Effect of Er Microalloying and Zn/Mg Ratio on Dry Sliding Wear Properties of Al-Zn-Mg Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
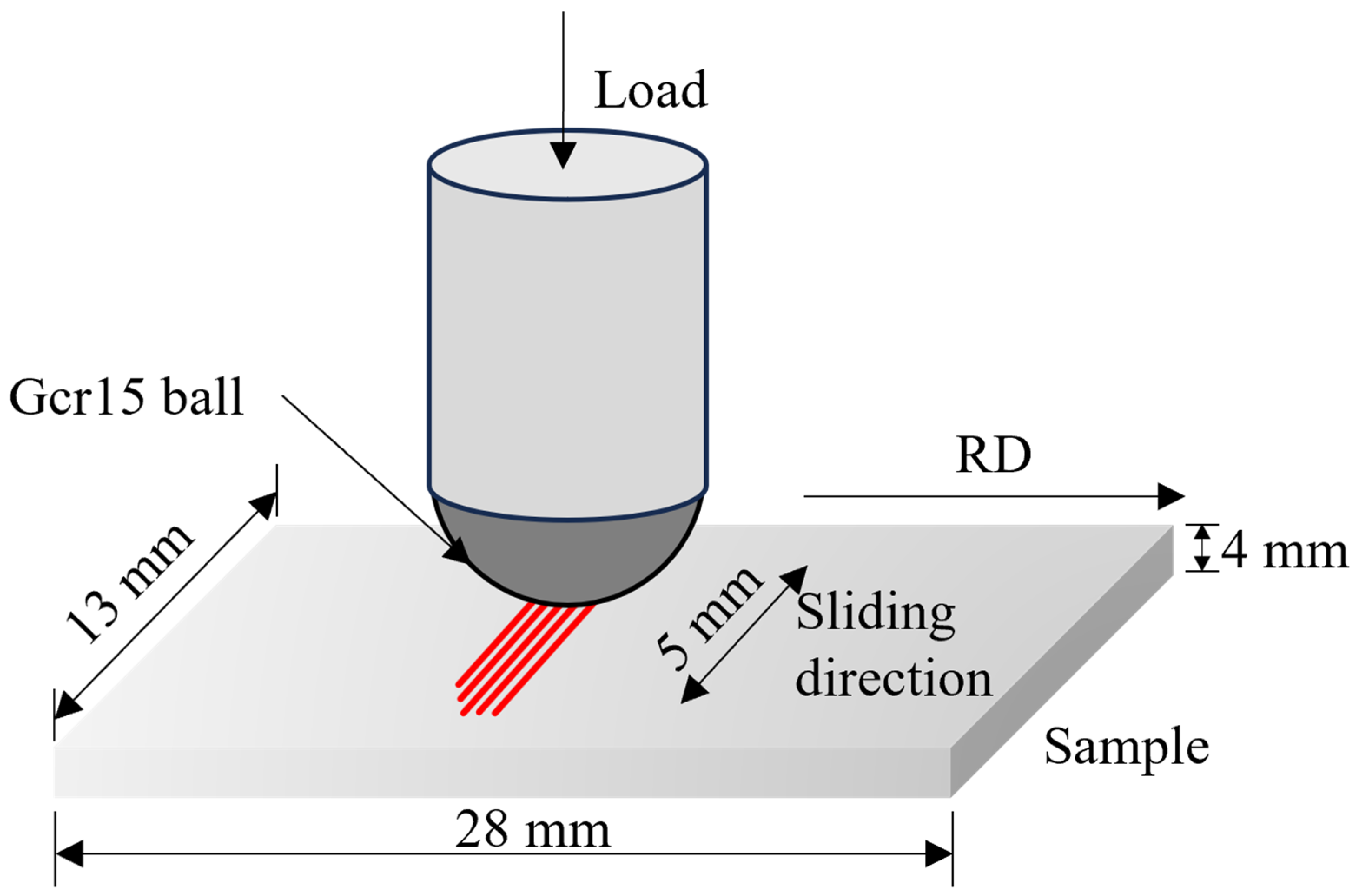
2. Experimental
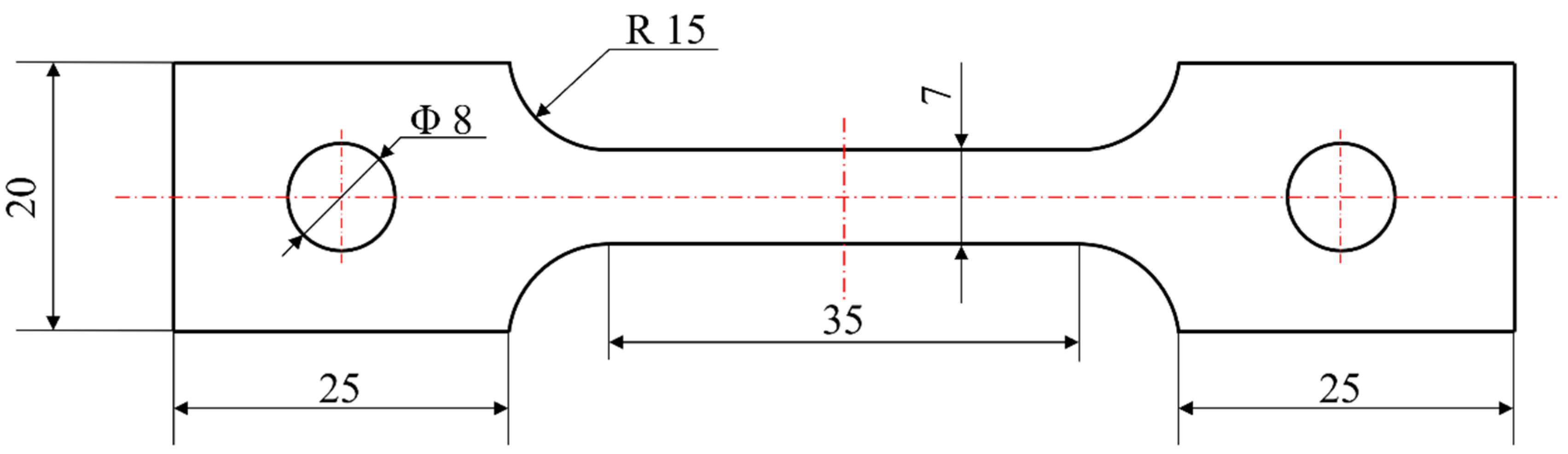
Experimental Material
3. Results and Discussion
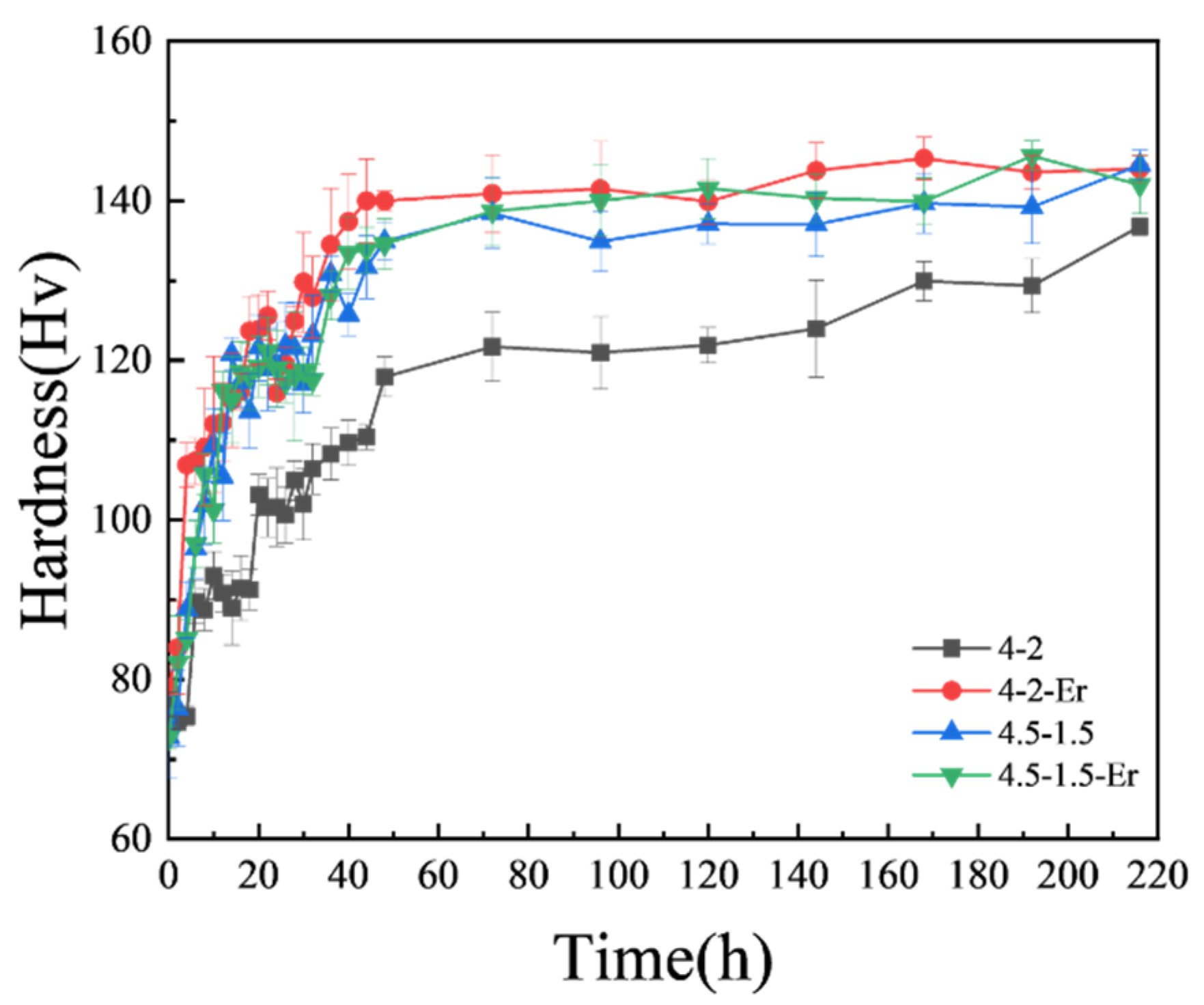
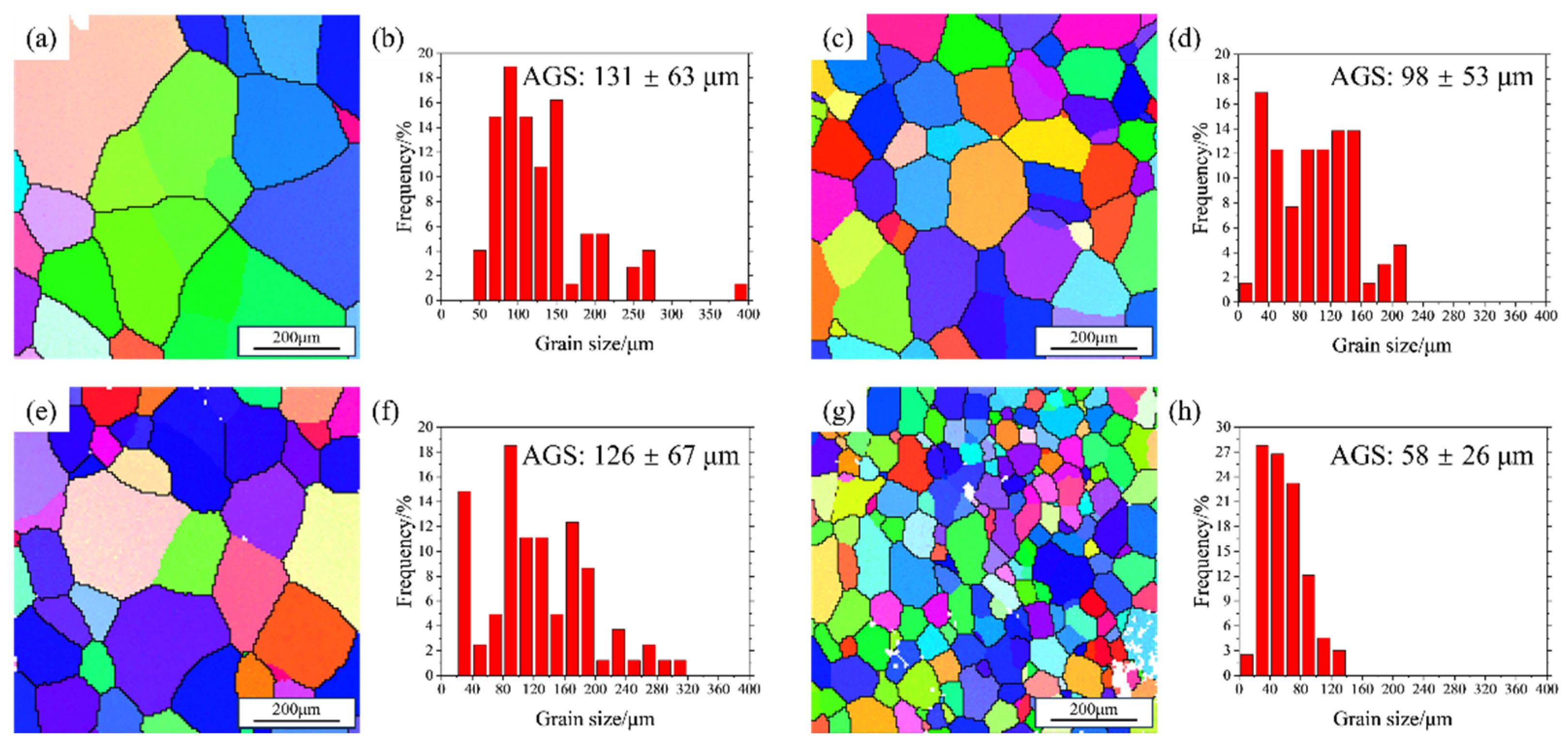
3.1. Mechanical Properties and Microstructure Analysis
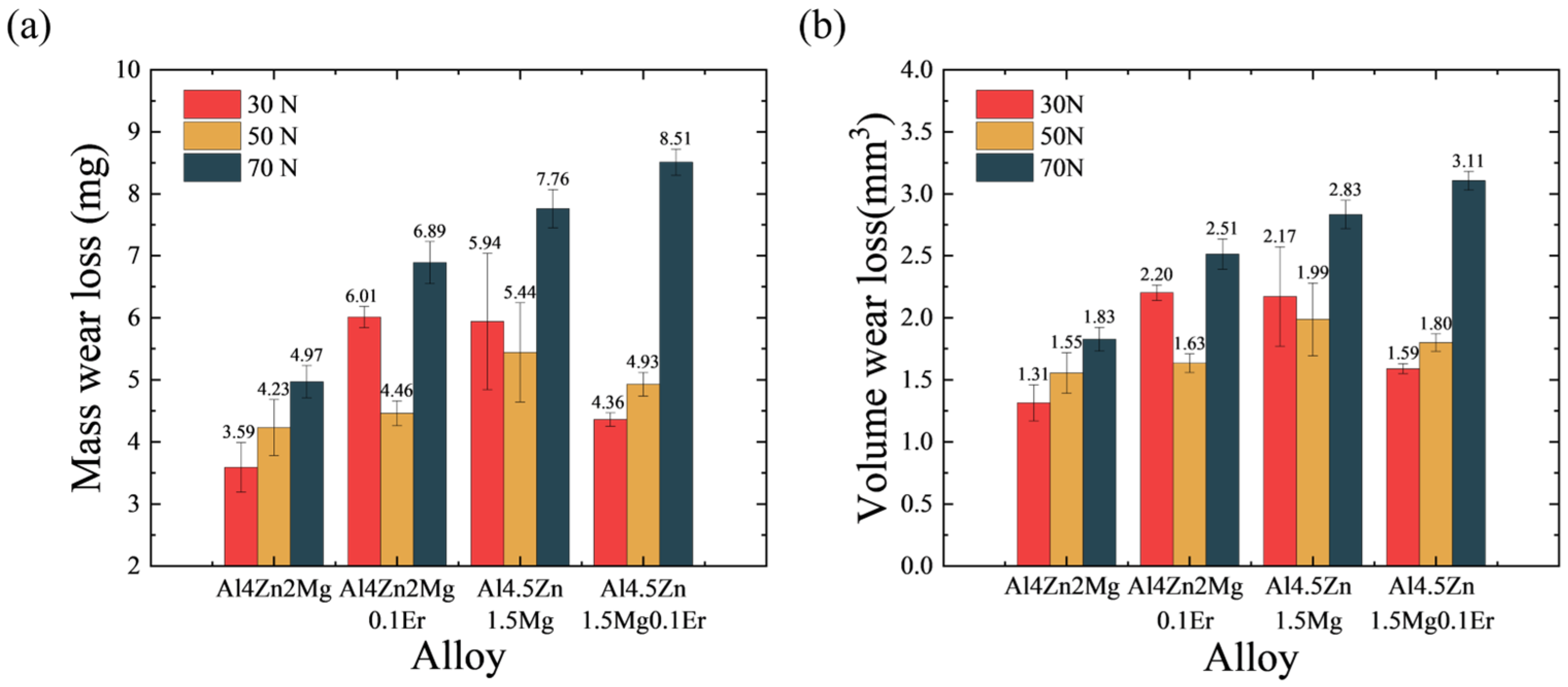
3.2. Wear Rate
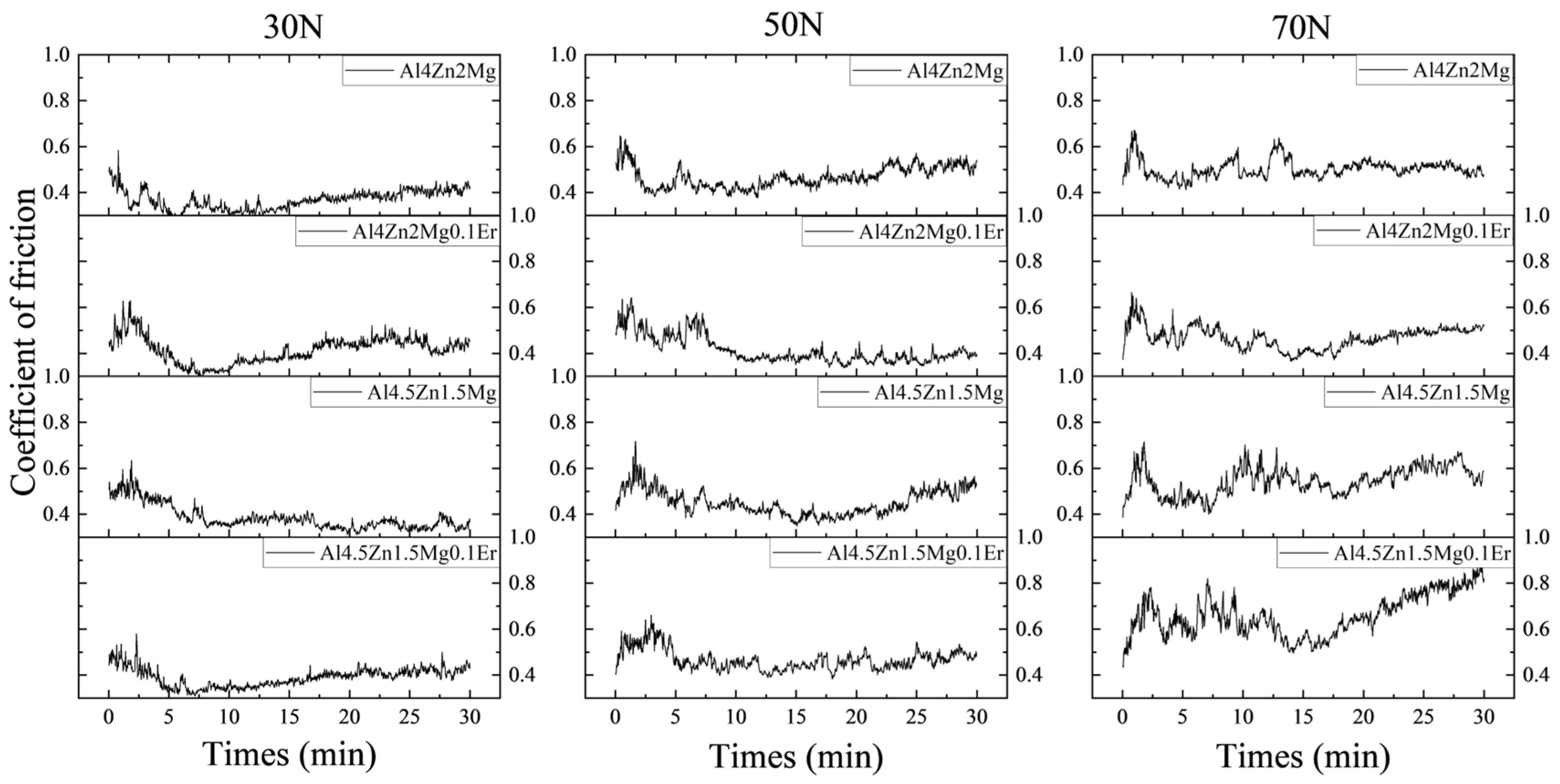
3.3. Wear Coefficient
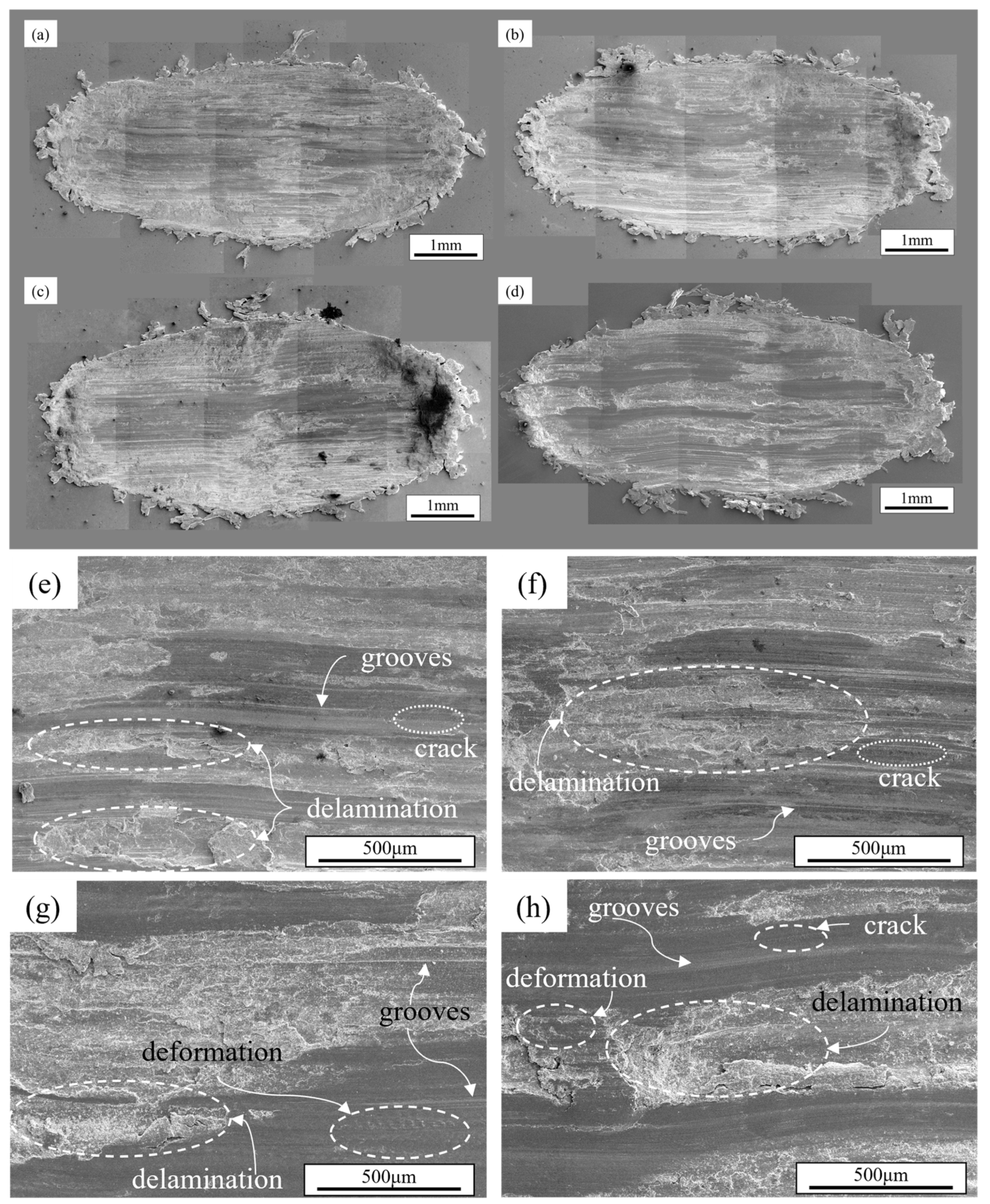
3.4. Worn Surfaces
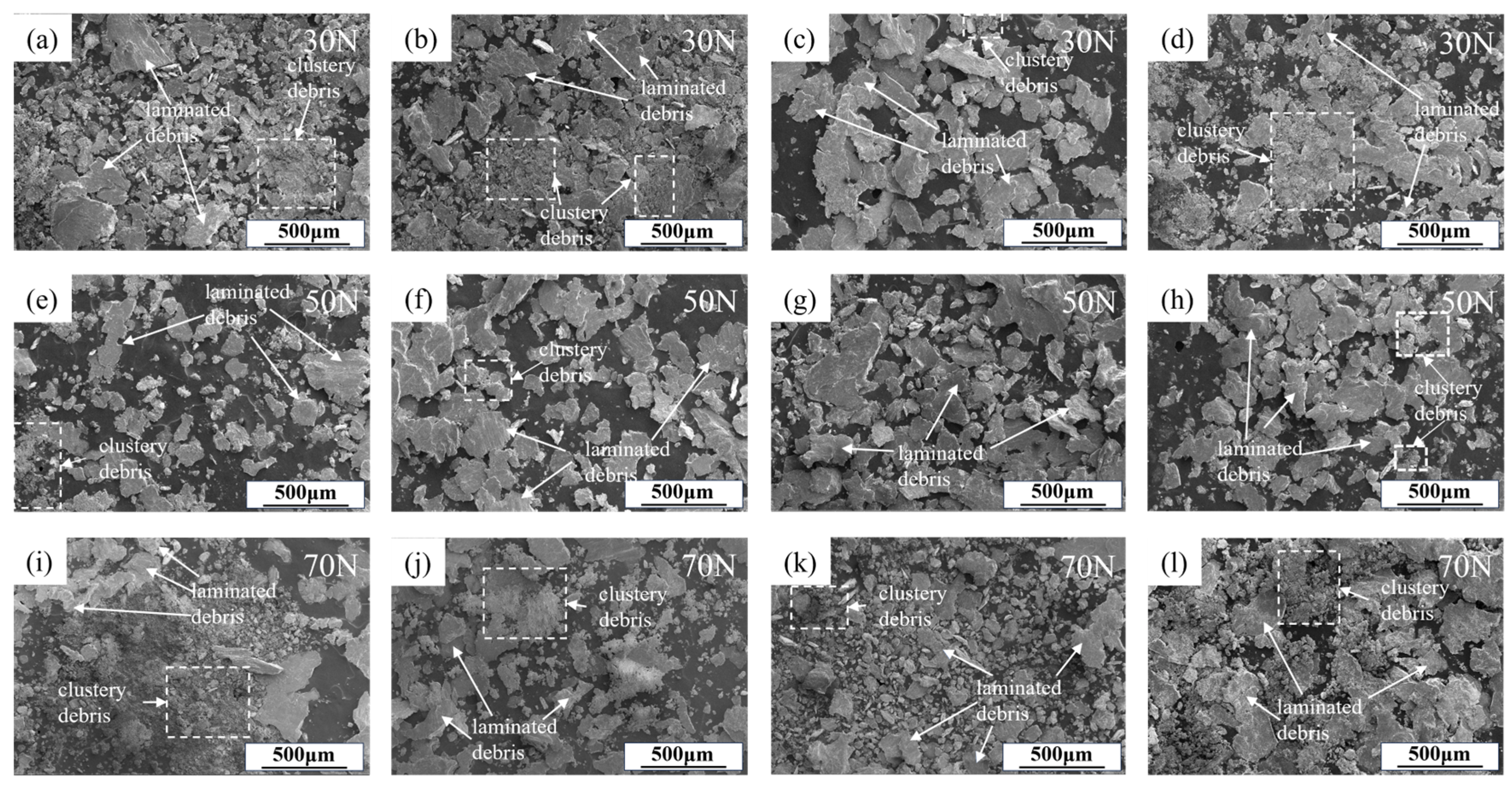
3.5. Wear Debris
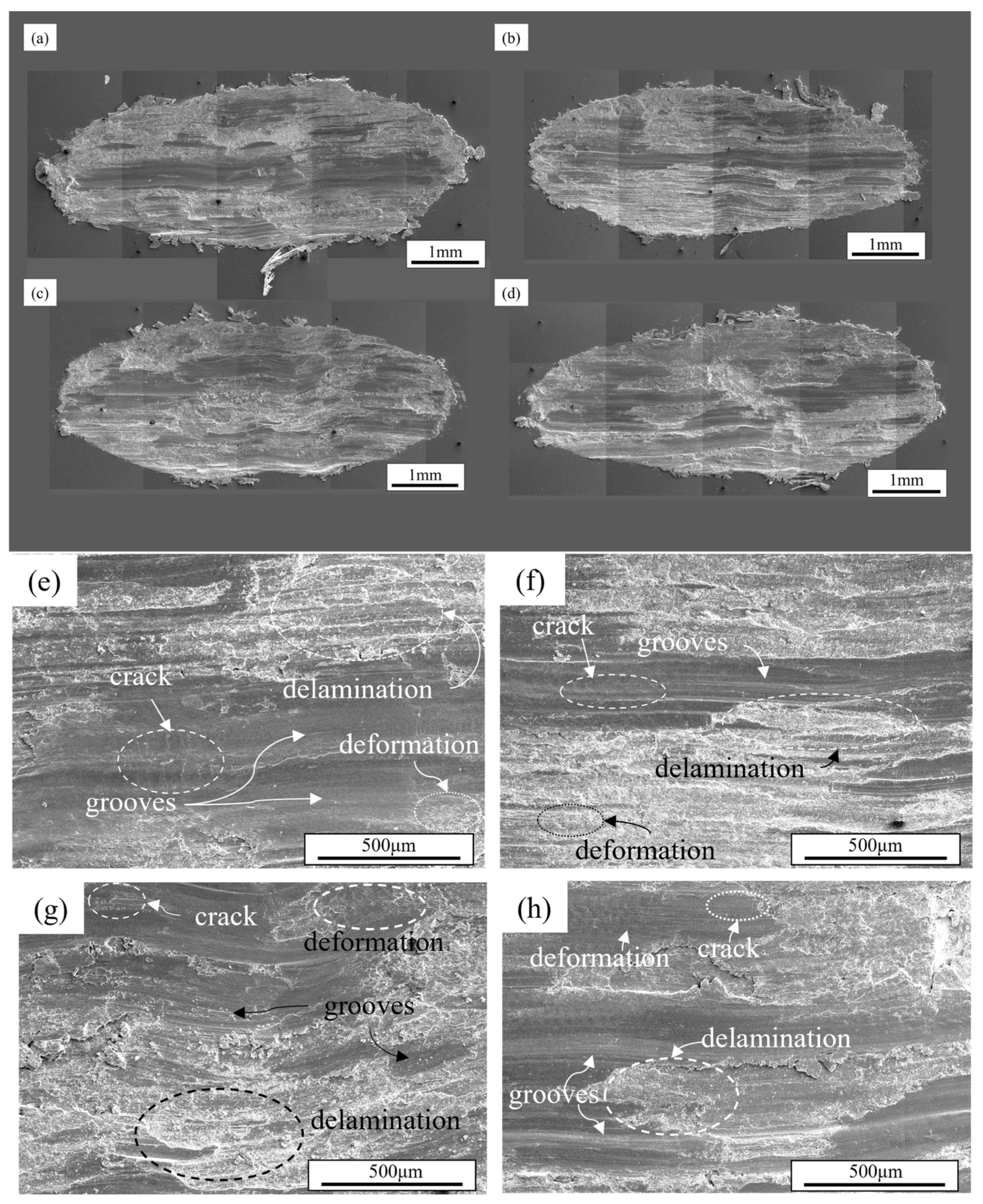
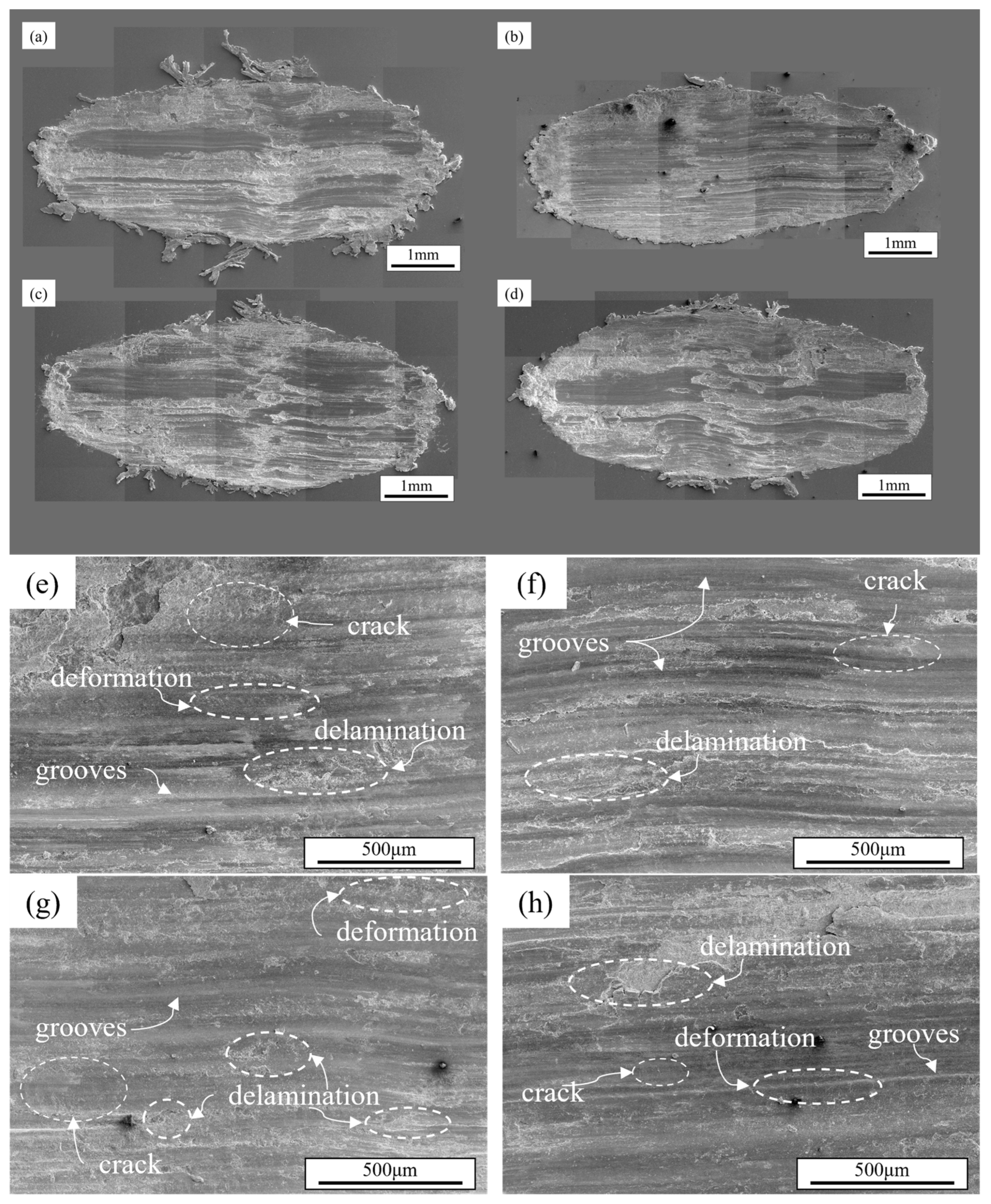
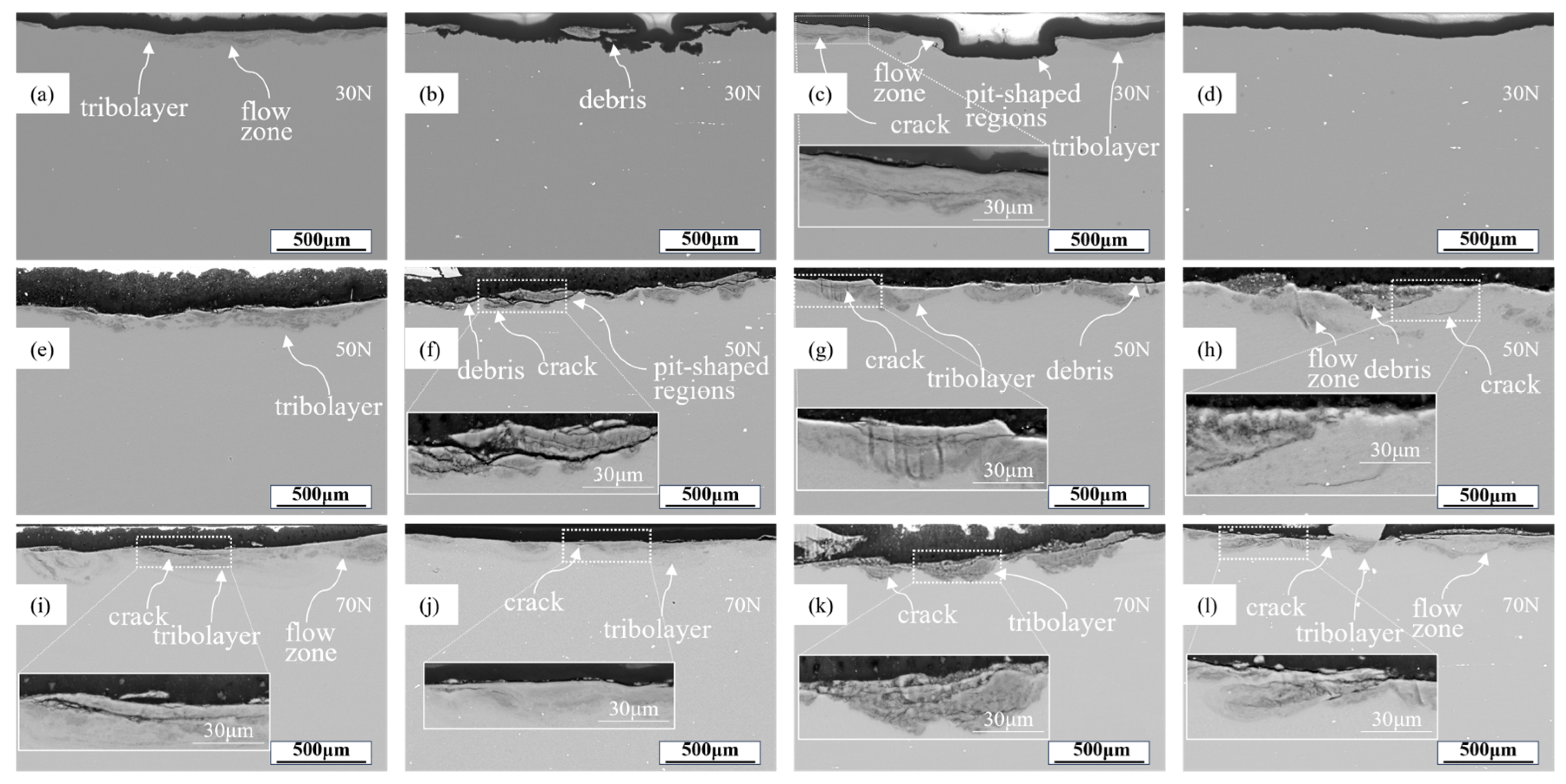
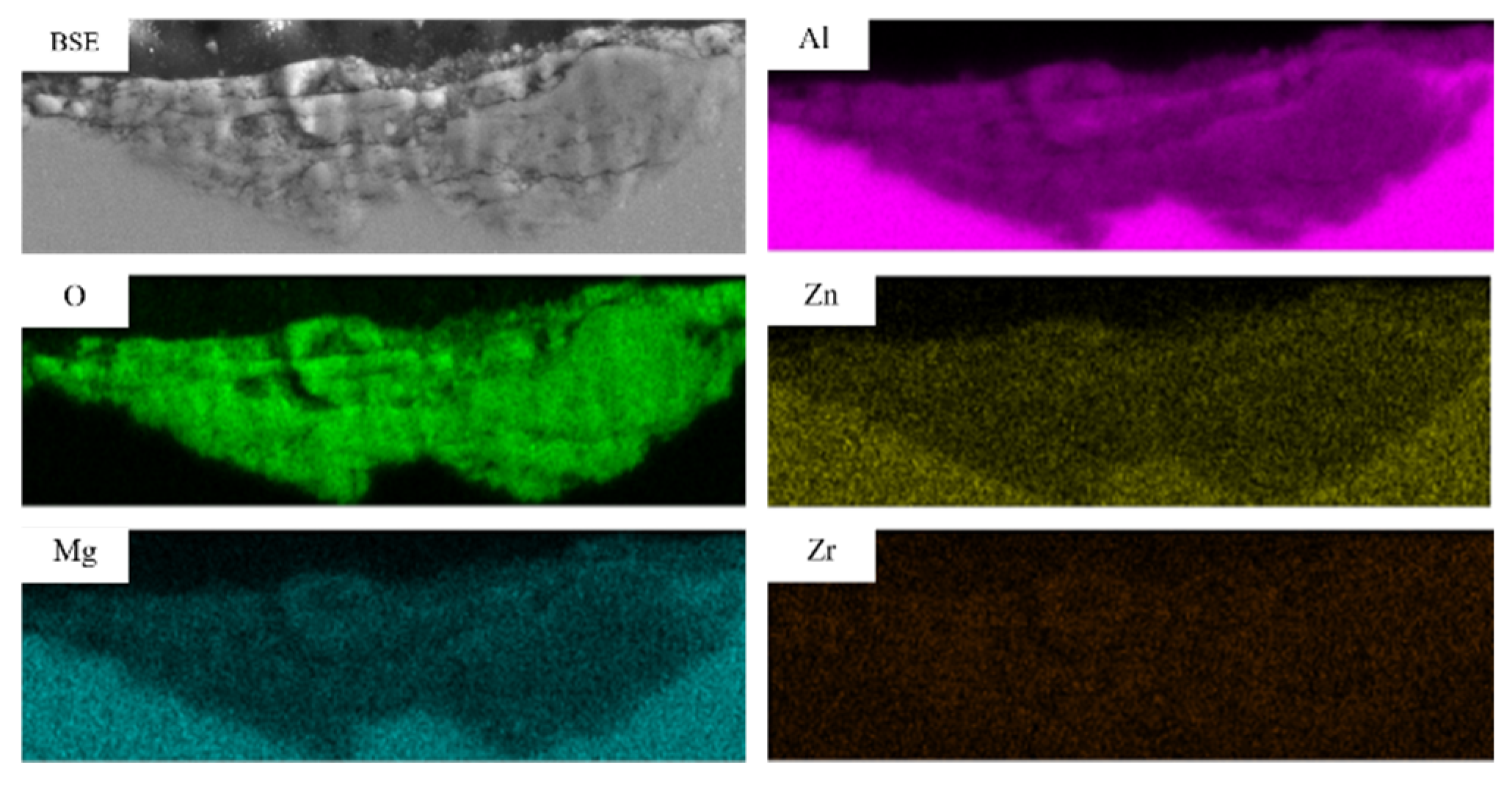
3.6. Cross-Sectional Surface Analysis
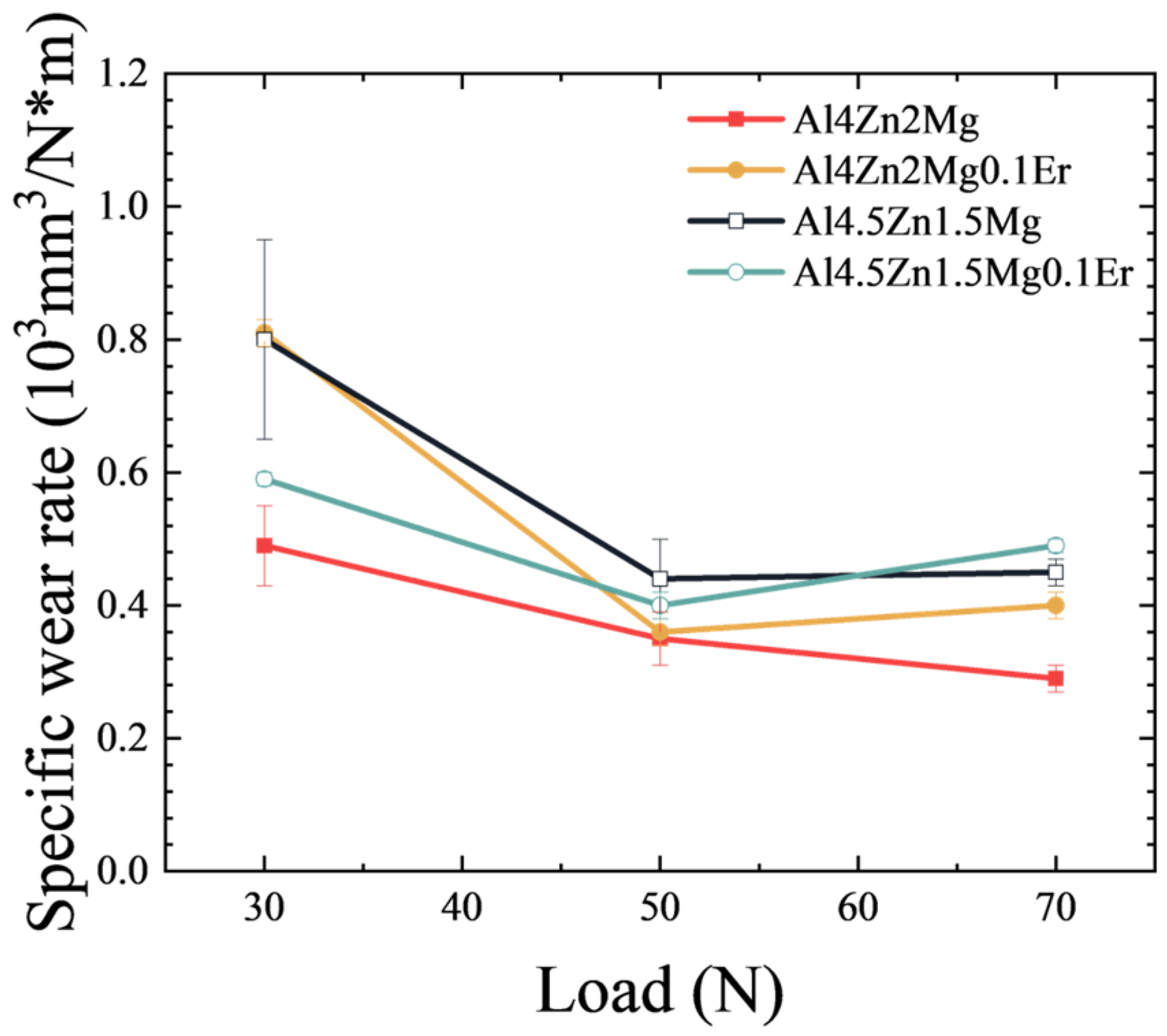
3.7. Specific Wear Rate Discussion
4. Conclusions
- Er micro-alloying induced pronounced grain refinement and further shortened the peak aging duration for alloys with a Zn/Mg ratio of 1.7:1. Compared with the Al4.5Zn1.5Mg alloy, Er micro-alloying marginally enhances the ductility of the Al4.5Zn1.5Mg0.1Er alloy.
- Reducing the Zn/Mg ratio mitigated wear volume across all tested loads. For the Al4.5Zn1.5Mg alloy, Er microalloying significantly reduced wear volume under moderate-to-low loads (30 N, 50 N)
- Er microalloying did not alter the wear mechanisms. At the load of 30 N, the wear mechanism of the Al-Zn-Mg alloy is a combined action of abrasive wear, fatigue wear, and adhesive wear. At a load of 50 N, abrasive wear becomes the dominant mechanism, accompanied by fatigue wear and partial adhesive wear. At a load of 70 N, the primary wear mechanisms of the alloy are abrasive wear and fatigue wear, with adhesive wear being of secondary importance.
- Due to the formation of the stabilized tribolayers, the specific wear rate decreased with load elevated from 30 to 50 N. When the load increased from 50 N to 70 N, the alloy’s tribolayer thickness remained stable, maintaining specific wear rate. Notwithstanding, crack proliferation within the tribolayer at a load of 70 N caused aggravated volume wear loss.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, S.; Yue, X.; Li, Q.; Peng, H.; Dong, B.; Liu, T.; Yang, H.; Fan, J.; Shu, S.; Qiu, F.; et al. Development and Applications of Aluminum Alloys for Aerospace Industry. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 27, 944–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Liu, B.; Zhang, S. The Advancement of 7XXX Series Aluminum Alloys for Aircraft Structures: A Review. Metals 2021, 11, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.J.; Liu, F.C.; Liu, J.; Tan, M.J.; Blackwood, D.J. Friction Stir Processing of Aluminium Alloy AA7075: Microstructure, Surface Chemistry and Corrosion Resistance. Corros. Sci. 2016, 106, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, Z.; Bai, S.; Huang, T.; Wang, J.; Xie, H.; Zeng, D.; Luo, L. Effect of Various Aging Treatment on Thermal Stability of a Novel Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloy for Oil Drilling. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 803, 140490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X. Influence of Trace Ti on the Microstructure, Age Hardening Behavior and Mechanical Properties of an Al–Zn–Mg–Cu–Zr Alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 598, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Saso, T.; Yu, N.; Sokoluk, M.; Yao, G.; Umehara, N.; Li, X. New Study on Tribological Performance of AA7075-TiB2 Nanocomposites. Tribol. Int. 2020, 152, 106565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.N.; Das, S.; Mondal, D.P.; Dixit, G.; Tulasi Devi, S.L. Dry Sliding Wear Maps for AA7010 (Al–Zn–Mg–Cu) Aluminium Matrix Composite. Tribol. Int. 2013, 60, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Song, Y.; Hua, L.; Zhou, P.; Xie, G. Effect of Temperature on Friction and Galling Behavior of 7075 Aluminum Alloy Sheet Based on Ball-on-Plate Sliding Test. Tribol. Int. 2019, 140, 105872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chegini, M.; Shaeri, M.H. Effect of Equal Channel Angular Pressing on the Mechanical and Tribological Behavior of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloy. Mater. Charact. 2018, 140, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhefnawey, M.; Shuai, G.L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, D.T.; Tawfik, M.M.; Li, L. On Achieving Ultra-High Strength and Improved Wear Resistance in Al–Zn–Mg Alloy via ECAP. Tribol. Int. 2021, 163, 107188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Cai, M.; Liu, Q.; He, Y. Effects of Sliding Speed on the Tribological Behavior of AA 7075 Petroleum Casing in Simulated Drilling Environment. Tribol. Int. 2020, 145, 106194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avcu, E. The Influences of ECAP on the Dry Sliding Wear Behaviour of AA7075 Aluminium Alloy. Tribol. Int. 2017, 110, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour, M.; Azarbarmas, M.; Heydari, F.; Hoghoughi, M.; Alidoost, M.; Emamy, M. The Effect of Al–8B Grain Refiner and Heat Treatment Conditions on the Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Dry Sliding Wear Behavior of an Al–12Zn–3Mg–2.5Cu Aluminum Alloy. Mater. Des. 2012, 38, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.N.; Das, S. Effect of Matrix Alloy and Influence of SiC Particle on the Sliding Wear Characteristics of Aluminium Alloy Composites. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 1200–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, H. Characteristics of Friction and Wear of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloy after Application of Ultrasonic Shot Peening Technology. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2021, 423, 127615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Wang, Z.; Yu, H.; Wang, W. Microstructure, Aging Behavior, and Friction and Wear Properties of Ultrafine-Grained 7050 Aluminum Alloy Produced by Cryogenic Temperature Extrusion Machining. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 39, 109344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezende, A.B.; Fonseca, S.T.; Fernandes, F.M.; Miranda, R.S.; Grijalba, F.A.F.; Farina, P.F.S.; Mei, P.R. Wear Behavior of Bainitic and Pearlitic Microstructures from Microalloyed Railway Wheel Steel. Wear 2020, 456–457, 203377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Wang, R.; Fu, H.; Absi, R.; Bennacer, R.; Yang, X.; La, P. Wear Properties of Titanium Microalloying Carbidic Austempered Ductile Iron and Refining Mechanism of TiC on M3C. Wear 2023, 516–517, 204603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akçil, M.; Akça, Y. The Effect of Sc Element Modification on the Corrosion Patterns and Wear Properties of AA5754 Aluminium Alloy. Mater. Lett. 2025, 394, 138472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, D.P.; Li, X.Y.; Tandon, K.N.; Caley, W.F. Dry Sliding Wear Behaviour of Aluminum Alloy 2014 Microalloyed with Sn and Ag. Wear 1998, 222, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, K.; Li, H.; Zhao, Y.; Yin, Z. Wear and Corrosion Resistance of Al1.2CoCrFeNiScx High Entropy Alloys with Scandium Addition. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 27, 8023–8036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, D.; De Andrade, V.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, W.; Wen, S.; Gao, K.; Huang, H.; Chen, S.; Nie, Z. Dry Sliding Wear of Microalloyed Er-Containing Al–10Sn–4Si–1Cu Alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 14828–14840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knipling, K.E.; Dunand, D.C.; Seidman, D.N. Criteria for Developing Castable, Creep-Resistant Aluminum-Based Alloys—A Review. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2006, 97, 246–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.-J.; Li, H.-Y.; Tao, H.-J.; Liu, W.-J. The Precipitation Evolution and Coarsening Resistance of Dilute Al-Zr-Er-Yb (-Sc) Alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2025, 224, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cao, L.; Wu, X.; Lin, X.; Yao, T.; Peng, L. Multi-Alloying Effect of Ti, Mn, Cr, Zr, Er on the Cast Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloys. Mater. Charact. 2023, 201, 112984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, S.; Lai, Y.X.; Xiang, X.M.; He, Y.T.; Wu, C.L.; Chen, J.H. Enhanced Strength of AlErZr Alloys by Tailoring Al3(Er,Zr) Precipitates with Fe-Impurities. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1020, 179452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Mou, S.; Yang, J.; Jin, T.; Nie, Z.; Yin, Z. Effect of Trace Rare Earth Element Er on Al-Zn-Mg Alloy. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2006, 16, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Cao, L.; Tong, X.; Couper, M.J.; Liu, Q. Effect of Trace Er on the Microstructure and Properties of Al–Zn–Mg–Cu–Zr Alloys during Heat Treatments. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 792, 139807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhao, G.; Chen, X.-G. Effects of Homogenization Treatment on Recrystallization Behavior of 7150 Aluminum Sheet during Post-Rolling Annealing. Mater. Charact. 2016, 114, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhou, Q.; Han, M.; Sha, S.; Luo, Y.; Xu, X. Effect of Rare Earth Element Er on the Microstructure and Properties of Highly Alloyed Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr-Ti Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 956, 170248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Wu, X.; Tang, S.; Zhu, Q.; Song, H.; Guo, M.; Cao, L. Investigation on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloys with Various Zn/Mg Ratios. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 85, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Wen, K.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Yan, L.; Yan, H.; Yu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, B. Effect of Zn/Mg Ratio on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of as-Cast Al–Zn–Mg–Cu Alloys and the Phase Transformation during Homogenization. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 3646–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Luo, B.; Bai, Z.; He, C.; Tan, S.; Jiang, G. Effect of Zn/Mg Ratios on Microstructure and Stress Corrosion Cracking of 7005 Alloy. Materials 2019, 12, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jan, J.; Lee, S.; Chen, M.; Lee, S.; Lin, C.; Tzeng, Y. Effect of Homogenization and Zn/Mg Ratio on the Mechanical Properties, Stress Corrosion Cracking Resistance, and Quench Sensitivity of Al–Zn–Mg–2.5Cu (AA7095) Alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2025, 27, 2402281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Lan, Y.; Pan, Q.; Deng, Y. Effect of the Zn/Mg Ratio on Microstructures, Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Performances of Al-Zn-Mg Alloys. Materials 2020, 13, 3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wen, S.; Lu, J.; Mi, Z.; Zeng, X.; Huang, H.; Nie, Z. Microstructural Evolution of New Type Al–Zn–Mg–Cu Alloy with Er and Zr Additions during Homogenization. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2017, 27, 1476–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E8/E8M-24; Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Azarniya, A.; Taheri, A.K.; Taheri, K.K. Recent Advances in Ageing of 7xxx Series Aluminum Alloys: A Physical Metallurgy Perspective. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 781, 945–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Wen, K.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Yan, L.; Yan, H.; Yu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, B. Investigation on Precipitate Behavior and Mechanical Properties of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloys with Various Zn/Mg Ratios. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 33, 5769–5783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Huang, P.; Tian, Y.; Ma, L. Principles of Tribology, 5th ed.; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2018; pp. 271–298. ISBN 978-7-302-50008-7. [Google Scholar]
- Mezlini, S.; Kapsa, P.; Henon, C.; Guillemenet, J. Abrasion of Aluminium Alloy: Effect of Subsurface Hardness and Scratch Interaction Simulation. Wear 2004, 257, 892–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaya, M. Influence of Grain Size on Fatigue Strength of Austenitic Stainless Steel (Investigation of Ultimate Strength Dependency of Fatigue Strength). Int. J. Fatigue 2023, 177, 107947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.W.; Zhang, Z.J.; Hou, J.P.; Gong, B.S.; Wang, H.W.; Zhou, X.H.; Purcek, G.; Sheinerman, A.G.; Zhang, Z.F. Influence of Microstructure Characteristics on the Fatigue Properties of 7075 Aluminum Alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2024, 912, 146976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Jin, J.; Liu, C.; Yang, Y. Study on the Influence Mechanism of Internal Strain on Wide-Temperature Range Tribological Behavior of Ti6Al4V Alloy. Tribol. Int. 2025, 204, 110488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, J.A.; Kailas, S.V. Evolution of Wear Debris Morphology during Dry Sliding of Ti–6Al–4V against SS316L under Ambient and Vacuum Conditions. Wear 2020, 456–457, 203378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, N.P. The Delamination Theory of Wear. Wear 1973, 25, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, N.P. An Overview of the Delamination Theory of Wear. Wear 1977, 44, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.; Alpas, A.T. Wear Mechanism Maps for Metal Matrix Composites. Wear 1997, 212, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Rainforth, W.M.; Jones, H.; Lieblich, M. Dry Wear Behaviour and Its Relation to Microstructure of Novel 6092 Aluminium Alloy–Ni3Al Powder Metallurgy Composite. Wear 2001, 251, 1421–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Liu, Y.; Fu, D.; Jin, B.; Lu, J. Effect of Surface Mechanical Attrition Treatment on Tribological Behavior of the AZ31 Alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavizadeh, K.; Eyre, T.S. Oxidative Wear of Aluminium Alloys. Wear 1982, 79, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, Y.; Du, H.; Xiong, T.; Wang, Y. Evolution Behaviors of Oxides in Severely Plastic Deformed Region of AISI 52100 Steel during Dry Sliding Wear. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2017, 33, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archard, J.F. Surface Topography and Tribology. Tribology 1974, 7, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archard, J.F. Contact and Rubbing of Flat Surfaces. J. Appl. Phys. 1953, 24, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rominiyi, A.L.; Mashinini, P.M.; Ogunbiyi, O. Enhancing Microstructure, Nanomechanical and Anti-Wear Characteristics of Spark Plasma Sintered Ti6Al4V Alloy via Nickel-Silicon Carbide Addition. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2024, 9, 100810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phaneendra, Y.; Mohan Rao, I.; Kumar, P.V.; Santhoshi Kumari, P.; Suresh Babu, K.; Avinash Ben, B.; Dhanunjayarao, B.N.; Swamy Naidu, N.V.; Hemalatha, S. Enhancement of Tribological Properties of AA7075 Aluminum Alloy Using Nano-Silicon Carbide Reinforcement: A Detailed Wear Analysis and Microhardness Study. Mater. Today Proc. 2024, 115, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.; Tieu, A.K.; Lan, X.; Su, L.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Q.; Zhu, H. Effects of Normal Load and Velocity on the Dry Sliding Tribological Behavior of CoCrFeNiMo0.2 High Entropy Alloy. Tribol. Int. 2020, 144, 106116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Alloy | Zn | Mg | Er | Zr | Al | Zn/Mg Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al4Zn2Mg | 3.61 | 2.17 | - | 0.09 | Bal. | 1.66 |
| Al4Zn2Mg0.1Er | 3.80 | 2.13 | 0.08 | 0.10 | Bal. | 1.78 |
| Al4.5Zn1.5Mg | 4.43 | 1.58 | - | 0.10 | Bal. | 2.80 |
| Al4.5Zn1.5Mg0.1Er | 4.47 | 1.60 | 0.09 | 0.09 | Bal. | 2.79 |
| Alloy | YS (MPa) | UTS (MPa) | Elongation (%) | Hardness (HV0.3) | Density (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al4Zn2Mg | 298 ± 10 | 355 ± 6 | 18.7 ± 2.1 | 118 ± 3 | 2.721 |
| Al4Zn2Mg0.1Er | 332 ± 11 | 379 ± 8 | 17.2 ± 1.2 | 140 ± 1 | 2.730 |
| Al4.5Zn1.5Mg | 407 ± 3 | 444 ± 3 | 12.8 ± 0.6 | 135 ± 2 | 2.739 |
| Al4.5Zn1.5Mg0.1Er | 405 ± 1 | 443 ± 2 | 16.7 ± 0.9 | 135 ± 3 | 2.740 |
| Alloy | Mass Wear Loss (mg) | Volume Wear Loss (mm3) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 N | 50 N | 70 N | 30 N | 50 N | 70 N | |
| Al4Zn2Mg | 3.59 ± 0.40 | 4.23 ± 0.45 | 4.97 ± 0.26 | 1.31 ± 0.15 | 1.56 ± 0.16 | 1.83 ± 0.10 |
| Al4Zn2Mg0.1Er | 6.01 ± 0.17 | 4.46 ± 0.20 | 6.86 ± 0.34 | 2.20 ± 0.06 | 1.63 ± 0.07 | 2.51 ± 0.12 |
| Al4.5Zn1.5Mg | 5.94 ± 1.10 | 5.44 ± 0.80 | 7.76 ± 0.31 | 2.17 ± 0.40 | 1.99 ± 0.29 | 2.83 ± 0.11 |
| Al4.5Zn1.5Mg0.1Er | 4.36 ± 0.11 | 4.93 ± 0.19 | 8.51 ± 0.21 | 1.59 ± 0.04 | 1.80 ± 0.07 | 3.11 ± 0.08 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, H.; Wu, X.; Ding, X.; Wen, S.; Hong, L.; Gao, K.; Wei, W.; Rong, L.; Huang, H.; Nie, Z. Effect of Er Microalloying and Zn/Mg Ratio on Dry Sliding Wear Properties of Al-Zn-Mg Alloy. Materials 2025, 18, 3541. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153541
Chen H, Wu X, Ding X, Wen S, Hong L, Gao K, Wei W, Rong L, Huang H, Nie Z. Effect of Er Microalloying and Zn/Mg Ratio on Dry Sliding Wear Properties of Al-Zn-Mg Alloy. Materials. 2025; 18(15):3541. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153541
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Hanyu, Xiaolan Wu, Xuxu Ding, Shengping Wen, Liang Hong, Kunyuan Gao, Wu Wei, Li Rong, Hui Huang, and Zuoren Nie. 2025. "Effect of Er Microalloying and Zn/Mg Ratio on Dry Sliding Wear Properties of Al-Zn-Mg Alloy" Materials 18, no. 15: 3541. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153541
APA StyleChen, H., Wu, X., Ding, X., Wen, S., Hong, L., Gao, K., Wei, W., Rong, L., Huang, H., & Nie, Z. (2025). Effect of Er Microalloying and Zn/Mg Ratio on Dry Sliding Wear Properties of Al-Zn-Mg Alloy. Materials, 18(15), 3541. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153541







