Study on the Influence of Aging Temperature on the Microstructure and Properties of Ti-38644 Metastable β-Type Titanium Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
3. Results
3.1. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Alloys After Solid Solution Treatment
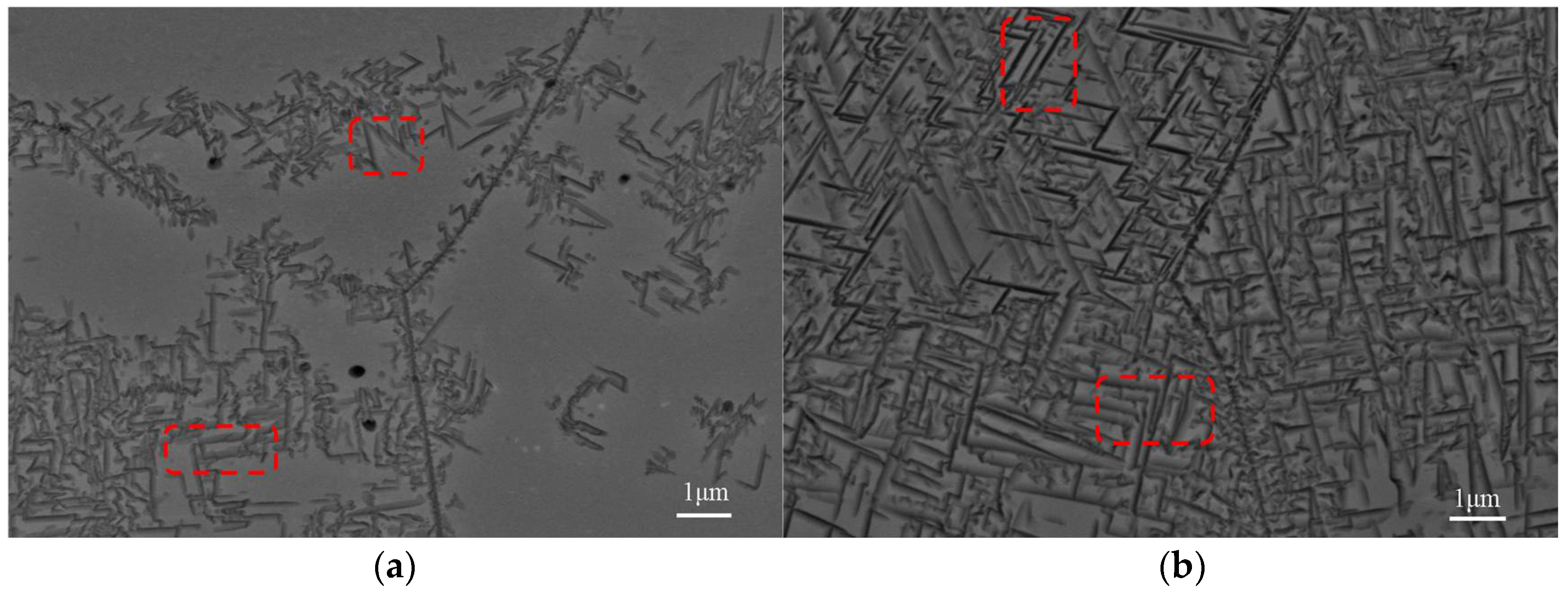
3.2. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Alloy After Solid Solution Aging Treatment
4. Discussion
4.1. Study on the Precipitation Behavior of αs Phase
4.2. The Effect of αs-Phase Precipitation on Enhancing Yield Strength
5. Conclusions
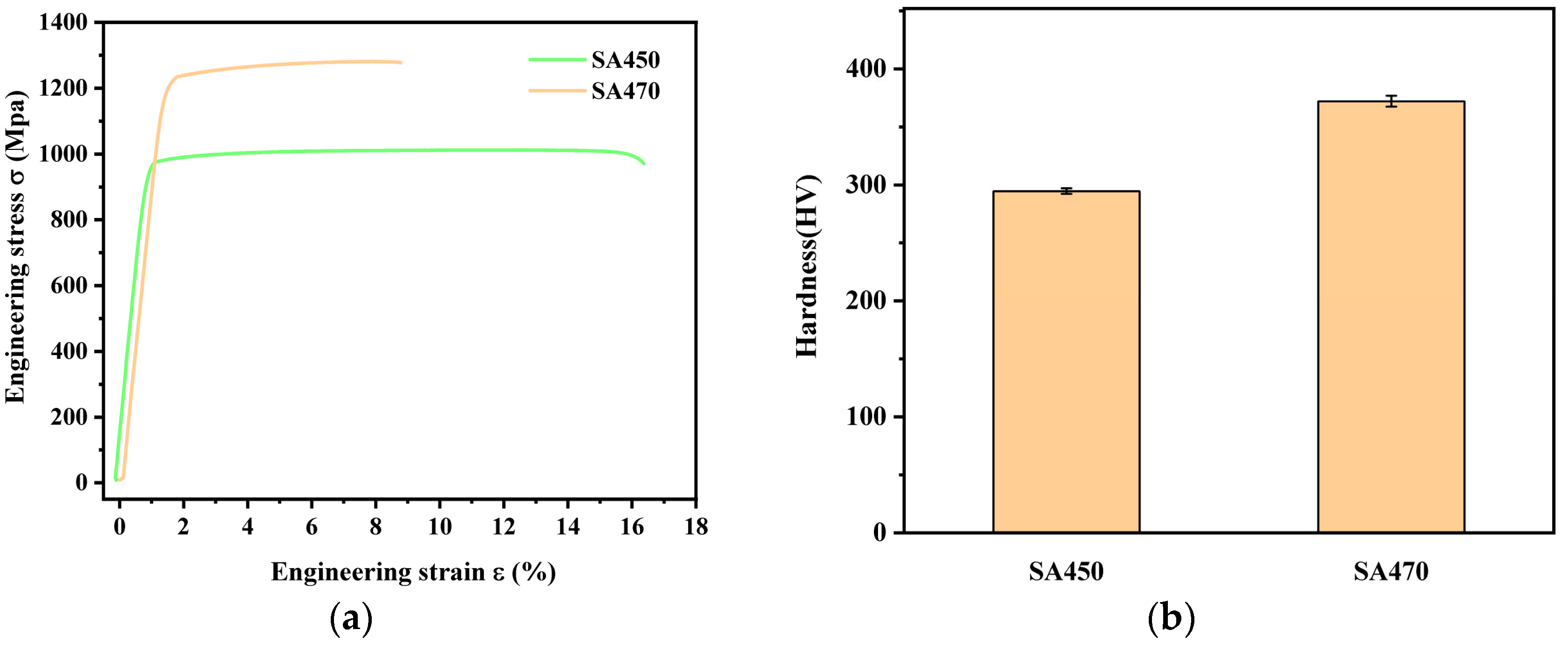
- After undergoing solid solution treatment at 760 °C, the Ti-38644 titanium alloy undergoes complete recrystallization, resulting in equiaxed grains of the β phase. An XRD analysis indicates that only the matrix β phase is present in the alloy at this stage, with a σb of 898 ± 1.5 MPa and a σs of 876 ± 15.0 MPa.
- Through the analysis of the microstructure and mechanical properties of titanium alloys subjected to aging at various temperatures, it can be concluded that, at 450 °C, the αs phase appears as needle-shaped precipitates that are unevenly distributed, lacking distinct precipitation zones, and preferentially forms at grain boundaries. The area percentage of the αs phase is approximately 42.36%. When the aging temperature is increased to 470 °C, the amount of αs-phase precipitation increases and becomes uniformly distributed, with an area percentage of about 57.34% for the αs phase.
- The substantial precipitation of the αs phase significantly enhances the mechanical properties of the alloy. Compared to the solid solution state alloy, the σs of the specimen treated at 760 °C for 1 h, followed by 470 °C for 10 h, increased by 335 MPa. For the specimens subjected to the treatment at 760 °C for 1 h, followed by 470 °C for 10 h, (284.73 MPa) plays a major role in the increase in σs, in contrast to (62.37 MPa).
- The experimental results demonstrate that the alloy aged at 470 °C (1211 MPa) exhibits significantly improved mechanical properties compared to those processed at 450 °C (967 MPa). Consequently, for industrial applications, the aging treatment at 470 °C should be adoptedif a higher strength is desired.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeng, L.; Yang, G.; Ge, P.; Mao, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, L. Processing Map of One Kind of Metastable β Titanium Alloy. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2010, 39, 1505–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, J.H.; Wu, X.; van der Zwaag, S. A Comparative Study of the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of α + β Titanium Alloys. Met. Sci. Heat Treat. 2014, 56, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Sun, Q.; Xin, S.; Chen, Y.; Wu, C.; Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Wan, M.; Zeng, W.; Zhao, Y. High-Strength Titanium Alloys for Aerospace Engineering Applications: A Review on Melting-Forging Process. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 845, 143260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolli, R.P.; Devaraj, A. A Review of Metastable Beta Titanium Alloys. Metals 2018, 8, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, R.R.; Briggs, R.D. The Use of β Titanium Alloys in the Aerospace Industry. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2005, 14, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.; Kumpfert, J.; Ward, C.H.; Leyens, C. Titanium Alloys for Aerospace Applications. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2003, 5, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotton, J.D.; Briggs, R.D.; Boyer, R.R.; Tamirisakandala, S.; Russo, P.; Shchetnikov, N.; Fanning, J.C. State of the Art in Beta Titanium Alloys for Airframe Applications. JOM 2015, 67, 1281–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, E.; Teng, A.; Geng, N.; Fang, Q.; Kang, Q.; Guo, J.; Zhang, T. Evolution of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of TB9 Alloy Bar and Wire during Production Process. Dev. Appl. Mater. 2024, 39, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yumak, N.; Aslantaş, K. A Review on Heat Treatment Efficiency in Metastable β Titanium Alloys: The Role of Treatment Process and Parameters. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 15360–15380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semiatin, S.L.; Lehner, T.M.; Miller, J.D.; Doherty, R.D.; Furrer, D.U. Alpha/Beta Heat Treatment of a Titanium Alloy with a Nonuniform Microstructure. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2007, 38, 910–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W. Impact of Cold Drawing Deformation and Aging on Microstructure and Mechanical Property of TB9 Titanium Alloy. World Nonferrous Met. 2020, 12, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Q.; Guo, J.; Wang, G.; Xue, S.; Su, Y.; Ma, B. Effects of Solution and Aging Treatment on Microstrucure and Mechanical Properties of TB9 Titanium Alloy. Hot Work. Technol. 2023, 52, 147–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Shang, Q.; Wang, G.; Guo, X.; Ma, B.; Liu, Y. The Effect of Heat Treatment on Microstrucures and Mechanical Properties of TB9 Titanium Alloy Rod. Hunan Nonferrous Met. 2023, 39, 44–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Hu, F.; Ma, L.; Qu, F.; Yan, Z. Effect of aging treatment on microstructure and properties of solution treated and cold-drawn TB9 titanium alloy. Heat Treat. Metals. 2024, 49, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, C.G.; Paton, N.E. The Influence of Microstructure on Mechanical Properties in Ti-3AI-8V-6Cr-4Mo-4Zr (Beta-C). Metall. Trans. A 1977, 8, 1749–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, L.; Gregory, J.K. Improvement of Mechanical Behavior in Ti-3Al-8V-6Cr-4Mo-4Zr by Duplex Aging; The Minerals, Metals Materials Society: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1993; pp. 199–209. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/284758438_Improvement_of_mechanical_behavior_in_Ti-3Al-8V-6Cr-4Mo-4Zr_by_duplex_aging (accessed on 2 August 2025).
- Schmidt, P.; El-Chaikh, A.; Christ, H.-J. Effect of Duplex Aging on the Initiation and Propagation of Fatigue Cracks in the Solute-rich Metastabie β Titanium Alloy Ti 38-644. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2011, 42, 2652–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Huang, T.; Luo, T.; Huang, X.; Li, J.S.; Lai, M.J. Manipulation of the α-Phase Precipitation Behavior through Dual-Aging Treatment and Its Correlation with Mechanical Properties in a Metastable β Titanium Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1005, 175891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Qiu, J.; Lei, X.; Zhang, J.; Dong, L.; Yang, R. Precipitation behavior of secondary α phase and mechanical properties of high strength TB9 titanium alloy. Aeronaut. Mater. 2024, 44, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaikh, A.E.; Schmidt, P.; Christ, H.-J. Fatigue Properties of Duplex-Aged Ti 38-644 Metastable Beta Titanium Alloy. Procedia Eng. 2010, 2, 1973–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Hou, J.; Zhang, D.; Yue, Y.; Liu, G.; Sun, J. Making a Low-Cost Duplex Titanium Alloy Ultra-Strong and Ductile via Interstitial Solutes. Acta Mater. 2022, 241, 118411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.-H.; Xu, X.; Dye, D.; Rivera-Díaz-del-Castillo, P.E.J. Microstructural Evolution and Strain-Hardening in TWIP Ti Alloys. Acta Mater. 2020, 183, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhu, J.; Yang, T.; Luan, J.; Kong, H.; Liu, W.; Cao, B.; Wu, S.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; et al. A New α + β Ti-Alloy with Refined Microstructures and Enhanced Mechanical Properties in the as-Cast State. Scr. Mater. 2022, 207, 114260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda-Caraballo, I.; Rivera-Díaz-del-Castillo, P.E.J. Modelling Solid Solution Hardening in High Entropy Alloys. Acta Mater. 2015, 85, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, H. Effect of Interstitial Solutes on the Strength and Ductility of Titanium. Prog. Mater. Sci. 1981, 26, 123–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyakonov, G.S.; Mironov, S.; Semenova, I.P.; Valiev, R.Z. Chapter 7—Strengthening Mechanisms and Super-Strength of Severely Deformed Titanium. In Nanocrystalline Titanium; Garbacz, H., Semenova, I.P., Zherebtsov, S., Motyka, M., Eds.; Micro and Nano Technologies; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 123–143. ISBN 978-0-12-814599-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Emura, S.; Min, X.; Tsuchiya, K. Strain-Rate Effect on Work-Hardening Behavior in β-Type Ti-10Mo-1Fe Alloy with TWIP Effect. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 707, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.-H.; Liang, X.Z.; Kim, B.; Rivera-Díaz-del-Castillo, P.E.J. Modelling Strengthening Mechanisms in Beta-Type Ti Alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 756, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.L.; Bao, X.Y.; Zhang, D.D.; Chen, W.; Zhang, J.Y.; Kuang, J.; Liu, G.; Sun, J. Achieving Superior Strength-Ductility Balance in a Novel Heterostructured Strong Metastable β-Ti Alloy. Int. J. Plast. 2021, 147, 103126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suri, S.; Viswanathan, G.B.; Neeraj, T.; Hou, D.-H.; Mills, M.J. Room Temperature Deformation and Mechanisms of Slip Transmission in Oriented Single-Colony Crystals of an α/β Titanium Alloy. Acta Mater. 1999, 47, 1019–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pande, C.S.; Cooper, K.P. Nanomechanics of Hall–Petch Relationship in Nanocrystalline Materials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2009, 54, 689–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Awady, J.A. Unravelling the Physics of Size-Dependent Dislocation-Mediated Plasticity. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 5926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, D.; Williams, J.C. Perspectives on Titanium Science and Technology. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 844–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutor, R.K.; Cao, Q.; Wei, R.; Su, Q.; Du, G.; Wang, X.; Li, F.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, J.-Z. A Dual-Phase Alloy with Ultrahigh Strength-Ductility Synergy over a Wide Temperature Range. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabi4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Bao, X.; Hao, M.; Chen, W.; Zhang, D.; Wang, D.; Zhang, J.; Liu, G.; Sun, J. Hierarchical Nano-Martensite-Engineered a Low-Cost Ultra-Strong and Ductile Titanium Alloy. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.Y.; Kotoka, R.; Ligda, J.P.; Cao, B.B.; Yarmolenko, S.N.; Schuster, B.E.; Wei, Q. The Microstructure and Mechanical Behavior of Mg/Ti Multilayers as a Function of Individual Layer Thickness. Acta Mater. 2014, 63, 216–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Luo, X.-M.; Lei, L.-M.; Fu, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, G.-P. Theoretical Evaluation of Strengthening Ability of Phase Interfaces in Lamellar Ti Alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2022, 24, 2101570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, J.S. Attempt to Design a Strong Solid. Phys. Rev. B 1970, 2, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atri, R.R.; Ravichandran, K.S.; Jha, S.K. Elastic Properties of In-Situ Processed Ti–TiB Composites Measured by Impulse Excitation of Vibration. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1999, 271, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, T.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, J.Y.; Wu, K.; Li, G.; Kuang, J.; Liu, G.; Sun, J. Unraveling the Discrepancies in Size Dependence of Hardness and Thermal Stability in Crystalline/Amorphous Nanostructured Multilayers: Cu/Cu–Ti vs. Cu/HfO2. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 14331–14341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshelby, J.D. The distribution of dislocations in an elliptical glide zone. Phys. Stat. Sol. 1963, 3, 2057–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Element | Ti | Al | V | Mo | Cr | Zr | Pb | Fe | O | N | C | H |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composition | Bal. | 3.83 | 8.02 | 3.81 | 6.26 | 4.14 | <0.010 | 0.097 | 0.08 | 0.007 | 0.009 | 0.0023 |
| Heat Treatment | Heat Treatment Parameter 1 |
|---|---|
| ST760 | 760 °C/1 h/WQ |
| SA450 | 760 °C/1 h/WQ + 450 °C/10 h/AC |
| SA470 | 760 °C/1 h/WQ + 470 °C/10 h/AC |
| Sample Number | Tensile Strength σb (MPa) | Yield Strength σs (MPa) | Hardness (HV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ST760 | 898 MPa | 876 MPa | 274.0 HV |
| SA450 | 998 MPa | 967 MPa | 294.6 HV |
| SA470 | 1297 MPa | 1211 MPa | 372.1 HV |
| Element | Grain Boundaries/Atom% | Grain Interior/Atom% |
|---|---|---|
| Al | 8.28 | 7.93 |
| Mo | 3.13 | 3.52 |
| Cr | 5.01 | 5.46 |
| V | 8.01 | 8.10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, P.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Sun, Z.; Hao, J.; Pan, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z. Study on the Influence of Aging Temperature on the Microstructure and Properties of Ti-38644 Metastable β-Type Titanium Alloy. Materials 2025, 18, 3825. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18163825
Li P, Zhang X, Liu X, Li Z, Sun Z, Hao J, Pan J, Li Z, Wang Z. Study on the Influence of Aging Temperature on the Microstructure and Properties of Ti-38644 Metastable β-Type Titanium Alloy. Materials. 2025; 18(16):3825. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18163825
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Peiyue, Xinqi Zhang, Xingyu Liu, Zhiqiang Li, Zhihua Sun, Jian Hao, Jinping Pan, Zhi Li, and Zhihua Wang. 2025. "Study on the Influence of Aging Temperature on the Microstructure and Properties of Ti-38644 Metastable β-Type Titanium Alloy" Materials 18, no. 16: 3825. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18163825
APA StyleLi, P., Zhang, X., Liu, X., Li, Z., Sun, Z., Hao, J., Pan, J., Li, Z., & Wang, Z. (2025). Study on the Influence of Aging Temperature on the Microstructure and Properties of Ti-38644 Metastable β-Type Titanium Alloy. Materials, 18(16), 3825. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18163825





