Electrospun Nanofibers of Polyvinylidene Fluoride Enriched with Active Antimicrobial Tannic Acid for the Improvement of the Shelf Life of Cherry Tomatoes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Solutions and the Process of Electrospinning
2.3. Characterization Techniques
2.4. Thermal Shrinkage
2.5. Water-Contact Angle
2.6. Packaging Application
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Surface Analysis of NFs
3.1.1. Analysis of Surface Morphology by SEM Image
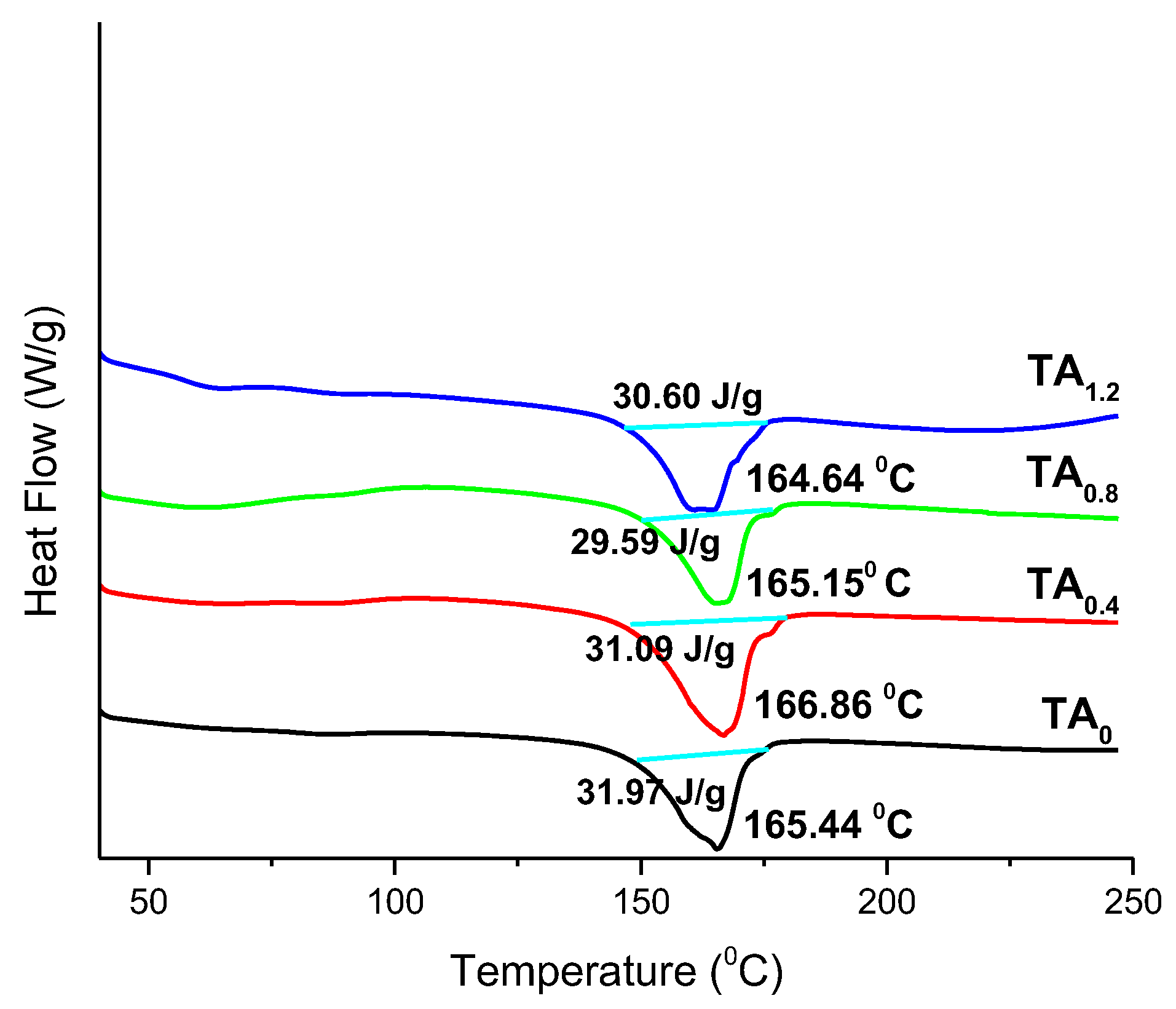
DSC Analysis
Stability Aspects with DSC Analysis
3.2. The Hydrophilic to Hydrophobic Nature of NFs for Release Behavior
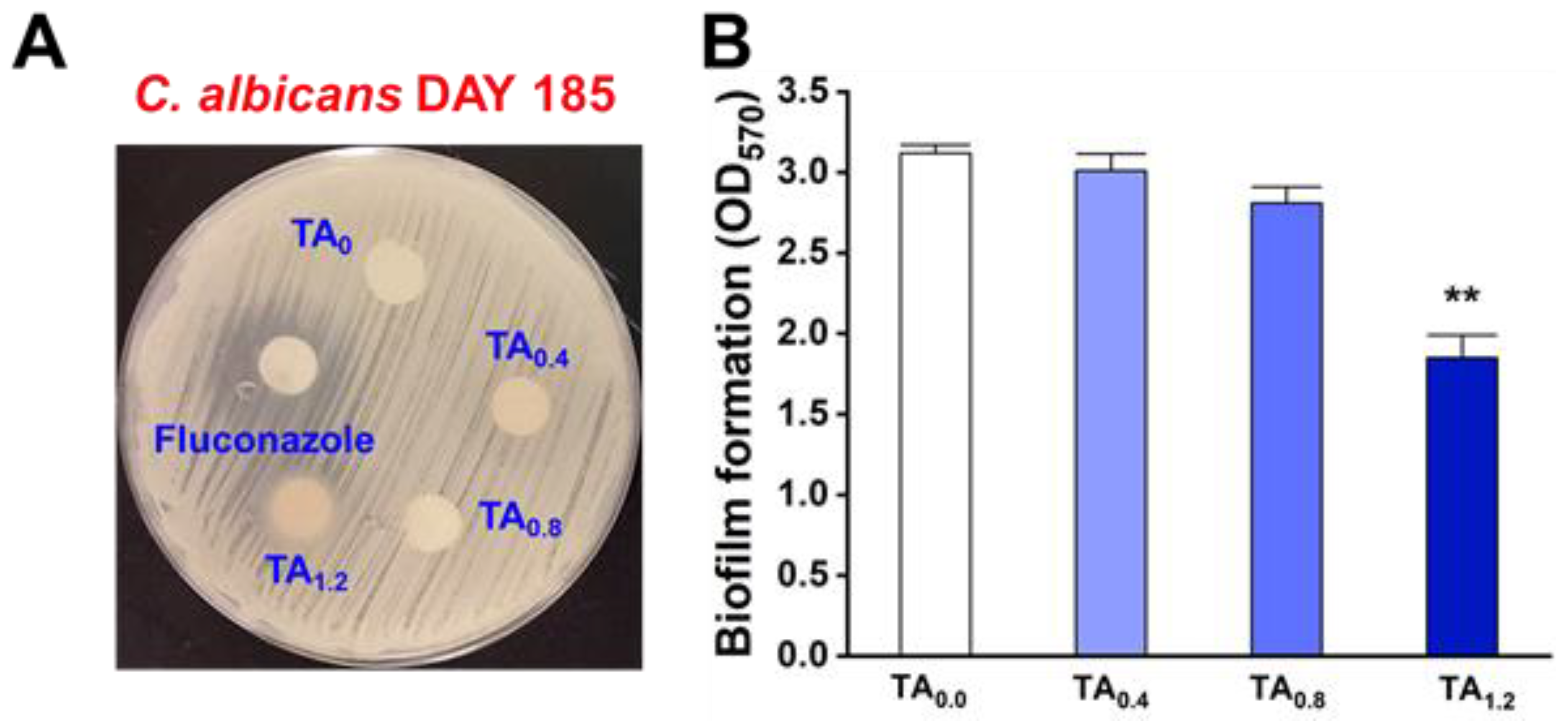
3.3. Antifungal and Antibiofilm Efficacy of NFs
3.4. Antioxidant (AO) Analysis
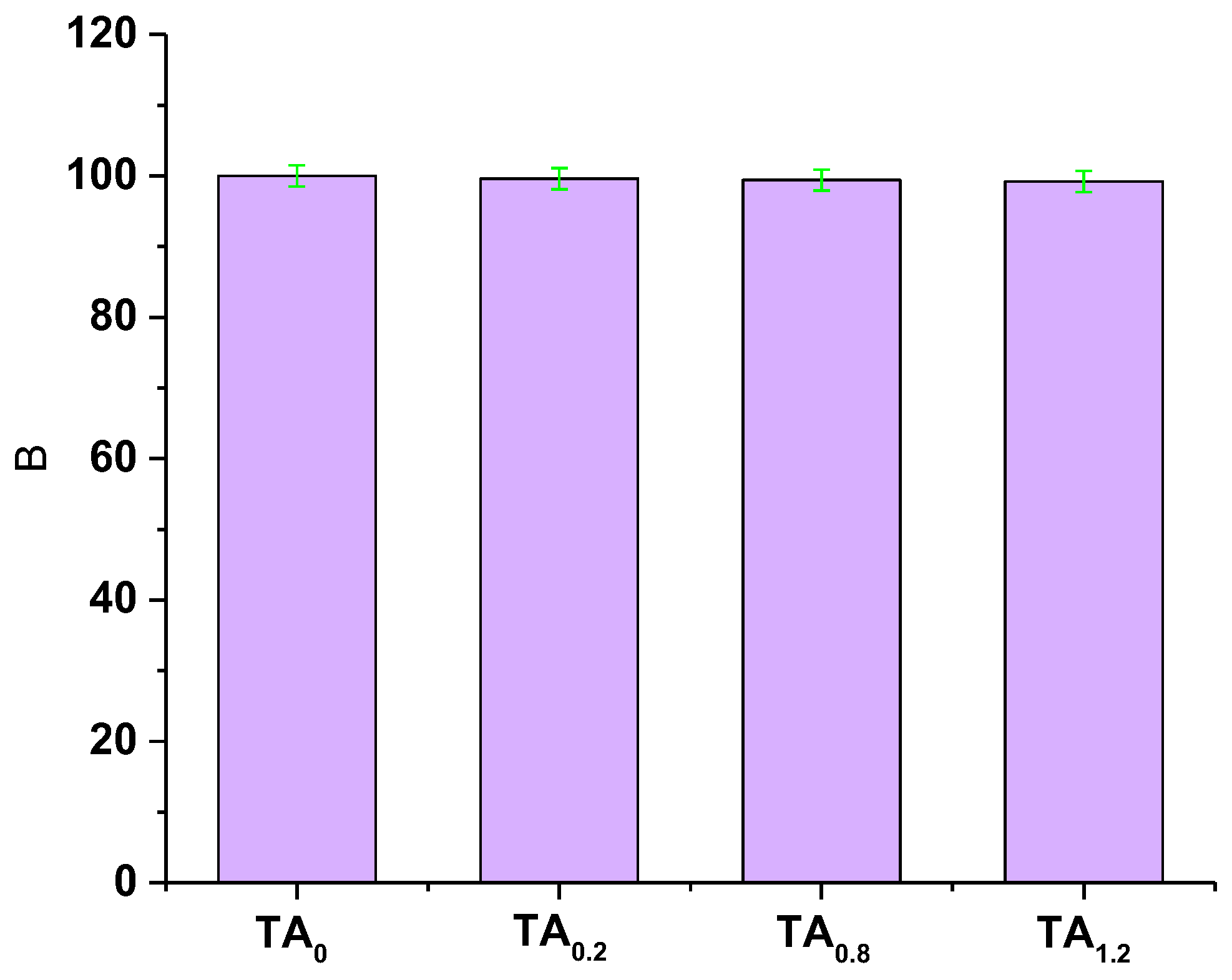
3.5. In Vitro Biocompatibility
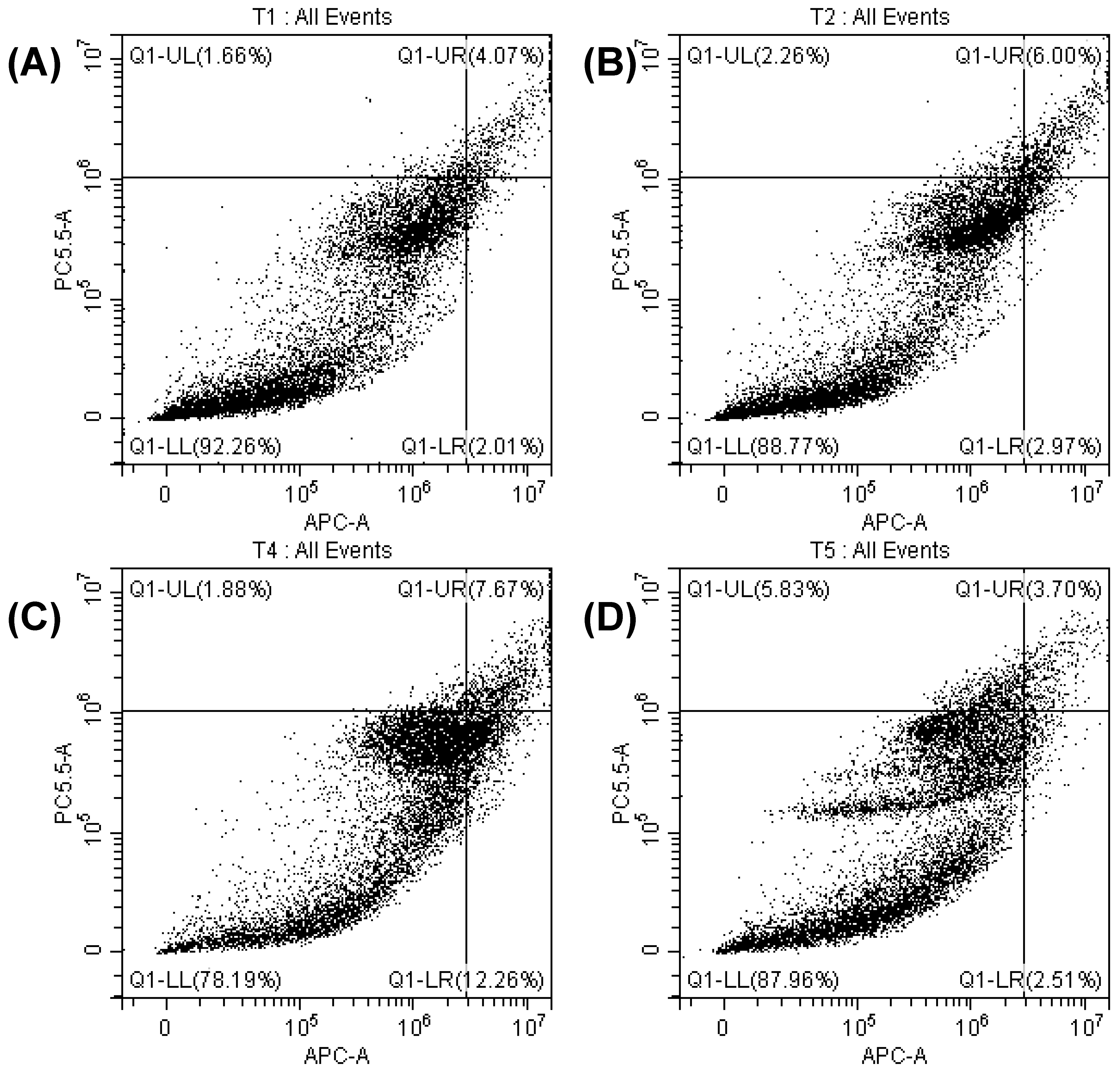
3.6. Determination of Apoptosis by Cell Cycle Analysis
3.7. Food-Packaging Analysis
3.7.1. Water-Contact Angle
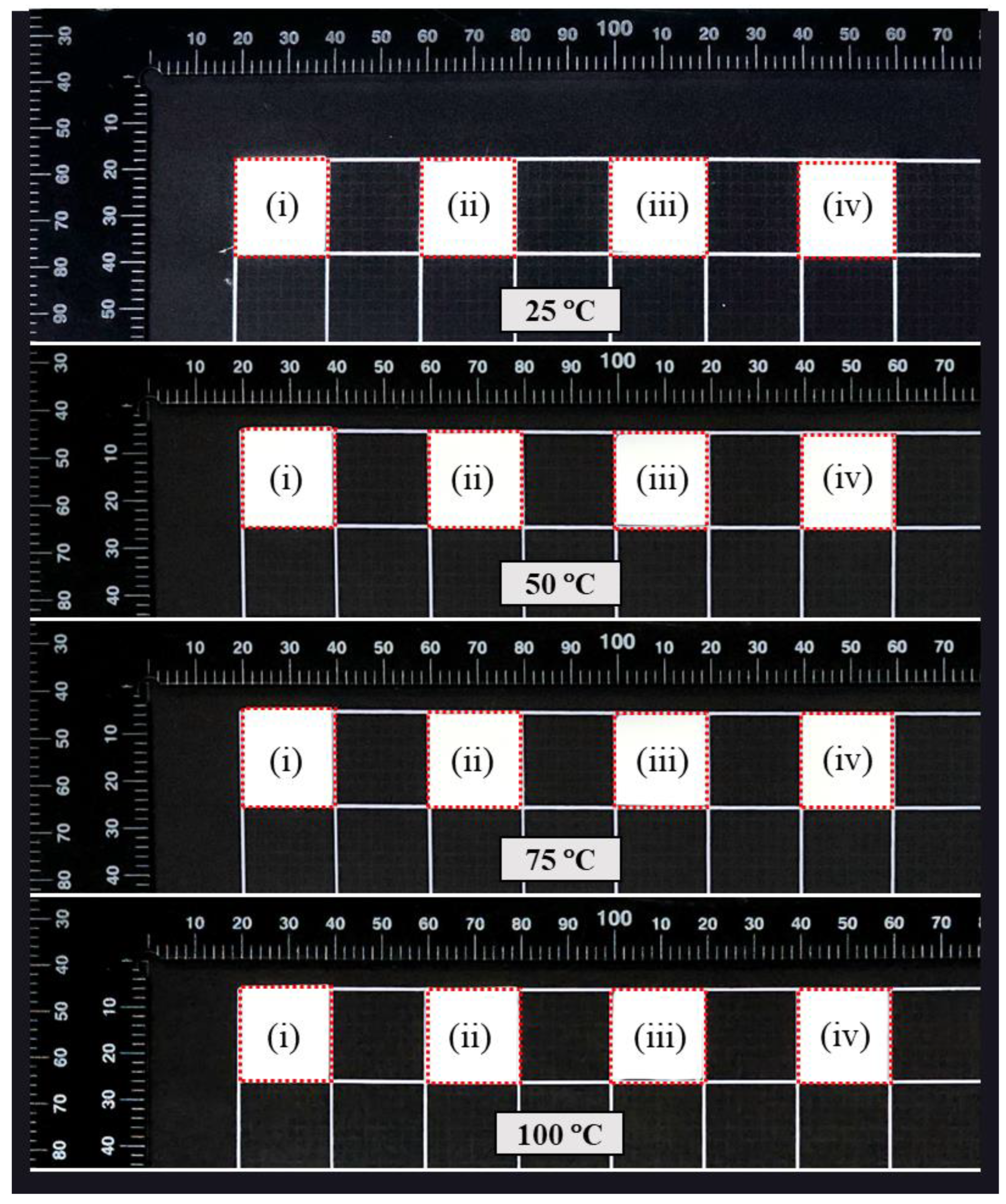
3.7.2. Thermal Shrinkage
3.7.3. Packaging Study
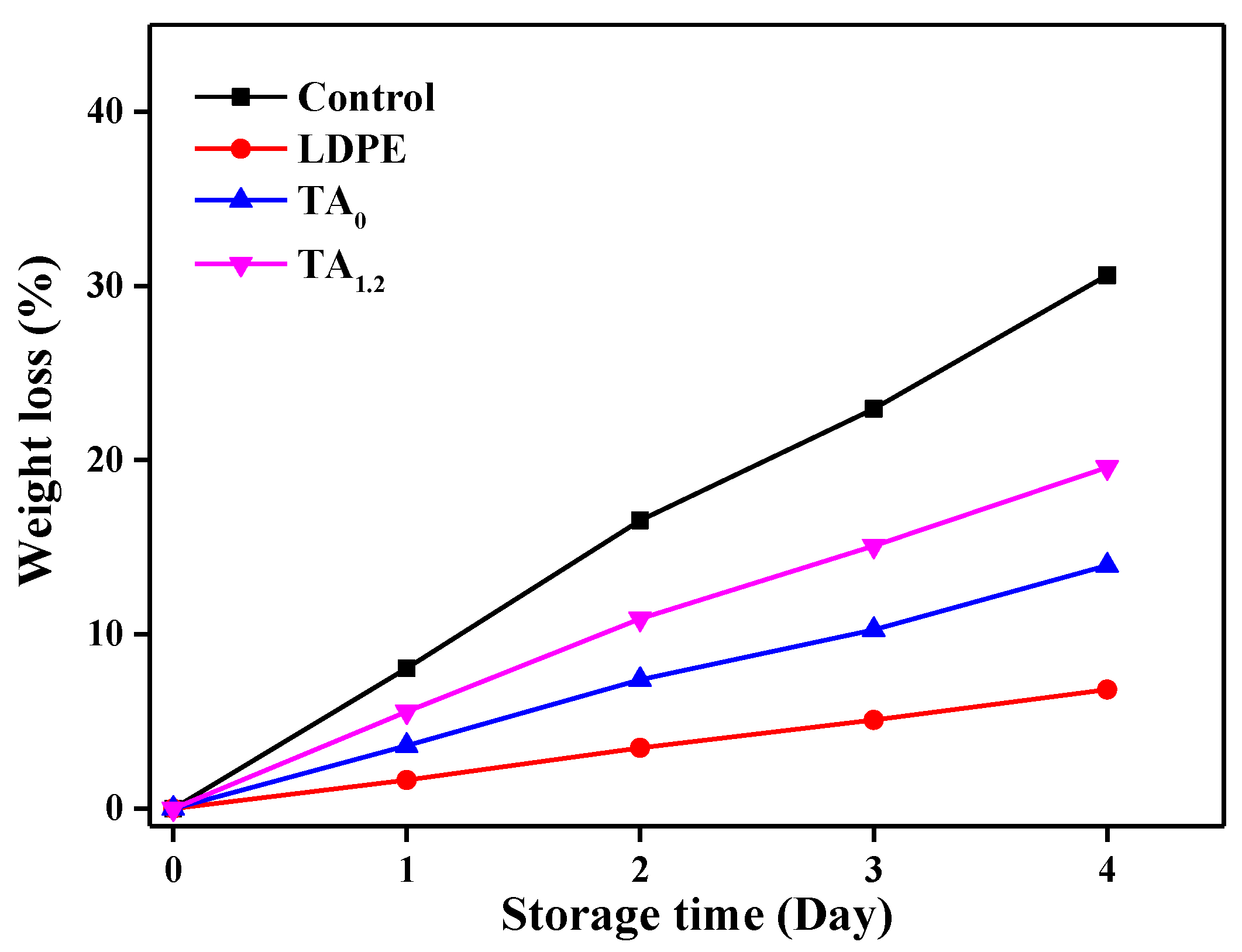
3.7.4. Weight Loss
3.7.5. Comparison of Food Preservation with the Literature
4. Conclusions
5. Study Limitations
6. Future Scope of the Current Study
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, M.; Ahmed, A.; Xu, L. Electrospun nanofibers for functional food packaging application. Materials 2023, 16, 5937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Du, Y.; Huang, C.; Ji, Y.; Yu, D.G. Electrospun zein nanofibers: From food to food. ES Food Agrofor. 2023, 12, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azaz Ahmad, A.Z.R.; Ahmad, M.F.; Siddiqui, W.A. Food spoilage and food contamination. In Health and Safety Aspects of Food Processing Technologies, 1st ed.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 9–28. [Google Scholar]
- Amorim, L.F.; Mouro, C.; Gouveia, I.C. Electrospun fiber materials based on polysaccharides and natural colorants for food packaging applications. Cellulose 2024, 31, 6043–6069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Fang, D.; Huang, C.; Lyu, L.; Wu, W.; Li, W. Electrospun biopolymer material for antimicrobial function of fresh fruit and vegetables: Application perspective and challenges. LWT 2023, 174, 114374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wu, T.; Dai, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning and Electrospun Nanofibers: Methods, Materials, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5298–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, T.; Zhou, L.; Sun, X.; Du, H.; Zhu, Z.; Wen, Y. Electrospun functional polymeric nanofibers for active food packaging: A review. Food Chem. 2022, 391, 133239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, H. Electrospinning of nanofibers: Potentials and perspectives for active food packaging. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 479–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Dong, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Aboalhassan, A.A.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Multifunctional flexible membranes from sponge-like porous carbon nanofibers with high conductivity. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayomipo, M.O.; Oluwatoyin, I.O.; Joseph, O. Perspective Chapter: Functionalization of Nanofibers–Applications in Food Technology. In Advances in Nanofiber Research-Properties and Uses, 1st ed.; IntechOpen Publishers: London, UK, 2024; p. 194. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, T.S.M.; Kumar, K.S.; Rajini, N.; Siengchin, S.; Ayrilmis, N.; Rajulu, A.V. A comprehensive review of electrospun nanofibers: Food and packaging perspective. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 175, 107074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakhar, A.M.; Aziz, I.; Kaleri, A.R.; Hasnain, M.; Haider, G.; Ma, J.; Abideen, Z. Nanofertilizers: A sustainable technology for improving crop nutrition and food security. NanoImpact 2022, 27, 100411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, L.E.A.; de Farias Cabral, V.P.; Rodrigues, D.S.; Barbosa, A.D.; Silveira, M.J.C.B.; Coutinho, T.D.N.P.; Barbosa, S.A.; Sá, L.G.D.A.V.; de Andrade Neto, J.B.; da Rocha, S.N.C.; et al. Antifungal activity of tannic acid against Candida spp. and its mechanism of action. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2024, 55, 3679–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Lei, M.; Andargie, M.; Zeng, J.; Li, J. Antifungal activity and mechanism of action of tannic acid against Penicillium digitatum. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2019, 107, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-López, A.L.; Dávila-Aviña, J.; González, G.M.; Flores-Maldonado, O. Antifungal and Antivirulence Activity of Vanillin and Tannic Acid Against Aspergillus fumigatus and Fusarium solani. Curr. Microbiol. 2024, 81, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Fu, L.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Narcisse, K.E.; Qi, H.; Han, C.; Wang, X.; Ma, H.; Zhu, C.; et al. Tannic acid exerts antifungal activity in vitro and in vivo against Alternaria alternata causing postharvest rot on apple fruit. Physiolog. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2023, 125, 102012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek, B. Tannic acid with antiviral and antibacterial activity as a promising component of biomaterials. A minireview. Materials 2020, 13, 3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevallier, P.; Wiggers, H.J.; Copes, F.; Zorzi Bueno, C.; Mantovani, D. Prolonged Antibacterial Activity in Tannic Acid–Iron Complexed Chitosan Films for Medical Device Applications. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che Lah, N.A.; Kamaruzaman, A. The physico-chemical and antimicrobial properties of nano ZnO functionalised tannic acid. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 18596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidipour, M.; Abbaszadeh, S.; Birjandi, M.; Pajouhi, N.; Ahmadi Somaghian, S.; Goudarzi, G.; Shahryarhesami, S.; Moradi Sarabi, M.; Babaeenezhad, E. Antimicrobial activity and cytotoxic and epigenetic effects of tannic acid-loaded chitosan nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 30405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajamohan, R.; Raorane, C.J.; Kim, S.C.; Ramasundaram, S.; Oh, T.H.; Murugavel, K.; Lee, Y.R. Encapsulation of tannic acid in polyvinylidene fluoride mediated electrospun nanofibers and its antibiofilm and antibacterial activities. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2023, 34, 1911–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, L.; Langley, S.; Verghese, K.; Lockrey, S.; Ryder, M.; Francis, C.; Phan-Le, N.T.; Hill, A. The role of packaging in fighting food waste: A systematised review of consumer perceptions of packaging. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 281, 125276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammed, A.P.; Thangarasu, S.; Oh, T.H. Green interconnected network structure of chitosan-microcrystalline cellulose-lignin biopolymer film for active packaging applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammed, A.P.; Thangarasu, S.; Manoharan, R.K.; Oh, T.H. Ex-situ fabrication of engineered green network of multifaceted bacterial cellulose film with enhanced antimicrobial properties for post-harvest preservation of table grapes. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2024, 43, 101284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaram, R.; Angaiah, S.; Lee, Y.R. Polymer supported electrospun nanofibers with supramolecular materials for biological applications–a review. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2023, 72, 1042–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkadir, B.A.; Dennis, J.O.; Adam, A.A.; Al-Dhahebi, A.M.; Shukur, M.F. Novel electrospun separator-electrolyte based on PVA-K2CO3-SiO2-cellulose nanofiber for application in flexible energy storage devices. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, 52308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, F.; Latifi, M.; Shamshirsaz, M. Electrospinning/electrospray of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF): Piezoelectric nanofibers. J. Text. Inst. 2016, 107, 1037–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaram, R.; Yong, R.L.; Sundarrajulu, K.; Meenakshisundaram, S.; Samikannu, P.; Kuppusamy, M. Effect of proton ion concentration on the supramolecular interaction between phenoxazine and β-cyclodextrin. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2023, 51, 100229. [Google Scholar]
- Rajaram, R.; Lee, Y.R.; Angaiah, S. Supramolecular assembly of benzocaine bearing cyclodextrin cavity via host-guest complexes on polyacrylonitrile as an electrospun nanofiber. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 225, 115223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayakrishnan, G.; Vanaraj, R.; Kitauchi, T.; Kanthapazham, R.; Kim, S.C.; Kim, I.S. Preparation and Characterization of Polymer-Based Electrospun Nanofibers for Flexible Electronic Applications. Coatings 2024, 14, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragar, Č.; Roškar, R.; Kocbek, P. The Incorporated Drug Affects the Properties of Hydrophilic Nanofibers. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abednejad, A.; Ghaee, A.; Morais, E.S.; Sharma, M.; Neves, B.M.; Freire, M.G.; Nourmohammadi, J.; Mehrizi, A.A. Polyvinylidene fluoride–Hyaluronic acid wound dressing comprised of ionic liquids for controlled drug delivery and dual therapeutic behavior. Acta Biomater. 2019, 100, 142–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, M.; Ahmad, R.; Tantry, I.Q.; Ahmad, W.; Siddiqui, S.; Alam, M.; Abbas, K.; Hassan, M.I.; Habib, S.; Islam, S. Apoptosis: A comprehensive overview of signaling pathways, morphological changes, and physiological significance and therapeutic implications. Cells 2024, 13, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Shi, Y. Apoptosis signaling pathways and lymphocyte homeostasis. Cell Res. 2007, 17, 759–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topuz, F.; Uyar, T. Electrospinning of sustainable polymers from biomass for active food packaging. Sustain. Food Technol. 2024, 2, 1266–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olawuyi, I.F.; Park, J.J.; Lee, J.J.; Lee, W.Y. Combined effect of chitosan coating and modified atmosphere packaging on fresh-cut cucumber. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Yang, X.; Yin, H.; Lu, Y.; Dou, H.; Liu, Y.; Yu, D.G. Polymeric Nanofibers via Green Electrospinning for Safe Food Engineering. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2025, 46, 2401152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, A.S.; Sidong, K.; Inho, H. Cell-Cell Communication Between Fibroblast and 3T3-L1 Cells Under Co-culturing in Oxidative Stress Condition Induced by H2O2. Appl. Biochem. Biotech. 2016, 180, 668–681. [Google Scholar]
- Rajan, R.; Chandran, K.; Sivakumar, A.S.; Palaniappan, P.; Abhay Kumar, V.K.; Kwan Seob, S.; Chul-Gyu, S.; Soon-Il, Y. Anticancer activity of biologically synthesized silver and gold nanoparticles on mouse myoblast cancer cells and their toxicity against embryonic zebrafish. Mat. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 73, 674–683. [Google Scholar]
- Chaitany, J.R.; Vinit, R.; Jin-Hyung, L.; Jintae, L. Antifungal activities of fluoroindoles against the postharvest pathogen Botrytis cinerea: In vitro and in silico approaches. Int. J. Food. Microbiol. 2022, 362, 109492. [Google Scholar]
- Chaitany, J.R.; Thirukumaran, P.; Rajesh, H.; Shakila, P.A.; Vinit, R.; Seong-Cheol, K. Synthesis of bio-based polybenzoxazine and its antibiofilm and anticorrosive activities. Materials 2023, 16, 2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gendi, H.; Salama, A.; El-Fakharany, E.M.; Saleh, A.K. Optimization of bacterial cellulose production from prickly pear peels and its ex situ impregnation with fruit byproducts for antimicrobial and strawberry packaging applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 302, 120383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allur Subramaniyan, S.; Chinzorio, O.; Soo-Hyun, C.; Jieun, Y.; Inho, H. Antiapoptotic effect of a novel synthetic peptide from bovine muscle and MPG peptide on H2O2-induced C2C12 cells. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2014, 50, 630–639. [Google Scholar]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rajamohan, R.; Muhammed, A.P.; Raorane, C.J.; Ramasundaram, S.; Raja, I.S.; Subramanian, S.A.; Kim, S.C.; Oh, T.H.; Sun, S. Electrospun Nanofibers of Polyvinylidene Fluoride Enriched with Active Antimicrobial Tannic Acid for the Improvement of the Shelf Life of Cherry Tomatoes. Materials 2025, 18, 3112. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18133112
Rajamohan R, Muhammed AP, Raorane CJ, Ramasundaram S, Raja IS, Subramanian SA, Kim SC, Oh TH, Sun S. Electrospun Nanofibers of Polyvinylidene Fluoride Enriched with Active Antimicrobial Tannic Acid for the Improvement of the Shelf Life of Cherry Tomatoes. Materials. 2025; 18(13):3112. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18133112
Chicago/Turabian StyleRajamohan, Rajaram, Ajmal P. Muhammed, Chaitany Jayprakash Raorane, Subramaniyan Ramasundaram, Iruthayapandi Selestin Raja, Sivakumar Allur Subramanian, Seong Cheol Kim, Tae Hwan Oh, and Seho Sun. 2025. "Electrospun Nanofibers of Polyvinylidene Fluoride Enriched with Active Antimicrobial Tannic Acid for the Improvement of the Shelf Life of Cherry Tomatoes" Materials 18, no. 13: 3112. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18133112
APA StyleRajamohan, R., Muhammed, A. P., Raorane, C. J., Ramasundaram, S., Raja, I. S., Subramanian, S. A., Kim, S. C., Oh, T. H., & Sun, S. (2025). Electrospun Nanofibers of Polyvinylidene Fluoride Enriched with Active Antimicrobial Tannic Acid for the Improvement of the Shelf Life of Cherry Tomatoes. Materials, 18(13), 3112. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18133112











