Study on the Microstructure Evolution and Ablation Mechanism of SiCp/Al Composites Processed by a Water-Jet Guided Laser
Highlights
- Demonstration of the feasibility of water-guided laser processing of SiCp/Al composites;
- The relationship between laser power, scanning speed, and water jet pressure on the processing quality of SiCp/Al composites was investigated;
- Removal mechanism of SiC/Al composites under the action of water-guided laser revealed.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Setup
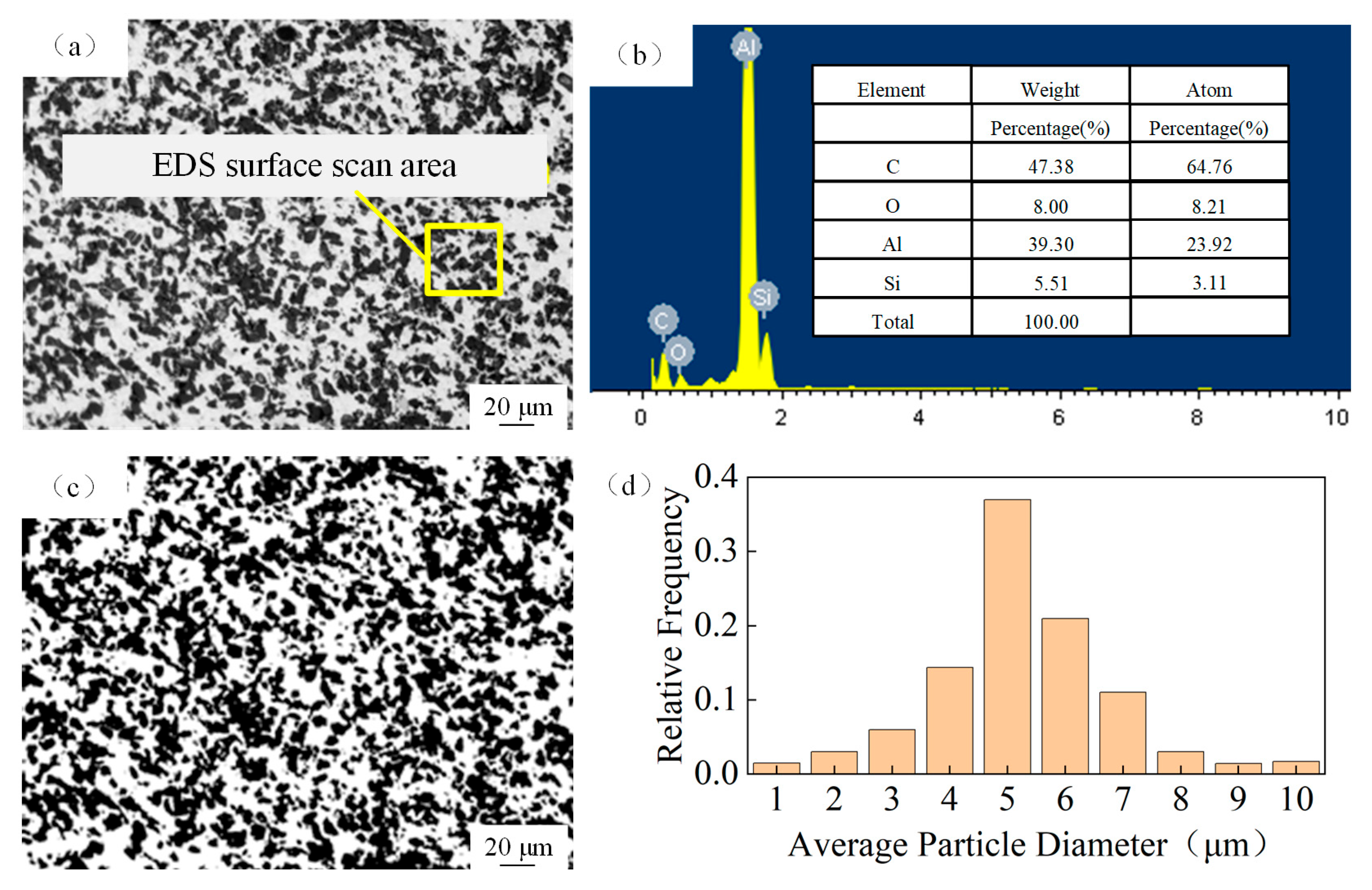
2.1. SiCp/Al Composites
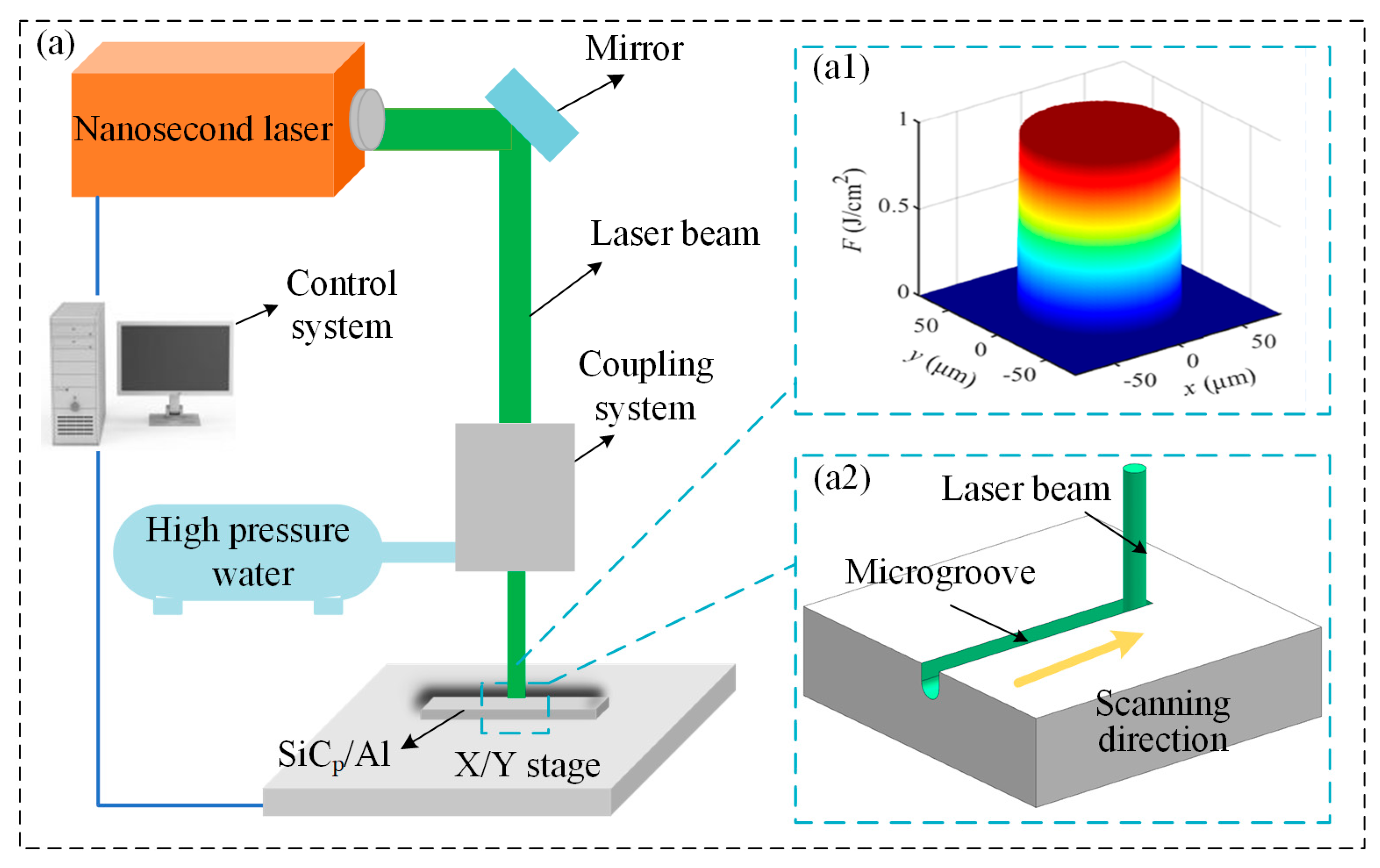
2.2. Equipment and Procedure
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
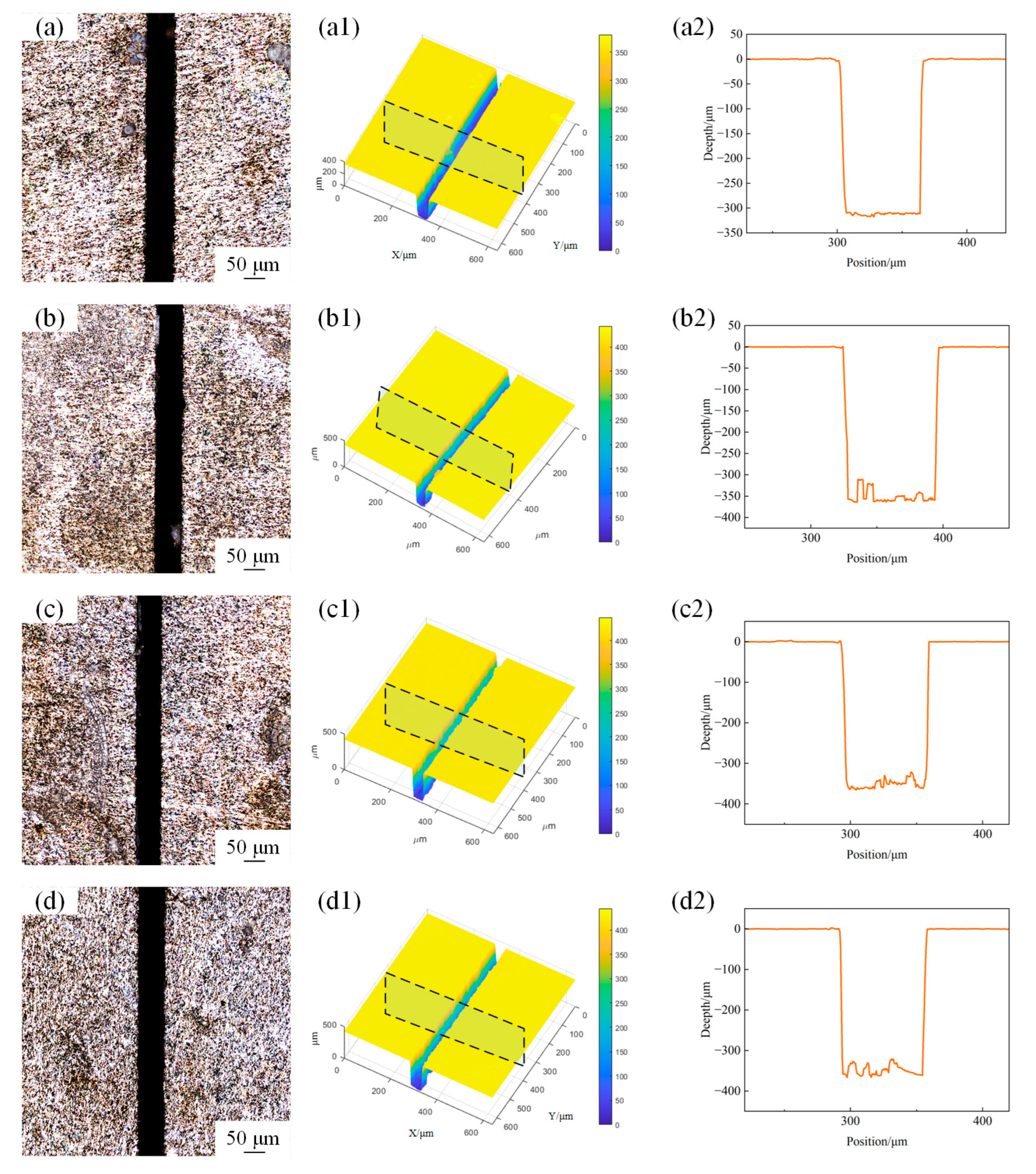
3.1. Microgroove Quality
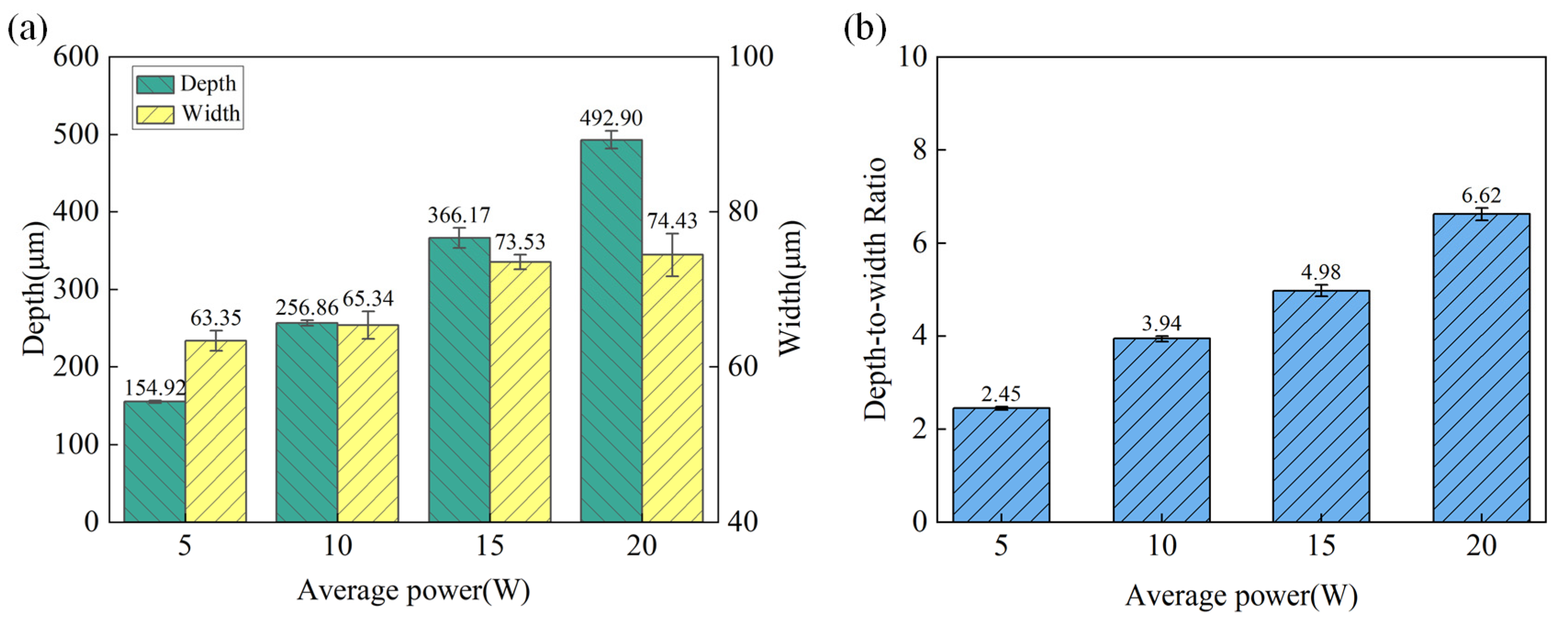
3.1.1. Effects of Laser Power
3.1.2. Effects of Scanning Speed
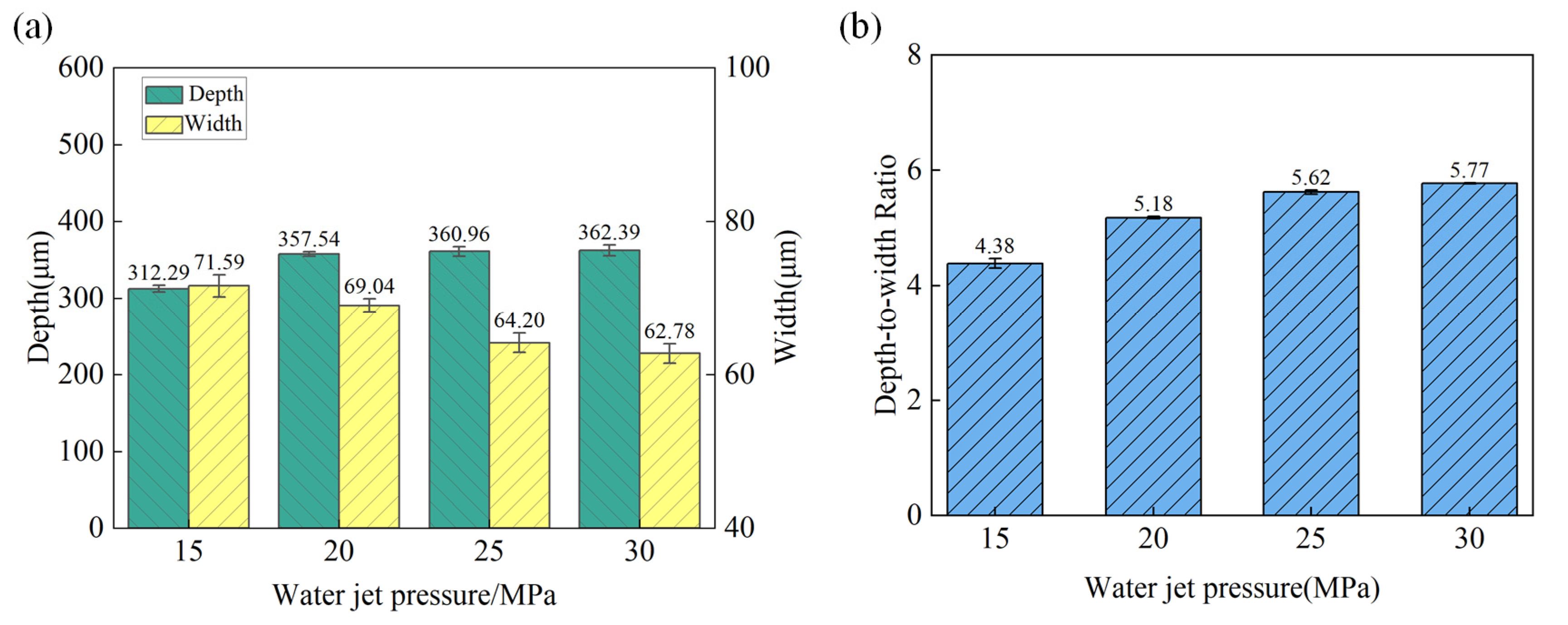
3.1.3. Effects of Water Jet Pressure
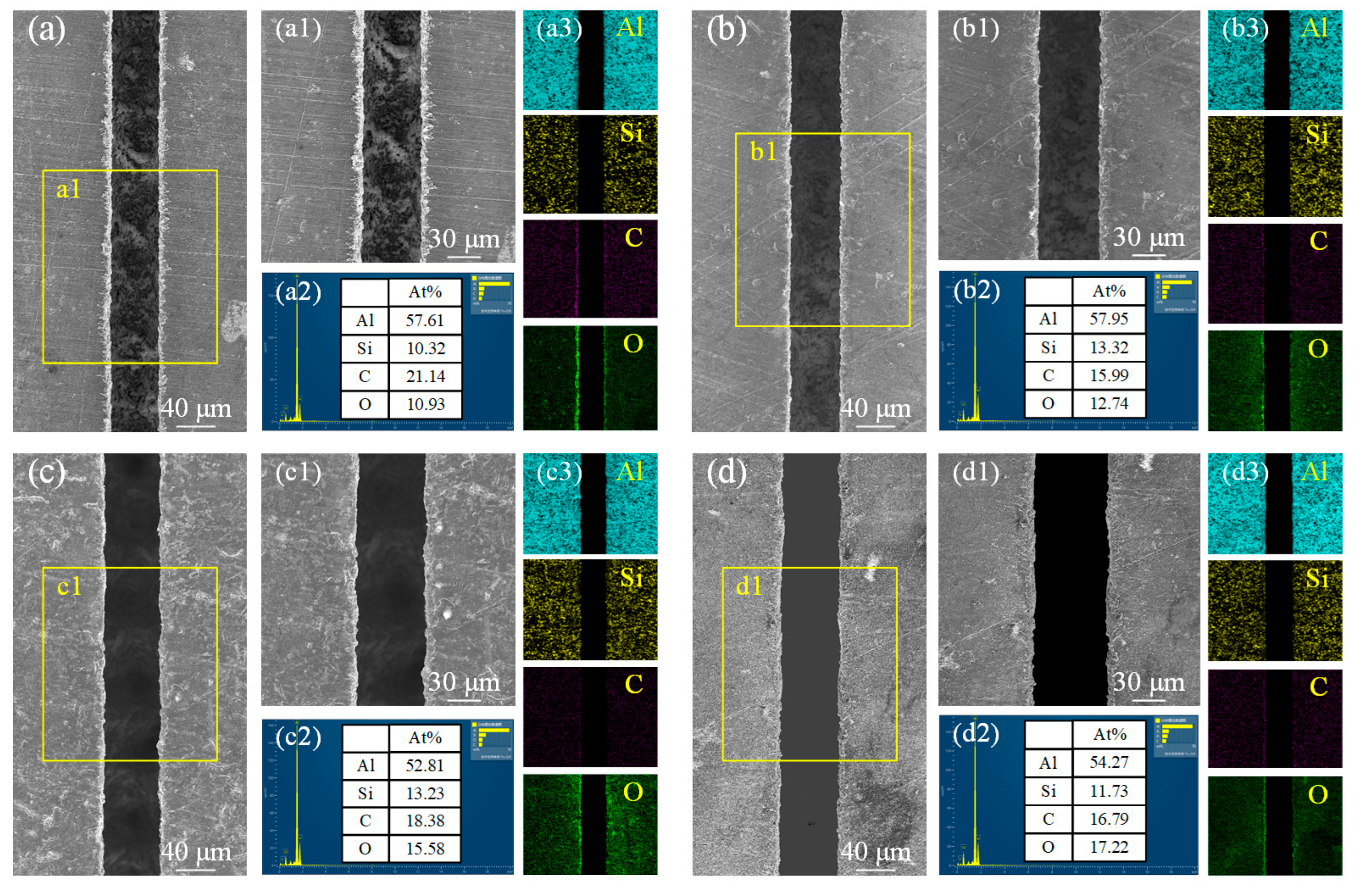
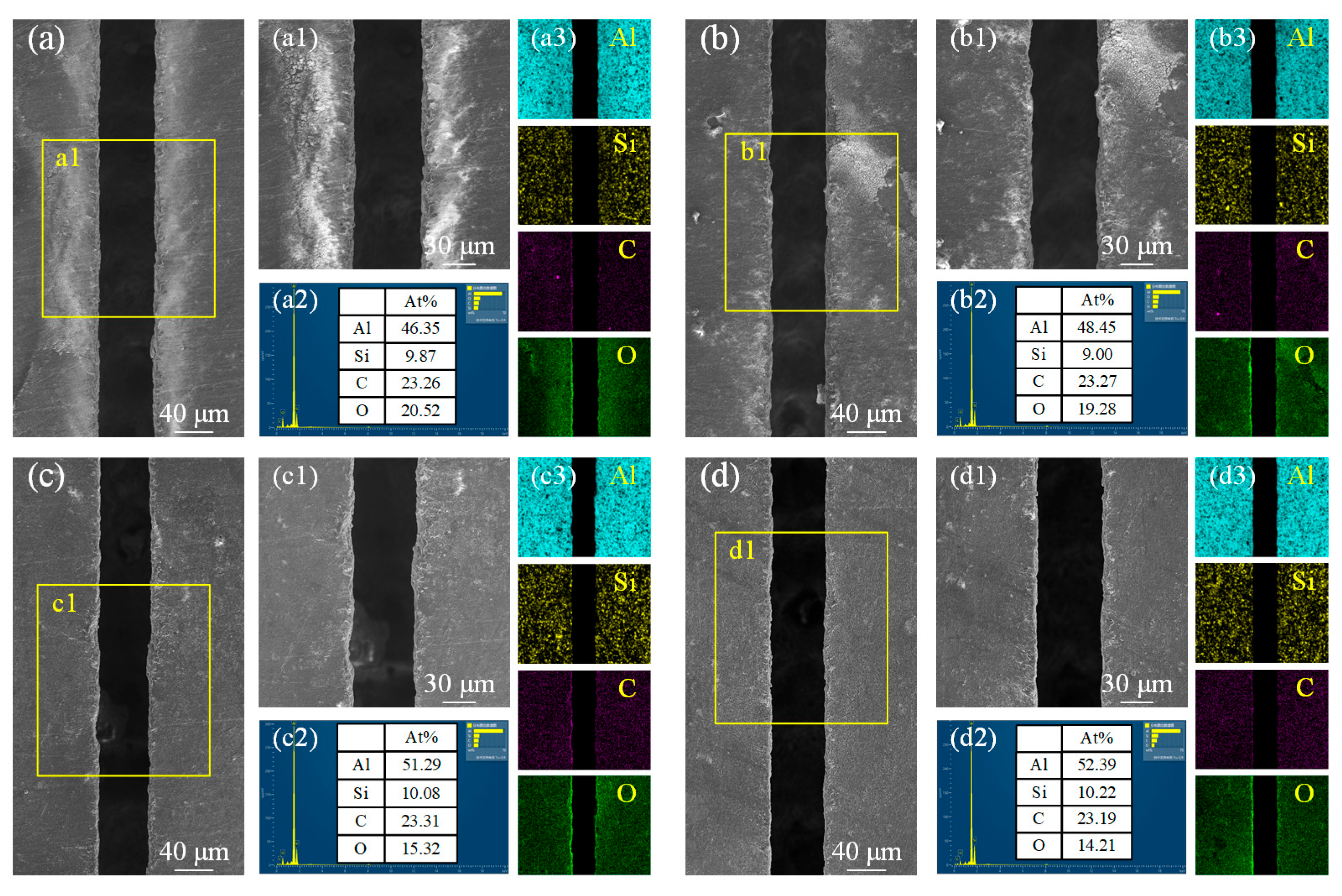
3.2. Microstructure Evolution
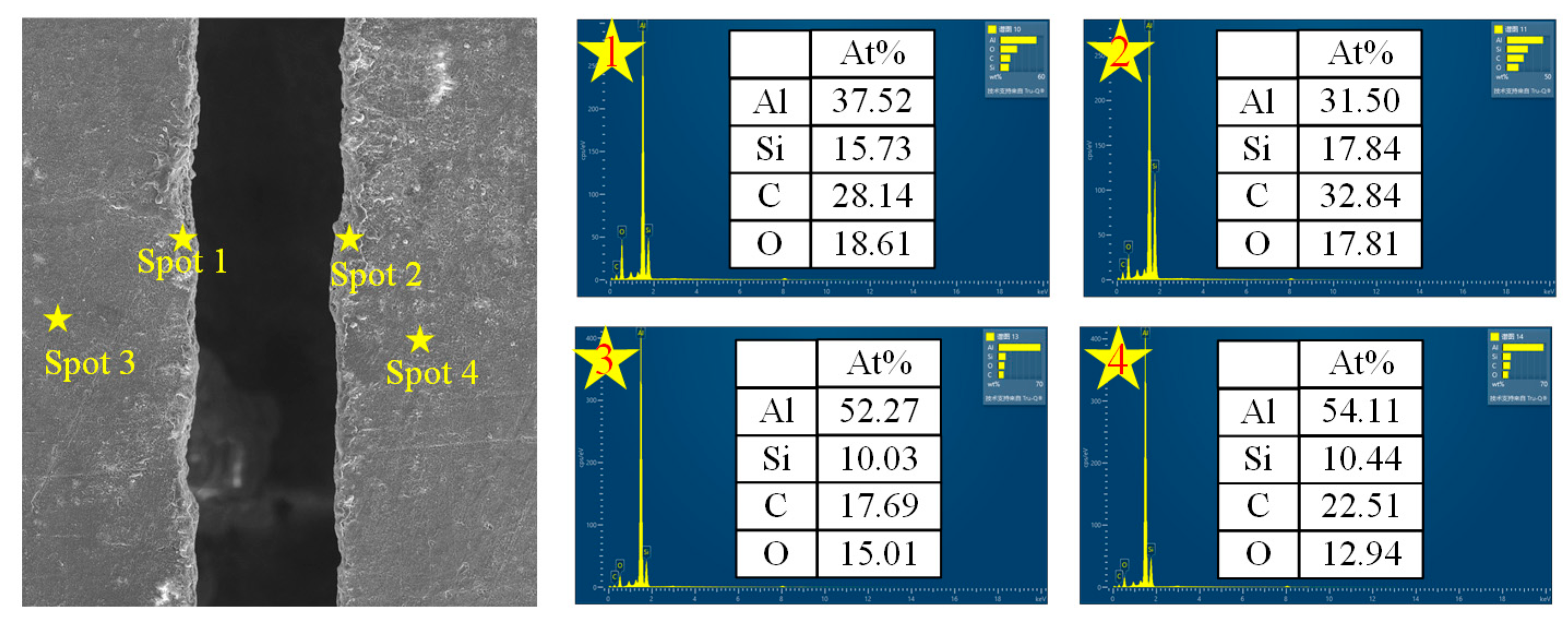
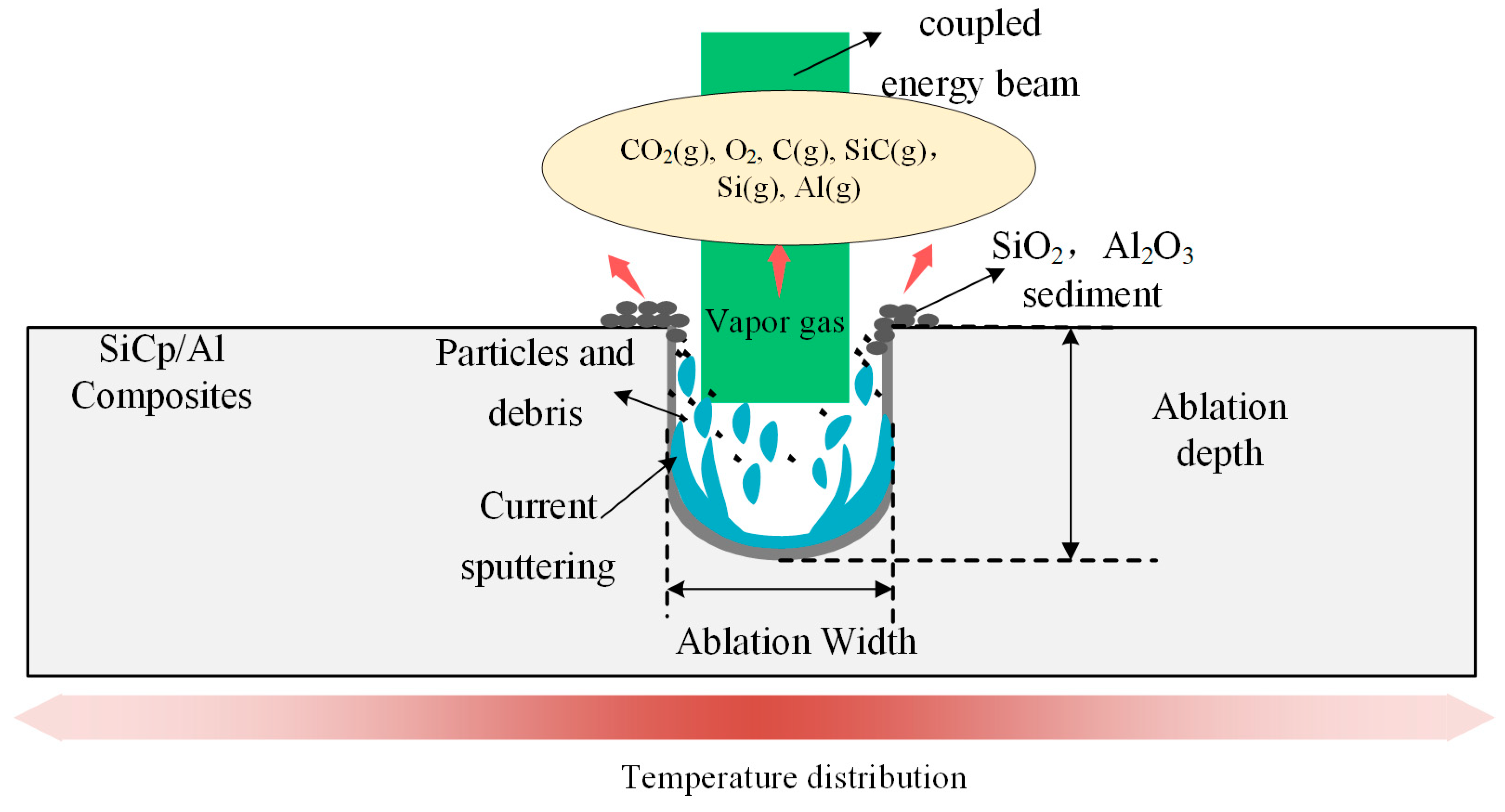
3.3. Ablative Mechanism
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- During the water-jet guided laser machining of the microgroove of SiCp/Al composites,. With the increase in laser power, the depth of the microgroove increases from 154 μm to 492 μm, the width from 63 μm to 74 μm, and the depth-to-width ratio from 2.45 to 6.62; with the increase in scanning speed, the depth of the microgroove decreases from 525.33 μm to 227.16 μm, and the width from 67.61 μm to 71.02 μm, and the depth-to-width ratio from 7.77 to 3.20. With the increase in water jet pressure, the depth increases from 312.29 μm to 3.20. With the increase in water jet pressure, the depth increased from 312.29 μm to 362.39 μm, the width decreased from 71.59 μm to 62.78 μm, and the depth-to-width ratio increased from 4.38 to 5.77.
- (2)
- Under laser irradiation, Al matrix and SiC particles have different chemical reactions at different temperatures. After the action of the water-jet guided laser, the content of Al in the sediments decreased, while the content of C, Si, and O increased.
- (3)
- Water-jet guided laser processing SiCp/Al composites mainly produces thermal–mechanical coupling and a chemical reaction synergistic effect: the material is melted and vaporized under the action of high energy laser beam, and the SiC particles are oxidized and thermally decomposed at local high temperatures due to high thermal stability; at the same time, under the action of a high pressure water beam, the molten residue and other substances are removed, ensuring the high cleanliness and precision of microgroove processing.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ogawa, F.; Masuda, C. Fabrication and the mechanical and physical properties of nanocarbon-reinforced light metal matrix composites: A review and future directions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2021, 820, 141542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Lu, M.; Lin, J.; Li, Y.; Sun, S. Investigation on machinability of SiCp/Al composites under the synergistic effect of pulsed laser assisted and ultrasonic elliptical vibration cutting. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2024, 332, 118561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthil, S.; Raguraman, M.; Manalan, D.T. Manufacturing processes & recent applications of aluminium metal matrix composite materials: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 45, 5934–5938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzamtzis, S.; Barekar, N.S.; Babu, N.H.; Patel, J.; Dhindaw, B.K.; Fan, Z. Processing of advanced Al/SiC particulate metal matrix composites under intensive shearing—A novel rheo-process. Compos. Part A 2009, 40, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Abdelhafeez, A.; Li, H.; Yang, Y.; Diaz, O.G.; Axinte, D. State-of-the-art of surface integrity in machining of metal matrix composites. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2019, 143, 63–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, A.; Bhattacharayya, B. A study on machinability of Al/SiC-MMC. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2003, 140, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-P.; Wu, Y.-L.; Jin, J.; Liu, J.; Qu, L.-Q. Optimization of milling tool parameters and experimental study of cryogenic minimum quantity lubrication (CMQL) for SiCp/Al composites. Ferroelectrics 2023, 610, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Popov, V.L.; Yu, Z.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, Q.; Yu, H. Preparation of micro-pit-textured PCD tools and micro-turning experiment on SiCp/Al composites. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Z.W.; Hung, N.P. Grinding of alumina/aluminum composites. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2002, 123, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, P.; Zhu, C.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; Tao, Z.; Shi, Z. Surface roughness prediction of SiCp/Al composites in ultrasonic vibration-assisted grinding. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 101, 687–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yingfei, G.; Jiuhua, X.; Hui, Y. Diamond tools wear and their applicability when ultra-precision turning of SiCp/2009Al matrix composite. Wear 2010, 269, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Yuan, S.; Wei, J.; Zhou, N.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, X. Water jet guided laser grooving of SiCf/SiC ceramic matrix composites. Opt. Laser Technol. 2024, 168, 109991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Yuan, S.; Yang, S.; Gao, M.; Fu, Y.; Hu, T.; Li, X.; Fan, X.; Zhang, W. Waterjet-guided laser processing of SiC/SiC ceramic matrix composites to obtain high cleanliness and low oxidation damage characteristics surfaces. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 484, 130791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Ding, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, J.Y.; Xu, J.J.; Li, Q.; Yang, L.J. Coaxial helical gas assisted laser water jet machining of SiC/SiC ceramic matrix composites. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2021, 293, 117067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Xu, W.; Zhang, L. Machining of particulate-reinforced metal matrix composites: An investigation into the chip formation and subsurface damage. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2019, 274, 116315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Sun, D. Research on SiC/Al laser-assisted nano-cutting based on molecular dynamics simulation. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 41, 116315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Properties | Parameters |
|---|---|
| Density [kg·m−3] | 2.88 |
| Elastic modulus [GPa] | 95 |
| Tensile strength [MPa] | 480 |
| Thermal conductivity [W·m−1·C−1] | 225.3 |
| Specific heat capacity [J·Kg−1·°C−1] | 522.1 |
| particle volume fraction [%] | 15 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Wavelength λ [nm] | 532 |
| Nozzle diameter d [µm] | 50 |
| Beam height h [µm] | 30 |
| Repetition frequency f [kHz] | 10 |
| Laser Processing Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Laser power P [W] | 10, 15, 20, 25 |
| Scanning speed v [mm/s] | 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2 |
| Water jet pressure F [MPa] | 15, 20, 25, 30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, W.; Yu, Z.; Xing, G.; Yang, F.; Dong, Z. Study on the Microstructure Evolution and Ablation Mechanism of SiCp/Al Composites Processed by a Water-Jet Guided Laser. Materials 2025, 18, 2749. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122749
Yin W, Yu Z, Xing G, Yang F, Dong Z. Study on the Microstructure Evolution and Ablation Mechanism of SiCp/Al Composites Processed by a Water-Jet Guided Laser. Materials. 2025; 18(12):2749. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122749
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Wendian, Ze Yu, Guanghao Xing, Feng Yang, and Zhigang Dong. 2025. "Study on the Microstructure Evolution and Ablation Mechanism of SiCp/Al Composites Processed by a Water-Jet Guided Laser" Materials 18, no. 12: 2749. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122749
APA StyleYin, W., Yu, Z., Xing, G., Yang, F., & Dong, Z. (2025). Study on the Microstructure Evolution and Ablation Mechanism of SiCp/Al Composites Processed by a Water-Jet Guided Laser. Materials, 18(12), 2749. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122749






