The Study on the Electrochemical Efficiency of Yttrium-Doped High-Entropy Perovskite Cathodes for Proton-Conducting Fuel Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Preparation
2.2. Characterization Techniques
3. Results and Discussion
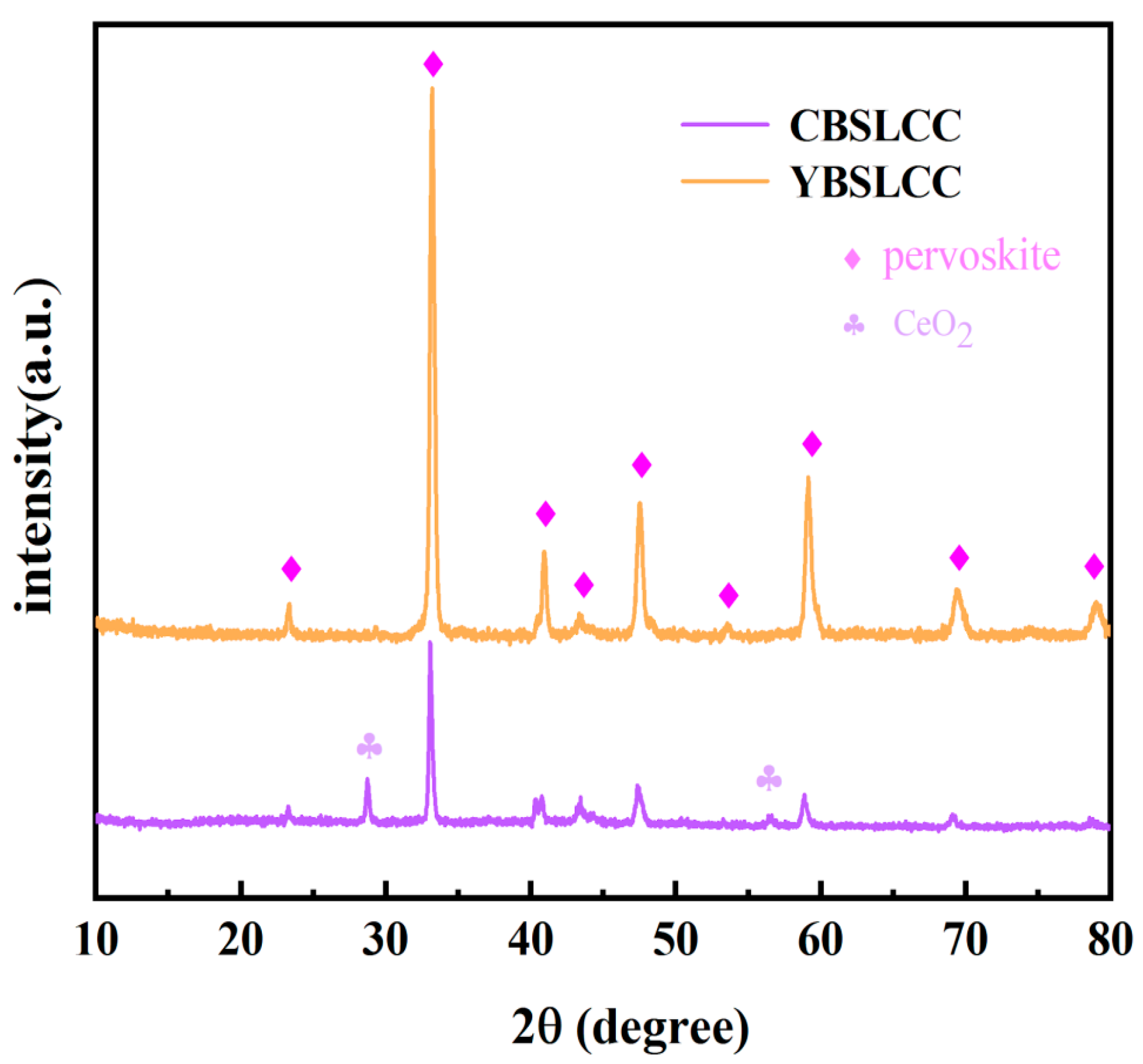
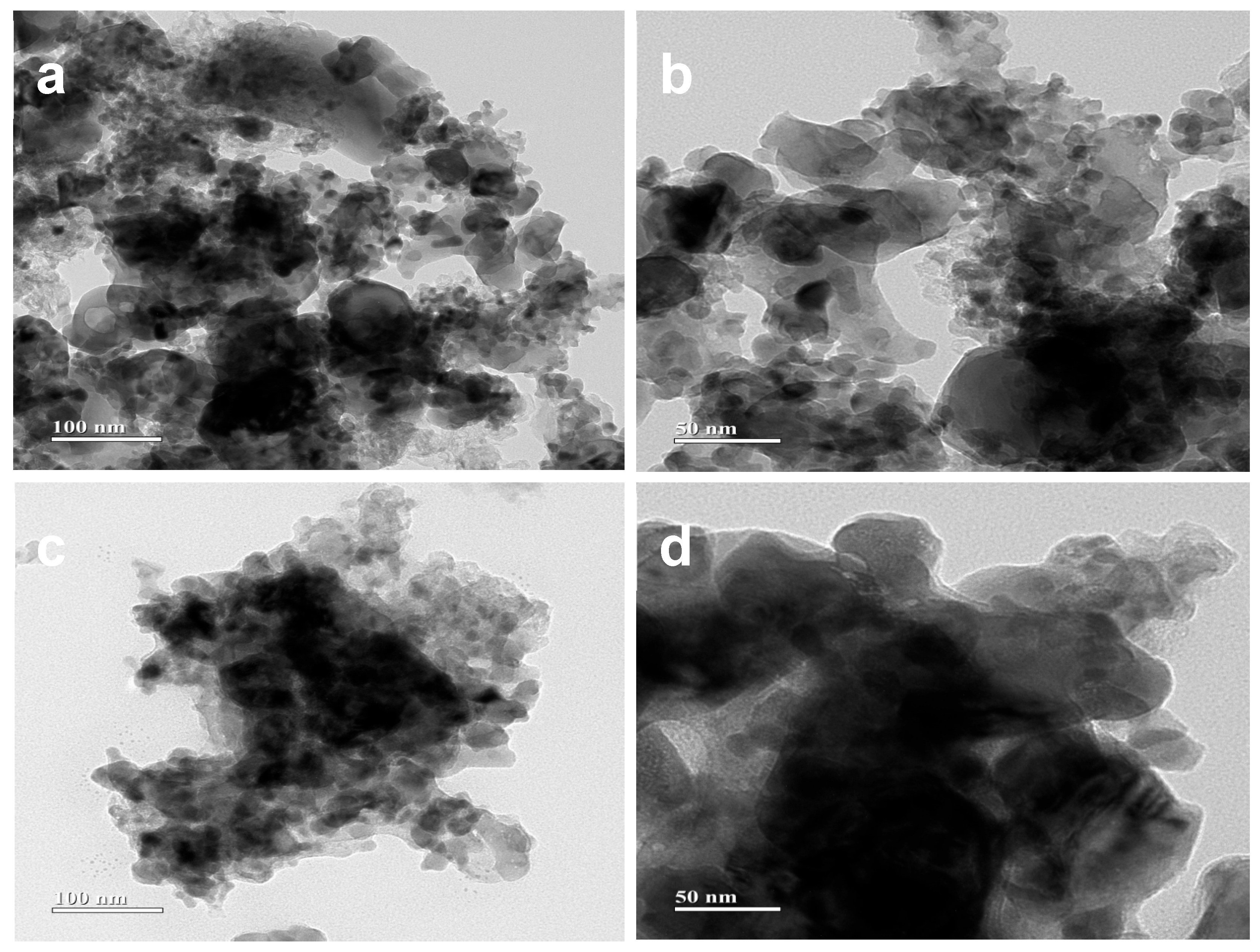
3.1. Morphological and Structural Analysis
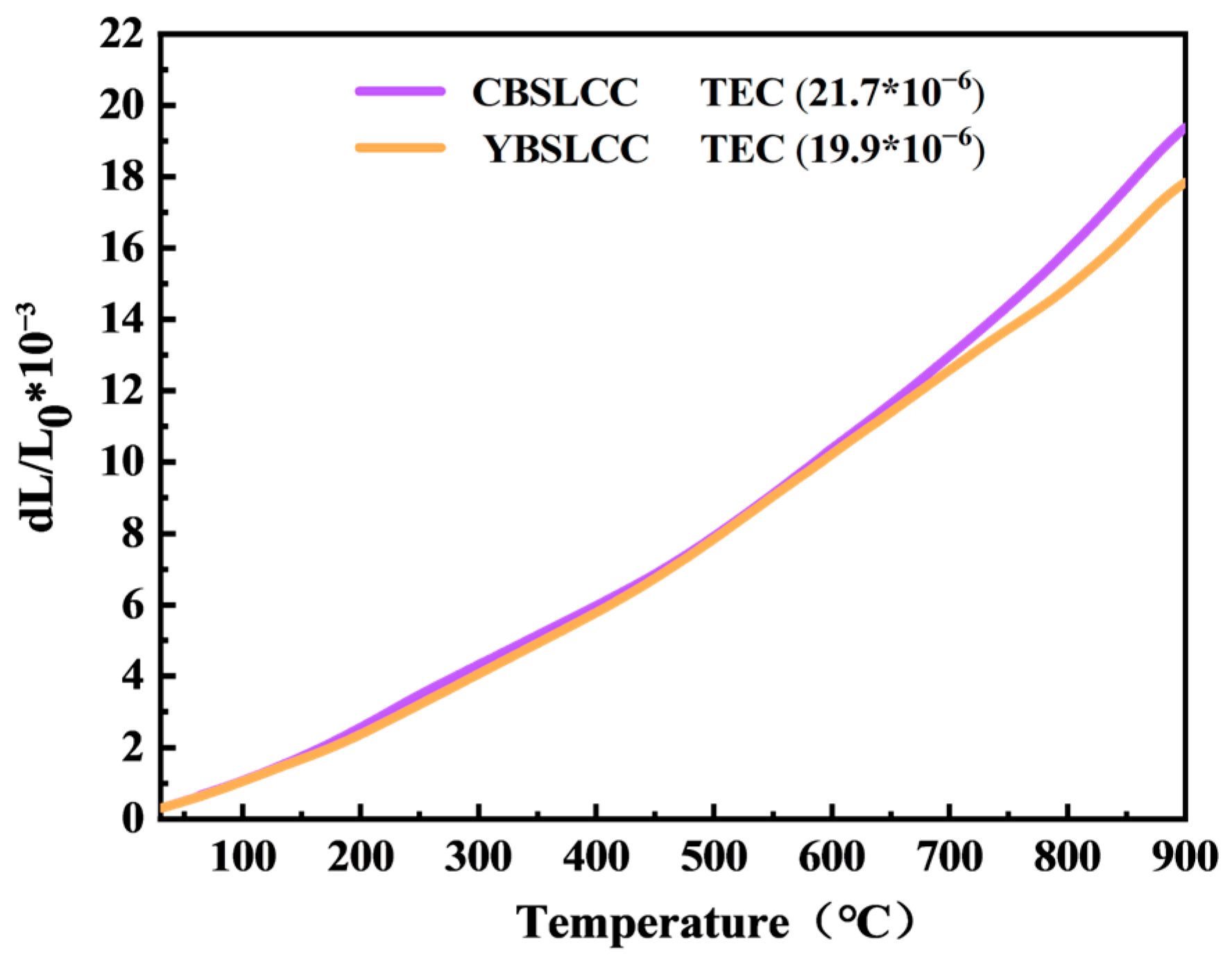
3.2. Thermal Property and Elemental Analysis
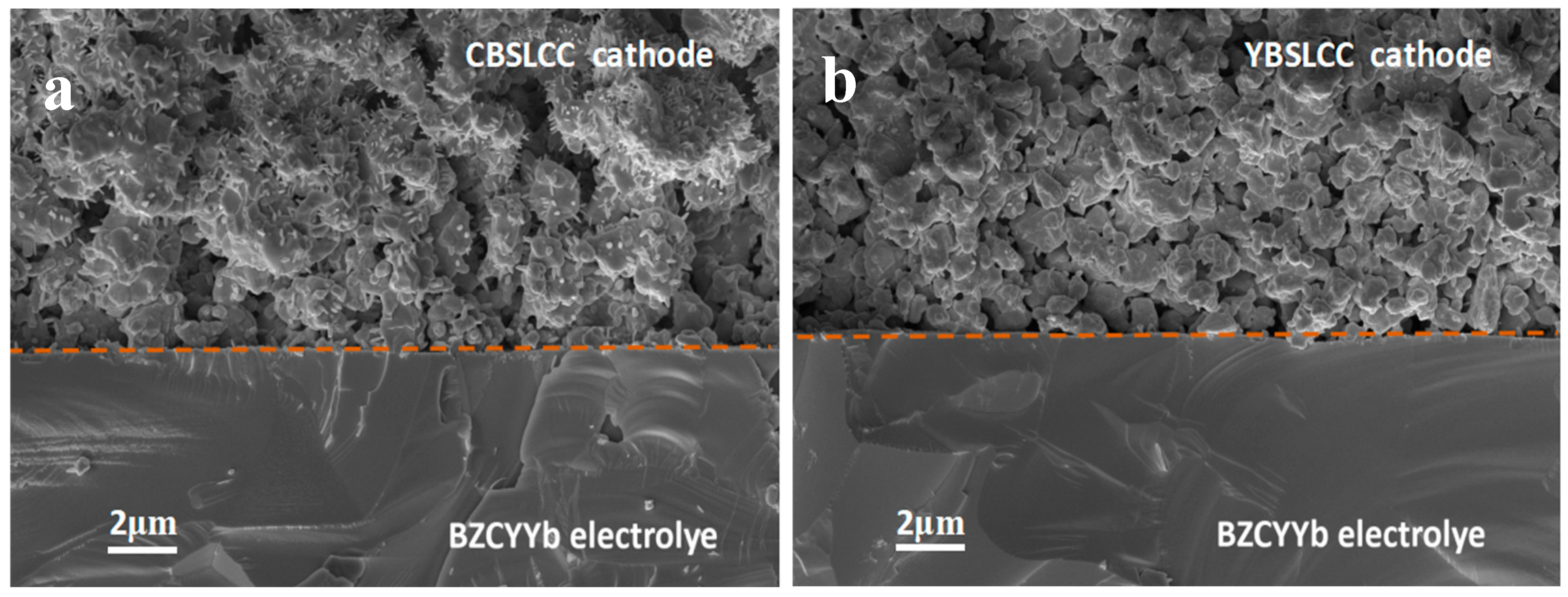
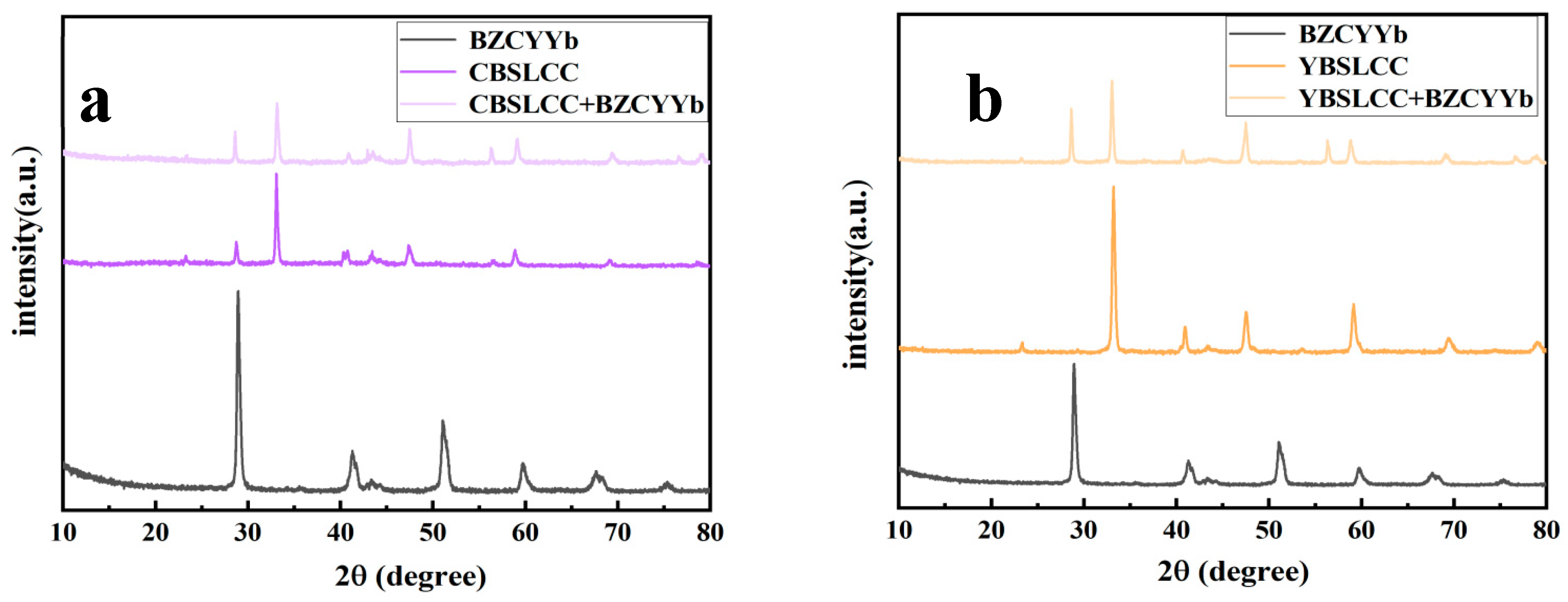
3.3. Micro-Structural Characterization of Single Cells Before Electrochemical Tests
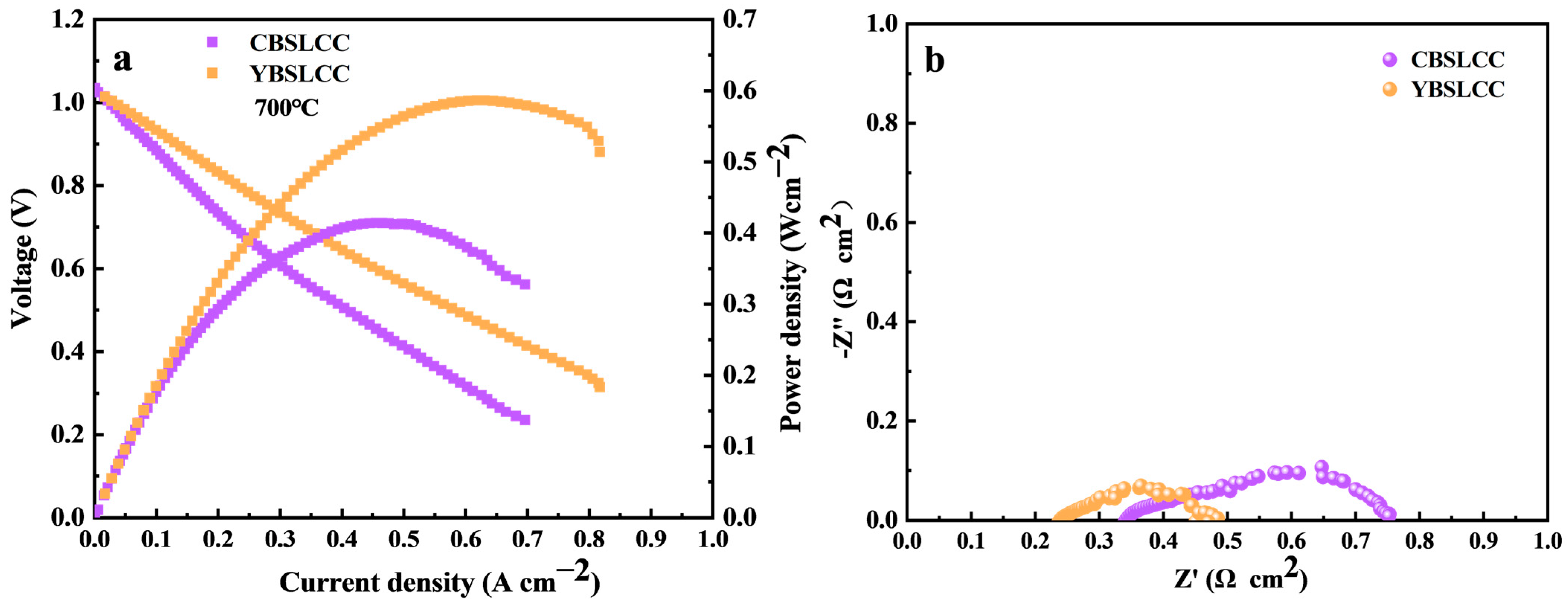
3.4. Electrochemical Efficiency of Single Cells
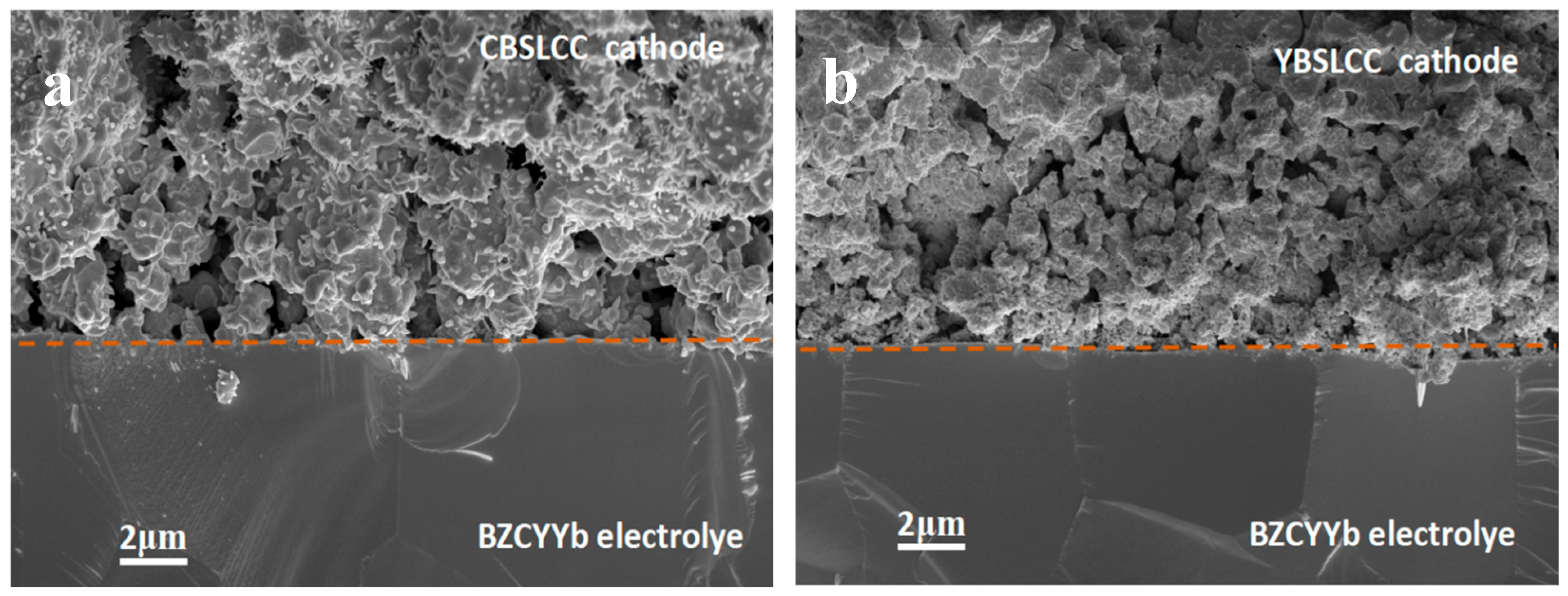
3.5. Micro-Structural Characterization of Single Cells After Tests
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PCFCs | Proton-conducting fuel cells |
| HEP | High-entropy perovskite |
| ORR | Oxygen reduction reaction |
| CO | Carbon monoxide |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| XRD | X-Ray diffraction |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| EIS | Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy |
| TEC | Thermal expansion coefficient |
| OCV | Open-circuit voltage |
References
- He, F.; Hou, M.; Liu, D.; Ding, Y.; Sasaki, K.; Choi, Y.; Guo, S.; Han, D.; Liu, Y.; Liu, M.; et al. Phase segregation of a composite air electrode unlocks the high performance of reversible protonic ceramic electrochemical cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2024, 17, 3898–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Zhou, Y.C.; Hu, T.; Xu, Y.S.; Hou, M.Y.; Zhu, F.; Liu, D.; Zhang, H.; Xu, K.; Liu, M.; et al. An efficient high-entropy perovskite-type air electrode for reversible oxygen reduction and water splitting in protonic ceramic cells. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, e2209469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y.C.; Pei, K.; Pan, Y.X.; Xu, K.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, B.; Sasaki, K.; Choi, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. An efficient and durable anode for ammonia protonic ceramic fuel cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2022, 15, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.H.; Wang, J.; Song, Y.F.; Robson, M.J.; Seong, A.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Belotti, A.; Liu, J.; et al. Rational design of perovskite ferrites as high-performance proton-conducting fuel cell cathodes. Nat. Catal. 2022, 5, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, K.; Zhou, Y.C.; Xu, K.; Zhang, H.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, B.T.; Yuan, W.; Sasaki, K.; Choi, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Surface restructuring of a perovskite-type air electrode for reversible protonic ceramic electrochemical cells. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Q.; Tang, Z.J.; Song, Y.F.; Yang, G.M.; Qian, W.R.; Yang, M.T.; Zhu, Y.; Ran, R.; Wang, W.; Zhou, W.; et al. High-entropy perovskite oxide: A new opportunity for developing highly active and durable air electrode for reversible protonic ceramic electrochemical cells. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.Z.; Zhu, Y.J.; Song, Y.F.; Guan, D.Q.; Luo, Z.X.; Yang, G.M.; Jiang, S.P.; Zhou, W.; Ran, R.; Shao, Z. A new durable surface nanoparticles-modified perovskite cathode for protonic ceramic fuel cells from selective cation exsolution under oxidizing atmosphere. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e2106379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Liu, S.; Wu, T.; Yang, M.T.; Li, W.H.; Yang, G.M.; Zhu, F.; Zhang, H.; Pei, K.; Chen, Y.; et al. Catalytic self-assembled air electrode for highly active and durable reversible protonic ceramic electrochemical cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2206756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, W.J.; Wu, W.; Wang, B.M.; Tang, W.; Zhou, M.; Jin, C.R.; Ding, H.; Fan, W.; Dong, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Revitalizing interface in protonic ceramic cells by acid etch. Nature 2022, 604, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.C.; Zhang, W.L.; Kane, N.; Luo, Z.Y.; Pei, K.; Sasaki, K.; Choi, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ding, D.; Liu, M. An efficient bifunctional air electrode for reversible protonic ceramic electrochemical cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2105386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.F.; Liu, J.P.; Wang, Y.H.; Guan, D.Q.; Seong, A.; Liang, M.Z.; Robson, M.J.; Xiong, X.; Zhang, Z.; Kim, G.; et al. Nanocomposites: A new opportunity for developing highly active and durable bifunctional air electrodes for reversible protonic ceramic cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2101899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Gao, Q.N.; Liu, Z.Q.; Yang, M.T.; Ran, R.; Yang, G.M.; Wang, W.; Zhou, W.; Shao, Z. A new Pd doped proton conducting perovskite oxide with multiple functionalities for efficient and stable power generation from ammonia at reduced temperatures. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2003916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.; Paik, J.; Kim, D.; Woo, D.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, J.; Lee, W. Exceptionally high performance of protonic ceramic fuel cells with stoichiometric electrolytes. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 6476–6483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Zhu, F.; Liu, D.; Zhou, Y.; Sasaki, K.; Choi, Y.; Liu, M.; Chen, Y. A reversible perovskite air electrode for active and durable oxygen reduction and evolution reactions via the A-site entropy engineering. Mater. Today 2023, 63, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.F.; Chen, Y.B.; Xu, M.G.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, G.M.; Ran, R.; Zhou, W.; Shao, Z. A cobalt-free multi-phase nanocomposite as near-ideal cathode of intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cells developed by smart self-assembly. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e1906979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, N.; Wang, C.C.; Jiang, S.P.; Skinner, S.J. Synergistic effects of temperature and polarization on Cr poisoning of La0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3−δ solid oxide fuel cell cathodes. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2019, 7, 9253–9262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, S.P.; Zhao, L.; Ai, N.; Wang, X.; Shao, Y.; Guan, C.; Fang, H.; Luo, Y.; et al. Promotional role of BaCO3 on the chromium-tolerance of La0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3−δ cathodes of solid oxide fuel cells. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2023, 321, 122080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Chen, T.; Wang, C.X.; Sun, N.; Zhang, G.J.; Zhou, Y.C.; Wang, M.; Zhu, J.; Xu, L.; Wang, S.; et al. An active and stable high-entropy ruddlesden-popper type La1.4Sr0.6Co0.2Fe0.2Ni0.2Mn0.2Cu0.2O4±δ oxygen electrode for reversible solid oxide cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 52, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, M.; Dong, J.; Xu, R.; Cheng, J.; Xiong, K.; Rao, M.; Chen, C.; Shen, C.; et al. Boosting the CO2 electrolysis performance using high entropy stable La0.2Pr0.2Sm0.2Sr0.2Ca0.2Fe0.9Ni0.1O3−δ electrode for symmetric solid oxide electrolysis cells. Fuel 2024, 359, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Robson, M.J.; Manzotti, A.; Ciucci, F. High-entropy perovskites materials for next-generation energy applications. Joule 2023, 7, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Ling, Y.; Gong, Y.; Wang, R.; Wang, H.; Jin, J.; Zhao, L.; He, B. Atomistic insights into medium-entropy perovskites for efficient and robust CO2 electrolysis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 45905–45914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretschuh, P.; Egger, A.; Brunner, R.; Bucher, E. Electrochemical and microstructural characterization of the high-entropy perovskite La0.2Pr0.2Nd0.2Sm0.2Sr0.2CoO3−δ for solid oxide cell air electrodes. Fuel Cells 2023, 23, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.; Kim, M.-C.; Lee, K.B.; Choi, H.; Zhang, L.; Sohn, J.I. Nonprecious high-entropy chalcogenide glasses-based electrocatalysts for efficient and stable acidic oxygen evolution reaction in proton exchange membrane water electrolysis. Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2301420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Wang, G.; Wu, H.; Beshiwork, B.A.; Tian, D.; Zhu, S.; Yang, Y.; Lu, X.; Ding, Y.; Ling, Y.; et al. A high-entropy perovskite cathode for solid oxide fuel cells. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 872, 159633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Gao, Y.; Liu, L.; Gao, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Hao, H.; Hao, W.; Lou, X.; Lv, Z.; et al. High entropy double perovskite cathodes with enhanced activity and operational stability for solid oxide fuel cells. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2024, 44, 3267–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Sun, L.; Li, Q.; Huo, L.; Zhao, H. B-site modulating medium-entropy oxide PrSr(Fe0.2Co0.2Ni0.2Cu0.2Zn0.2)O4 as potential cathode for solid oxide full cells. Mater. Today Chem. 2024, 36, 101960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Ling, Y.; Wang, X.; Jin, F.; Meng, D.; Lv, Z.; Wei, B. Sr-deficient medium-entropy Sr1−xCo0.5Fe0.2Ti0.1Ta0.1Nb0.1O3−δ cathodes with high Cr tolerance for solid oxide fuel cells. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 479, 147665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Shao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chen, H. Novel high-entropy oxides for energy storage and conversion: From fundamentals to practical applications. Green Energy Environ. 2023, 8, 1341–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.H.; Luo, X.L.; Hou, B.X.; Liu, B.; Jia, L.C.; Xie, X.P.; Luo, D.; Wang, C.C. Novel high entropy double pervoskite cathode for solid oxide fuel cells. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 968, 172102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Dang, L.; Yan, J.; Wan, F.; Gong, W. Preparation of a nano-size (La0.2Nd0.2Sm0.2Sr0.2Ba0.2)Co0.2Fe0.8O3−δ/SDC high-entropy oxide composite cathode. Mater. Lett. 2023, 338, 134029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Dang, L.; Yan, J.; Wan, F.; Gong, W. A new (La0.2Nd0.2Gd0.2Sr0.2Ba0.2)Co0.2Fe0.8O3−δ high-entropy oxide cathode for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cell. Solid State Ion. 2023, 397, 116233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Ling, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wei, B.; Lv, Z. Utilizing high entropy effects for developing chromium-tolerance cobalt-free cathode for solid oxide fuel cells. Adv. Func. Mater. 2023, 33, 2304728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Dong, J.; Chen, Z.; Rao, M.; Li, M.; Li, T.; Ling, Y. Enhanced compatibility and activity of high-entropy double perovskite cathode material for IT-SOFC. J. Inorg. Mater. 2023, 38, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Li, N.; Sun, L.; Li, Q.; Huo, L.; Zhao, H. A novel high-entropy cathode with the A2BO4-type structure for solid oxide fuel cells. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 895, 162548. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, C.; Bucher, E.; Merkle, R.; Nader, C.; Lammer, J.; Grogger, W.; Maier, J.; Sitte, W. Influence of Y-substitution on phase composition and proton uptake of self-generated Ba(Ce,Fe)O3−δ-Ba(Fe,Ce)O3−δ composites. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 2474–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.; Kang, K.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, C.C. New oxygen regulation strategy to enhance the oxygen reduction reaction of the Pr0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3−δ cathode through a-site high-entropy engineering. ACS Sust. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 8366–8378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.G.; Yang, J.X.; Zhang, H.X.; Lang, X.S.; Cai, K.D. Ca-doped PrBa1−xCaxCoCuO5+δ (x = 0 − 0.2) as cathode materials for solid oxide fuel cells. Ceram. Intern 2022, 48, 7652–7662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hong, T.; Li, Y.H.; Xia, C.R. CaO effect on the electrochemical performance of lanthanum strontium cobalt ferrite cathode for intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 17242–17250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yoo, S.; Choi, Y.; Kim, J.H.; Ding, Y.; Pei, K.; Murphy, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, W.; et al. A highly active, CO2-tolerant electrode for the oxygen reduction reaction. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 2458–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhong, J.; Li, Z.; Xiang, J.; Hou, B.; Tan, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, C.C. Chromium tolerance of high entropy BaO impregnated-(La0.2Pr0.2Sm0.2Gd0.2Nd0.2)Ba0.5Sr0.5Co1.5Fe0.5O5(LPSGNBSCF) cathodes for solid oxide fuel cell. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2025, 29, 1787–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, B.; Wang, X.; Tang, R.; Zhong, W.; Zhu, M.; Tan, Z.; Wang, C. The Study on the Electrochemical Efficiency of Yttrium-Doped High-Entropy Perovskite Cathodes for Proton-Conducting Fuel Cells. Materials 2025, 18, 3569. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153569
Hou B, Wang X, Tang R, Zhong W, Zhu M, Tan Z, Wang C. The Study on the Electrochemical Efficiency of Yttrium-Doped High-Entropy Perovskite Cathodes for Proton-Conducting Fuel Cells. Materials. 2025; 18(15):3569. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153569
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Bingxue, Xintao Wang, Rui Tang, Wenqiang Zhong, Meiyu Zhu, Zanxiong Tan, and Chengcheng Wang. 2025. "The Study on the Electrochemical Efficiency of Yttrium-Doped High-Entropy Perovskite Cathodes for Proton-Conducting Fuel Cells" Materials 18, no. 15: 3569. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153569
APA StyleHou, B., Wang, X., Tang, R., Zhong, W., Zhu, M., Tan, Z., & Wang, C. (2025). The Study on the Electrochemical Efficiency of Yttrium-Doped High-Entropy Perovskite Cathodes for Proton-Conducting Fuel Cells. Materials, 18(15), 3569. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153569




