Analysis of Dynamic Properties and Johnson–Cook Constitutive Relationship Concerning Polytetrafluoroethylene/Aluminum Granular Composite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
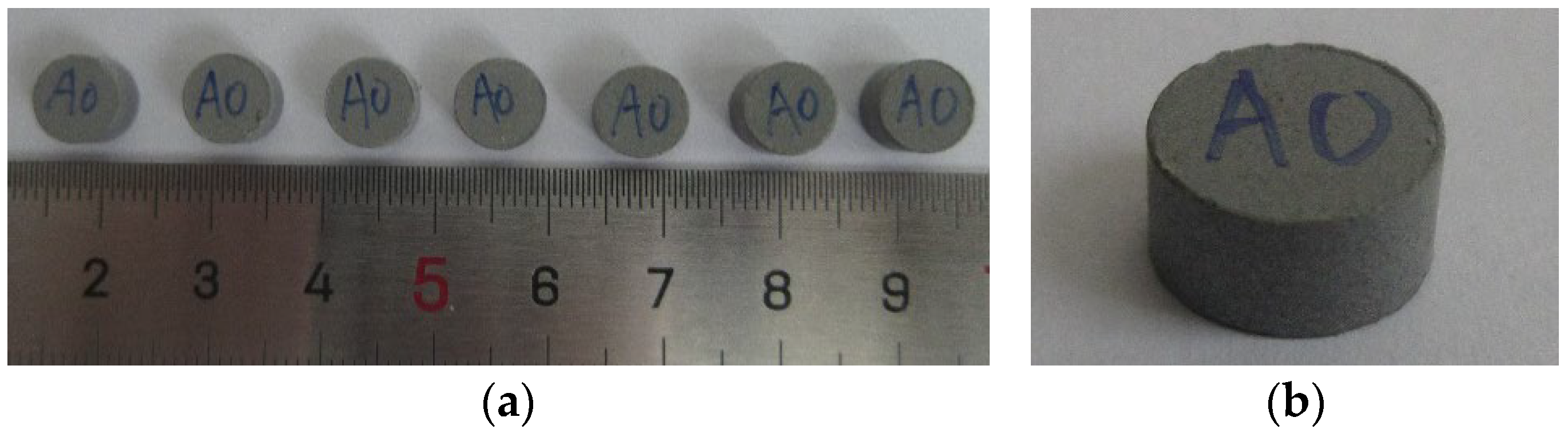
2.1. Preparation of Specimens
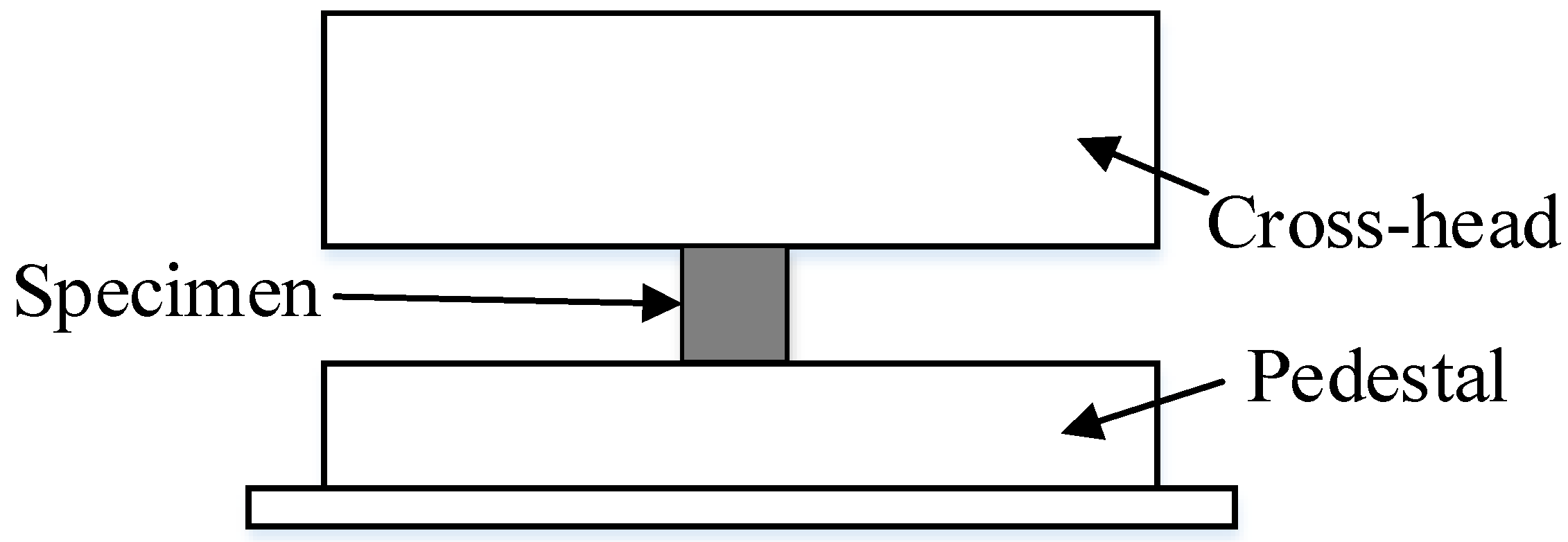
2.2. Experimental Method of Quasi-Static Compression
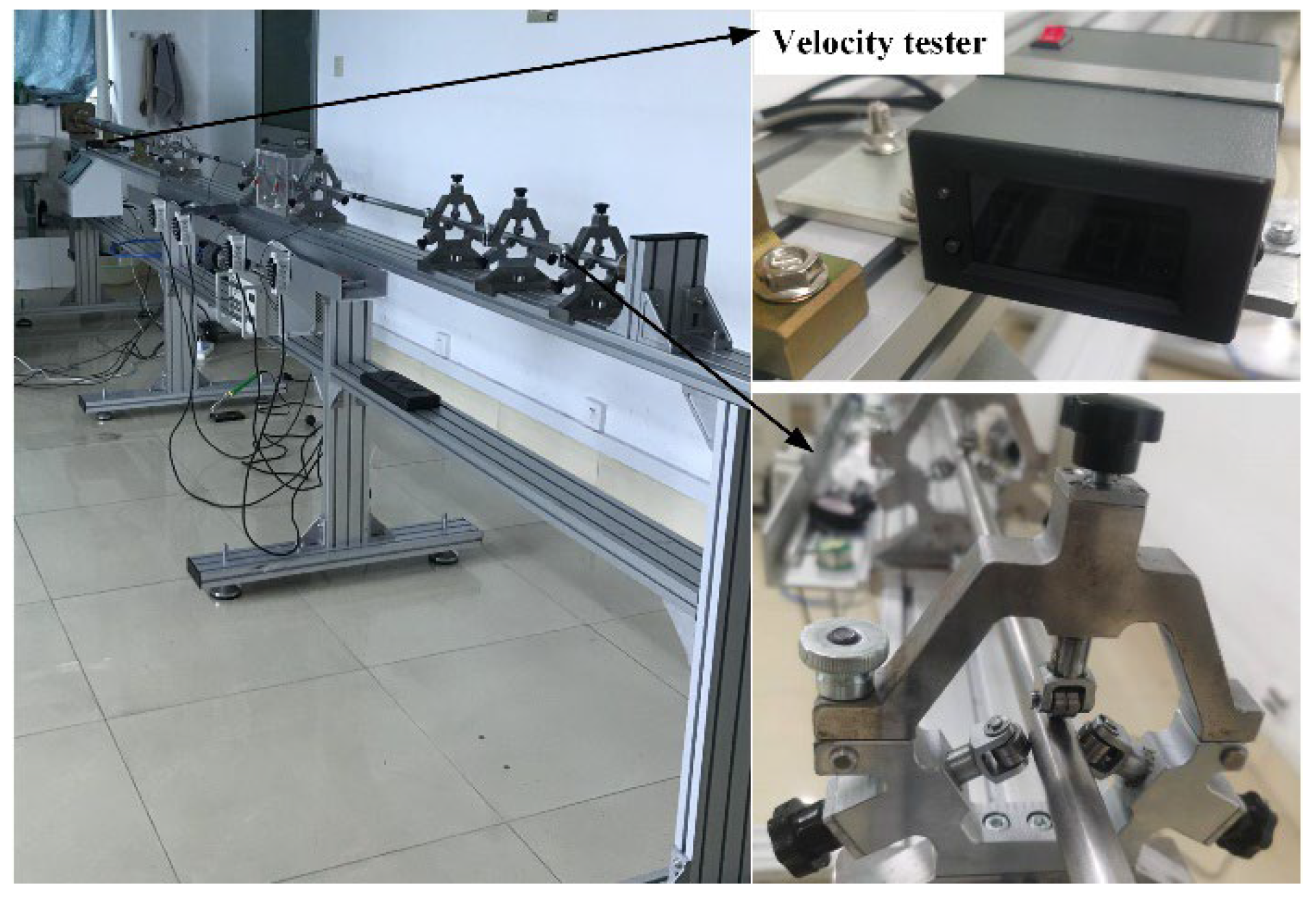
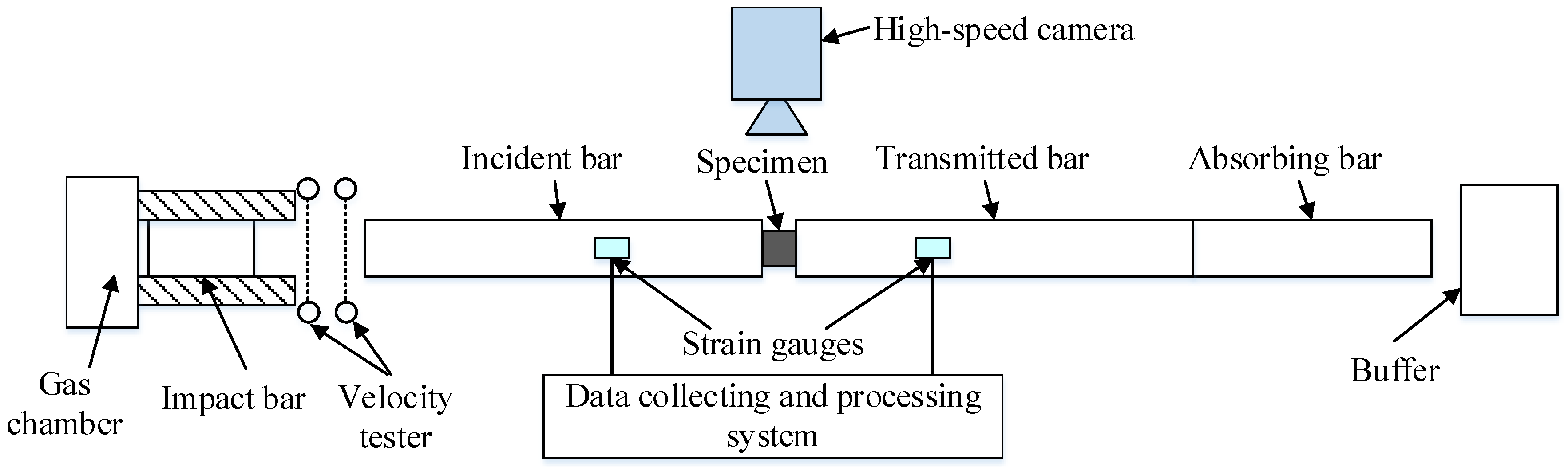
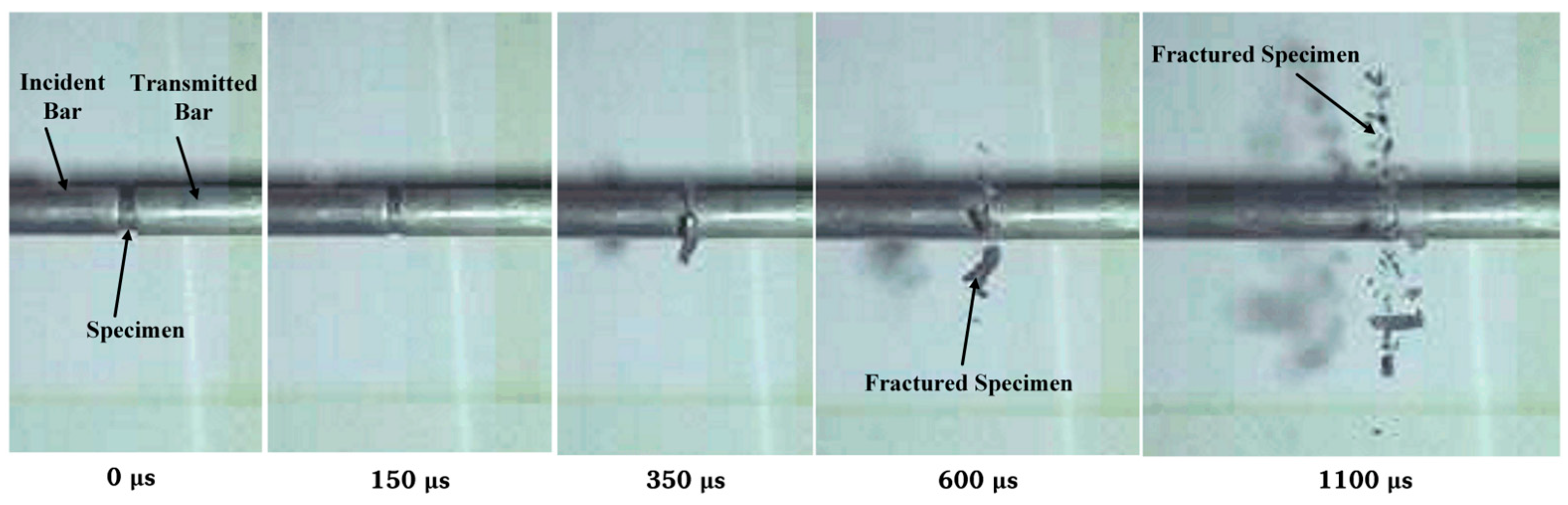
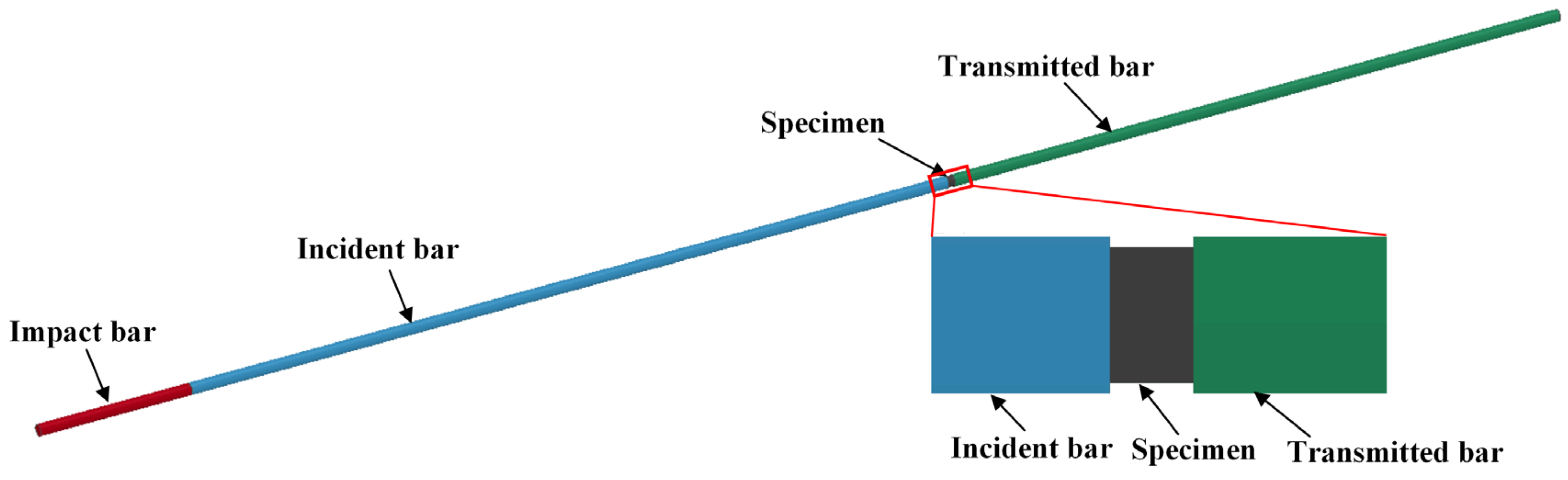
2.3. Experimental Method of Hopkinson Bar Tests
3. Results and Discussion
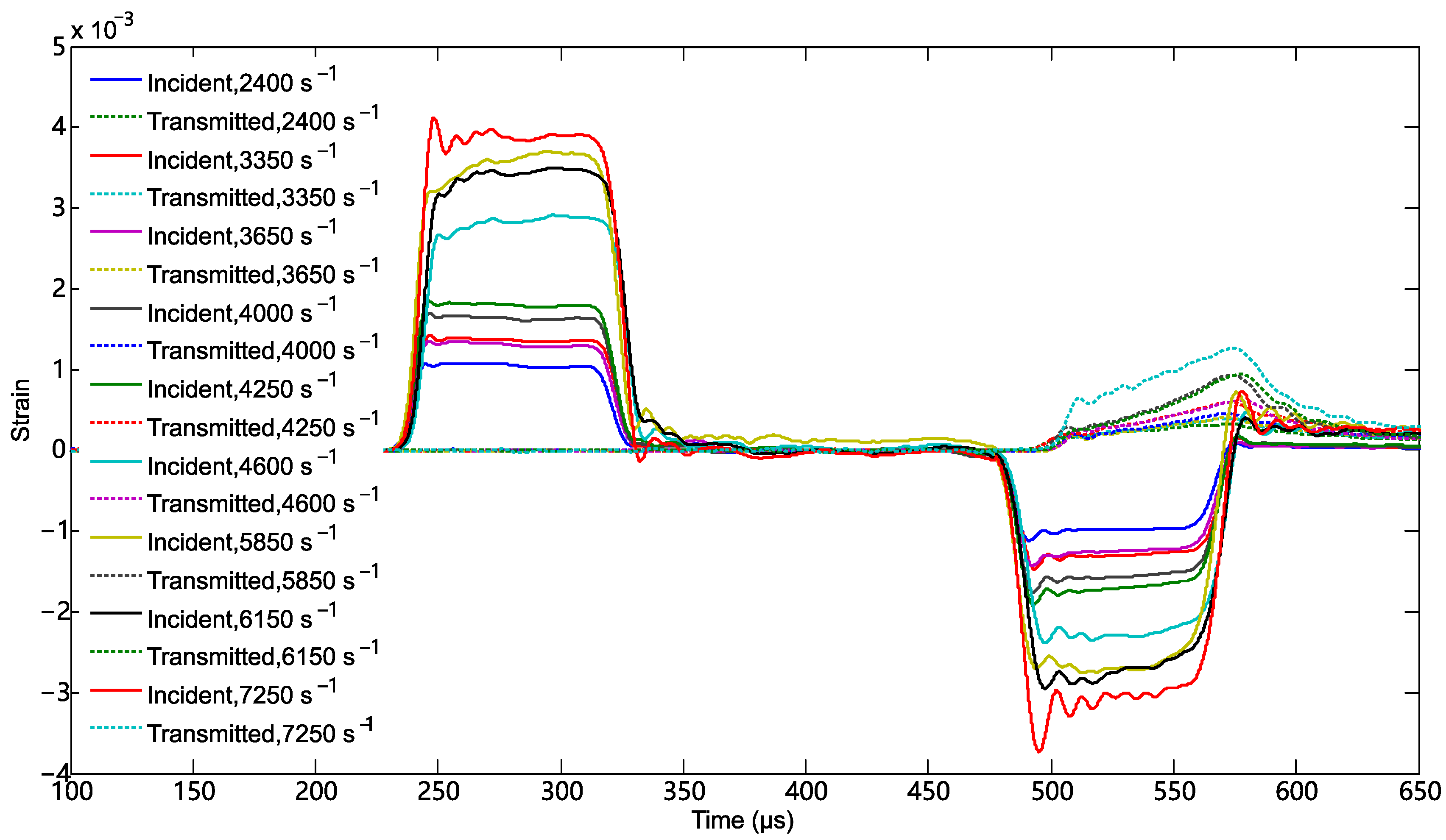
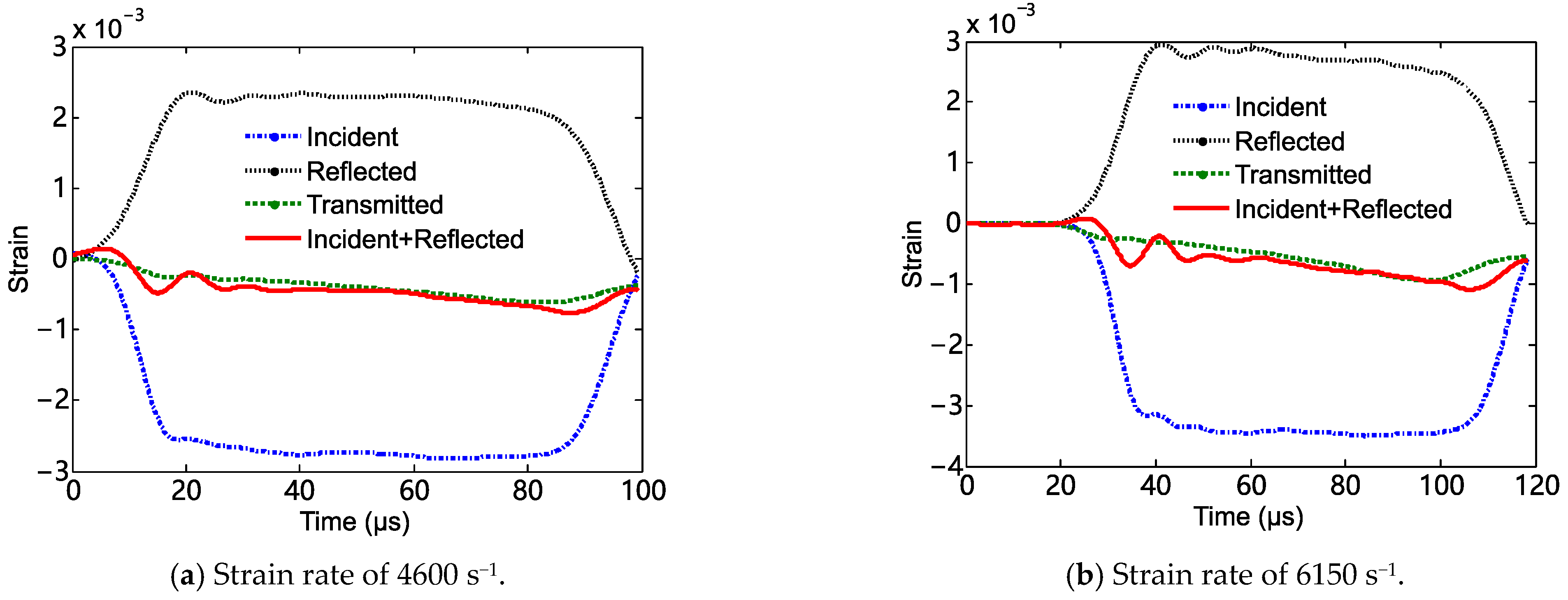
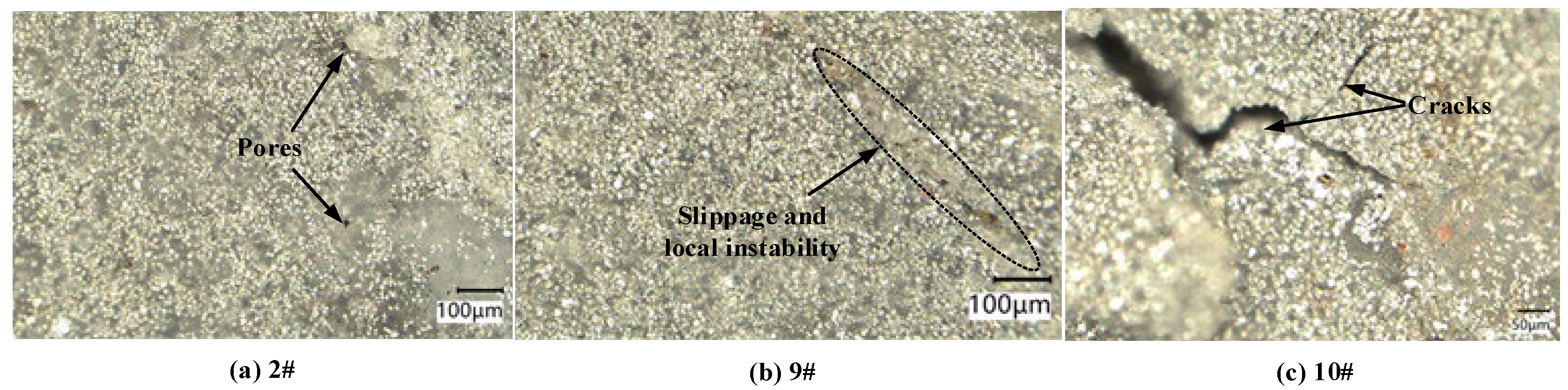
3.1. Experimental Results
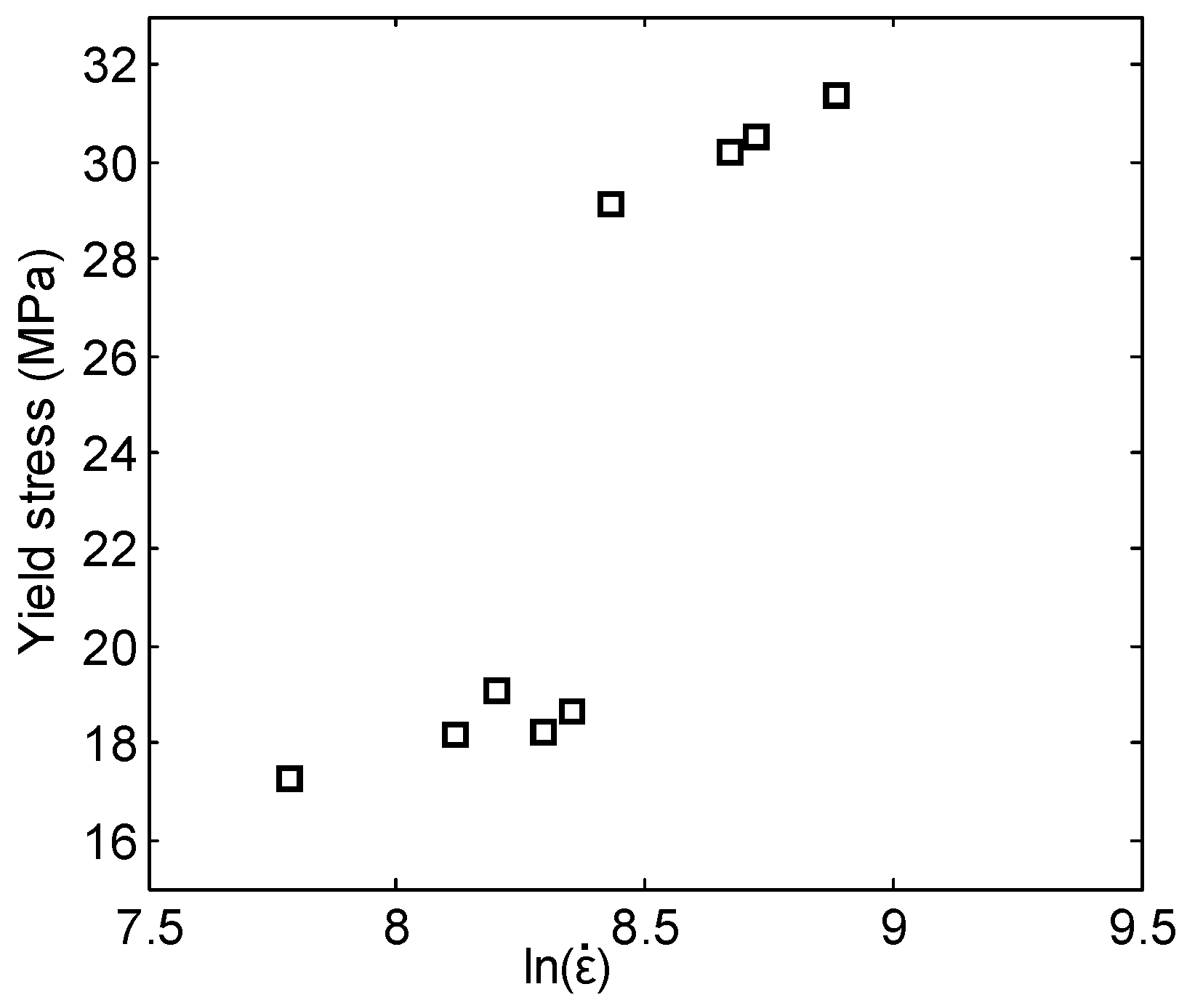
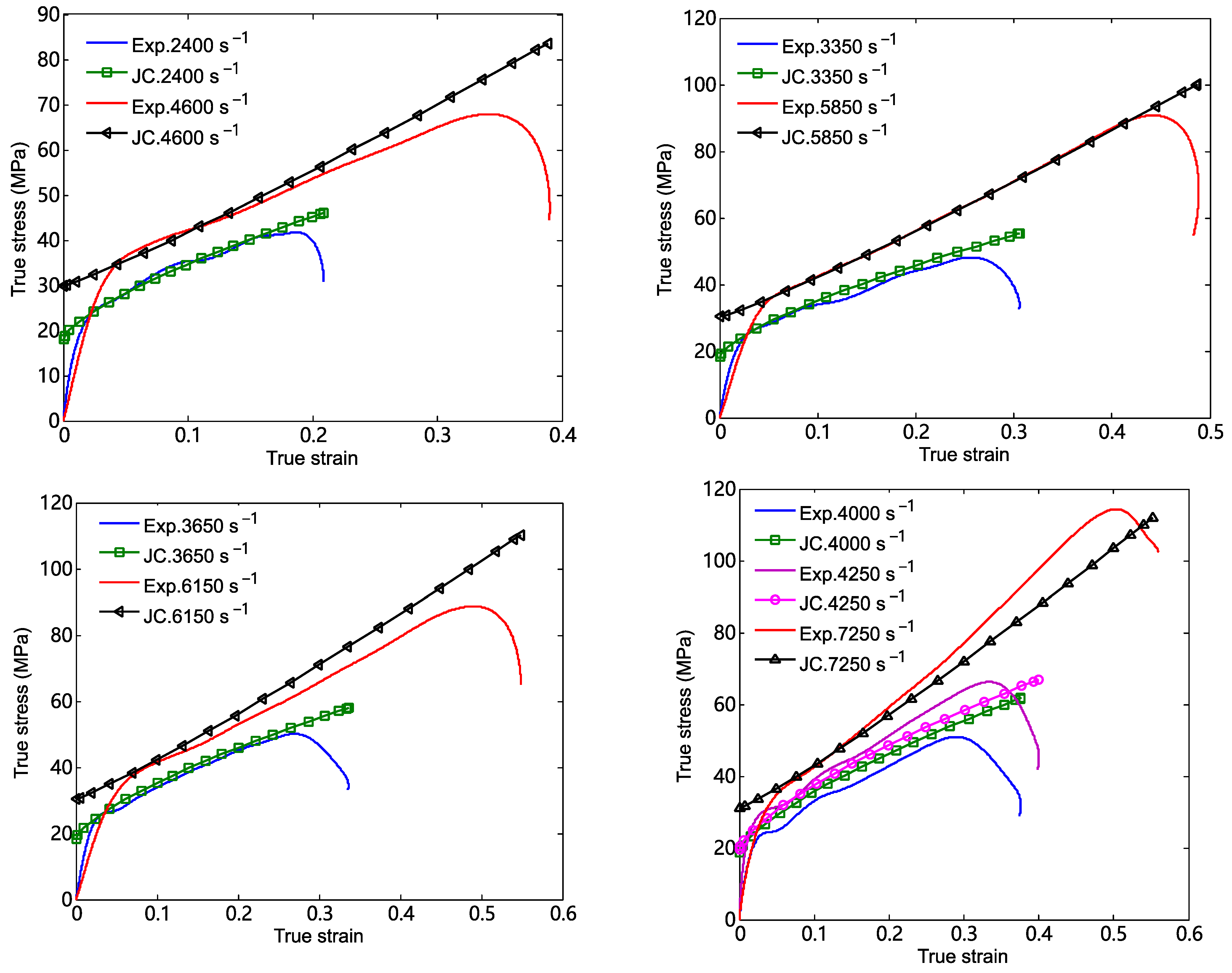
3.2. Simplified Johnson–Cook Constitutive Relationship
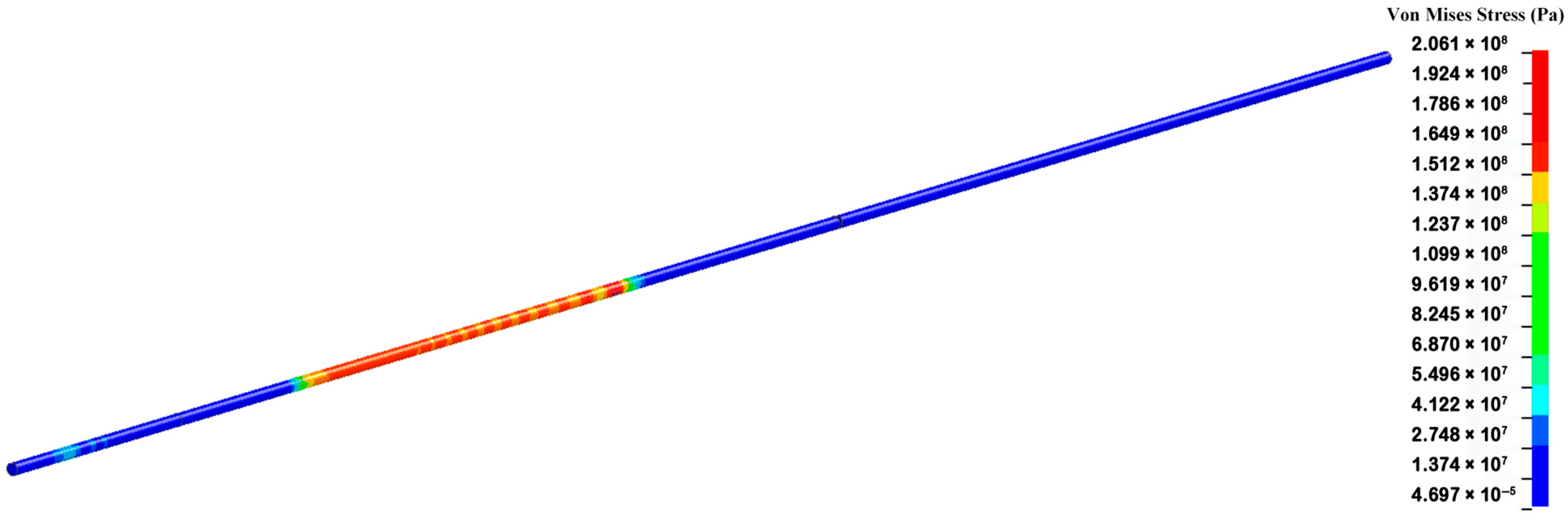
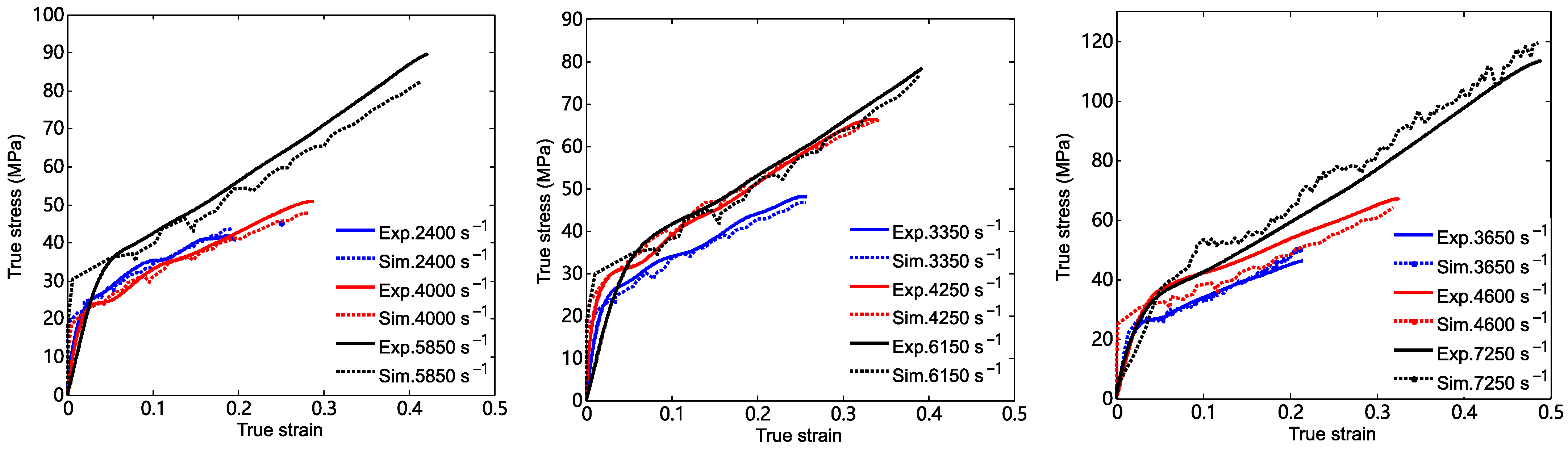
3.3. Numerical Simulation of Dynamic Compression of PTFE/Al Composite
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Symbol | Meaning |
| σt | True stress in the specimen |
| εt | True strain in the specimen |
| A0 | Initial cross-sectional area of specimen |
| Engineering strain | |
| H | Height of deformed specimen |
| H0 | Initial height of specimen |
| C0 | Velocity of elastic wave in the metal bars |
| E | Elasticity modulus of the metal bars |
| Reflected strain in the incident bar | |
| Transmission strain in the transmitted bar | |
| A | Cross-sectional area of the metal bars |
| T | Temperature |
| Reference temperature | |
| As | Cross-sectional area of specimen |
| Ls | Length of specimen |
| t | Time |
| Stress in the specimen under dynamic compression | |
| Strain in the specimen under dynamic compression | |
| Strain rate of the specimen under dynamic compression | |
| Stress | |
| εp | Effective plastic strain |
| Plastic strain rate | |
| Reference strain rate | |
| A, B, C, n, and m | Material constants |
| Melting point of material | |
| Yield stress |
References
- Wang, H.F.; Xiang, J.A. Progress in reactive materials and their applications (in Chinese). Sci. Sin. Technol. 2023, 53, 1434–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DE Technologies Inc. Reactive Fragment Warhead for Enhanced Neutralization of Mortar, Rocket, & Missile Threats ONR-SRIR: N04-903. 2006. Available online: https://www.detk.com (accessed on 9 October 2024).
- Cai, Y.; Feng, X.Y.; He, C.; Zhang, S.; Li, S.K.; Liu, J.X. A 7.62 mm energetic bullet filled with PTFE-Mg-based reactive materials for anti-drone application. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 30, 8749–8759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasant, S.J.; Waldorf, M.D. Process for Making Polytetrafluoroethylene-Aluminum Composites and Product Made. Patent No. US 6547993B1, 15 April 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Nielson, D.B.; Truitt, R.M.; Rasmussen, N. Lower Temperature, Extrudable, High Density Reactive Materials. Patent No. US 6962634, 8 November 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ames, R.G. Energy release characteristics of impact-initiated energetic materials. MRS Online Proc. Libr. 2005, 896, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ames, R.G. A Standardized Evaluation Technique for Reactive Warhead Fragments. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Symposium on Ballistics, Tarragona, Spain, 16–20 April 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Chonowski, D.P. Small Scaled Reactive Materials Combustion Test Facility. Master’s Thesis, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Champaign, IL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Raftenberg, M.N.; Mock, W.; Kirby, G.C. Modeling the Impact Deformation of Rods of a Pressed PTFE/Al Composite Mixture. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2008, 35, 1735–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.J.; Mock, W.; Carney, J.R.; Holt, W.H.; Pangilinan, G.I.; Gamache, R.M.; Boteler, J.M.; Bohl, D.G.; Drotar, J.; Lawrence, G.W. Reactive materials studies. Shock. Compress. Condens. Matter 2006, 845, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mock, W., Jr.; Drotar, J.T. Effect of Aluminum Particle Size on the Impact Initiation of Pressed PTFE/Al Composite Rods. Shock Compress. Condens. Matter 2007, 955, 971–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.L.; Li, W.; Ning, J.G.; Liu, Y.B. The Influence of Initial Defects on Impact Ignition of Aluminum/Polytetrafluoroethylene Reactive Material. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2019, 22, 1900821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Wang, H.F.; Lu, G.C.; Zhang, H.; Ge, C. Mesoscale study on the shock response and initiation behavior of Al-PTFE granular composites. Mater. Des. 2021, 200, 109446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.G.; Wang, Z.; Nie, Z.Y.; Tang, E.L.; Zhang, X.P. Evaluation of Hugoniot parameters for unreacted Al/PTFE reactive materials by modified SHPB test. AIP Adv. 2020, 10, 045211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.L.; Cai, S.Y.; Mao, L.; Wang, Z.C. Effect of Porosity on Dynamic Mechanical Properties and Impact Response Characteristics of High Aluminum Content PTFE/Al Energetic Materials. Materials 2020, 13, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Walley, S.M.; Hunt, R.J.A.; Proud, W.G.; Nesterenko, V.F.; Meyers, M.A. High-strain high-strain-rate flow and failure in PTFE/Al/W granular composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 472, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbold, E.B.; Nesterenko, V.F.; Benson, D.J.; Cai, J.; Vecchio, K.S.; Jiang, F.; Addiss, J.W.; Walley, S.M.; Proud, W.G. Particle size effect on strength, failure, and shock behavior in polytetrafluoroethylene-Al-W granular composite materials. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 104, 103903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, B.Q.; Wang, H.F.; Yu, Q.B.; Zheng, Y.F.; Ge, C. Bulk Density Homogenization and Impact Initiation Characteristics of Porous PTFE/Al/W Reactive Materials. Materials 2020, 13, 2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, H.F.; Ge, C. Characterization of the Dynamic Response and Constitutive Behaviour of PTFE/Al/W Reactive materials. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2020, 45, 788–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glavier, L.; Taton, G.; Ducéré, J.M.; Baijot, V.; Pinon, S.; Calais, T.; Estève, A.; Rouhani, M.D.; Rossi, C. Nanoenergetics as pressure generator for nontoxic impact primers: Comparison of Al/Bi2O3, Al/CuO, Al/MoO3 nanothermites and Al/PTFE. Combust. Flame 2015, 162, 1813–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Y.; Jiang, J.W.; Li, M.; Men, J.B.; Wang, S.Y. Improving the damage potential of W-Zr reactive structure material under extreme loading condition. Def. Technol. 2021, 17, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.Y.; Ding, L.L.; Tang, W.H.; Ran, X.W. Experimental Study of Mechanical Properties and Impact-Induced Reaction Characteristics of PTFE/Al/CuO Reactive Materials. Materials 2020, 13, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.L.; Hu, S.S.; Yang, L.M.; Dong, X.L. Kinetics of Materials; University of Science and Technology of China Press: Hefei, China, 2017; pp. 177–208. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, G.R.; Cook, W.H. A constitutive model and data for metals subjected to large strains, high strain rates, and high temperatures. In Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Ballistics, The Hague, The Netherlands, 19–21 April 1983; pp. 541–547. [Google Scholar]
- Holmquist, T.J.; Johnson, G.R. Determination of constants and comparison of results for various constitutive models. J. Phys. IV 1991, 1, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

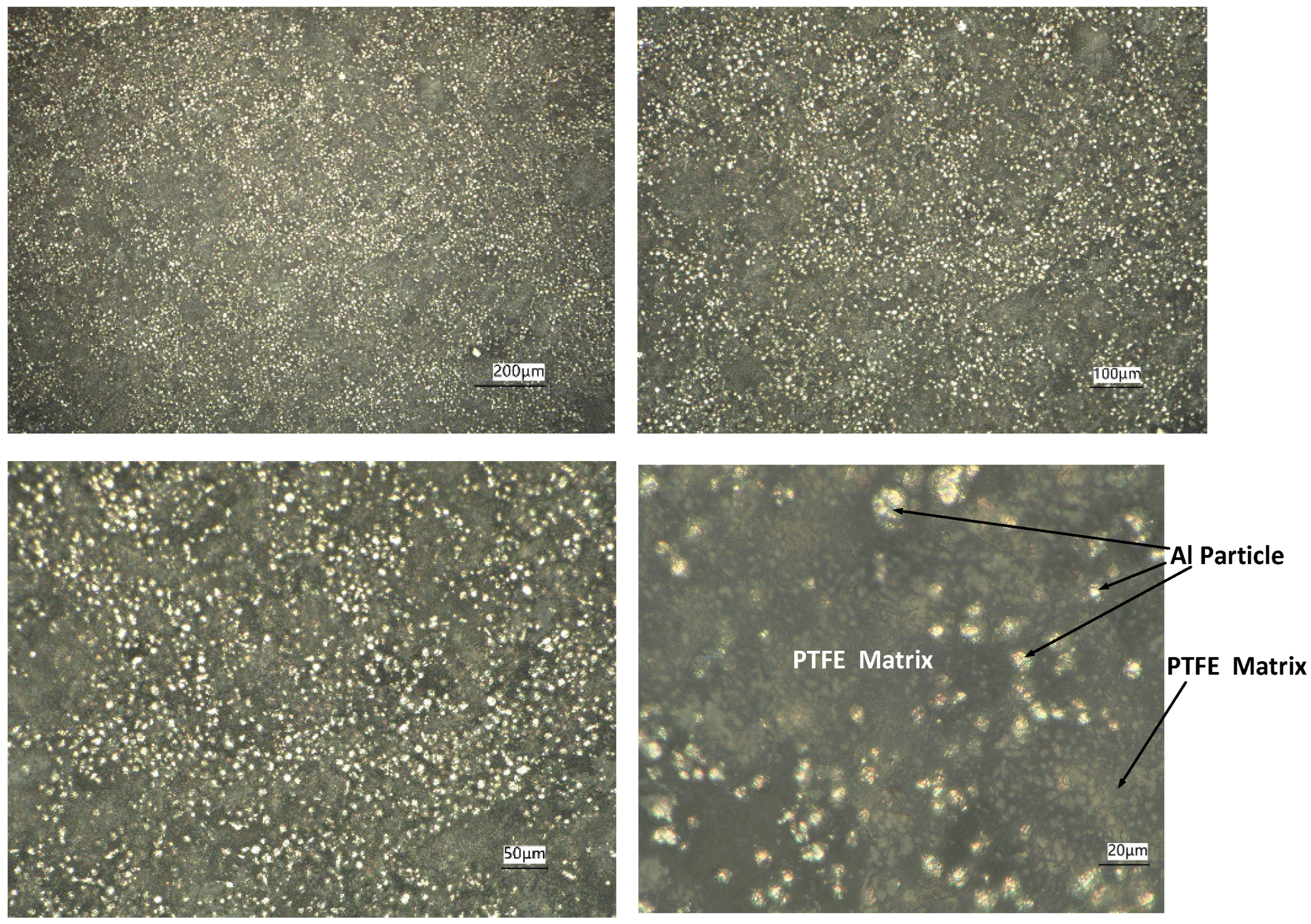



| Test No. | Strain Rate (s−1) | Yield Stress (MPa) | Ultimate Strength (MPa) | Limited Strain | Engineering Yield Stress (MPa) | Engineering Ultimate Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-1# | 0.001 | 8.0 | -- | -- | 8.02 | -- |
| 1-2# | 0.001 | -- | -- | -- | ||
| 1-3# | 0.001 | -- | -- | -- | ||
| 2# | 2400 | 17.28 | 41.70 | 0.1872 | 17.31 | 50.28 |
| 3# | 3350 | 18.16 | 53.53 | 0.2565 | 18.20 | 69.18 |
| 4# | 3650 | 19.07 | 55.70 | 0.2698 | 19.11 | 72.95 |
| 5# | 4000 | 18.25 | 59.45 | 0.2904 | 18.29 | 79.48 |
| 6# | 4250 | 18.64 | 66.27 | 0.3348 | 18.68 | 92.62 |
| 7# | 4600 | 29.12 | 67.91 | 0.3416 | 29.18 | 95.56 |
| 8# | 5850 | 30.22 | 90.79 | 0.4426 | 30.28 | 141.34 |
| 9# | 6150 | 30.52 | 92.97 | 0.4904 | 30.58 | 151.82 |
| 10# | 7250 | 31.36 | 114.31 | 0.5037 | 31.42 | 189.16 |
| The Value of Strain Rate | A (MPa) | B (MPa) | n | C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8.0 | 36.89 | 0.7005 | 0.087 | |
| 8.0 | 40.62 | 1.117 | 0.182 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, F.; Li, J.; Yang, D.; Luo, S. Analysis of Dynamic Properties and Johnson–Cook Constitutive Relationship Concerning Polytetrafluoroethylene/Aluminum Granular Composite. Materials 2025, 18, 3615. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153615
Xu F, Li J, Yang D, Luo S. Analysis of Dynamic Properties and Johnson–Cook Constitutive Relationship Concerning Polytetrafluoroethylene/Aluminum Granular Composite. Materials. 2025; 18(15):3615. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153615
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Fengyue, Jiabo Li, Denghong Yang, and Shaomin Luo. 2025. "Analysis of Dynamic Properties and Johnson–Cook Constitutive Relationship Concerning Polytetrafluoroethylene/Aluminum Granular Composite" Materials 18, no. 15: 3615. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153615
APA StyleXu, F., Li, J., Yang, D., & Luo, S. (2025). Analysis of Dynamic Properties and Johnson–Cook Constitutive Relationship Concerning Polytetrafluoroethylene/Aluminum Granular Composite. Materials, 18(15), 3615. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153615





