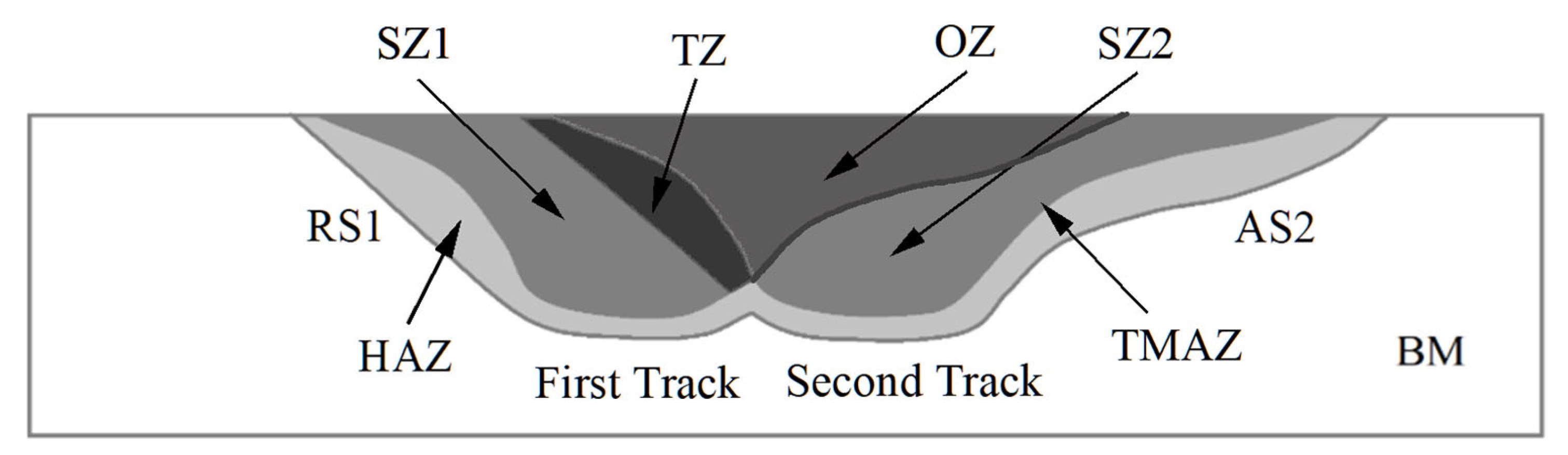
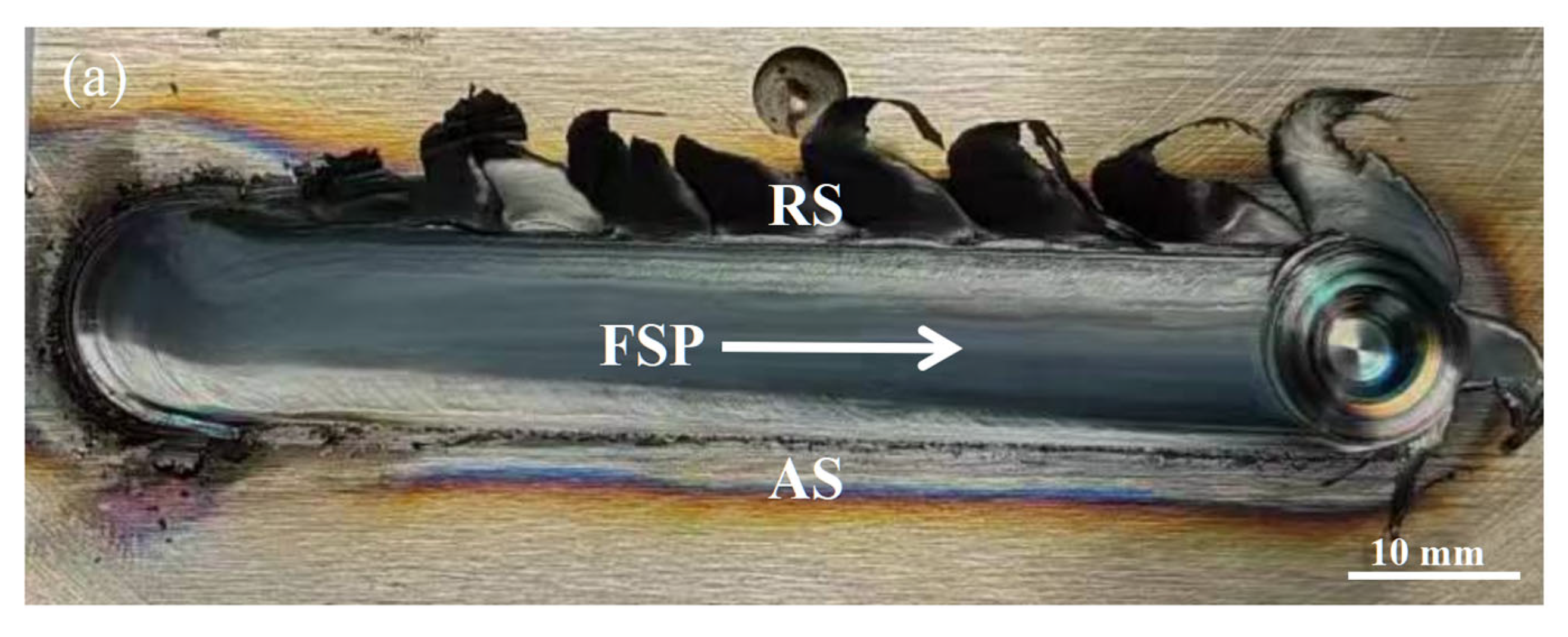
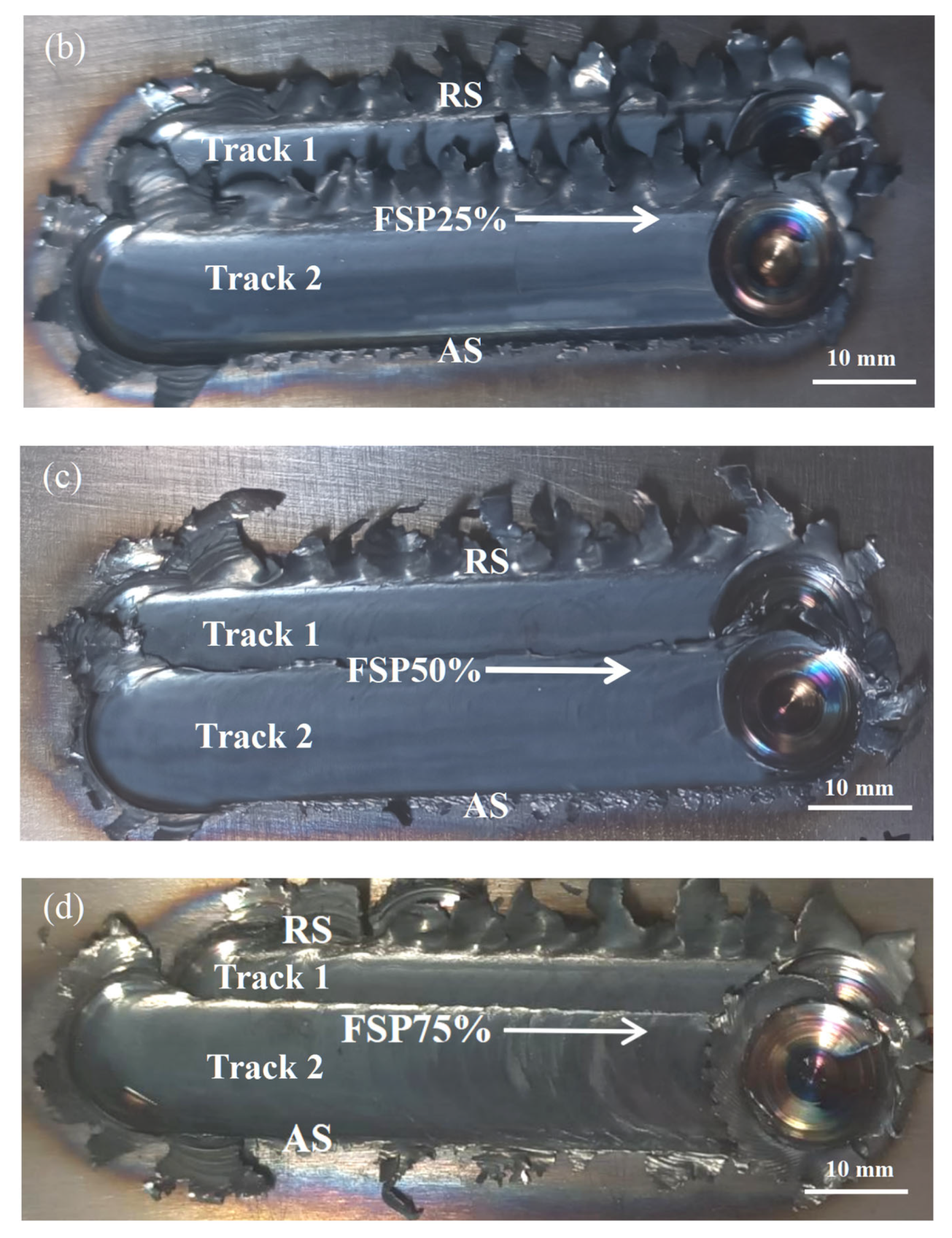
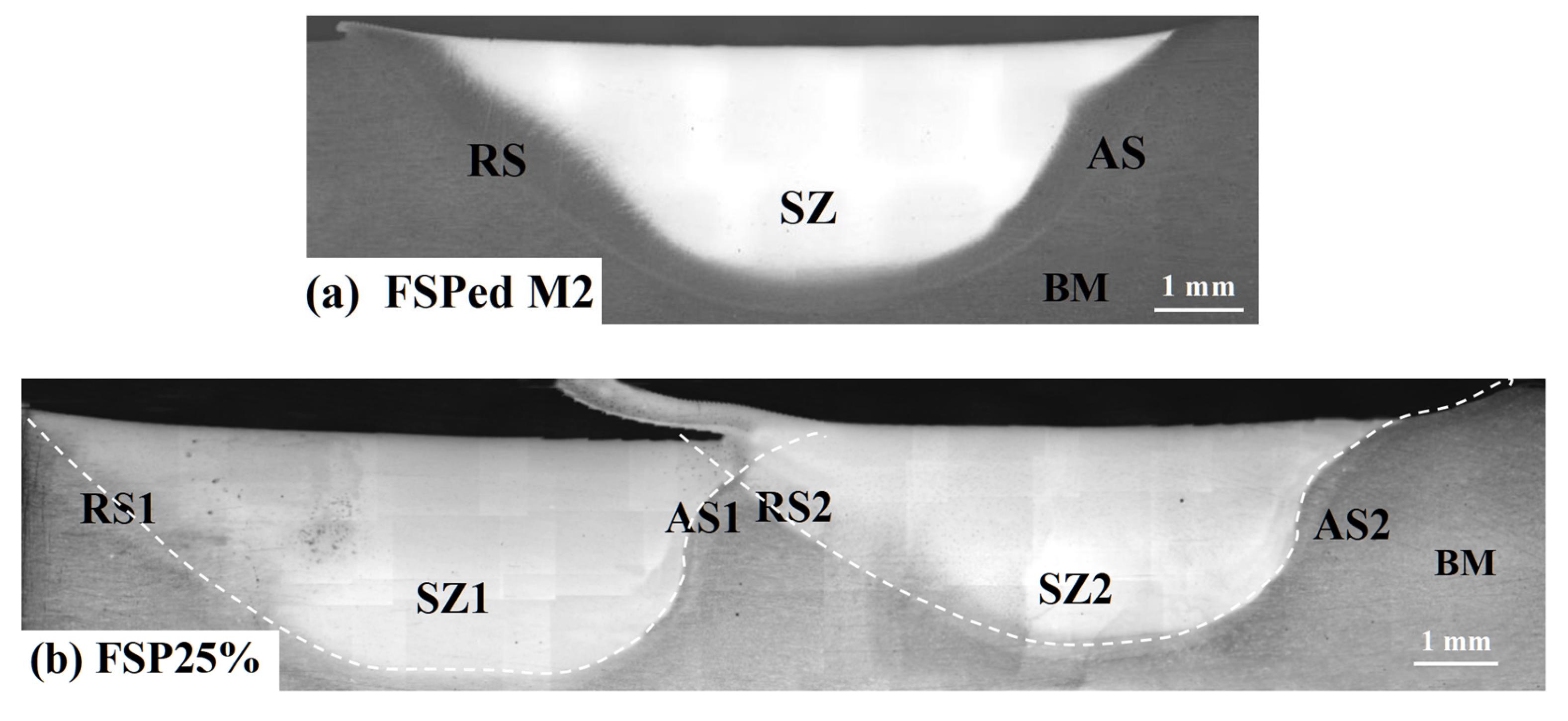
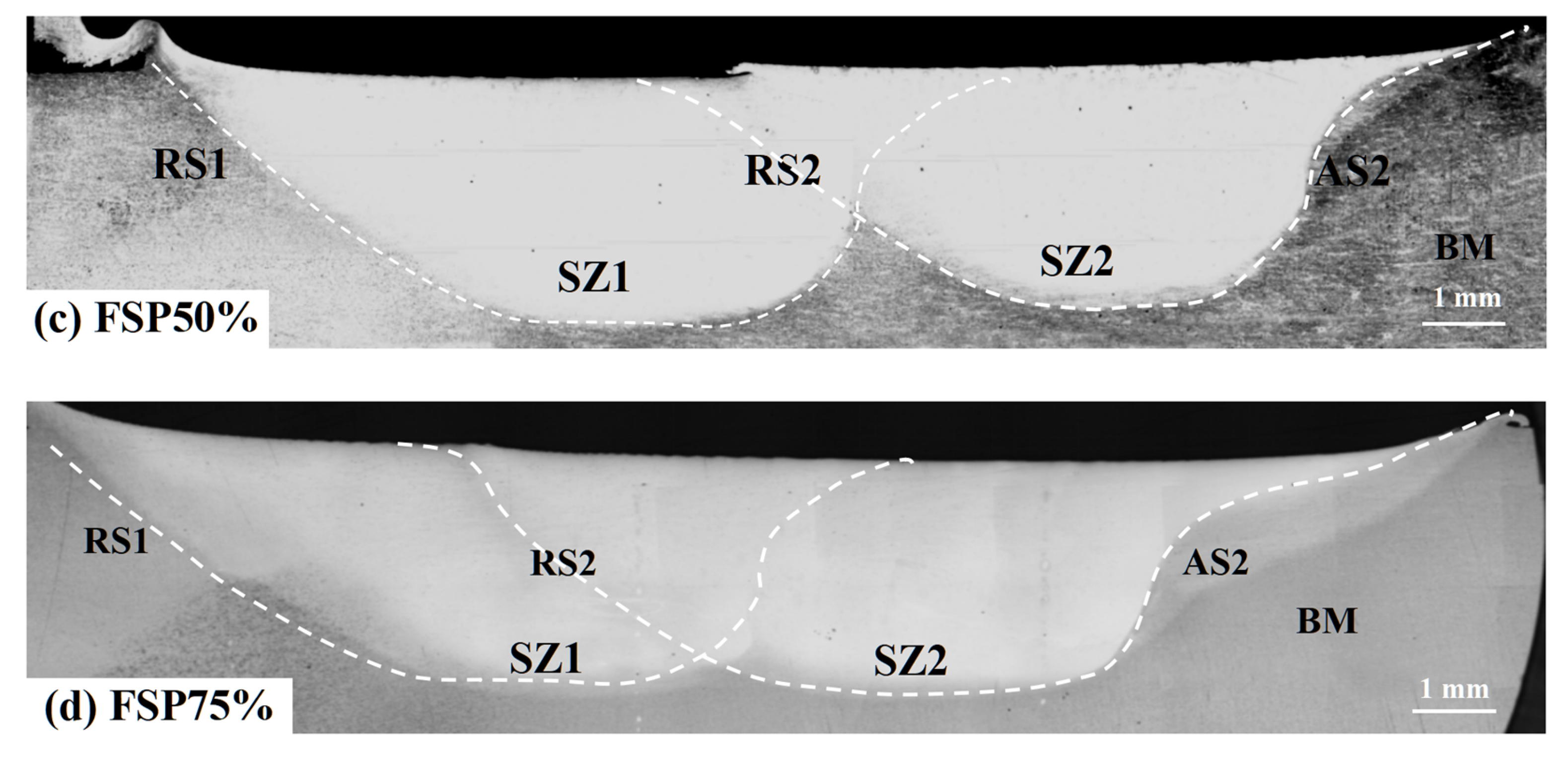
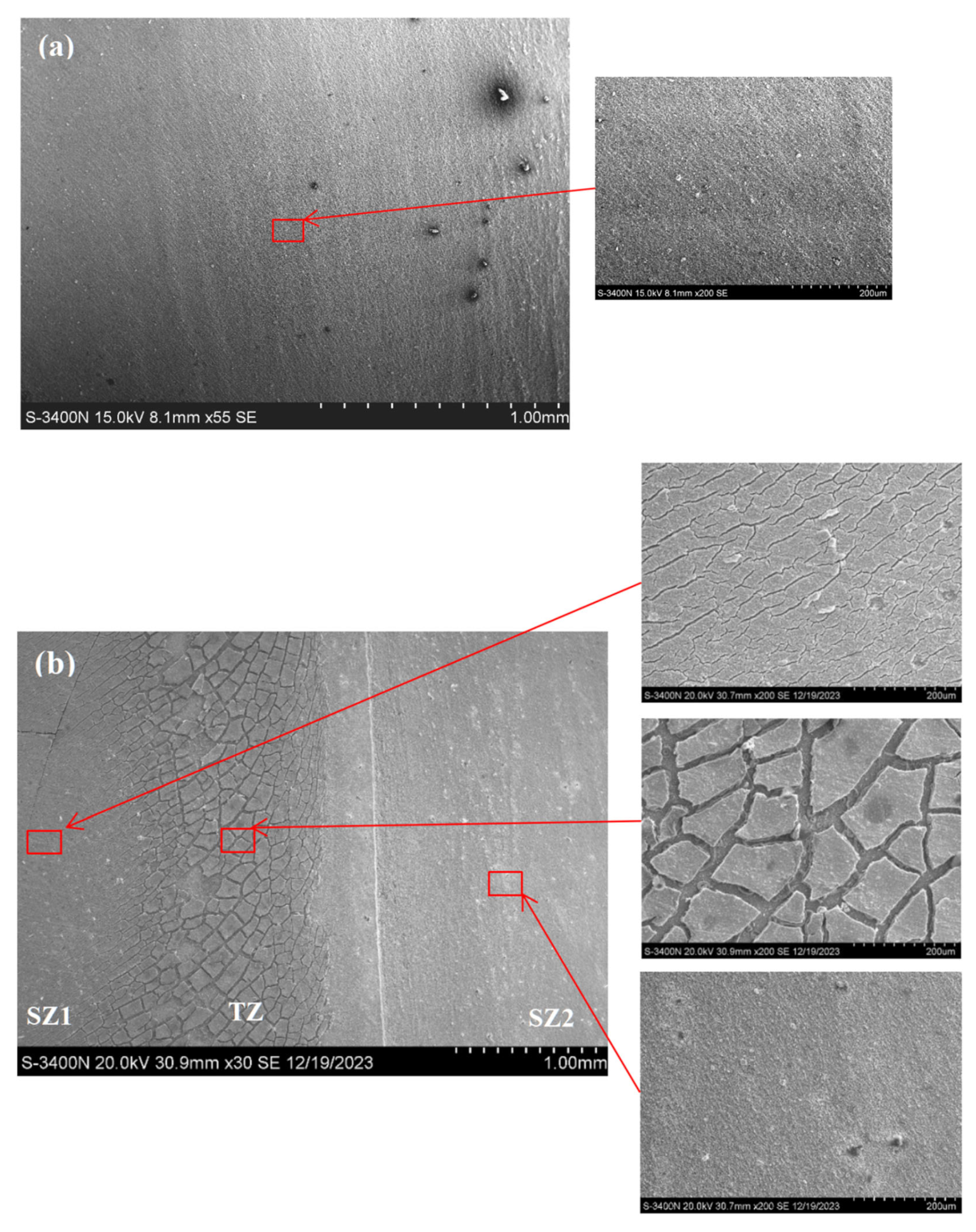
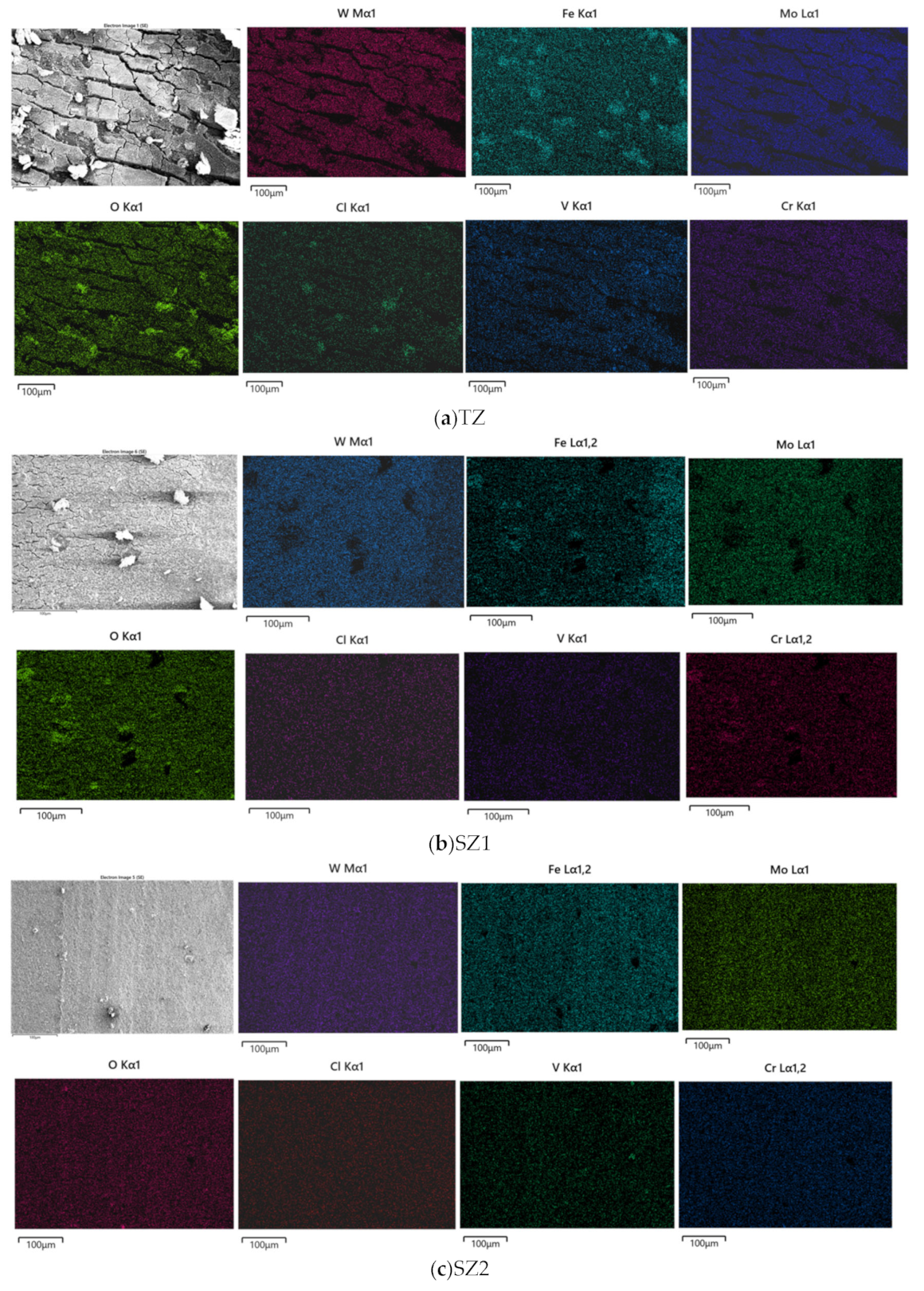
3.1. Macrostructural and Microstructural Analyses
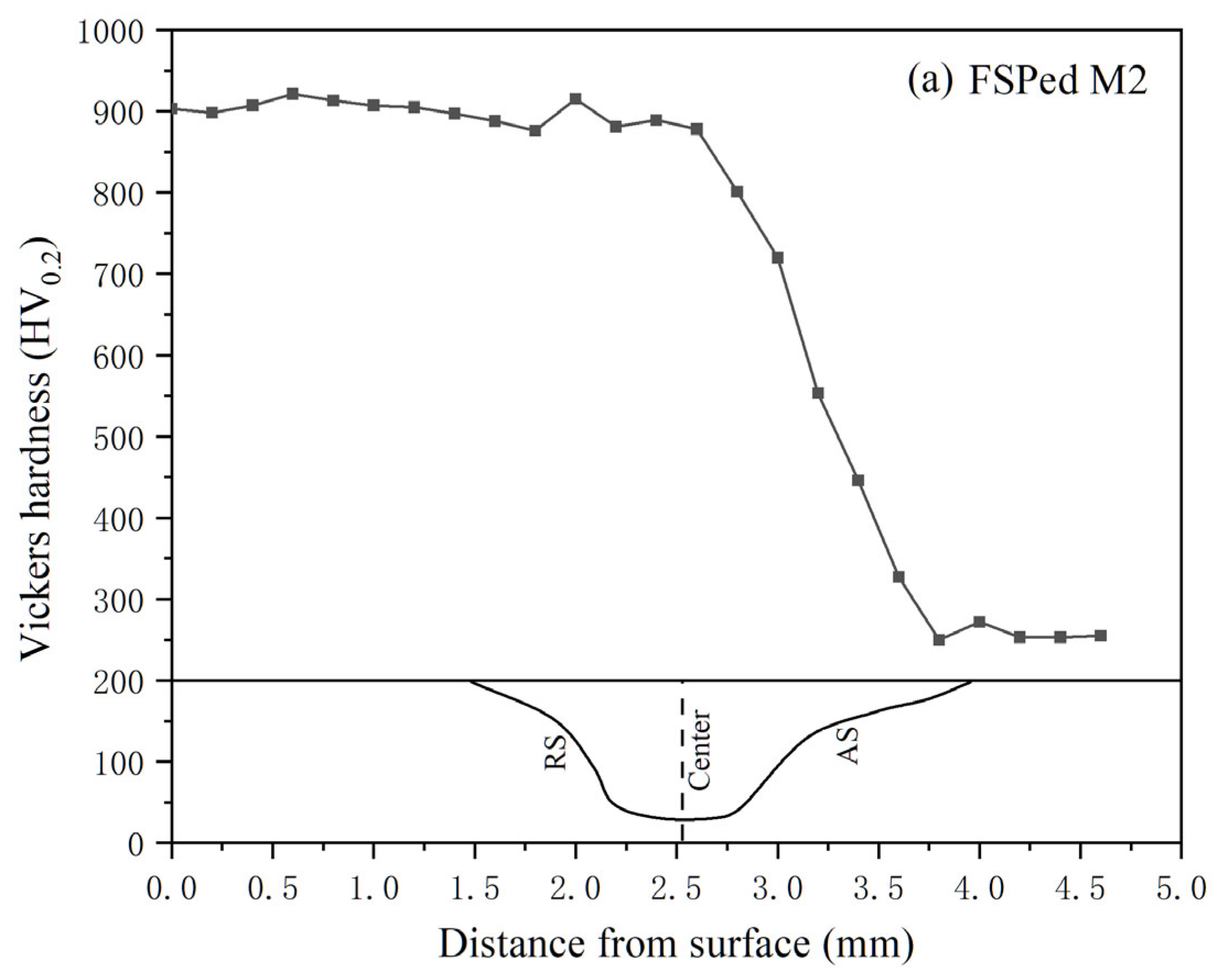
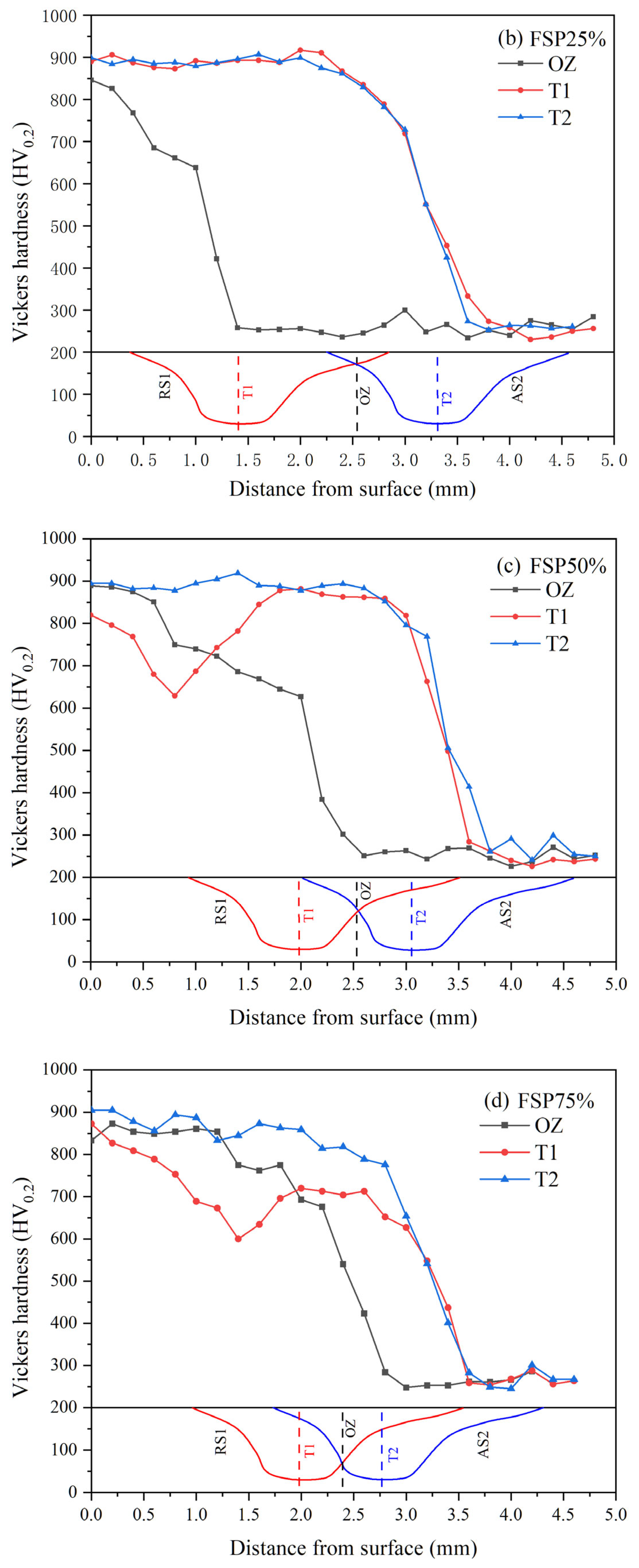
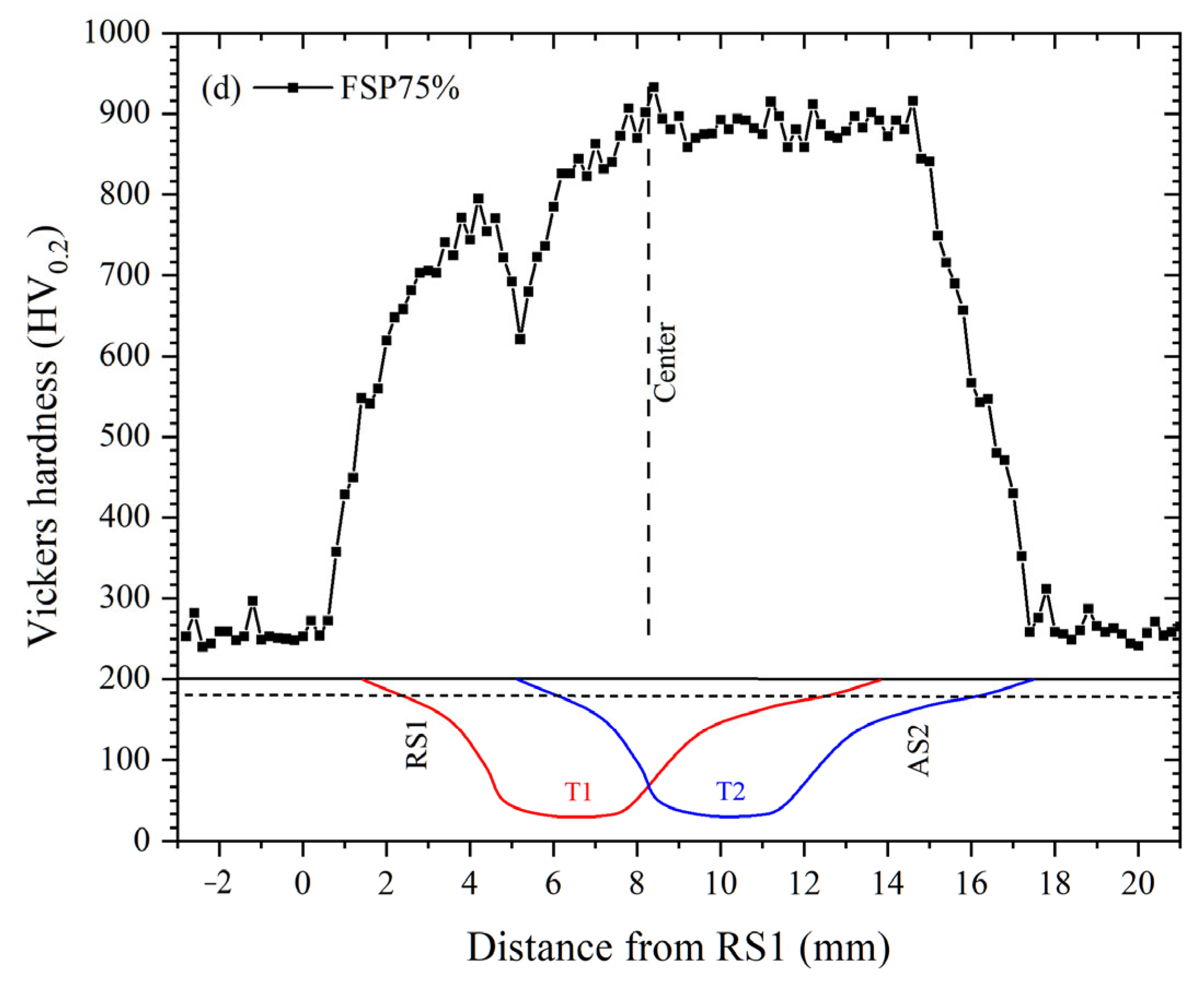
3.2. Hardness
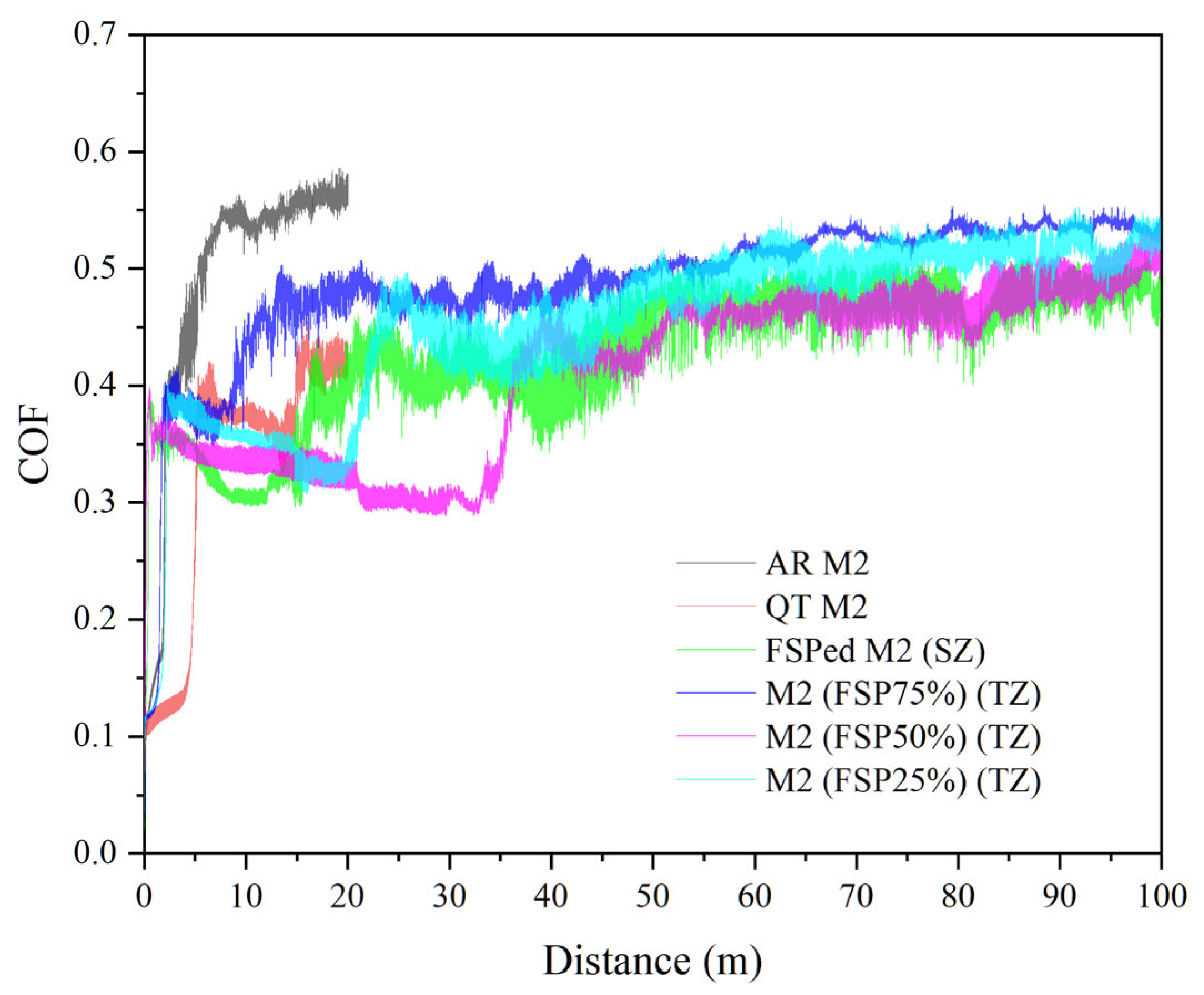
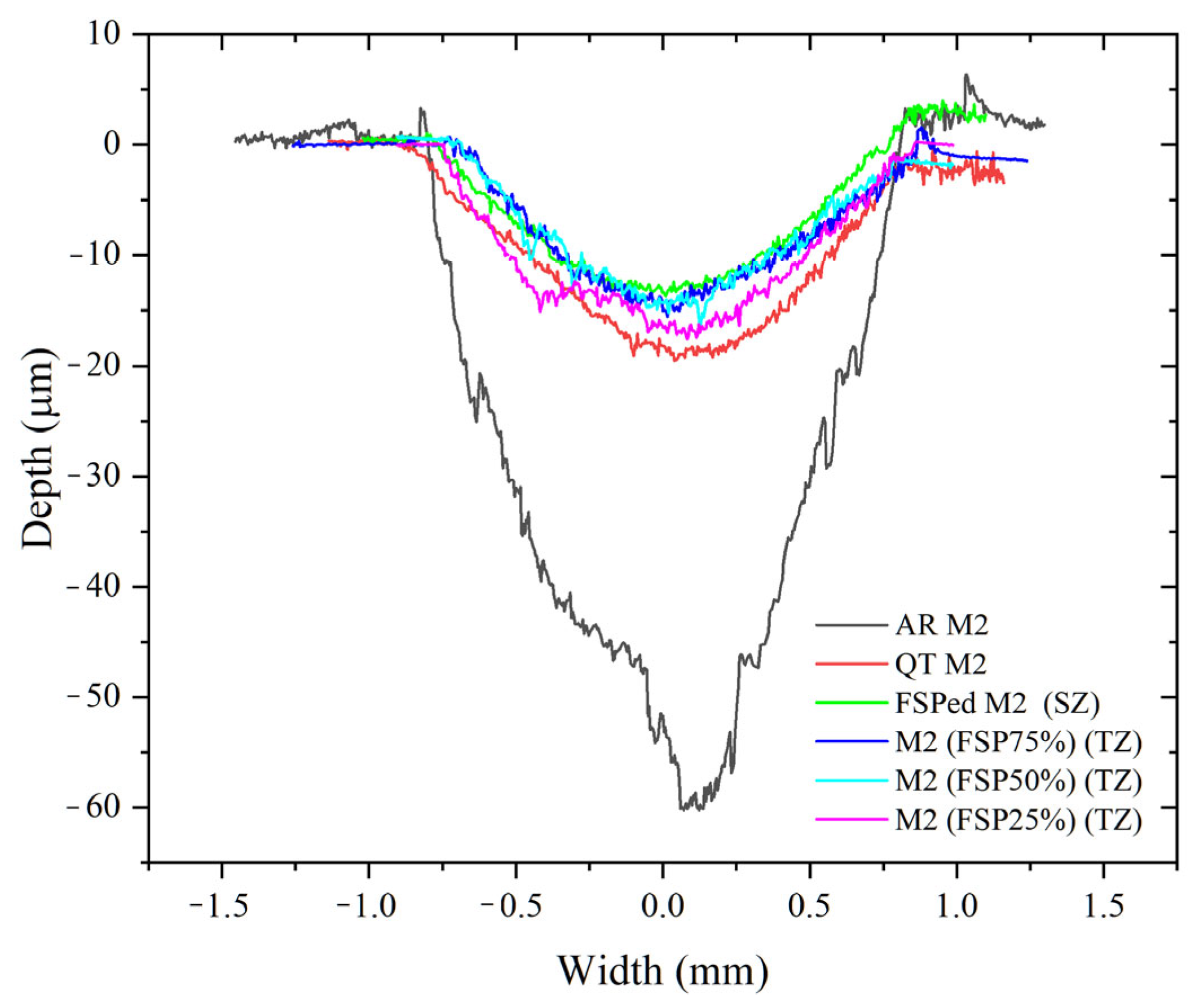
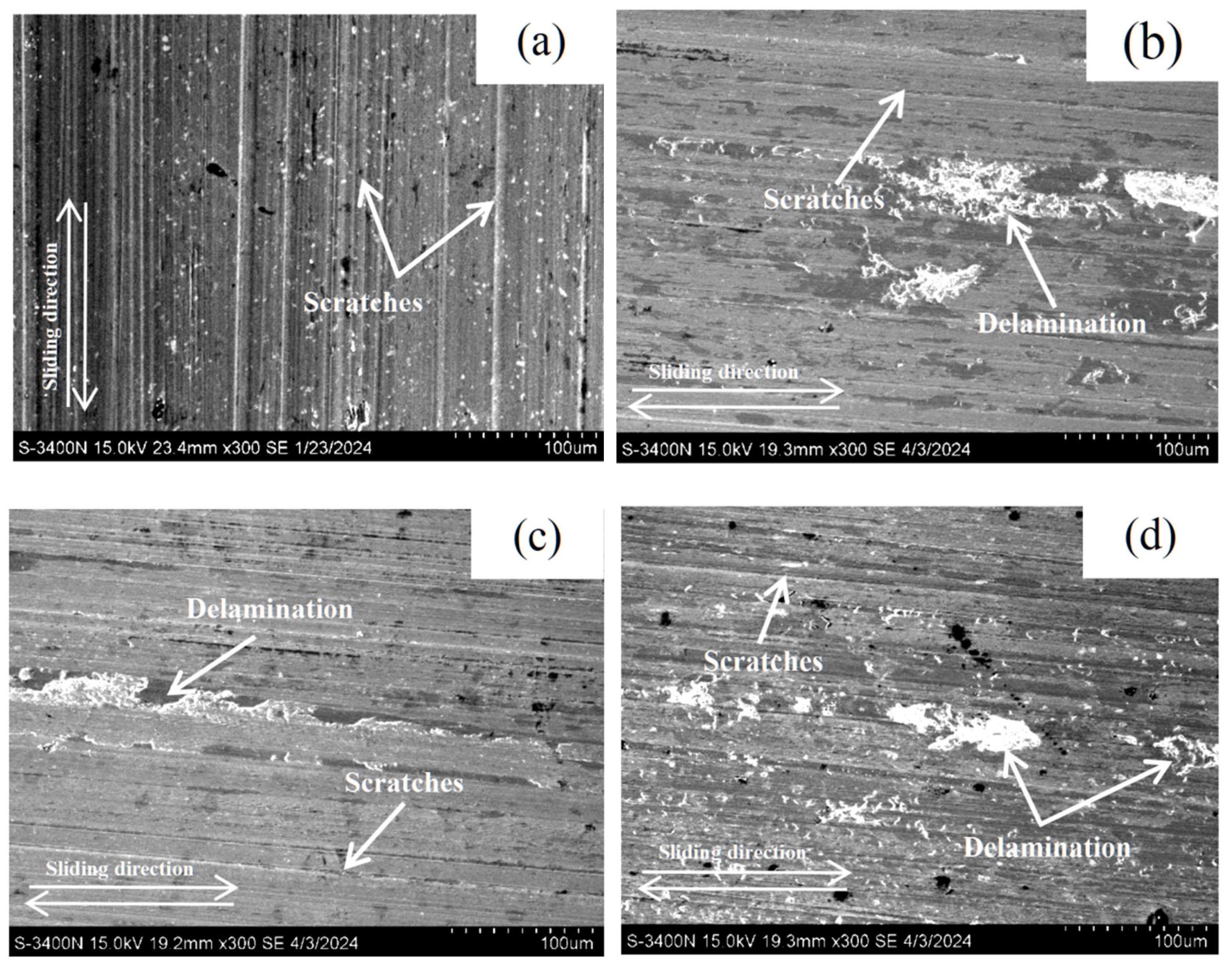
3.3. Wear Behavior
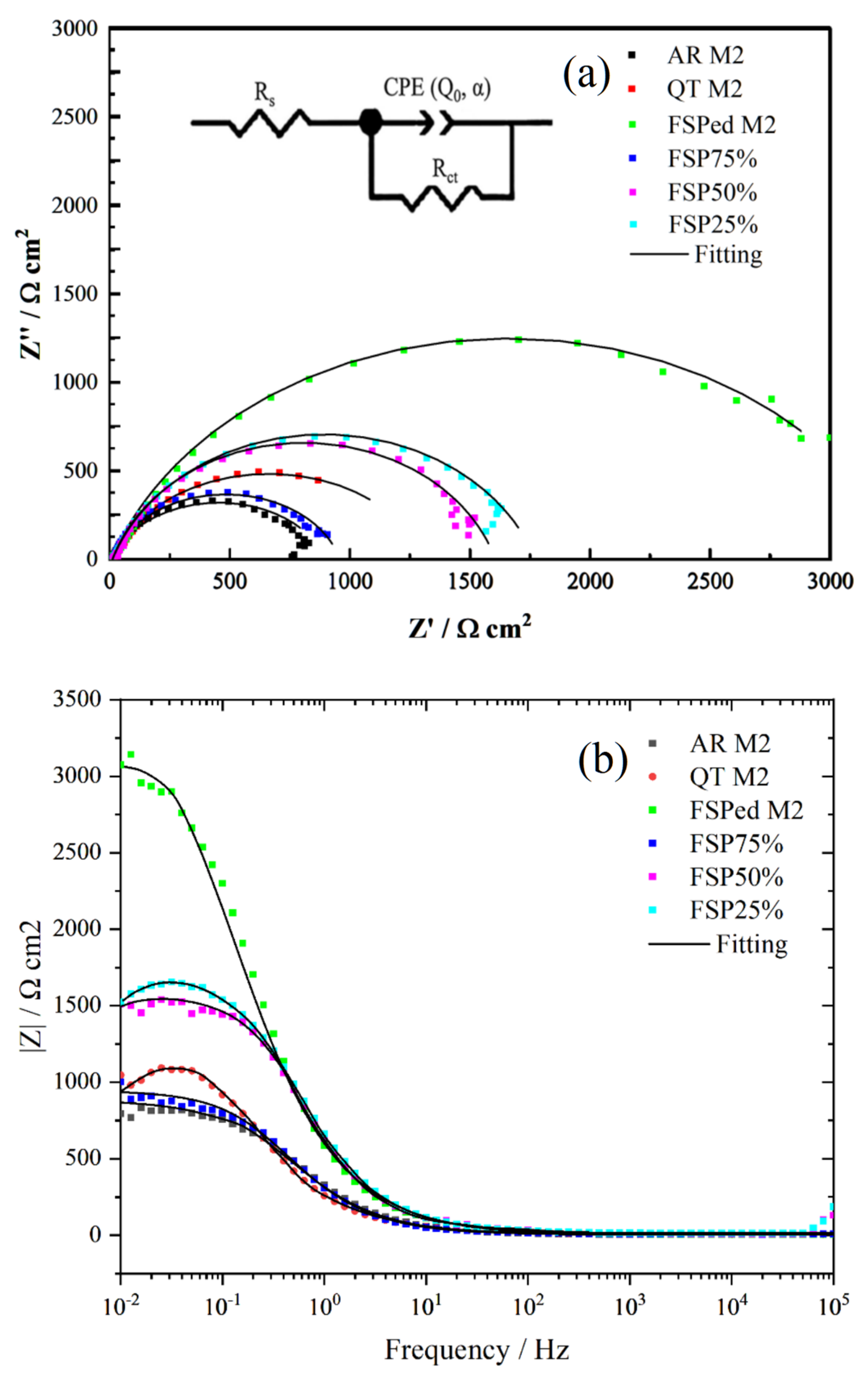
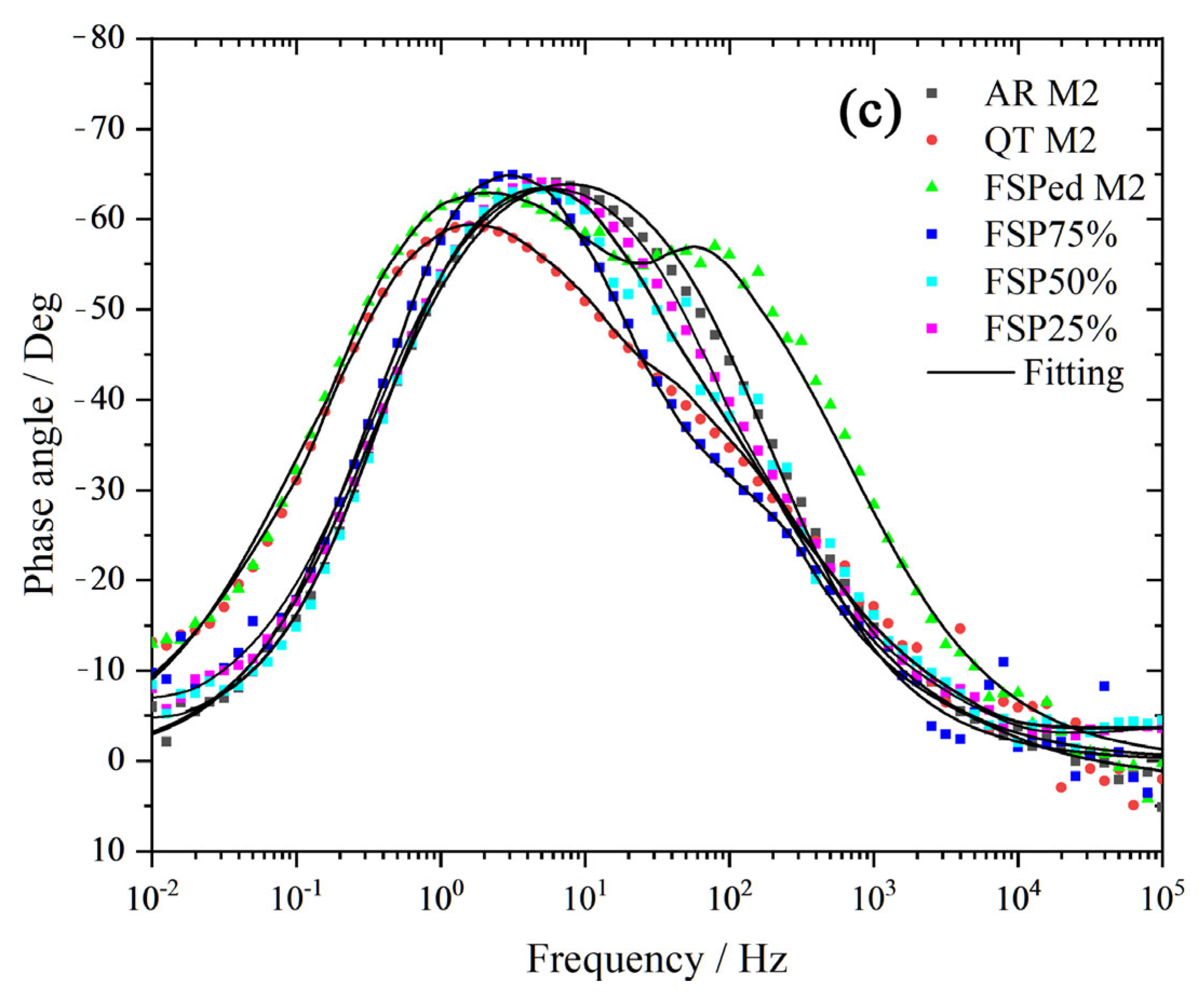
3.4. Corrosion Behavior
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FSP | Friction stir processing |
| FSW | Friction stir welding |
| HSS | High-speed steel |
| HCP | Hexagonal close packing |
| UTS | Ultimate tensile strength |
| EDS | Energy disperse spectroscopy |
| FCC | Face center cubic |
| BCT | Body-centered tetragonal |
| BCC | Body-centered cubic |
| OZ | Overlapped zone |
| TZ | Tempered zone |
| SZ | Stir zone |
| T1 | First track |
| T2 | Second track |
| TMAZ | Thermal mechanically affected zone |
| HAZ | Heat affected zone |
| BM | Base material |
| AR M2 | As-received AISI M2 HSS |
| QT M2 | Quenched and tempered M2 |
| FSP25% | Multiple-pass FSPed M2 with overlapping ratio of 25% |
| FSP50% | Multiple-pass FSPed M2 with overlapping ratio of 50% |
| FSP75% | Multiple-pass FSPed M2 with overlapping ratio of 75% |
| NETD | Noise equivalent temperature difference |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| TWI | The Welding Institute |
| HEA | High entropy alloy |
| OR | Overlapping ratio |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscope |
| RS | Retreating side |
| AS | Advancing side |
| COF | Coefficient of friction |
| SCE | Saturated calomel electrode |
| OCP | Open circuit potential |
| PD | Potentiodynamic polarization |
| EIS | Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy |
| Ecorr | Corrosion potential |
| Icorr | Corrosion current |
| CPE | Constant phase element |
| CR | Corrosion resistance |
References
- Zhang, M.; Chen, C.; Qin, L.; Yan, K.; Cheng, G.; Jing, H.M.; Zou, T. Laser additive manufacturing of M2 high-speed steel. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2017, 34, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, X.; Liu, K.; Cristino, V.A.M.; Lo, K.H.; Xie, Z.C.; Kwok, C.T. Friction stir processing of M2 and D2 tool steels for improving hardness, wear and corrosion resistances. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 481, 130609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merah, N.; Azeem, M.A.; Abubaker, H.M.; Al-Badour, F.; Albinmousa, J.; Sorour, A.A. Friction Stir Processing Influence on Microstructure, Mechanical, and Corrosion Behavior of Steels: A Review. Materials 2021, 14, 5023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, R.S.; Ma, Z.Y. Friction stir welding and processing. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2005, 50, 1–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.Y. Friction Stir Processing Technology: A Review. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2008, 39, 642–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Kwok, C.T.; Lo, K.H. Enhancement in hardness and corrosion resistance of AISI 420 martensitic stainless steel via friction stir processing. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 357, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Kwok, C.T.; Lo, K.H. Friction-stir processing of AISI 440C high-carbon martensitic stainless steel for improving hardness and corrosion resistance. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2020, 277, 116448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, C.D.; Nelson, T.W.; Packer, S.M.; Allen, C. Friction stir processing of D2 tool steel for enhanced blade performance. TMS Annu. Meet. 2007, 2007, 409–418. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Zhou, C.; Shi, Y.; Cui, Q.; Ji, S.; Yang, K. Grain-Refinement and Mechanical Properties Optimisation of A356 Casting Al by Ultrasonic-Assisted Friction Stir Processing. Met. Mater. Int. 2021, 27, 5374–5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, X.M.; Liu, K.; Cristino, V.A.M.; Lo, K.H.; Xie, Z.C.; Guo, D.W.; Tam, L.M.; Kwok, C.T. Influence of Processing Parameters on Microstructure and Surface Hardness of Hypereutectic Al-Si-Fe-Mg Alloy via Friction Stir Processing. Coatings 2024, 14, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.Q.; Nelson, T.W.; Sterling, C.J. Friction stir processing of large-area bulk UFG aluminum alloys. Scr. Mater. 2005, 52, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, F.; Santos, T.; Vilaça, P.; Miranda, R.M.; Quintino, L. Microstructural modification and ductility enhancement of surfaces modified by FSP in aluminium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 506, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.I.; Du, X.H.; Huang, J.C. Achieving ultrafine grain size in Mg–Al–Zn alloy by friction stir processing. Scr. Mater. 2007, 57, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Han, P.; Peng, P.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Q.; Yuan, S.N.; Huang, L.Y.; Yu, H.L.; Qiao, K.; Wang, K.S. Friction Stir Processing of Magnesium Alloys: A Review. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 2019, 33, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.Q.; Nelson, T.W.; McNelley, T.R.; Mishra, R.S. Development of nanocrystalline structure in Cu during friction stir processing (FSP). Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 5458–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avettand-Fènoël, M.N.; Simar, A.; Shabadi, R.; Taillard, R.; Meester, B.D. Characterization of oxide dispersion strengthened copper based materials developed by friction stir processing. Mater. Des. 2014, 60, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajian, M.; Abdollah-zadeh, A.; Rezaei-Nejad, S.S.; Assadi, H.; Hadavi, S.M.M.; Chung, K.; Shokouhimehr, M. Microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir processed AISI 316L stainless steel. Mater. Des. 2015, 67, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Garcia, D.; Wang, T.; Escobar, J.D.; Pole, M.; Nwe, K.; Brown, D.M.; Ross, K.A.; Olszta, M.J.; Kappagantula, K.S.; et al. Meshfree simulation and prediction of recrystallized grain size in friction stir processed 316L stainless steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2025, 337, 118751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.K.; Sharma, H.; Rao, A.U. A comprehensive review of the recent developments in friction stir welding of metals, alloys, and polymers: A review of process parameters and properties. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2024, 38, 3179–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, A.R.; Su, H.; Wu, C.S. The Influence of multiple-pass Friction Stir Processing on the Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of IS2062 Steel. Metals 2024, 14, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldajah, S.H.; Ajayi, O.O.; Fenske, G.R.; David, S. Effect of friction stir processing on the tribological performance of high carbon steel. Wear 2009, 267, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, N.; Rao, A.G.; Dommeti, S.G.; Prabhu, N. Effect of multiple-pass Friction Stir Processing on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Metastable Dual-Phase High Entropy Alloy. Lubricants 2022, 11, 2125–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.L.; Kwok, C.T.; Lo, K.H. Effect of Multiple-Pass Friction Stir Processing on Hardness and Corrosion Resistance of Martensitic Stainless Steel. Coatings 2019, 9, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASM International. Properties of the AISI M2 Steel. In ASM Metals Handbook, 10th ed.; ASM International: Novelty, OH, USA, 1990; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM Standard E384-17; Standard Test Method for Microindentation Hardness of Materials. ASTM Committee: West Conshehawken, PA, USA, 2003.
- ASTM Standard G133-05; Standard Test Method for Linearly Reciprocating Ball-on-Flat Sliding Wear. ASTM Committee: West Conshehawken, PA, USA, 2016.
- Gandra, J.; Miranda, R.M.; Vilaca, P. Effect of overlapping direction in multipass friction stir processing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 5592–5599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, D.; Bauri, R. Effect of friction stir processing on microstructure and mechanical properties of aluminium. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 539, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, J.A.; Giorjao, R.A.R.; Rodriguez, J.; Fonseca, E.B.; Ramirez, A.J. Modeling of thermal cycles and microstructural analysis of pipeline steels processed by friction stir processing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 98, 2611–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossam, H. Thermodynamic Calculation for Silicon ModifiedAISI M2 High Speed Tool Steel. J. Miner. Mater. Charact. Eng. 2013, 1, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Godec, M.; Večko Pirtovšek, T.; Šetina Batič, B.; McGuiness, P.; Burja, J.; Podgornik, B. Surface and Bulk Carbide Transformations in High-Speed Steel. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minggui, Q.U.; Zhenhua, W.; Hui, L.I.; Zhiqing, L.V.; Sun, S.H.; Fu, W.T. Effects of mischmetal addition on phase transformation and as-cast microstructure characteristics of M2 high-speed steel. J. Rare Earths 2013, 31, 628–633. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Qin, T.; Xu, W.; Jia, C.; Wu, Q.; Chen, M.; Liu, Z. Effect of Tempering Conditions on Secondary Hardening of Carbides and Retained Austenite in Spray-Formed M42 High-Speed Steel. Materials 2019, 12, 3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carasi, G.; Yu, B.; Hutten, E.; Zurob, H.; Casati, R.; Vedani, M. Effect of Heat Treatment on Microstructure Evolution of X38CrMoV5-1 Hot-Work Tool Steel Produced by L-PBF. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2021, 52, 2564–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Xu, B.; Huang, J.; Zhang, P.; Wu, Y. Study on the softening in overlapping zone by laser-overlapping scanning surface hardening for carbon and alloyed steel. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2010, 48, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iino, Y.; Shimoda, K. Effect of overlap pass tempering on hardness and fatigue behaviour in laser heat treatment of carbon steel. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1987, 6, 1193–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorleo, L.; Previtali, B.; Semeraro, Q. Modelling of back tempering in laser hardening. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2010, 54, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isfahany, A.N.; Saghafian, H.; Borhani, G. The effect of heat treatment on mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of AISI420 martensitic stainless steel. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 3931–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H.; Honeycombe, R.W.K. Diffusion in Solids-Fundamentals, Methods, Materials, Diffusion-Controlled Process, 3rd ed.; Elsevier Ltd.: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Mesquita, R.A.; Schneider, R.; Goncalves, C.S.; Dossett, J.L.; Totten, G.E. Heat Treating of High-Speed Tool Steels, in ASM Handbook Volume 4D: Heat Treating of Irons and Steels. In Heat Treating of Irons and Steels; Dossett, G.E.T.J.L., Ed.; ASM International: Novelty, OH, USA, 2014; pp. 347–357. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Chen, C.; Zhang, M. Effect of Mo and Tempering Treatment on the Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties of M2 High-Speed Steel Prepared by Laser-Directed Energy Deposition. Steel Res. Int. 2021, 92, 2100225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunil Kumar, B.; Kain, V.; Vishwanadh, B. Effect of Tempering Treatments on Microstructure and Intergranular Corrosion of 13wt% Cr Martensitic Stainless Steel. Corrosion 2017, 73, 362–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, A.A.; Omar, M.Z.; Junaidi, S.; Sajuri, Z. Effect of Different Heat Treatment on the SS440C Martensitic Stainless Steel. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2011, 5, 867–871. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, D.C.; Biro, E.; Gerlich, A.P.; Zhou, Y. Effects of tempering mode on the structural changes of martensite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 673, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollomon, J.H.; Jaffe, L.D. Time-Temperature Relations in Tempering Steel. Trans AIM 1945, 162, 223–249. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, J.; Zhao, J.; Dou, S. Friction Characteristics Analysis of Symmetric Aluminum Alloy Parts in Warm Forming Process. Symmetry 2022, 14, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Q.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, Y. Experimental Investigation into the Friction Coefficient of Ball-on-Disc in Dry Sliding Contact Considering the Effects of Surface Roughness, Low Rotation Speed, and Light Normal Load. Lubricants 2022, 10, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjavadi, S.S.; Alipour, M.; Emamian, S.; Kord, S.; Hamouda, A.M.S.; Koppad, P.G.; Keshavamurthy, R. Influence of TiO2 nanoparticles incorporation to friction stir welded 5083 aluminum alloy on the microstructure, mechanical properties and wear resistance. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 712, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Dong, J.; Xiong, J.; Jiang, N.; Li, J.L.; Guo, W. Microstructure characteristics and corrosion behavior of refill friction stir spot welded 7050 aluminum alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 20, 1302–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y. Influence of carbides on the high-temperature tempered martensite embrittlement of martensitic heat-resistant steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 670, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurči, P.; Bartkowska, A.; Hudáková, M.; Dománková, M.; Čaplovičová, M.; Bartkowski, D. Effect of Sub-Zero Treatments and Tempering on Corrosion Behaviour of Vanadis 6 Tool Steel. Materials 2021, 14, 3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripoll, M.R.; Ojala, N.; Katsich, C.; Totolin, V.; Tomastik, C.; Hradil, K. The role of niobium in improving toughness and corrosion resistance of high speed steel laser hardfacings. Mater. Des. 2016, 99, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katiyar, P.K.; Misra, S.; Mondal, K. Comparative Corrosion Behavior of Five Microstructures (Pearlite, Bainite, Spheroidized, Martensite, and Tempered Martensite) Made from a High Carbon Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2019, 50, 1489–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Composition (wt%) | Fe | W | Mo | Cr | V | Mn | Ni | Si | C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M2 | Bal. | 8.52 | 6.52 | 3.33 | 2.13 | 0.31 | 0.29 | 0.23 | 0.90 |
| FSP parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Rotation speed | 600 rpm |
| Traveling speed | 100 mm/min |
| Plunged depth | 4.1 mm |
| Plunged speed | 5 mm/min |
| Z-axis lifting speed | 50 mm/min |
| Z-axis lifting height | 20 mm |
| Plunged delay time | 7 s |
| Lift delay time | 2 s |
| Overlapping ratios | 25%, 50%, and 75% |
| Specimen | Average Hardness | COF | Wear Volume (mm3) | Wear Rate (10−5 mm3/N·m) | Normalized Wear Resistance * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FSPed M2 (SZ) | 896 ± 6 | 0.45 ± 0.02 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 0.75 ± 0.05 | 14.0 |
| FSP25% (TZ) | 679 ± 78 | 0.50 ± 0.02 | 0.28 ± 0.04 | 1.40 ± 0.20 | 7.5 |
| FSP50% (TZ) | 699 ± 63 | 0.47 ± 0.03 | 0.24 ± 0.02 | 1.20 ± 0.10 | 8.8 |
| FSP75% (TZ) | 710 ± 32 | 0.50 ± 0.03 | 0.20 ± 0.01 | 1.00 ± 0.05 | 10.5 |
| QT M2 | 779 ± 10 | 0.42 ± 0.03 | 0.12 ± 0.02 | 3.00 ± 0.50 | 3.5 |
| AR M2 | 360 ± 3 | 0.55 ± 0.01 | 0.42 ± 0.06 | 10.50 ± 1.50 | 1.0 |
| Specimens | Ecorr (mVSCE) | Icorr (μA/cm2) |
|---|---|---|
| FSPed M2 | −342.4 ± 2.7 | 4.5 ± 0.9 |
| FSP25% | −397.6 ± 5.6 | 9.5 ± 0.8 |
| FSP50% | −424.4 ± 6.0 | 14.7 ± 1.7 |
| FSP75% | −440.9 ± 2.8 | 17.1 ± 1.9 |
| QT M2 | −430.7 ± 3.3 | 24.2 ± 1.5 |
| AR M2 | −441.5 ± 3.1 | 34.2 ± 1.0 |
| Specimen | Rs (Ω·cm2) | CPE | Rct (Ω·cm2) | χ2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α (0–1) | Q0/(Ω−1 cm−2 sα) | ||||
| AR M2 | 5.85 | 0.795 | 0.0061038 | 898.70 | 0.000222 |
| QT M2 | 7.84 | 0.685 | 0.0010131 | 1629.56 | 0.00125 |
| FSPed M2 | 5.45 | 0.735 | 0.00039844 | 3647.03 | 0.00123 |
| FSP75% | 9.85 | 0.835 | 0.00055001 | 937.85 | 0.0104 |
| FSP50% | 7.96 | 0.813 | 0.00041941 | 1805.98 | 0.0401 |
| FSP25% | 10.89 | 0.797 | 0.00039977 | 1957.55 | 0.0541 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Q.; Li, S.; Rao, G.; Chen, X.; Liu, K.; Zhou, M.; Guo, D.; Cristino, V.A.M.; Lo, K.-H.; Tam, L.-M.; et al. Effect of Back-Tempering on the Wear and Corrosion Properties of Multiple-Pass Friction Stir Processed High-Speed Steel. Materials 2025, 18, 4125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174125
Liu Q, Li S, Rao G, Chen X, Liu K, Zhou M, Guo D, Cristino VAM, Lo K-H, Tam L-M, et al. Effect of Back-Tempering on the Wear and Corrosion Properties of Multiple-Pass Friction Stir Processed High-Speed Steel. Materials. 2025; 18(17):4125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174125
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Quan, Shiye Li, Guochong Rao, Xiaomi Chen, Kun Liu, Min Zhou, Dawei Guo, Valentino A. M. Cristino, Kin-Ho Lo, Lap-Mou Tam, and et al. 2025. "Effect of Back-Tempering on the Wear and Corrosion Properties of Multiple-Pass Friction Stir Processed High-Speed Steel" Materials 18, no. 17: 4125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174125
APA StyleLiu, Q., Li, S., Rao, G., Chen, X., Liu, K., Zhou, M., Guo, D., Cristino, V. A. M., Lo, K.-H., Tam, L.-M., & Kwok, C.-T. (2025). Effect of Back-Tempering on the Wear and Corrosion Properties of Multiple-Pass Friction Stir Processed High-Speed Steel. Materials, 18(17), 4125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174125








