Critical Questions Surrounding the Shot-Blasting Treatment of Titanium Dental Implants
Abstract
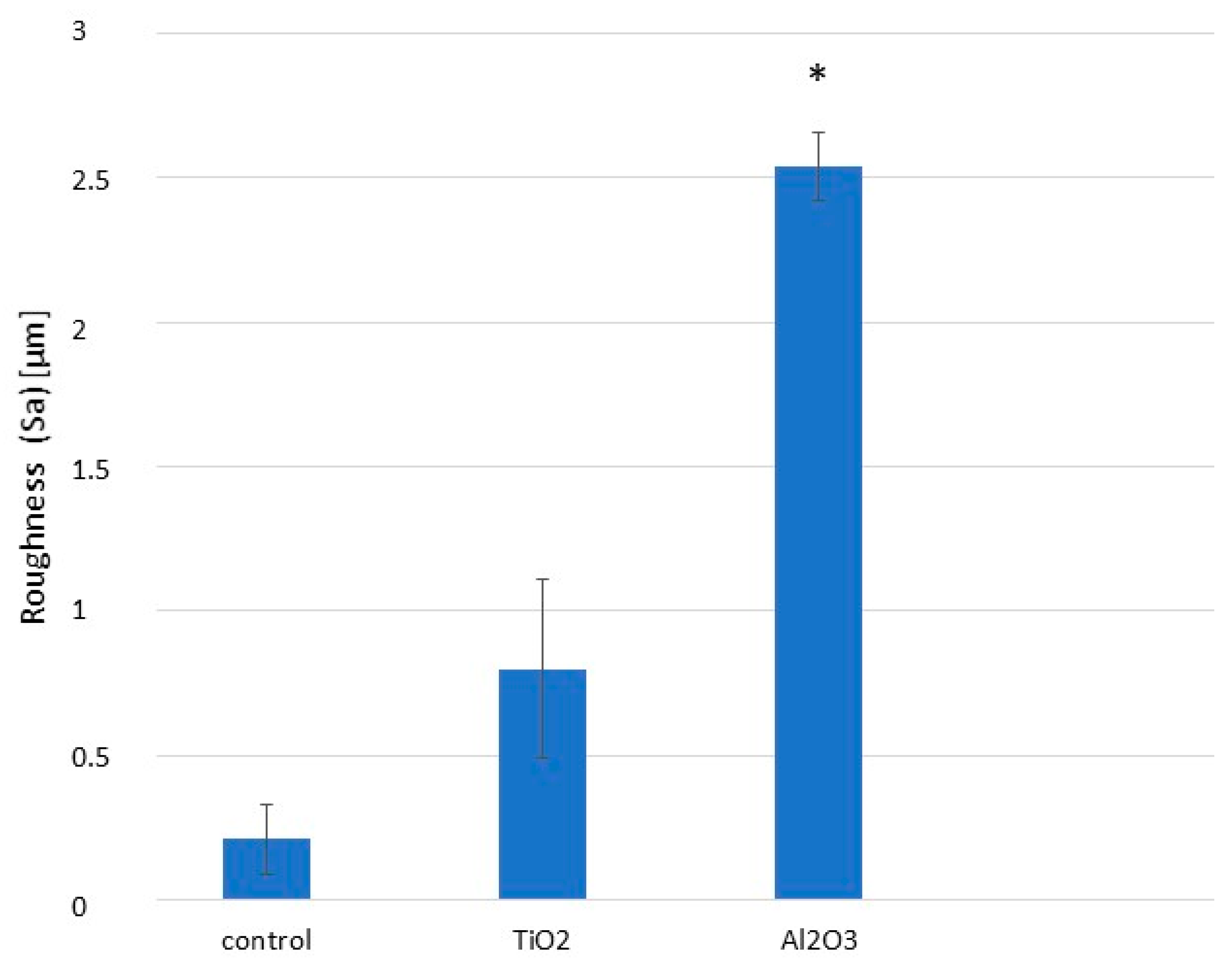
1. Are Alumina Residues on Titanium Surfaces Harmful?
| Surface | Sa (µm) | Sm (µm) | Index Area | CA’ [o] | Surface Energy (mJ/m2) | Dispersive Component | Polar Component |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ctr | 0.21 ± 0.02 * | 0.34 ± 0.02 * | 1.09 ± 0.01 * | 66.3 ± 0.5 * | 40.0 ± 3.5 * | 24.8 ± 3.2 * | 15.2 ± 4.0 * |
| Al2O3 | 2.35 ± 0.13 ** | 5.41 ± 0.21 ** | 1.18 ± 0.06 ** | 75.4 ± 0.5 ** | 28.2 ± 1.9 ** | 17.7 ± 1.1 ** | 10.5 ± 3.1 ** |
| Clean | 2.34 ± 0.25 ** | 5.67 ± 1.07 ** | 1.16 ± 0.04 ** | 66.8 ± 0.7 * | 38.8 ± 2.5 * | 26.8 ± 2.6 * | 11.0 ± 3.4 ** |
2. Is Shot Blasting with Titanium Oxide Suitable?
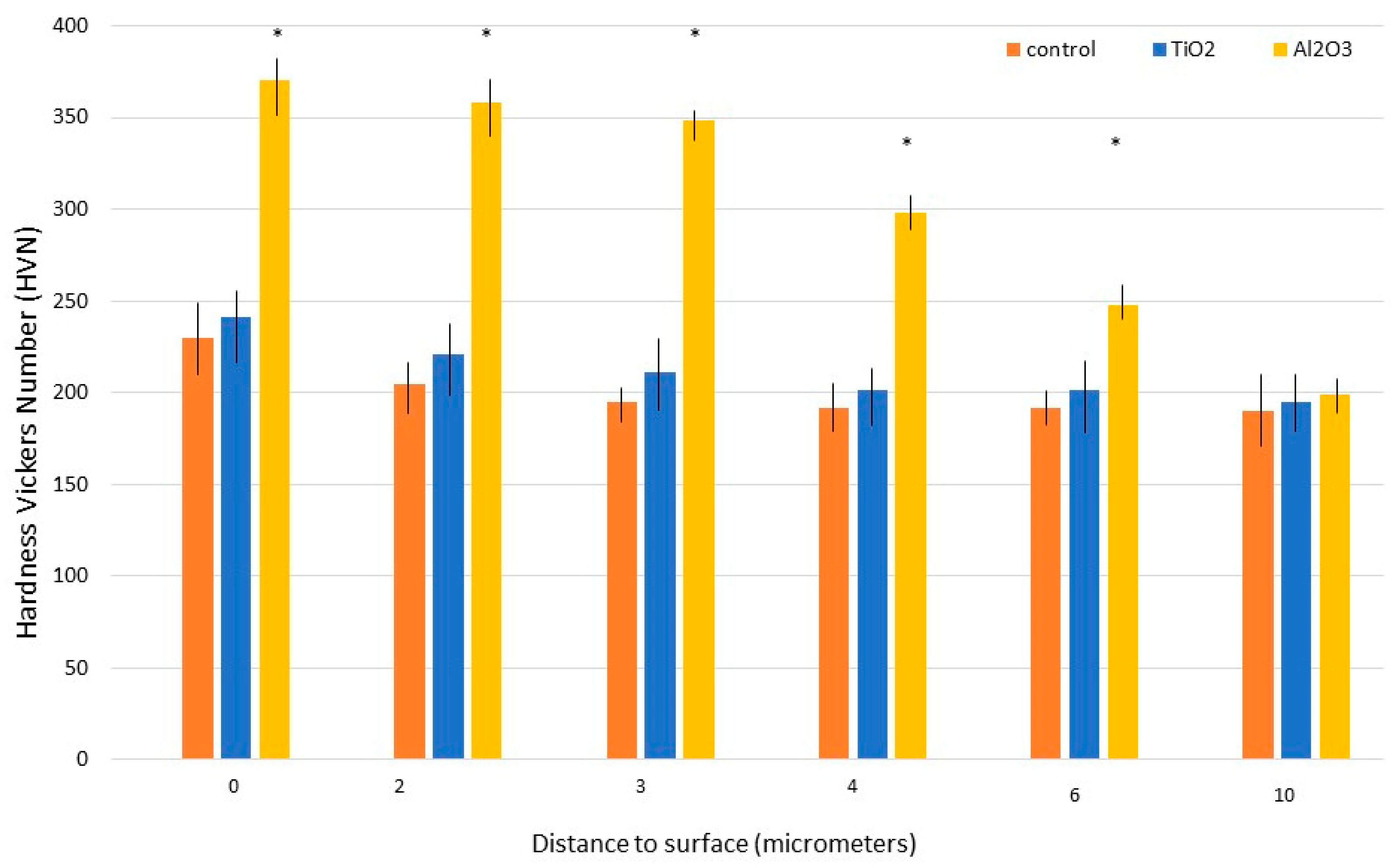
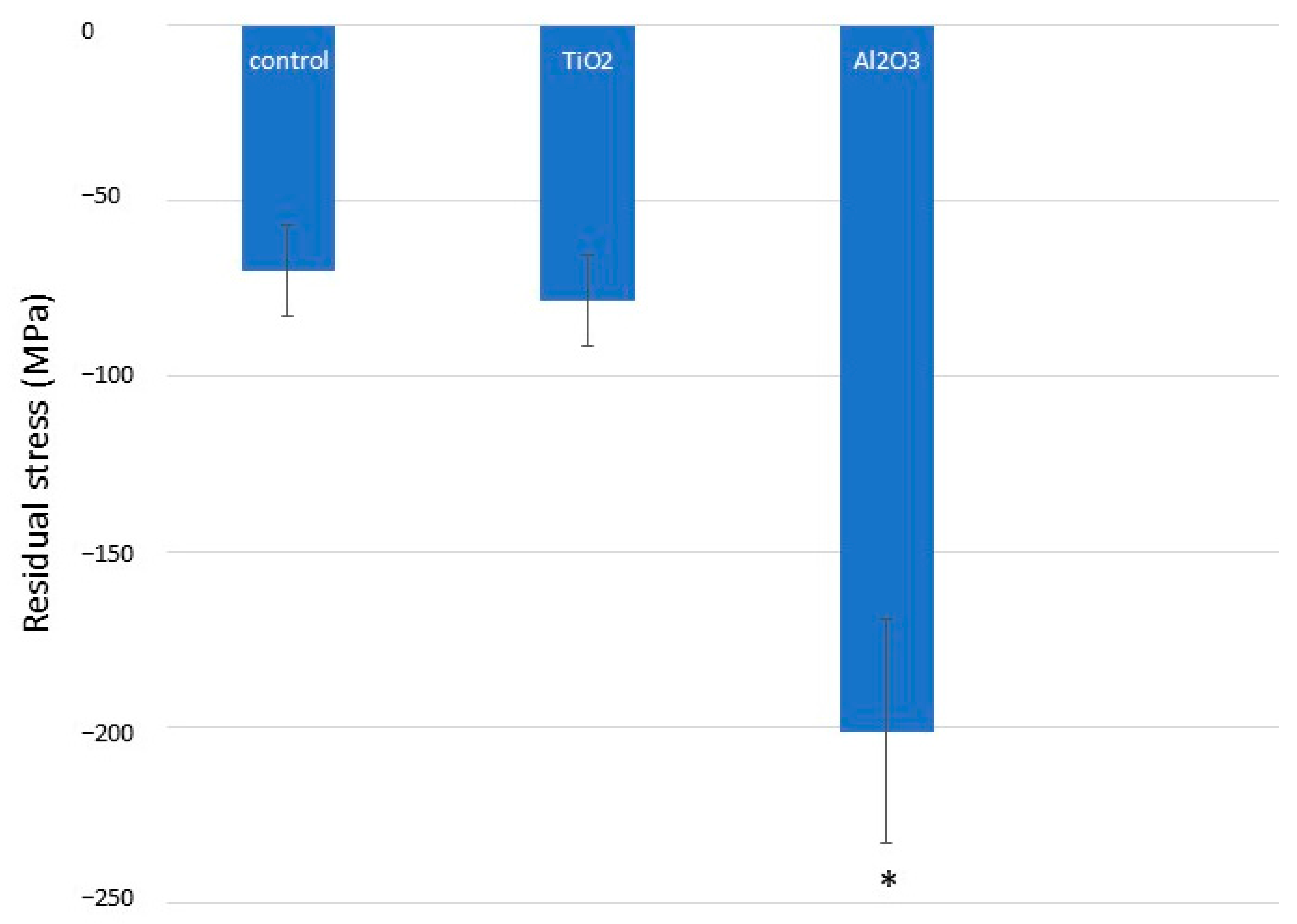
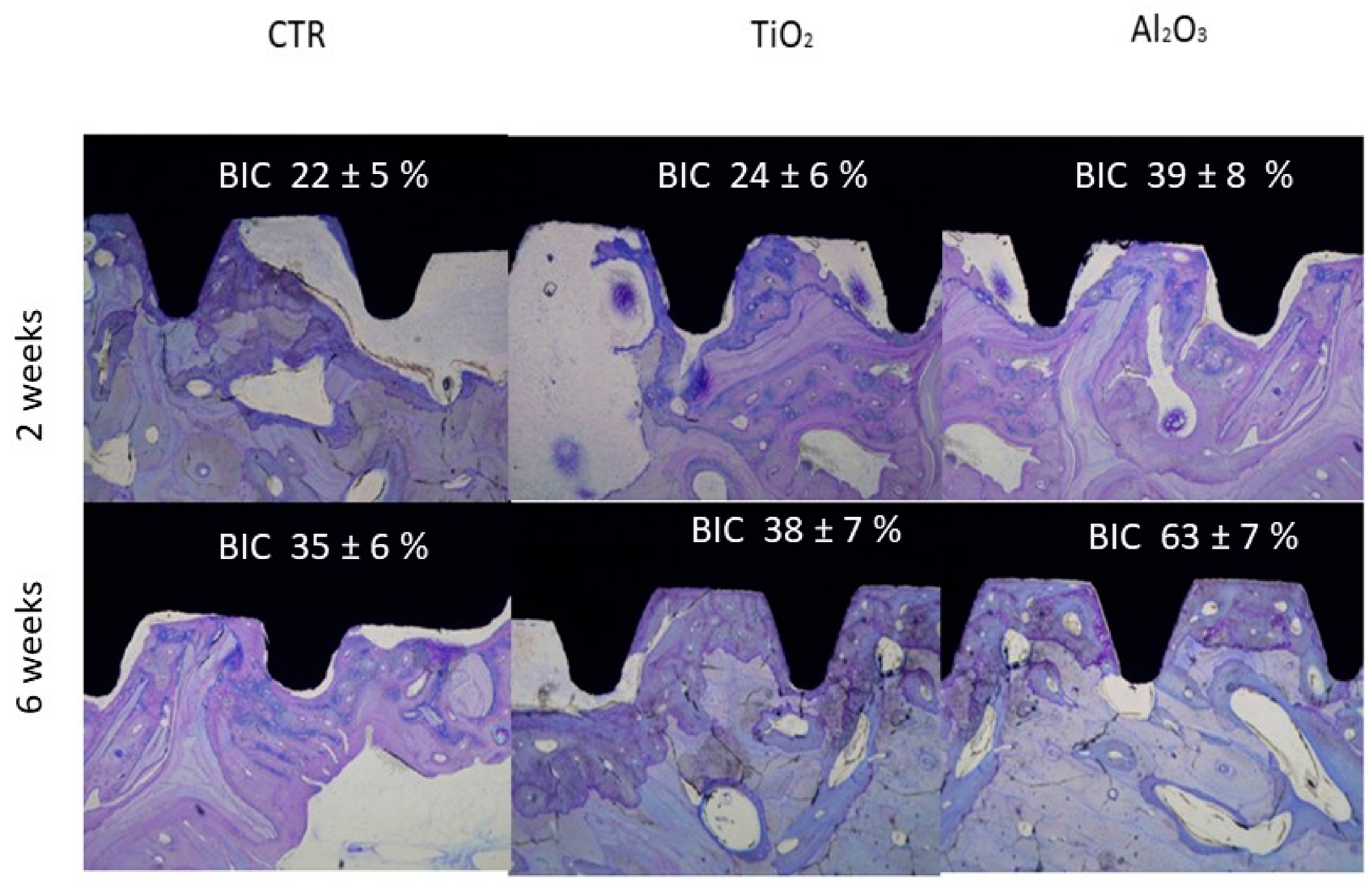
3. Do Surface Residual Stresses Contribute to Osseointegration?
- S: Smooth titanium without residual stress
- S+RS: Smooth titanium with residual stress
- R: Roughened titanium without residual stress
- R+RS: Roughened titanium with residual stress
4. Does the Acid Etching After Shot Blasting Have Any Influence?

5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yan Guo, C.; Matinlinna, J.P.; Tsoi, J.K.-H.; Tang, A.T.H. Residual contaminations of silicon-based glass, alumina an aluminum grits on a Titanium surface after sandblasting. Silicon 2019, 11, 2313–2320. [Google Scholar]
- Canabarro, A.; Diniz, M.G.; Paciornik, L.; Sampaio, E.M.; Beloti, M.M.; Rosa, A.L.; Fischer, R.G. High concentration of residual aluminum oxide on titanium surface inhibits extracellular matrix mineralization. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2008, 87A, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piattelli, A.; Degidi, M.; Paolantonio, M.; Mangano, C.; Scarano, A. Residual aluminum oxide on the surface of titanium implants has no effect on osseointegration. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 4081–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.K.; Rao, K.H. Analysis of different approaches for evaluation of surface energy of microbial cells by contact angle goniometry. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 98, 341–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annarelli, C.C.; Fornazero, J.; Cohen, R.; Bert, J.; Besse, J.L. Colloidal protein solutions as a new standard sensor for adhesive wettability measurements. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 213, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, J.; Pérez, R.; Herrero-Climent, M.; Rizo-Gorrita, M.; Torres, D.; Gutierrez, J.L. Benefits of residual aluminium oxide for sand blasting titanium dental implants: Osseointegration and bactericidal effects. Materials 2022, 15, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasik, M. Understanding biomaterial-tissue interface quality: Combined in vitro evaluation. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2017, 18, 550–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirynen, M.; Bollen, C.M. The influence of surface roughness and surface-free energy on supra- and subgingival plaque formation in man. A review of the literature. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1995, 22, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kock-Yee, L.; Hong, Z. (Eds.) Surface Wetting. Chapter 2: Contact Angle Measurements and Surface Characterization Techniques. In Characterization, Contact Angle, and Fundamentals, 1st ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Boyan, B.D.; Hummert, T.W.; Dean, D.D.; Schwartz, Z. Role of material surfaces in regulating bone and cartilage cell response. Biomaterials 1996, 17, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, G.; Mendonça, D.B.S.; Aragao, F.J.L.; Cooper, L.F. Advancing dental implant surface technology—From micron—To nanotopography. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 3822–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altankov, G.; Groth, T. Fibronectin matrix formation by human fibroblasts on surfaces varying in wettability. J. Biomater. Sci.-Polym. Ed. 1996, 8, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altankov, G.; Groth, T. Fibronectin matrix formation and the biocompatibility of materials. J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. Med. 1996, 7, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drelich, J.W.; Chibowski, E.; Meng, D.D.; Terpilowski, K. Hydrophilic and Superhydrophilic Surfaces and Materials. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 9804–9828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altankov, G.; Groth, T.; Krasteva, N.; Albrecht, W.; Paul, D. Morphological evidence for a different fibronectin receptor organization and function during fibroblast adhesion on hydrophilic and hydrophobic glass substrata. J. Biomater. Sci.-Polym. Ed. 1997, 8, 721–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drake, D.R.; Paul, J.; Keller, J.C. Primary bacterial adhesion of implant surfaces. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1999, 14, 226–232. [Google Scholar]
- Wassmannet, T.; Kreis, S.; Behr, M.; Buergers, R. The influence of surface texture and wettability on initial bacterial adhesion on titanium and zirconium oxide dental implants. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2017, 3, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Hernández, A.; Espinar, E.; Llamas, J.M.; Barrera, J.M.; Gil, F.J. Alumina shot-blasted particles on commercially pure titanium surfaces prevent bacterial attachment. Mater. Lett. 2013, 92, 42–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushinsky, D.A.; Sprague, S.M.; Hallegot, P.; Girod, C.; Chabala, J.M.; Levi-Setti, R. Effects of aluminum on bone surface ion composition. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1995, 10, 1988–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schupbach, P.; Glauser, R.; Bauer, S. Al2O3 Particles on Titanium Dental Implant Systems following Sandblasting and Acid-Etching Process. Int. J. Biomater. 2019, 2, 6318429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansone, V.; Pagani, D.; Melato, M. The effect on bone cells of metal ion released from orthopaedic implants. A review. Clin. Cases Miner. Bone Metab. 2013, 10, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrabeah, G.O.; Brett, P.; Knowles, J.C.; Petridis, H. The effect of metal ions released from different dental implant-abutment couples on osteoblast function and secretion of bone resorbing mediators. J. Dent. 2017, 66, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimb, L.; Jensen, J.S.; Lekholm, U.; Thomsen, P. Interface mechanics and histomorphometric analysis of hydroxyapatited-coated and porous glass-ceramic implants in canine bone. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1995, 29, 1477–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarles, L.D.; Wenstrup, R.J.; Castillo, S.A.; Drezner, M.K. Aluminum induced mitogenesis in MC3T3-E1 osteoblats: Potential mechanism underlying neoosteogenesis. Endocrinology 1991, 128, 3144–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.H.; Yoo, A.; Wang, S.P. Aluminum stimulates the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts in vitro by a mechanism that is the different from fluorine. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 1991, 105, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Ruiz, R.; Romanos, G. Potential Causes of Titanium Particle and Ion Release in Implant Dentistry: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buxadera-Palomero, J.; Calvo, C.; Torrent-Camarero, S.; Gil, F.J.; Mas-Moruno, C.; Canal, C.; Rodríguez, D. Biofunctional polyethylene glycol coatings on titanium: An in vitro-based comparison of functionalization methods. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 152, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, F.J.; Solano, E.; Peña, J.; Engel, E.; Mendoza, A.; Planell, J.A. Microstructural, mechanical and citotoxicity evaluation of different NiTi and NiTiCu shape memory alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2004, 15, 1181–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feighan, J.E.; Goldberg, V.M.; Davy, D.; Parr, J.A.; Stevenson, S. The influence of surface-blasting on the incorporation of titanium-alloy implants in a rabbit intramedullary model. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 1995, 77A, 1380–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noumbissi, S.; Scarano, A.; Gupta, S. A Literature Review Study on Atomic Ions Dissolution of Titanium and Its Alloys in Implant Dentistry. Materials 2019, 12, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piattelli, A.; Manzon, L.; Scarano, A.; Paolantonio, M.; Piattelli, M. Histologic and hismorphometric analysis of the bone response to machined and sandblasted titanium implants: An experimental study in rabbits. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1998, 13, 805–810. [Google Scholar]
- Wenneberg, A.; Albrektsson, T.; Lausmaa, J. Torque and histomorphometric evaluation of c.p. titanium screws blasted with 25- and 75-mm sized particles of Al2O3. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1996, 30, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, F.X.; Rodriguez, D.; Planell, J.A. Grain growth kinetics of pure titanium. Scr. Metall. Mater. 1995, 3, 1361–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraris, S.; Cochis, A.; Cazzola, M.; Tortello, M.; Scalia, A.; Spriano, S.; Rimondini, L. Cytocompatible and Anti-bacterial Adhesion Nanotextured Titanium Oxide Layer on Titanium Surfaces for Dental and Orthopedic Implants. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granato, R.; Bonfante, E.A.; Castellano, A.; Khan, R.; Jimbo, R.; Marin, C.; Morsi, S.; Witek, L.; Coelho, P.G. Osteointegrative and microgeometric comparison between micro-blasted and alumina blasting/acid etching on grade II and V titanium alloys (Ti-6Al-4V). J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 97, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.C.S.; Agrelli, A.; Andrade, A.N.; Mendes-Marques, C.L.; Arruda, I.R.S.; Santos, L.R.L.; Vasconcelos, N.F.; Machado, G. Titanium Dental Implants: An Overview of Applied Nanobiotechnology to Improve Biocompatibility and Prevent Infections. Materials 2022, 15, 3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, M.; Lausmaa, J.; Hirsch, J.M.; Thomsen, P. Surface analysis of failed oral titanium implants. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1999, 48, 559–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandaswamy, E.; Harsha, M.; Joshi, V.M. Titanium corrosion products from dental implants and their effect on cells and cytokine release: A review. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2024, 84, 127464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lugowski, S.J.; Smith, D.C.; McHugh, A.D.; Van Loon, J.C. Release of metal ions from dental implant materials in vivo: Determination of Al, Co, Cr, Mo, Ni, V, and Ti in organ tissue. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1991, 25, 1443–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuling, N.; Wisser, W.; Jung, A.; Denschlag, H.O. Release and detection of dental corrosion products in vivo: Development of an experimental model in rabbits. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1990, 24, 979–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passi, P.; Zadro, A.; Galassini, S.; Rossi, P.; Moschini, G. PIXE micro-beam mapping of metals in human peri-implant tissues. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2002, 13, 1083–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, B. The Aluminium Oxide Family. In Rubies and Implants; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Housheng, S.; Minghao, L.; Li, R.; Pan, D.; Yang, X.; Yang, X.; Xu, Z. Effect of surface polarity on the structure and dynamics of liquids at the alumina solid–liquid interface. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2025, 249, 113675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bursill, L.A.; Peng, J.L. Surface facetting and polarity of alumina. Ultramicroscopy 1987, 23, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, F.J.; Planell, J.A.; Padrós, A.; Aparicio, C. The effect of sand blasting and heat treatment on the fatigue behavior of titanium for dental implant applications. Dent. Mater. 2007, 23, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronold, H.J.; Ellingsen, J.E. Effect of micro-roughness produced by TiO2 blasting-tensiles testing of bone attachment by using coin-shaped implants. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 4211–4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehrke, S.A.; Ramírez-Fernandez, M.P.; Granero Marín, J.M.; Barbosa Salles, M.; Del Fabbro, M.; Calvo Guirado, J.L. A comparative evaluation between aluminium and titanium dioxide microparticles for blasting the surface titanium dental implants: An experimental study in rabbits. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2018, 29, 802–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valverde, G.B.; Jimbo, R.; Teixeira, H.S.; Bonfante, E.A.; Janal, M.N.; Coelho, P.G. Evaluation of Surface roughness as a function of múltiple blasting processing variables. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2013, 24, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, F.J.; Pérez, R.A.; Olmos, J.; Herraez-Galindo, C.; Gutierrez-Pérez, J.L.; Torres-Lagares, D. The effect of using Al2O3 and TiO2 in sandblasting of titanium dental implants. J. Mater. Res. 2022, 37, 2604–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, F.J.; Espinar, E.; Llamas, J.M.; Sevilla, P. Fatigue life of bioactive titanium dental implants treated by means of grit-blasting and thermo-chemical treatment. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2014, 16, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemtov-Yona, K.; Rittel, D. An Overview of the Mechanical Integrity of Dental Implants. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 547384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrcanovic, B.R.; Kisch, J.; Albrektsson, T.; Wennerberg, A. Factors Influencing Early Dental Implant Failures. J. Dent. Res. 2016, 95, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Sanchez, R.; Dopico, J.; Kalemaj, Z.; Buti, J.; Pardo Zamora, G.; Mardas, N. Comparison of clinical outcomes of immediate versus delayed placement of dental implants: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2022, 33, 231–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ickroth, A.; Seyssens, L.; Christiaens, V.; Pitman, J.; Cosyn, J. Immediate versus early implant placement for single tooth replacement in the aesthetic area: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2024, 35, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tettamanti, L.; Andrisani, C.; Bassi, M.A.; Vinci, R.; Silvestre-Rangil, J.; Tagliabue, A. Immediate loading implants: Review of the critical aspects. Oral Implantol. 2017, 10, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzoneva, R.; Groth, T.; Altankov, G.; Paul, D. Remodeling of fibrinogen by endothelial cells in dependence on fibronectin matrix assembly. Effect of substratum wettability. J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. Med. 2002, 13, 1235–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altankov, G.; Richau, K.; Groth, T. The role of surface zeta potential and substratum chemistry for regulation of dermal fibroblasts interaction. Mater. Werkst. 2003, 34, 1120–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buser, D. Titanium for Dental Applications (II): Implants with Roughened Surfaces. In Titanium in Medicine: Material Science, Surface Science, Engineering, Biological Responses and Medical Applications; Brunette, D.M., Tengvall, P., Textor, M., Thomsen, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 875–888. [Google Scholar]
- Rønold, H.J.; Lyngstadaas, S.P.; Ellingsen, J.E. A study on the effect of dual blasting with TiO2 on titanium implant surfaces on functional attachment in bone. J. Biomed. Mater. Res.—Part A 2003, 67, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serov, D.A.; Gritsaeva, A.V.; Yanbaev, F.M.; Simakin, A.V.; Gudkov, S.V. Review of Antimicrobial Properties of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiris, M.; Gunasekara, T.; Jayaweera, P.M.; Fernando, S. TiO2 Nanoparticles from Baker’s Yeast: A Potent Antimicrobial. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 28, 1664–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddiki, O.; Harnagea, C.; Levesque, L.; Mantovani, D.; Rosei, F. Evidence of antibacterial activity on titanium surfaces through nanotextures. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 308, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, H.J.; Schulz, K.H.; Walters, K.B. Piranha Treated Titanium Compared to Passivated Titanium as Characterized by XPS. Surf. Sci. Spectra 2008, 15, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio, C.; Engel, E.; Gil, F.J.; Planell, J.A. Human-osteoblast proliferation and differentiation on grit-blasted and bioactive titanium for dental applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2002, 13, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselme, K. Osteoblast adhesion on biomaterials. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 667–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owens, D.K.; Wendt, R.C. Estimation of the Surface Free Energy of Polymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1969, 13, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, G.R.M. Surface Roughness of Dental Implant and Osseointegration. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 2021, 20, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, J.Y.; Schwartz, Z.; Hummert, T.W. Effect of titanium surface roughness on proliferation, differentiation, and protein synthesis of human osteoblast-like cells (MG63). J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1995, 29, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.; Maia, P.; Rios-Santos, J.V.; Herrero-Climent, M.; Rios-Carrasco, B.; Aparicio, C.; Gil, J. Influence of Titanium Surface Residual Stresses on Osteoblastic Response and Bacteria Colonization. Materials 2024, 17, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegueroles, M.; Aparicio, C.; Bosio, M.; Engel, E.; Gil, F.J.; Planell, J.A.; Altankov, G. Spatial Organization of Osteoblast Fi-bronectin-Matrix on Titanium Surface—Effects of Roughness, Chemical Heterogeneity, and Surface Free Energy. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orimo, H. The mechanism of mineralization and the role of alkaline phosphatase in health and disease. J. Nippon Med. Sch. 2010, 77, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferron, M.; Karsenty, G. Regulation of energy metabolism by bone-derived hormones. In Principles of Bone Biology; Bilezikian, J.P., Martin, T.J., Clemens, T.L., Rosen, C.J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 303–318. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, A.; Engel, E.; Juárez, A.; Gil, F.J. Bacterial response to different cp-Ti surfaces. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2009, 36, 78. [Google Scholar]
- Schneiderman, N.; Ironson, G.; Siegel, S.D. Stress and health: Psychological, behavioral, and biological determinants. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2005, 1, 607–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciarletta, P.; Destrade, M.; Gower, A.L. On residual stresses and homeostasis: An elastic theory of functional adaptation in living matter. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riccobelli, D.; Agosti, A.; Ciarletta, P. On the existence of elastic minimizers for initially stressed materials. Philos. Trans. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2019, 6, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, F.J.; Rodriguez, A.; Espinar, E.; Llamas, J.M.; Padulles, E.; Juarez, A. Effect of the oral bacteria on the mechanical behavior of titanium dental implants. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2012, 27, 64–68. [Google Scholar]
- Degidi, M.; Piattelli, A.; Felice, P.; Carinci, F. Immediate functional loading of edentulous maxilla: A 5-year retrospective study of 388 titanium implants. J. Periodontol. 2005, 76, 1016–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrektsson, T.; Wennerberg, A. On osseointegration in relation to implant surfaces. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2019, 21 (Suppl. 1), 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevins, M.; Langer, B. The successful application of osseointegrated implants to the posterior jaw: A long-term retrospective study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1993, 8, 428–432. [Google Scholar]
- Fugazzotto, P.A.; Gulbransen, H.J.; Wheeler, S.L.; Lindsay, J.A. The use of IMZ osseointegrated implants in partially and completely edentulous patients: Success and failure rates of 2,023 implant cylinders up to 60+ months in function. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1993, 8, 617–621. [Google Scholar]
- Buser, D.; Sennerby, L.; De Bruyn, H. Modern implant dentistry based on osseointegration: 50 years of progress, current trends and open questions. Periodontol. 2000 2016, 73, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buser, D.; Chappuis, V.; Belser, U.C.; Chen, S. Implant placement post extraction in esthetic single tooth sites: When immediate, when early, when late? Periodontol. 2000 2016, 73, 84–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero-Climent, M.; Lázaro, P.; Vicente Rios, J.; Lluch, S.; Marqués, M.; Guillem-Martí, J.; Gil, F.J. Influence of acid-etching after grit-blasted on osseointegration of titanium dental implants: In vitro and in vivo studies. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2013, 24, 2047–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Hu, W.; Chung, K.H.; Yang, F.; Yang, H. Effects of different acid etching protocols on the enhanced osteogenic potential of titanium surfaces: An in vitro study. Dent. Mater. J. 2025, 44, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramaglia, L.; Postiglione, L.; Di Spigna, G.; Capece, G.; Salzano, S.; Rossi, G. Sandblasted-acid-etched titanium surface influences in vitro the biological behavior of SaOS-2 human osteoblast-like cells. Dent. Mater. J. 2011, 30, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhabra, K.; Rajasekar, A. Comparison of Roughness, Wettability, and SEM Features between Sandblasted Acid-Etched and Oxidized Titanium Dental Implants. J. Long Term Eff. Med. Implant. 2024, 34, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.H.; Wang, Y.T.; Tsai, W.F.; Ai, C.F.; Lin, M.C.; Huang, H.H. Effect of oxygen plasma immersion ion implantation treatment on corrosion resistance and cell adhesion of titanium surface. Clin Oral Implant. Res. 2011, 22, 1426–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, J.M.; Pires, J.M.; Souza, J.G.S.; Lima, C.V.; Bertolini, M.M.; Rangel, E.C.; Barão, V.A.R. Optimizing citric acid protocol to control implant-related infections: An in vitro and in situ study. J. Periodontal Res. 2021, 56, 558–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias Corpa Tardelli, J.; Bolfarini, C.; Cândido Dos Reis, A. Comparative analysis of corrosion resistance between beta titanium and Ti-6Al-4V alloys: A systematic review. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2020, 62, 126618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagay, B.E.; Cordeiro, J.M.; Barao, V.A.R. Insight Into Corrosion of Dental Implants: From Biochemical Mechanisms to Designing Corrosion-Resistant Materials. Curr. Oral Health Rep. 2022, 9, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakka, S.; Baroudi, K.; Nassani, M.Z. Factors associated with early and late failure of dental implants. J. Investig. Clin. Dent. 2012, 3, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

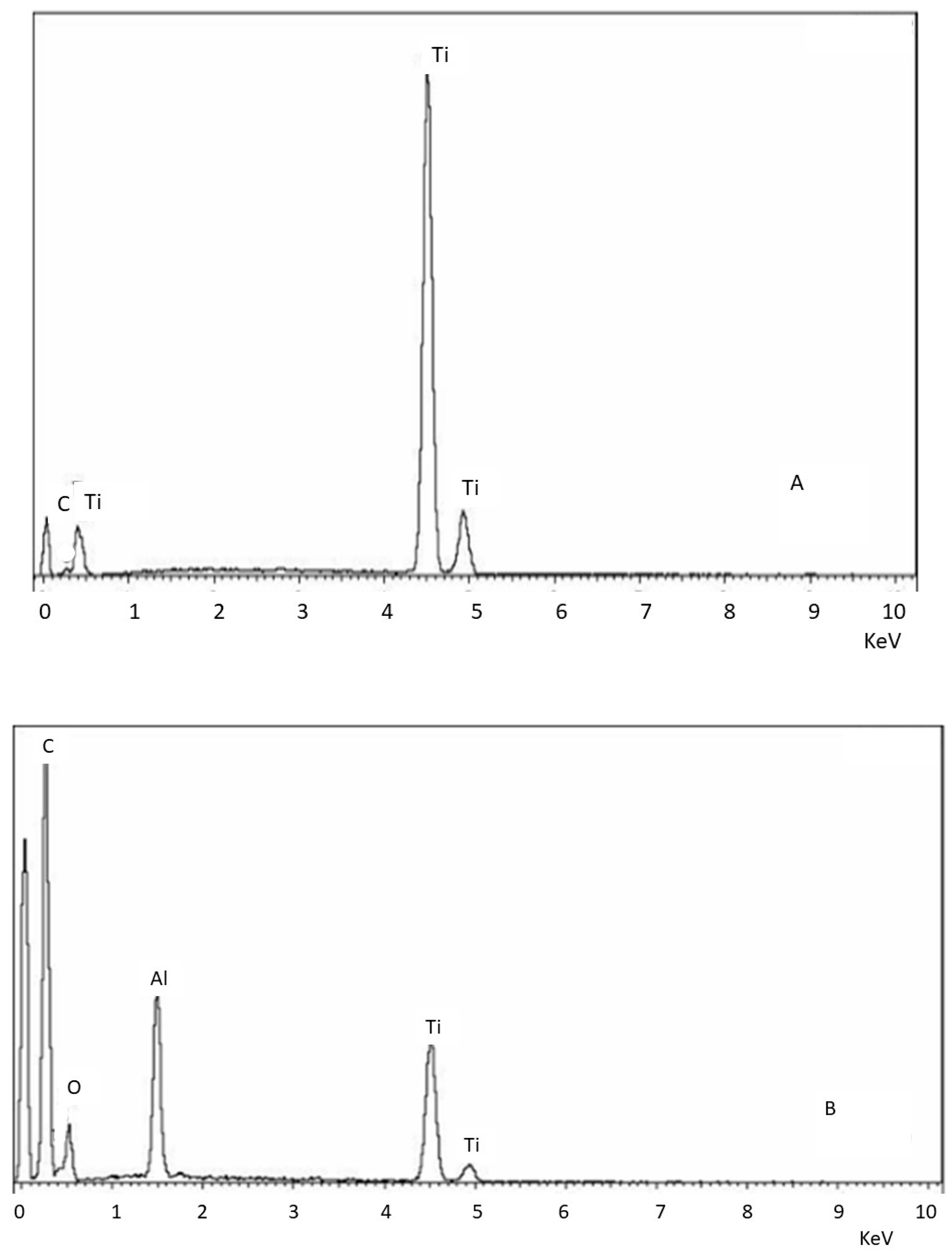
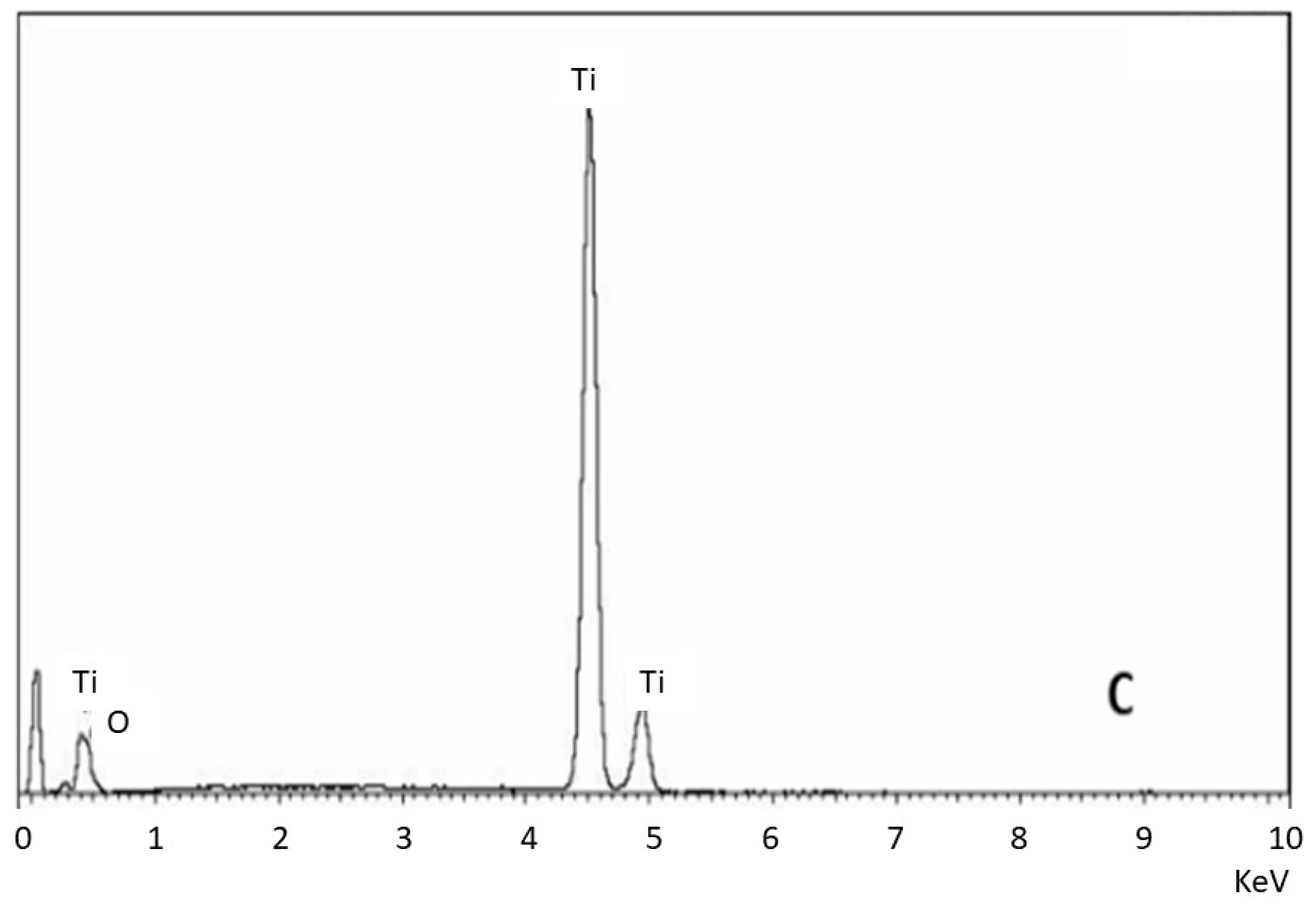
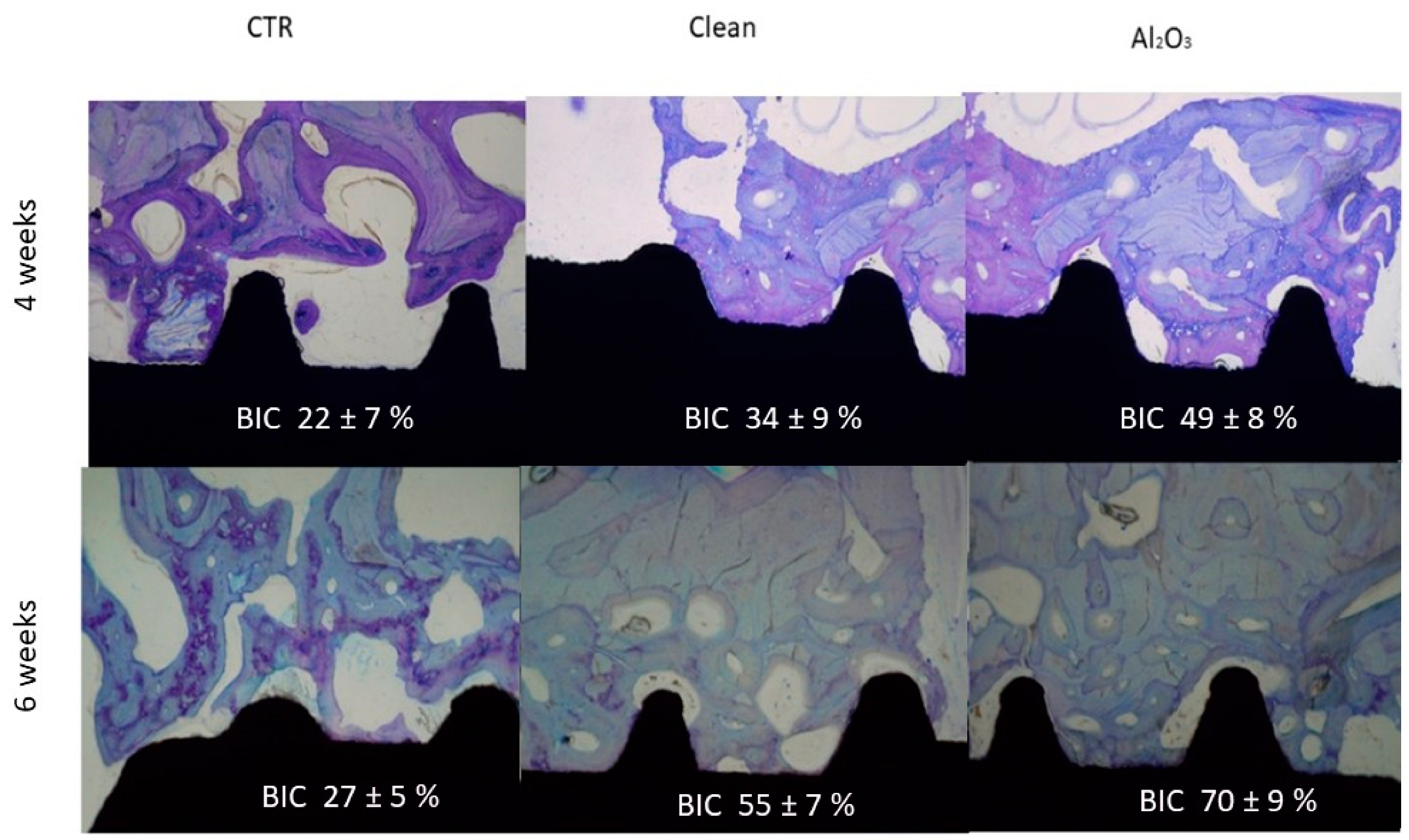
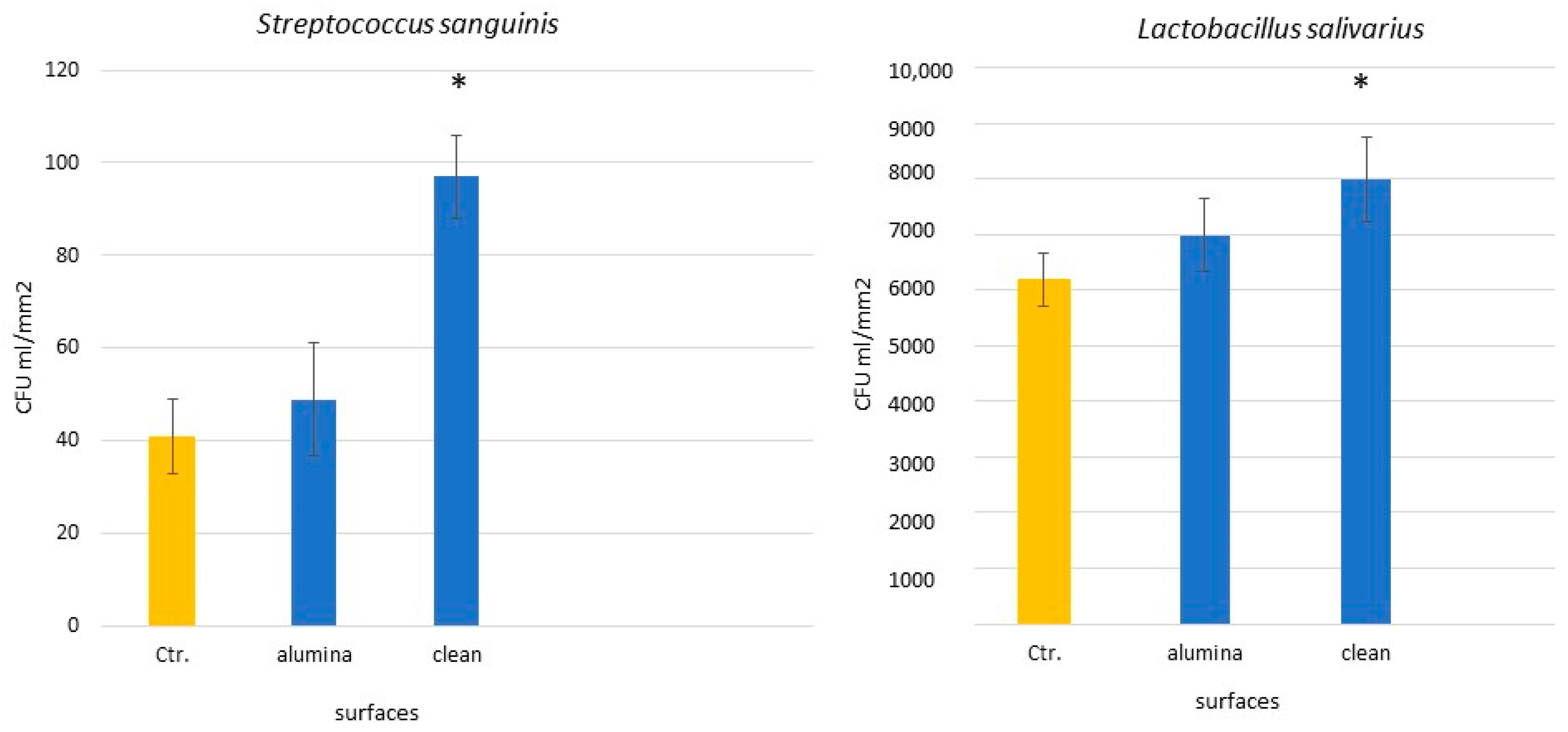


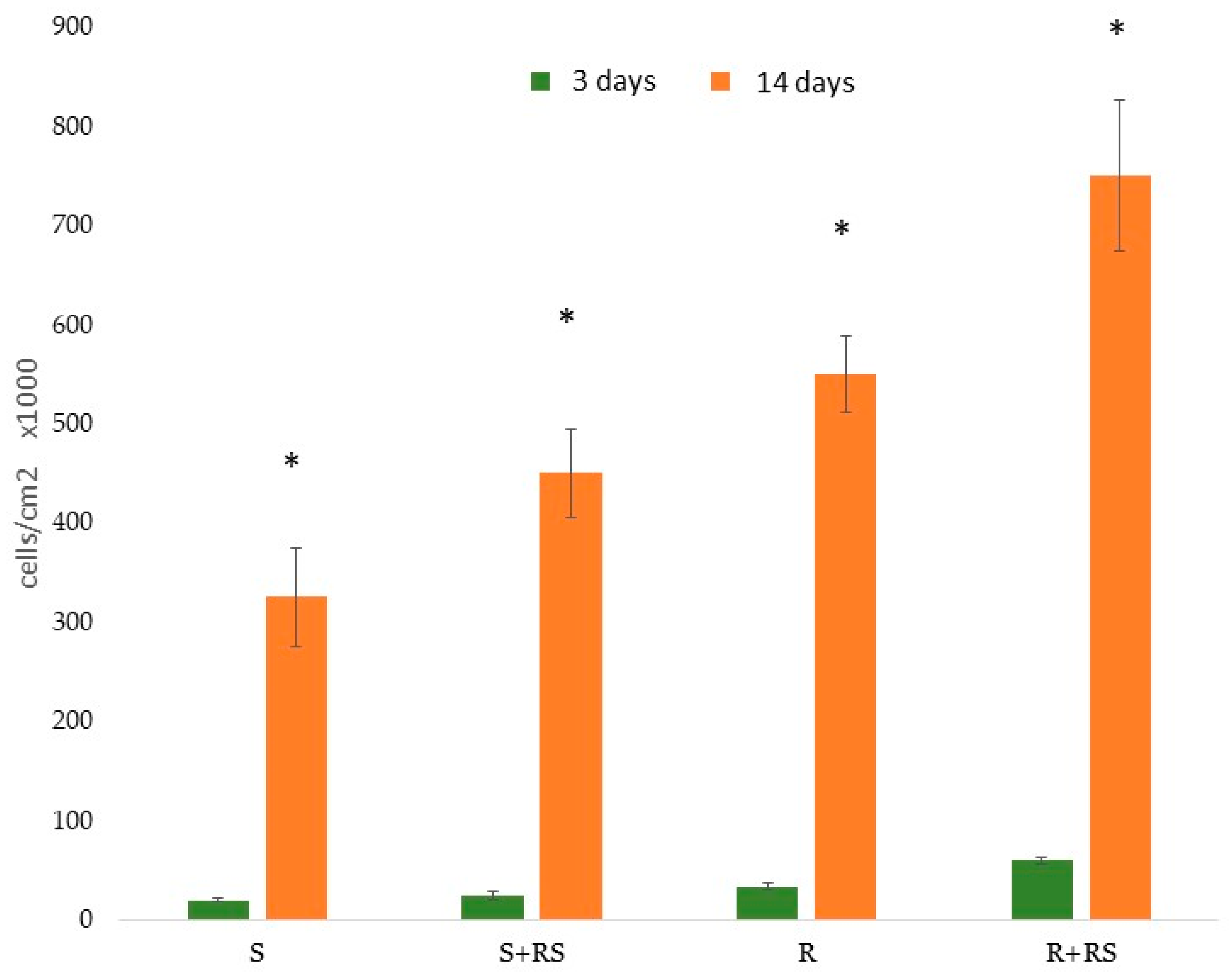
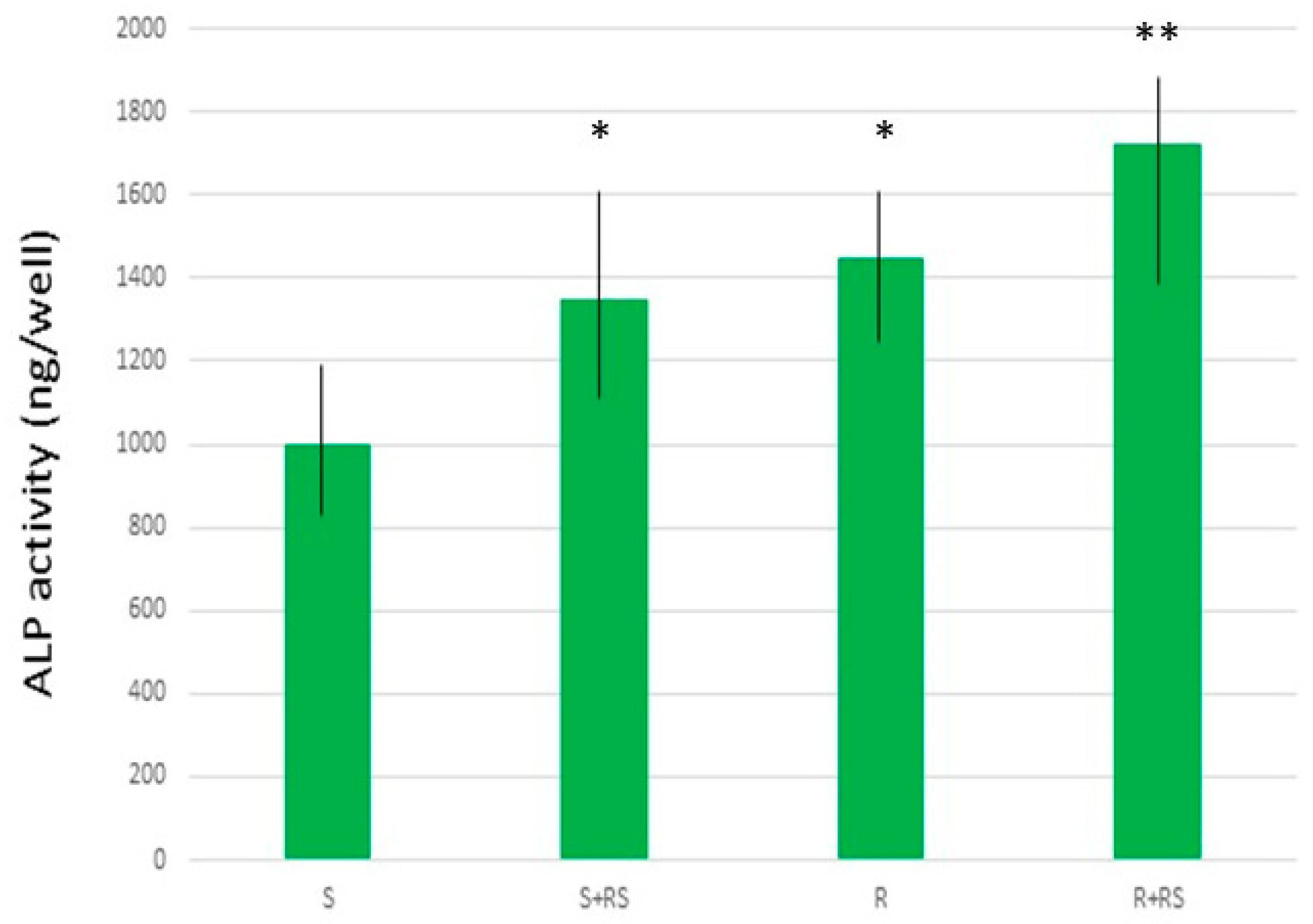
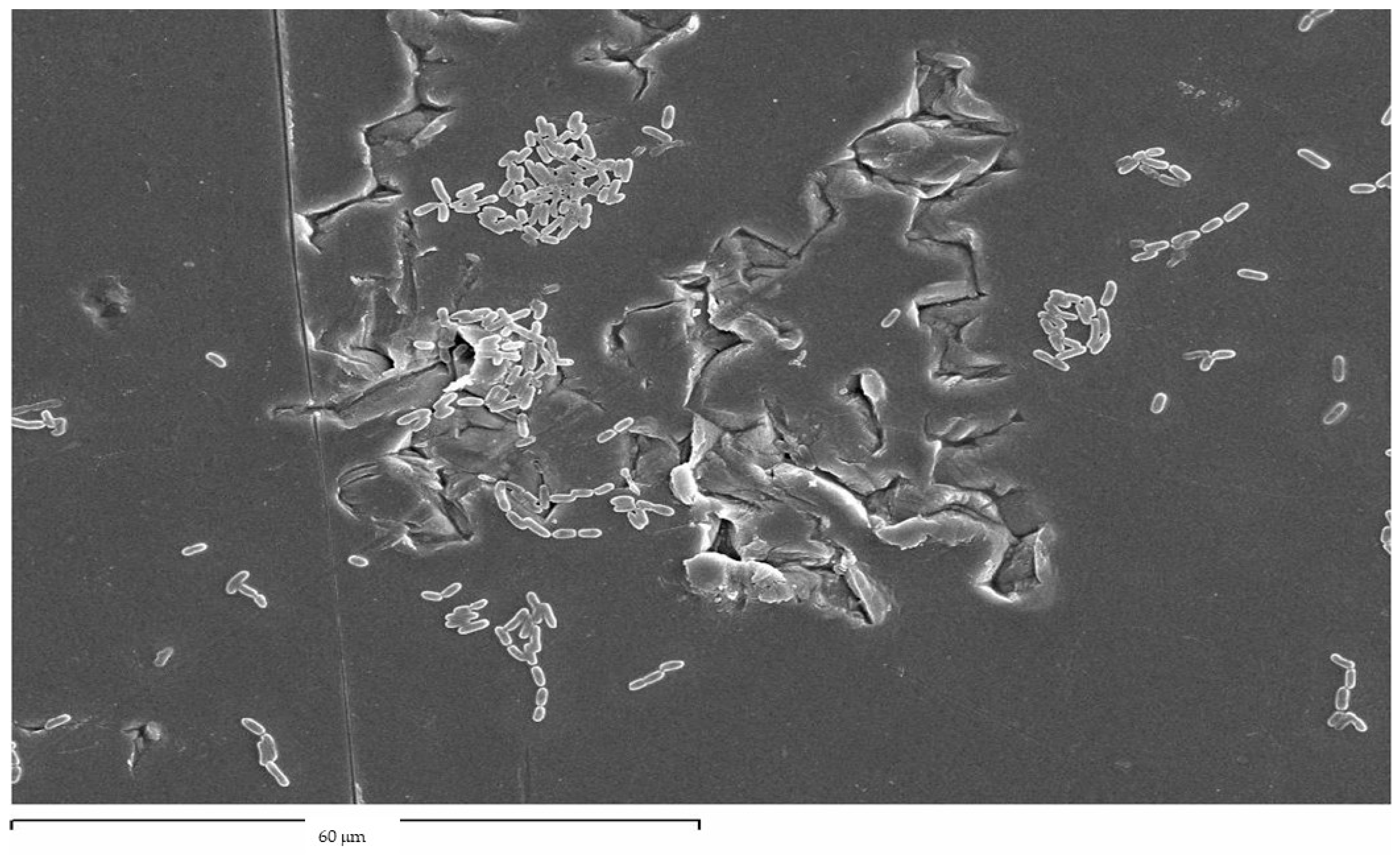
| Sa (µm) | CA (˚) | DC (mJ/m2) | PC (mJ/m2) | SFE (mJ/m2) | σresidual (MPa) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | 0.21 ± 0.02 * | 77 ± 5 * | 24.8 ± 1.2 * | 10.2 ± 2.0 * | 35.0 ± 3.2 * | −10 ± 2 * |
| S+RS | 0.24 ± 0.10 * | 58 ± 3 ** | 27.2 ± 1.2 ** | 18.3 ± 1.8 ** | 45.5 ± 2.2 ** | −189 ± 20 ** |
| R | 2.04 ± 0.15 ** | 69 ± 4 * | 27.7 ± 1.3 ** | 12.5 ± 2.1 * | 40.2 ± 1.2 ** | −8 ± 3 * |
| R+RS | 1.99 ± 0.18 ** | 53 ± 2 ** | 29.0 ± 2.2 ** | 20.4 ± 1.9 ** | 49.4 ± 1.8 ** | −201 ± 12 ** |
| Surface | Ra (μm) | Pc (cm−1) | CA’ [°] | Total Surface Free Energy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ctr | 0.33 ± 0.1 | 150.9 ± 69 | 66.3 ± 5 | 42.74 ± 1.54 |
| AEtch | 1.69 ± 0.1 | 198.3 ± 34 | 66.8 ± 7 | 49.52 ± 3.11 * |
| SBlast | 4.74 ± 0.2 | 82.1 ± 10 | 75.4 ± 5 * | 42.67 ± 1.18 |
| SBlast+AEtch | 4.23 ± 0.2 | 92.1 ± 13 | 82.1 ± 5 * | 43.08 ± 1.96 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gil, J.; Velasco-Ortega, E.; Monsalve-Guil, L.; Moreno-Muñoz, J.; Rondón-Romero, J.L.; Matos-Garrido, N.; Jiménez-Guerra, Á.; Núñez-Márquez, E.; Ortiz-García, I. Critical Questions Surrounding the Shot-Blasting Treatment of Titanium Dental Implants. Materials 2025, 18, 4120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174120
Gil J, Velasco-Ortega E, Monsalve-Guil L, Moreno-Muñoz J, Rondón-Romero JL, Matos-Garrido N, Jiménez-Guerra Á, Núñez-Márquez E, Ortiz-García I. Critical Questions Surrounding the Shot-Blasting Treatment of Titanium Dental Implants. Materials. 2025; 18(17):4120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174120
Chicago/Turabian StyleGil, Javier, Eugenio Velasco-Ortega, Loreto Monsalve-Guil, Jesús Moreno-Muñoz, José Luis Rondón-Romero, Nuno Matos-Garrido, Álvaro Jiménez-Guerra, Enrique Núñez-Márquez, and Iván Ortiz-García. 2025. "Critical Questions Surrounding the Shot-Blasting Treatment of Titanium Dental Implants" Materials 18, no. 17: 4120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174120
APA StyleGil, J., Velasco-Ortega, E., Monsalve-Guil, L., Moreno-Muñoz, J., Rondón-Romero, J. L., Matos-Garrido, N., Jiménez-Guerra, Á., Núñez-Márquez, E., & Ortiz-García, I. (2025). Critical Questions Surrounding the Shot-Blasting Treatment of Titanium Dental Implants. Materials, 18(17), 4120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174120








