Directional Effect of Plasticity Ball Burnishing on Surface Finish, Microstructure, Residual Stress and Hardness of Laser Direct Energy Deposited Stellite 21 Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Direct Metal Deposition and Specimen Preparation
2.2. Ball Burnishing Surface Treatment
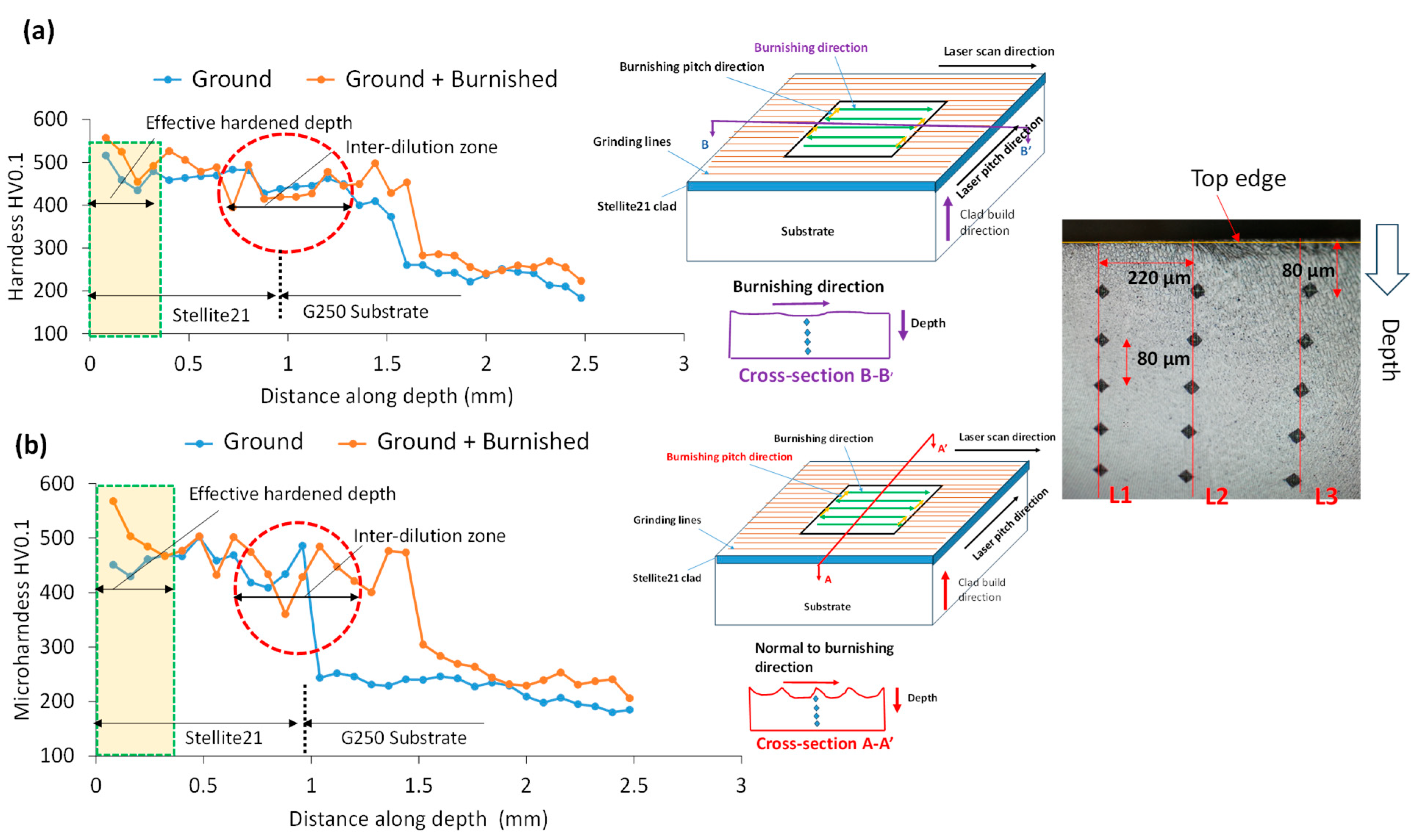
2.3. Characterisations
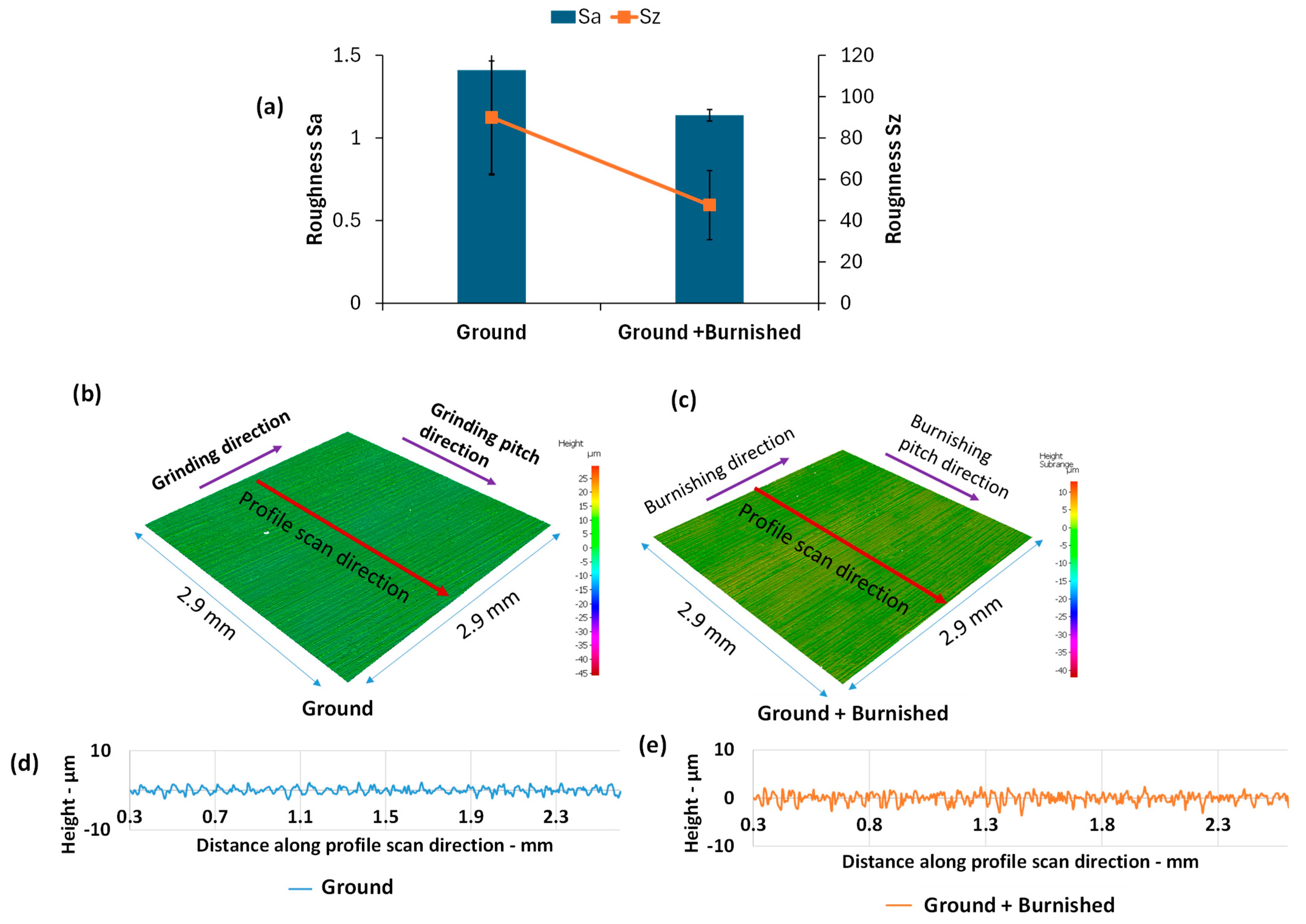
2.3.1. Surface Roughness
2.3.2. Microstructure
2.3.3. XRD
2.3.4. Microhardness
3. Results
3.1. Surface Roughness and Topography
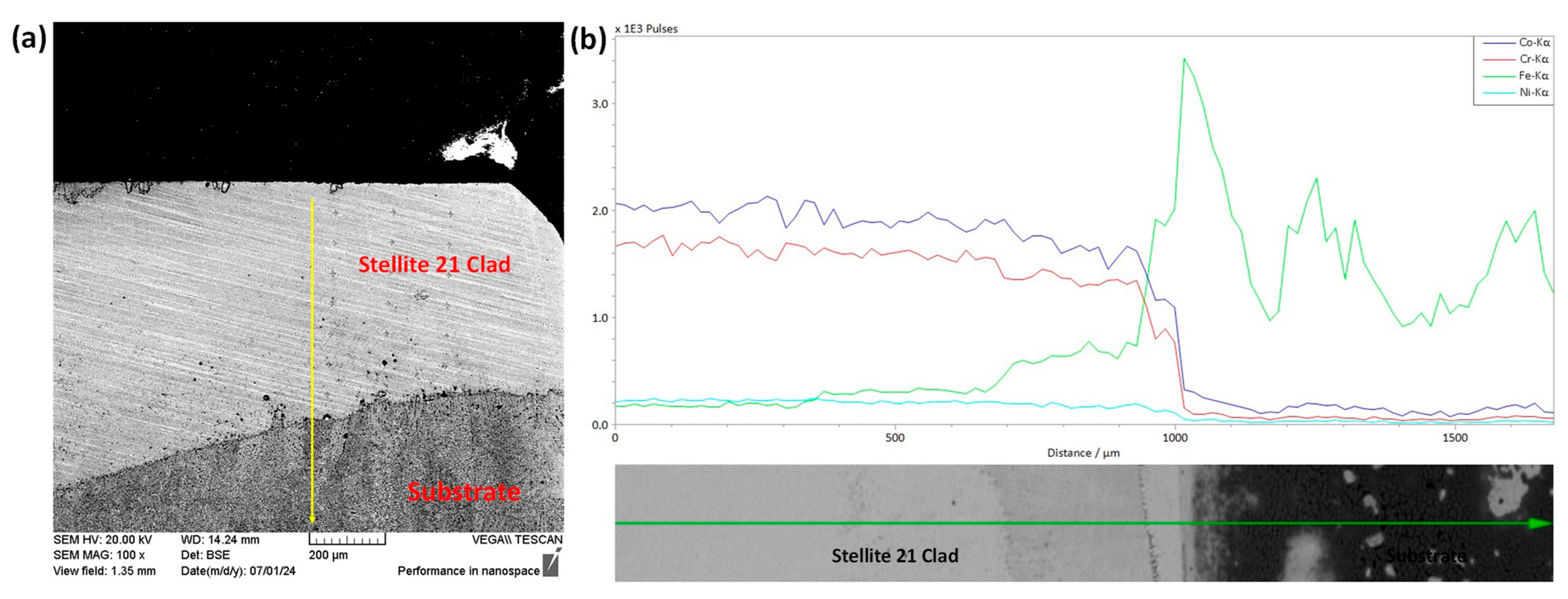
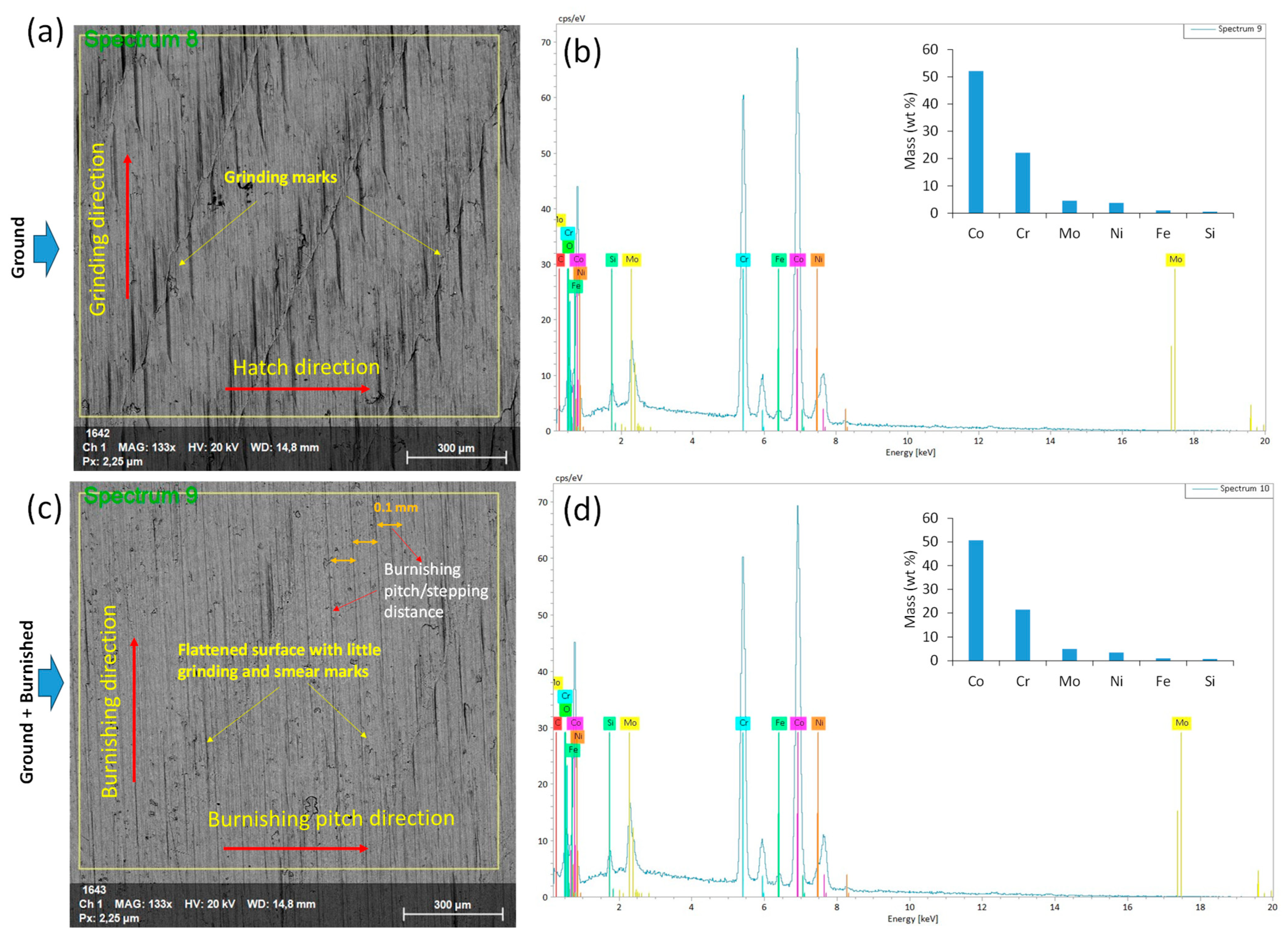
3.2. SEM and EDS Analysis
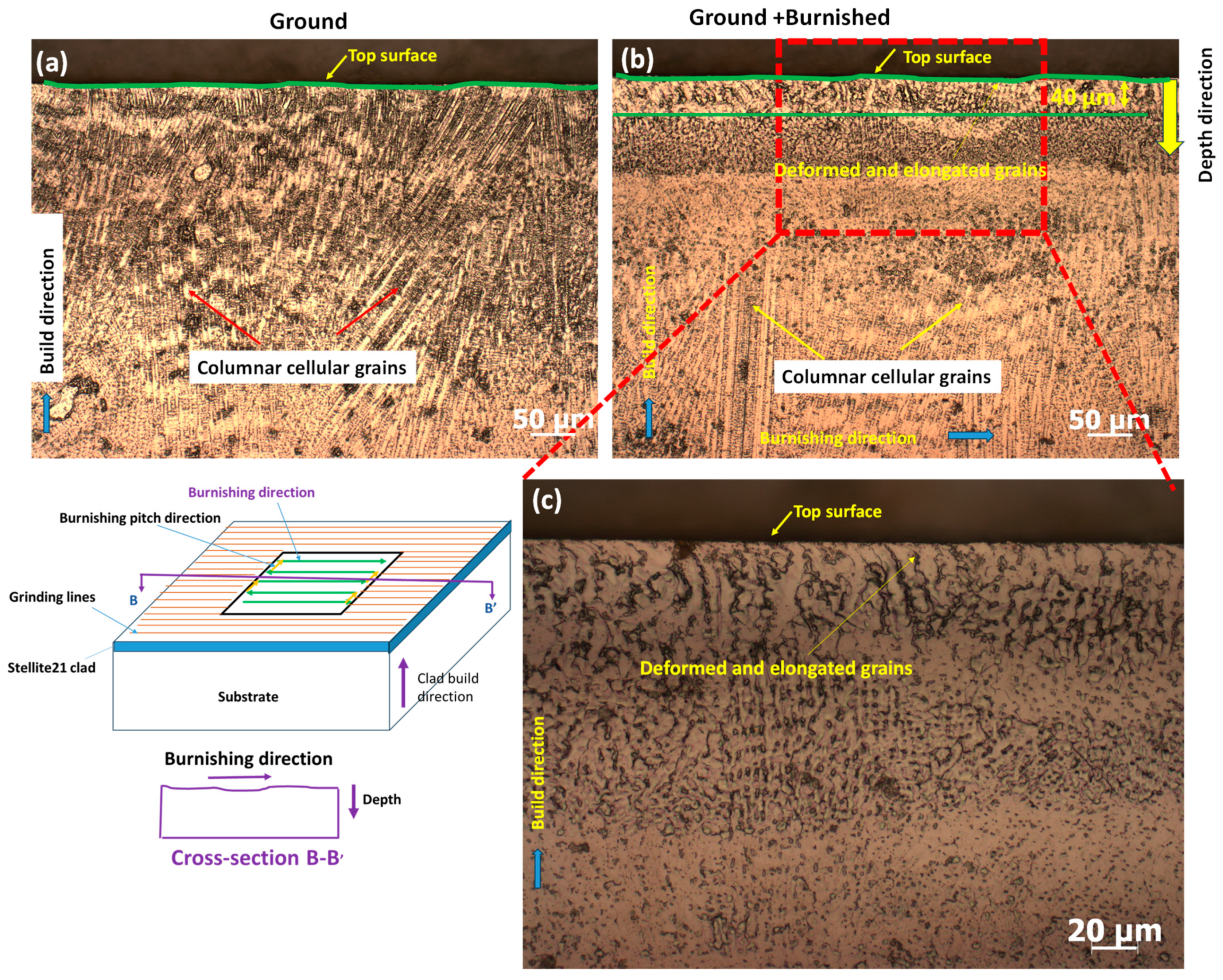
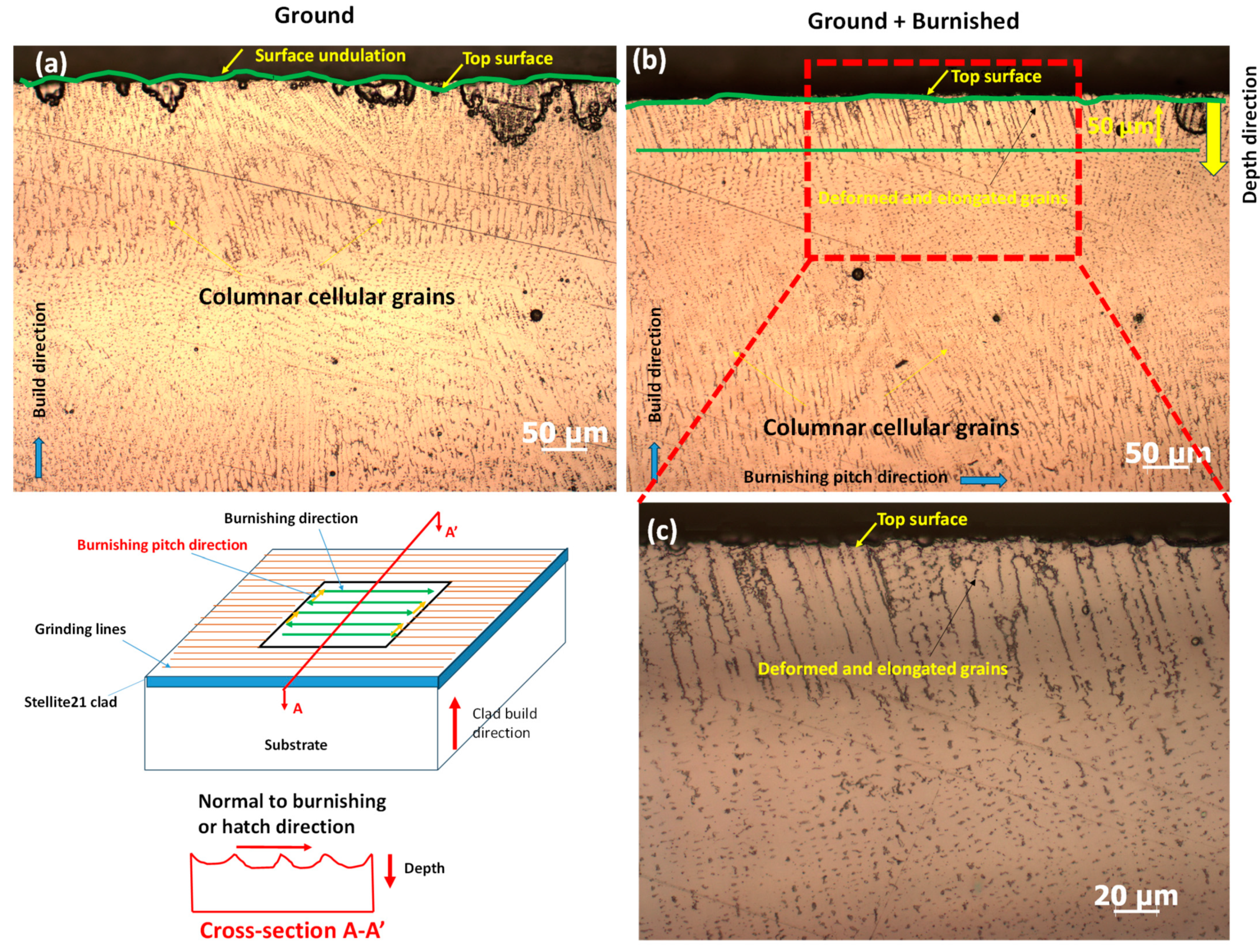
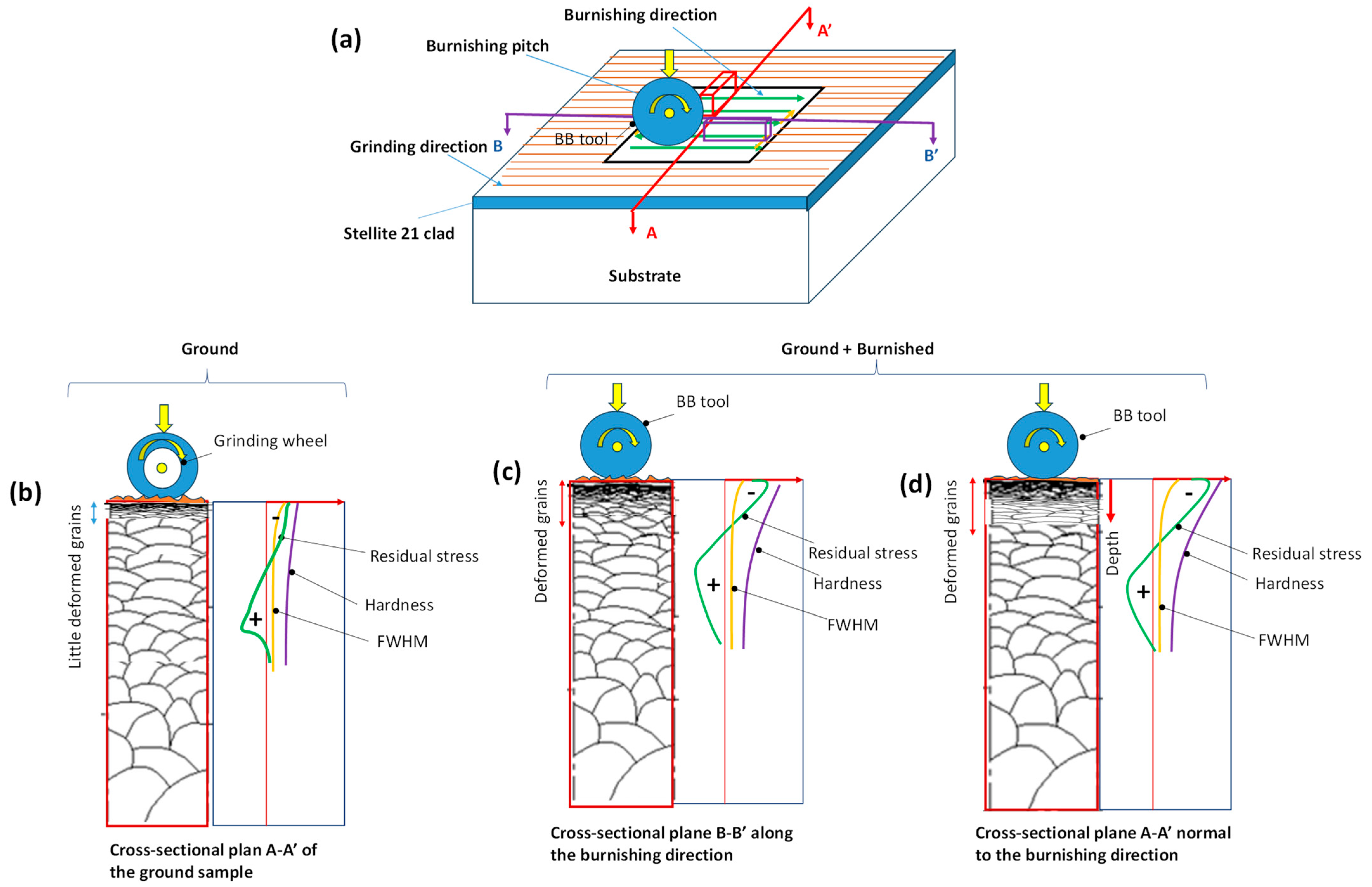
3.3. Microstructural Analysis
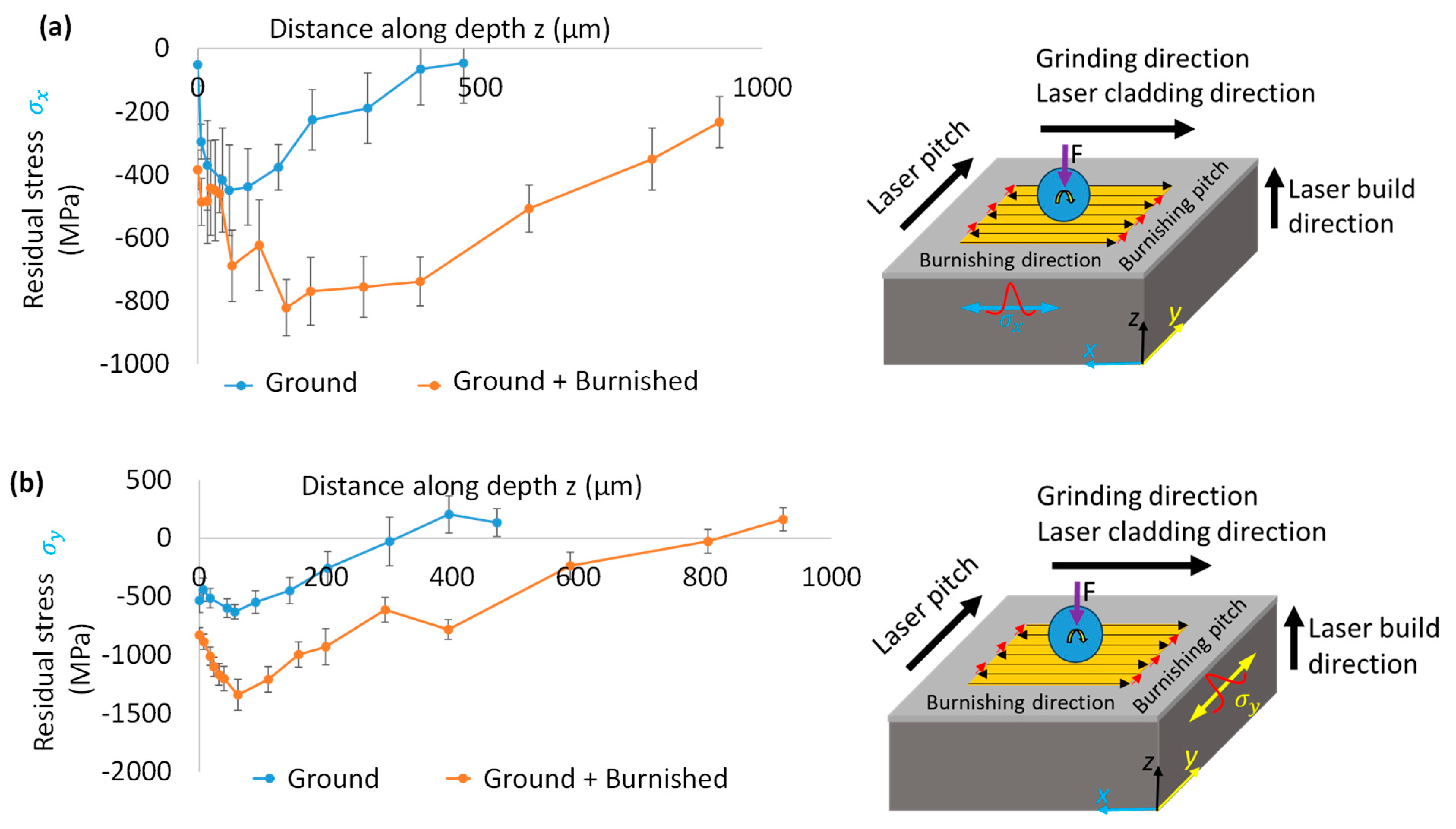
3.4. Residual Stress
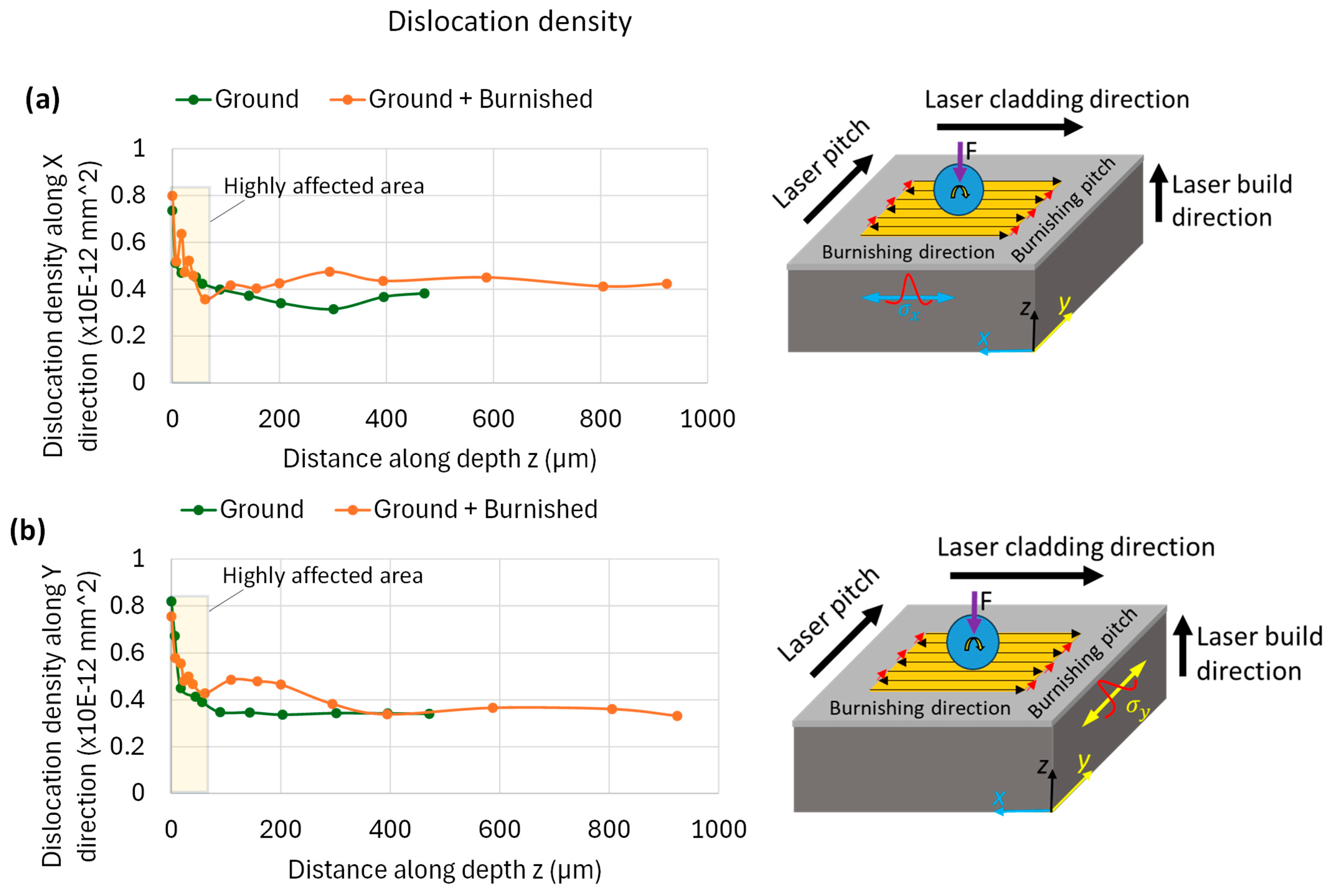
3.5. FWHM Analysis
3.6. Micro-Hardness Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The burnishing further improved the surface finish of the ground specimen by plastically deforming the surface peaks and valleys.
- The burnishing modified the Co-based dendrite structure beneath the surface, creating a flattened cellular/columnar grain structure, but the modification was more pronounced on the plane perpendicular to the burnishing direction, compared to the plane parallel to the burnishing direction.
- The burnishing effectively induced higher and deeper compressive stresses. The maximum in-depth compressive stress was higher on the plane normal to the burnishing direction than on the plane aligned with the burnishing direction, as was supported by the FWHM results.
- Due to grain refinement and potential dislocation movement, the hardness improvement was greater in the cross-sectional plane normal to the burnishing direction than along the burnishing direction.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hiew, A.; Maung, P.T.; Prusty, B.G.; Lai, Q.; Pun, C.L.; Abrahams, R.; Yan, W. Ratcheting Behaviour of Stellite 21 as Laser Cladding Material for Flange Tip Lift Crossings Repair. Int. J. Fatigue 2025, 192, 108726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoqi, Z.; Toddy, J.; Halliday, H.S.; Shield, J.E.; Rao, P. Process-Structure Relationship in the Directed Energy Deposition of Cobalt-Chromium Alloy (Stellite 21) Coatings. Mater. Des. 2021, 197, 109229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, S.; Luo, J. A New Laser Remelting Strategy for Direct Energy Deposition of 316L Stainless Steel. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2024, 238, 2139–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, P.; Moitra, A.; Tiwari, P.; Sathyanarayanan, S.; Kumar, H.; Rai, S.K.; Kaul, R.; Paul, C.P.; Prasad, R.C.; Kukreja, L.M. Fracture Behavior of Laser-Clad Joint of Stellite 21 on AISI 316L Stainless Steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 3748–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi Jeshvaghani, R.; Shamanian, M.; Jaberzadeh, M. Enhancement of Wear Resistance of Ductile Iron Surface Alloyed by Stellite 6. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 2028–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoumi, H.; Safavi, S.M.; Salehi, M.; Nahvi, S.M. Effect of Grinding on the Residual Stress and Adhesion Strength of HVOF Thermally Sprayed WC–10Co–4Cr Coating. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2014, 29, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Patel, K.V.; Jarosz, K.; Özel, T. Surface Integrity Induced in Machining Additively Fabricated Nickel Alloy Inconel 625. Procedia CIRP 2020, 87, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.R.; Liu, Z.Q.; Guo, Y.B. Machinability for Dry Turning of Laser Cladded Parts with Conventional vs. Wiper Insert. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 28, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomienne, V.; Valiorgue, F.; Rech, J.; Verdu, C. Development of a Surface Engineering Strategy to Quantify the Sensitivity of Surface Integrity Features in Fatigue Performance. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B 2023, 237, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avilés, A.; Avilés, R.; Albizuri, J.; Pallarés-Santasmartas, L.; Rodríguez, A. Effect of Shot-Peening and Low-Plasticity Burnishing on the High-Cycle Fatigue Strength of DIN 34CrNiMo6 Alloy Steel. Int. J. Fatigue 2019, 119, 338–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, E.; Bagherifard, S.; Unal, O.; Shao, S.; Shamsaei, N.; Guagliano, M. Assessing the Efficacy of Several Impact-Based Mechanical Techniques on Fatigue Behavior of Additive Manufactured AlSi10Mg. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 872, 144940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandmann, P.; Keller, S.; Kashaev, N.; Ghouse, S.; Hooper, P.A.; Klusemann, B.; Davies, C.M. Influence of Laser Shock Peening on the Residual Stresses in Additively Manufactured 316L by Laser Powder Bed Fusion: A Combined Experimental–Numerical Study. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 60, 103204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomienne, V.; Valiorgue, F.; Rech, J.; Verdu, C. Influence of Ball Burnishing on Residual Stress Profile of a 15-5PH Stainless Steel. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2016, 13, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.; Santifoller, R.; Hall, C.; Schlaefer, T. Effect of Combined Grinding–Burnishing Process on Surface Integrity, Tribological, and Corrosion Performance of Laser-Clad Stellite 21 Alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2023, 25, 2201332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.; Santifoller, R.; Hall, C.; Schlaefer, T. A Grinding-Burnishing Approach to Enhancing Surface Integrity, Tribological, and Corrosion Behavior of Laser-Cladded AISI 431 Alloys. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2021, 144, 071003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anirudh, P.V.; Kumar, B.; Girish, G.; Shailesh, S.; Oyyaravelu, R.; Kannan, C.; Balan, A.S.S. Effect of Cryogenics-Assisted Low-Plasticity Burnishing on Laser-Clad Stellite 6 over SS420 Substrate. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2020, 29, 6861–6869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radziejewska, J.; Skrzypek, S.J. Microstructure and Residual Stresses in Surface Layer of Simultaneously Laser Alloyed and Burnished Steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 2047–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courbon, C.; Sova, A.; Valiorgue, F.; Pascal, H.; Sijobert, J.; Kermouche, G.; Bertrand, P.; Rech, J. Near Surface Transformations of Stainless Steel Cold Spray and Laser Cladding Deposits after Turning and Ball-Burnishing. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 371, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjhi, S.K.; Oyyaravelu, R.; Bontha, S.; Balan, A.S.S. Effect of Burnishing Strategies on Surface Integrity, Microstructure and Corrosion Performance of Wire Arc Additively Manufactured AZ31 Mg Alloy. Int. J. Lightweight Mater. Manuf. 2024, 8, 355–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thit, M.; Rocissano, A.; Hatem, A.; Uddin, M.; Hall, C.; Schlaefer, T. Surface Integrity and High-Cycle Fatigue Life of Direct Laser Metal Deposited AISI 431 Alloys Modified by Plasticity Ball Burnishing. Int. J. Fatigue 2025, 190, 108614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Su, Y.; Pi, X.; Wen, D.; Liu, D.; Lin, Y. Enhanced Electrochemical Corrosion Resistance of 316L Stainless Steel Manufactured by Ultrasonic Rolling Assisted Laser Directed Energy Deposition. China Foundry 2024, 22, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Yu, T.; Wang, G. Microstructure and Tribological Property of Laser Cladding Stellite 6 Alloy by Laser Remelting and Ultrasonic Surface Rolling. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2025, 495, 131560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedini, M.; Lopez de Arcaute y Lozano, C.; Kostka, A.; Hanke, S. Influence of Surface Finishing by Grinding on the Cavitation Erosion Resistance of 316L and NiAl-Bronze. Wear 2024, 554–555, 205432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, M.S.; Orowan, E. X-Ray Line Broadening in Cold-Worked Metals. Nature 1948, 162, 991–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.; Chai, Z.; Huang, X.; Guo, W.; Ren, X.; Chen, H.; Chen, X. Surface Integrity Improvement of the Ground Surface of Inconel 718 Fabricated by Forging and Additive Manufacturing Using a Robotic Rotational Burnishing Method. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 125, 566–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-García, S.; Martínez-Pérez, C.E.; Rubio-González, C.; Banderas-Hernández, J.A.; Félix-Martínez, C.; Jiménez, S.M.A. Fatigue Life and Residual Stress of Flat Stainless Steel Specimens Laser-Cladded with a Cobalt-Based Alloy and Postprocessed with Laser Shock Peening. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2024, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

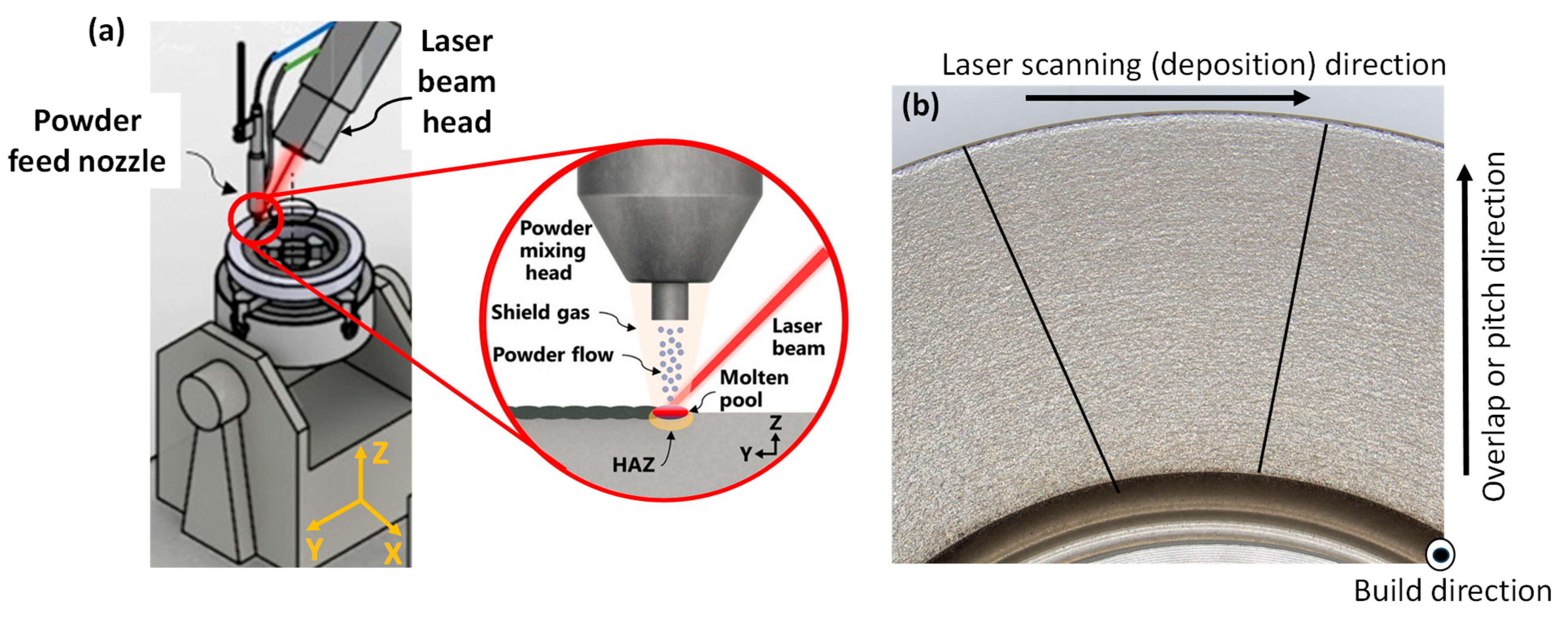




| Laser Spot | Laser Power | Laser Scanning Speed | Sheilding Gas Flowrate | Carrier Gas Flow Rate | Nozzle Stand-Off Distance | Pitching Disance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.8 mm | 5 kW | 1.5 m/min | Helium and Argon (5 LPM) | Nitrogen (7 LPM) | 17–19 mm | 2 mm |
| Material | Fe | Cr | Co | Ni | Mo | Mn | C | Si | P | S | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DEDed Stellite 21 alloy | <2.0 | 28 | Bal. | 3 | 5 | - | <1 | - | - | - | - |
| Substrate G250 | Bal. | - | - | - | - | 0.25 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.07 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Diffraction condition | Mn Kα X-ray tube 18 kV and 40 mA |
| X-ray beam size | 2 mm |
| X-ray wavelength | 2.103 Angstrom |
| X-ray penetration | up to 5 µm |
| Bragg’s angle 2-theta | 150.41° |
| Plane {hkl} | {211} |
| Bragg’s d-spacing | 1.0876296 Angstrom |
| -S1(v/E) | 0.98 × 10−6 [1/[MPa]] |
| S2/2(1 + v)/E | 5.63 × 10−6 [1/[MPa]] |
| Acquisition | mode, 7 angles from −30 to +30°, exposure of 8 s |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uddin, M.; Rech, J.; Hall, C.; Schlaefer, T. Directional Effect of Plasticity Ball Burnishing on Surface Finish, Microstructure, Residual Stress and Hardness of Laser Direct Energy Deposited Stellite 21 Alloy. Materials 2025, 18, 2971. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18132971
Uddin M, Rech J, Hall C, Schlaefer T. Directional Effect of Plasticity Ball Burnishing on Surface Finish, Microstructure, Residual Stress and Hardness of Laser Direct Energy Deposited Stellite 21 Alloy. Materials. 2025; 18(13):2971. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18132971
Chicago/Turabian StyleUddin, Mohammad, Joel Rech, Colin Hall, and Thomas Schlaefer. 2025. "Directional Effect of Plasticity Ball Burnishing on Surface Finish, Microstructure, Residual Stress and Hardness of Laser Direct Energy Deposited Stellite 21 Alloy" Materials 18, no. 13: 2971. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18132971
APA StyleUddin, M., Rech, J., Hall, C., & Schlaefer, T. (2025). Directional Effect of Plasticity Ball Burnishing on Surface Finish, Microstructure, Residual Stress and Hardness of Laser Direct Energy Deposited Stellite 21 Alloy. Materials, 18(13), 2971. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18132971








