Towards a Sustainable Material Protection: Olanzapine Drugs and Their Derivatives as Corrosion Inhibitors for C1018 Steel in 1 M Hydrochloric Acid
Abstract
1. Introduction
| No. | Drug Name | Metal/Alloy | Corrosive Medium | Used Methods | Max IE% | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Helicure drug | Carbon Steel | 1 M HCl | WL + EIS + EFM | 85.8% (at 300 ppm) | [11] |
| 2 | Spironolactone drug | n C38 Carbon Steel | 10% HCl | WL + EIS + PDP | 95.8% (at 7.2 × 10−3 M) | [12] |
| 3 | Atenolol | Carbon Steel | 1 M HCl | WL + EIS + PDP | 93.8% (at 300 ppm) | [13] |
| 4 | Irbesartan | Carbon Steel | 1 M HCl | OCP + EIS + LPR + PDP + CV | 94% at 300 mg L−1 | [14] |
| 5 | Metoprolol | Steel alloy (st 37) | 1 M HCl | EIS + PDP | 87% (300 ppm) | [15] |
| 6 | Hydralazine | Carbon Steel | 1 M HCl | WL + EIS + PDP | 91.44% (1250 ppm at 323 K) | [16] |
| 7 | Ciprofloxacin | Carbon Steel | 1 M HCl | WL + EIS | 69.99% (at 0.7% v/v%) | [17] |
| 8 | Doxofylline | Soft Steel | 1 M HCl | WL + EIS | 72.6% (200 ppm) | [18] |
| 9 | Irnocam | Carbon Steel | 1 M HCl | WL + EIS | 75.4% (at 600 ppm) | [19] |
| 10 | Lumerax | Carbon Steel | 1 M HCl | EIS + PDP | 97.6% (100 mg/L) | [20] |
| 11 | Meloxicam | Carbon Steel | 1 M HCl | EIS + PDP | 80.8% (30 ppm) | [21] |
| 12 | Ornidazole | Carbon Steel | 1 M HCl | WL + EIS + PDP | 71.61% (2 × 10−5 M) | [22] |
| 13 | Tramadol | Carbon Steel | 1 M HCl | EIS + PDP | 97.2% (100 ppm) | [23] |
| 14 | Dulcolax | Carbon Steel | 1 M HCl | EIS + PDP + AAS | 92.5% (500 ppm) | [24] |
| 15 | Gentamicin | Carbon Steel | 1 M HCl | WL + EIS + PDP | 75.06% (0.9% v/v) | [25] |
| 16 | Norfloxacin | Carbon Steel | 1 M HCl | WL + EIS + PDP | 89.8% | [26] |
| 17 | Olanzapine | Carbon Steel | 1 M HCl | LPR | 92.47 | Our work |
2. Experimental Section
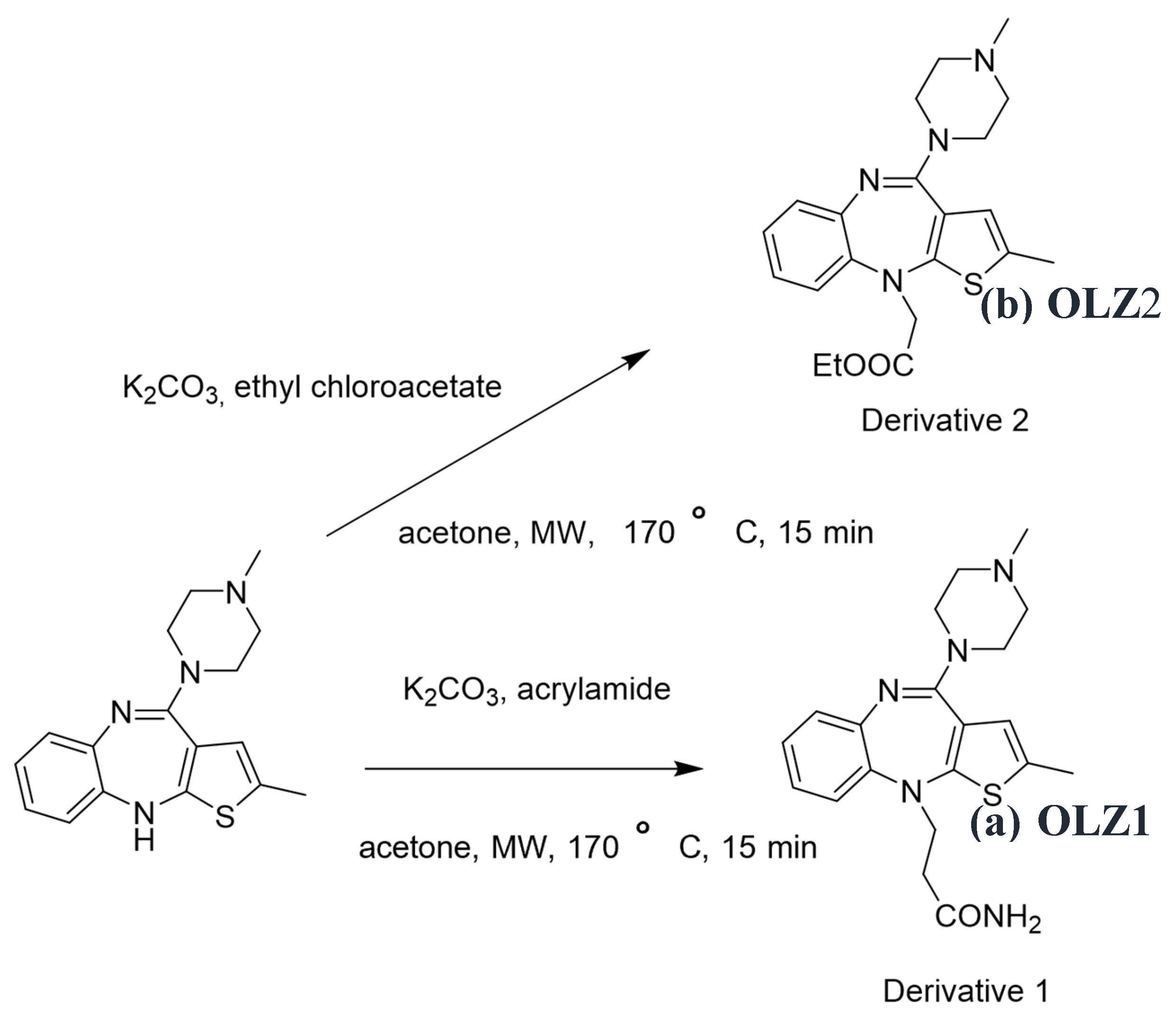
2.1. Synthesis of the Corrosion Inhibitors
2.2. Weight Loss Measurements
2.3. Electrochemical Measurements
2.4. Computational Methods
2.4.1. DFT Calculations
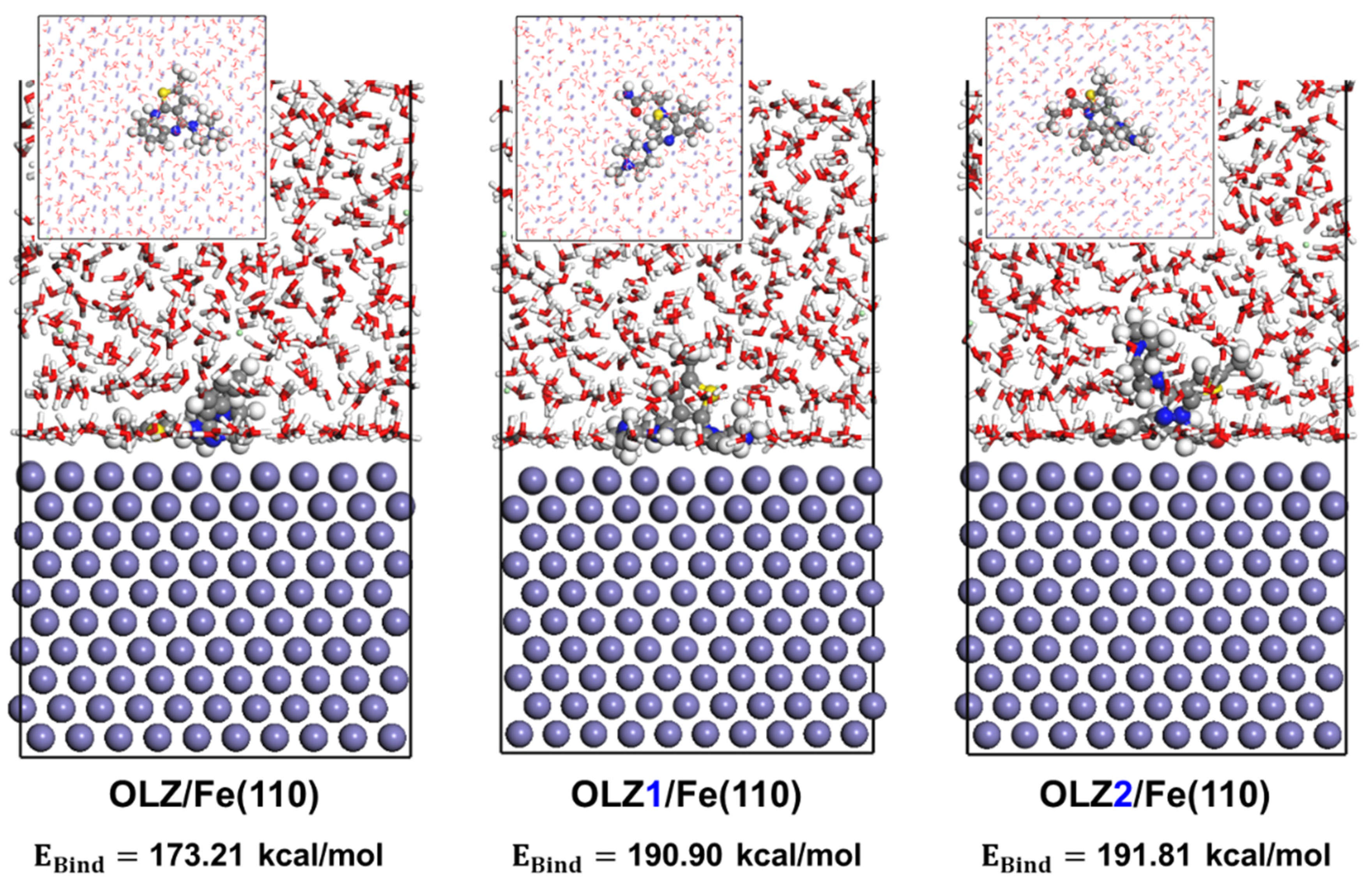
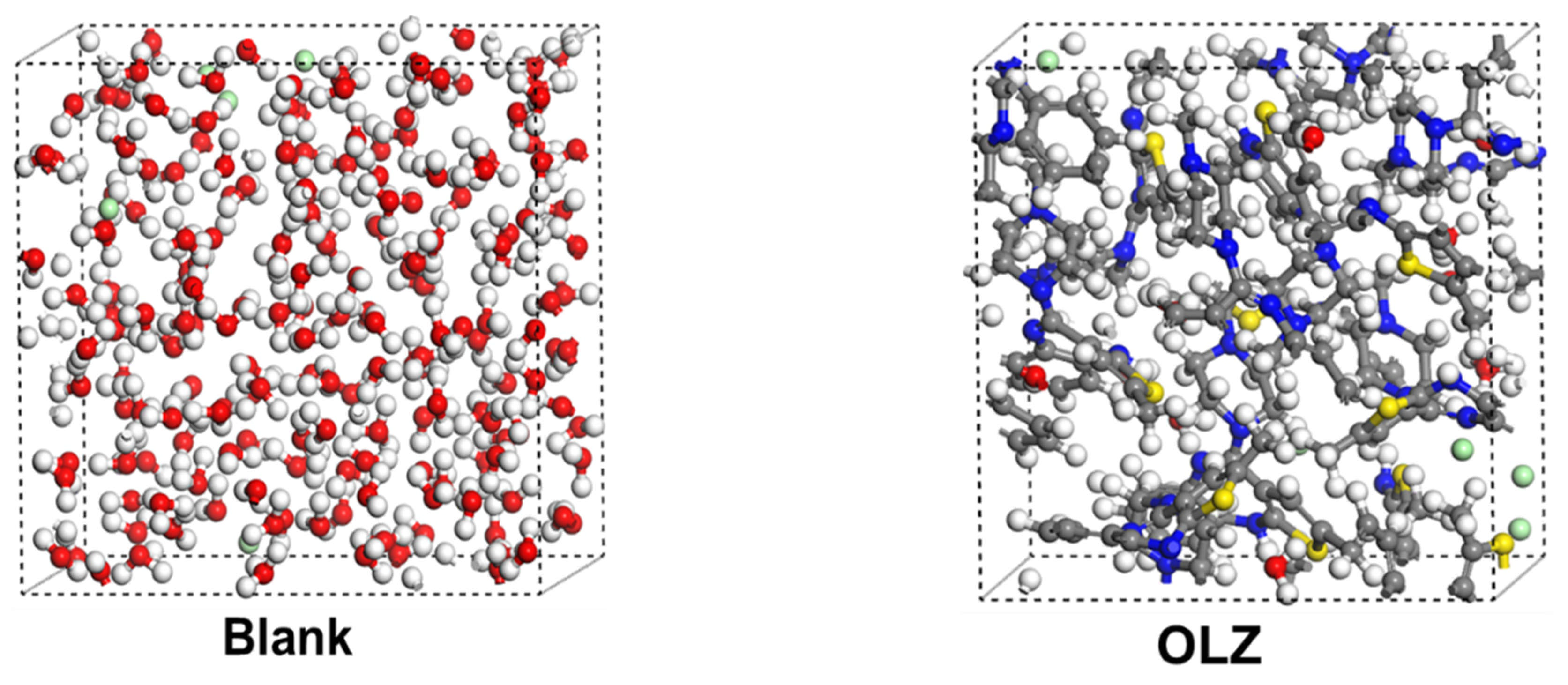
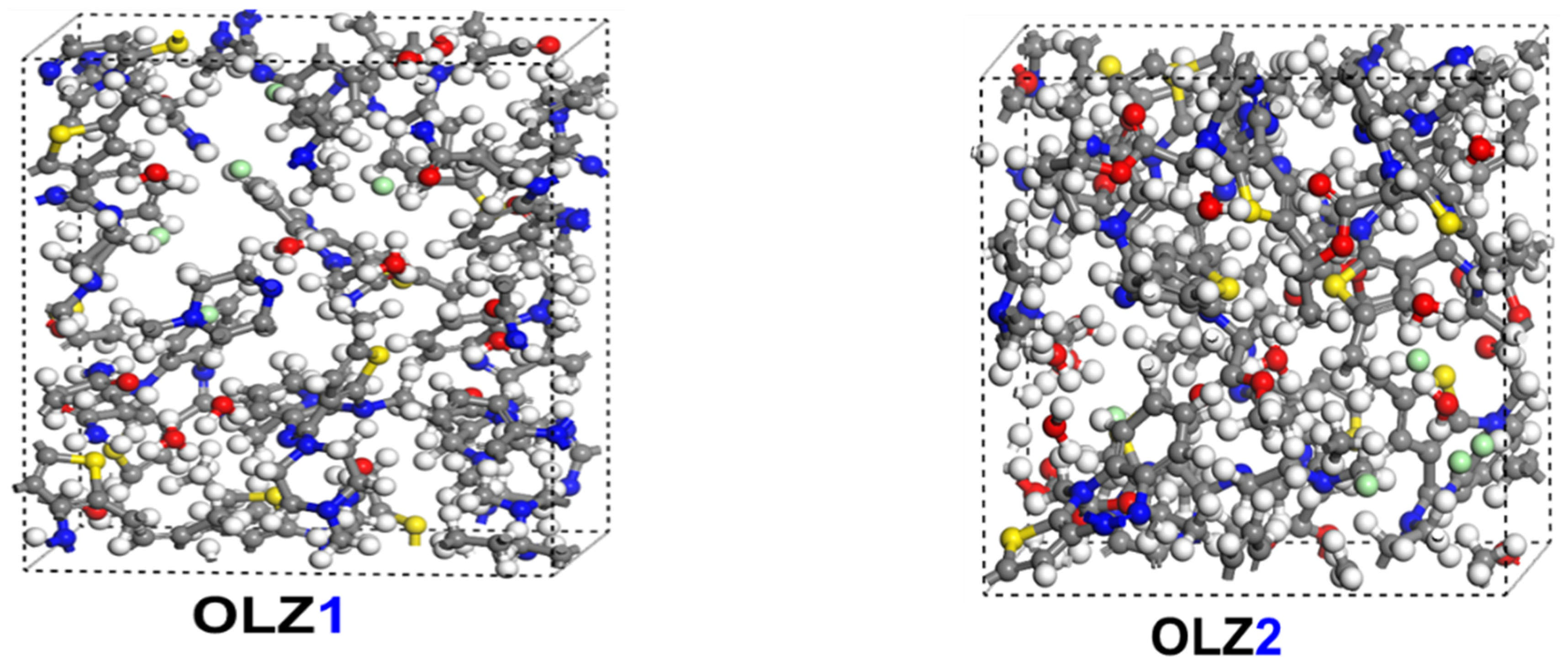
2.4.2. MD Simulations
2.5. Surface Analyses
2.5.1. FTIR Analysis
2.5.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Weight Loss Measurements
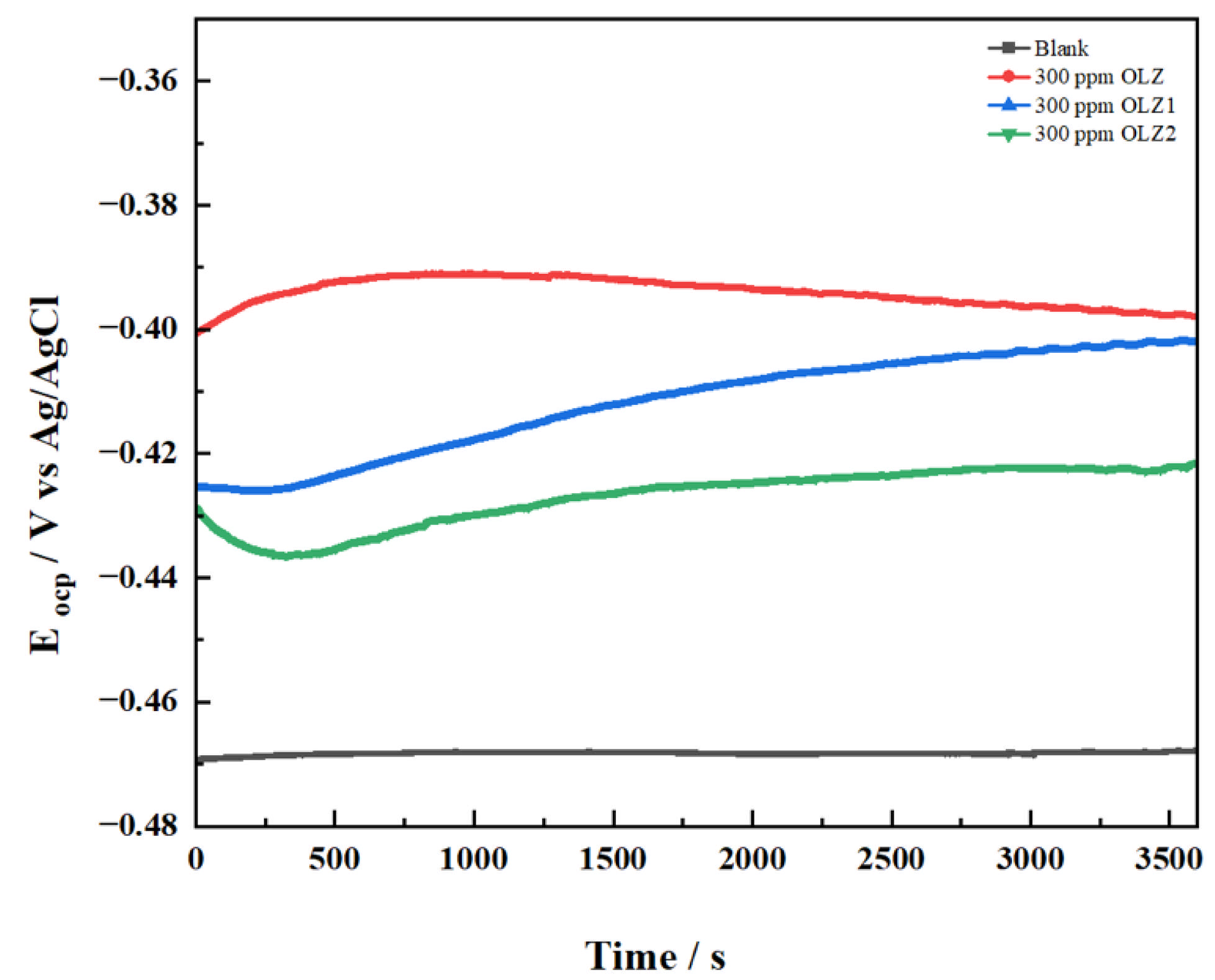
3.2. Open Circuit Potential Measurements
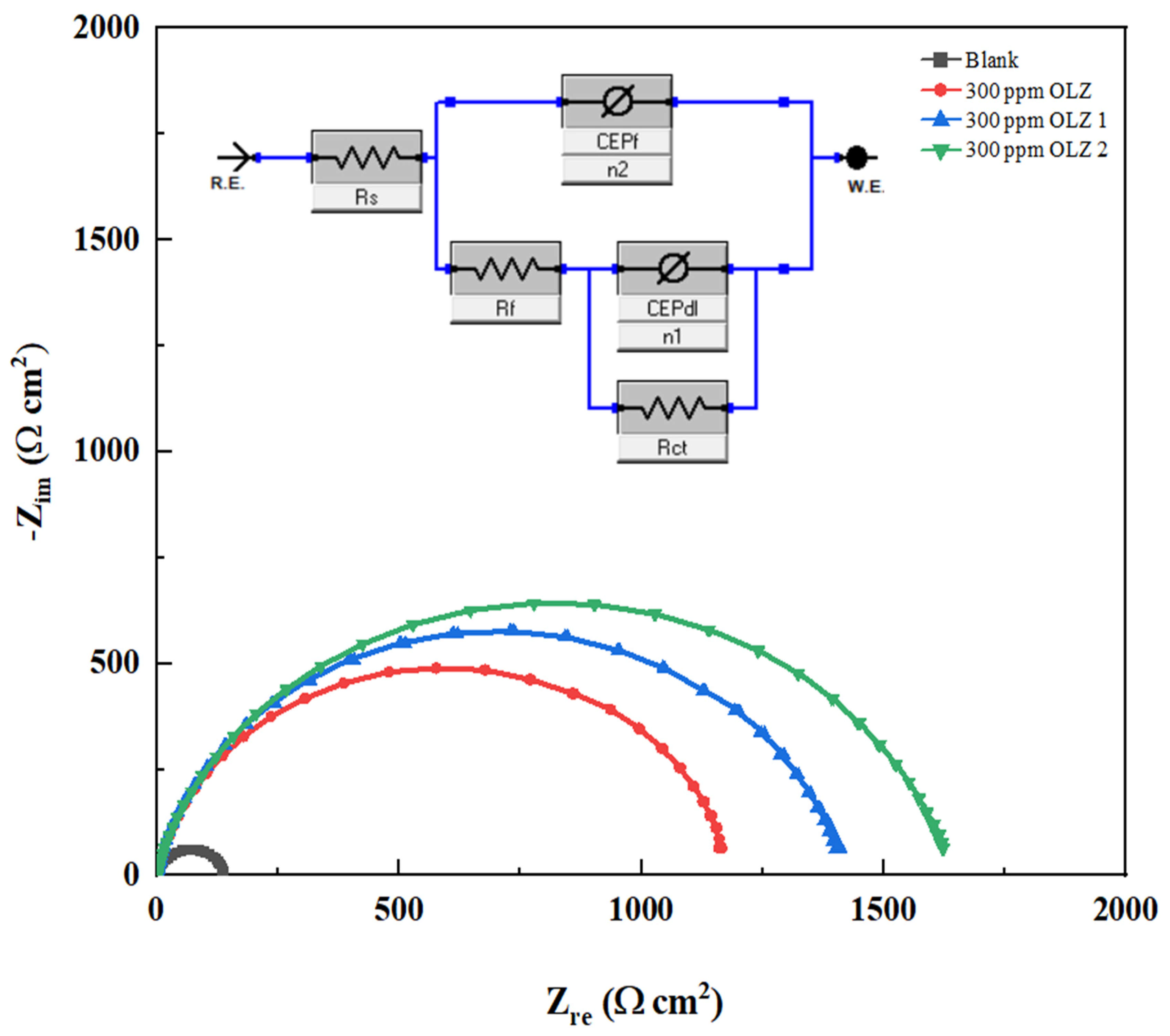
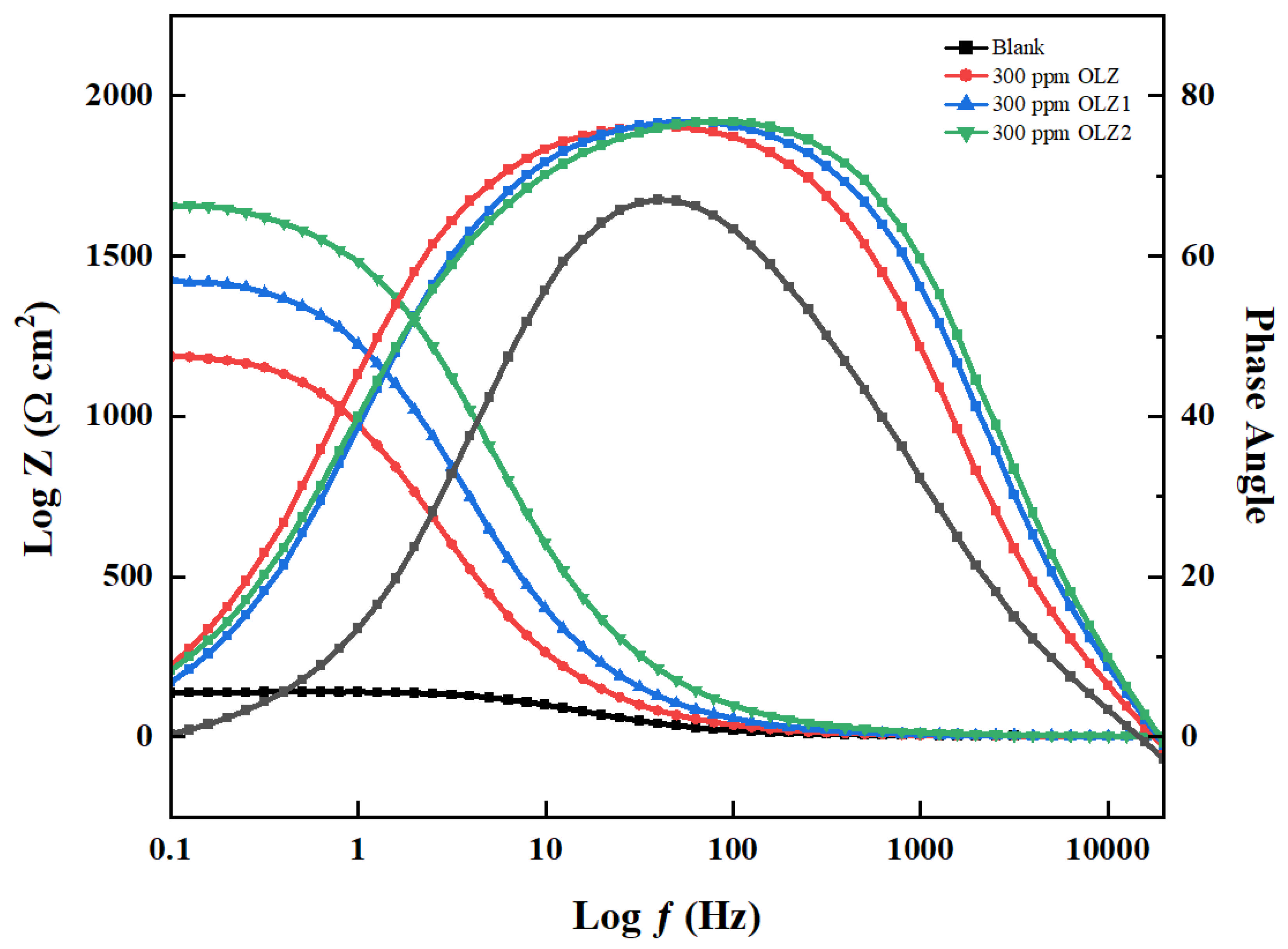
3.3. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS)
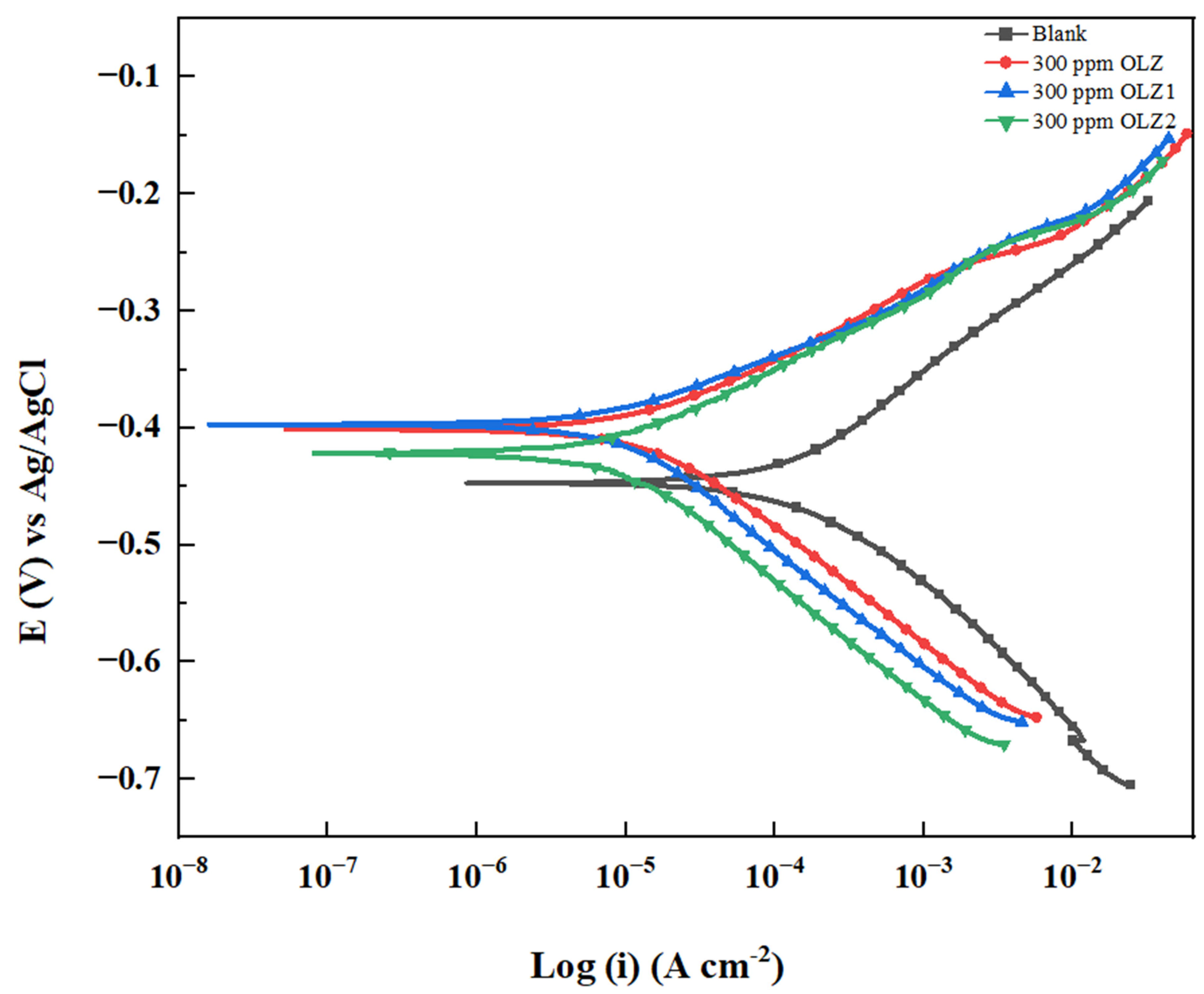
3.4. Potentiodynamic Polarization (PDP) Studies
3.5. Linear Polarization Resistance (LPR)
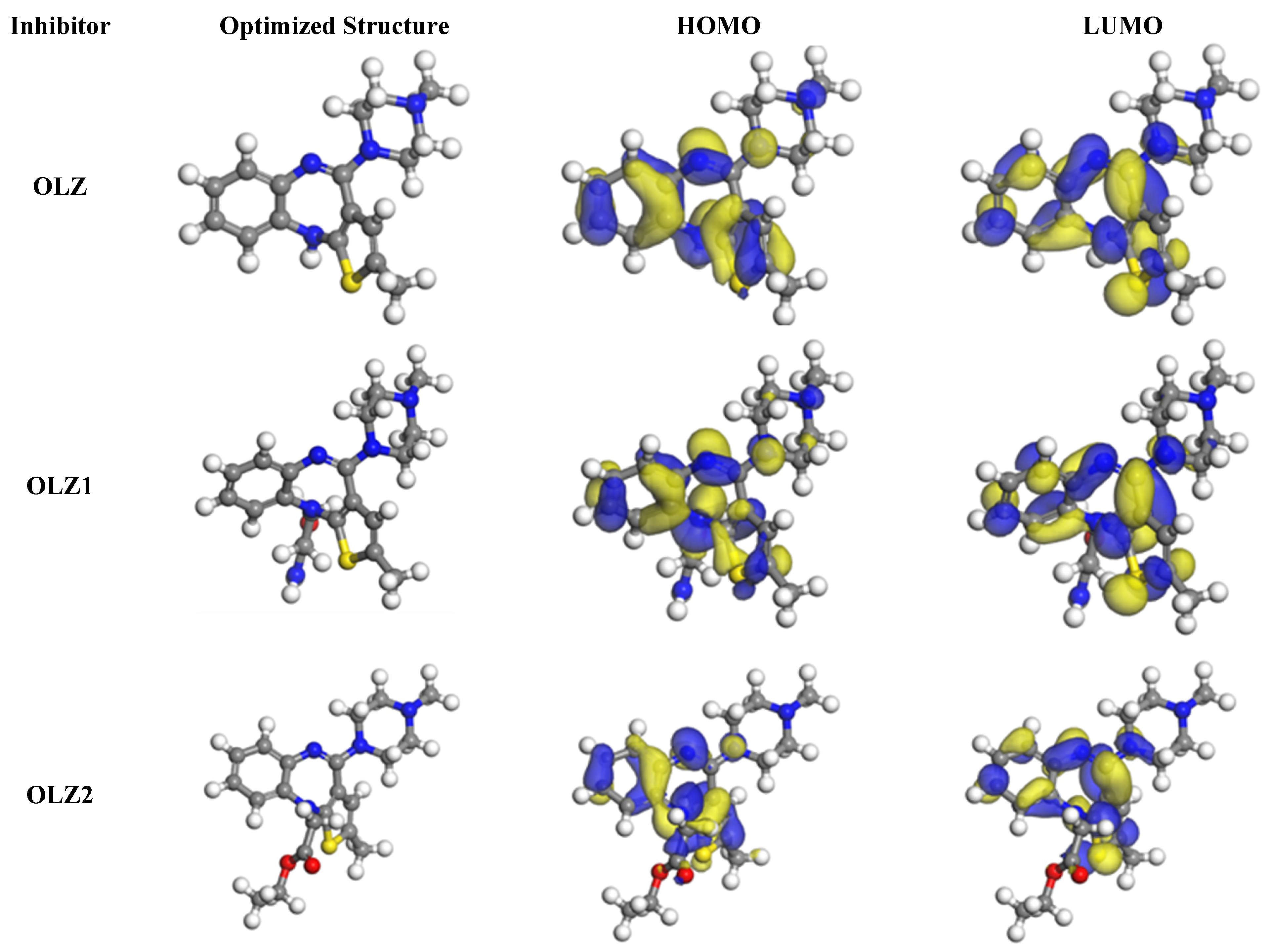
3.6. Quantum Chemistry Calculations
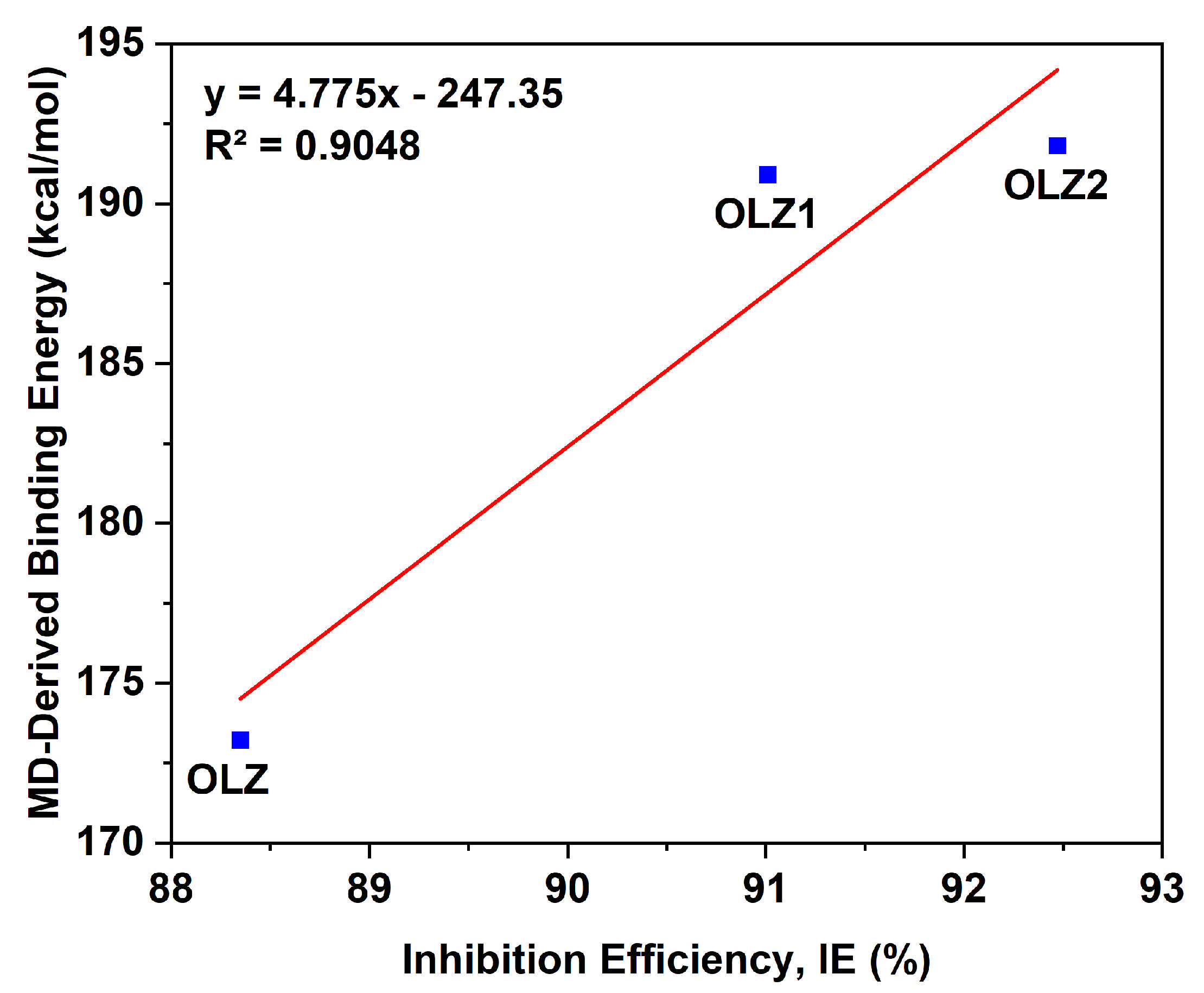
3.7. Adsorption Behavior
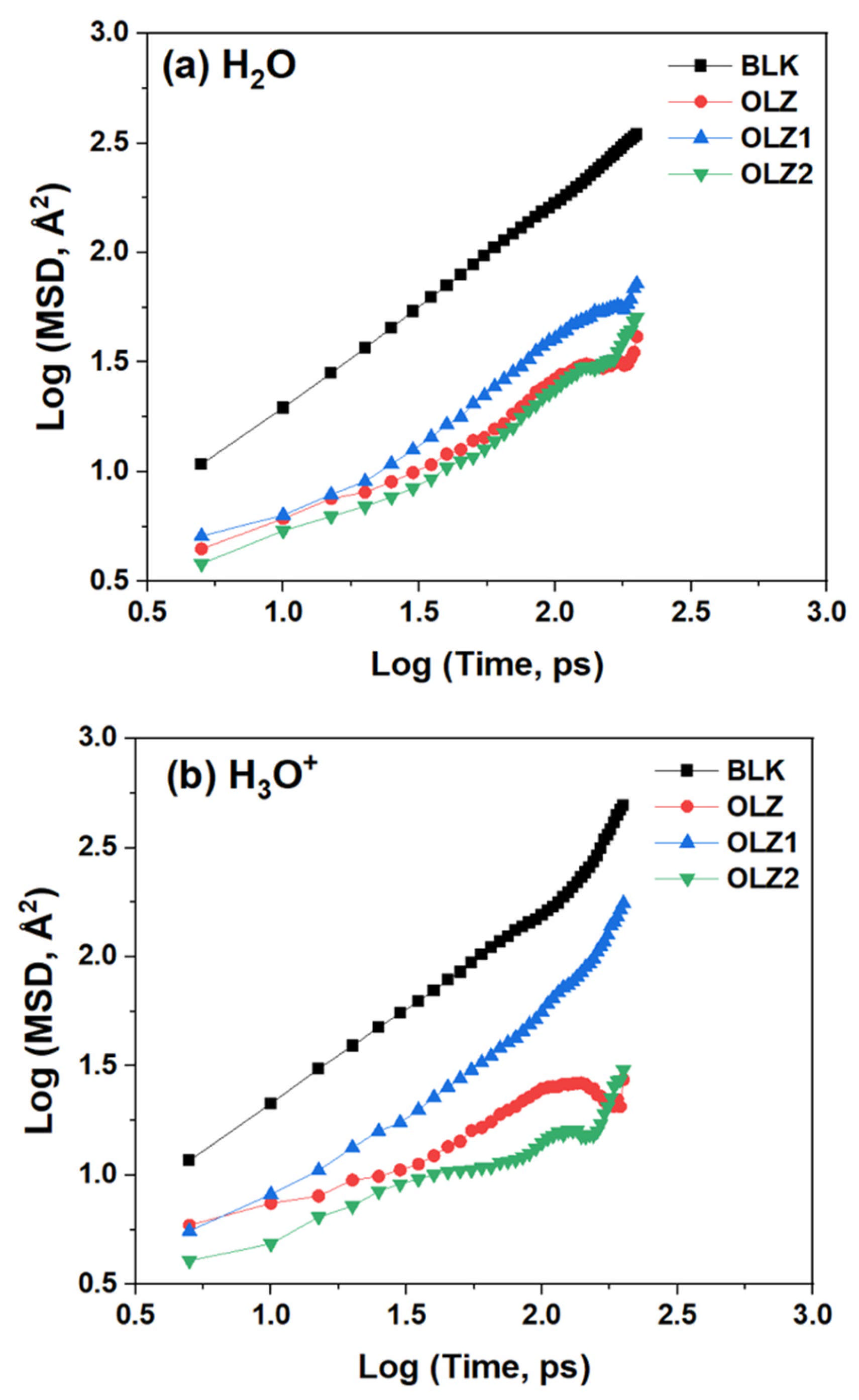
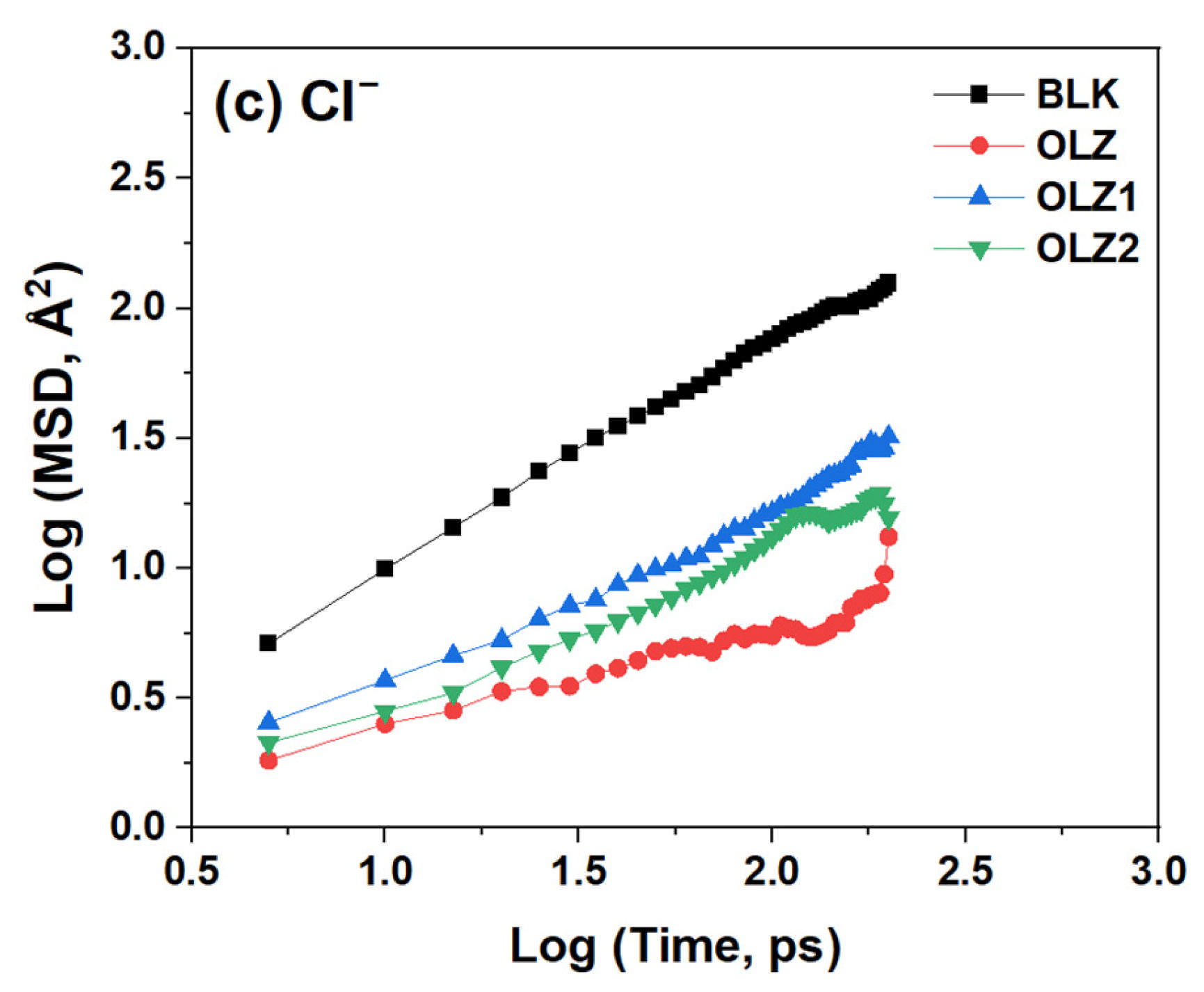
3.8. Diffusion Study
3.9. Surface Analysis
3.9.1. SEM-EDX Analysis
3.9.2. FTIR Spectroscopy
3.10. Inhibition Mechanism
4. Conclusions
- The three inhibition properties of OLZ and its derivatives on C1018 carbon steel in 1 M HCl solution were very high at 300 ppm, where inhibition efficiencies exceeded 88%. However, inhibition efficiency was temperature- and concentration-dependent.
- Electrochemical studies indicate that the three inhibitors are predominantly anodic. PDP-derived inhibition efficiencies agreed with those obtained from EIS measurements.
- At 298 K, the inhibition efficiency followed the order OLZ2 > OLZ1 > OLZ, while at 318 K, it followed the order OLZ1 > OLZ2 > OLZ, which confirms that the structural modifications enhanced the corrosion inhibition properties of the parent molecule.
- The SEM-EDX analysis demonstrates that OLZ and its derivatives effectively inhibit steel corrosion in 1 M HCl compared to the uninhibited solution.
- The FTIR spectroscopy results show that the metal surface active sites include -NH, -C=N, C=C, and aromatic ring structures.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jacobson, G.A. NACE international’s IMPACT study breaks new ground in corrosion management research and practice. Bridge 2016, 46, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayomi, O.; Akande, I.; Odigie, S. Economic Impact of Corrosion in Oil Sectors and Prevention: An Overview. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1378, 022037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Moubaraki, A.H.; Obot, I.B. Corrosion challenges in petroleum refinery operations: Sources, mechanisms, mitigation, and future outlook. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2021, 25, 101370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavendra, N. Green compounds to attenuate aluminum corrosion in HCl activation: A necessity review. Chem. Afr. 2020, 3, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baari, M.J.; Sabandar, C.W. A Review on expired drug-based corrosion inhibitors: Chemical composition, structural effects, inhibition mechanism, current challenges, and future prospects. Indones. J. Chem. 2021, 21, 1316–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narang, R.; Vashishth, P.; Bairagi, H.; Sehrawat, R.; Shukla, S.; Mangla, B. Applicability of drugs as sustainable corrosion inhibitors. Adv. Mater. Lett. 2023, 14, 2304-1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanwer, S.; Shukla, S.K. Recent advances in the applicability of drugs as corrosion inhibitor on metal surface: A review. Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2022, 5, 100227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piggott, T.; Moja, L.; Huttner, B.; Okwen, P.; Raviglione, M.C.B.; Kredo, T.; Schünemann, H.J. WHO Model list of essential medicines: Visions for the future. Bull. World Health Organ. 2024, 102, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehan, S.T.; Siddiqui, A.H.; Khan, Z.; Imran, L.; Syed, A.A.; Tahir, M.J.; Jassani, Z.; Singh, M.; Asghar, M.S.; Ahmed, A. Samidorphan/olanzapine combination therapy for schizophrenia: Efficacy, tolerance and adverse outcomes of regimen, evidence-based review of clinical trials. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 79, 104115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinCalc DrugStats Database. The Top 300 Drugs of 2022 in the United States by Prescription; ClinCalc LLC: Rockville, MD, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Nami, S.Y. Investigation of Adsorption and Inhibitive Effect of Expired Helicure Drug on Mild Steel Corrosion in Hydrochloric Acid Solution. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2020, 15, 2685–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maduelosi, N.J.; Iroha, N.B. Insight into the adsorption and inhibitive effect of spironolactone drug on C38 carbon steel corrosion in hydrochloric acid environment. J. Bio-Tribo-Corros. 2021, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, G.; Sundaravadivelu, M. Studies on the inhibition of mild steel corrosion in hydrochloric acid solution by atenolol drug. Egypt. J. Pet. 2016, 25, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, M.; Tiwari, P.; Srivastava, S.K.; Prakash, R.; Ji, G. Electrochemical investigation of Irbesartan drug molecules as an inhibitor of mild steel corrosion in 1 M HCl and 0.5 M H2SO4 solutions. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 236, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadinejad, F.; Zandi, M.S.; Bahrami, M.J.; Golshani, Z. Metoprolol: New and efficient corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in hydrochloric and sulfuric acid solutions. Acta Chim. Slov. 2020, 67, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, B.; Praveen, B.; Hebbar, N.; Venkatesha, T. Anticorrosion potential of hydralazine for corrosion of mild steel in 1 m hydrochloric acid solution. J. Fundam. Appl. Sci. 2015, 7, 222–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geethamani, P.; Kasthuri, P.; Aejitha, S. An expired non-toxic drug acts as corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in hydrochloric acid medium. Int. J. Chem. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 3, 1442. [Google Scholar]
- Kalkhambkar, A.G.; Rajappa, S.; Manjanna, J.; Malimath, G. Effect of expired doxofylline drug on corrosion protection of soft steel in 1 M HCl: Electrochemical, quantum chemical and synergistic effect studies. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2022, 99, 100639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Ganjoo, R.; Thakur, A.; Kumar, A. Investigation of corrosion performance of expired Irnocam on the mild steel in acidic medium. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 66, 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohare, P.; Chauhan, D.S.; Hammouti, B.; Quraishi, M.A. Experimental and DFT investigation on the corrosion inhibition behavior of expired drug lumerax on mild steel in hydrochloric acid. Bioanal. Electrochem. 2017, 9, 762. [Google Scholar]
- Abdollahi, F.; Foroughi, M.; Shahidi Zandi, M.; Kazemipour, M. Electrochemical investigation of meloxicam drug as a corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in hydrochloric and sulfuric acid solutions. Prog. Color Color. Coat. 2020, 13, 155–165. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Bai, W.; Guo, J.; Gao, L.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liang, L. Inhibition of three kinds of expired nitroimidazole antibiotics. Anti-Corros. Methods Mater. 2018, 65, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohare, P.; Chauhan, D.; Sorour, A.; Quraishi, M. DFT and experimental studies on the inhibition potentials of expired Tramadol drug on mild steel corrosion in hydrochloric acid. Mater. Discov. 2017, 9, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, R.A.; Aleid, G.M.; Khaled, A.; Mohammad, D.; Aljuhani, E.H.; Al-Mhyawi, S.R.; Alshammary, F.; Abdallah, M. Expired dulcolax drug as corrosion inhibitor for low carbon steel in acidic environment. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2022, 17, 220655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasulu, A.; Kasthuri, P. Study of inhibition and adsorption properties of mild steel corrosion by expired pharmaceutical Gentamicin drug in hydrochloric acid media. Orient. J. Chem. 2017, 33, 2616–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuehui, P.; Xiangbin, R.; Kuang, F.; Jiandong, X.; Baorong, H. Inhibiting effect of ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and ofloxacin on corrosion of mild steel in hydrochloric acid. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 18, 337–345. [Google Scholar]
- Obermayer, D.; Glasnov, T.N.; Kappe, C.O. Microwave-assisted and continuous flow multistep synthesis of 4-(pyrazol-1-yl) carboxanilides. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 76, 6657–6669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obermayer, D.; Kappe, C.O. On the importance of simultaneous infrared/fiber-optic temperature monitoring in the microwave-assisted synthesis of ionic liquids. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2010, 8, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawan, R.; Nandiyanto, A.B.D. How to read and interpret 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR spectrums. Indones. J. Sci. Technol. 2021, 6, 267–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- G31-72; Standard Practice for Laboratory Immersion Corrosion Testing of Metals. Annual Book of ASTM Standards; ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2004.
- Satapathy, A.; Gunasekaran, G.; Sahoo, S.; Amit, K.; Rodrigues, P. Corrosion inhibition by Justicia gendarussa plant extract in hydrochloric acid solution. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 2848–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM G1-03; Standard Practice for Preparing, Cleaning, and Evaluating Corrosion Test Specimens. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2004.
- Shankar, U.; Gogoi, R.; Sethi, S.K.; Verma, A. Introduction to materials studio software for the atomistic-scale simulations. In Forcefields for Atomistic-Scale Simulations: Materials and Applications; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 299–313. [Google Scholar]
- Klamt, A.; Schüürmann, G. COSMO: A new approach to dielectric screening in solvents with explicit expressions for the screening energy and its gradient. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2 1993, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, Y.; Zhi, H.; Guo, L.; Fu, A.; Xiang, T.; Jin, Y. Experimental and molecular modeling studies of multi-active tetrazole derivative bearing sulfur linker for protecting steel from corrosion. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 351, 118638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obot, I.; Bahraq, A.A.; Alamri, A.H. Density functional theory and molecular dynamics simulation of the corrosive particle diffusion in pyrimidine and its derivatives films. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2022, 210, 111428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, I.M.; Klafter, J. From diffusion to anomalous diffusion: A century after Einstein’s Brownian motion. Chaos: Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2005, 15, 026103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.-Q.; Guo, A.-L.; Yan, Y.-G.; Jia, X.-L.; Geng, Y.-F.; Guo, W.-Y. Computer simulation of diffusion of corrosive particle in corrosion inhibitor membrane. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2011, 964, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, A. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. In Spectroscopic Methods for Nanomaterials Characterization; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 73–93. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, A.; Abdullah, A. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM): A review. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Hydraulics and Pneumatics—HERVEX, Băile Govora, Romania, 7–9 November 2018; pp. 77–85. [Google Scholar]
- Nahlé, A.; Abu-Abdoun, I.I.; Abdel-Rahman, I. Effect of Temperature on the Corrosion Inhibition of Trans-4-Hydroxy-4′-Stilbazole on Mild Steel in HCl Solution. Int. J. Corros. 2012, 2012, 380329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obot, I.; Obi-Egbedi, N.; Umoren, S. Adsorption characteristics and corrosion inhibitive properties of clotrimazole for aluminium corrosion in hydrochloric acid. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2009, 4, 863–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, T.K.; Saraswat, V.; Mitra, R.K.; Obot, I.; Yadav, M. Mitigation of corrosion in petroleum oil well/tubing steel using pyrimidines as efficient corrosion inhibitor: Experimental and theoretical investigation. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 26, 101862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wang, H.; Jiang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Xie, J.; Tang, J.; Wang, Y.; Chamas, M.; Zhu, Y.; Tian, H. Electrochemical behavior of jasmine tea extract as corrosion inhibitor for carbon steel in hydrochloric acid solution. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2018, 13, 3625–3642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguzie, E.; Li, Y.; Wang, F. Corrosion inhibition and adsorption behavior of methionine on mild steel in sulfuric acid and synergistic effect of iodide ion. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 310, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruna, K.; Saleh, T.A.; Quraishi, M. Expired metformin drug as green corrosion inhibitor for simulated oil/gas well acidizing environment. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 315, 113716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobin, M.; Zamindar, S.; Banerjee, P. Mechanistic insight into adsorption and anti-corrosion capability of a novel surfactant-derived ionic liquid for mild steel in HCl medium. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 385, 122403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touir, R.; Errahmany, N.; Rbaa, M.; Benhiba, F.; Doubi, M.; Kafssaoui, E.E.; Lakhrissi, B. Experimental and computational chemistry investigation of the molecular structures of new synthetic quinazolinone derivatives as acid corrosion inhibitors for mild steel. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1303, 137499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, C.M.; Costa, A.R.; Leite, M.C.; Martins, V.; Lee, H.-S.; da CS Boechat, F.; de Souza, M.C.; Batalha, P.N.; Lgaz, H.; Ponzio, E.A. A detailed experimental performance of 4-quinolone derivatives as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in acid media combined with first-principles DFT simulations of bond breaking upon adsorption. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 375, 121299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acidi, A.; Sedik, A.; Rizi, A.; Bouasla, R.; Rachedi, K.O.; Berredjem, M.; Delimi, A.; Abdennouri, A.; Ferkous, H.; Yadav, K.K. Examination of the main chemical components of essential oil of Syzygium aromaticum as a corrosion inhibitor on the mild steel in 0.5 M HCl medium. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 391, 123423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millard, S.; Law, D.; Bungey, J.; Cairns, J. Environmental influences on linear polarisation corrosion rate measurement in reinforced concrete. NDT E Int. 2001, 34, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olasunkanmi, L.O.; Obot, I.B.; Kabanda, M.M.; Ebenso, E.E. Some quinoxalin-6-yl derivatives as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in hydrochloric acid: Experimental and theoretical studies. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 16004–16019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umoren, S.A. Polypropylene glycol: A novel corrosion inhibitor for ×60 pipeline steel in 15% HCl solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 219, 946–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qiao, G.; Hu, S.; Yan, Y.; Ren, Z.; Yu, L. Theoretical evaluation of corrosion inhibition performance of imidazoline compounds with different hydrophilic groups. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Kaya, S.; Obot, I.B.; Zheng, X.; Qiang, Y. Toward understanding the anticorrosive mechanism of some thiourea derivatives for carbon steel corrosion: A combined DFT and molecular dynamics investigation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 506, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Kang, Q.; Wang, Y. Theoretical study of N-thiazolyl-2-cyanoacetamide derivatives as corrosion inhibitor for aluminum in alkaline environments. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2018, 1131, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obi-Egbedi, N.; Obot, I.; El-Khaiary, M.I. Quantum chemical investigation and statistical analysis of the relationship between corrosion inhibition efficiency and molecular structure of xanthene and its derivatives on mild steel in sulphuric acid. J. Mol. Struct. 2011, 1002, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, C.; Quraishi, M.; Singh, A. 5-Substituted 1H-tetrazoles as effective corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in 1 M hydrochloric acid. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2016, 10, 718–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouakki, M.; Galai, M.; Rbaa, M.; Abousalem, A.S.; Lakhrissi, B.; Rifi, E.; Cherkaoui, M. Investigation of imidazole derivatives as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in sulfuric acidic environment: Experimental and theoretical studies. Ionics 2020, 26, 5251–5272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, C.; Quraishi, M.; Rhee, K.Y. Electronic effect vs. molecular size effect: Experimental and computational based designing of potential corrosion inhibitors. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, B.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, G. Influence of corrosion products on the inhibition effect of pyrimidine derivative for the corrosion of carbon steel under supercritical CO2 conditions. Corros. Sci. 2020, 166, 108442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lu, M. Theoretical insights into the inhibition performance of three neonicotine derivatives as novel type of inhibitors on carbon steel. J. Renew. Mater. 2020, 8, 819–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.; Cao, X.; Zhang, J. Molecular dynamics simulation of corrosive species diffusion in imidazoline inhibitor films with different alkyl chain length. Corros. Sci. 2013, 73, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, I.A.A.; Abdulkareem, M.H.; Annon, I.A.; Hanoon, M.M.; Al-Kaabi, M.H.; Shaker, L.M.; Alamiery, A.A.; Isahak, W.N.R.W.; Takriff, M.S. Weight loss, thermodynamics, SEM, and electrochemical studies on N-2-methylbenzylidene-4-antipyrineamine as an inhibitor for mild steel corrosion in hydrochloric acid. Lubricants 2022, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obot, I.; Umoren, S.; Ankah, N. Pyrazine derivatives as green oil field corrosion inhibitors for steel. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 277, 749–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, D.Q.; Hieu, T.D.; Le Minh Pham, T.; Tuan, D.; Nam, P.C.; Obot, I.B. DFT study of the interactions between thiophene-based corrosion inhibitors and an Fe 4 cluster. J. Mol. Model. 2017, 23, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saranya, J.; Sounthari, P.; Parameswari, K.; Chitra, S. Acenaphtho [1,2-b] quinoxaline and acenaphtho [1,2-b] pyrazine as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in acid medium. Measurement 2016, 77, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Srivastava, V.; Quraishi, M. Novel quinoline derivatives as green corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in acidic medium: Electrochemical, SEM, AFM, and XPS studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 216, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Inhibitor | At 298 K | At 318 K | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| △ w | C.R | IE% | △ w | C.R | IE% | |||
| mpy | mmpy | mpy | mmpy | |||||
| Blank | 1.034 | 1876.08 | 47.63 | - | 2.875 | 5361.45 | 136.13 | - |
| OLZ | 0.07 | 131.7 | 3.34 | 92.98% | 0.688 | 1353.4 | 34.36 | 74.75% |
| OLZ1 | 0.092 | 172.05 | 4.36 | 90.82% | 0.495 | 984.8 | 25 | 81.63% |
| OLZ2 | 0.035 | 70.51 | 1.79 | 96.23% | 0.541 | 1101.85 | 27.97 | 79.44% |
| Inh. | Rs Ω·cm2 | CPEdl | Rct Ω·cm2 | CPEf | Rf Ω·cm2 | Cdl μF·cm−2 | Rp Ω·cm2 | IE % | STD IE | χ2 × 10−3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y01 (mΩ sn cm−2) | n1 | Y02 (mΩ sn cm−2) | n2 | |||||||||
| Blank | 131.15 | 89.380 | 0.867 | 1.74 | 70.465 | 0.958 | 8.005 | 193.850 | 140.897 | - | - | 9.94 |
| OLZ | 0.74 | 63.657 | 0.967 | 10.89 | 92.736 | 0.882 | 1189.333 | 79.578 | 1200.97 | 88.28 | 0.0940 | 4.14 |
| OLZ1 | 1.64 | 47.53 | 0.972 | 1416.3 | 20.820 | 0.984 | 12.449 | 65.471 | 1430.42 | 90.15 | 0.1956 | 3.21 |
| OLZ2 | 1.32 | 50.41 | 0.996 | 898.06 | 29.413 | 0.904 | 747.033 | 51.416 | 1646.42 | 91.45 | 0.2043 | 5.14 |
| Inhibitor | PDP | LPR | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ecorr (mV/SCE) | icorr (μA cm−2) | βa (mV/dec) | βc (mV/dec) | IE % | χ2 × 10−3 | Rp Ω·cm2 | IE % | STD CR | |
| Blank | −447.00 | 200.00 | 160.80 | 120.00 | - | 23.93 | 132.20 | - | - |
| OLZ | −401.000 | 20.100 | 100.00 | 132.700 | 89.95 | 191.6 | 1135.66 | 88.35 | 0.0655 |
| OLZ1 | −397.000 | 15.900 | 89.000 | 218.600 | 92.05 | 75.34 | 1473.00 | 91.01 | 0.2311 |
| OLZ2 | −422.000 | 14.600 | 91.400 | 241.600 | 92.70 | 821.1 | 1760.66 | 92.47 | 0.3597 |
| Parameters | Inhibitor Molecules | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| OLZ | OLZ1 | OLZ2 | |
| EHOMO (eV) | −4.643 | −4.637 | −4.669 |
| ELUMO (eV) | −1.865 | −1.852 | −1.879 |
| I (eV) | 4.643 | 4.637 | 4.669 |
| A (eV) | 1.865 | 1.852 | 1.879 |
| ΔE (eV) | 2.778 | 2.785 | 2.790 |
| χ (eV) | 3.254 | 3.245 | 3.274 |
| η (eV) | 1.389 | 1.393 | 1.395 |
| ΔN (eV) | −2.697 | −2.697 | −2.671 |
| μ (Debye) | 4.603 | 6.510 | 5.160 |
| Inhibitor Film | D (×10−9 m2·s−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| H2O | H3O+ | Cl− | |
| Blank | 2.79 | 2.57 | 1.24 |
| OLZ | 0.39 | 0.35 | 0.07 |
| OLZ1 | 0.66 | 0.87 | 0.25 |
| OLZ2 | 0.35 | 0.17 | 0.19 |
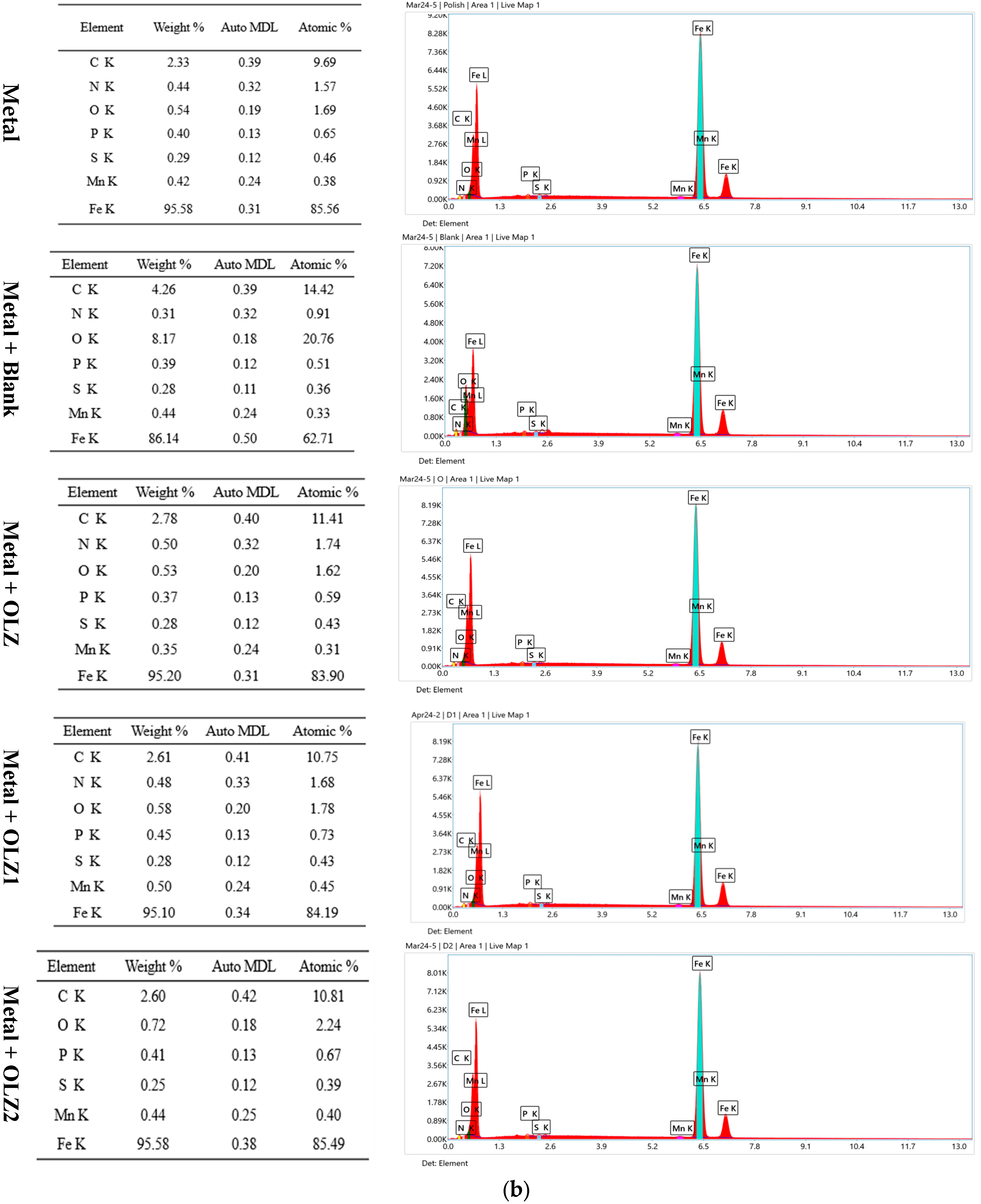
| Element | Metal | Metal with HCl | Metal with OLZ | Metal with OLZ1 | Metal with OLZ2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 1.57 | 0.91 | 1.74 | 1.68 | 1.68 |
| O | 1.69 | 20.76 | 1.62 | 1.78 | 2.24 |
| C | 9.69 | 14.42 | 11.41 | 10.75 | 10.81 |
| S | 0.46 | 0.36 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.39 |
| P | 0.65 | 0.51 | 0.59 | 0.73 | 0.67 |
| Mn | 0.38 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 0.45 | 0.40 |
| Fe | 85.56 | 62.71 | 83.90 | 84.19 | 85.49 |
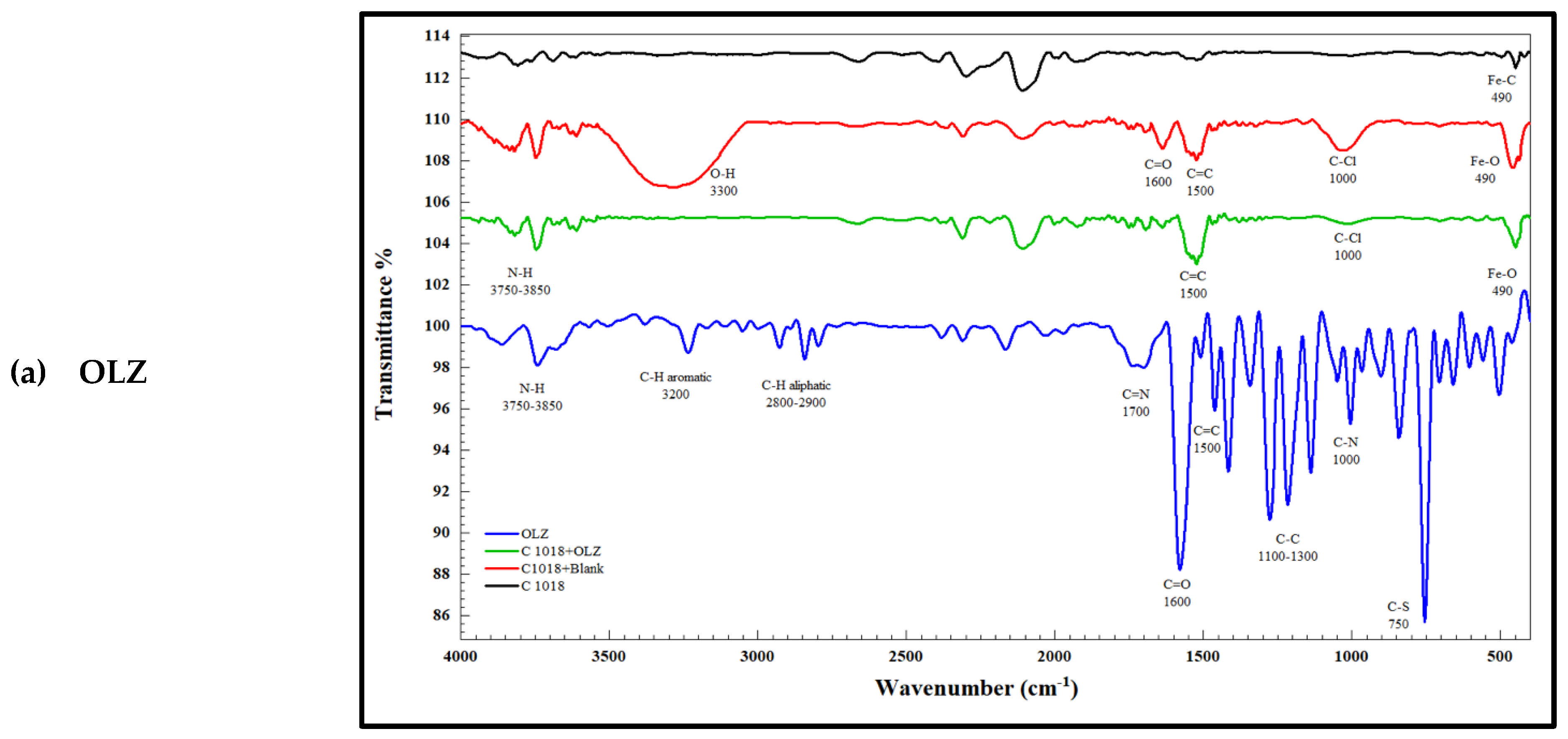
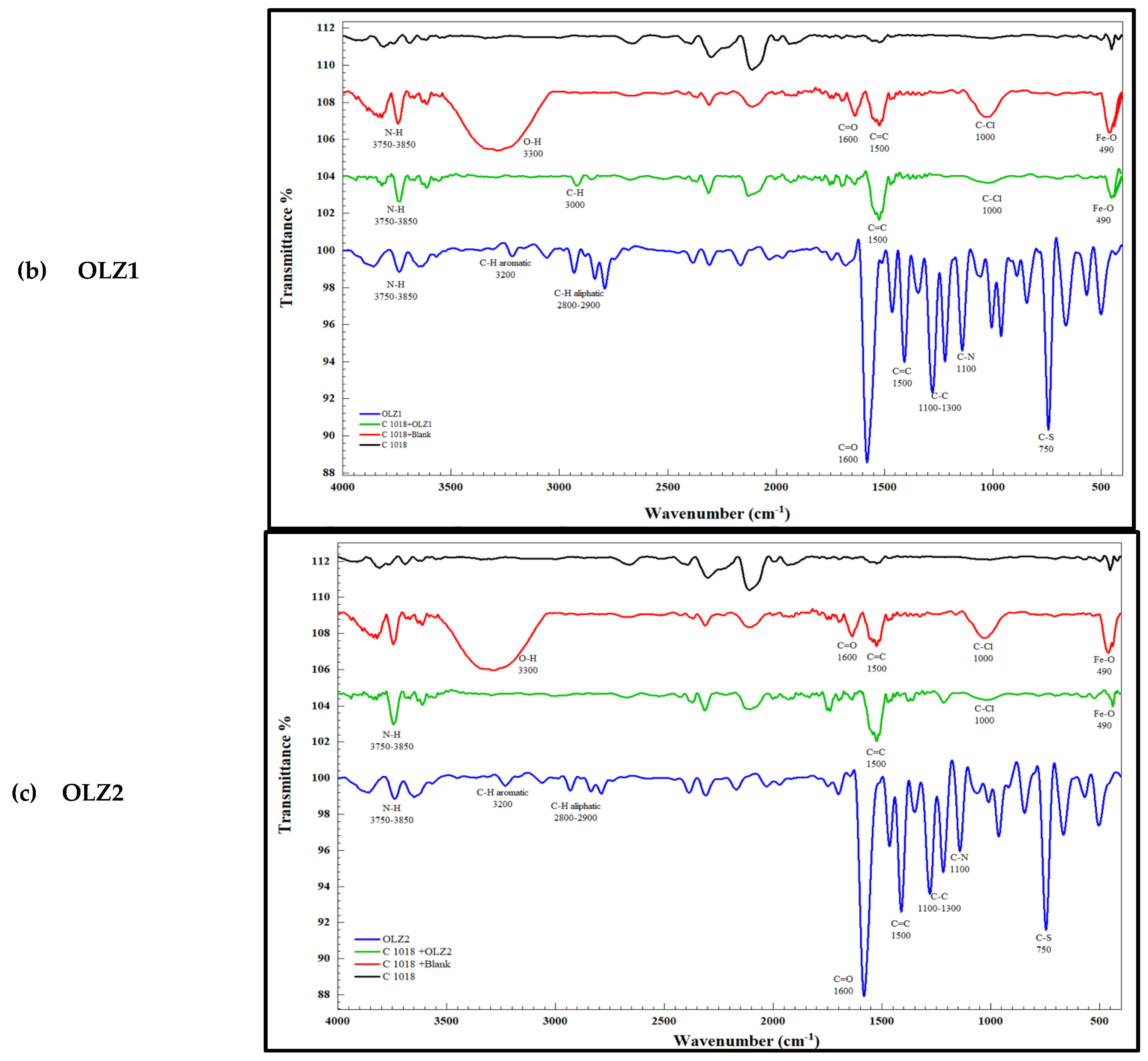
| NO. | Band | Absorbance Peak | Reason |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fe-O | 450 | The presence of a sharp, intense peak indicates the formation of ferrous and ferric oxides or hydroxides |
| 2 | O-H | 3300 | The presence of a hydroxyl group is an indication of the formation of ferric oxides or hydroxides |
| 3 | C-Cl | 1000 | Presence of chloride ions as corrosion products |
| 4 | Fe-O | 490 | Reduction in peak intensity due to the presence of the inhibitor |
| 5 | C-Cl | 1000 | Reduction in peak intensity due to the presence of the inhibitor |
| 6 | O-H | 3300 | Disappearance of the hydroxyl group in the presence of the inhibitor |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Omar, H.M.A.; Ankah, N.; Gomaa, M.S.; Alkhaldi, M.Y.; Osman, N.M.A.; Al-Subaie, A.R.; Aldossary, I.; Baig, I.; Bahraq, A.A.; Aljohani, M.; et al. Towards a Sustainable Material Protection: Olanzapine Drugs and Their Derivatives as Corrosion Inhibitors for C1018 Steel in 1 M Hydrochloric Acid. Materials 2025, 18, 2902. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122902
Omar HMA, Ankah N, Gomaa MS, Alkhaldi MY, Osman NMA, Al-Subaie AR, Aldossary I, Baig I, Bahraq AA, Aljohani M, et al. Towards a Sustainable Material Protection: Olanzapine Drugs and Their Derivatives as Corrosion Inhibitors for C1018 Steel in 1 M Hydrochloric Acid. Materials. 2025; 18(12):2902. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122902
Chicago/Turabian StyleOmar, Habibah M. A., Nestor Ankah, Mohamed S. Gomaa, Malak Y. Alkhaldi, Nadir M. A. Osman, Abdullah R. Al-Subaie, Ibrahim Aldossary, Irshad Baig, Ashraf A. Bahraq, Marwah Aljohani, and et al. 2025. "Towards a Sustainable Material Protection: Olanzapine Drugs and Their Derivatives as Corrosion Inhibitors for C1018 Steel in 1 M Hydrochloric Acid" Materials 18, no. 12: 2902. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122902
APA StyleOmar, H. M. A., Ankah, N., Gomaa, M. S., Alkhaldi, M. Y., Osman, N. M. A., Al-Subaie, A. R., Aldossary, I., Baig, I., Bahraq, A. A., Aljohani, M., Toor, I. U., & Alamri, A. H. (2025). Towards a Sustainable Material Protection: Olanzapine Drugs and Their Derivatives as Corrosion Inhibitors for C1018 Steel in 1 M Hydrochloric Acid. Materials, 18(12), 2902. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122902








