Filamentary Resistive Switching Mechanism in CuO Thin Film-Based Memristor
Highlights
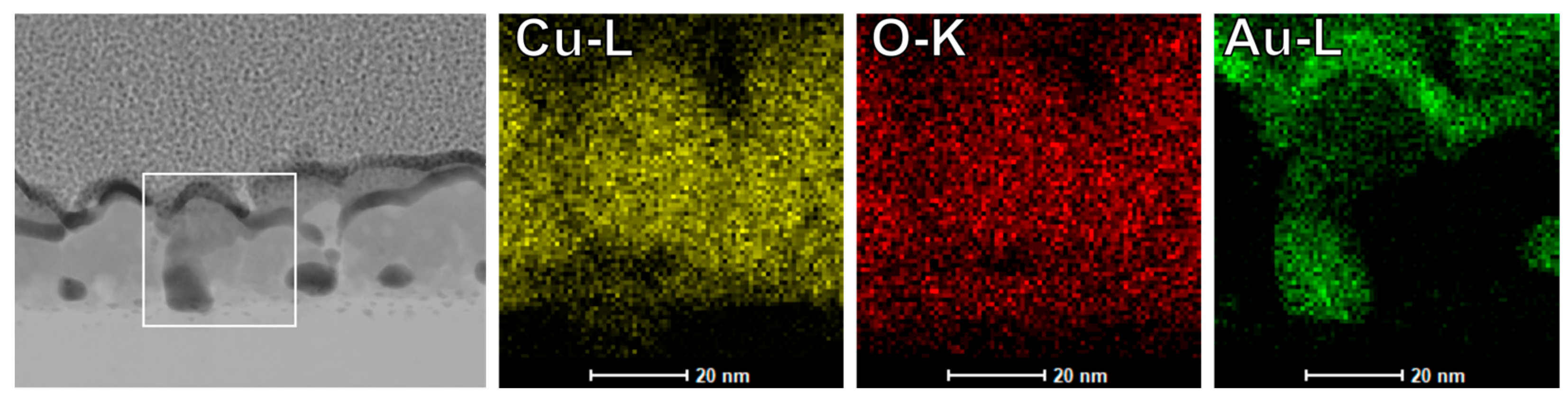
- C-AFM and TEM confirm filament formation preferentially at grain boundaries.
- Au migration in CuO drives resistive switching via ECM-like filamentary mechanism.
- EDS shows localized Au enrichment at sites of conductive filament formation.
- Au nanoseeds critically influence resistive switching in CuO switching layers.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
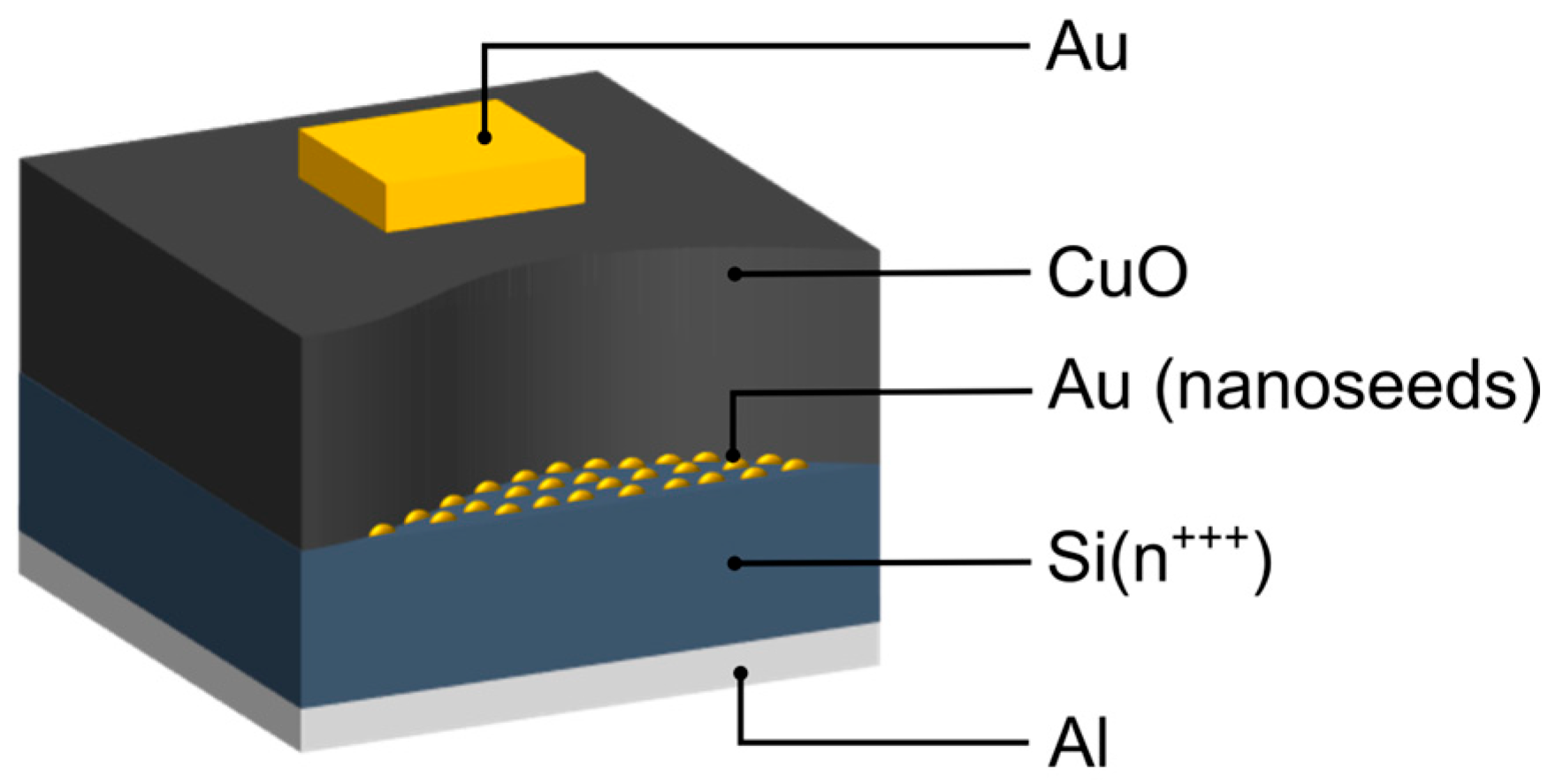
2.1. Single-Layer CuO Memristor Structure
2.1.1. Substrate Preparation
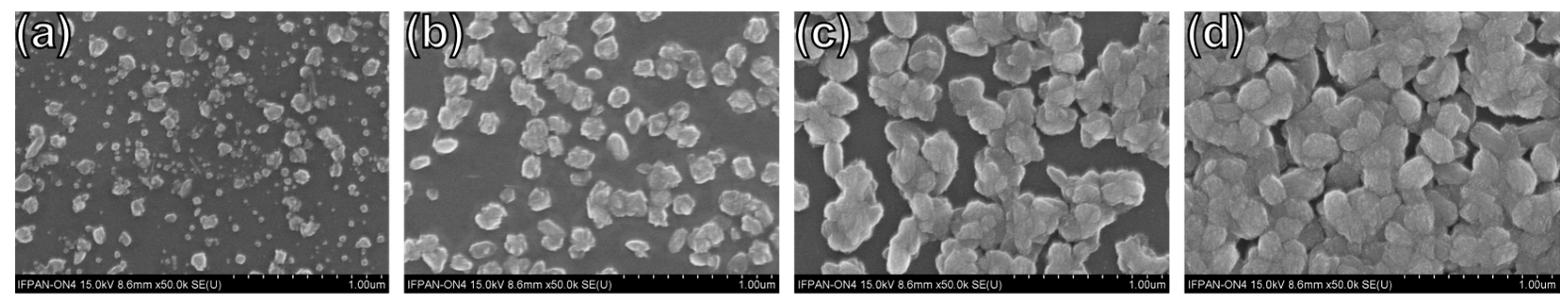
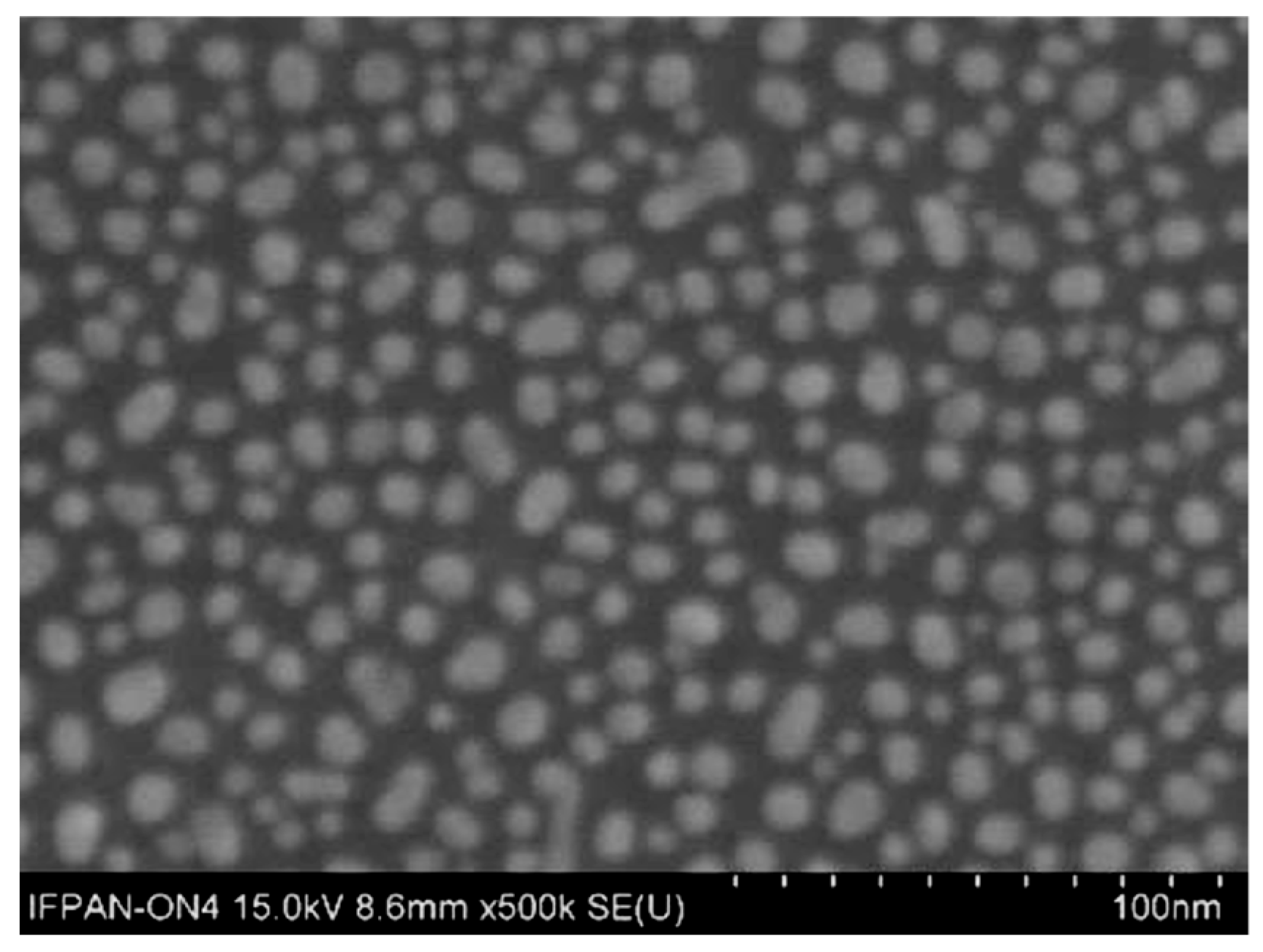
2.1.2. Synthesis of CuO Thin Films
2.2. Measurement Equipment
2.2.1. Electron Microscopy Techniques
2.2.2. Scanning Probe Microscopy Techniques
2.2.3. I–V Measurements
2.2.4. Data Processing and Software
3. Results
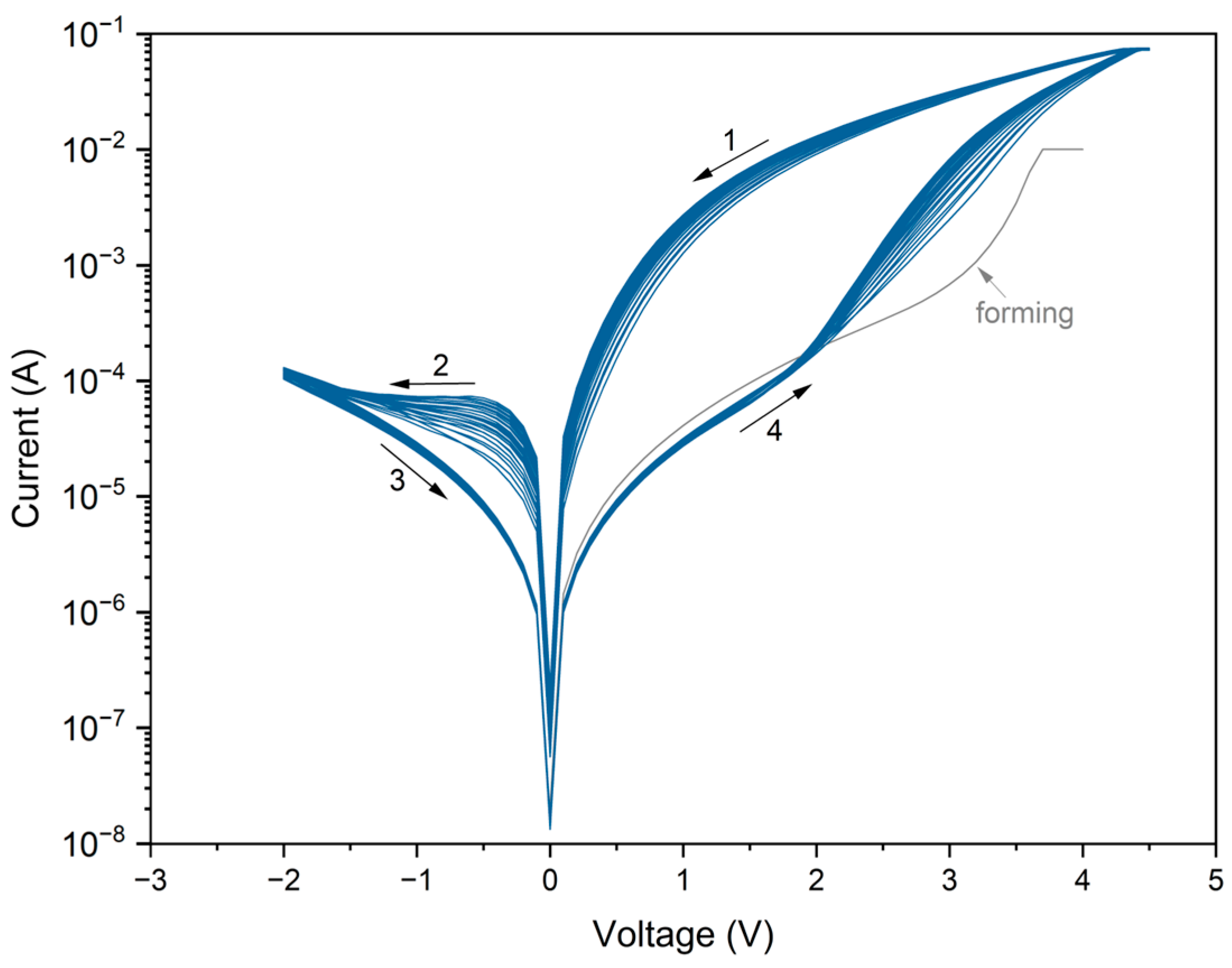
3.1. Evidence of Resistive Switching and Memristor Performance
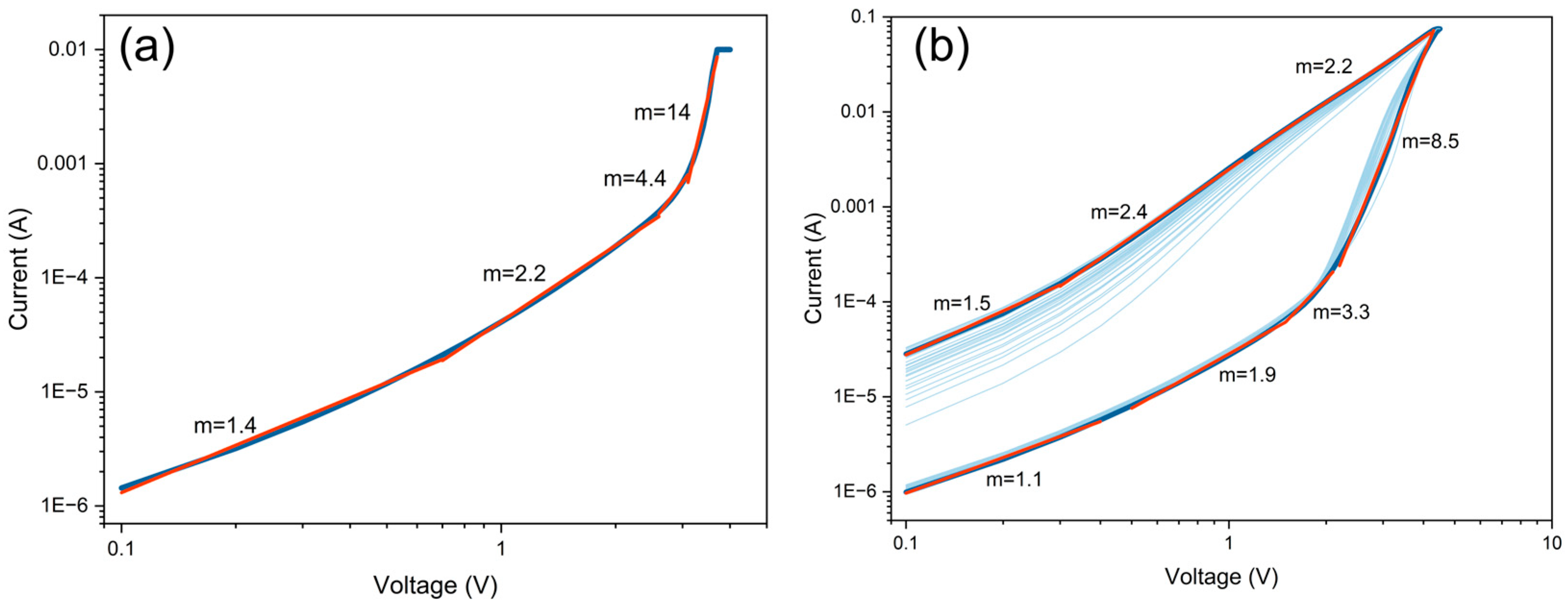
3.2. Conduction Mechanism
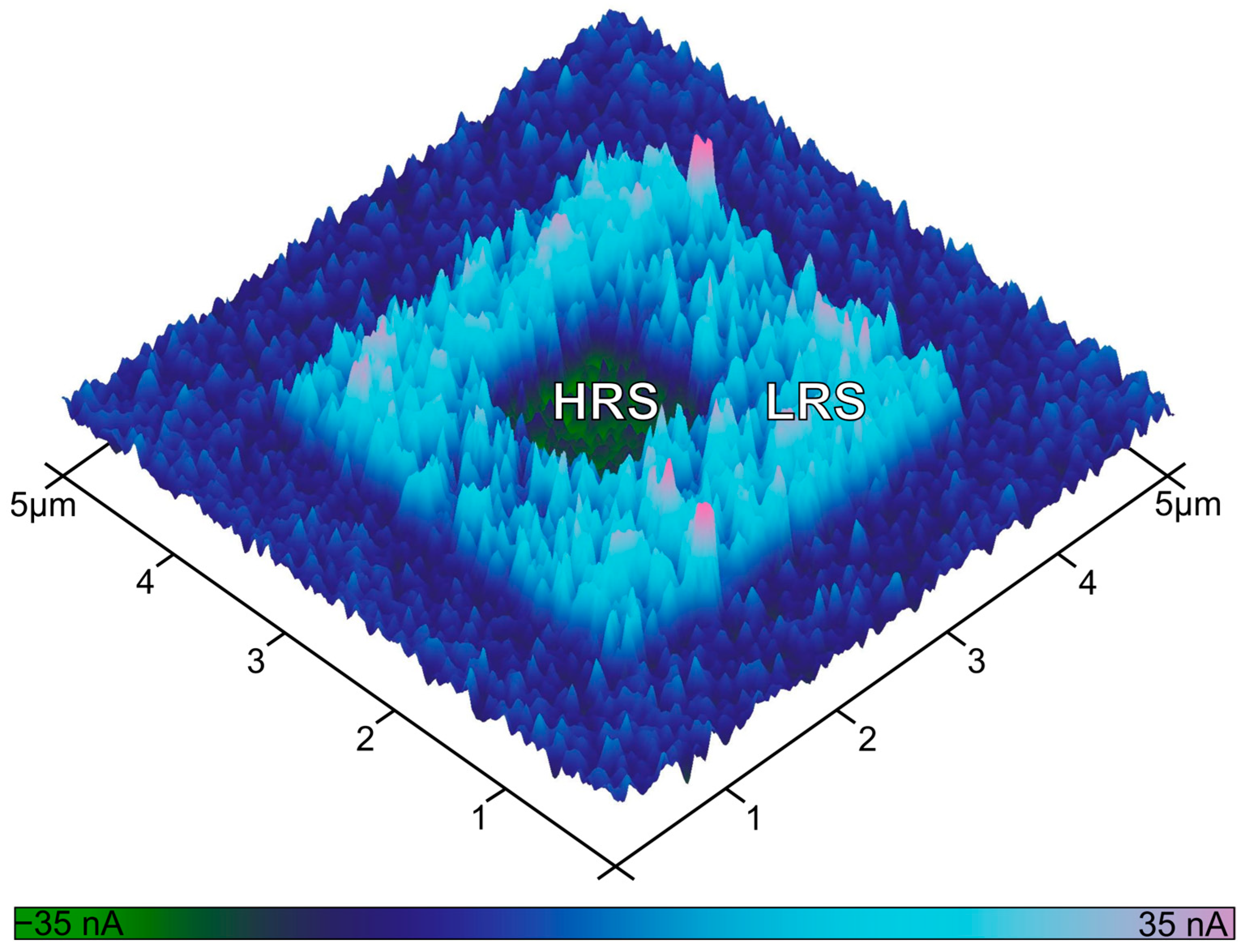
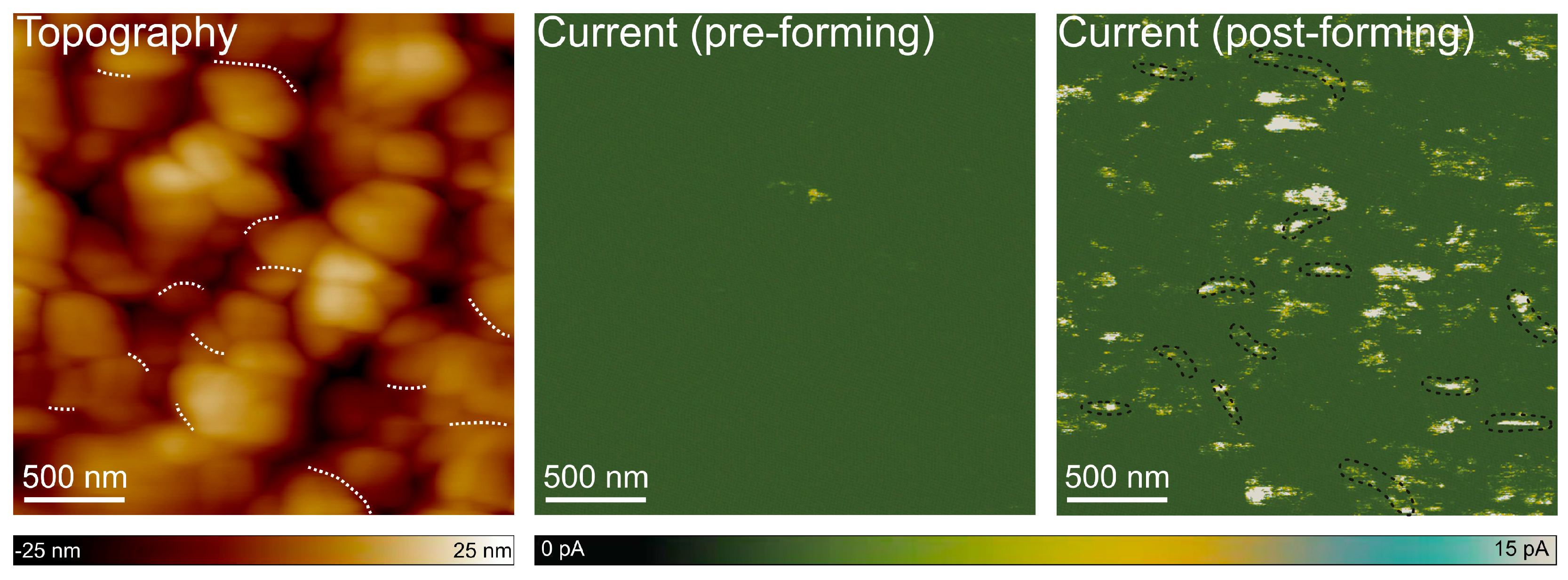
3.3. Preferential CF Formation at Grain Boundaries
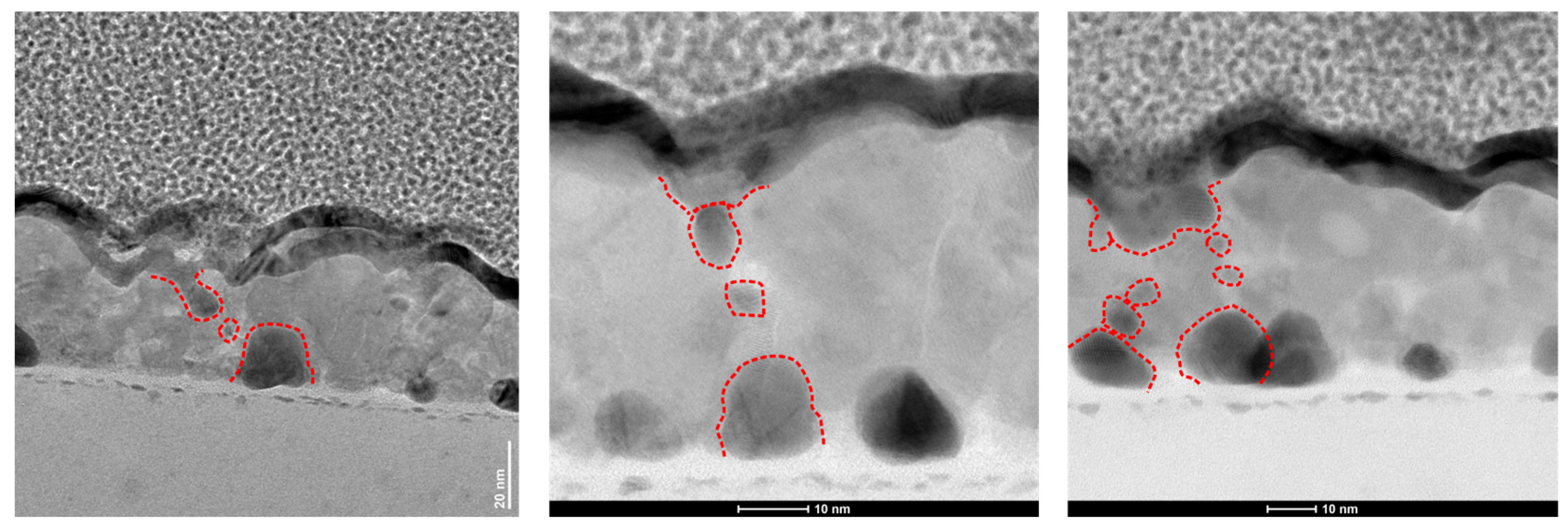
3.4. Post-Switching Microstructure Characterization via TEM and EDX
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Chua, L. Memristor-The Missing Circuit Element. IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory 1971, 18, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, L. Resistance Switching Memories Are Memristors. In Handbook of Memristor Networks; Chua, L., Sirakoulis, G.C., Adamatzky, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 197–230. ISBN 978-3-319-76375-0. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Ke, S.; Jin, Y.; Wen, X.; Ye, C. A Review of Memristor: Material and Structure Design, Device Performance, Applications and Prospects. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2023, 24, 2162323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Gao, B.; Chi, M.; Xia, Q.; Yang, J.J.; Qian, H.; Wu, H. Understanding Memristive Switching via in Situ Characterization and Device Modeling. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Kang, K.; Sun, Y.; Hong, Q.; Wang, C. A Multi-Value 3D Crossbar Array Nonvolatile Memory Based on Pure Memristors. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2022, 231, 3119–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Pan, K.; Jiao, Y.; Sun, B.; Du, C.; Mills, J.P.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, X.; Wei, L.; Zhou, Y.N.; et al. Versatile Memristor for Memory and Neuromorphic Computing. Nanoscale Horiz. 2022, 7, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A. Memristor-Based Neural Networks. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2013, 46, 093001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Fardad, M.; Varshney, P.K. A Memristor-Based Optimization Framework for Artificial Intelligence Applications. IEEE Circuits Syst. Mag. 2018, 18, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Midya, R.; Xia, Q.; Yang, J.J. Review of Memristor Devices in Neuromorphic Computing: Materials Sciences and Device Challenges. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2018, 51, 503002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J. Emerging Resistive Switching Memories; Springer Nature: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, X.; Ong, H.G.; You, L.; Chen, W.; Ding, H.; Funakubo, H.; Chen, L.; Wang, J. Charge trapping-detrapping induced resistive switching in Ba0.7Sr0.3TiO3. AIP Adv. 2012, 2, 032166. [Google Scholar]
- Mazurak, A.; Mroczyński, R.; Jasiński, J.; Tanous, D.; Majkusiak, B.; Kano, S.; Sugimoto, H.; Fujii, M.; Valenta, J. Technology and Characterization of MIS Structures with Co-Doped Silicon Nanocrystals (Si-NCs) Embedded in Hafnium Oxide (HfOx) Ultra-Thin Layers. Microelectron. Eng. 2017, 178, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Reyes, J.; Hernandez-Martinez, L. Understanding the Resistive Switching Phenomena of Stacked Al/Al2O3/Al Thin Films from the Dynamics of Conductive Filaments. Complexity 2017, 2017, 8263904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Park, S.; Kim, S. Dynamic NiOx-Based Memristors for Edge Computing. Chin. J. Phys. 2025, 95, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, E. TiO2-Based Memristors and ReRAM: Materials, Mechanisms and Models (a Review). Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2016, 29, 104004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Thomas, J.P.; Leung, K.T. Programmable, Electroforming-Free TiOx/TaOx Heterojunction-Based Non-Volatile Memory Devices. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 18159–18168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.-C.; Chen, B.; Qian, Y. Effect of Fatigue Fracture on the Resistive Switching of TiO2-CuO Film/ITO Flexible Memory Device. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2018, 18, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Wei, M.; Deng, H. Bipolar Resistive Switching Characteristics in CuO/ZnO Bilayer Structure. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 114, 134502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojcieszak, D.; Domaradzki, J.; Mazur, M.; Kotwica, T.; Kaczmarek, D. Investigation of a Memory Effect in a Au/ (Ti–Cu)Ox-Gradient Thin Film/TiAlV Structure. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2022, 13, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-C.; Zhang, X.-Z.; Jhang, W.-C.; Cheng, C.-W.; Wu, Y.-M.; Tsai, J.-E.; Joodaki, M. Write-Once-Read-Many-Times Characteristics of CuO Layer with Ag Conductive Bridges. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2021, 36, 095016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-C.; Lin, Y.-S.; Cheng, C.-W.; Jhang, W.-C. Annealing Effect on the Performance of Copper Oxide Resistive Memory Devices. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2020, 67, 976–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-C.; Lin, Y.-S. Electrode Dependence of Resistive Switching Characteristics in Copper (II) Oxide Memory Devices. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2019, 34, 075012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Aquila, K.; Phatak, C.; Holt, M.V.; Stripe, B.D.; Tong, S.; Park, W.I.; Hong, S.; Petford-Long, A.K. Bipolar Resistance Switching in Pt/CuOx/Pt via Local Electrochemical Reduction. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 242902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongale, T.D.; Pawar, P.S.; Tikke, R.S.; Mullani, N.B.; Patil, V.B.; Teli, A.M.; Khot, K.V.; Mohite, S.V.; Bagade, A.A.; Kumbhar, V.S.; et al. Mimicking the Synaptic Weights and Human Forgetting Curve Using Hydrothermally Grown Nanostructured CuO Memristor Device. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 18, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mroczyński, R.; Ożga, M.; Godlewski, M.; Witkowski, B.S. Hydrothermally Formed Copper Oxide (CuO) Thin Films for Resistive Switching Memory Devices. Solid-State Electron. 2022, 194, 108357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudheer, S.; Mondal, P.; Rai, V.N.; Srivastava, A.K. A study of growth and thermal dewetting behavior of ultra-thin gold films using transmission electron microscopy. AIP Adv. 2017, 7, 075303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozga, M.; Kaszewski, J.; Seweryn, A.; Sybilski, P.; Godlewski, M.; Witkowski, B.S. Ultra-Fast Growth of Copper Oxide (II) Thin Films Using Hydrothermal Method. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2020, 120, 105279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Wu, W.; Ding, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Seedless Synthesis of Patterned ZnO Nanowire Arrays on Metal Thin Films (Au, Ag, Cu, Sn) and Their Application for Flexible Electromechanical Sensing. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 9469–9476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Facile Hydrothermal Approach for the Density-Tunable Growth of ZnO Nanowires and Their Electrical Characterizations. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15187. [CrossRef]
- Ozga, M.; Zielony, E.; Wierzbicka, A.; Wolska, A.; Klepka, M.; Godlewski, M.; Kowalski, B.J.; Witkowski, B.S. Effect of Repeating Hydrothermal Growth Processes and Rapid Thermal Annealing on CuO Thin Film Properties. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2024, 15, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, C.; Kinoshita, K.; Yamasaki, T.; Sugiyama, Y. Direct Observation of Oxygen Movement during Resistance Switching in NiO/Pt Film. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 042106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozga, M.; Mroczynski, R.; Wolska, A.; Klepka, M.; Godlewski, M.; Witkowski, B.S. Studies on Resistive Switching Mechanisms in RRAM Memory Structures Based on Copper (II) Oxide. Solid-State Electron. 2025, 228, 109140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wu, H.; Gao, B.; Zhang, T.; Yang, Y.; Qian, H. Conduction Mechanisms, Dynamics and Stability in ReRAMs. Microelectron. Eng. 2018, 187–188, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.; Park, J.; Kang, M.; Kim, S. Coexistence of Non-Volatile and Volatile Characteristics of the Pt/TaOx/TiN Device. Results Phys. 2022, 34, 105307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Vogel, T.; Piros, E.; Nasiou, D.; Kaiser, N.; Schreyer, P.; Winkler, R.; Zintler, A.; Arzumanov, A.; Petzold, S.; et al. Oxide Thickness-Dependent Resistive Switching Characteristics of Cu/HfO2/Pt ECM Devices. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2023, 122, 023502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teja Nibhanupudi, S.S.; Roy, A.; Veksler, D.; Coupin, M.; Matthews, K.C.; Disiena, M.; Ansh; Singh, J.V.; Gearba-Dolocan, I.R.; Warner, J.; et al. Ultra-Fast Switching Memristors Based on Two-Dimensional Materials. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Yin, K.; Puzyrev, Y.S.; Liu, Y.; Sun, L.; Li, R.-W.; Pantelides, S.T. Two-Dimensional Nanovaristors at Grain Boundaries Account for Memristive Switching in Polycrystalline BiFeO3. Adv. Elect. Mater. 2015, 1, 1500019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J. Nanoionic RRAMs. In Emerging Resistive Switching Memories; Ouyang, J., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 63–76. ISBN 978-3-319-31572-0. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Z.; Fan, X.; Li, A.; Dong, L. Resistive Switching in Copper Oxide Nanowire-Based Memristor. In Proceedings of the 2012 12th IEEE International Conference on Nanotechnology (IEEE-NANO), Birmingham, UK, 20–23 August 2012; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Wu, Y.; Xie, M.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Shi, X.; Zeng, H. CuO/ZnO Memristors via Oxygen or Metal Migration Controlled by Electrodes. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 025018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariffar, A.; Salman, H.; Siddique, T.A.; Gebril, W.; Manasreh, M.O. Resistive Switching in FTO/CuO–Cu2O/Au Memory Devices. Micro Nano Lett. 2020, 15, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medgyes, B.; Gharaibeh, A.; Rigler, D.; Harsányi, G. On the Electrochemical Migration Mechanism of Gold in Electronics—Less Reliable Than Expected? Materials 2021, 14, 5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čechal, J.; Polčák, J.; Šikola, T. Detachment Limited Kinetics of Gold Diffusion through Ultrathin Oxide Layers. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 17549–17555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaram, A.K.; Kharwar, S.; Agarwal, T.K. Investigation of Resistive Switching in Au/MoS2/Au Using Reactive Molecular Dynamics and Ab-Initio Quantum Transport Calculations. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.11437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ozga, M.; Mroczynski, R.; Matus, K.; Arabasz, S.; Witkowski, B.S. Filamentary Resistive Switching Mechanism in CuO Thin Film-Based Memristor. Materials 2025, 18, 3820. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18163820
Ozga M, Mroczynski R, Matus K, Arabasz S, Witkowski BS. Filamentary Resistive Switching Mechanism in CuO Thin Film-Based Memristor. Materials. 2025; 18(16):3820. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18163820
Chicago/Turabian StyleOzga, Monika, Robert Mroczynski, Krzysztof Matus, Sebastian Arabasz, and Bartłomiej S. Witkowski. 2025. "Filamentary Resistive Switching Mechanism in CuO Thin Film-Based Memristor" Materials 18, no. 16: 3820. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18163820
APA StyleOzga, M., Mroczynski, R., Matus, K., Arabasz, S., & Witkowski, B. S. (2025). Filamentary Resistive Switching Mechanism in CuO Thin Film-Based Memristor. Materials, 18(16), 3820. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18163820







