Comparative Study of the Bulk and Foil Zinc Anodic Behavior Kinetics in Oxalic Acid Aqueous Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation and Kinetic Studies
- (i)
- Bulk electrodes: Pure zinc (p.a.) was melted in a sealed, evacuated tube of fused silica at 700 °C. It was then quenched in water with ice at about 0 °C to obtain a zinc rod. Cylindrical pieces were cut from this rod, and one of the bases was used as a working surface with an area of 0.8 cm2. A thick Cu wire was soldered to the other base. All surfaces except the working one were isolated with a thick layer of epoxy resin. The bare surface was treated with emery paper and then polished with a polishing paste with a grain size down to 0.5 µm. After this, the electrode was washed with neutral detergent and double-distilled water.
- (ii)
- Foil electrodes: The second type of electrode, with an area of 2 cm2, was cut out of zinc foil (Alfa Aesar 99.98%). They were degreased with nital and washed with distilled water. The working surfaces were electropolished in an alcoholic solution of phosphoric acid for 20 min at an electric potential of 20 V and 5 °C. The electrodes were then washed with double-distilled water.
2.2. Characterization Methods
3. Results and Discussion
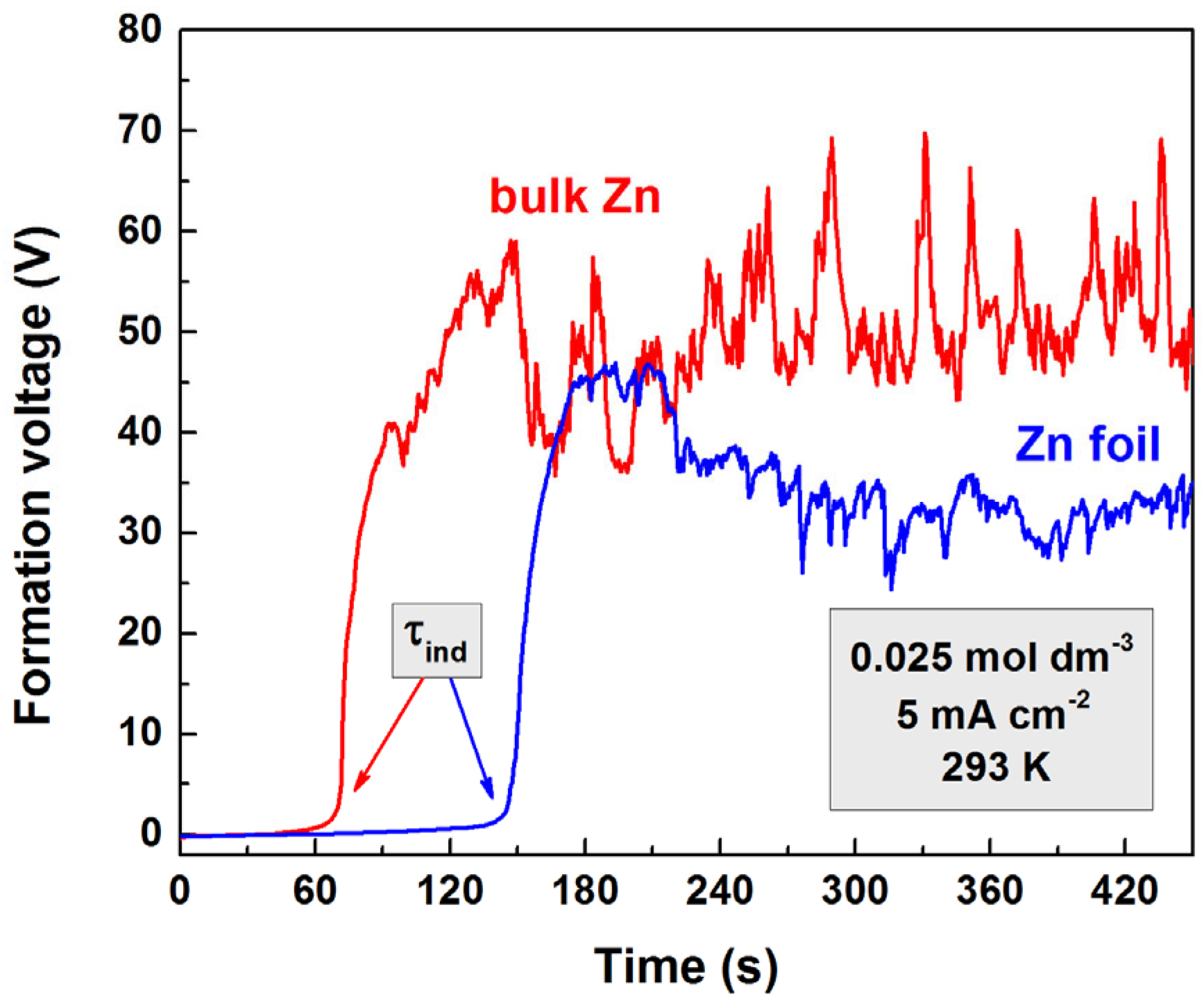
3.1. Dependence of Induction Period Durations on the Forming Electrolyte Concentration
3.2. Dependence of Induction Period Durations on the Applied Current Density
3.3. Dependence of Induction Period Durations on the Forming Electrolyte Temperature
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holmes, S.P.; Wilcox, G.D.; Robins, P.J.; Glass, G.K.; Roberts, A.C. Responsive behaviour of galvanic anodes in concrete and the basis for its utilization. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 3450–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayatdavoudi, H.; Rahsepar, M. A mechanistic study of the enhanced cathodic protection performance of graphene-reinforced zinc rich nanocomposite coating for corrosion protection of carbon steel substrate. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 727, 1148–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, I.M.; Abdel-Salam, O.E.; Ahmed, T.S.; Soliman, A.; Khattab, I.A.; Al-Ebrahim, M.F. Investigation of the anodic dissolution of zinc in sodium chloride electrolyte—A green process. Port. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 31, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsipur, M.; Roushani, M.; Pourmortazavi, S.M. Electrochemical synthesis and characterization of zinc oxalate nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 2013, 48, 1275–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas-Granados, B.; Sánchez-Tovar, R.; Fernández-Domene, R.M.; García-Antón, J. Fabrication of ordered and high-performance nanostructured photoelectrocatalysts by electrochemical anodization: Influence of hydrodynamic conditions. In Nanostructures in Energy Generation, Transmission and Storage, 1st ed.; Fedorenko, Y., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; Chapter 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Canon, A.; Medina-Llamas, M.; Vezzoli, M.; Mattia, D. Multiscale design of ZnO nanostructured photocatalysts. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 6648–6656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.; Bakar, W.A.W.A.; Teck, L.K. Zn/ZnO/TiO2 and Al/Al2O3/TiO2 photocatalysts for the degradation of cypermethrin. Mod. Appl. Sci. 2010, 4, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harito, C.; Zaidi, S.Z.J.; Bavykin, D.V.; Martins, A.S.; Yuliarto, B.; Walsh, F.C.; de León, C.P. PbO2 decorated ZnO-TiO2 core-shell nanoflower structures by zinc anodising for photo- and anodic degradation of Reactive Black-5 dye. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2020, 11, 035018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebwogen, J.; Munyati, O.; Hatwaambo, S.; Mwamburi, M.; Maghanga, C. Fabrication and characterization of cobalt pigmented anodized zinc for photocatalytic application. Int. J. Thin Film Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 127–132. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Tantray Ab, M.; Mir, J.F.; Mir, M.A.; Rather, J.; Shah, M.A. Random oriented ZnO nanorods fabricated through anodization of Zinc in KHCO3 electrolyte. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2021, 10, 081003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, P.K.; Bhattacharyya, P.; Saha, N.; Saha, H.; Basu, S. The superior performance of the electrochemically grown ZnO thin films as methane sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 133, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz Cano, A.I.; El Filali, B.; Torchynska, T.V.; Casas Espinola, J.L. Structure and emission transformations in ZnO nanosheets at thermal annealing. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2013, 74, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Zhou, J.; Virtanen, S. Fabrication of ZnO nanotube layer on Zn and evaluation of corrosion behavior and bioactivity in view of biodegradable applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 494, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katwal, G.; Paulose, M.; Rusakova, I.A.; Martinez, J.E.; Varghese, O.K. Rapid growth of zinc oxide nanotube–nanowire hybrid architectures and their use in breast cancer-related volatile organics detection. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 3014–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galstyan, V.; Comini, E.; Baratto, C.; Faglia, G.; Sberveglieri, G. Nanostructured ZnO chemical gas sensors. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 14239–14244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Chen, F. Rectification performance of ZnO-Zn Schottky diode growth by anodization. ECS Solid State Lett. 2014, 3, P41–P44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, R.; Kowalski, D.; Kitano, S.; Aoki, Y.; Nozawa, T.; Habazaki, H. Characterization of dark-colored nanoporous anodic films on zinc. Coatings 2020, 10, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Liu, Z.; Dong, J.; Ariyanti, D.; Niu, Z.; Huang, S.; Zhang, W.; Gao, W. Self-organized ZnO nanorods prepared by anodization of zinc in NaOH electrolyte. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 72968–72974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voon, C.H.; Tukiman, N.T.; Lim, B.Y.; Hashim, U.; Ten, S.T.; Derman, M.N.; Foo, K.L.; Md Arshad, M.K. Synthesis of zinc oxide thin film by anodizing. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Semiconductor Electronics (ICSE2014), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 27–29 August 2014; pp. 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekantan, S.; Gee, L.R.; Lockman, Z. Room temperature anodic deposition and shape control of one-dimensional nanostructured zinc oxide. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 476, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.W.; Yam, F.K.; Low, L.L.; Beh, K.P.; Mustapha, M.F.; Sota, E.N.; Tneh, S.S.; Hassan, Z. Self-assembled ZnO nanostripes prepared by acidified ethanolic anodization. Optoelectron. Adv. Mat. 2011, 5, 89–91. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Lu, G.; Li, C.; Shi, G. Room-temperature fabrication of highly oriented ZnO nanoneedle arrays by anodization of zinc foil. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Canon, A.; Miles, D.O.; Cameron, P.J.; Mattia, D. Zinc oxide nanostructured films produced via anodization: A rational design approach. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 25323–25330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Kobayashi, R.; Asoh, H. Fabrication of self-organized nanoporous oxide semiconductors by anodization. ECS Trans. 2008, 16, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaraska, L.; Mika, K.; Syrek, K.; Sulka, G.D. Formation of ZnO nanowires during anodic oxidation of zinc in bicarbonate electrolytes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 801, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Meng, Y.; Xu, X.; Tang, C. Controllable growth of zinc oxide nanosheets and sunflower structures by anodization method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 126, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelkemeier, K.; Sun, A.; Voswinkel, D.; Grydin, O.; Schaper, M.; Bremser, W. Zinc anodizing: Structural diversity of anodic zinc oxide controlled by the type of electrolyte. ChemElectroChem. 2021, 8, 2155–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mika, K.; Wiercigroch, E.; Pisarek, M.; Kozieł, M.; Majda, D.; Lytvynenko, A.S.; Sulka, G.D.; Zaraska, L. Nanostructured films formed on Zn during anodic oxidation in different carbonate-based electrolytes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 623, 157102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mary, S.; Norbert, A.; Shaji, S.; Philip, R.R. Electrochemically anodized solid and stable ZnO nanorods as an adsorbent/nanophotocatalyst: ROS mediated degradation of azo dyes congo red and methyl orange. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 428, 139466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, E.T.; Kartal, U.; Dikici, T.; Erol, M.; Yurddaskal, M. A comparative study on structural, morphological and photocatalytic properties of anodically grown ZnO nanowires under varying parameters. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 27398–27408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mika, K.; Syrek, K.; Uchacz, T.; Sulka, G.D.; Zaraska, L. Dark nanostructured ZnO films formed by anodic oxidation as photoanodes in photoelectrochemical water splitting. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 414, 140176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilov, E.; Lilova, V.; Girginov, C.; Garova, V. Anodic behaviour of zinc. Layers obtained by anodic polarization of zinc. In Electrochemical Methods for the Synthesis and Analysis of Advanced Functional Layers and Coatings, 1st ed.; Kozhukharov, S., Ed.; Cambridge Scholars Publishing: Newcastle, UK, 2024; Chapter VI; pp. 220–282. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Kim, K.; Choi, J. Formation of ZnO nanowires during short durations of potentiostatic and galvanostatic anodization. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2013, 13, 1370–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilov, E.; Lilova, V.; Girginov, C.; Kozhukharov, S.; Nedev, S.; Tsanev, A.; Yancheva, D.; Velinova, V. Anodic behavior of zinc in aqueous borate electrolytes. Mat. Chem. Phys. 2020, 239, 122081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilov, E.; Lilova, V.; Girginov, C.; Kozhukharov, S.; Tsanev, A.; Yancheva, D. Induction periods during anodic polarization of zinc in aqueous oxalic acid solutions. Mat. Chem. Phys. 2019, 223, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilov, E.; Lilova, V.; Nedev, S.; Kozhukharov, S.; Adam, A.M.; Girginov, C. Voltage Oscillations during Anodic Polarization of Zinc in Water Solutions of NaOH. J. Hunan Univ. Nat. Sci. 2022, 49, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Pandey, G. A review on the factors affecting the photocatalytic degradation of hazardous materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. Int. J. 2017, 1, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnis, J.M.; Oldham, K.B. Beyond the Beer–Lambert law: The dependence of absorbance on time in photochemistry. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2013, 267, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, K.M.; Kurny, A.S.W.; Gulshan, F. Parameters affecting the photocatalytic degradation of dyes using TiO2: A review. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 1569–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, P.; Mehar, M.V.K.; Emmanuel, K.A. Factors influencing the rate of photocatalytic degradation of hazardous organic pollutants from industrial effluents: A review. IJESI 2018, 6, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Gnanaprakasam, A.; Sivakumar, V.M.; Thirumarimurugan, M. Influencing parameters in the photocatalytic degradation of organic effluent via nanometal oxide catalyst: A review. Indian J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 2015, 601827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Hu, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, X.; Zhong, S.; Zhang, H.; Yu, X. A generalized predictive model for TiO2–Catalyzed photo-degradation rate constants of water contaminants through artificial neural network. Environ. Res. 2020, 187, 109697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtani, B. Photocatalysis A to Z—What we know and what we do not know in a scientific sense. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2010, 11, 157–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Lee, J.; Choi, J. Understanding of anodization of zinc in an electrolyte containing fluoride ions. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 7941–7945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, R.A.; Stokes, R.H. Electrolyte Solutions, 2nd ed.; Foreign Literature Publishing House: Moscow, Russia, 1963; pp. 158–161. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Miles, D.O.; Cameron, P.J.; Mattia, D. Hierarchical 3D ZnO nanowire structures via fast anodization of zinc. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 17569–17577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampson, N.A.; Shawt, P.E.; Taylor, R. Anodic behaviour of zinc in potassium hydroxide solution: II.* Horizontal anodes in electrolytes containing Zn(II). Br. Corros. J. 1969, 4, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mah, C.F.; Beh, K.P.; Yam, F.K.; Hassan, Z. Rapid formation and evolution of anodized-Zn nanostructures in NaHCO3 solution. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2016, 5, M105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantray, A.M.; Shah, M.A. Photo electrochemical ability of dense and aligned ZnO nanowire arrays fabricated through electrochemical anodization. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2020, 747, 137346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Szpunar, J.A. The role of texture and morphology in optimizing the corrosion resistance of zinc-based electrogalvanized coatings. Corros. Sci. 1998, 40, 525–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, R.F.; Hepworth, M.T. Effect of crystal orientation on the anodic polarization and passivity of zinc. Corrosion 1968, 24, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Światowska-Mrowiecka, J.; Banaś, J. Anodic behaviour of zinc in methanol solutions of lithium perchlorate. Electrochim. Acta 2005, 50, 1829–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lilova, V.; Lilov, E.; Kozhukharov, S.; Avdeev, G.; Girginov, C. Comparative Study of the Bulk and Foil Zinc Anodic Behavior Kinetics in Oxalic Acid Aqueous Solutions. Materials 2025, 18, 3635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153635
Lilova V, Lilov E, Kozhukharov S, Avdeev G, Girginov C. Comparative Study of the Bulk and Foil Zinc Anodic Behavior Kinetics in Oxalic Acid Aqueous Solutions. Materials. 2025; 18(15):3635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153635
Chicago/Turabian StyleLilova, Vanya, Emil Lilov, Stephan Kozhukharov, Georgi Avdeev, and Christian Girginov. 2025. "Comparative Study of the Bulk and Foil Zinc Anodic Behavior Kinetics in Oxalic Acid Aqueous Solutions" Materials 18, no. 15: 3635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153635
APA StyleLilova, V., Lilov, E., Kozhukharov, S., Avdeev, G., & Girginov, C. (2025). Comparative Study of the Bulk and Foil Zinc Anodic Behavior Kinetics in Oxalic Acid Aqueous Solutions. Materials, 18(15), 3635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153635






