Study of the Influence of Gas Tungsten Arc (GTA) Welding on the Microstructure and Properties of Mg–Al–RE-Type Magnesium Alloys
Highlights
- Two new Mg-Al-RE-type alloys (with 3 and 5 wt% of RE—rare-earth elements) were successfully GTA welded.
- The chemical composition of the alloys influenced the solidification range and prevented the formation a partially melted zone.
- The DAS parameter in the fusion zone for both the alloys was about 75% lower than for the base metal.
- The GTA welding process caused an increase in microhardness by about 21% in comparison to the base metal for both the investigated alloys.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, X.; Jahazi, M.; Immarigeon, J.P.; Wallace, W. A review of laser welding techniques for magnesium alloys. J. Mater. Proc. Tech. 2006, 171, 188–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abderrazak, K.; Kriaa, W.; Salem, W.B.; Mhiri, H.; Lepalec, G.; Autic, M. Numerical and experimental studies of molten pool formation during an interaction of a pulse laser (Nd:YAG) with a magnesium alloy. Opt. Laser Technol. 2009, 41, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, Y.; Sun, G.P.; Wang, H.-Y.; Jia, S.Q.; Jia, S.S. Laser (Nd:YAG) cladding of AZ91D magnesium alloys with Al + Si + Al2O3. J. Alloys Compd. 2006, 407, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Shen, J.; Xie, W.; Wang, L.; Wang, D.; Min, D. Abnormal distribution of microhardness in tungsten inert gas arc butt-welded AZ61 magnesium alloy plates. Mater. Charact. 2010, 61, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuPoint, J.N. On optimization of the powder plasma arc surfacing process. Metal. Mater. Trans. B 1998, 29, 932–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Y.J.; Chen, Z.H.; Gong, X.S.; Yu, Z.H. Effects of heat input on microstructure and tensile properties of laser welded magnesium alloy AZ31. Mater. Charact. 2008, 59, 1491–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Li, L.; Liu, Z. CO2 and diode laser welding of AZ31 magnesium alloy. App. Sur. Sci. 2005, 247, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.L.; Zhou, G.; Yuan, S.Q. Study on hybrid heat source overlap welding of magnesium alloy AZ31B. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 499, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Jahazi, M. Effect of welding speed on the quality of friction stir welded butt joints of a magnesium alloy. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 2033–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.M.; Ma, Z.Y.; Geng, L.; Chen, R.S. Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of friction stir welded Mg–Zn–Y–Zr alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 471, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.M.; Chen, D.L.; Bhole, S.D.; Cab, X.; Powidajko, E.; Weckman, D.C.; Zhou, Y. Tensile properties and strain-hardening behavior of double-sided arc welded and friction stir welded AZ31B magnesium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 2951–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.S.; Hwan, S.; Park, C.; Michiuchi, M.; Kokawa, H. Constitutional liquation during dissimilar friction stir welding of Al and Mg alloys. Scripta Mater. 2004, 50, 1233–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, D.C.; Chai, X.; Tang, X.; Kou, S. Liquation cracking in arc and friction-stir welding of Mg-Zn Alloys. Matall. Mater. Trans. A 2015, 46, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.-S.; Liu, L.-M.; Song, G. Infrared temperature measurement and interference analysis alloys in hybrid laser-TIG welding process. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 447, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, D.; Shen, J.; Lai, S.; Chen, J. Effect of heat input on the microstructure and mechanical properties of tungsten inert gas arc butt-welded AZ61 magnesium alloy plates. Mater. Charact. 2009, 60, 1583–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, C.-T.; Chao, C.-G.; Liu, T.-F.; Wang, C.-C. A study of weldability and fracture modes in electron beam weldments of AZ series magnesium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 435–436, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Liu, J. Microstructural evolution in AZ91D magnesium alloy during electron beam welding. Vacuum 2011, 85, 1004–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, S.; Ravi Bharath, R.; Atrens, A.; Srinivasan, P.B. Fusion Welding of Magnesium Alloys: Process Variants, Metallurgical Challenges, and Structure–Property Relationships—A Critical Review. JMEP 2025, 34, 9247–9280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; You, G.; Long, S.; Pan, F. Abnormal macropore formation during double-sided gas tungsten arc welding of magnesium AZ91D alloy. Mater. Charact. 2008, 59, 1059–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Dong, C. Gas tungsten-arc filler welding of AZ31 magnesium alloy. Mater. Letters 2006, 60, 2194–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzelecka, M.; Iwaszko, J.; Malik, M.; Tomczyński, S. Surface modification of the AZ91 magnesium alloy. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2015, 15, 854–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenbin, D.; Haiyan, J.; Xiaoqin, Z.; Dehui, L.; Shoushan, Y. Microstructure and mechanical properties of GTA surface modified composite layer on magnesium alloy AZ31 with SiCP. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 429, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winzer, N.; Xu, P.; Bender, S.; Gross, T.; Unger, W.E.S.; Cross, C.E. Stress corrosion cracking of gas-tungsten arc welds in continuous-cast AZ31Mg alloy sheet. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 1950–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, A.; Munitz, A. Partially melted zone microstructural characterization from gas tungsten-arc bead on plate welds of magnesium AZ91 alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Letters 1999, 18, 853–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Yamamoto, N.; Nakata, K. Gas tungsten arc welding of fine-grained AZ31B magnesium alloys made by powder metallurgy. Mater. Des. 2014, 56, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braszczyńska-Malik, K.N.; Mróz, M. Gas-tungsten arc welding of AZ91 magnesium alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 9951–9958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marya, M.; Edwords, G.R.; Liu, S. An investigation on the effects of gases in GTA welding of a wrought AZ80 magnesium alloy. Weld. J. July 2004, 83, 203-S. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, T.; Chen, Z.W.; Gao, W. Microstructure formation in partially melted zone during gas tungsten arc welding of AZ91 Mg cast alloy. Mater. Charact. 2008, 59, 1550–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munitz, A.; Cotler, C.; Stern, A.; Kohn, G. Mechanical properties and microstructure of gas tungsten arc welded magnesium AZ91D plates. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 302, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Hamu, G.; Eliezer, D.; Cross, C.E.; Böllinghaus, T. The relation between microstructure and corrosion behavior of GTA welded AZ31B magnesium sheet. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 452–453, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Le, Q.; Shi, Y.; Liao, Q.; Wang, T.; Zou, Q.; Aranas, C., Jr. Enhencement of mechanical properties of GTAW joints for AZ63 magnesium Alloys by post weld hat treatment. J. Mater. Sci. Techn. 2024, 169, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braszczyńska-Malik, K.N. Precipitates of α-Mg17Al12 phase in AZ91 alloy. In Magnesium Alloys—Design, Processing and Properties; Czerwinski, F., Ed.; INTECH Open Access Publisher: London, UK, 2011; Chapter 5; pp. 95–112. [Google Scholar]
- Dieringa, H.; Hort, N.; Kainer, K.U. Investigation of minimum creep rates and stress exponents calculated from tensile and compressive creep data of magnesium alloy AE42. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 510–511, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braszczyńska-Malik, K.N.; Grzybowska, A. Microstructure of Mg-5Al-0.4Mn-xRE (x = 3 and 5 wt.%) alloys in as-cast conditions and after annealing. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 663, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargusch, M.S.; Zhu, S.M.; Nie, J.F.; Dunlop, G.L. Microstructural analysis of the improved creep resistance of a die-cast magnesium–aluminium–rare earth alloy by strontium additions. Scr. Mater. 2009, 60, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braszczyńska-Malik, K.N.; Grzybowska, A. Influence of phase composition on microstructure and properties of Mg-5Al-0.4Mn-xRE (x = 0, 3 and 5 wt.%) alloys. Mater. Charact. 2016, 115, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nami, B.; Razavi, H.; Mirdamadi, S.; Shabestari, S.G.; Miresmaeili, S.M. Effect of Ca and rare earth elements on impression creep properties of AZ91 magnesium alloy. Metal. Mater. Trans. A 2010, 41, 1973–1982. [Google Scholar]
- Braszczyńska-Malik, K.N. Types of component interfaces in metal matrix composites on the example of magnesium matrix composites. Materials 2021, 14, 5182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braszczyńska-Malik, K.N.; Przełożyńska, E. The influence of Ti particles on microstructure and mechanical properties Of Mg-5Al-5RE matrix alloy composite. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 728, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braszczyńska, K.N. Contribution of SiC particles to the formation of the structure of Mg-3 wt.% RE cast composites. Z. Für Met. 2003, 94, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Du, W.; Liu, K.; Wang, Z.; Li, S. Microstructure, tensile properties and creep behaviors of as-cast Mg–2Al–1Zn–xGd (x = 1, 2, 3, and 4 wt.%) alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 522, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.; Han, E.; Liu, L. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-3Al-1Zn-xRE alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2009, 25, 356–360. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Leng, Z.; Zhang, M.; Meng, J.; Wu, R. Microstructure and mechanical properties of heat-resistant HPDC Mg-4Al-based alloys containing cheap misch metal. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 2670–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Ning, Z. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-4Al-4Nd-0.5Zn-0.3Mn alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 515, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braszczyńska-Malik, K.N. Some mechanical properties of experimental Mg-Al-RE-Mn magnesium alloys. Arch. Foundry Eng. 2014, 14, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, K.; Fang, D.; Qiu, X.; Tang, D.; Meng, J. Microstructure, tensile properties and creep behavior of high-pressure die-cast Mg-4Al-4RE-0.4Mn (RE = La, Ce) alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 2046–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.D.; Dieringa, H.; Hort, N.; Maier, P.; Kainer, K.U.; Liu, Y.L. Evolution of microstructure and hardness of AE42 alloy after heat treatment. J. Alloys Comp. 2008, 463, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Dong, X.; Xia, M.; Zhu, X.; Ji, G.; Yang, H.; Wang, B.; Nyberg, E.A.; Ji, S. Development of high thermal conductivity, enhanced strength and cost-effective die-cast Mg alloy compared with AE44 alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 22, 2955–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braszczyńska-Malik, K.N. Mg-Al-RE magnesium alloys for high-pressure die-casting. Arch. Foundry Eng. 2014, 14, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmikhanth, R.S.; Lakshminarayanan, A.K. On the mechanical, microstructural, and corrosion properties of pulsed gas tungsten arc and friction stir welded RZ5 rare earth grade magnesium alloy. Mater. Res. Express 2022, 9, 126507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftekhar, A.H.; Sadrossadat, S.M.; Reihanian, M. Effect of heat input on microstructure and mechanical properties of TIG-welded semisolid cast AXE622 Mg alloy. Mater. Charact. 2022, 184, 111692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tong, X.; Wu, G.; Zhan, J.; Qi, F.; Zhang, L.; Liu, W. Microstructure and strengthening mechanism of TIG welded joints of a Mg-Nd-Gd alloy: Effects of heat input and pulse current. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 869, 144816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Le, Q.; Liao, Q.; Shi, Y.; Wang, T.; Hu, W. Study of GTA-welded joints of ZW61 magnesium alloy—effect of welding current on the microstructure and mechanical properties. Weld. J. 2025, 104, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powder Diffraction File; PDF-4 + 2015; International Centre for Diffraction Data (ICDD): Pennsylvania, PA, USA, 2015.
- Braszczyńska-Malik, K.N. Effect of high-pressure die casting on structure and properties of Mg-5Al-0.4Mn-xRE (x = 1, 3 and 5wt%) experimental alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 694, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braszczyńska-Malik, K.N. Magnesium Alloys and Composites on Their Matrix (Oryg. Title: Stopy Magnezu i Kompozyty na Ich Osnowie), 1st ed.; Czestochowa University Publisher: Czestochowa, Poland, 2017; pp. 82–133. ISBN 978-83-7193-674-6. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]

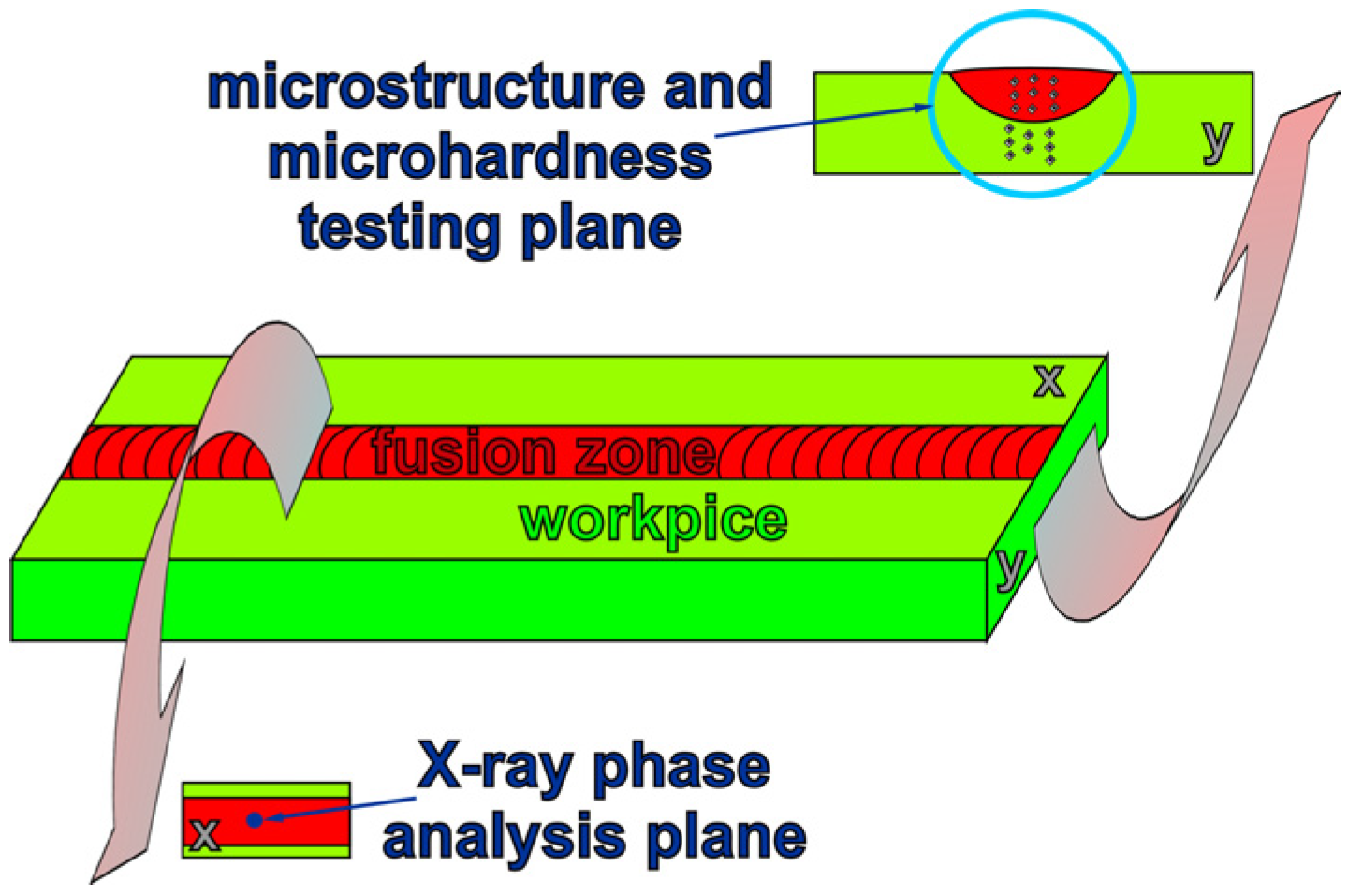
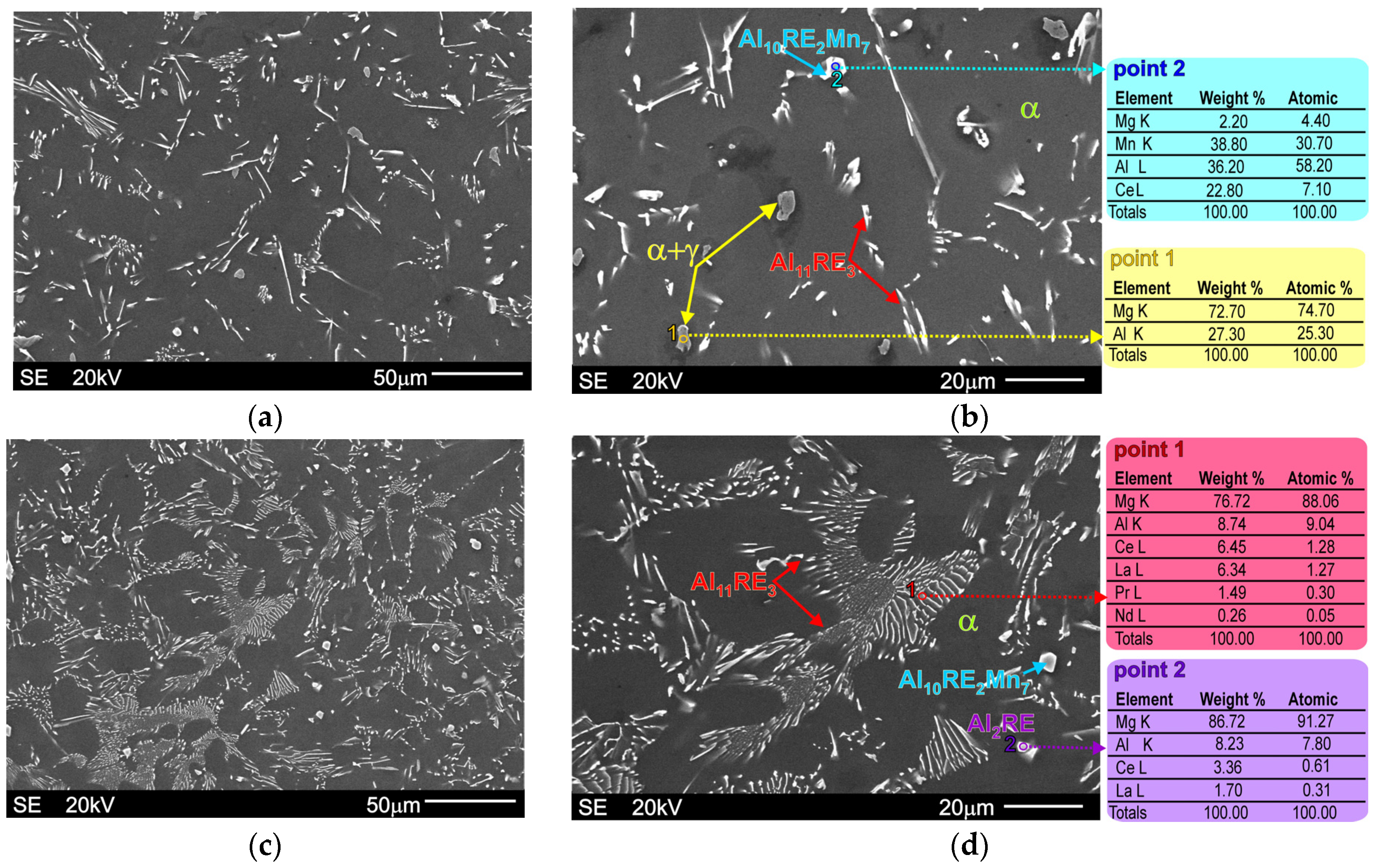

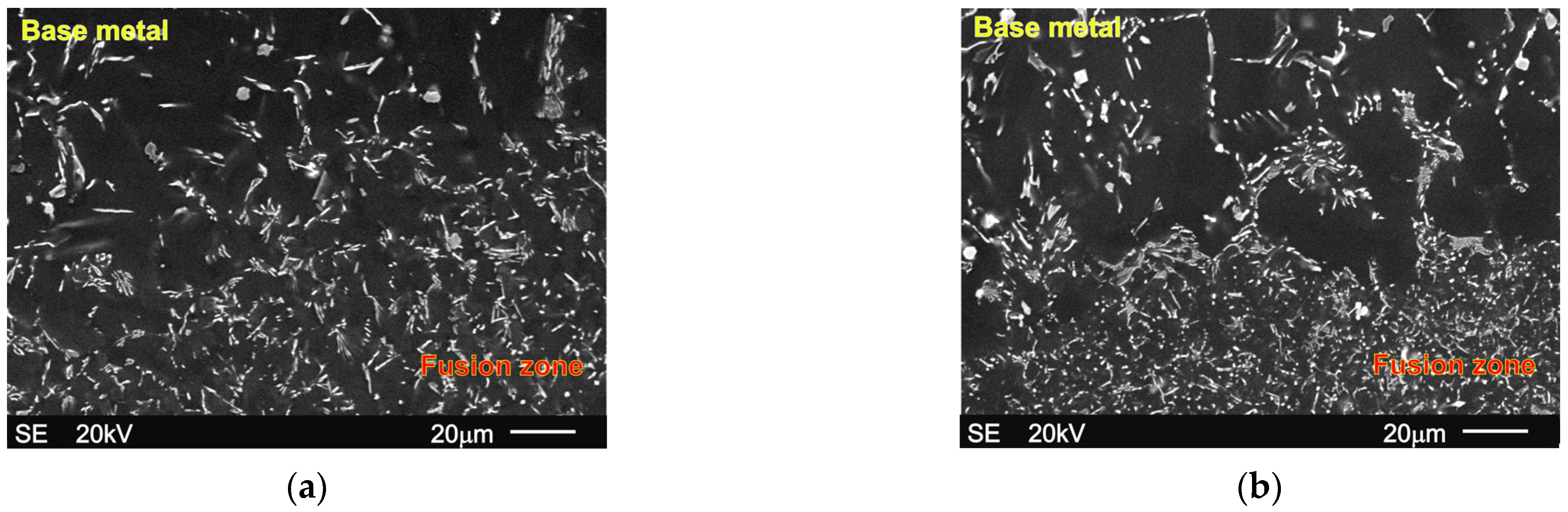
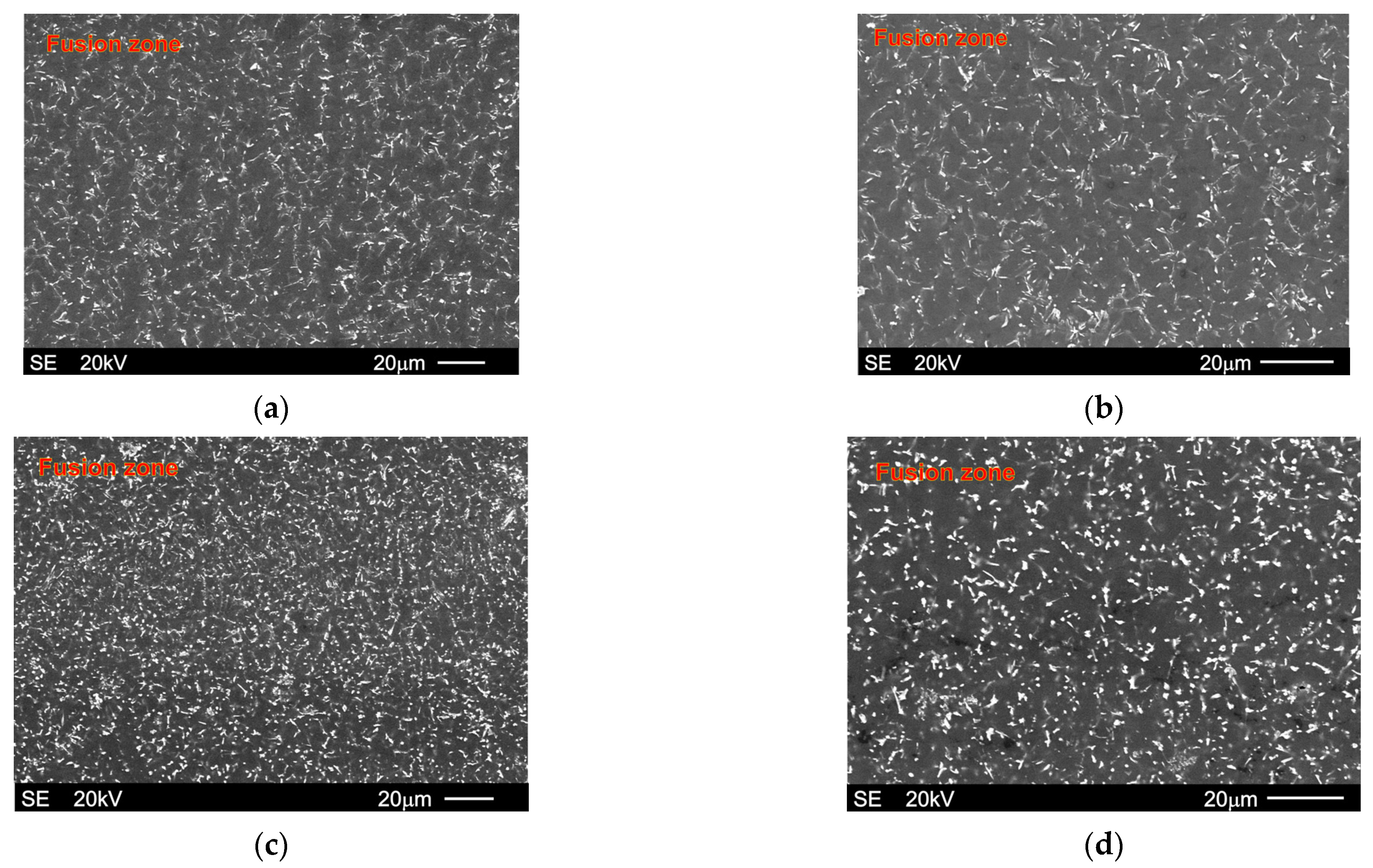
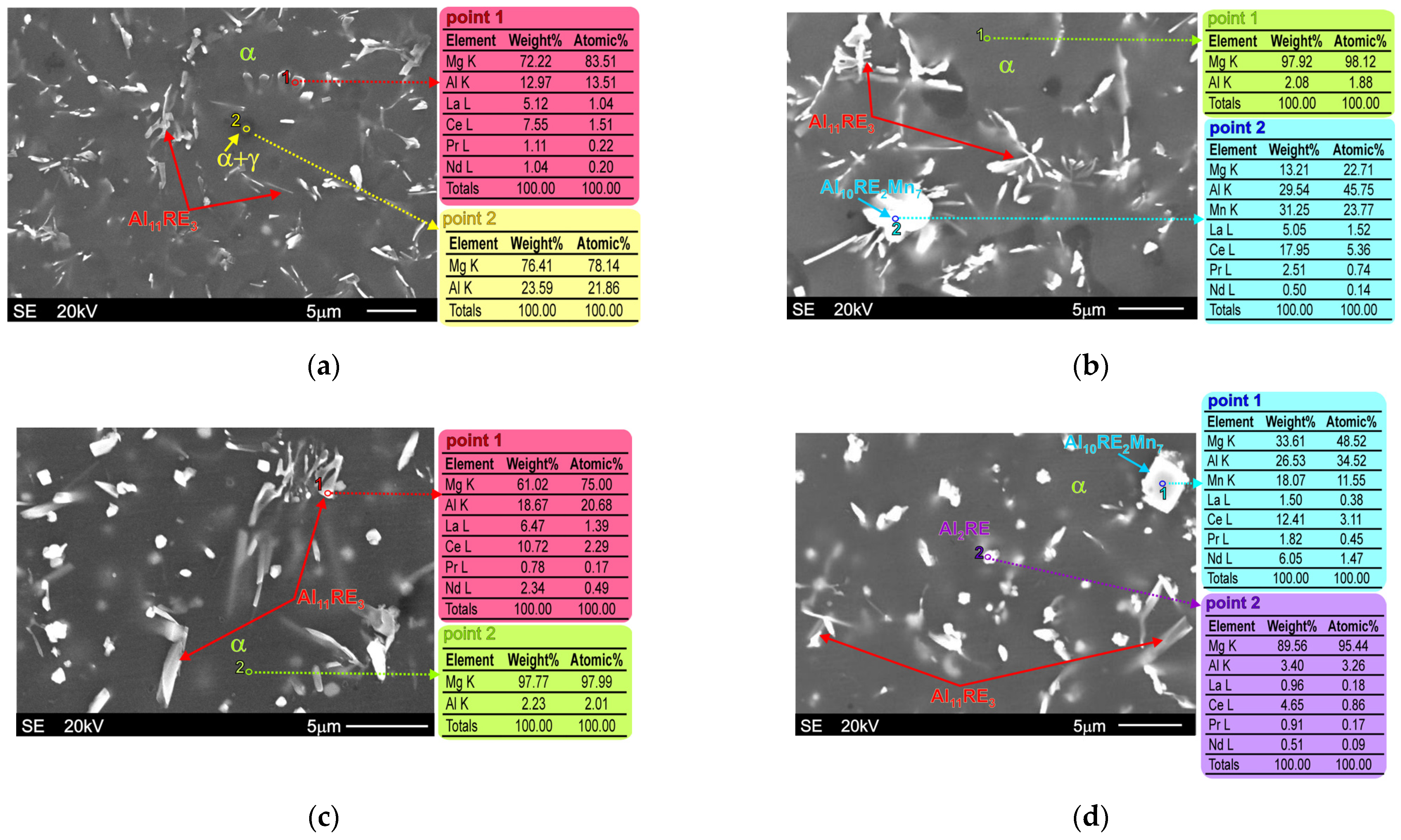
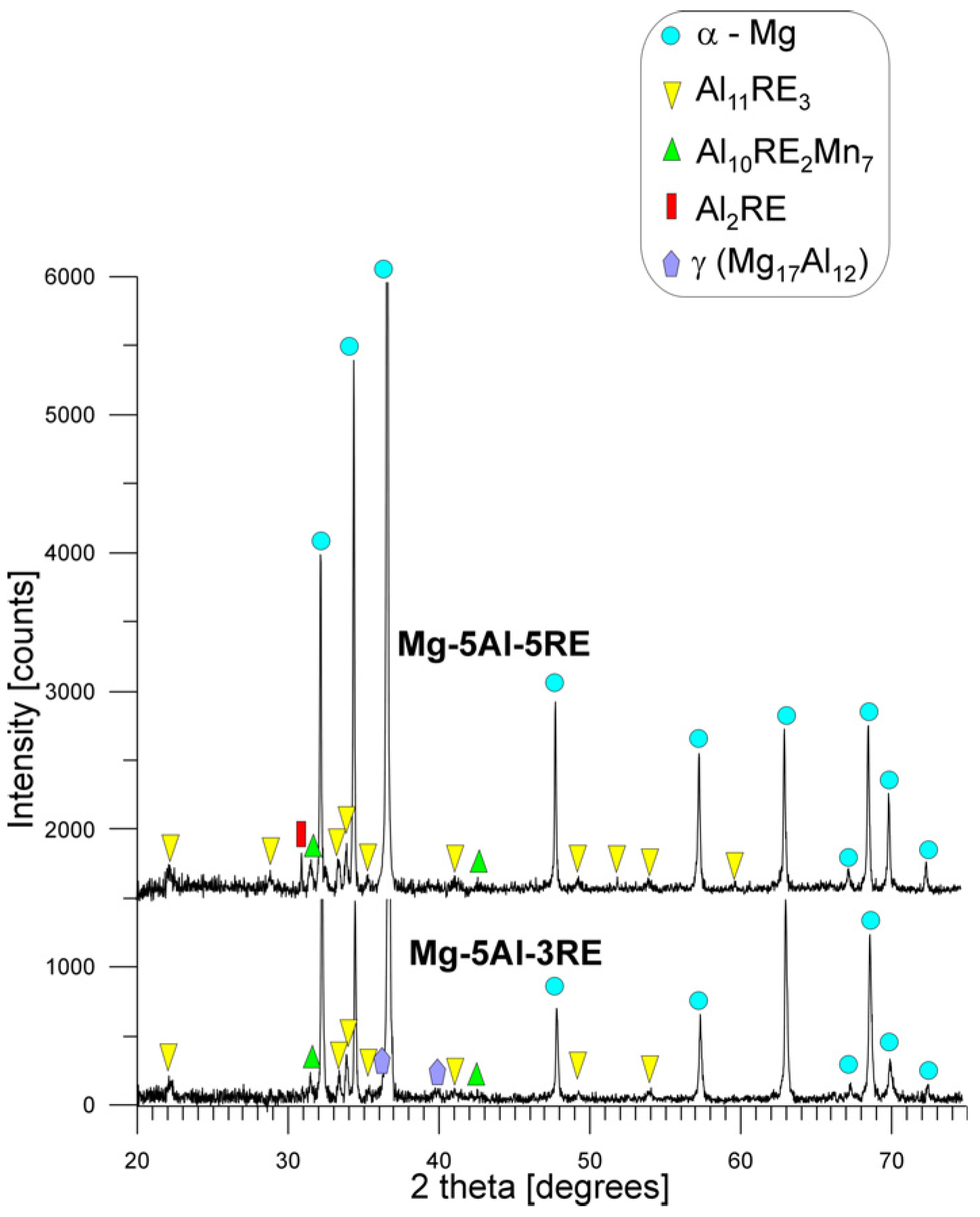
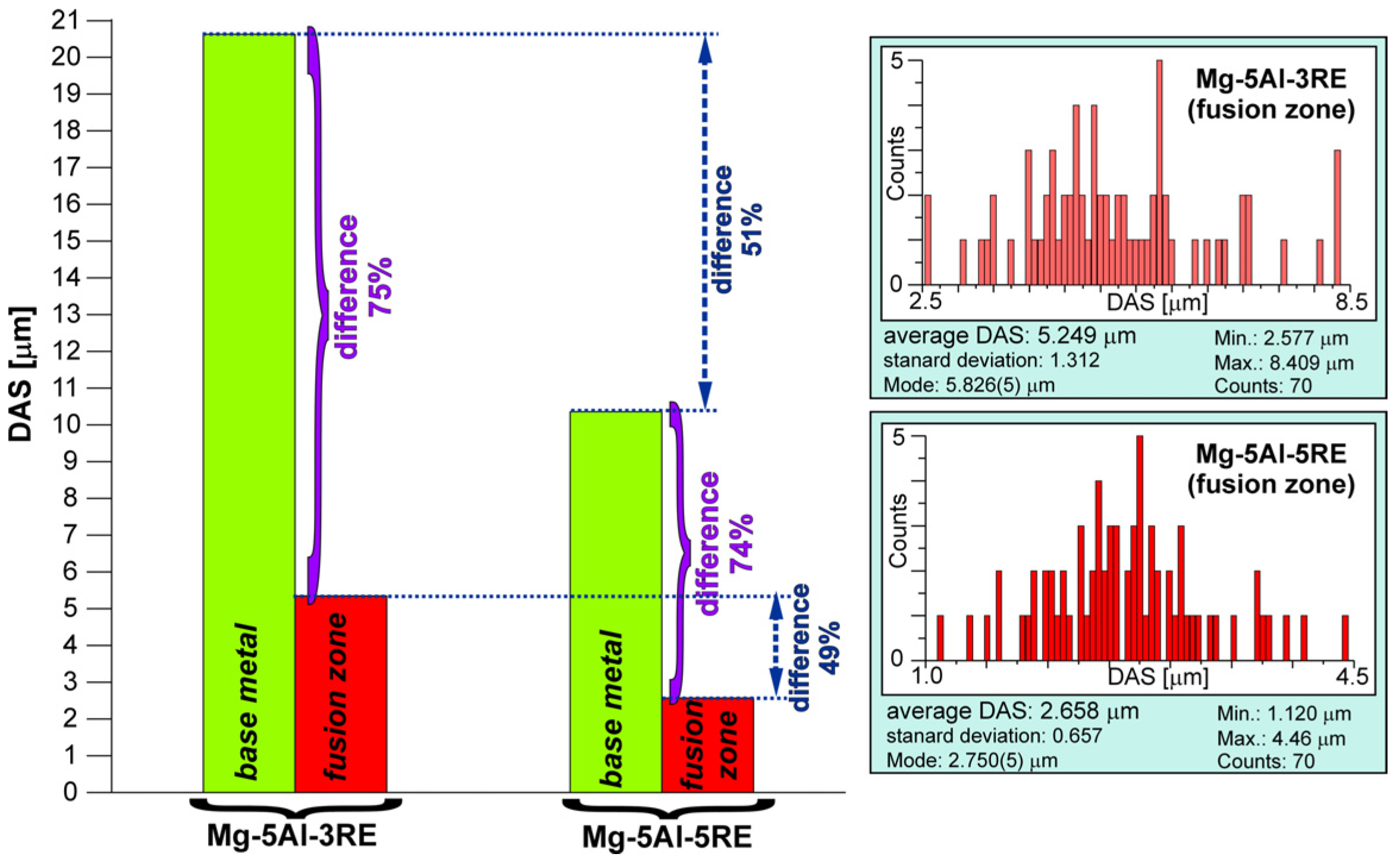
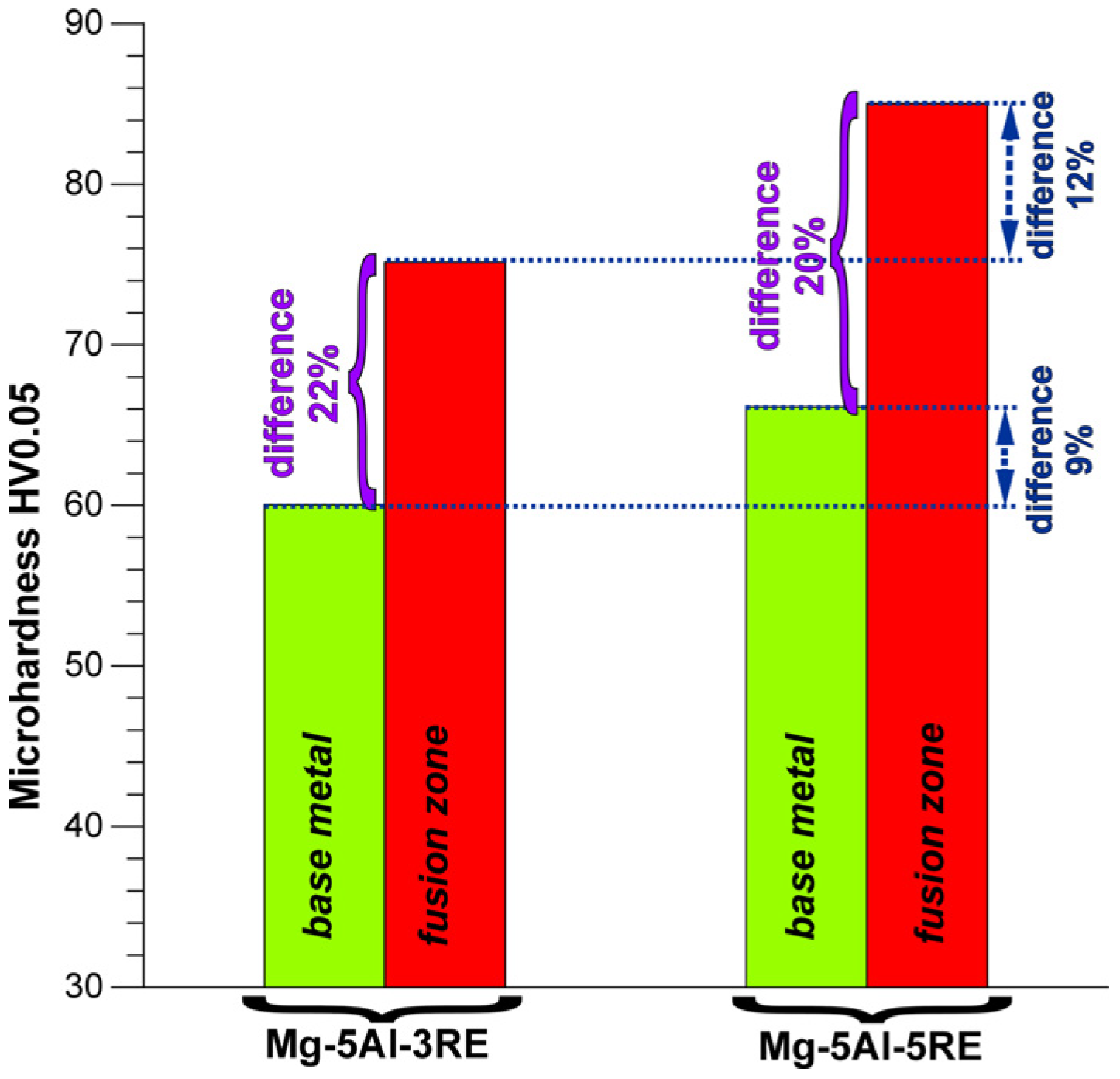
| Alloy | Chemical Composition wt% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | RE | Mn | Mg | |
| Mg-5Al-3RE | 5 | 3 | 0.4 | balance |
| Mg-5Al-5RE | 5 | 5 | 0.4 | balance |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Braszczyńska-Malik, K.N. Study of the Influence of Gas Tungsten Arc (GTA) Welding on the Microstructure and Properties of Mg–Al–RE-Type Magnesium Alloys. Materials 2025, 18, 3277. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143277
Braszczyńska-Malik KN. Study of the Influence of Gas Tungsten Arc (GTA) Welding on the Microstructure and Properties of Mg–Al–RE-Type Magnesium Alloys. Materials. 2025; 18(14):3277. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143277
Chicago/Turabian StyleBraszczyńska-Malik, Katarzyna N. 2025. "Study of the Influence of Gas Tungsten Arc (GTA) Welding on the Microstructure and Properties of Mg–Al–RE-Type Magnesium Alloys" Materials 18, no. 14: 3277. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143277
APA StyleBraszczyńska-Malik, K. N. (2025). Study of the Influence of Gas Tungsten Arc (GTA) Welding on the Microstructure and Properties of Mg–Al–RE-Type Magnesium Alloys. Materials, 18(14), 3277. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143277





