Research on the Size and Distribution of TiN Inclusions in High-Titanium Steel Cast Slabs
Abstract
1. Introduction
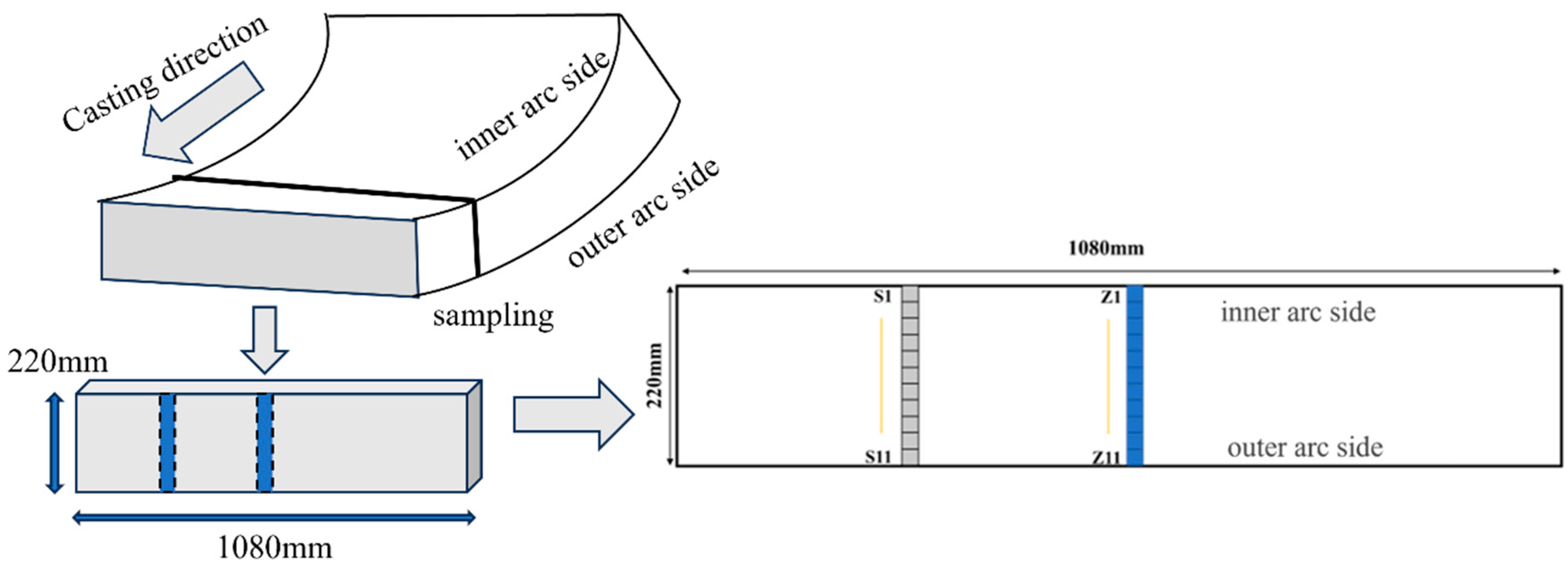
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Analysis
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Inclusion Analysis in Slab
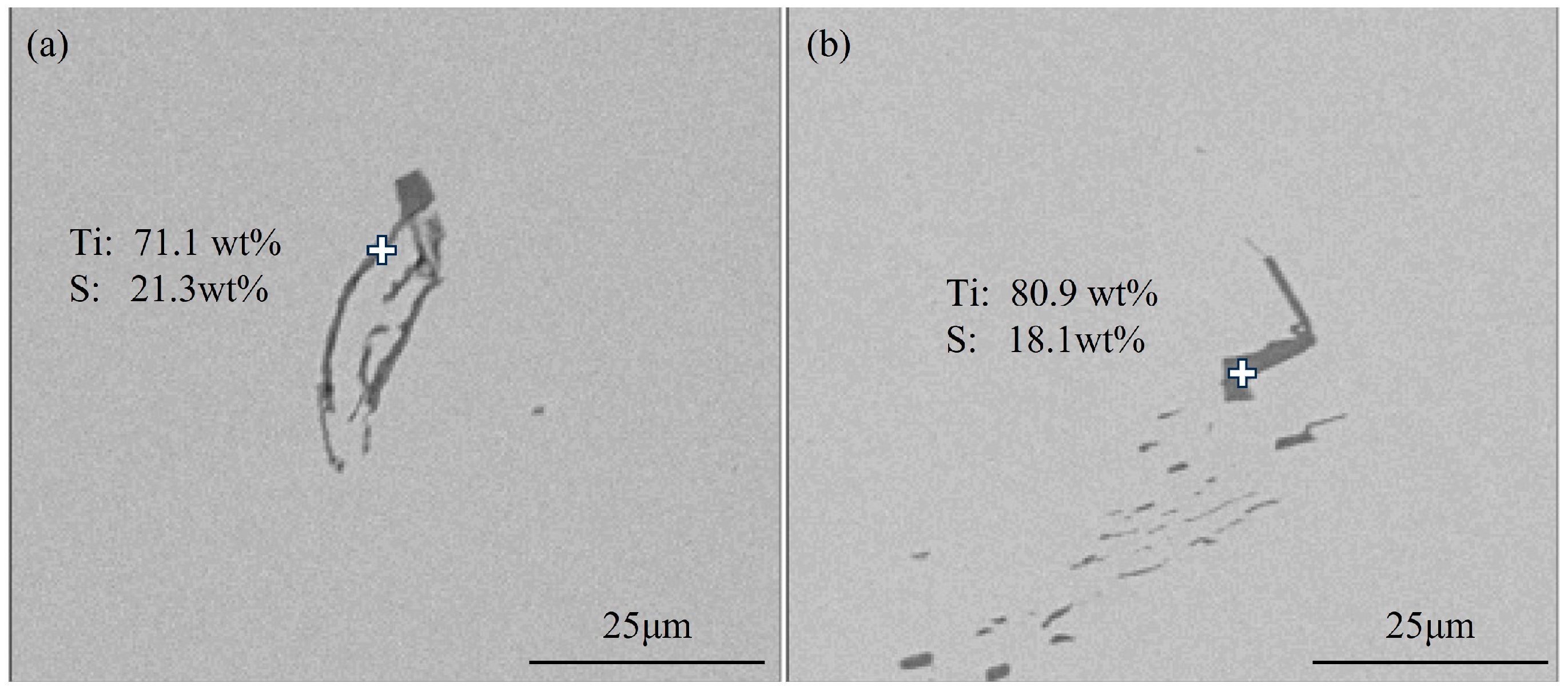
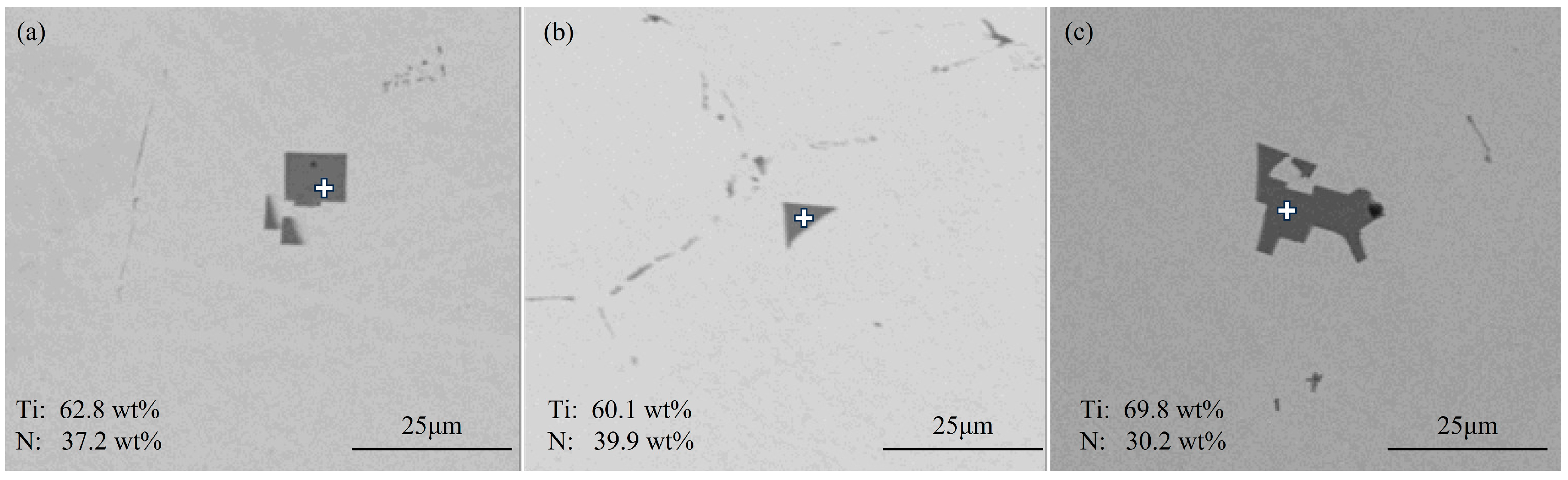
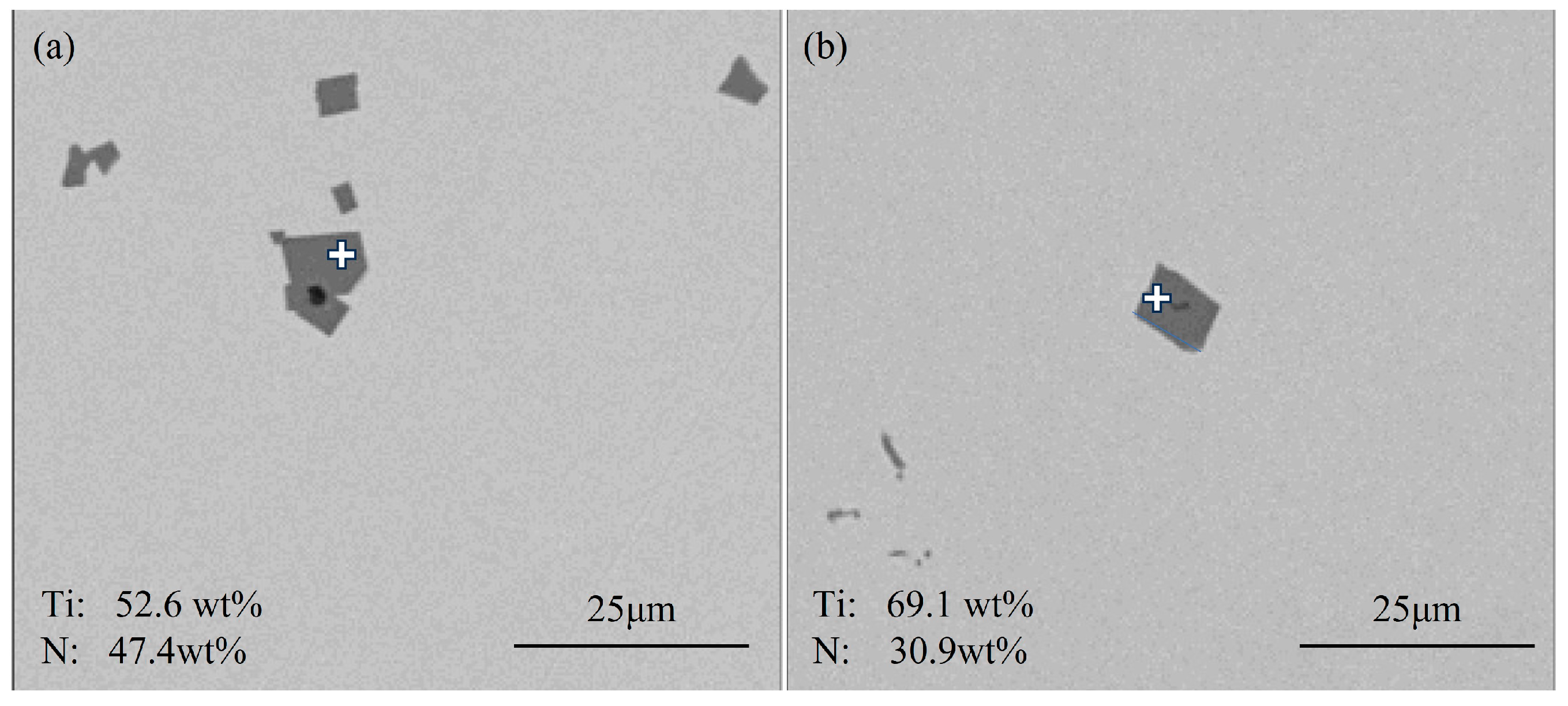
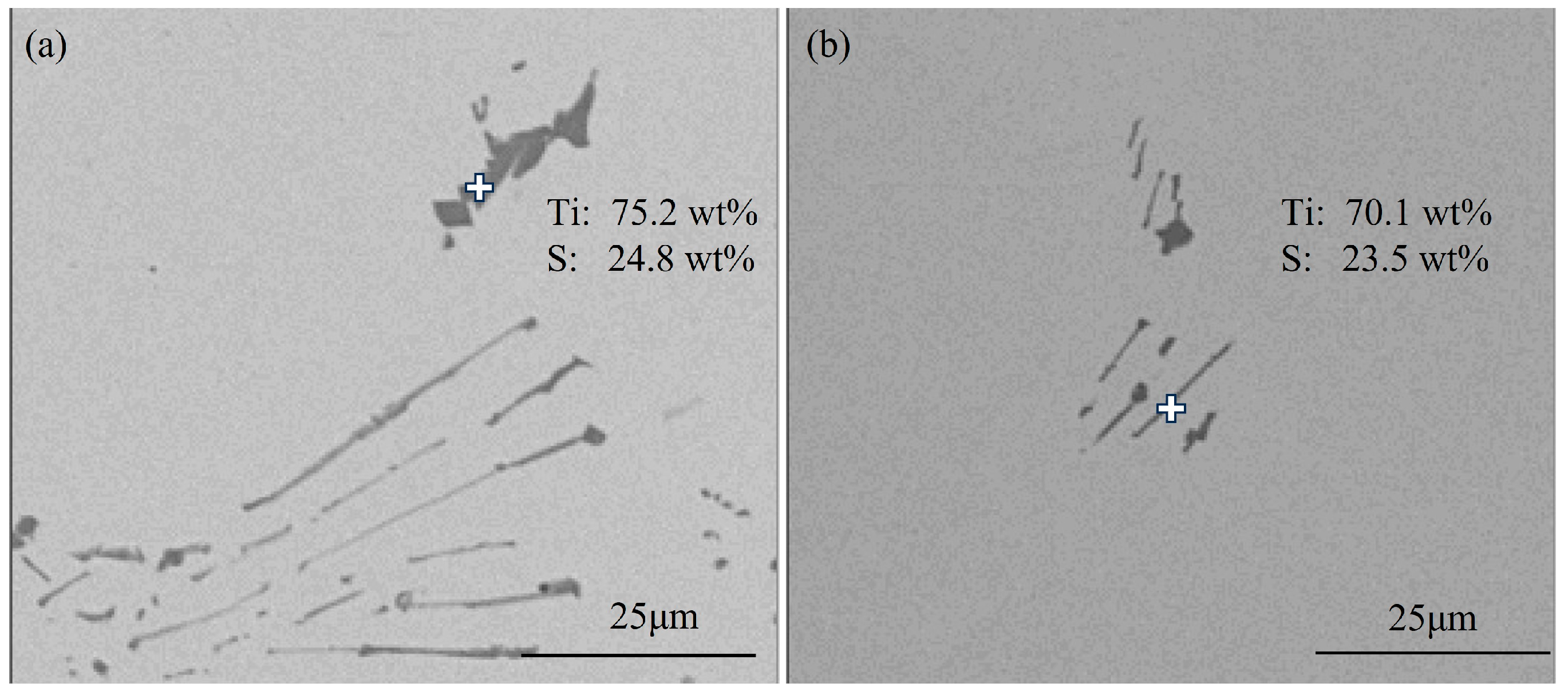
3.1.1. Typical Inclusions in Slab
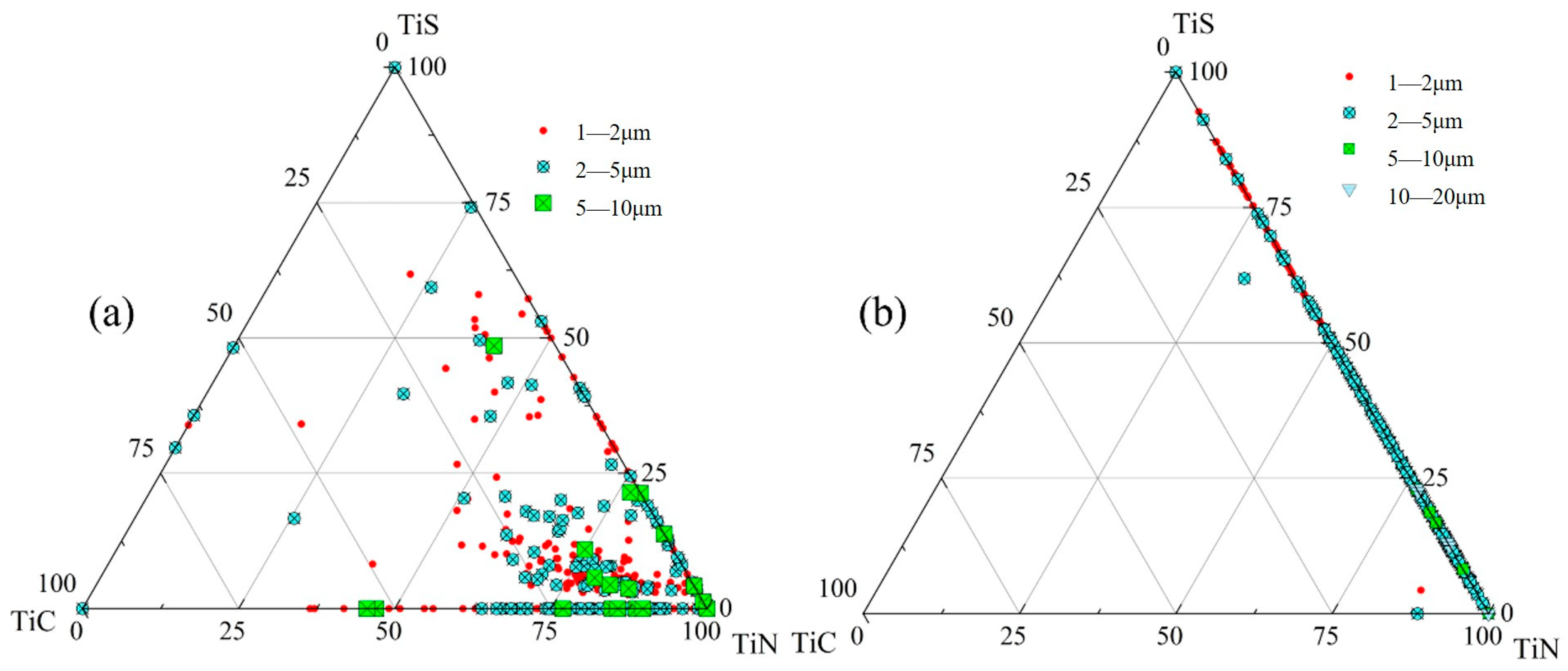
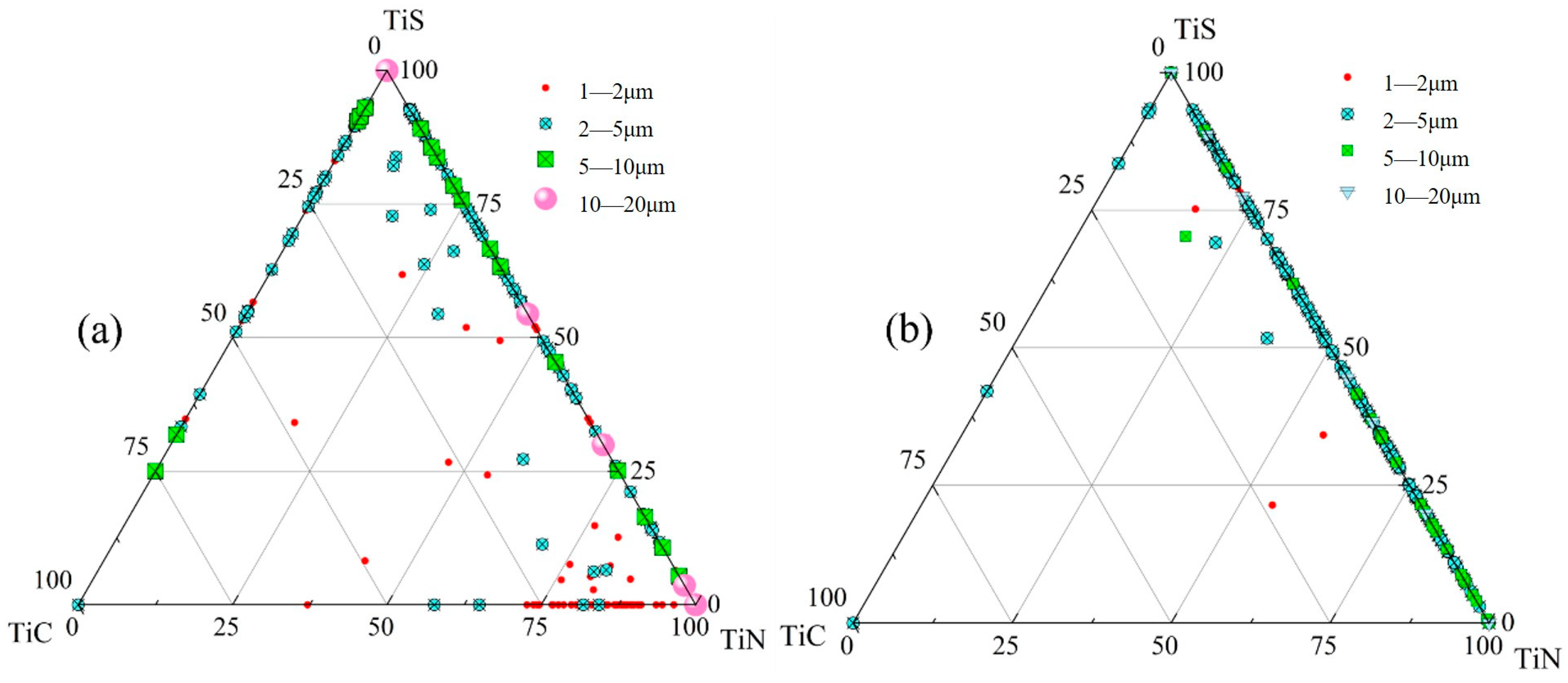
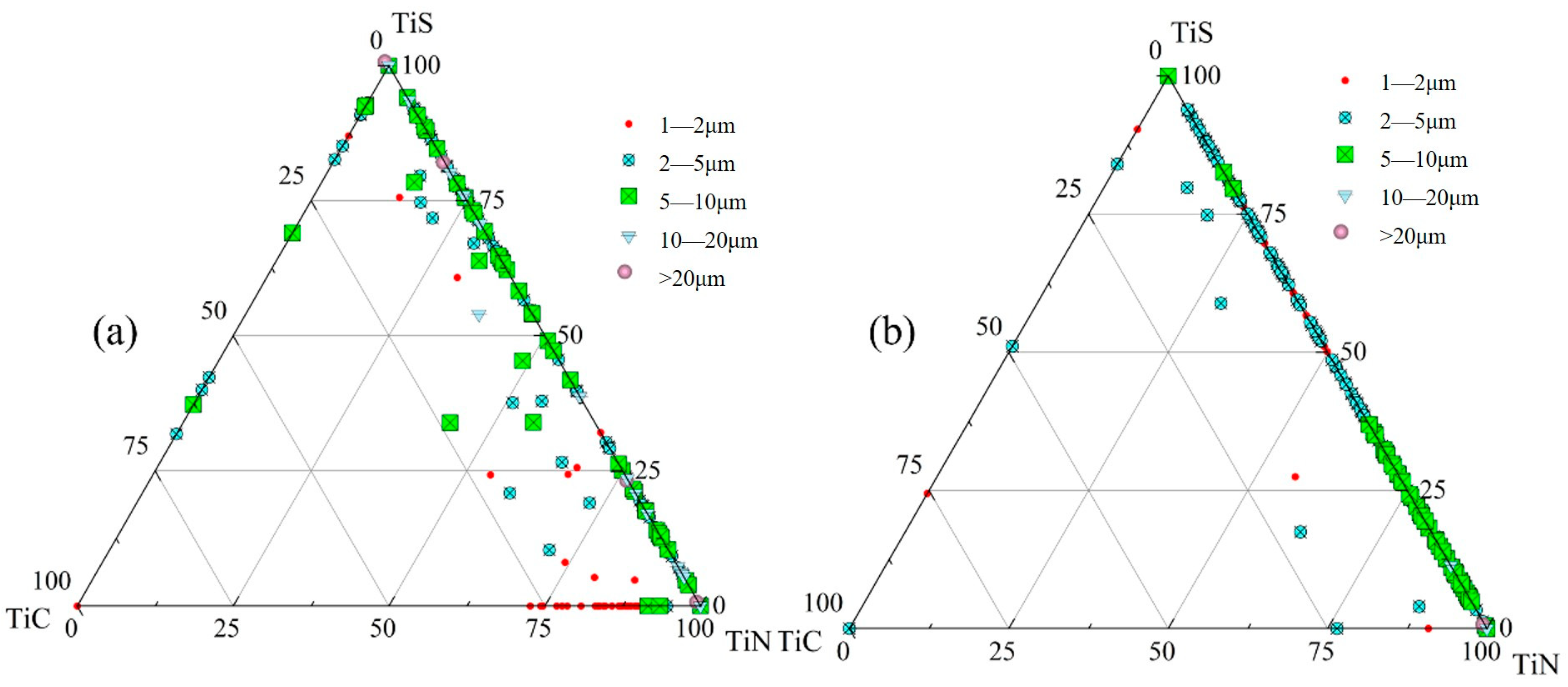
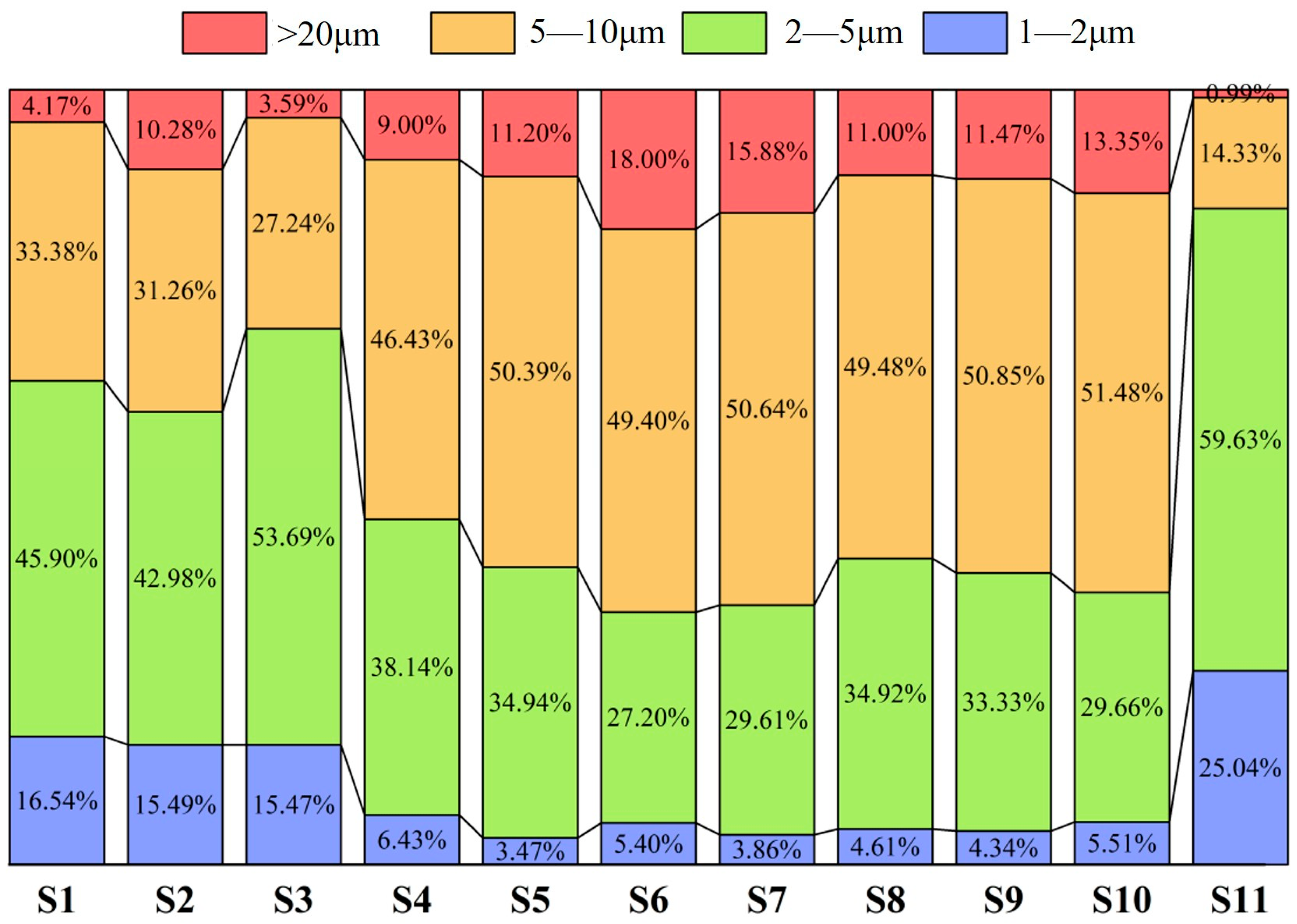
3.1.2. Inclusion Distribution Across Slab Thickness
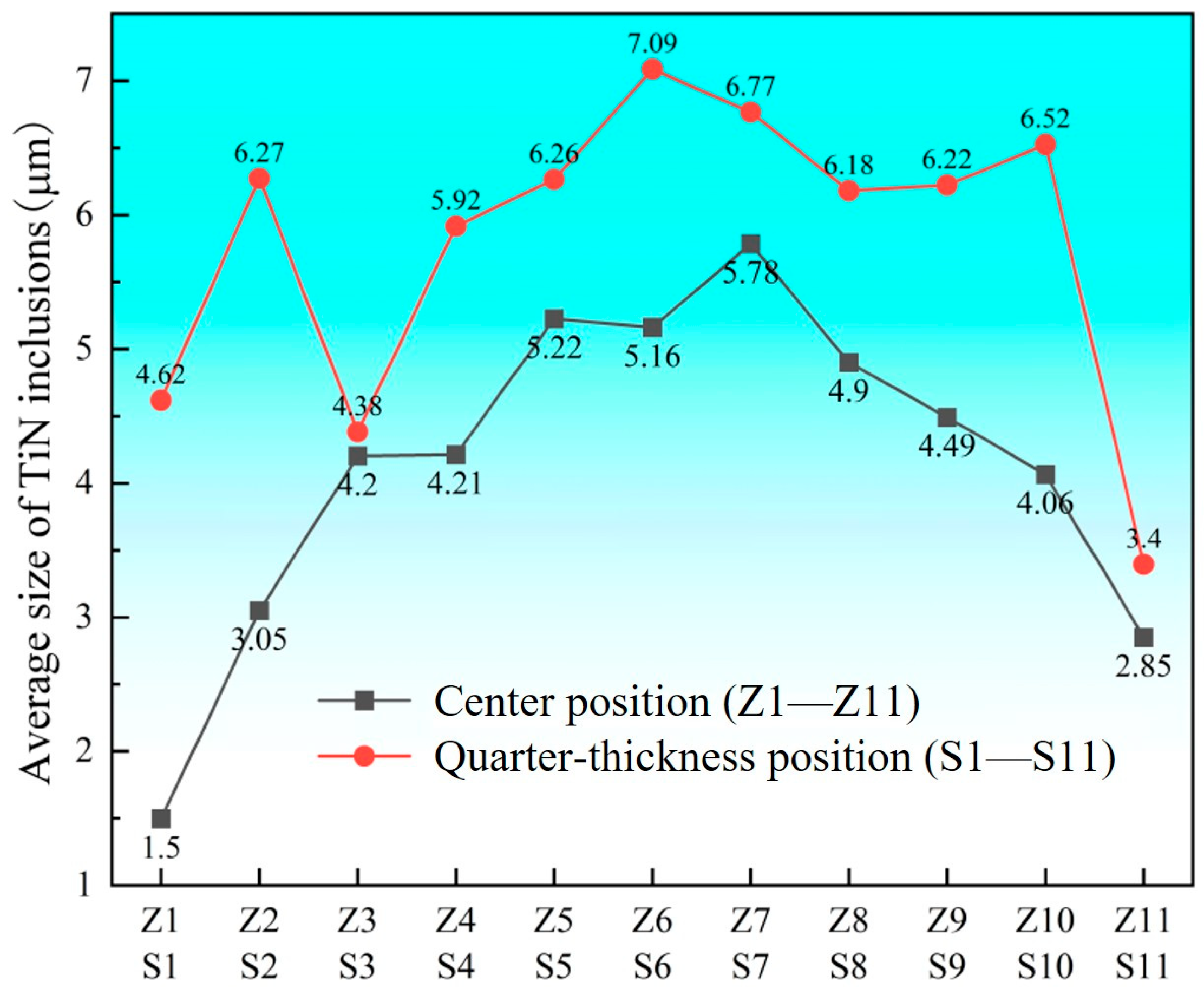
3.2. Size Distribution of TiN Inclusions
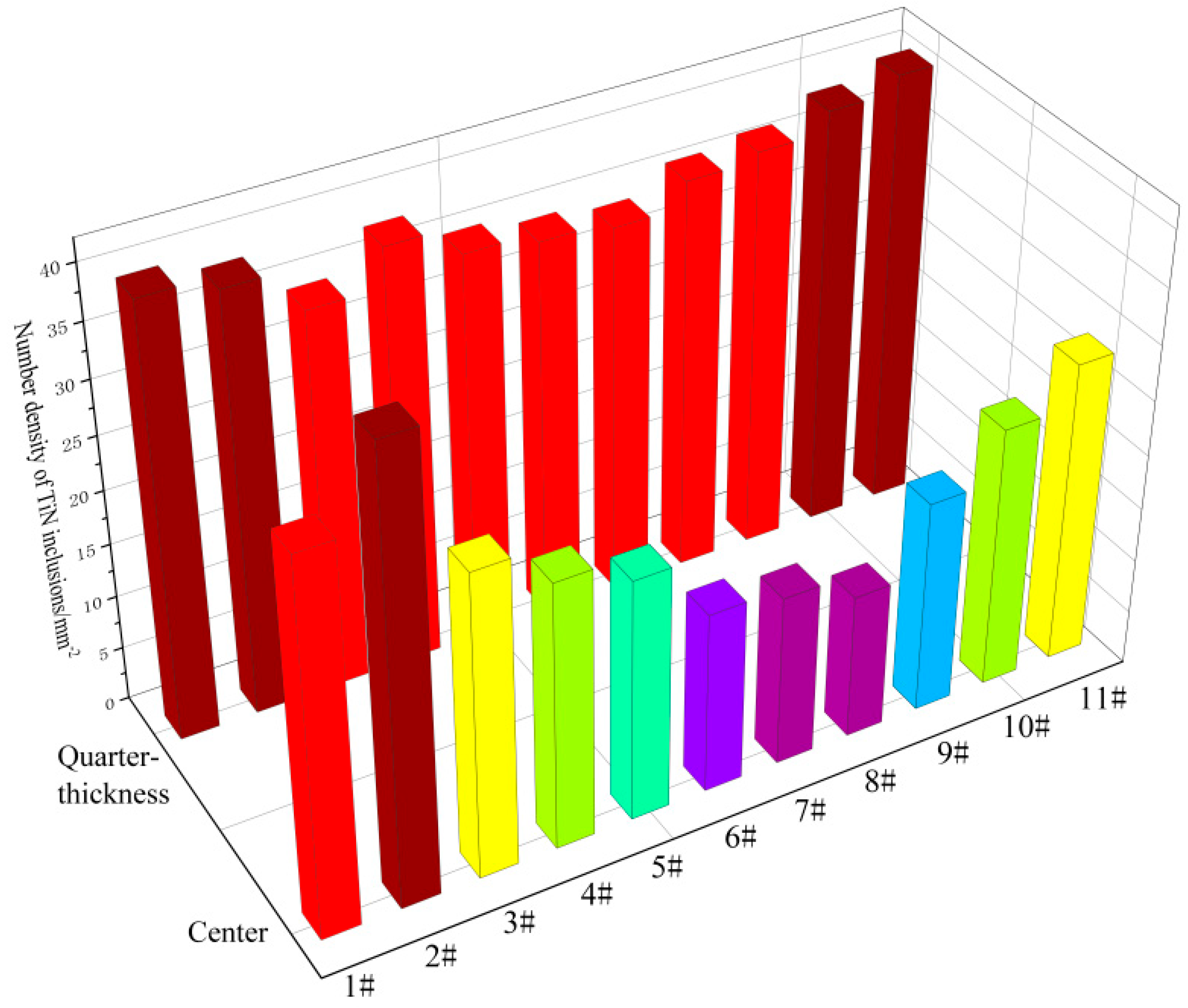
3.3. Number Density of TiN Inclusions
3.4. Calculation of TiN Inclusion Precipitation
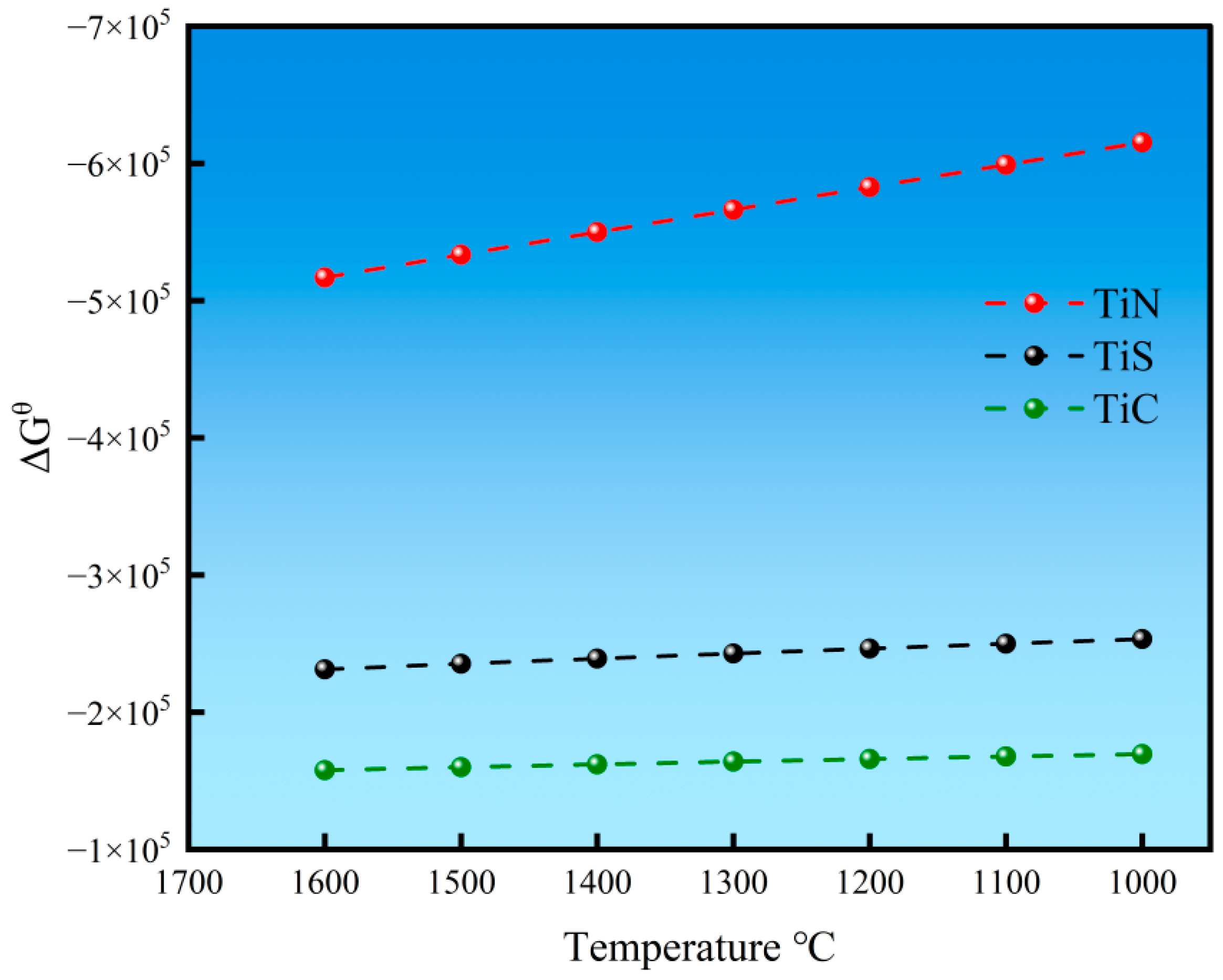
3.4.1. TiN Precipitation Temperature
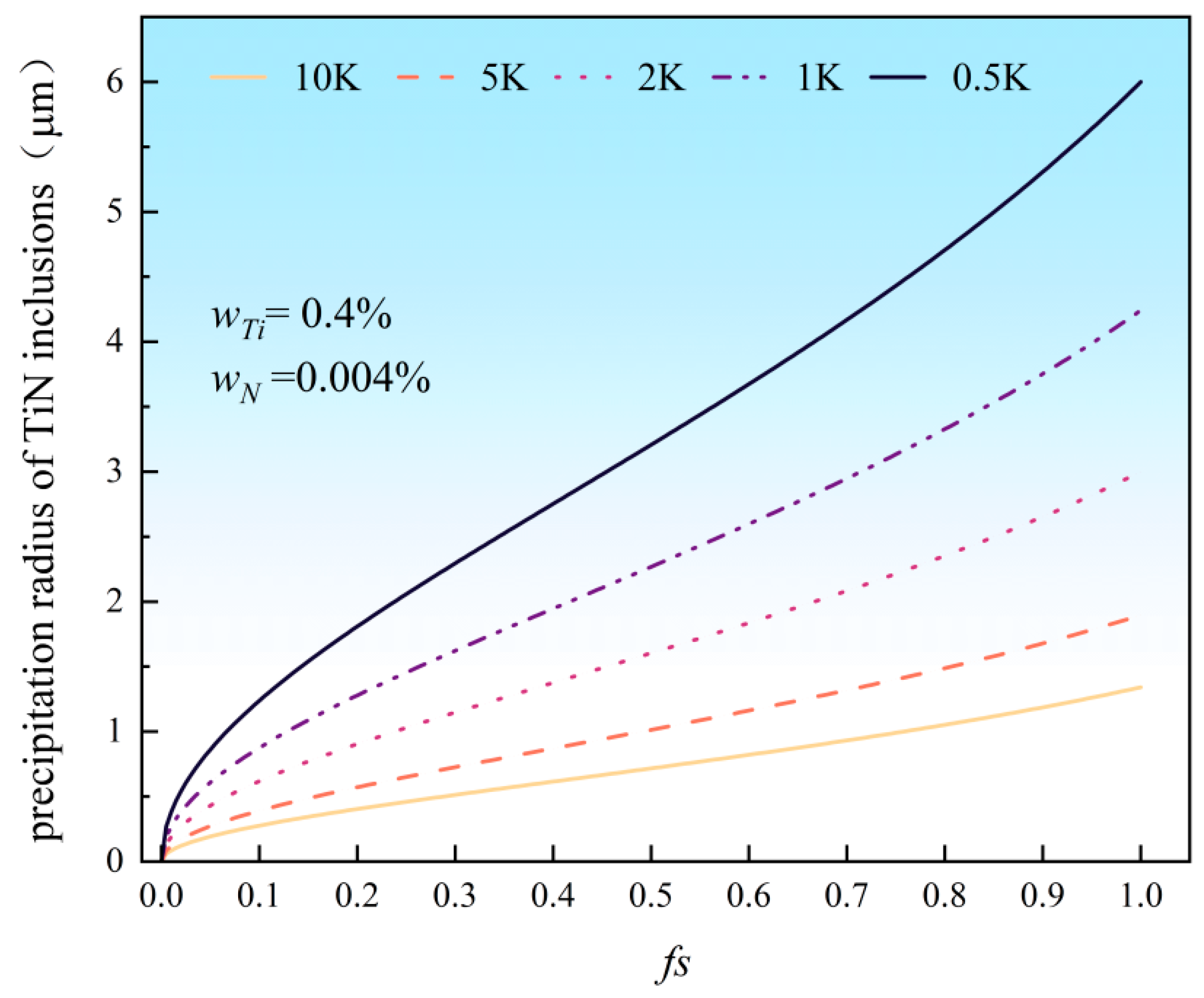
3.4.2. Calculation of TiN Inclusion Precipitation Size
4. Conclusions
- The primary inclusions in high-titanium steel consist of TiN, TiS, TiC and their composite forms. At the quarter-thickness position of the slab, inclusions demonstrate distinct size–composition correlations: small-sized inclusions (1–2 μm) are predominantly Ti (C,N) and TiN + TiS; medium-sized inclusions (2–10 μm) and large inclusions (>10 μm) are mainly TiS, TiN and their composite phases. Edge samples show TiN-rich characteristics, whereas interior and central regions exhibit increasing TiS content. The overall pattern reveals increasing TiN content with inclusion size growth. The inclusions in the central region of the slab are predominantly composed of TiN, TiS, and their composite phase TiN + TiS. The inclusion sizes are mainly distributed in the 2–10 μm range, exhibiting a distinct size–composition correlation: larger inclusions (greater than 5 μm) show higher TiN content, while the 2–5 μm TiS-TiN inclusions contain a relatively higher TiS composition. This size-dependent compositional variation demonstrates a progressive enrichment of TiN with increasing inclusion size.
- At the quarter-thickness position of the slab, TiN inclusions primarily range between 2 and 10 μm, with a small number of larger inclusions exceeding 10 μm. In contrast, at the slab center, TiN inclusions are mainly 1–5 μm in size, with no large-sized TiN inclusions observed. Due to cooling rate effects, samples from the edge regions at both positions exhibit a higher proportion of smaller TiN inclusions, whereas interior samples show a predominance of larger-sized TiN inclusions. Within the interior regions of the steel slab, a substantial proportion of large-sized TiN inclusions persist, which pose significant detrimental effects on material performance. To address this critical issue, process optimization strategies such as enhanced cooling rates or reduced titanium content must be implemented to effectively suppress the formation of these deleterious large-scale TiN precipitates.
- The number density of TiN inclusions at the center position of the slab is significantly lower than that at the quarter-thickness position. At both the quarter-thickness and center positions of the slab, the number density of TiN inclusions exhibits a gradual decrease from the edge to the interior regions in the samples. At the quarter-thickness of the slab, the highest number density is 40.3 mm−2 and the lowest number density is 34.2 mm−2. At the center of the slab, the highest number density is 41.3 mm−2 and the lowest number density is 13.4 mm−2.
- The calculation results demonstrate that in high-titanium steel containing 0.4% Ti, TiN inclusions begin to precipitate in the liquid phase; reducing the titanium content in the steel can effectively delay the precipitation of TiN. During solidification, TiN continuously precipitates with progressive size increases as solidification proceeds. Notably, the size of TiN inclusions decreases with increasing cooling rates. When the cooling rate is 0.5 K/s, the maximum size of TiN inclusions reaches 6 μm, whereas at a higher cooling rate of 10 K/s, the maximum size decreases significantly to 1.3 μm.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mao, X.P.; Huo, X.D.; Sun, X.J.; Chai, Z. Strengthening mechanisms of a new 700 MPa hot rolled Ti-microalloyed steel produced by compact strip production. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2010, 210, 1660–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Sun, Y.H.; Yang, Y.D.; Bai, X.F.; Barati, M.; Mclean, A. Formation of inclusions in Ti-stabilized 17Cr austenitic stainless steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2016, 47, 3274–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitsev, A.I.; Baklanova, O.N.; Koldaev, A.V.; Grishin, A.V.; Rodionova, I.G.; Yashchuk, S.V.; Lyasotskii, I.V. Microstructure and property formation for high-strength low-carbon steels microalloyed with titanium and molybdenum. Metallurgist 2016, 60, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Gan, X.L.; Ma, G.J.; Luo, F.; Zou, H. The development of Ti-alloyed high strength microalloy steel. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 2891–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Mao, W.M.; Chen, Y.J.; Jing, J.; Cheng, M. Effect of Ti content on grain size and mechanical properties of UNS S44100 ferritic stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 677, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.W.; Li, L.J.; Gao, J.X.; Huo, X.D. Precipitation strengthening of titanium microalloyed high-strength steel plates with isothermal treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 657, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, S.F.; Chapa, M.; Valles, P.; Quispe, A.; Vega, M.I. Influence of Ti and N contents on austenite grain control and precipitate size in structural steels. ISIJ Int. 1999, 39, 930–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunduz, S.; Erden, M.A.; Karabulut, H.; Turkmen, M. The effect of Vanadium and Titanium on mechanical properties of microalloyed PM steel. Powder Metall. Met. Ceram. 2016, 55, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H. Effect of inclusions on the solidification structures of ferritic stainless steel: Computational and experimental study of inclusion evolution. Calphad 2011, 35, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.J.; Li, L.J.; Peng, Z.W.; Huo, X.D.; Sun, H.B. On the correlation among continuous cooling transformations, interphase precipitation and strengthening mechanism in Ti-microalloyed steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 10, 580–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, T.R.; Wang, W.L.; Kang, J.B.; Luo, S.; Zhu, M.Y. Precipitation behavior of TiN in solidification of 20CrMnTi under continuous casting conditions. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 3608–3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.W.; Qiu, W.X.; Nie, Q.Q.; Wu, Y.C. Precipitation of TiN during solidification of AISI 439 stainless steel. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 699, 938–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, L.T.; Long, M.J.; Zhang, H.D.; Chen, D.F.; Liu, S.; Wang, Q.Z.; Duan, H.M. Study on the precipitation and coarsening of TiN inclusions in Ti-microalloyed steel by a modified coupling model. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 5499–5514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, M.T.; Speer, J.G.; Matlock, D.K. Titanium nitride precipitation behavior in thin-slab cast high-strength low-alloy steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2002, 33, 3099–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.W.; Song, S.W.; Seo, S.J.; Hong, S.G.; Lee, C.S. Development of Ti and Mo micro-alloyed hot-rolled high strength sheet steel by controlling thermomechanical controlled processing schedule. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 565, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Q.F.; Visuri, V.V.; Alatarvas, T.; Fabritius, T. Model for inclusion precipitation kinetics during solidification of steel applications in MnS and TiN inclusions. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2020, 51, 2905–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelic, S.K.; Loder, D.; Reip, T.; Ardehali Barani, A.; Bernhard, C. Characterization of TiN, TiC and Ti(C,N) in titanium-alloyed ferritic chromium steels focusing on the significance of different particle morphologies. Mater. Charact. 2015, 100, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, X.H.; Gong, Z.X.; Jiang, M.; Wang, G.C.; Huang, F.X. Precipitation thermodynamics analysis and control of titanium nitride inclusions in extra-low oxygen wheel steel. Chin. J. Eng. 2010, 32, 1138–1143. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, W.; Shan, Y.Y.; Yang, K. Influence of TiN inclusions on the cleavage fracture behavior of low-carbon microalloyed steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2007, 38, 1211–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.C.; Zhu, J.; Di, L.; Tong, F.S.; Liu, D.L.; Wang, Y.L. Study on the precipitation behavior of TiN in the microalloyed steels. Acta Metall. Sin. 2000, 36, 801. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.Y.; Wang, H.L.; Zheng, J.Q.; Li, H.Y.; Zheng, X.Y. Investigation of Ti inclusions in wire cord steel. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2011, 38, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Strangwood, M.; Davis, C.L. Effect of TiN particles and grain size on the charpy impact transition temperature in steels. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2012, 28, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capurro, C.; Cicutti, C. Analysis of titanium nitrides precipitated during medium carbon steels solidification. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2018, 7, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.L.; Du, S.L. Precipitation behaviour and control of TiN inclusions in rail steels. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2016, 45, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.J.; Bao, Y.P.; Zhao, L.H.; Wang, M. Control of the precipitation of TiN inclusions in gear steels. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2014, 21, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Shan, Y.Y.; Yang, K. Effect of TiN inclusions on the impact toughness of low-carbon microalloyed steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2006, 37, 2147–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.R.; Wang, G.C.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Q. Precipitation behaviors of TiN inclusion in GCr15 bearing steel billet. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2018, 49, 1149–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.M.; Song, S.Q.; Xue, Z.L.; Zietsman, J.; Qi, J.H.; Deng, Z.X. Formation of TiN Inclusions During Solidification of Titanium Micro-Alloyed Steel: Modeling With ChemAppPy. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2023, 54, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.j.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, L.F. Distribution of TiN inclusions in Ti-stabilized ultra-pure ferrite stainless steel slab. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2019, 26, 962–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, G.R.; Song, S.Q.; Nyembwe, A.; Xue, Z.L.; Qi, J.H.; Deng, Z.X. TiN inclusions distribution in the composite cross section of Titanium Micro-alloyed Steel slab: Thermo-chemical modeling and automatic statistic analysis. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 5383–5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Xing, L.D.; Li, X.; Bao, Y.P.; Wang, M. Study on Inclusions Distribution Across the Thickness of Enameled Steel Slabs. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2024, 55, 4432–4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Wang, M.; Guo, J.L.; Wang, H.; Zhi, J.G.; Bao, Y.P. Extraction, Distribution, and Precipitation Mechanism of TiN–MnS Complex Inclusions in Al-Killed Titanium Alloyed Interstitial Free Steel. Met. Mater. Int. 2021, 27, 1306–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qu, T.Q.; Liang, T.; Li, X.L.; Wang, D.Y.; Fan, L.; Zhang, Z.X.; Yang, Z.H. A new mathematical model for investigating solidification, solute transportation, and TiN precipitation in a micro-alloy steel containing Ti. China Foundry 2025, 22, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Matsuura, H.; Tsukihashi, F. Effect of Non-metallic Inclusions in Fe-Al-Ti-O-N-S Alloy on Grain Size. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2016, 47, 1851–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Matsuura, H.; Tsukihashi, F. Evolution of TiS and TiN in Fe-40 MassPctNi Austenitic Alloy During Heating at 1273 K (1000 °C). Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2019, 50, 2993–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, P.; Shang, D.; Wang, G.; Xiao, Y.; Cao, L. Precipitation of TiS in Al–Ti Simultaneously Deoxidized Steel. Steel Res. Int. 2021, 92, 2000614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimahashi, M.; Muto, I.; Sugawara, Y.; Hara, N. The Role of Oxide Films on TiS and Ti4C2S2 Inclusions in the Pitting Corrosion Resistance of Stainless Steels. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2013, 160, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, B.; Matway, R.; Fruehan, R.J. Thermodynamics of inclusion formation in Fe-Cr-Ti-N alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 1995, 26, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PAK, J.J.; Jeong, Y.S.; Hong, I.K.; Cha, W.Y.; Kim, D.S.; Lee, Y.Y. Thermodynamics of TiN Formation in Fe-Cr Melts. ISIJ Int. 2005, 4, 1106–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.Q.; Li, Y.; Lin, W.M.; Che, J.L.; Zhou, F.; Tan, Y.F.; Li, D.L.; Dang, J.; Chen, C. Assessment of Inclusion Removal Ability in Refining Slags Containing Ce2O3. Crystals 2023, 13, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; Ren, R.J.; Xue, Z.X.; Wang, H.Z.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Wang, J.X.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Mu, W.Z. Ferrite formation and decomposition in 316H austenitic stainless steel electro slag remelting ingot for nuclear power applications. Mater. Charact. 2024, 218, 114581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; Yang, X.Y.; Zhang, Z.R.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, L.; Mu, W.Z. Solidification modes and delta-ferrite of two types 316L stainless steels: A combination of as-cast microstructure and HT-CLSM research. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2025, 32, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xue, Z.; Ban, X.; Hu, C.; Li, H.; Tian, J.; Mu, W. Effect of Nickel Content and Cooling Rate on the Microstructure of as Cast 316 Stainless Steels. Crystals 2025, 15, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Element | C | N | Si | Mn | S | P | Mo | Ti | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content | 0.18 | 0.004 | 0.22 | 1.3 | 0.015 | 0.02 | 0.22 | 0.40 | 0.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Guo, Z.; Sun, Y. Research on the Size and Distribution of TiN Inclusions in High-Titanium Steel Cast Slabs. Materials 2025, 18, 3527. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153527
Zhang M, Li X, Guo Z, Sun Y. Research on the Size and Distribution of TiN Inclusions in High-Titanium Steel Cast Slabs. Materials. 2025; 18(15):3527. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153527
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Min, Xiangyu Li, Zhijie Guo, and Yanhui Sun. 2025. "Research on the Size and Distribution of TiN Inclusions in High-Titanium Steel Cast Slabs" Materials 18, no. 15: 3527. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153527
APA StyleZhang, M., Li, X., Guo, Z., & Sun, Y. (2025). Research on the Size and Distribution of TiN Inclusions in High-Titanium Steel Cast Slabs. Materials, 18(15), 3527. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153527





