Abstract
Memristors with resistive switching capabilities are vital for information storage and brain-inspired computing, making them a key focus in current research. This study demonstrates non-volatile analog resistive switching behavior in Al/TiOx/TiN/Si(n++)/Al memristive devices. Analog resistive switching offers gradual, controllable conductance changes, which are essential for mimicking brain-like synaptic behavior, unlike digital/abrupt switching. The amorphous titanium oxide (TiOx) active layer was deposited using the pulsed-DC reactive magnetron sputtering technique. The impact of increasing the oxide thickness on the electrical performance of the memristors was investigated. Electrical characterizations revealed stable, forming-free analog resistive switching, achieving endurance beyond 300 DC cycles. The charge conduction mechanisms underlying the current–voltage (I–V) characteristics are analyzed in detail, revealing the presence of ohmic behavior, Schottky emission, and space-charge-limited conduction (SCLC). Experimental results indicate that increasing the TiOx film thickness from 31 to 44 nm leads to a notable change in the current conduction mechanism. The results confirm that the memristors have good stability (>1500 s) and are capable of exhibiting excellent long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD) properties. The analog switching driven by oxygen vacancy-induced barrier modulation in the TiOx/TiN interface is explained in detail, supported by a proposed model. The remarkable switching characteristics exhibited by the TiOx-based memristive devices make them highly suitable for artificial synapse applications in neuromorphic computing systems.
1. Introduction
Brain-inspired computational systems based on artificial synapse networks have garnered significant attention due to their potential to surpass the traditional von Neumann computing paradigm. Memristive devices, as the core of artificial synapse networks, play a crucial role in mimicking the biological structure and function of synapses due to their non-volatility, precise and repeatable analog switching, and the potential for large-scale integration through crossbar array architectures [1,2,3]. Transition metal oxide-based memristive devices with resistive switching behavior in metal–insulator–metal (MIM) structures have been widely studied due to their scalability, low power consumption, CMOS compatibility, and simplicity [4]. In recent years, considerable efforts have been made to modulate the memristive properties or phase-transition dynamics of the active switching layer through photonic stimulation [5]. The resistance state of the active layer in a memristive device can be dynamically modulated by applying an external electrical bias [6]. Resistive switching (RS) primarily has two types: filamentary and homogeneous. Filamentary RS, also known as digital switching, involves the development of conductive filaments (CFs) within the active layer, with the switching process occurring between the filament tip and the electrode. This mechanism is widely documented and is notable for its abrupt SET/RESET transitions, distinct resistance states, and high resistance ratios, making it well suited for digital logic and data storage applications [7,8]. In contrast, homogeneous RS, also referred to as analog switching, exhibits a gradual variation in the conductance of the active layer. This behavior is attributed to a uniform current distribution over the whole cross-sectional area, indicating the absence of filament formation [9,10]. Such gradual modulation closely resembles synaptic behavior in biological systems, making it a promising approach for neuromorphic computing technologies [11,12]. These features are crucial for the crossbar-based hardware acceleration of neural networks, as discussed in several recent review articles that address device-level mechanisms, integration challenges, and system-level performance bottlenecks in neuromorphic architectures [13,14,15,16]. RS behavior has been reported in several metal oxide-based materials, including HfOx [17], NiOx [18], VOx [19], TaOx [20], TiOx [21], and WOx [22]. Among transition metal oxides, titanium oxide (TiOx) stands out due to its simple chemical structure, multiple switching modes, and diverse oxidation states. Due to a well-balanced combination of physical and chemical properties, along with excellent environmental compatibility, TiO2, a high-k dielectric with a wide bandgap and inherent oxygen vacancies, is particularly favorable for RS applications [23,24,25]. When oxygen atoms are removed from the TiO2 matrix, the remaining electrons occupy titanium’s conduction band, creating an oxygen-deficient structure with n-type conductivity [26]. Moreover, titanium-based perovskite oxides, such as lead zirconate titanate (PZT) films, have been extensively studied for high-frequency transducer applications [27]. Strontium titanate (SrTiO3) has gained attention as a promising material for RS devices [28]. TiO2 and TiO2-based thin films have been prepared using various techniques, including the sol–gel process [29,30], hydrothermal method [31], magnetron sputtering [32,33], electrochemical anodization [34], atomic layer deposition (ALD) [35], and several other fabrication approaches [36,37,38]. Magnetron sputtering (DC or RF) stands out as a relatively cost-effective deposition technique, offering precise control over film stoichiometry and uniformity in thickness across the substrate. Sputtering offers significant flexibility, enabling the deposition of a wide range of materials, including metals, semiconductors, and dielectric materials [39,40]. Despite ongoing research, several aspects of TiO2-based resistive random-access memory (RRAM) remain uncertain. Notably, the electrical performance of these devices often exhibits variability, and the underlying mechanisms governing resistive switching are not yet fully understood [41]. Interestingly, digital and analog resistive switching behaviors have been observed within the same devices, though the mechanism behind this is still unclear [42,43,44]. However, challenges related to device reliability and reproducibility persist. Therefore, improving the device’s performance and gaining deeper insight into its switching behavior remain essential research goals. While many researchers have recently reported that bilayer or doped TiOx structures are effective to enhance the RS performance and improve the distribution of switching parameters [45,46], TiO2 continues to be a widely studied resistive switching material, with different deposition methods such as sputtering and sol–gel still actively explored [32,43,47]. This study intentionally employs a pure TiOx layer to focus on its intrinsic switching behavior. This approach simplifies the material system, establishing a clear baseline for future investigations involving more-complex architectures. In this work, the TiOx layer was deposited using pulsed-DC sputtering at room temperature to fabricate the Al/TiOx/TiN MIM structure, which is compatible with CMOS integration due to its low thermal budget and use of CMOS-friendly materials. To the best of our knowledge, this specific technique has not been extensively reported for TiOx-based resistive switching devices. In this article, the authors present the existence of relatively stable analog RS in TiOx thin films deposited by pulsed-DC reactive sputtering at room temperature with Al and TiN electrodes at the top (TE) and bottom (BE), respectively. The electrical performance of fabricated Al/TiOx/TiN devices was investigated by varying the thickness of the TiOx thin film. Comprehensive structural characterization of the TiOx layer was conducted, and the current conduction mechanisms were analyzed based on the obtained electrical data. Moreover, a detailed discussion of the resistive switching mechanism was provided, supported by a proposed model.
2. Materials and Methods
In this work, the Al/TiOx/TiN/Si(n++)/Al MIM devices were fabricated using a multi-step pulsed-DC magnetron sputtering technique. The substrate was a highly doped n-type silicon (Si) wafer with arsenic doping and a 0.004–0.008 Ω·cm resistivity. Initially, the silicon substrates underwent standard RCA cleaning, followed by a 1% hydrofluoric acid (HF) etching step for 1 min before being transferred into the load-lock chamber. A 60 nm titanium nitride (TiN) bottom electrode was first deposited on the Si substrates by pulsed-DC reactive magnetron sputtering from a metallic titanium target in an argon/nitrogen (Ar/N2) gas environment. The deposition was carried out at a chamber pressure of 3 mTorr using a 1:2 Ar:N2 gas flow ratio, and the sputtering power was set to 1000 W. Subsequently, without breaking the vacuum, a TiOx active layer was deposited on top of the TiN layer. This was achieved by reactive sputtering of a metallic Ti target in an argon/oxygen (Ar/O2) atmosphere. A 3:2 Ar:O2 gas ratio was maintained to form a near-stoichiometric TiO2 film at a working pressure of 5 mTorr, again using a sputtering power of 1000 W. TiOx thin films with thicknesses of 31 nm and 44 nm were obtained by conducting the deposition process for 7 and 10 min, respectively. All the depositions were carried out at room temperature. Specialized measurements were undertaken to elucidate the chemical composition and structural characteristics of the thin films. Film thicknesses were determined via spectroscopic ellipsometry using a Jobin-Yvon UVISEL (Horiba, Lille, France) system. The structure and crystallinity of the deposited films were characterized using grazing incidence X-ray diffraction (GI-XRD) with a PANalytical Empyrean Series 2 diffractometer equipped with a PIXcel3D detector (Panalytical, Almelo, The Netherlands), utilizing Cu-Kα radiation (λ = 1.54 Å). Measurements were conducted in the 2θ range of 20–80°, with a fixed angle of incidence. The elemental composition and the surface morphology were investigated through energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) and field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), utilizing a Hitachi SU-70 scanning electron microscope (Hitachi High-Technologies Corporation, Tokyo, Japan). To perform electrical characterization of the TiOx films with thicknesses of 31 and 44 nm, top 100 nm thick Al contact pads were patterned using standard photolithography with ultraviolet (UV) exposure at 380 nm, followed by a lift-off process. The Al was deposited by magnetron sputtering using a high-purity (99.99%) aluminum target. This step was conducted at a power of 350 W with an argon gas flow rate of 25 sccm and a working pressure of 2 mTorr. To ensure improved electrical contact, the backside of the Si substrates was also coated with an aluminum layer. Electrical characterization was performed using a Keithley 4200 semiconductor parameter analyzer (Tektronix, Beaverton, OR, USA) equipped with a SUSS PM-8 probe station (SUSS MicroTec Semiconductor, Garching, Germany). The results presented in this work pertain to MIM devices featuring a top electrode diameter of 150 μm. The scheme of the Al/TiOx/TiN/Si(n++)/Al MIM device structure is presented in Figure 1a.
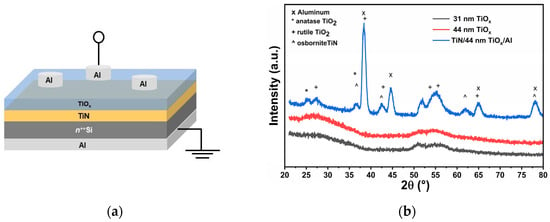
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic diagram of Al/TiOx/TiN/Si(n++)/Al MIM device structure. (b) GI-XRD patterns of the TiOx thin films deposited on Si(100) for different thicknesses and the TiN/TiOx (44 nm)/Al tri-layer structure.
3. Results and Discussion
Figure 1b displays the GI-XRD patterns of the deposited thin films. The TiOx films with thicknesses of 31 and 44 nm exhibited amorphous characteristics, as evidenced by the presence of broad halos centered around 26° and 55° in their diffraction patterns. In contrast, the GI-XRD pattern of the Al/TiOx (44 nm)/TiN stack revealed distinct crystalline peaks corresponding to both rutile and anatase phases of TiO2, along with peaks from the Al top electrode and the TiN (osbornite) bottom electrode.
Specifically, the Bragg peak positions and corresponding Miller indices for the Al/TiOx/TiN tri-layer identified with the HighScore Plus suite (Database PDF-5+2025) include TiO2 anatase: 25.30° (011), 38.56° (112) (ref. code: 01-083-5914), TiO2 rutile: 27.08° (110), 38.66° (020), 43.45° (120), 53.77° (121), 55.83° (220), 64.75° (221) (ref. code: 98-016-5921), Al metal (TE): 38.48° (111), 44.72° (002), 65.10° (022), 78.24° (113) (ref. code: 98-024-0129), and TiN osbornite (BE): 36.73° (111), 42.67° (002), 61.93° (022), 78.13° (222) (ref. code: 04-018-2321). It was fascinating to see that the 44 nm TiOx film displayed distinct crystallization when inserted between the TiN and Al electrodes, while it remained amorphous without electrodes. This crystallization is likely facilitated by metal-induced crystallization (MIC) or interfacial effects, where the neighboring metal layers may promote structural ordering through mechanisms such as localized thermal effects during deposition, stress-driven phase transformation, or diffusion-enhanced crystallization at the interfaces [48]. The insertion of the TiOx layer between the TiN and Al electrodes resulted in stress formation within the TiOx film. The nature of this stress was identified using the Δd parameter, estimated by the following equation [49]:
where d represents the measured interplanar spacing, and d′ is the standard interplanar spacing value. A negative Δd indicates compressive stress, while a positive value suggests tensile stress present in the thin film [49]. Based on X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, a Δd value of −0.49% was observed, confirming the presence of compressive stress within the TiOx layer.
Figure 2a,b display FE-SEM images of TiOx thin films with 31 nm and 44 nm thicknesses, respectively. Both films exhibit a uniform surface structure. The surface of the 31 nm TiOx film appears very smooth, while the 44 nm film shows a comparatively rougher surface, attributed to a higher concentration of agglomerates [50]. Given that the 44 nm TiOx film exhibits a rougher surface than the 31 nm film, only the 44 nm film was selected for quantitative surface roughness analysis using atomic force microscopy (AFM). The surface morphology was investigated using a Bruker Dimension Icon AFM system (Santa Barbara, CA, USA) operated in PeakForce Tapping mode (Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA) with silicon nitride probes featuring sharp tips (tip radius ~ 2 nm). A representative AFM image over a 1 × 1 μm2 area of the 44 nm TiOx film is illustrated in Figure 2c. The surface roughness was quantified by calculating the root mean square (RMS) roughness from AFM height data collected over a 10 × 10 μm2 scan area. The RMS roughness was determined to be 0.2 ± 0.05 nm, indicating a homogeneous surface with small grains, consistent with observations from the SEM analysis.
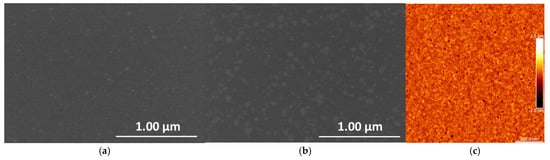
Figure 2.
FE-SEM images of TiOx thin films for two different thicknesses, (a) 31 nm and (b) 44 nm. (c) AFM topographic image of the 44 nm TiOx thin film.
Figure 3 shows the EDX spectrum of the TiOx films. The chemical compositions of the films were determined to be Ti26.8O73.2 for 31 nm and Ti27.6O72.4 for 44 nm TiOx, indicating a slight excess of oxygen content relative to the stoichiometric composition of TiO2 (Ti33.3O66.7).
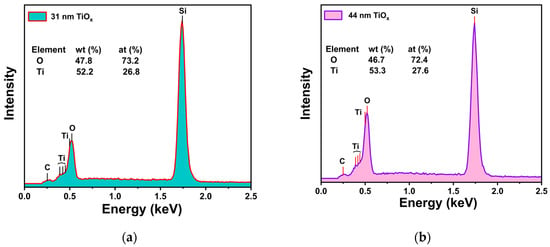
Figure 3.
EDX spectrum of TiOx thin films for two different thicknesses, (a) 31 nm and (b) 44 nm.
To investigate the electrical behavior of TiOx thin films, I–V measurements were conducted on asymmetric Al/TiOx/TiN/Si(n++)/Al structures. A voltage bias was applied exclusively to the top electrode (TE), while the bottom electrode (BE) was maintained at ground potential. Figure 4a,b illustrate the I–V curves for devices with 31 nm and 44 nm TiOx thin films as the insulating layers, respectively. Both devices demonstrated forming-free switching behavior, characterized by a homogenous transition to LRS (SET) when a positive voltage was applied and a return to HRS (RESET) under a negative voltage. This gradual resistance change suggests the absence of conductive filament (CF) formation in the TiOx layers. For the 31 nm and 44 nm films, the SET voltages were 3.5 V and 3.6 V, respectively. The RESET voltages were observed at approximately −3.4 V for the 31 nm film and −3.1 V for the 44 nm film.
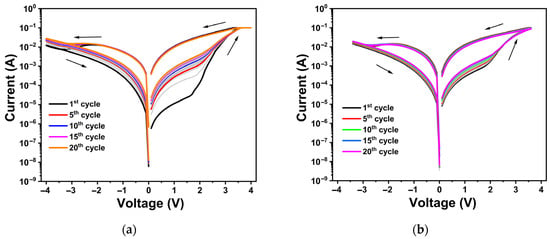
Figure 4.
The semi-logarithmic I-V curves (20 cycles) of the Al/TiOx/TiN/Si(n++)/Al memristor with a TiOx thickness of (a) 31 nm and (b) 44 nm. A current compliance of Ic = 100 mA was used during the measurements, and the arrow indicates the sweep direction. The light gray lines indicate in-between cycles.
During the RESET operation, the current began to decline from −2.0 V for the 31 nm film and from −1.8 V for the 44 nm film, continuing to drop until reaching the RESET voltage in both cases. This region, known as the negative differential resistance (NDR) region, is characterized by an increase in resistance as the voltage increases. An ideal NDR region is particularly interesting for oscillators and diodes [51]. The observed non-filamentary switching behavior is primarily linked to the modulation of the Schottky barrier at the metal–oxide interface [52].
A comprehensive understanding of the physical mechanisms driving resistive switching is essential for advancing memristive device optimization and commercial development. Despite decades of extensive research, the exact nature of resistive switching remains a topic of ongoing debate. The electrical conduction in the MIM structure may not be fully captured through simple I–V fitting using predefined models. However, it is often possible to identify the main current pathway within the device among the various possible conduction mechanisms. In general, a non-linear I–V curve can result from various charge transport mechanisms, such as Schottky or thermionic emission, Poole–Frenkel (P–F) emission, and space-charge-limited current (SCLC) conduction [53]. Specifically, the Schottky mechanism is typically characterized by a log(I) ∝ V1/2 dependence, while the SCLC mechanism follows a quadratic relationship, expressed as I ∝ V2 [54,55,56].
Figure 5a displays the double-logarithmic I–V fitting for the 31 nm TiOx film under positive voltage bias. During the first positive bias sweep, the slopes of the log I–log V plot of HRS changed from 1.2 to 1.7, followed by a sharp increase in current with increasing voltage. As the voltage sweep was repeated, the slopes in the HRS region increased further, reaching 1.3 at a lower bias and 2.0 at a higher bias. For LRS, the I–V curve showed a linear behavior with a slope of approximately 1.2 in the low-bias region, indicating ohmic conduction. At higher bias, the slope increased to 1.7, and the data fit well with a log I–V1/2 plot, as illustrated in Figure 5b. This suggests that the conduction in LRS is governed predominantly by ohmic and Schottky emission mechanisms. The inset of Figure 5b presents the fitting for the first HRS cycle at higher bias, which also fitted well to the log I–V1/2 plot. This observation indicates that, in HRS, the conduction initially transitions from ohmic in the low-field region to Schottky emission in the high-field region. With repeated cycling, the dominant mechanisms evolve towards a combination of ohmic and space-charge-limited conduction (SCLC).
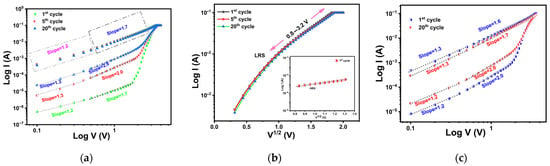
Figure 5.
(a) Double-logarithmic I–V plots and (b) log I–V1/2 plots for the 1st, 5th, and 20th cycles. The inset shows the corresponding log I–V1/2 plot in HRS for the 1st cycle of 31 nm TiOx, under positive bias. (c) Double-logarithmic I–V plots for the 1st and 20th cycles of 44 nm TiOx in the positive bias region.
Figure 5c shows the double-logarithmic I–V curves for the 44 nm TiOx film under positive bias. Regardless of the number of cycles, HRS displayed a change in slope from 1.2 to 2.0, followed by a sharp increase in current as voltage increases, consistent with the trap-controlled SCLC model [57]. In LRS, the log I–log V curves showed a slope of approximately 1.3 at low bias and 1.7 at high bias, again suggesting that ohmic and Schottky emission mechanisms dominate the conduction process.
Figure 6a,b illustrate the double-logarithmic I–V curves of the 31 nm and 44 nm TiOx films, respectively, under negative voltage bias. In HRS, the slope of the log I–log V plot for the 31 nm film changed from 1.3 to 2.6, while for the 44 nm film, it varied from 1.3 to 2.4 with increasing voltage. These results indicate ohmic conduction at a lower bias and SCLC at a higher bias in HRS for both films. With increasing cycle number, the slope of the ohmic region remained nearly constant at 1.3 for both resistance states. However, the slope of the SCLC region decreased from 2.6 to 2.1 for the 31 nm film and from 2.4 to 2.1 for the 44 nm film, respectively. Notably, the slope at higher bias in HRS decreases with successive cycles, suggesting electric field-induced charge trapping in the TiOx film [58]. In contrast, the LRS of both films exhibited a linear relationship between log I and log V, indicating ohmic conduction across the bias range.
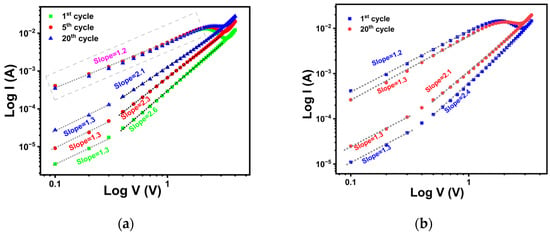
Figure 6.
(a) Double-logarithmic I–V plots for the 1st, 5th, and 20th cycles of 31 nm TiOx, (b) double-logarithmic I–V plots for the 1st and 20th cycles of 44 nm TiOx, in the negative bias region.
Figure 7a presents the endurance performance of the fabricated TiOx-based memristors, highlighting consistent and repeatable resistive switching behavior over 300 DC cycles. The HRS and LRS currents were recorded at a read voltage of 2.0 V. The variation of the current in LRS was insignificant, while a noticeable gradual increase in HRS current was observed with increasing resistive switching cycle number. Notably, these variations were more pronounced in the 31 nm TiOx film than in the 44 nm film, indicating that the 44 nm film exhibits better stability and endurance in resistive switching performance. The observed increase in HRS current over repeated cycling suggests a reduction in trap density within the TiOx layer, which enhances carrier transport across the Al/TiOx/TiN structure [59]. The fatigue in the RS behavior in the successive cycles can be explained by the variation of vacancy densities and oxygen ions [60]. The observed increase in HRS current with cycling is consistent with the recent literature findings [61]. It is attributed to interface degradation at the TiOx/TiN interface. Studies have identified mechanisms such as ion accumulation, interfacial roughening, and chemical instability as key contributors. In particular, repeated switching cycles lead to the accumulation of oxygen vacancies near the TiOx/TiN interface, which enhances trap-assisted tunneling and results in an increase in HRS current. Under prolonged cycling, partial reduction or nitridation of the TiOx layer at the TiN interface may form a TiOxNy phase, thereby modifying the local defects and barrier height [61,62,63]. The ability of memristors to retain data plays a crucial role in developing highly stable memory devices. The retention characteristics of the devices utilizing TiOx films with thicknesses of 31 nm and 44 nm are shown in Figure 7b. The measurements were conducted under ambient conditions at room temperature. During the retention test, resistance states were monitored using a read voltage of 0.5 V. The results indicate strong non-volatile behavior in both HRS and LRS, with clear separation maintained between the two states. Although a minor decline in LRS was observed for both types of devices over the 1500 s measurement duration, the overall stability remained good throughout the test. The devices based on the 44 nm TiOx layer demonstrated a greater ON/OFF ratio than those with the 31 nm layer. However, the results suggest that both film thicknesses exhibited relatively stable performance.
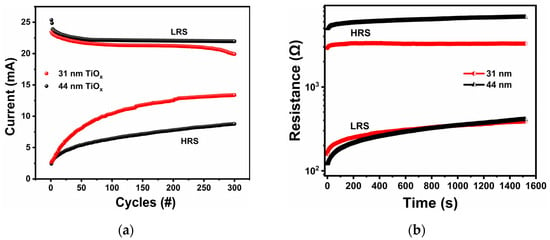
Figure 7.
(a) Endurance plot for 31 and 44 nm TiOx thin-film HRS and LRS currents read at 2.0 V (300 cycles, Ic = 100 mA). (b) Retention performance of the devices based on 31 and 44 nm TiOx thin films, read at 0.5 V.
This type of RS mechanism consists of an interface-type model resulting from Schottky barrier height modulation caused by charge trapping and de-trapping at the TiN/TiOx interface under external electric fields, as presented in Figure 8a. The Al top electrode in contact with TiOx forms an effective ohmic contact due to the close match between the work function of Al (~4.1 eV) and the electron affinity of TiOx (~4.0 eV) [64,65]. However, TiN has a work function of ~4.7 eV [66], so it is reasonable to assume the occurrence of a Schottky barrier at the TiN/TiOx interface. Thin films deposited at room temperature tend to exhibit a higher concentration of oxygen vacancies near the bottom interface, often attributed to the existence of reduced Ti3+ [43]. According to Park et al., the upper surface of spin-coated films becomes more stoichiometric because it is the only side exposed to atmospheric conditions during deposition, resulting in a gradient of oxygen vacancies across the film thickness [67]. The RS effect is associated with the movement of these oxygen vacancies under an electric field, which modulates the potential barrier at the TiN/TiOx interface. These vacancies introduce extra interface potential, effectively lowering the Schottky barrier height [68]. When a positive bias is applied to the Al TE, the TiN BE is under negative bias, attracting oxygen vacancies (positive charge traps) toward the TiN/TiOx interface. This leads to electron de-trapping and migration away from the interface, causing a shift in the local potential and Fermi level alignment, which reduces the Schottky barrier height at the BE interface. As a result, the electrons can move easily through the barrier and trigger a transition from HRS to LRS [69]. Conversely, applying a negative bias to the TE (BE is at a positive bias) causes the oxygen vacancies to migrate away from the TiN/TiOx interface. In addition, oxygen vacancies situated in the vicinity of the BE interface can trap electrons during electron movement as well. As electrons are injected and begin to occupy these trap states, the local positive charge is partially neutralized, leading to an increase in the Schottky barrier height. This reduces the free carrier density and raises the interfacial resistance, thereby switching the device from LRS back to HRS [70]. This interface-type RS behavior, involving Schottky barrier modulation due to oxygen vacancy migration or electron trap dynamics, has been widely observed in TiOx and other resistive switching materials [43,59,67,71,72]. Thus, the Al/TiOx/TiN device operates through interface-type RS, characterized by Schottky barrier height modulations at the TiN/TiOx interface that can be attributed to the oxygen vacancy migration at the interface.
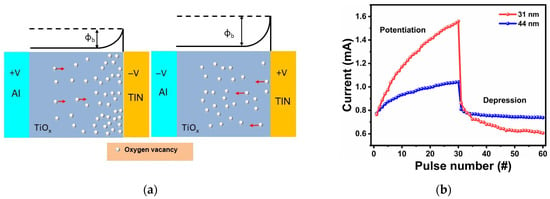
Figure 8.
(a) Schematic illustration of the proposed model depicting the switching mechanism. (b) Potentiation and depression behavior of 31 nm and 44 nm thin-film-based memristor synapses under stimulation by 30 identical positive voltage pulses (+2 V, 200 ms) followed by 30 identical negative voltage pulses (−2 V, 200 ms).
To replicate key functionalities of biological synapses using the Al/TiOx/TiN memristor, pulsed current–voltage (I–V) measurements were conducted for devices with both 31 nm and 44 nm TiOx film thicknesses. In this context, the applied voltage pulses act as external stimuli, while the resulting current responses represent changes in synaptic weight. A critical feature of biological synapses is their ability to modulate synaptic strength incrementally in response to repeated stimuli, known as long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD). These synaptic behaviors can be emulated in memristors by controlling the direction and duration of the applied voltage pulses, in line with the flux-controlled memristor model [73]. When 30 consecutive positive voltage pulses (2 V, 200 ms) are applied, the conductance of the memristors gradually increases. Conversely, applying 30 successive negative pulses (−2 V, 200 ms) leads to a gradual reduction in conductance as illustrated in Figure 8b. This bidirectional modulation corresponds to LTP (increased conductance) and LTD (decreased conductance), both of which are crucial for mimicking the adaptive learning processes observed in computational neuroscience, neural networks, and biological systems [74].
The analog and non-volatile switching characteristics of these devices make them highly suitable for implementation as artificial synapses in neuromorphic computing systems [75]. Their ability to achieve continuous resistance modulation enhances fault tolerance and enables high-density data storage. Future investigations should aim to address the remaining challenges, including temperature-dependent stability, long-term data retention, scaling effects on resistive switching behavior within crossbar array architectures, and a detailed evaluation of synaptic plasticity characteristics in Al/TiOx/TiN memristors.
4. Conclusions
In this study, TiOx-based Al/TiOx/TiN memristive devices were fabricated on a highly doped n-type Si substrate, exhibiting analog resistive switching behavior. Structural analysis confirmed that the sputter-deposited TiOx films are initially amorphous when solely deposited on Si but crystallize into a mixed anatase–rutile phase when sandwiched between TiN and Al electrodes. These films are slightly overoxidized compared with stoichiometric TiO2. Surface morphology analysis showed that the 31 nm TiOx film is relatively smooth, whereas the 44 nm film displays a slightly rougher texture due to a higher density of agglomerates. The analysis of the current-conduction mechanism revealed that in HRS, current conduction is mainly governed by ohmic behavior at low bias and SCLC at high bias. In LRS, ohmic conduction dominates at low bias, while Schottky emission prevails at high bias. The devices demonstrated excellent endurance, maintaining stable performance over more than 300 DC switching cycles. Furthermore, evaluation of the retention time in both HRS and LRS confirmed that the resistance states remained stable, with minimal degradation observed in LRS over 1500 s. The resistive switching mechanism is attributed to the drift of oxygen vacancies, which modulate the Schottky barrier at the TiN/TiOx interface. Additionally, the memristors effectively exhibited strong LTP and LTD characteristics. Among the tested structures, the memristor with a 44 nm TiOx film showed superior performance in terms of switching stability, ON/OFF ratio, and endurance. Overall, TiOx film thickness plays a crucial role in optimizing device performance. The fabricated Al/TiOx/TiN memristive devices exhibit promising characteristics for future applications in non-volatile memory and neuromorphic computing devices.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.I.; methodology, K.I. and R.S.; software, K.I.; validation, K.I., R.S. and R.M.; formal analysis, K.I.; investigation, K.I. and R.S.; resources, R.M.; data curation, K.I. and R.S.; writing—original draft preparation, K.I.; writing—review and editing, K.I., R.S. and R.M.; visualization, K.I. and R.S.; supervision, R.M.; project administration, R.M.; funding acquisition, R.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Warsaw University of Technology within the Excellence Initiative: Research University (IDUB) programme under agreement No. CPR-IDUB/375/Z01/2023.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the support of Aleksandra Dzięgielewska from the Faculty of Physics of the Warsaw University of Technology for providing the XRD data of investigated materials and Bartosz Witkowski from the Institute of Physics of the Polish Academy of Sciences for SEM/EDX measurements.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ha, H.; Pyo, J.; Lee, Y.; Kim, S. Non-volatile memory and synaptic characteristics of TiN/CeOx/Pt RRAM devices. Materials 2022, 15, 9087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ielmini, D. Brain-inspired computing with resistive switching memory (RRAM): Devices, synapses and neural networks. Microelectron. Eng. 2018, 190, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Gi, S.; Yeo, I.; Choi, S.; Jang, S.; Ham, S.; Lee, B.; Wang, G. A Learning-rate modulable and reliable TiOx memristor array for robust, fast, and accurate neuromorphic computing. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2201117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waser, R.; Dittmann, R.; Staikov, G.; Szot, K. Redox-based resistive switching memories—Nanoionic Mechanisms, Prospects, and Challenges. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2632–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, X.; Zeng, J.; Chen, Q.; Gu, G. High spatial resolution recording of near-infrared hologram based on photo-induced phase transition of vanadium dioxide film. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 1595–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, I.G.; Kim, D.C.; Lee, M.J.; Kim, H.J.; Yim, E.K.; Lee, M.S.; Lee, J.E.; Ahn, S.E.; Seo, S.; Lee, J.H.; et al. Multi-layer cross-point binary oxide resistive memory (OxRRAM) for post-NAND storage application. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, 2005 IEDM, Washington, DC, USA, 5–7 December 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, M.; Nisa, S.-U.; Rana, A.M.; Akbar, T.; Lee, J.; Kim, S. Enhancement of resistive switching performance by introducing a thin non-stoichiometric CeO2−x layer in TiO2 switching-based resistive random access memory. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2019, 114, 012101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, C.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W. High-performance flexible polymer memristor based on stable filamentary switching. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 7246–7253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawa, A. Resistive switching in transition metal oxides. Mater. Today 2008, 11, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kumar, A.; Zhou, Y.; Oh, S.; Kim, J.H.; Shi, Y.; Jain, S.; Hota, G.; Qiu, E.; Nagle, A.L.; et al. Multi-level, forming and filament free, bulk switching trilayer RRAM for neuromorphic computing at the edge. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jena, A.K.; Sahu, M.C.; Mohanan, K.U.; Mallik, S.K.; Sahoo, S.; Pradhan, G.K.; Sahoo, S. Bipolar resistive switching in TiO2 artificial synapse mimicking pavlov’s associative learning. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 3574–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Xia, X.; Zhu, C.; Steichen, P.; Quan, W.; Mao, W.; Yang, J.; Chu, L.; Li, X.A. Memristive artificial synapses for neuromorphic computing. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barraj, I.; Mestiri, H.; Masmoudi, M. Overview of memristor-based design for analog applications. Micromachines 2024, 15, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanan, K.U. Resistive switching devices for neuromorphic computing: From foundations to chip level innovations. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Gao, C.; Jin, J.; Sun, W.; Wang, B.; Bao, Y.; Liu, C.; Huang, W.; Zeng, H.; Yu, Y. Recent progress in neuromorphic computing from memristive devices to neuromorphic chips. Adv. Devices Instrum. 2024, 5, 0044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Gao, B.; Tang, J.; Qian, H.; Wu, H. Emerging memory-based chip development for neuromorphic computing: Status, challenges, and perspectives. IEEE Electron Devices Mag. 2023, 1, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ryu, H.; Kim, S. Resistive and synaptic properties modulation by electroforming polarity in CMOS-compatible Cu/HfO2/Si device. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 145, 110783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fang, P.; Fan, X.; Pei, Y. NiO-based memristor with three resistive switching modes. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2020, 35, 055004. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, P.; Kumbhar, D.D.; Li, H.; Tytov, S.; Syed, A.M.; Atab, N.E. A VOx-based optoelectronic memristor for application in visual perception. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2025, 58, 045108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, S.; Choi, C.; Kim, S. Transition of short-term to long-term memory of Cu/TaOx/CNT conductive bridge random access memory for neuromorphic engineering. Carbon 2023, 215, 118438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongale, T.D.; Desai, N.D.; Khot, K.V.; Volos, C.K.; Bhosale, P.N.; Kamat, R.K. An Electronic Synapse Device Based on TiO2 Thin Film Memristor. J. Nanoelectron. Optoelectron. 2018, 13, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Ren, K.; Qin, X.; Zhu, S.; Yang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Tunable negative differential resistance and resistive switching properties of amorphous WOx devices. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2021, 68, 3807–3812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, M.K.; Maiti, C.K. Electrical properties of SiO2/TiO2 high-κ gate dielectric stack. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process 2006, 9, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mesoudy, A.; Machon, D.; Ruediger, A.; Jaouad, A.; Alibart, F.; Ecoffey, S.; Drouin, D. Band gap narrowing induced by oxygen vacancies in reactively sputtered TiO2 thin films. Thin Solid Film. 2023, 769, 139737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.H.; Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, D.L.; Wang, J.H. Preparation of aluminum titanate film via non-hydrolytic sol-gel method and its fused salt corrosion resistance. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 38, 783–787. [Google Scholar]
- Diebold, U. The surface science of titanium dioxide. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2003, 48, 53–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.P.; Wu, D.W.; Zhou, Q.F.; Shi, J.; Shung, K.K. Lead zirconate titanate thick film with enhanced electrical properties for high frequency transducer applications. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 012905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, S.; Baeumer, C.; Gutsche, A.; Witzleben, M.V.; Waser, R.; Menzel, S.; Dittmann, R. Trade-off between data retention and switching speed in resistive switching ReRAM devices. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2021, 7, 2000815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Han, W.; Wang, H. Resistive switching and synaptic learning performance of a TiO2 thin film based device prepared by sol–gel and spin coating techniques. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 155202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Y.; Jiang, W.H.; Feng, G.; Liu, J.M.; Wu, Q. Low Temperature preparation of aluminum titanate film via sol-gel method. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 936, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, C.; Jiang, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Du, Z.; Sun, J.; Abrahams, I.; Huang, X. Nitrogen-doped titanium dioxide nanorod array memristors with synaptic features and tunable memory lifetime for neuromorphic computing. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 868, 159194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Y.; Yang, Y.; Lv, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Cui, D.; Liu, Y.; Yu, C.F.; Wei, G. Resistive switching characteristics of TiO2 films prepared by DC magnetron sputtering: Effects of nitrogen composition and phase structure. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 2025, 43, 022208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Fu, D. Coexistence of bipolar and unipolar resistive switching characteristics of thin TiO2 film grown on Cu foil substrate for flexible nonvolatile memory device. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 695, 2669–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, K.; Sun, F.; Guo, C.; Wu, X.; Cheng, G.; Zheng, R. Core-shell copper nanowire-TiO2 nanotube arrays with excellent bipolar resistive switching properties. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 316, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.E.; Lee, J.G.; Ling, L.; Liu, S.E.; Lim, H.K.; Sangwan, V.K.; Hersam, M.C.; Lee, H.B. Sodium-Doped Titania Self-Rectifying Memristors for Crossbar Array Neuromorphic Architectures. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2106913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, D.W.; Younis, A.; Li, S.A. Direct growth of TiO2 nanotubes on transparent substrates and their resistive switching characteristics. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2012, 45, 355306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogle, K.A.; Bachhav, M.N.; Deo, M.S.; Valanoor, N.; Ogale, S.B. Enhanced nonvolatile resistive switching in dilutely cobalt doped TiO2. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 203502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Hu, W.; Xie, W.; Bao, D. Uniform resistive switching properties of fully transparent TiO2-based memory devices. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 693, 1180–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, R.; Islam, K.; Chakraborty, S. Tuning Optical and Electrochemical Properties of Nb2O5 Thin Films via WO3 Doping. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. 2025, 26, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toma, F.T.Z.; Rahman, S.; Hussain, K.M.; Ahmed, S. Thin film deposition techniques: A comprehensive review. J. Mod. Nanotechnol. 2024, 4, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Gao, B.; Huang, P.; Kang, J. Microstructure evolution characteristics induced by oxygen vacancy generation in anatase TiO2 based resistive switching devices. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2017, 32, 035018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Yang, R.; Guo, X. Coexistence of analog and digital resistive switching in BiFeO-based memristive devices. Solid State Ion. 2016, 296, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagyalakshmi, K. Analog and digital resistive switching in W/TiO2/ITO devices: The impact of crystallinity and Indium diffusion. Phys. Scr. 2024, 99, 105977. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.; Wang, Y.; Ren, Z.; Wang, H.; Xu, X.; Zhao, J.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y. Analog–digital hybrid memristive devices for image pattern recognition with tunable learning accuracy and speed. Small Methods 2019, 3, 1900160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Huang, H.; Xia, Q.; Ye, C.; Wei, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, L.Q. Role of oxygen vacancies at the TiO2/HfO2 interface in flexible oxide-based resistive switching memory. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2019, 5, 1800833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapatseli, M.; Khiat, A.; Cortese, S.; Serb, A.; Carta, D.; Prodromakis, T. Engineering the switching dynamics of TiOx-based RRAM with Al doping. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 120, 025108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Li, X.; Tang, J.; Li, Y.; Zheng, X.; Gao, B.; Qian, H.; Wu, H. Investigation of resistive switching mechanisms in Ti/TiOx/Pd-based RRAM devices. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2022, 8, 2100827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lermusiaux, L.; Mazel, A.; Carretero-Genevrier, A.; Sanchez, C.; Drisko, G.L. Metal-Induced Crystallization in Metal Oxides. Acc. Chem. Res. 2022, 55, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obstarczyk, A.; Kaczmarek, D.; Mazur, M.; Wojcieszak, D.; Domaradzki, J.; Kotwica, T.; Morgiel, J. The effect of post-process annealing on optical and electrical properties of mixed HfO2–TiO2 thin film coatings. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 6358–6369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.; Monteiro, C.S.; Silva, S.O.; Frazão, O.; Pinto, J.V.; Raposo, M.; Ribeiro, P.A.; Sério, S. Sputtering Deposition of TiO2 Thin Film Coatings for Fiber Optic Sensors. Photonics 2022, 9, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Wang, W.; Sun, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, G. Refining the negative differential resistance effect in a TiOx-based memristor. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 5377–5383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.T.; Ahn, G.; Choi, S.J.; Kim, D.M.; Kim, D.H. Control of the boundary between the gradual and abrupt modulation of resistance in the schottky barrier tunneling-modulated amorphous indium-gallium-zinc-oxide memristors for neuromorphic computing. Electronics 2019, 8, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, E.; Ismail, R. Conduction Mechanism of Valence Change Resistive Switching Memory: A Survey. Electronics 2015, 4, 586–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, R.; Islama, K.; Rakshita, A.; Mukherjeea, M.; Chakraborty, S. Effect of Zr doping and lattice oxygen release on the resistive switching properties of ZrxHf1−xO2-based metal-oxide-semiconductor devices. Microelectron. Eng. 2019, 216, 111099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, F.C. A Review on Conduction Mechanisms in Dielectric Films. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 2014, 578168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funck, C.; Menzel, S. Comprehensive model of electron conduction in oxide-based memristive devices. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2021, 3, 3674–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, D.S.; Wang, Q.; Chen, L.D.; Dong, R.; Li, X.M.; Zhang, W.Q. Effect of carrier trapping on the hysteretic current-voltage characteristics in Ag∕La0.7 Ca0.3MnO3∕ Pt heterostructures. Phys. Rev. B—Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 2006, 73, 245427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-K.; Pyo, J.; Kim, S. Low-Frequency Noise-Based Mechanism Analysis of Endurance Degradation in Al/αTiOx/Al Resistive Random Access Memory Devices. Materials 2023, 16, 2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, X.L.; Zhou, L.W.; Yoon, K.J.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, J.S.; Zhang, K.L.; Yoo, S.; Hwang, C.S. Electronic resistance switching in the Al/TiOx/Al structure for forming-free and area-scalable memory. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 11063–11074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Sachdev, M.; Miao, G.X. Stack Optimization of TiOx-based resistive switching devices through interface engineering. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2025, 72, 2964–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.S.; Do, Y.H.; Bae, Y.C.; Im, H.S.; Yoo, J.H.; Sung, M.G.; Hwang, Y.T.; Hong, J.P. Roles of interfacial TiOxN1−x layer and TiN electrode on bipolar resistive switching in TiN/TiO2/TiN frameworks. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 223502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.R.; Bae, Y.C.; Im, H.S.; Hong, J.P. Complementary resistive switching mechanism in Ti-based triple TiOx/TiN/TiOx and TiOx/TiOxNy/TiOx matrix. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 274, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, A.O.M.; Abdel-wahab, M.S.; Alayash, M.; Aida, M.S. Metals and ITO contact nature on ZnO and NiO thin films. Braz. J. Phys. 2021, 51, 1159–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastment, R.M.; Mee, C.H. Work function measurements on (100), (110) and (111) surfaces of aluminium. J. Phys. F 1973, 3, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.G.; Rhee, S.W. Effect of the top electrode material on the resistive switching of TiO2 thin film. Microelectron. Eng. 2010, 87, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzolari, A.; Catellani, A. Controlling the TiN electrode work function at the atomistic level: A first principles investigation. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 156308–156313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.H.; Jeong, J.H.; Kim, W.; Park, S.; Lim, B.M.; Lee, H.S.; Kang, S.J. A facile solution processible self-rectifying and sub-1 V operating memristor via oxygen vacancy gradient within a TiO2 single layer. J. Mater. Chem. C 2024, 12, 6881–6892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cao, M.; Bian, J.; Li, Q.; Su, J. Flexible ZnO nanosheet-based artificial synapses prepared by low-temperature process for high recognition accuracy neuromorphic computing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2209907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung Lee, J.; Buhm Lee, S.; Kahng, B.; Won Noh, T. Two opposite hysteresis curves in semiconductors with mobile dopants. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 253503. [Google Scholar]
- Linkai, W.; Ze, J.; Tianling, R. Bipolar switching analysis and negative resistance phenomenon in TiOx-based devices. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference of Electron Devices and Solid-State Circuits (EDSSC), Hong Kong, China, 15–17 December 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Xu, X.; Xu, Z.; Wang, M.; Liu, Q.; Ma, Y.; Chen, J.; Meng, K.; Wu, Y.; Miao, J.; et al. Self-rectifying and forming-free resistive switching behaviors in Pt/La2Ti2O7/Pt structure. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 4693–4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Li, A.; Wu, D. Resistive switching in BiFeO3 based heterostructures due to ferroelectric modulation on interface Schottky barriers. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2014, 25, 3251–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsukatova, A.N.; Vdovichenko, A.Y.; Patsaev, T.D.; Forsh, P.A.; Kashkarov, P.K.; Demin, V.A.; Emelyanov, A.V. Scalable nanocomposite parylene-based memristors: Multifilamentary resistive switching and neuromorphic applications. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 3207–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S. Neuro-inspired computing with emerging nonvolatile memorys. Proc. IEEE 2018, 106, 260–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, H.; Ma, Z.; Chen, K.; Huang, X.; Wang, K. HfO2/TiOx bilayer structure memristor with linear conductance tuning for high density memory and neuromorphic computing. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 128, 184902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).