A Low-Cost and Environmentally Friendly Electrochemical Biosensor for the Determination of Estradiol
Highlights
- A new electrochemical biosensor for β-estradiol determination was developed;
- The biorecognition layer is based on the enzyme laccase;
- Laccase was immoblilized using an innovative soft plasma polymerization technique;
- The biosensor preparation method is fast, inexpensive, and eco-friendly;
- The proposed biosensor was used for β-estradiol determination in real samples.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Biosensor Preparation
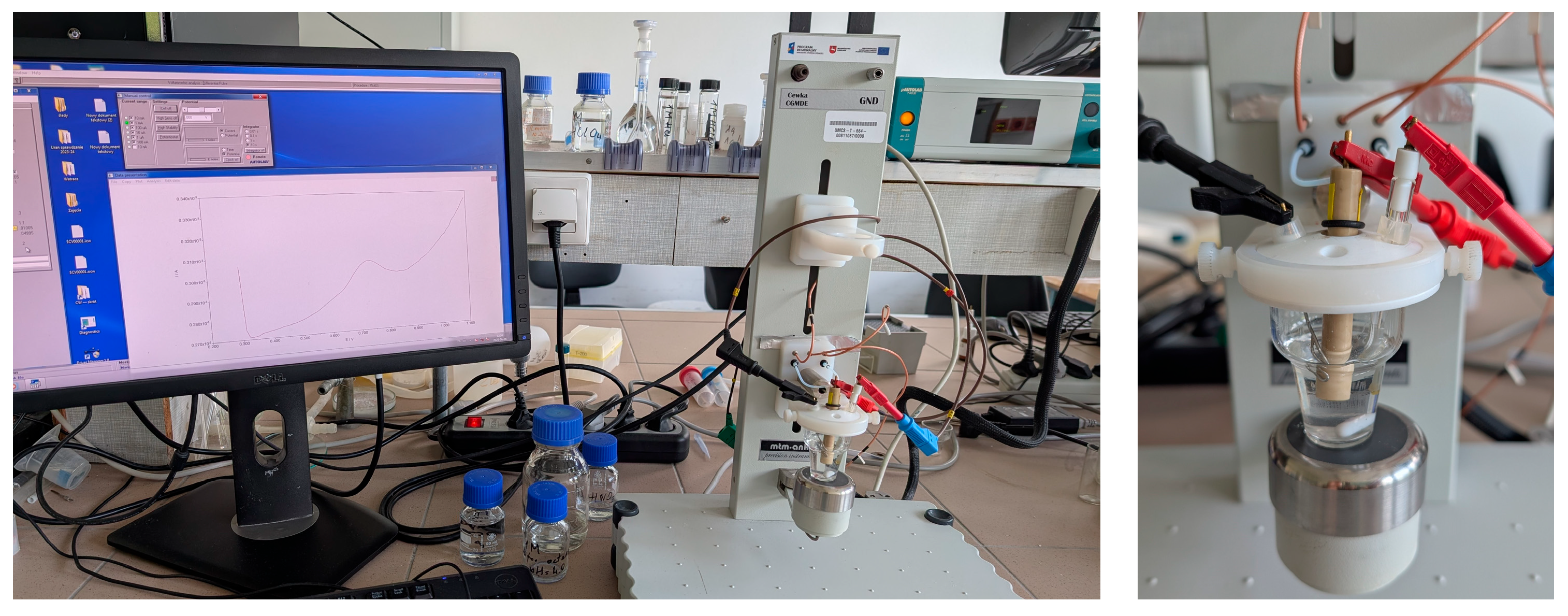
2.3. Electrochemical Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
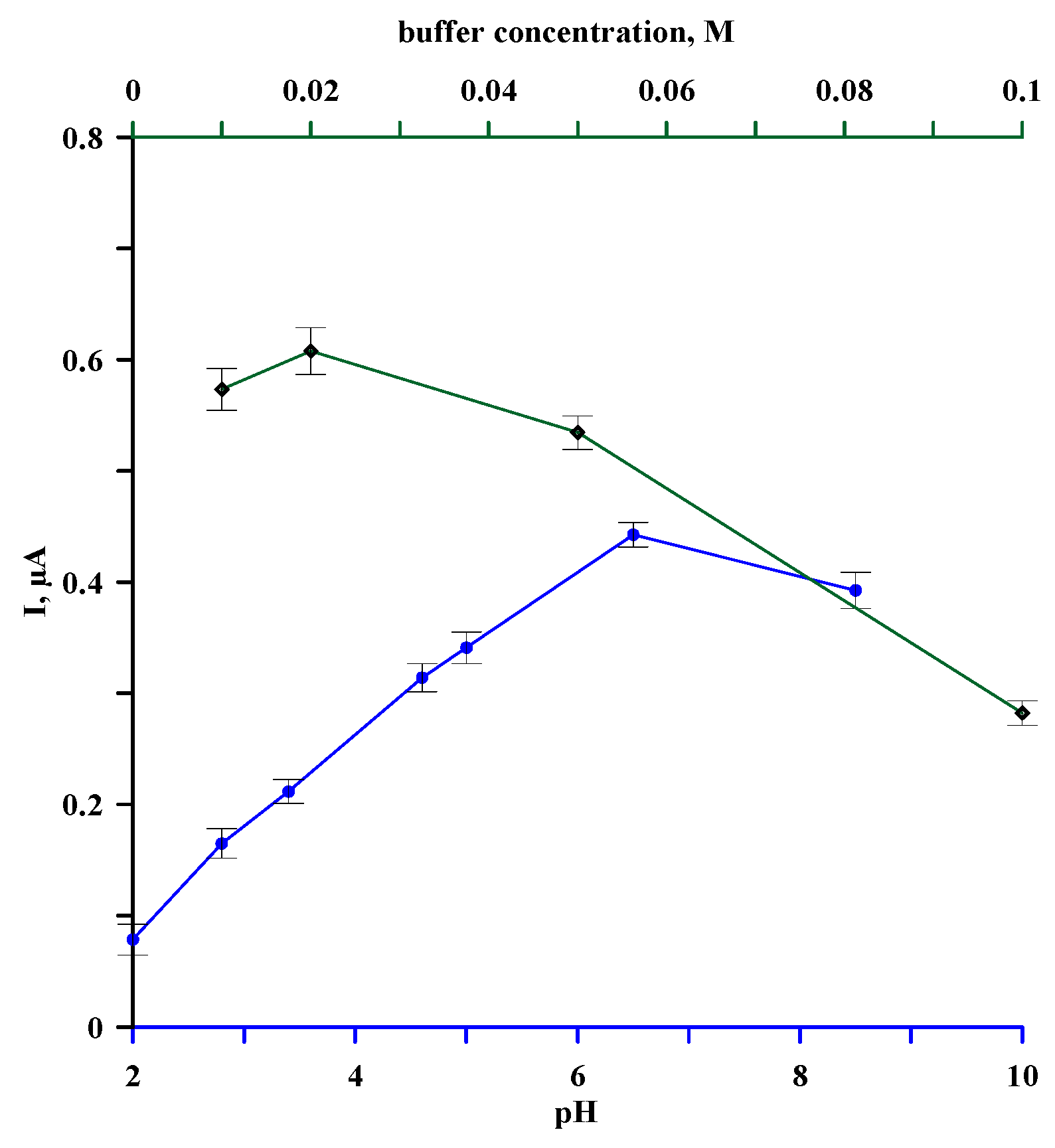
3.1. Optimization of Supporting Electrolyte Solution
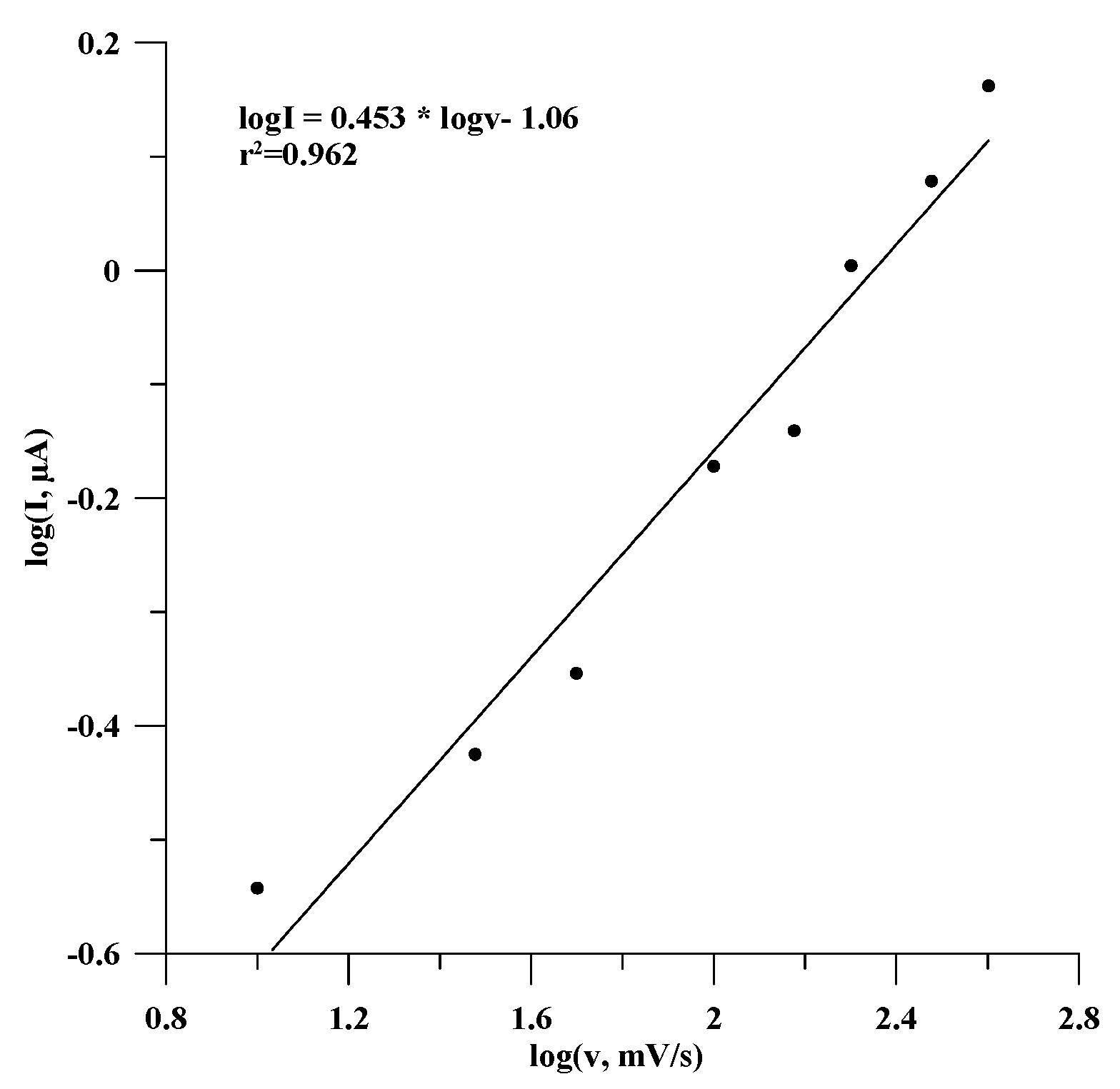
3.2. Effect of Scan Rate and Potential Step
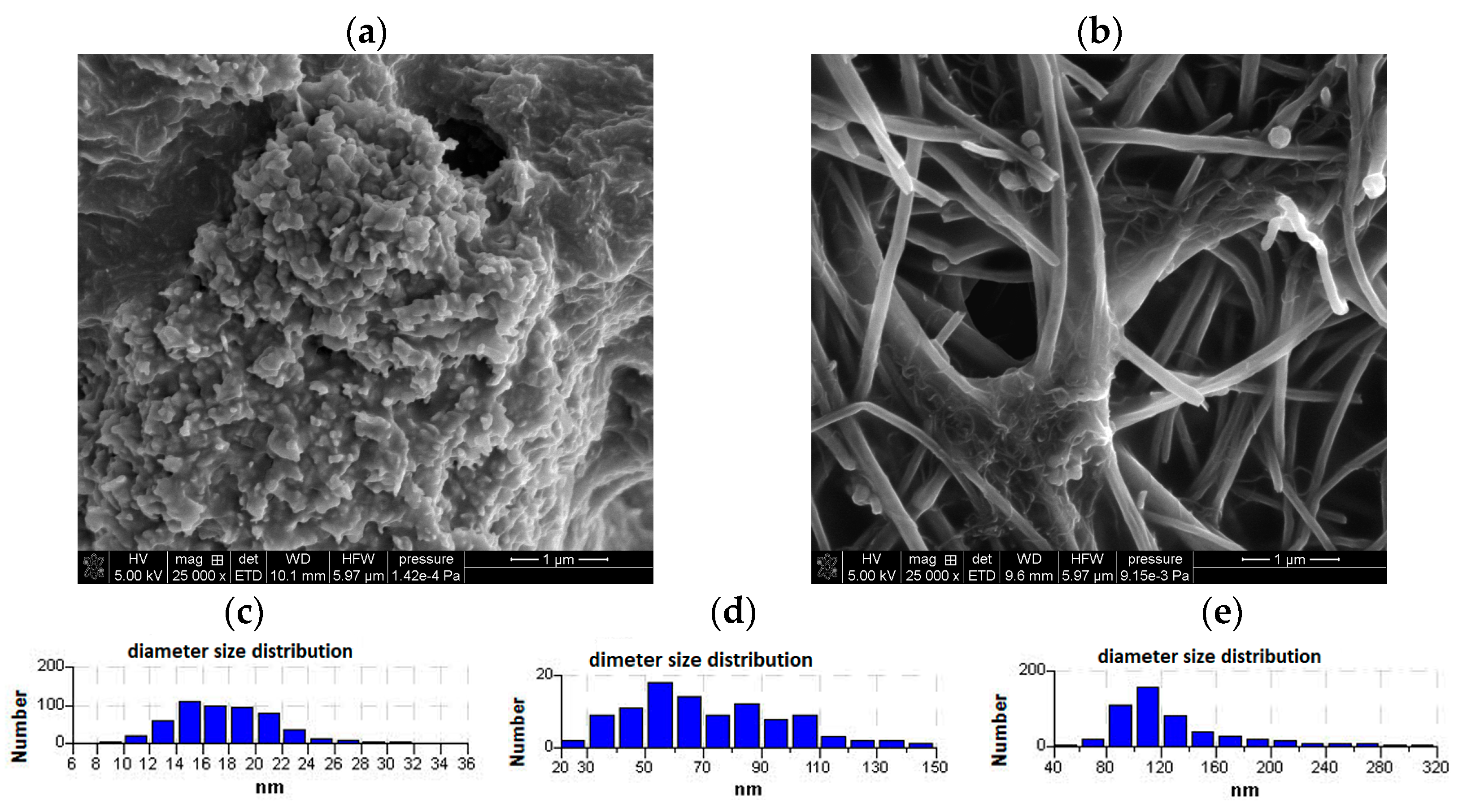
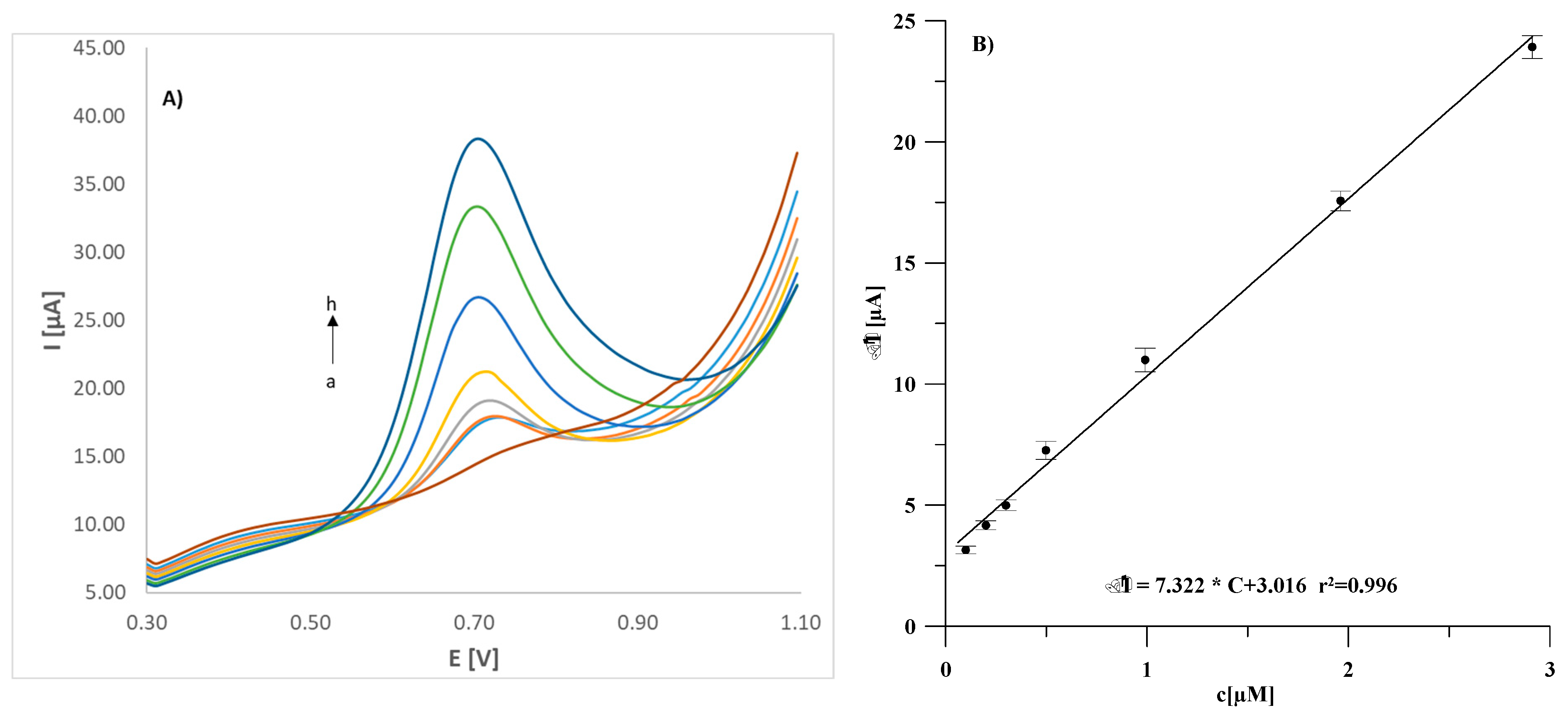
3.3. Electrochemical Response of GCE/Lac, GCE/(CuONP/CNT)/Lac, and GCE/(CNF/CNT)/Lac
3.4. Interference Studies for GCE/(CNF/CNT)/Lac Biosensor
3.5. Reproducibility and Stability of GCE/(CNF/CNT)/Lac Biosensor
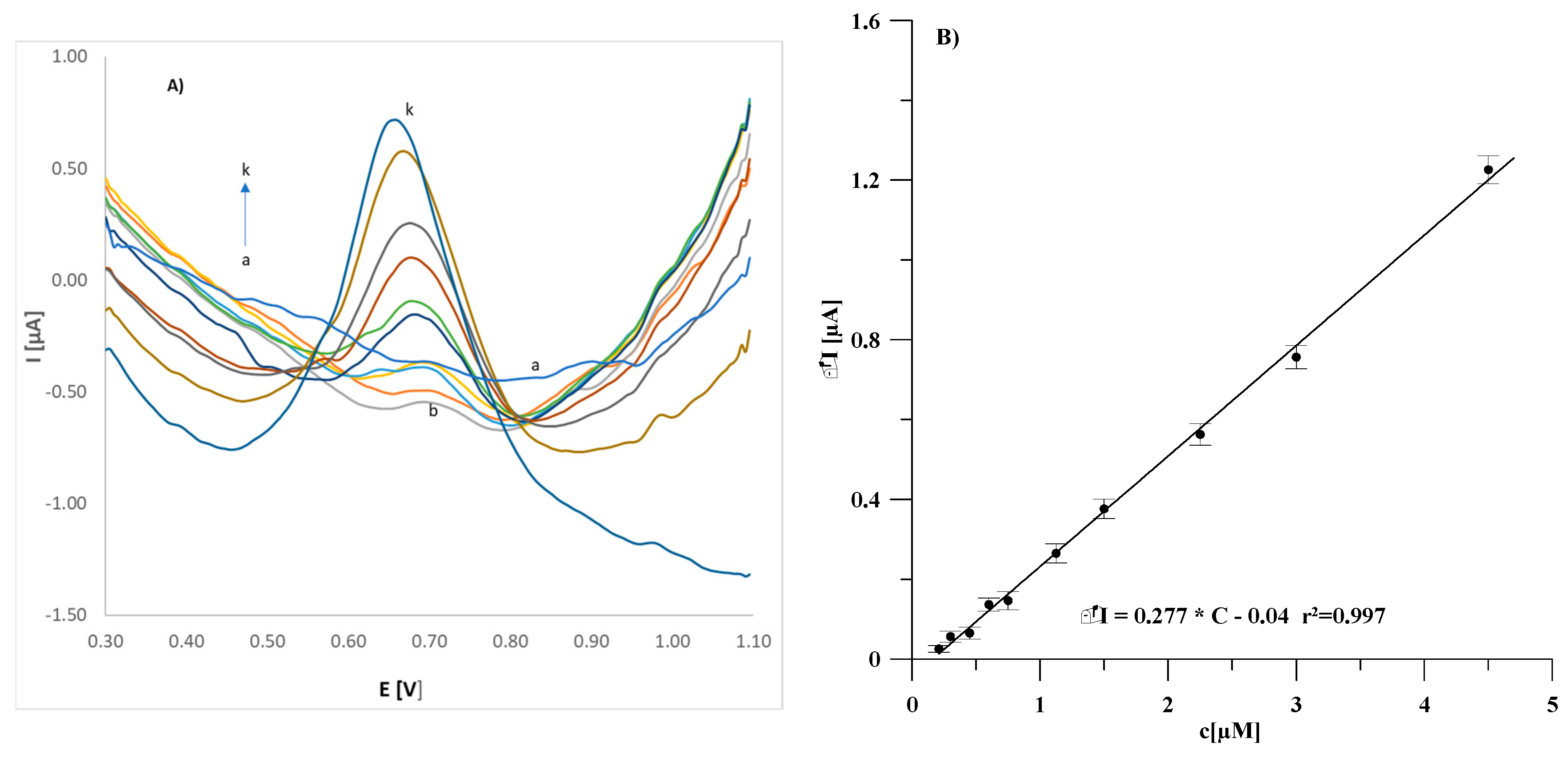
3.6. Analytical Application of GCE/(CNF/CNT)/Lac Biosensor
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baronti, C.; Curini, R.; D’Ascenzo, G.; Di Corcia, A.; Gentili, A.; Samperi, R. Monitoring Natural and Synthetic Estrogens at Activated Sludge Sewage Treatment Plants and in a Receiving River Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 5059–5066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Wang, B.; Ren, D.; Jin, W.; Liu, J.; Peng, J.; Pan, X. Occurrence, Removal and Bioaccumulation of Steroid Estrogens in Dianchi Lake Catchment, China. Environ. Int. 2013, 59, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combalbert, S.; Hernandez-Raquet, G. Occurrence, Fate, and Biodegradation of Estrogens in Sewage and Manure. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 86, 1671–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spychalska, K.; Zając, D.; Cabaj, J. Electrochemical Biosensor for Detection of 17β-Estradiol Using Semi-Conducting Polymer and Horseradish Peroxidase. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 9079–9087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, K.A.; Blanchfield, P.J.; Mills, K.H.; Palace, V.P.; Evans, R.E.; Lazorchak, J.M.; Flick, R.W. Collapse of a Fish Population after Exposure to a Synthetic Estrogen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 8897–8901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinowski, S.; Wardak, C.; Jaroszyńska-Wolińska, J.; Herbert, P.A.F.; Panek, R. Cold Plasma as an Innovative Construction Method of Voltammetric Biosensor Based on Laccase. Sensors 2018, 18, 4086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranwal, J.; Barse, B.; Gatto, G.; Broncova, G.; Kumar, A. Electrochemical Sensors and Their Applications: A Review. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, U.N.; Singh, P.; Pandey, V.P.; Kumar, A. Structure–Function Relationship among Bacterial, Fungal and Plant Laccases. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2011, 68, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Delgado, M.M.; Alemán-Nava, G.S.; Rodríguez-Delgado, J.M.; Dieck-Assad, G.; Martínez-Chapa, S.O.; Barceló, D.; Parra, R. Laccase-Based Biosensors for Detection of Phenolic Compounds. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 74, 21–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahtouri, M.G.; Fooladi, E.; Marrazza, G.; Jahani, M.; Feizy, J. Development of Laccase Electrochemical Biosensor for Detection of Dephostatin Using ZrO2/β-Cyclodextrin/Polyaniline Nanocomposite. Microchem. J. 2025, 210, 112930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Huang, B.; Han, L. Enhanced Performance of Bacterial Laccase via Microbial Surface Display and Biomineralization for Portable Detection of Phenolic Pollutants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 491, 137957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, L.C.; Zeferino, J.F.; Branco, C.; Squillaci, G.; Morana, A.; Santos, R.; Ihalainen, P.; Sobhana, L.; Correia, J.P.; Viana, A.S. Polynorepinephrine and Polydopamine-Bacterial Laccase Coatings for Phenolic Amperometric Biosensors. Bioelectrochemistry 2025, 161, 108826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Leng, J.; Yang, X.; Liao, L.; Liu, L.; Xiao, A. Enhanced Performance of Magnetic Graphene Oxide-Immobilized Laccase and Its Application for the Decolorization of Dyes. Molecules 2017, 22, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, L.-P.; Feng, J.-J.; Wu, L.; Zhou, J.-Y.; Chen, J.-R.; Wang, A.-J. Novel Phenol Biosensor Based on Laccase Immobilized on Reduced Graphene Oxide Supported Palladium–Copper Alloyed Nanocages. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinowski, S.; Wardak, C.; Pietrzak, K. Effect of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes on Analytical Parameters of Laccase-Based Biosensors Received by Soft Plasma Polymerization Technique. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 8423–8428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinowski, S.; Wardak, C.; Jaroszyńska-Wolińska, J.; Herbert, P.A.F.; Pietrzak, K. New Electrochemical Laccase-Based Biosensor for Dihydroxybenzene Isomers Determination in Real Water Samples. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 34, 101150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yohan, R.K.; Jagannathan, M.; Sivalingam, G. The Role of Emerging Photoactive Nanostructures in Electrochemical Sensor Construction: Synthesis, Properties, Challenges, and Perspectives. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2025, 145, 234–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molaakbari, E.; Mostafavi, A.; Beitollahi, H. Simultaneous Electrochemical Determination of Dopamine, Melatonin, Methionine and Caffeine. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 208, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bounegru, A.V.; Dinu Iacob, A.; Iticescu, C.; Georgescu, P.L. Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors for the Detection of Pharmaceutical Contaminants in Natural Waters—A Comprehensive Review. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardak, C.; Pietrzak, K.; Morawska, K.; Grabarczyk, M. Ion-Selective Electrodes with Solid Contact Based on Composite Materials: A Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 5839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrzak, K.; Morawska, K.; Malinowski, S.; Wardak, C. Chloride Ion-Selective Electrode with Solid-Contact Based on Polyaniline Nanofibers and Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes Nanocomposite. Membranes 2022, 12, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenar, N.; Piech, R.; Paczosa-Bator, B. High Capacity Nanocomposite Layers Based on Nanoparticles of Carbon Materials and Ruthenium Dioxide for Potassium Sensitive Electrode. Materials 2021, 14, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardak, C.; Morawska, K.; Paczosa-Bator, B.; Grabarczyk, M. Improved Lead Sensing Using a Solid-Contact Ion-Selective Electrode with Polymeric Membrane Modified with Carbon Nanofibers and Ionic Liquid Nanocomposite. Materials 2023, 16, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardak, C.; Pietrzak, K.; Grabarczyk, M. Ionic Liquid-Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes Nanocomposite Based All Solid State Ion-Selective Electrode for the Determination of Copper in Water Samples. Water 2021, 13, 2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morawska, K.; Wardak, C. Application of Ionic Liquids in Ion-Selective Electrodes and Reference Electrodes: A Review. ChemPhysChem 2024, 25, e202300818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardak, C.; Pietrzak, K.; Morawska, K. Nanocomposite of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles and Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes as a Solid Contact of a Copper-Sensitive Ion-Selective Electrode: Intermediate Layer or Membrane Component–Comparative Studies. Appl. Nanosci. 2023, 13, 7017–7028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morawska, K.; Malinowski, S.; Krawczyk, J.; Wardak, C. Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes and Copper Oxide Nanoparticles Composite Used as Transducer Medias in Nitrate Ion-Selective Electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2024, 171, 087511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, H.; Hajian, A.; Rezaei, M.; Shirzadmehr, A. Composite of Cu Metal Nanoparticles-Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes-Reduced Graphene Oxide as a Novel and High Performance Platform of the Electrochemical Sensor for Simultaneous Determination of Nitrite and Nitrate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 324, 762–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Ouyang, X.; Ding, Y.; Luo, L.; Xu, D.; Ning, Y. Electrochemical Preparation of Nickel and Copper Oxides-Decorated Graphene Composite for Simultaneous Determination of Dopamine, Acetaminophen and Tryptophan. Talanta 2016, 146, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemiec, B.; Zambrzycki, M.; Piech, R.; Wardak, C.; Paczosa-Bator, B. Hierarchical Nanocomposites Electrospun Carbon NanoFibers/Carbon Nanotubes as a Structural Element of Potentiometric Sensors. Materials 2022, 15, 4803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navrotskaya, A.G.; Aleksandrova, D.D.; Krivoshapkina, E.F.; Sillanpää, M.; Krivoshapkin, P.V. Hybrid Materials Based on Carbon Nanotubes and Nanofibers for Environmental Applications. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smajdor, J.; Zambrzycki, M.; Paczosa-Bator, B.; Piech, R. Use of Hierarchical Carbon Nanofibers Decorated with NiCo Nanoparticles for Highly Sensitive Vortioxetine Determination. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazur, I.; Rola, B.; Stolarczyk, K.; Nazaruk, E.; Bilewicz, R.; Rogalski, J.; Ohga, S. The Large Scale Production of Cerrena Unicolor Laccase on Waste Agricultural Based Media. J. Fac. Agric. Kyushu Univ. 2015, 60, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinowski, S.; Wardak, M.; Wardak, C. Effect of Modification of a Laccase-Based Electrochemical Biosensor with Carbon Nanotubes on Signal Separation of Dihydroxybenzene Isomers. Langmuir 2023, 40, 3472–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardak, C.; Paczosa-Bator, B.; Malinowski, S. Application of Cold Plasma Corona Discharge in Preparation of Laccase-Based Biosensors for Dopamine Determination. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 116, 111199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinowski, S.; Herbert, P.A.F.; Rogalski, J.; Jaroszyńska-Wolińska, J. Laccase Enzyme Polymerization by Soft Plasma Jet for Durable Bioactive Coatings. Polymers 2018, 10, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, T.; Tan, Z.; Tian, X.; Hou, W. Ionic Liquid Functionalized Graphene Oxide-Au Nanoparticles Assembly for Fabrication of Electrochemical 2,4-Dichlorophenol Sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 246, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Wei, W.; Zeng, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y. Electrocatalytic Oxidation and Determination of Estradiol Using an Electrode Modified with Carbon Nanotubes and an Ionic Liquid. Microchim. Acta 2009, 166, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K.M.; Archer, R.D. PKa Values of Estrone, 17β-Estradiol and 2-Methoxyestrone. Steroids 1979, 34, 485–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SALIMI, A.; MIRANZADEH, L.; HALLAJ, R. Amperometric and Voltammetric Detection of Hydrazine Using Glassy Carbon Electrodes Modified with Carbon Nanotubes and Catechol Derivatives. Talanta 2007, 75, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, H.; Pajooheshpour, N.; Jamali, B.; Amidi, S.; Hajian, A.; Khoshsafar, H. A Novel Electrochemical Platform for Sensitive and Simultaneous Determination of Dopamine, Uric Acid and Ascorbic Acid Based on Fe3O4SnO2Gr Ternary Nanocomposite. Microchem. J. 2017, 131, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabarczyk, M.; Fialek, M.; Wardak, C. Use of Adsorption Properties of Resin for Water Sample Preparation in Voltammetric Determination of Se(IV) Using Bismuth Microelectrode. Molecules 2024, 29, 5501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arano-Martinez, J.A.; Martínez-González, C.L.; Salazar, M.I.; Torres-Torres, C. A Framework for Biosensors Assisted by Multiphoton Effects and Machine Learning. Biosensors 2022, 12, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Kong, F.; Liu, Y.; Lv, S.; Zhang, K.; Sun, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, M.; Cai, X.; Jin, H.; et al. 17β-Estradiol Biosensors Based on Different Bioreceptors and Their Applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1347625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, P.; Chen, J.; Wang, R.; Wen, T.; Li, Y.; Zhou, X.; Jiang, H. Electrochemical Sensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Membranes at Platinum Nanoparticles-Modified Electrode for Determination of 17β-Estradiol. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 29, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, P.; Tu, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhan, G.; Li, C. A Novel Electrochemical Sensor for Estradiol Based on Nanoporous Polymeric Film Bearing Poly{1-Butyl-3-[3-(N-Pyrrole)Propyl]Imidazole Dodecyl Sulfonate} Moiety. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 193, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniazzi, C.; de Lima, C.A.; Marangoni, R.; Spinelli, A.; de Castro, E.G. Voltammetric Determination of 17β-Estradiol in Human Urine and Buttermilk Samples Using a Simple Copper(II) Oxide-Modified Carbon Paste Electrode. J. Solid. State Electrochem. 2018, 22, 1373–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janegitz, B.C.; Dos Santos, F.A.; Faria, R.C.; Zucolotto, V. Electrochemical Determination of Estradiol Using a Thin Film Containing Reduced Graphene Oxide and Dihexadecylphosphate. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 37, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, F.C.; Rossi, B.; Donatoni, M.C.; de Oliveira, K.T.; Pereira, E.C. Sensitive Determination of 17β-Estradiol in River Water Using a Graphene Based Electrochemical Sensor. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 881, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


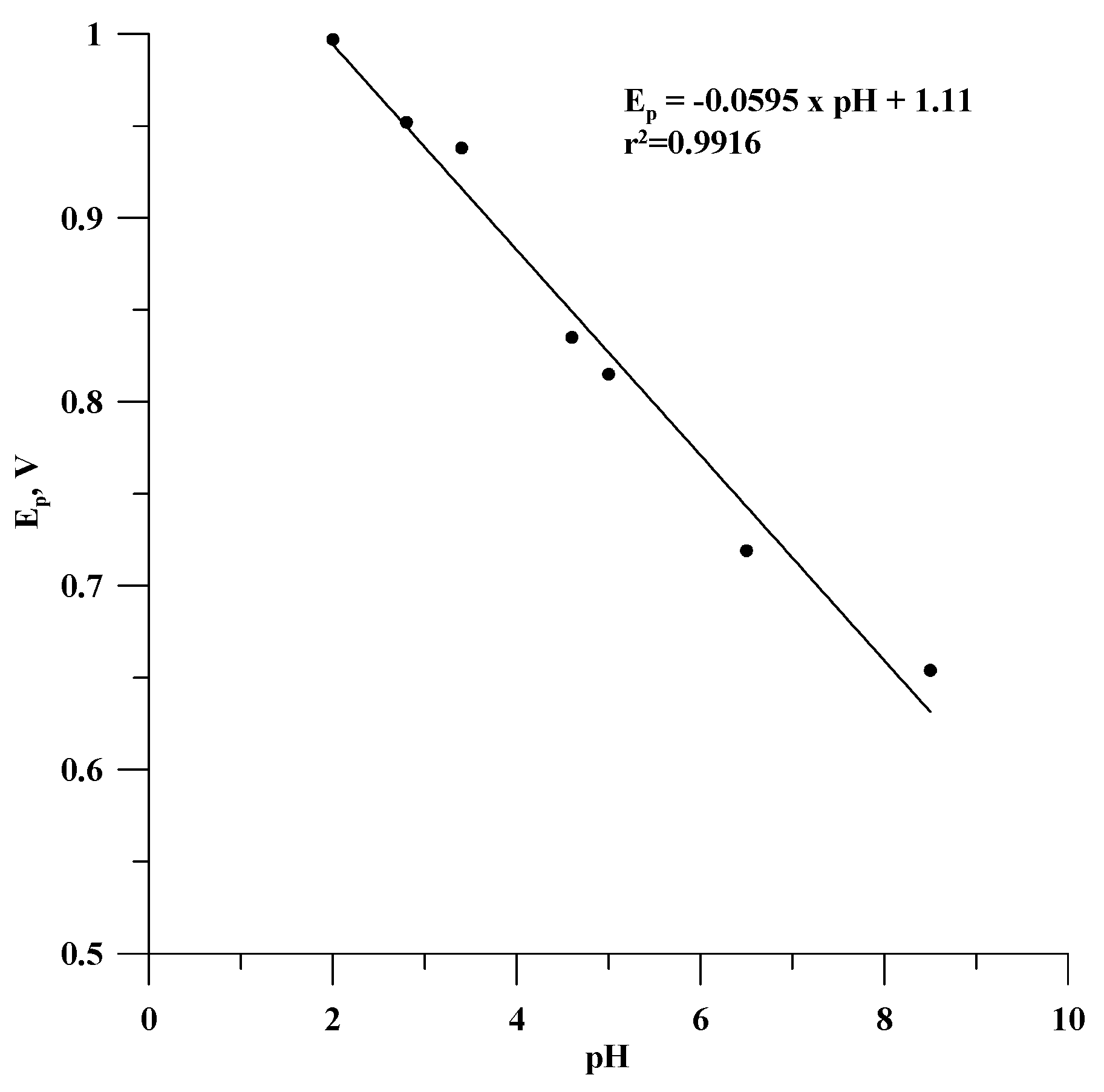


| Interferent | Selectivity Coefficient (SC), % | |
|---|---|---|
| [E]:[I] = 1:1 | [E]:[I] = 1:5 | |
| glutamic acid | 2.81 ± 0.30 | 2.66 ± 0.41 |
| lactose | 3.11 ± 0.51 | 2.87 ± 0.55 |
| glucose | 2.58 ± 0.42 | 2.79 ± 0.48 |
| glycine | 4.53 ± 1.10 | 4.78 ± 0.90 |
| mannitol | 3.42 ± 0.41 | 3.21 ± 0.52 |
| saccharose | 1.11 ± 0.02 | 1.15 ± 0.03 |
| starch | 0.2 ± 0.11 | 0.40 ± 0.13 |
| ascorbic acid | 1.12 ± 0.21 | 1.10 ± 0.28 |
| NaCl | 0.10 ± 0.06 | 0.12 ± 0.04 |
| humic substances | 4.90 ± 1.11 a | 7.84 ± 1.90 b |
| fulvic substances | 3.71 ± 0.92 a | 5.14 ± 1.41 b |
| Sample | Added, µM | Found, mg/Tablet; µM 1 | Declared Content, mg/Tablet | Recovery% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estrofem 2 mg | - | 1.98 ± 0.021 | 2 | 99.0 ± 1.1 |
| Estrofem mite | - | 0.966 ± 0.018 | 1 | 96.6 ± 1.8 |
| River water | - | - | ||
| River water + 0.1 µM | 0.1 µM | 0.0963 ± 0.0042 | 96.3 ± 4.2 | |
| River water + 0.5 µM | 0.5 µM | 0.476 ± 0.021 | 95.2 ± 4.2 |
| Linear Range, µM | Sensitivity µA/µM | LOD, µM | Accumulation Step | Additional Time (Accumulation/Incubation/Deaeration, min) | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIPs/PtNPs/GCE | 0.03–50 | 0.79 | 0.016 | ✓ | 14 | [45] |
| BPIDS/GCE | 0.1–10 | 0.19 | 0.050 | ✓ | 3 | [46] |
| CuO/CPE | 0.06–0.8 | 3.409 | 0.021 | ✗ | nm | [47] |
| rGO-DHP/GCE | 0.4–5.0 | 1.65 | 0.070 | ✓ | 2 | [48] |
| CuThP/rGO/GCE | 0.1–1 | 0.39 | 0.005 | ✗ | nm | [49] |
| GCE/(CNF/CNT)/Lac | 0.1–3 | 7.32 | 0.026 | ✗ | - | This Work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wardak, C.; Wólczyński, H.; Malinowski, S.; Paczosa-Bator, B.; Wardak, M. A Low-Cost and Environmentally Friendly Electrochemical Biosensor for the Determination of Estradiol. Materials 2025, 18, 2932. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18132932
Wardak C, Wólczyński H, Malinowski S, Paczosa-Bator B, Wardak M. A Low-Cost and Environmentally Friendly Electrochemical Biosensor for the Determination of Estradiol. Materials. 2025; 18(13):2932. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18132932
Chicago/Turabian StyleWardak, Cecylia, Hubert Wólczyński, Szymon Malinowski, Beata Paczosa-Bator, and Magdalena Wardak. 2025. "A Low-Cost and Environmentally Friendly Electrochemical Biosensor for the Determination of Estradiol" Materials 18, no. 13: 2932. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18132932
APA StyleWardak, C., Wólczyński, H., Malinowski, S., Paczosa-Bator, B., & Wardak, M. (2025). A Low-Cost and Environmentally Friendly Electrochemical Biosensor for the Determination of Estradiol. Materials, 18(13), 2932. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18132932








