Geopolymer Modified with Insoluble Calcite and Various Silica Fumes Originated from Different Manufacturing Processes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Mixing Proportion and Sample Preparation
2.3. Test Methods
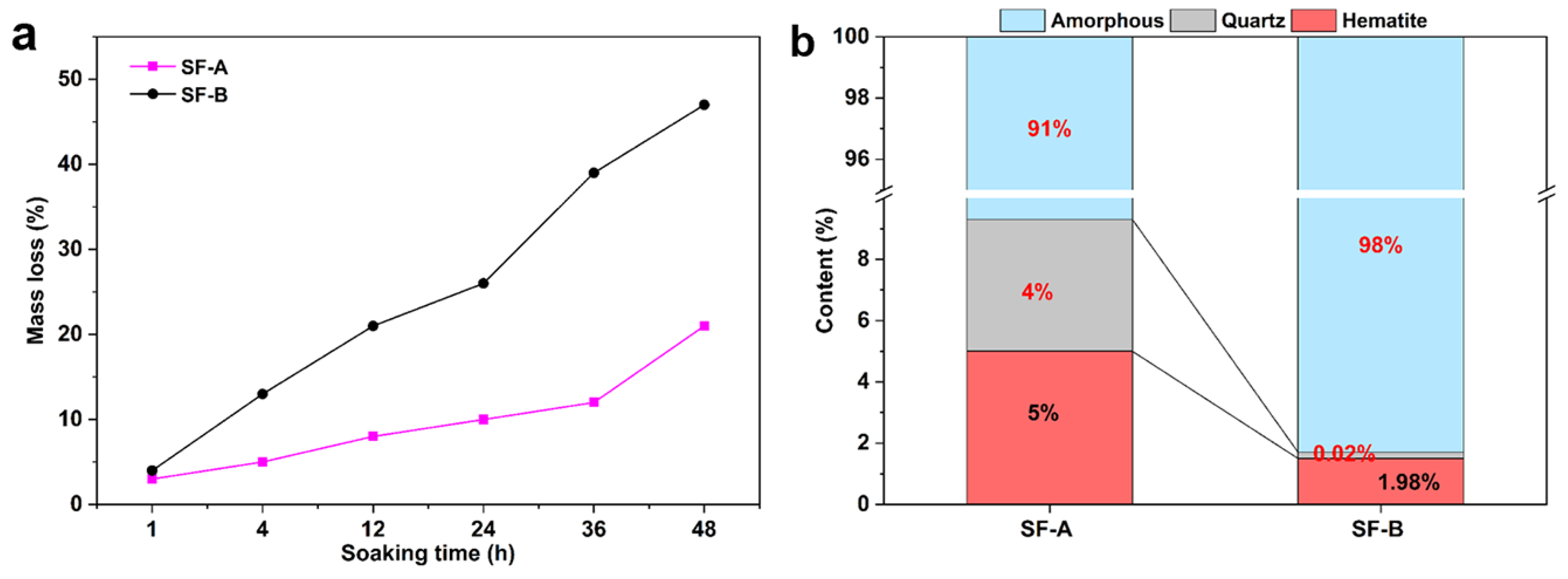
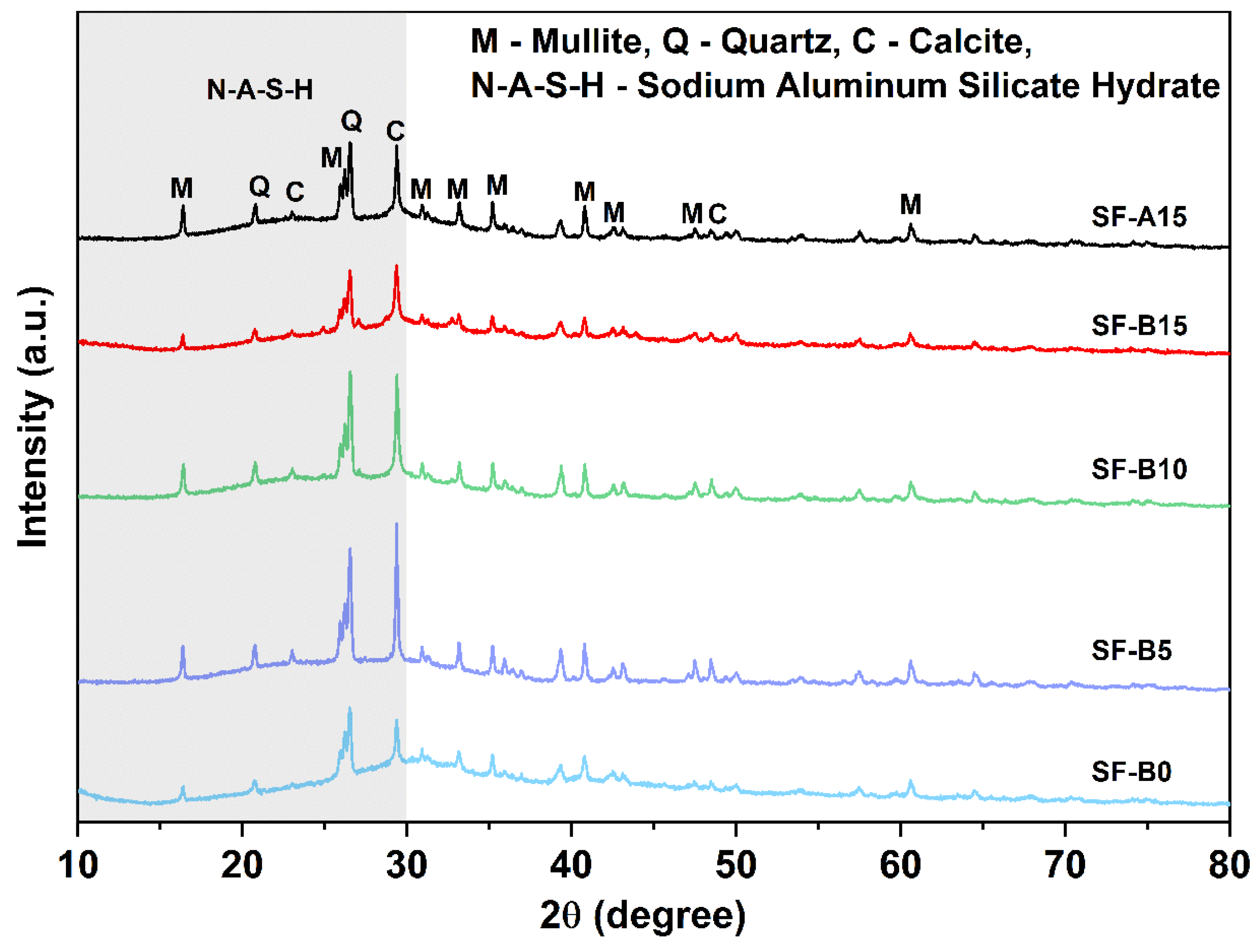
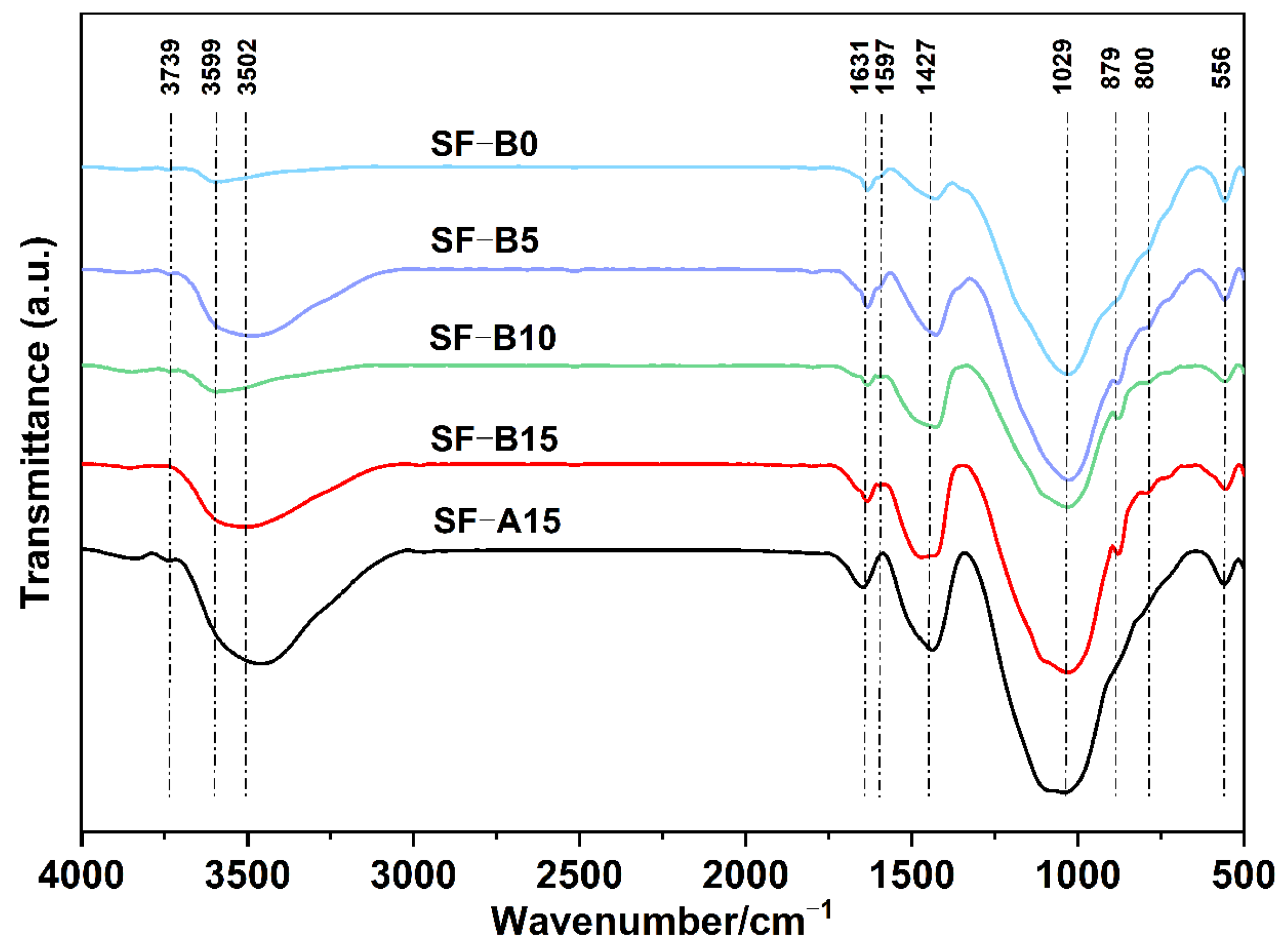
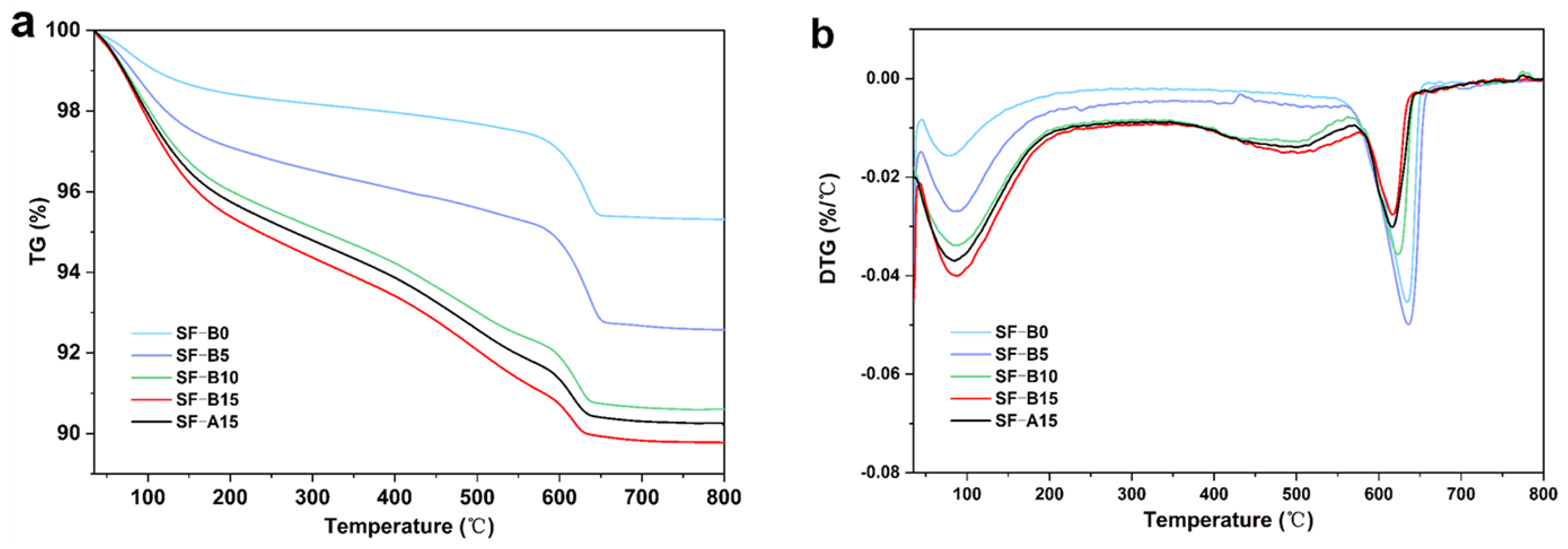
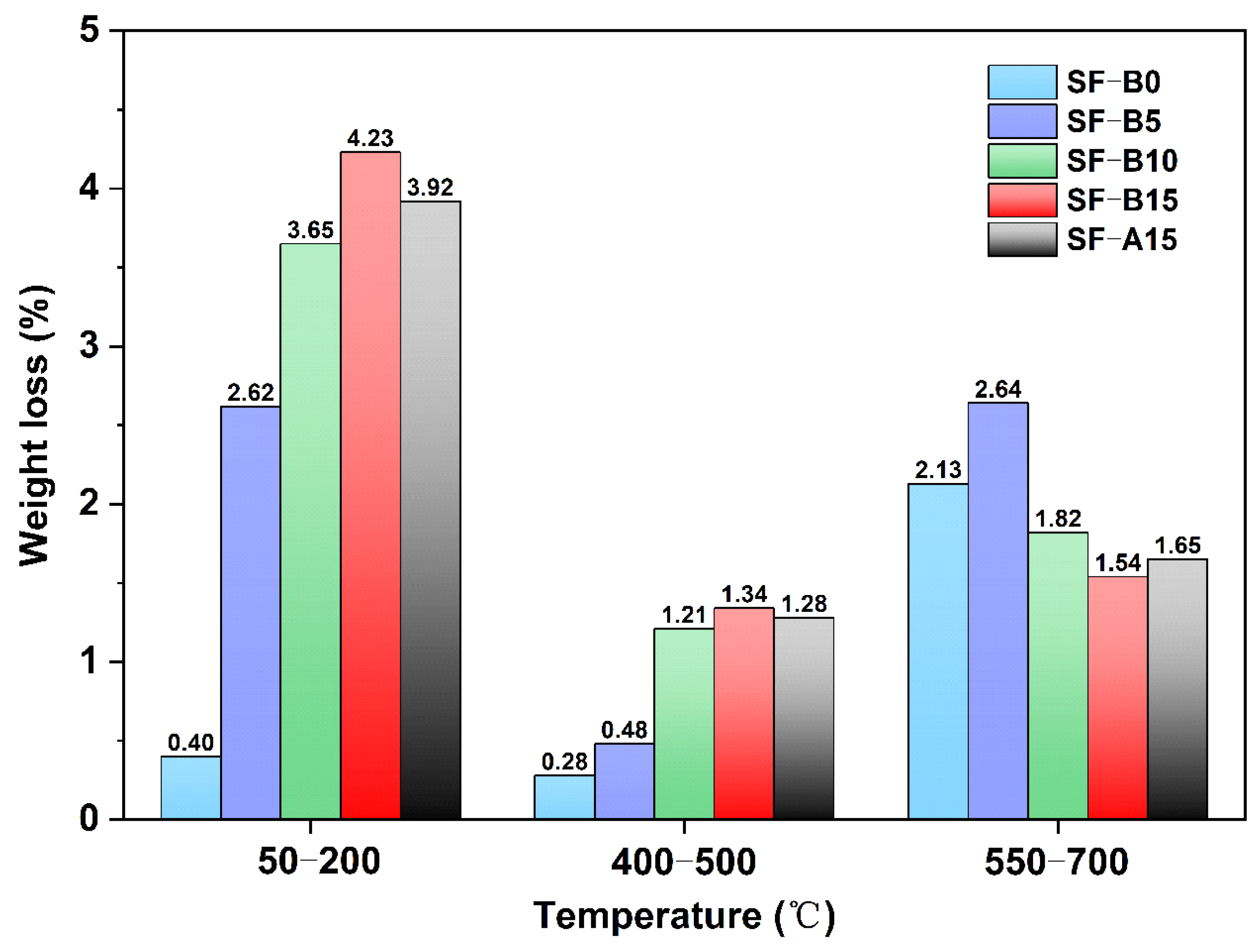
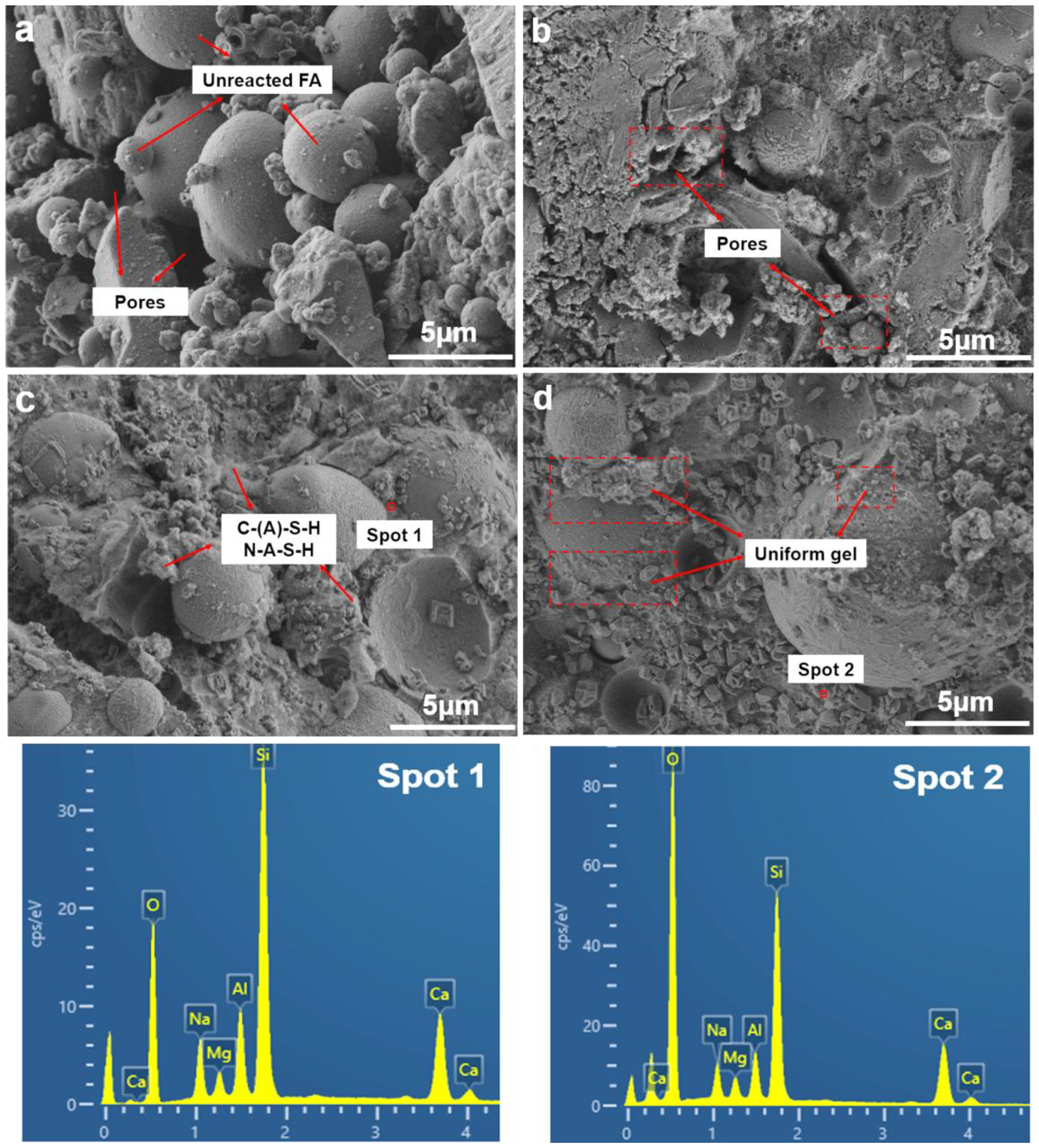
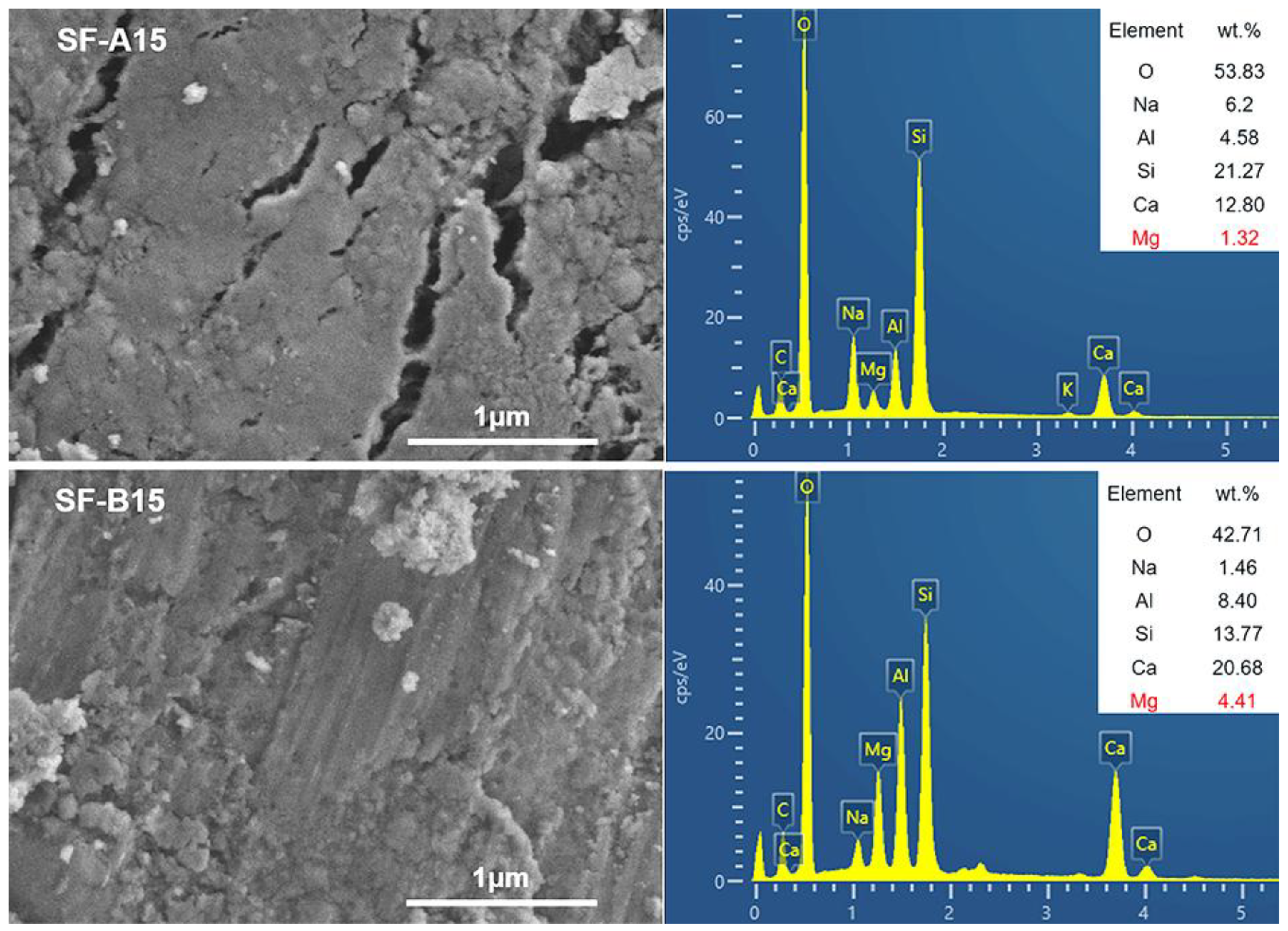
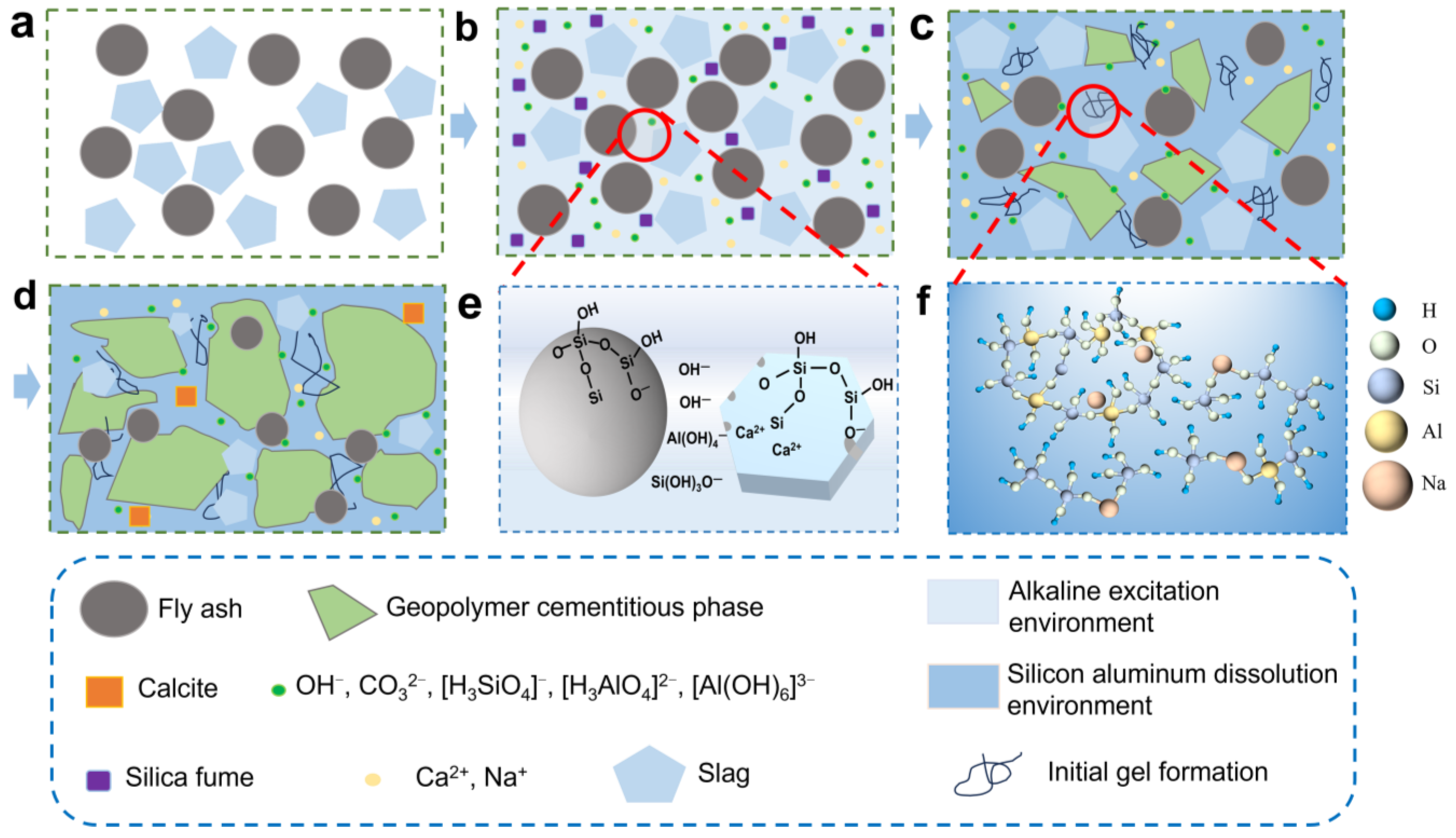
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The addition of SF can fill the pores and promote the formation of hydration products during the reaction process, improving compressive strength. Compared with a 60 wt.% fly ash and 40 wt.% limestone powder system, using 15 wt.% SF instead of fly ash significantly increased compressive strength by over 30 times.
- (2)
- Due to the small particle size and large specific surface area of SF, the interaction between particles is increased, resulting in a gradual decrease in workability.
- (3)
- The microstructure analysis results indicate that the SF is beneficial for activating fly ash and forming an N-A-S-H cementitious phase. Compared with SF with similar particle size and chemical composition, SF-B has a higher content of amorphous silica, and the generated cementitious material is more closely combined with partially reacted fly ash particles, showing a fairly strong strengthening effect.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bheel, N.; Nadeem, G.; Almaliki, A.H.; Al-Sakkaf, Y.K.; Dodo, Y.A.; Benjeddou, O. Effect of low carbon marble dust powder, silica fume, and rice husk ash as tertiary cementitious material on the mechanical properties and embodied carbon of concrete. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2024, 41, 101734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Yu, H.; Sun, S.; Wu, C.; Ding, H. Properties and microstructure of basic magnesium sulfate cement: Influence of silica fume. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 266, 121076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostami, M.; Behfarnia, K. The effect of silica fume on durability of alkali activated slag concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 134, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.B.; Khan, M.I.; Shafiq, N.; Abbas, Y.M.; Imran, M.; Fares, G.; Khatib, J.M. Enhancing the mechanical and environmental performance of engineered cementitious composite with metakaolin, silica fume, and graphene nanoplatelets. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 404, 133187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Gao, X.; Wang, H.; Ye, H. Influence of rice husk ash on strength and permeability of ultra-high performance concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 149, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyunbileg, D.; Amgalan, J.; Batbaatar, T.; Temuujin, J. Evaluation of thermal and freeze-thaw resistances of the concretes with the silica fume addition at different water-cement ratio. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 19, e02633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshani, F.; Allahverdi, A.; Kargari, A.; Norouzbeigi, R.; Mahmoodi, N.M. Effect of preparation parameters on properties of metakaolin-based geopolymer activated by silica fume- sodium hydroxide alkaline blend. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 60, 104984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, T.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, D.; Xu, F. Prediction of compressive and flexural strength of coal gangue-based geopolymer using machine learning method. Mater. Today Commun. 2025, 44, 2352–4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossein, H.A.; Hamzawy, E.M.A.; El-Bassyouni, G.T.; Nabawy, B.S. Mechanical and physical properties of synthetic sustainable geopolymer binders manufactured using rockwool, granulated slag, and silica fume. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 367, 130143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Jing, W.; Qin, L.; Duan, P.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, R.; Li, W. Thermal stability of geopolymer modified by different silicon source materials prepared from solid wastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 315, 125709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, P.; Mei, L. Using silica fume for improvement of fly ash/slag based geopolymer activated with calcium carbide residue and gypsum. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 275, 122171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Huang, Y.; Pei, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cui, N.; Zhao, P.; Hou, P.; Lu, L. Effect of spherical silica fume and fly ash on the rheological property, fluidity, setting time, compressive strength, water resistance and drying shrinkage of magnesium ammonium phosphate cement. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 63, 105484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Mustakim, S.M.; Adesina, A.; Mishra, J.; Alomayri, T.S.; Assaedi, H.S.; Kaze, C.R. Kaze, Fresh, strength and microstructure properties of geopolymer concrete incorporating lime and silica fume as replacement of fly ash. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 32, 101780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Ni, L.; Lv, Y.; Zheng, D.; Tang, W.; Cui, H. Role of silica fume in the hydration evolution of fly ash-slag-based geopolymers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 451, 138879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Yang, J.; Xiong, G. Influence of supplementary cementitious materials on rheological properties of 3D printed fly ash based geopolymer. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2020, 114, 103820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jithendra, C.; Elavenil, S. Effects of Silica Fume on Workability and Compressive Strength Properties of Aluminosilicate Based Flowable Geopolymer Mortar under Ambient Curing. Silicon 2020, 12, 1965–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Fan, X.; Gao, C. Strength, pore characteristics, and characterization of fly ash-slag-based geopolymer mortar modified with silica fume. Structures 2024, 69, 107525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Xu, X.; Chen, G.Z. Silicon prepared by electro-reduction in molten salts as new energy materials. J. Energy Chem. 2020, 47, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-C.; Dhage, S.; Akhtar, M.S.; Kwak, D.H.; Lee, W.J.; Kim, C.-Y.; Yang, O.-B. A simulation study on the direct carbothermal reduction of SiO2 for Si metal. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2010, 10, S218–S221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 50448-2015; Code for Application Technique of Cementitious Grout. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development: Beijing, China, 2015.
- ASTM C109; Standard Test Method for Compressive Strength of Hydraulic Cement Mortars (Using 2-in. or [50-mm] Cube Specimens). ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- Garcia-Lodeiro, I.; Palomo, A.; Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Macphee, D.E. Compatibility studies between N-A-S-H and C-A-S-H gels. Study in the ternary diagram Na2O–CaO–Al2O3–SiO2–H2O. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matinfar, M.; Nychka, J.A. A review of sodium silicate solutions: Structure, gelation, and syneresis. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 322, 103036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Bai, C.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, K.; Colombo, P. Preparation properties and applications of fly ash-based porous geopolymers: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 359, 132043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; He, M.; Cheng, J.; Wang, T.; Che, Y.; Du, Y. Study on the synergistic effects of OPC and silica fume on the mechanical and microstructural properties of geopolymer mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 434, 136740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chindaprasirt, P.; Sriopas, B.; Phosri, P.; Yoddumrong, P.; Anantakarn, K.; Kroehong, W. Hybrid high calcium fly ash alkali-activated repair material for concrete exposed to sulfate environment. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 45, 103590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkley, B.; Nicolas, R.S.; Sani, M.-A.; Rees, G.J.; Hanna, J.V.; Van Deventer, J.S.J.; Provis, J.L. Phase evolution of C-(N)-A-S-H/N-A-S-H gel blends investigated via alkali-activation of synthetic calcium aluminosilicate precursors. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 89, 120–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, B.; Chang, J. Adsorption behavior and solidification mechanism of Pb(II) on synthetic C-A-S-H gels with different Ca/Si and Al/Si ratios in high alkaline conditions. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 493, 152344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollah, M.Y.A.; Yu, W.; Schennach, R.; Cocke, D.L. A Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic investigation of the early hydration of Portland cement and the influence of sodium lignosulfonate. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trezza, M.A.; Lavat, A.E. Analysis of the system 3CaO·Al2O3–CaSO4·2H2O–CaCO3–H2O by FT-IR spectroscopy. Cem. Concr. Res. 2001, 31, 869–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Ayuso, E.; Querol, X.; Plana, F.; Alastuey, A.; Moreno, N.; Izquierdo, M.; Font, O.; Moreno, T.; Diez, S.; Vázquez, E.; et al. Environmental, physical and structural characterisation of geopolymer matrixes synthesised from coal (co-)combustion fly ashes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 154, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wei, Y.; Li, Z.; Farooqi, M.U. Rheological and viscoelastic characterizations of fly ash/slag/silica fume-based geopolymer. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 354, 131629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodeiro, I.G.; Macphee, D.E.; Palomo, A.; Fernández-Jiménez, A. Effect of alkalis on fresh C–S–H gels. FTIR analysis. Cem. Concr. Res. 2009, 39, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zheng, Z.; Yang, J.; Su, Y.; Wang, T.; Strnadel, B. Feasibility of incorporating autoclaved aerated concrete waste for cement replacement in sustainable building materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 250, 119455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalqader, A.F.; Jin, F.; Al-Tabbaa, A. Development of greener alkali-activated cement: Utilisation of sodium carbonate for activating slag and fly ash mixtures. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 113, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salha, M.S.; Yada, R.Y.; Farrar, D.H.; Chass, G.A.; Tian, K.V.; Bodo, E. Aluminium catalysed oligomerisation in cement-forming silicate systems. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2023, 25, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Xue, C.; Jia, Y.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, Y. Preparation and curing method of red mud-calcium carbide slag synergistically activated fly ash-ground granulated blast furnace slag based eco-friendly geopolymer. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 139, 104999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
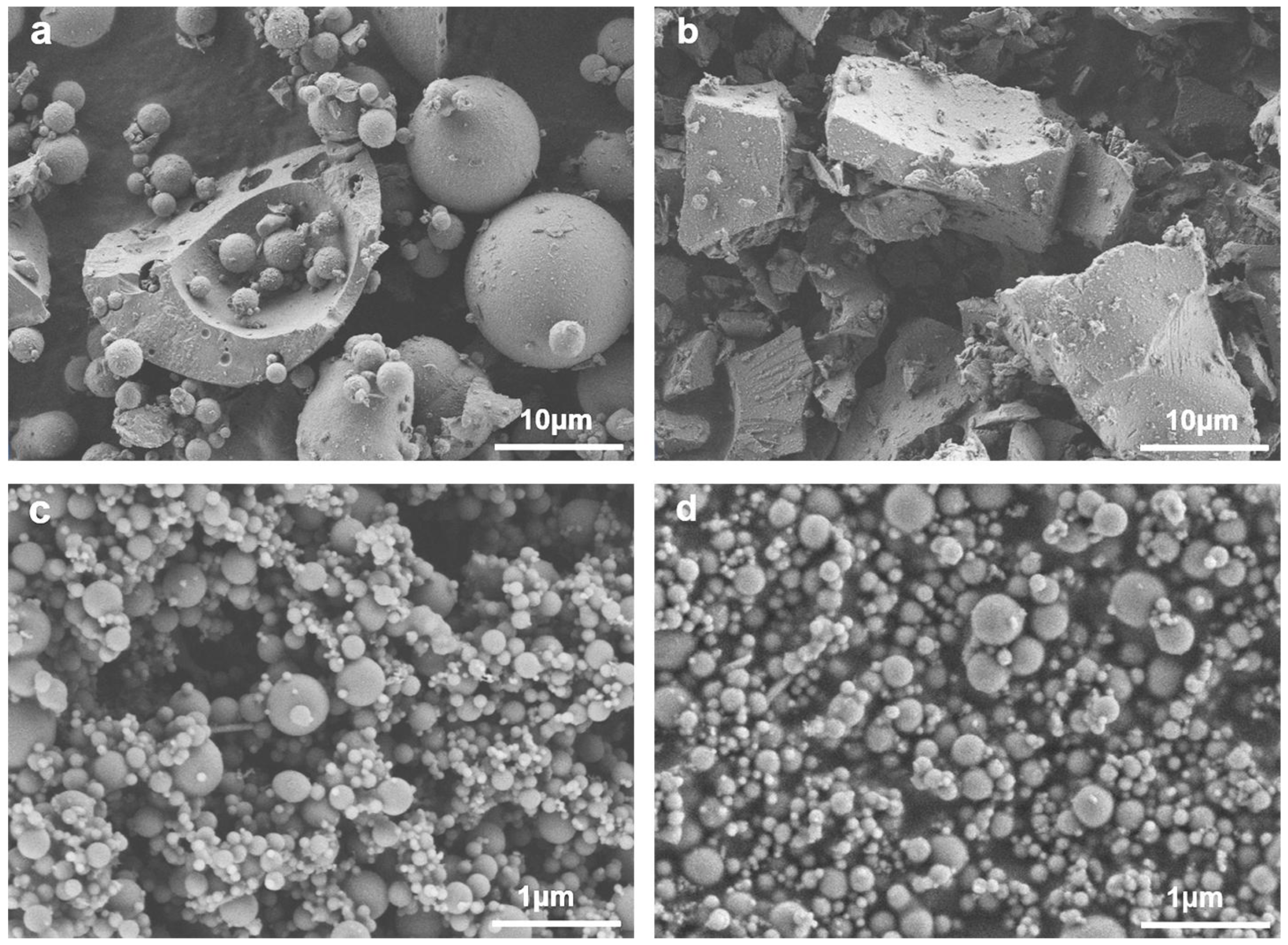
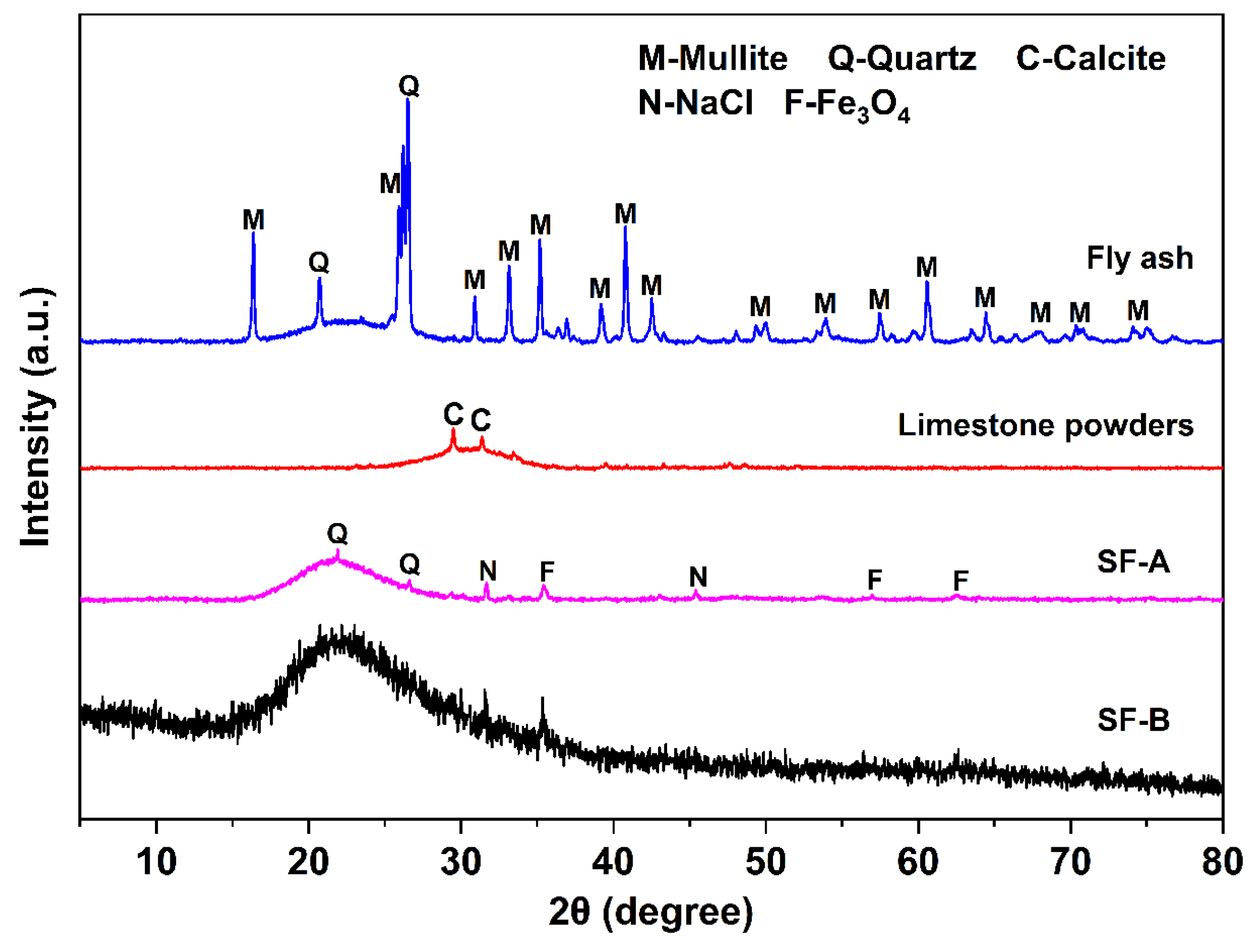
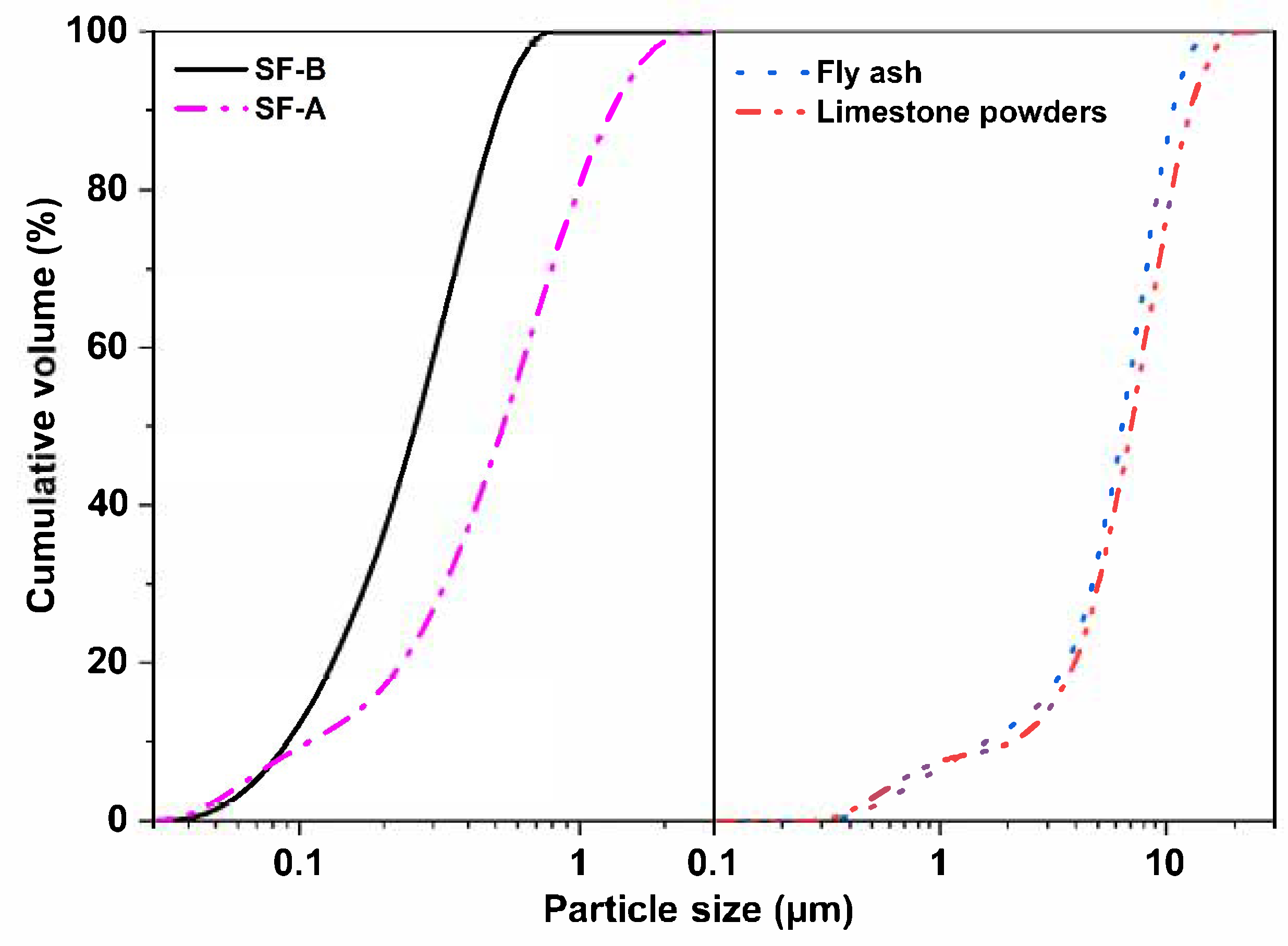

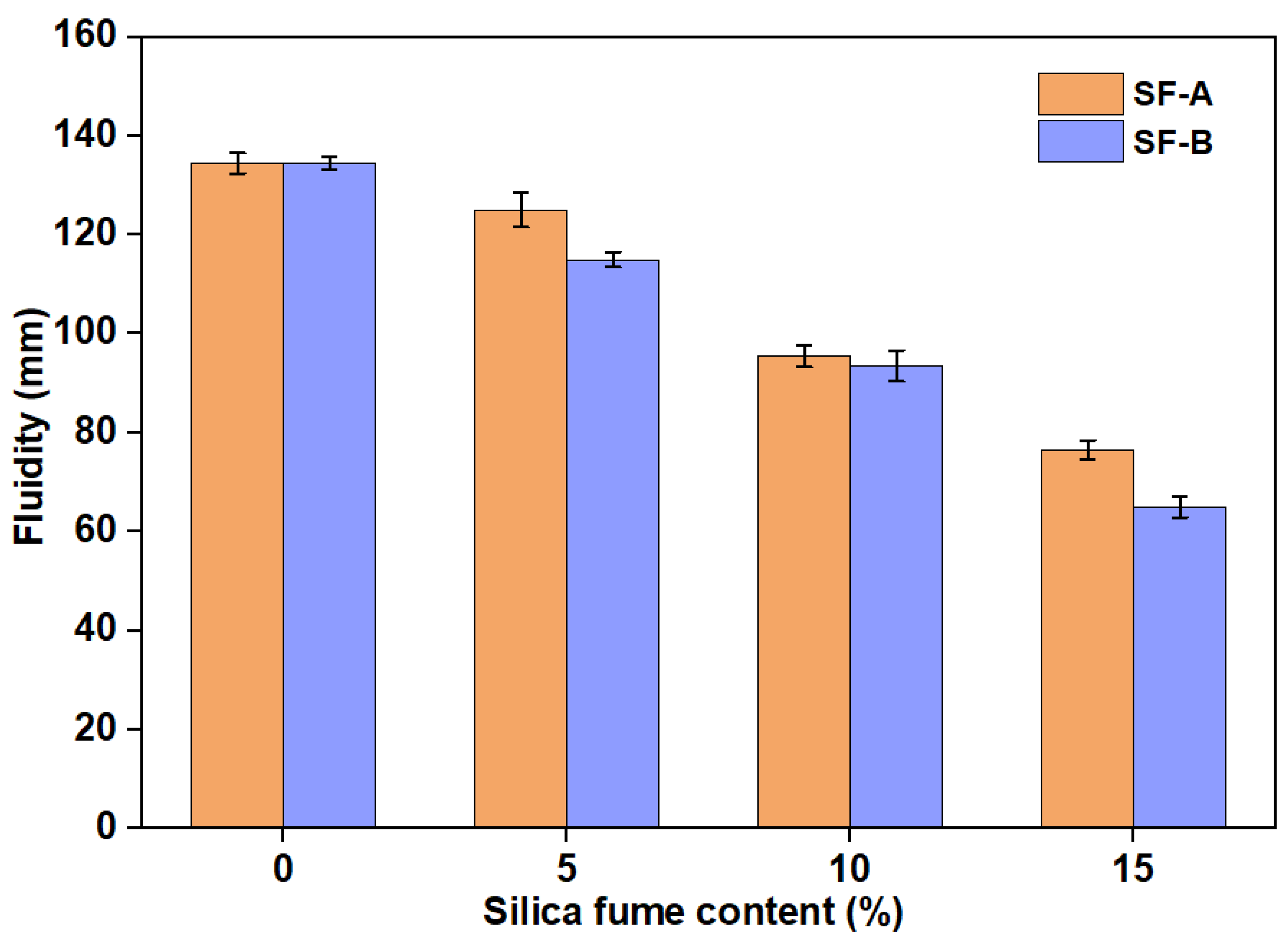
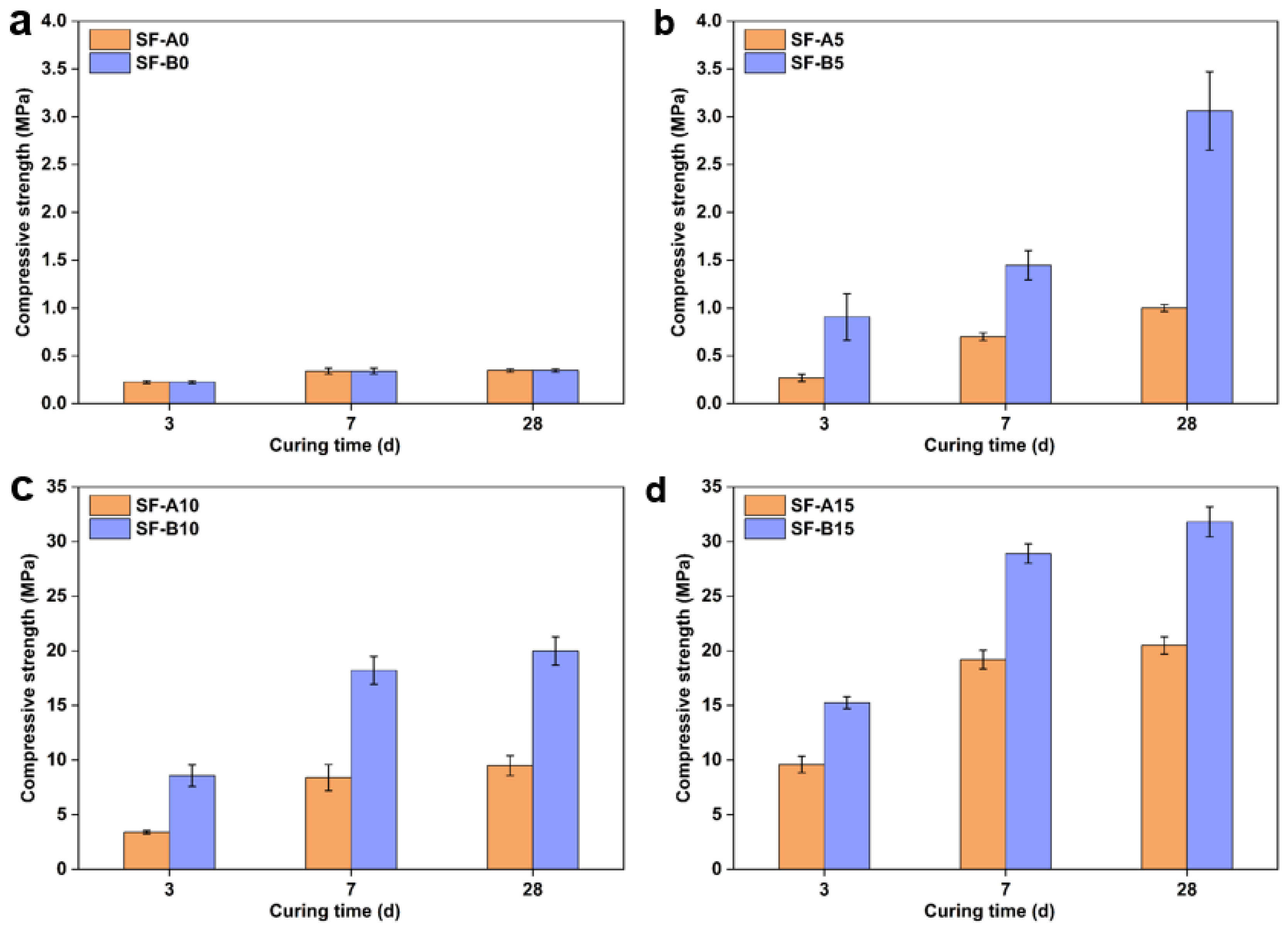
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | Fe2O3 | MgO | MnO | Na2O | K2O | SO3 | P2O5 | Others | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fly ash | 54.80 | 29.72 | 4.35 | 4.26 | 0.67 | 0.03 | 0.65 | 2.13 | 0.72 | 0.33 | 2.34 |
| Limestone powders | 11.36 | 15.66 | 56.88 | 2.75 | 1.32 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.72 | 9.45 | 0.08 | 1.66 |
| SF-A | 80.07 | 0.67 | 4.13 | 6.61 | 1.36 | 0.05 | 1.31 | 0.61 | 0.36 | 0.13 | 4.7 |
| SF-B | 84.77 | 0.49 | 0.81 | 1.48 | 8.26 | 0.11 | 2.37 | 0.94 | 0.23 | 0.08 | 0.46 |
| Sample Number | FA (%) | LS (%) | SF-A (%) | SF-B (%) | H2O (%) | NaOH (%) | WG (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SF-A0 | 60 | 40 | 0 | 0 | 32.1 | 2.5 | 12.6 |
| SF-A5 | 55 | 40 | 5 | 0 | 32.1 | 2.5 | 12.6 |
| SF-A10 | 50 | 40 | 10 | 0 | 32.1 | 2.5 | 12.6 |
| SF-A15 | 45 | 40 | 15 | 0 | 32.1 | 2.5 | 12.6 |
| SF-B0 | 60 | 40 | 0 | 0 | 32.1 | 2.5 | 12.6 |
| SF-B5 | 55 | 40 | 0 | 5 | 32.1 | 2.5 | 12.6 |
| SF-B10 | 50 | 40 | 0 | 10 | 32.1 | 2.5 | 12.6 |
| SF-B15 | 45 | 40 | 0 | 15 | 32.1 | 2.5 | 12.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Liu, Y.; Gao, T.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Xie, N.; Meng, J.; Ou, J.; et al. Geopolymer Modified with Insoluble Calcite and Various Silica Fumes Originated from Different Manufacturing Processes. Materials 2025, 18, 2795. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122795
Xu Y, Wang X, Yang L, Liu Y, Gao T, Li H, Wang Y, Xie N, Meng J, Ou J, et al. Geopolymer Modified with Insoluble Calcite and Various Silica Fumes Originated from Different Manufacturing Processes. Materials. 2025; 18(12):2795. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122795
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Yong, Xiaonan Wang, Lilin Yang, Yang Liu, Tong Gao, Han Li, Yukai Wang, Ning Xie, Jing Meng, Jinping Ou, and et al. 2025. "Geopolymer Modified with Insoluble Calcite and Various Silica Fumes Originated from Different Manufacturing Processes" Materials 18, no. 12: 2795. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122795
APA StyleXu, Y., Wang, X., Yang, L., Liu, Y., Gao, T., Li, H., Wang, Y., Xie, N., Meng, J., Ou, J., & Wang, W. (2025). Geopolymer Modified with Insoluble Calcite and Various Silica Fumes Originated from Different Manufacturing Processes. Materials, 18(12), 2795. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122795








