Different Innovative Laser Implants Characteristics Histomorphometric and SEM-EDX Comparison for In Vivo Applications
Abstract
1. Background
- The early and late osseointegration process around two different innovative laser implants (L1–L2) compared to sandblasted and acid-etched (SBAE) used as controls;
- If laser treatment and the chemical and physical surface properties influenced bone healing;
- If the laser technology is able to improve the osseointegration compared to sandblasted and acid-etched (SBAE) used as controls.
- The quality and the bone behavior during the osseointegration process.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Implant, SEM, Energy Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy (EDX) and Profilometric Analysis
2.2. Wettability
2.3. Surgical Protocol
2.4. Histomorphometric Analysis and Bone-to-Implant Contact (BIC) Percentage Evaluation
2.5. Dynamic Osseointegration Index (DOI)
2.6. Bone Quality Index (BQI)
3. Results
3.1. Electron Scanning Microscope (SEM) Analysis of Implants
3.2. Profilometric Analysis of Implants
3.3. Surface Chemical Characteristics and Wettability
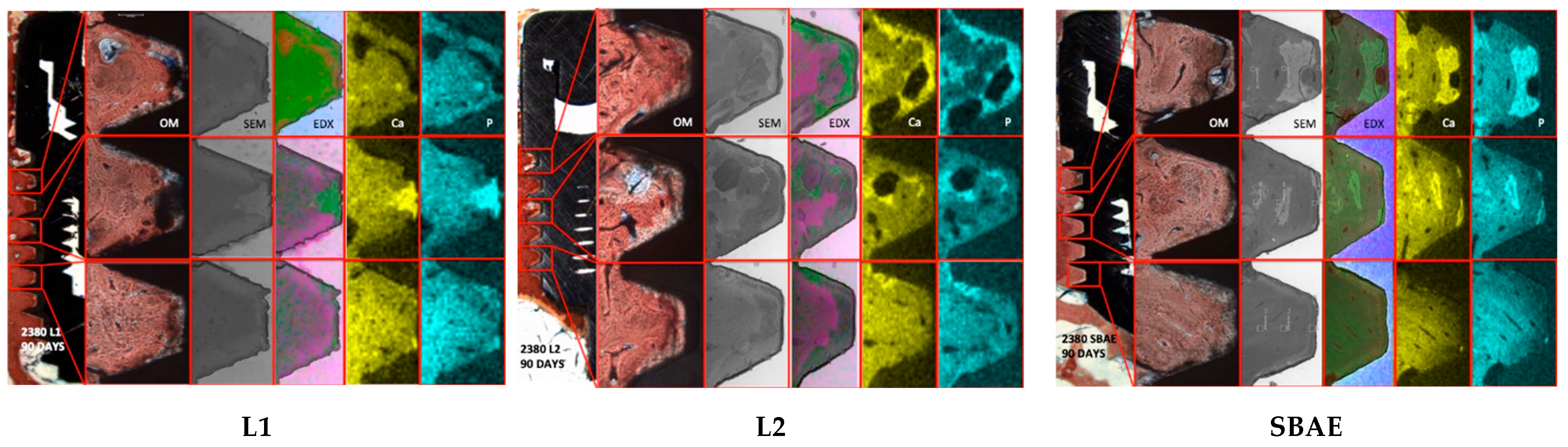
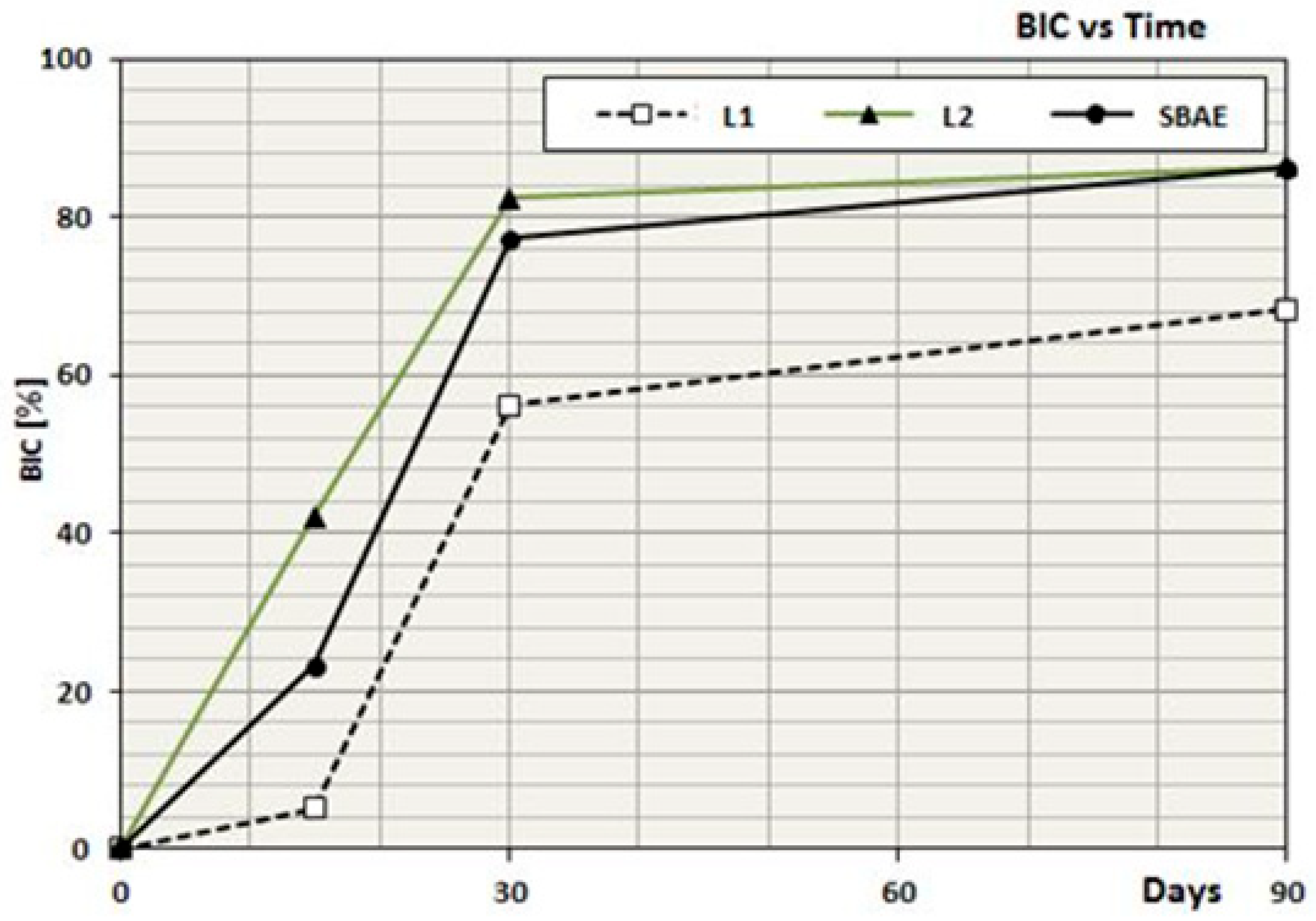
3.4. Histological and Histomorphometric Analysis
3.5. Dynamic Osseointegration Index (DOI)
3.6. Bone Quality Index (BQI)
4. Discussion
4.1. Histological Analysis
4.2. Histomorphometric Analysis
4.3. Bone Behavior During Osseointegration
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muller, F. Interventions for edentate elders—What is the evidence? Gerodontology 2014, 31, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastrangelo, F.; Parma-Benfenati, S.; Quaresima, R. Biologic Bone Behaviour During the Osseointegration Process: Histologic, Histomorphometric and SEM-EDX Evaluations. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2023, 43, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelis, N.; Benedicenti, S.; Zekiy, A.; Amaroli, A. Current Trends in Bone Augmentation Techniques and Dental Implantology: An Editorial Overview. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, C.; Rokaya, D.; Bhattarai, B.P. Contemporary Concepts in Osseointegration of Dental Implants: A Review. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 6170452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Jacobs, R.; Cao, Y.; Sun, X.; Qin, X. Tissue-engineered bone construct promotes early osseointegration of implants with low primary stability in oversized osteotomy. BMC Oral Health 2024, 24, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales-Leal, J.I.; Rodríguez-Valverde, M.A.; Mazzaglia, G.; Ramón-Torregrosa, P.J.; Díaz-Rodríguez, L.; García-Martínez, O.; Vallecillo-Capilla, M.; Ruiz, C.; Cabrerizo-Vílchez, M.A. Effects of roughness, wettability and morphology of engineered titanium surfaces on osteoblast-like cell adhesion. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2010, 365, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaviria, L.; Salcido, J.P.; Guda, T.; Ong, J.L. Current trends in dental implants. J. Korean Assoc. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 40, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Wu, R.; Wei, J. Construction of functional surfaces for dental implants to enhance osseointegration. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1320307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, E.; Lanzutti, A. Biomedical Applications of Titanium Alloys: A Comprehensive Review. Materials 2023, 17, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinemann, S.G. Titanium the material of choice? Periodontol. 2000 2012, 17, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trisi, P.; Lazzara, R.; Rao, W.; Rebaudi, A. Bone-implant contact and bone quality: Evaluation of expected and actual bone contact on machined and osseotite implant surfaces. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2002, 22, 535–545. [Google Scholar]
- Buser, D.; Nydegger, T.; Oxland, T.; Cochran, D.L.; Schenk, R.K.; Hirt, H.P.; Snétivy, D.; Nolte, L. Interface shear strength of titanium implants with a sandblasted and acid-etched surface: A biomechanical study in the maxilla of miniature pigs. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1999, 45, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetè, S.; Mastrangelo, F.; Traini, T.; Vinci, R.; Sammartino, G.; Marenzi, G.; Gherlone, E. A macro and nanostructure evaluation of a novel dental implant. Implant. Dent. 2008, 17, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetè, S.M.; Mastrangelo, F.M.; Quaresima, R.E.; Vinci, R.; Sammartino, G.M.; Stuppia, L.; Gherlone, E. Influence of novel nano-titanium surface on human osteoblast behaviour and growth. Implant. Dent. 2010, 19, 520–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filiberto, M.; Daniele, B.; Franco, B.; Antonio, S.; Adriano, P.; Giovanna, I.; Raimondo, Q. Histological and Histomorphometric Comparison of Innovative Dental Implants Laser Obtained: Animal Pilot Study. Materials 2021, 14, 1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buser, D.; Sennerby, L.; De Bruyn, H. Modern implant dentistry based on osseointegration: 50 years of progress, current trends and open questions. Periodontol. 2000 2017, 73, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennerberg, A.; Albrektsson, T. On implant surfaces: A review of current knowledge and opinions. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2010, 25, 63–74. [Google Scholar]
- Scarano, A.; Postiglione, F.; Khater, A.G.A.; Al-Hamed, F.S.; Lorusso, F. A Novel Technique to Increase the Thickness of TiO2 of Dental Implants by Nd: DPSS Q-sw Laser Treatment. Materials 2020, 13, 4178. [Google Scholar]
- Sul, Y.T.; Johansson, C.B.; Jeong, Y.; Wennerberg, A.; Albrektsson, T. Resonance frequency and removal torque analysis of implants with turned and anodized surface oxides. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2002, 13, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, F.A.; Thomsen, P.; Palmquist, A. Osseointegration and current interpretations of the bone-implant interface. Acta Biomater. 2019, 15, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrke, S.A.; Tumedei, M.; Aramburú Júnior, J.; Treichel, T.L.E.; Kolerman, R.; Lepore, S.; Piattelli, A.; Iezzi, G. Histological and Histomorphometrical Evaluation of a New Implant Macrogeometry. A Sheep Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korner, C.; Meyerhofer, R.; Hartmann, M.; Bergmann, H.W. Physical and material aspects in using visible laser pulses of nanosecond duration for ablation. Appl. Phys. A—Mater. Sci. Process. 1996, 63, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, R.; Tender, L.M.; Bradley, G.; O’Brien, M.J., 2nd; Cone, M.; Lopez, G.P. Computer-controlled laser ablation: A convenient and versatile tool for micropatterning biofunctional synthetic surfaces for applications in biosensing and tissue engineering. Biotechnol. Prog. 1998, 14, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norton, M.R. Marginal bone levels at single tooth implants with a conical fixture design. The influence of surface macro- and microstructure. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 1998, 9, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piattelli, A.; Scarano, A.; Piattelli, M. Detection of alkaline and acid phosphatases around titanium implants: A light microscopical and histochemical study in rabbits. Biomaterials 1995, 16, 1333–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanos, G.; Zamparini, F.; Spinelli, A.; Prati, C.; Gandolfi, M.G. ESEM-EDX Microanalysis at Bone-Implant Region on Immediately Loaded Implants Retrieved Postmortem. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2022, 37, e51–e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandolfi, M.G.; Zamparini, F.; Iezzi, G.; Degidi, M.; Botticelli, D.; Piattelli, A.; Prati, C. Microchemical and Micromorphologic ESEM-EDX Analysis of Bone Mineralization at the Thread Interface in Human Dental Implants Retrieved for Mechanical Complications After 2 Months to 17 Years. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2018, 38, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangano, C.; Piattelli, A.; Raspanti, M.; Mangano, F.; Cassoni, A.; Iezzi, G.; Shibli, J.A. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and X-ray dispersive spectrometry evaluation of direct laser metal sintering surface and human bone interface: A case series. Lasers Med. Sci. 2011, 26, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prati, C.; Zamparini, F.; Botticelli, D.; Ferri, M.; Yonezawa, D.; Piattelli, A.; Gandolfi, M.G. The Use of ESEM-EDX as an Innovative Tool to Analyze the Mineral Structure of Peri-Implant Human Bone. Materials 2020, 13, 1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, M.; Ardebili, Y.; Worthington, H.V. Interventions for replacing missing teeth: Different types of dental implants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, CD003815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, O.; Bengazi, F.; Ferri, M.; Gianfreda, F.; Velez, J.; Botticelli, D.; Canullo, L. Bioactivated Implant Surfaces Placed in Healed Sites or Extraction Sockets: A Preliminary Experimental Study in Dogs. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2022, 37, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, J.E. Understanding peri-implant endosseous healing. J. Dent. Educ. 2003, 67, 932–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misch, C.E.; Perel, M.L.; Wang, H.L.; Sammartino, G.; Galindo-Moreno, P.; Trisi, P.; Steigmann, M.; Rebaudi, A.; Palti, A.; Pikos, M.A.; et al. Implant success, survival, and failure: The International Congress of Oral Implantologists (ICOI) pisa consensus conference. Implant. Dent. 2008, 17, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorstensson, H.; Johansson, B. Why do some people lose teeth across their lifespan whereas others retain a functional dentition into very old age? Gerodontology 2010, 27, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeets, R.; Stadlinger, B.; Schwarz, F.; Beck-Broichsitter, B.; Jung, O.; Precht, C.; Kloss, F.; Gröbe, A.; Heiland, M.; Ebker, T. Impact of Dental Implant Surface Modifications on Osseointegration. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 6285620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, S.; Norton, M. The relation between surface roughness and interfacial shear strength for bone-anchored implants. A mathematical model. J. Biomech. 1999, 32, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamparini, F.; Prati, C.; Generali, L.; Spinelli, A.; Taddei, P.; Gandolfi, M.G. Micro-Nano Surface Characterization and Bioactivity of a Calcium Phosphate-Incorporated Titanium Implant Surface. J. Funct. Biomater. 2021, 12, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipal, J.; Lee, T.; Koshy, P.; Abdullah, H.; Idris, M. Evolution of anodised titanium for implant applications. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aneksomboonpol, P.; Mahardawi, B.; Na Nan, P.; Laoharungpisit, P.; Kumchai, T.; Wongsirichat, N.; Aimjirakul, N. Surface structure characteristics of dental implants and their potential changes following installation: A literature review. J. Korean Assoc. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2023, 49, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, I.S.; Han, J.S.; Yang, J.H. Biomechanical and histomorphometric study of dental implants with different surface characteristics. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2008, 87, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.Y.; Kang, S.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Yeo, I.L. Control Variable Implants Improve Interpretation of Surface Modification and Implant Design Effects on Early Bone Responses: An In Vivo Study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2018, 33, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunrath, M.F.; Garaicoa-Pazmino, C.; Giraldo-Osorno, P.M.; Haj Mustafa, A.; Dahlin, C.; Larsson, L.; Asa’ad, F. Implant surface modifications and their impact on osseointegration and peri-implant diseases through epigenetic changes: A scoping review. J. Periodontal Res. 2024, 59, 1095–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, N.P.; Jepsen, S. Implant surfaces and design (Working Group 4). Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2009, 20 (Suppl. S4), 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, F.P.; Weng, D.; Krämer, S.; Biesterfeld, S.; Jahn-Eimermacher, A.; Wagner, W. Osseointegration of one-Piece zirconia implants compared with a titanium implant of identical design: A histomorphometric study in the dog. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2010, 21, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoma, D.S.; Benic, G.I.; Muñoz, F.; Kohal, R.; Martin, I.S.; Cantalapiedra, A.G.; Hämmerle, C.H.F.; Jung, R.E. Histological analysis of loaded zirconia and titanium dental implants: An experimental study in the dog mandible. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2015, 42, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahlert, M.; Roehling, S.; Sprecher, C.M.; Kniha, H.; Milz, S.; Bormann, K. In vivo performance of zirconia and titanium implants: A histomorphometric study in mini pig maxillae. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2012, 23, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schliephake, H.; Hefti, T.; Schlottig, F.; Gédet, P.; Staedt, H. Mechanical anchorage and peri-implant bone formation of surface-modified zirconia in minipigs. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2010, 37, 818–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahlert, M.; Röhling, S.; Wieland, M.; Sprecher, C.M.; Kniha, H.; Milz, S. Osseointegration of zirconia and titanium dental implants: A histological and histomorphometrical study in the maxilla of pigs. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2009, 20, 1247–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboushelib, M.N.; Salem, N.A.; Taleb, A.L.A.; El Moniem, N.M.A. Moniem. Influence of surface nano-roughness on osseointegration of zirconia implants in rabbit femur heads using selective infiltration etching technique. J. Oral Implantol. 2013, 39, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohal, R.J.; Bächle, M.; Renz, A.; Butz, F. Evaluation of alumina toughened zirconia implants with a sintered, moderately rough surface: An experiment in the rat. Dent. Mater. 2016, 32, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, J.; Alexander, H. Cell Response to Surfaces: A Concise Summary. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2016, 36, S39–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiner, S.; Simon, J.; Ehrenberg, D.S.; Zweig, B.; Ricci, J.L. The effects of laser microtextured collars upon crestal bone levels of dental implants. Implant. Dent. 2008, 17, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trisi, P.; Berardini, M.; Colagiovanni, M.; Berardi, D.; Perfetti, G. Laser-Treated Titanium Implants: An In Vivo Histomorphometric and Biomechanical Analysis. Implant. Dent. 2016, 25, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafezeqoran, A.; Koodaryan, R. Effect of Zirconia Dental Implant Surfaces on Bone Integration: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 9246721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Tullio, I.; Berardini, M.; Di Iorio, D.; Perfetti, F.; Perfetti, G. Comparative evaluation among laser-treated, machined, and sandblasted/acid-etched implant surfaces: An in vivo histologic analysis on sheep. Int. J. Implant. Dent. 2020, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimes, D.; Becker, P.; Pabst, A.; Smeets, R.; Kraus, A.; Hartmann, A.; Sagheb, K.; Kämmerer, P.W. How does dental implant macrogeometry affect primary implant stability? A narrative review. Int. J. Implant. Dent. 2023, 9, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenfest, D.M.D.; Coelho, P.G.; Kang, B.S.; Sul, Y.T.; Albrektsson, T. Classification of osseointegrated implant surfaces: Materials, chemistry and topography. Trends Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrangelo, F.; Gastaldi, G.; Vinci, R.; Troiano, G.; Tettamanti, L.; Gherlone, E.; Muzio, L.L. Immediate postextractive implants with and without bone graft: 3-year follow-up results from a multicenter controlled randomized trialm. Implant. Dent. 2018, 27, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novaes, A.B., Jr.; Souza, S.L.S.D.; Barros, R.R.M.D.; Pereira, K.K.Y.; Iezzi, G.; Piattelli, A. Influence of implant surfaces on osseointegration. Braz. Dent. J. 2010, 21, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrektsson, T.; Jacobsson, M. Bone-metal interface in osseointegration. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1987, 57, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborn, J.; Newesely, H. Dynamic aspects of the implant-bone interface. In Dental Implants; Carl Hanser: Munich, Germany, 1980; pp. 111–123. [Google Scholar]
- Berglundh, T.; Abrahamsson, I.; Lang, N.P.; Lindhe, J. De novo alveolar bone formation adjacent to endosseous implants. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2003, 14, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, C.; Thomsen, P.; Lausmaa, J.; Rodahl, M.; Kasemo, B.; Ericson, L. Bone response to surface modified titanium implants: Studies on electropolished implants with different oxide thicknesses and morphology. Biomaterials 1994, 15, 1062–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norton, M.R.; Åström, M. The Influence of Implant Surface on Maintenance of Marginal Bone Levels for Three Premium Implant Brands: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2020, 35, 1099–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

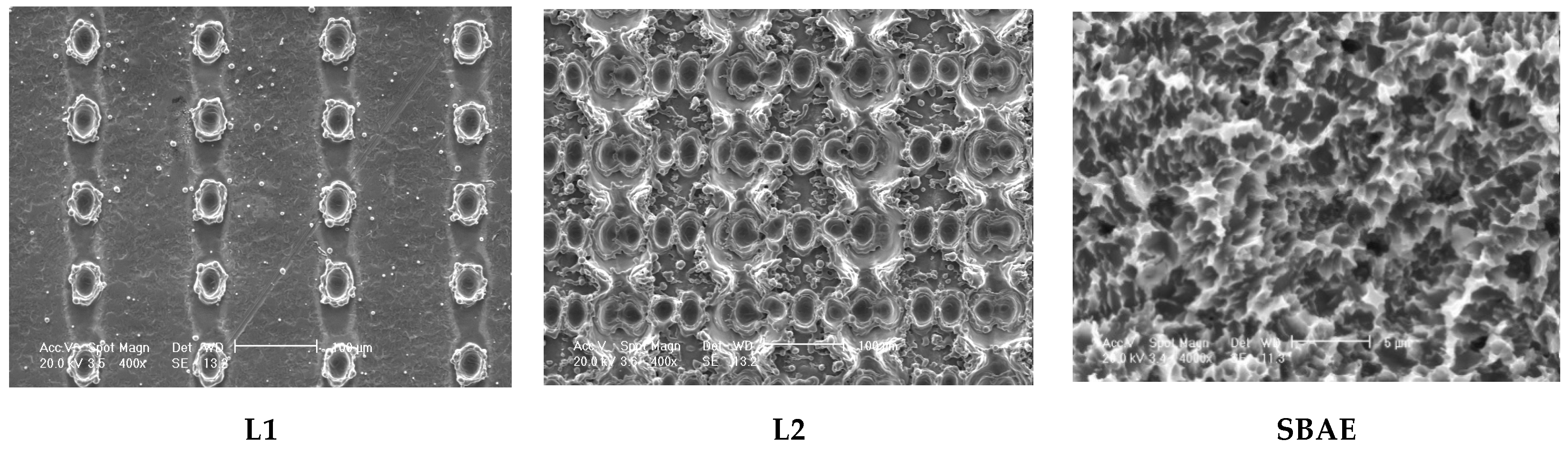
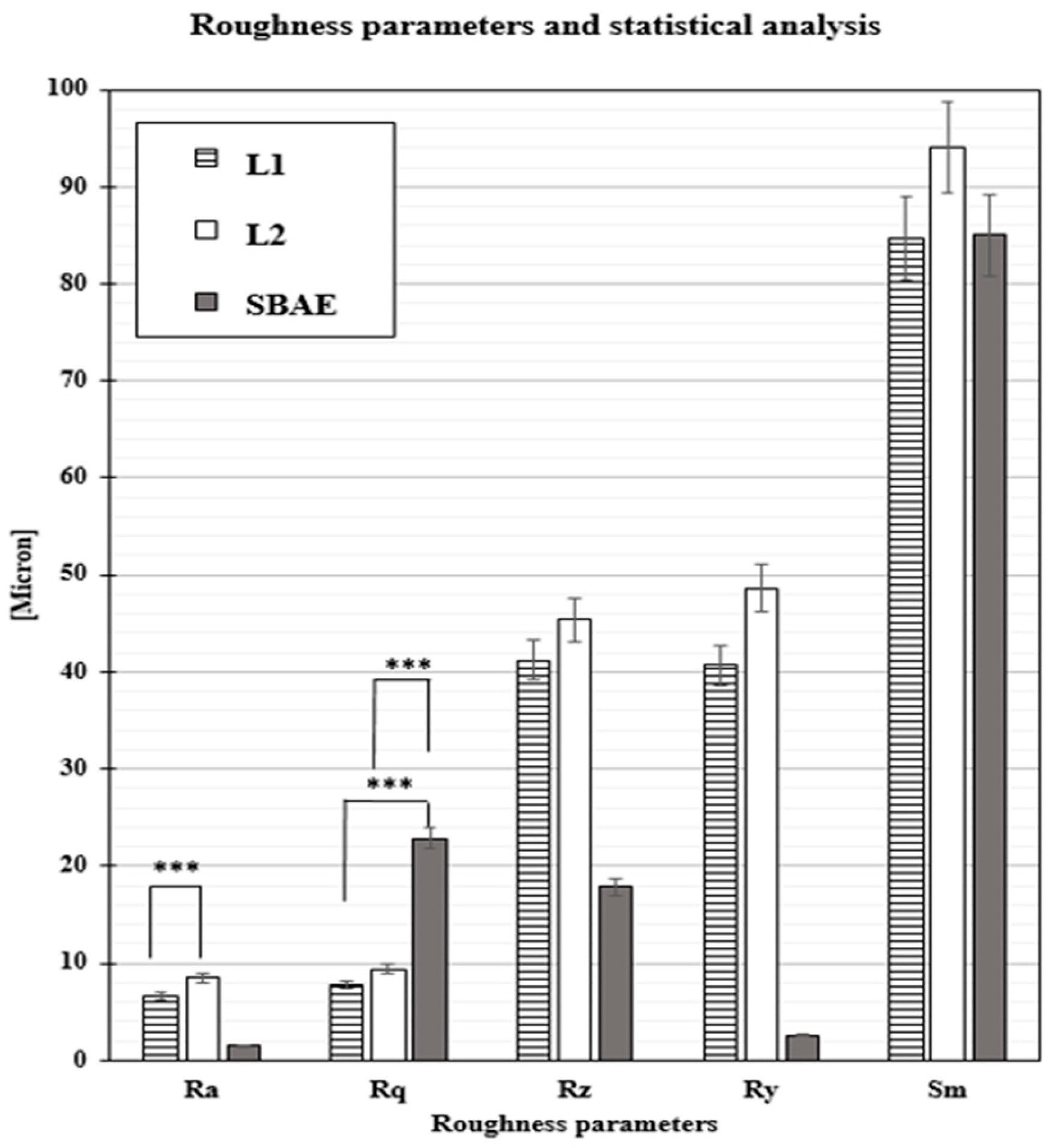
| Roughness Parameters t-Test (p-Value) | Ra | Rq | Rz | Ry | Sm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 vs. L2 | 0.00123 *** | 0.0549 * | 0.2966 * | 0.1935 * | 0.1053 * |
| L1 vs. SBAE | 0.0395 ** | 0.0001 *** | 0.0172 ** | 0.0077 ** | 0.1148 * |
| L2 vs. SBAE | 0.0201 ** | 0.0001 *** | 0.0143 ** | 0.0107 ** | 0.4837 * |
| Specimens | 15 Days Area A | 30 Days Area A | 90 Days Area A | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | BIC | 5.2 | 56.2 | 68.4 |
| DOI | 0.38 | 3.40 | 0.76 | |
| Ca | 19.49 | 24.00 | 25.57 | |
| P | 22.45 | 28.50 | 27.03 | |
| L2 | BIC | 42.1 | 82.4 | 86.4 |
| DOI | 2.81 | 2.83 | 0.95 | |
| Ca | 31.96 | 31.23 | 35.81 | |
| P | 33.97 | 32.84 | 38.85 | |
| SBAE | BIC | 23.3 | 77.3 | 86.2 |
| DOI | 1.55 | 2.58 | 0.96 | |
| Ca | 25.35 | 25.9 | 26.25 | |
| P | 27.16 | 26.86 | 27.82 |
| BQI (%) Mean Value | 15 Days | 30 Days | 90 Days |
|---|---|---|---|
| Area A | |||
| L1 | |||
| Ca | 19.49 ± 02.08 | 24.00 ± 05.55 | 25.57 ± 05.24 |
| P | 22.45 ±01.78 | 28.50 ± 06.35 | 27.03 ± 08.16 |
| L2 | |||
| Ca | 31.96 ± 02.91 | 31.23 ±07.18 | 35.81 ± 04.22 |
| P | 33.97 ± 02.98 | 32.84 ±07.74 | 38.85 ± 02.75 |
| SBAE | |||
| Ca | 25.35 ± 02.01 | 25.91 ± 01.90 | 26.25 ± 06.27 |
| P | 27.16 ± 03.15 | 26.86 ±03.15 | 27.82 ± 06.49 |
| L1–L2–SBAE | Area D | ||
| Ca | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 100.00 ± 0.00 |
| P | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 100.00 ± 0.00 |
| Specimens | BQI15 Mean Value | BQI30 Mean Value | BQI90 Mean Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | Areas A-B-C | ||
| Ca | 19.49 ± 2.08 | 39.54 ± 2.38 | 44.43 ± 0.08 |
| P | 22.45 ± 1.78 | 39.09 ± 3.29 | 46.14 ± 5.15 |
| L2 | Areas A-B-C | ||
| Ca | 35.15 ± 1.80 | 63.94 ± 0.80 | 79.81 ± 2.08 |
| P | 37.76 ± 1.87 | 71.84 ± 3.21 | 81.85 ± 3.14 |
| SBAE | Areas A-B-C | ||
| Ca | 22.99 ± 1.00 | 39.23 ± 2.00 | 45.31 ± 2.08 |
| P | 23.21 ± 1.01 | 43.45 ± 4.58 | 48.28 ± 1.12 |
| L1-L2-SBAE | Area D | Area D | Area D |
| Ca | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 100.00 ± 0.00 |
| P | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 100.00 ± 0.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mastrangelo, F.; Cicciù, M.; Quaresima, R.; Scarano, A. Different Innovative Laser Implants Characteristics Histomorphometric and SEM-EDX Comparison for In Vivo Applications. Materials 2025, 18, 3165. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18133165
Mastrangelo F, Cicciù M, Quaresima R, Scarano A. Different Innovative Laser Implants Characteristics Histomorphometric and SEM-EDX Comparison for In Vivo Applications. Materials. 2025; 18(13):3165. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18133165
Chicago/Turabian StyleMastrangelo, Filiberto, Marco Cicciù, Raimondo Quaresima, and Antonio Scarano. 2025. "Different Innovative Laser Implants Characteristics Histomorphometric and SEM-EDX Comparison for In Vivo Applications" Materials 18, no. 13: 3165. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18133165
APA StyleMastrangelo, F., Cicciù, M., Quaresima, R., & Scarano, A. (2025). Different Innovative Laser Implants Characteristics Histomorphometric and SEM-EDX Comparison for In Vivo Applications. Materials, 18(13), 3165. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18133165










