Corrosion-Wear Mechanism of (AlTiV)100−xCrx Lightweight High-Entropy Alloy in the 3.5 wt.% NaCl Solution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Materials
2.2. Microstructure and Mechanical Behaviors
2.3. Corrosion Behavior
2.4. Wear Test and Worn Scar Characterization
3. Results
4. Discussion
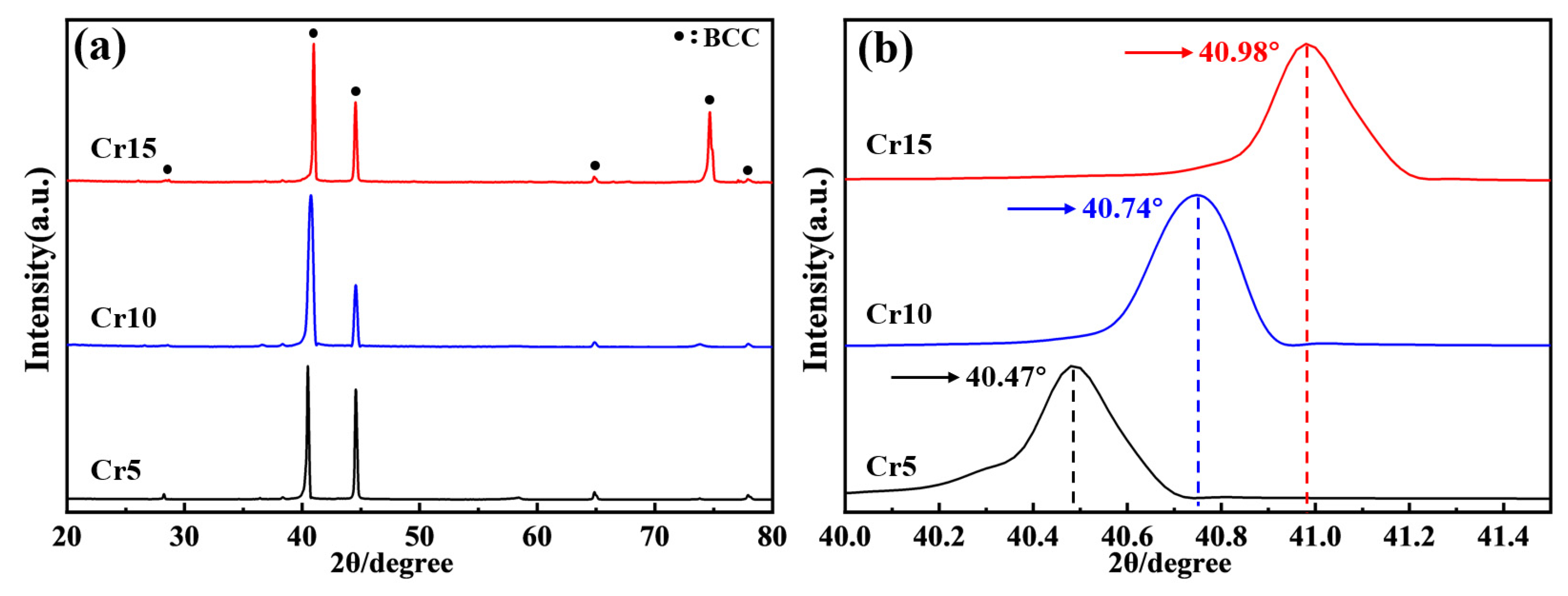
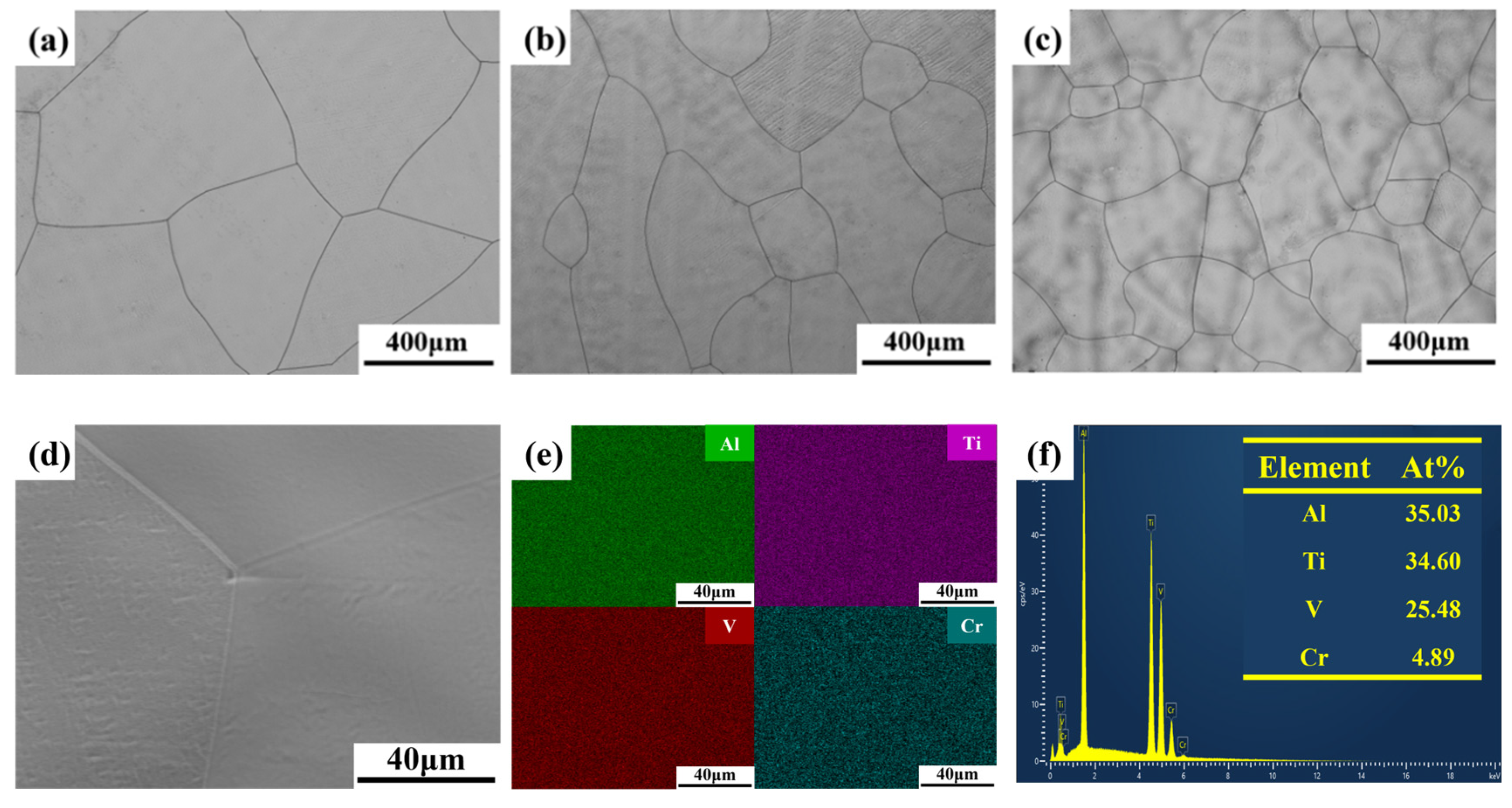
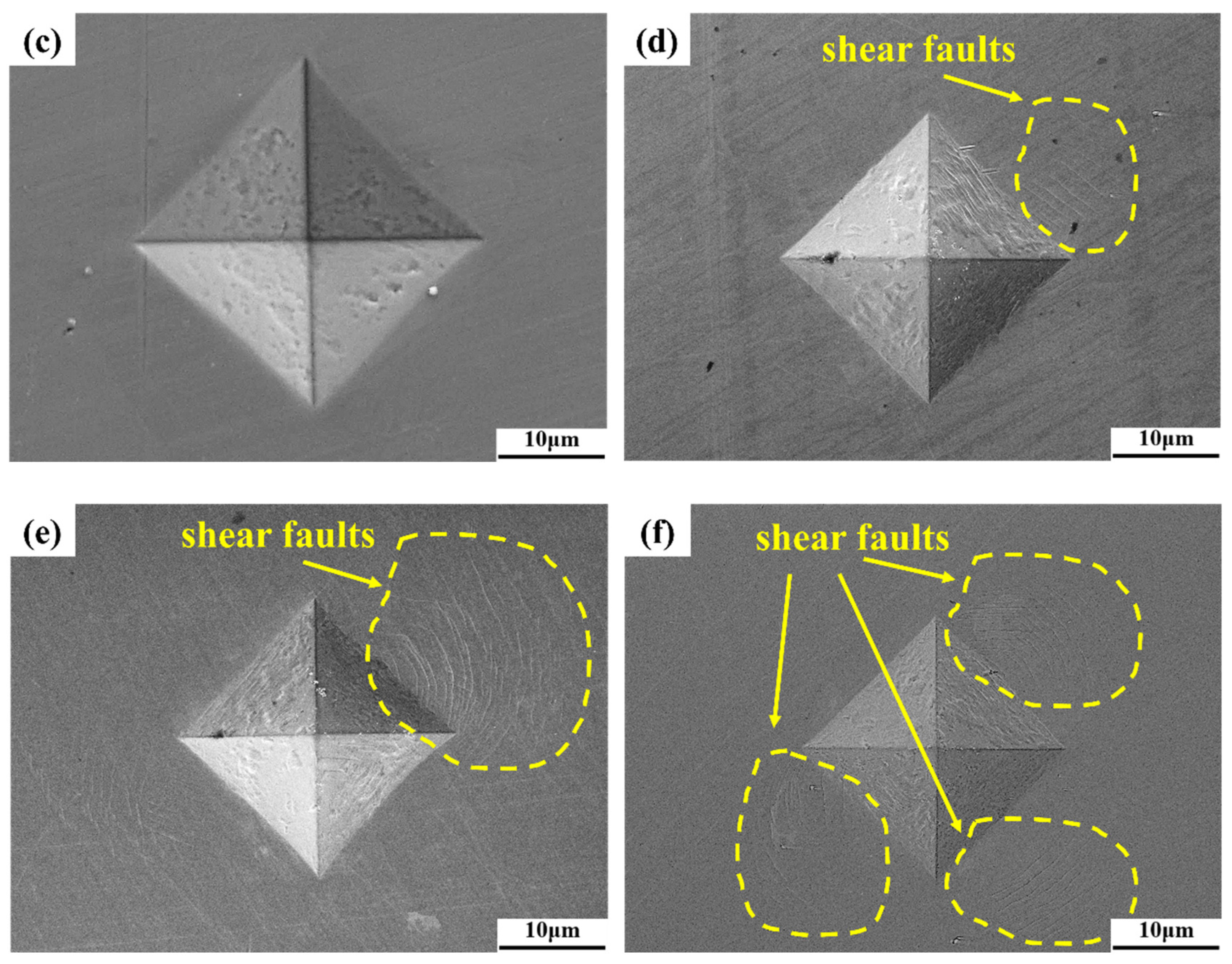
4.1. Microstructure, Mechanical and Corrosion Properties of (AlTiV)100−xCrx
4.2. Wear and Corrosion-Wear Behaviors of AlTiVCr
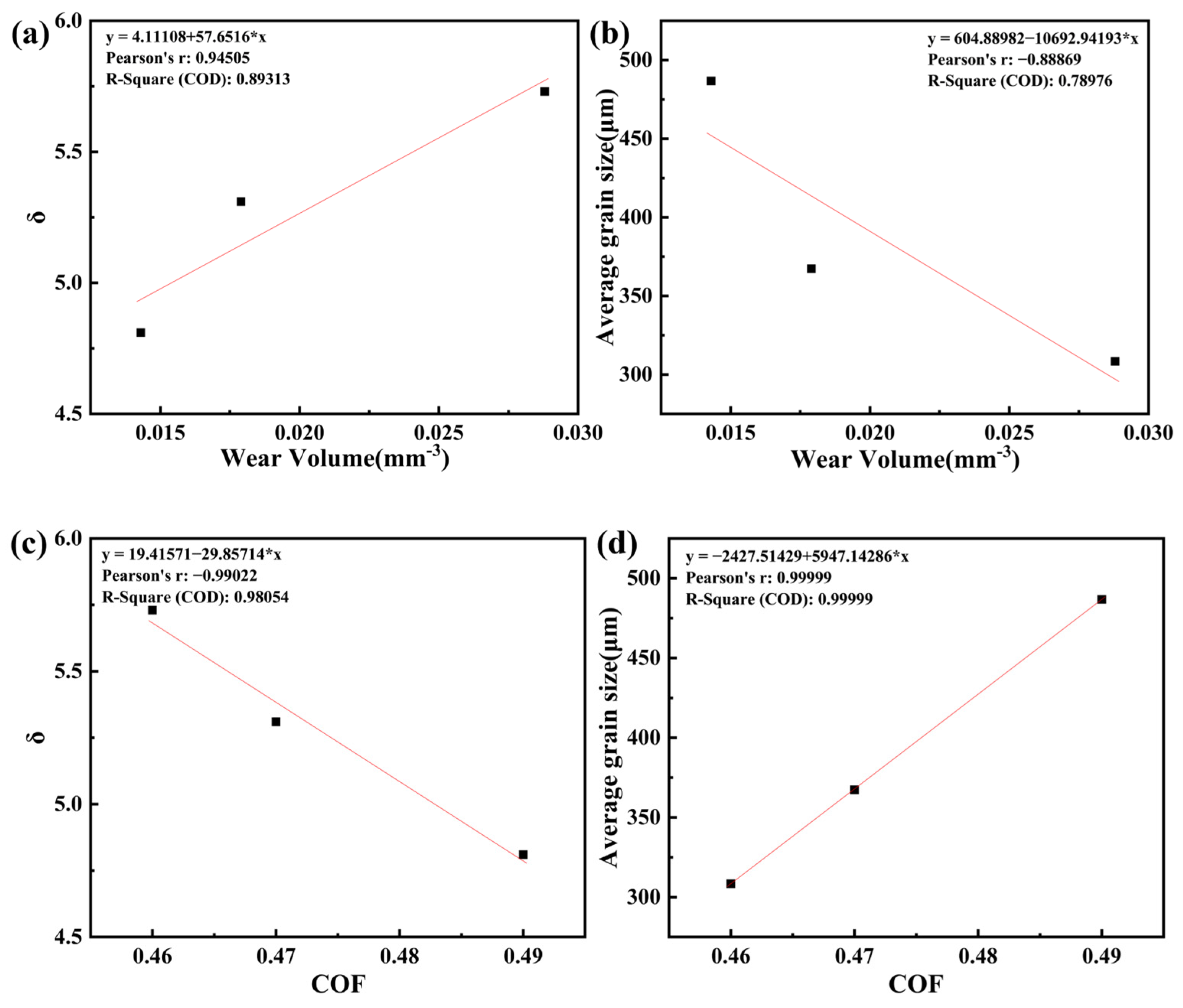
4.3. The Link Between Microstructure and Corrosion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
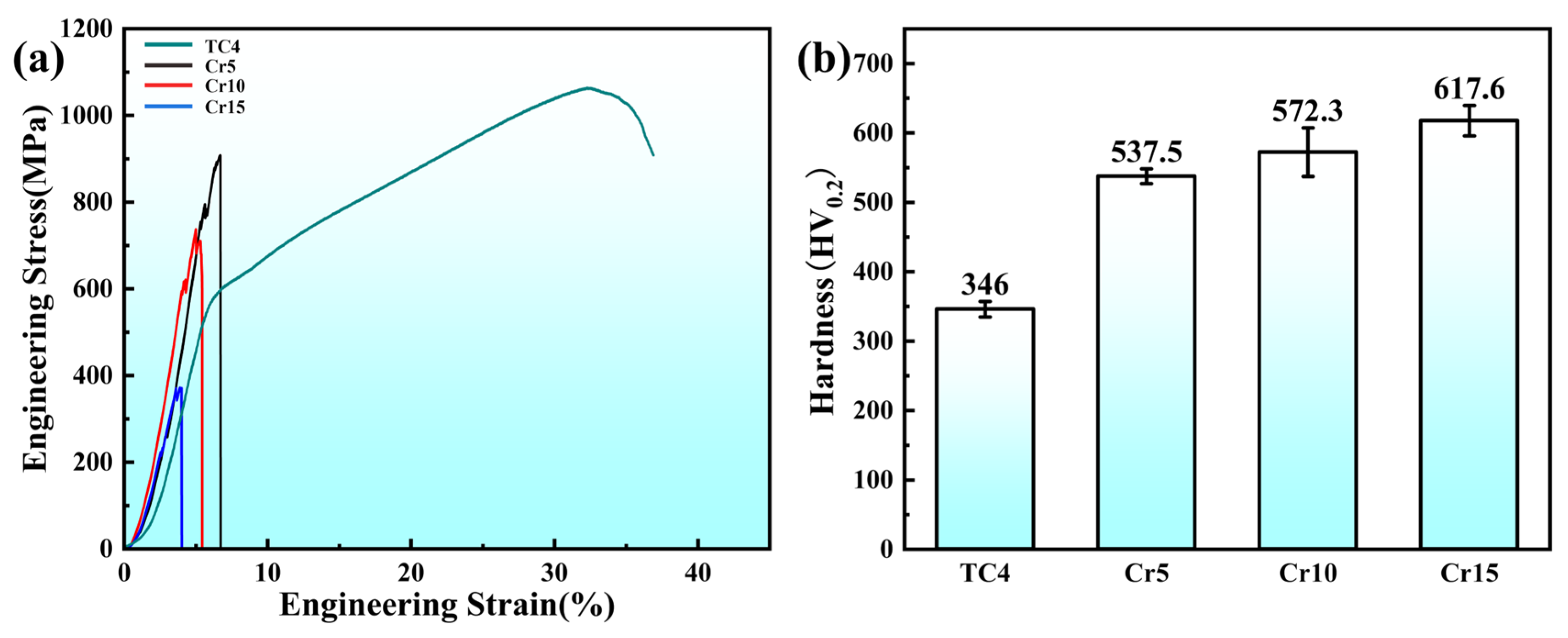
- The AlTiVCr alloy consists of single phase with BCC crystal structure. The increasing lattice distortion and grain refinement led to a gradual growth in the hardness of AlTiVCr (Cr5/537.5 HV0.2, Cr10/572.3 HV0.2 and Cr15/617.6 HV0.2), which are both greater higher than of TC4 (346 HV0.2).
- (2)
- The corrosion resistance of AlTiVCr alloy is superior to that of TC4 for its dense composite oxide film composed of Al2O3 + Cr2O3 + V2O5 + TiO2. However, the corrosion resistance of AlTiVCr alloys decreases gradually with the increasing Cr content for the growth of lattice distortion.
- (3)
- The wear volume in and without corrosion are both caused by the abrasive wear. However, the reduction in toughness and corrosion resistance as well as the aggravation in solution corrosivity could exacerbate the fatigue wear of AlTiVCr alloys.
- (4)
- In the deionized water, the wear volume of AlTiVCr decreases and then increases with increasing Cr content. Cr10 presents the best wear resistance, which is 56.4% higher than that of TC4.
- (5)
- In the 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution, the corrosion wear volume of AlTiVCr increases with the increase of Cr content. Cr5 presents the best corrosion-wear resistance, which is 65.5% higher than that of TC4.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liang, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, L.; Peng, Y. Microstructure and Wear Behavior of WMoTaNbV Refractory High-Entropy Alloy Coating on Ti6Al4V Alloy Surface Prepared by Laser Cladding. Materials 2025, 18, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, G.; Chong, Y.; Su, L.; Zhan, L.; Wei, P.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, H.; Tsuji, N. Mechanisms of remarkable wear reduction and evolutions of subsurface microstructure and nano-mechanical properties during dry sliding of nano-grained Ti6Al4V alloy: A comparative study. Tribol. Int. 2022, 169, 107464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, W.H.; Peng, H.; Lim, S.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Huang, A. The mechanisms behind the tribological behavior of titanium alloys processed by laser powder bed fusion sliding against steel. Tribol. Int. 2023, 180, 108279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.Y.; Fei, L.Y.; Nong, W.X.; Sun, D.; Lu, W.; Ko, T.J. Tribological characteristics of the dual titanium boride layers (TiB2 + TiB) on titanium alloy. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 13957–13969. [Google Scholar]
- Çömez, N.; Yurddaskal, M.; Durmuş, H. Effect of solutionizing and quenching treatment on Ti6Al4V alloy: A study on wear, cavitation erosion and corrosion resistance. J. Mater. Sci. 2023, 58, 10201–10216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, V.P.; Singh, R.C.; Chaudhary, R.; Kumar, D. Enhancing microstructural, tribological and corrosion responses of Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloy via nano-/micro-Al2O3 particulates. J. Mater. Sci. 2024, 59, 7235–7257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, J.T.; Mathew, J.; Kuriachen, B. Tribology of Ti6Al4V: A review. Friction 2019, 7, 497–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Su, Y.; Zhang, C.; Cai, W.; Lin, S. Influence of nitrogen flow rate on the structure and properties of (AlTiVCrMoSi) Nx high-entropy alloy nitride coatings via arc ion plating. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2025, 496, 131732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.X.; Dai, J.J.; Sun, C.X.; Li, S.Y. Microstructure and wear resistance of TiAlNiSiV high-entropy laser cladding coating on Ti-6Al-4V. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2020, 282, 116671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, T.D.; Tieu, A.K.; Wexler, D.; Su, L.; Nguyen, C.; Yang, J.; Deng, G. High temperature tribological performance of a cost-effective eutectic high entropy alloy Al0.8CrFeNi2.2: Comparison with AlCoCrFeNi2.1. Tribol. Int. 2023, 184, 108445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Yang, J.; He, M.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, P.; Tu, X.; Li, W. Microstructural and wear resistance evolution of Alx(TiVZr)100−x lightweight high-entropy alloys. Tribol. Int. 2024, 195, 109585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Wu, S.; Yu, H. Investigation of mechanical and corrosion properties of light and high hardness cast AlTiVCrCu0.4 high entropy alloy. Mater. Charact. 2023, 200, 112878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. Review on corrosion-wear resistance performance of materials in molten aluminum and its alloys. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 1715–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, R.J.K. Marine wear and tribocorrosion. Wear 2017, 376, 893–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer-Rodenbeck, G.; Hurd, T.; Ball, A. On the abrasive-corrosive wear of aluminium alloys. Wear 1992, 154, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Mol, J.M.C.; Janssen, G. Combined corrosion and wear of aluminium alloy 7075-T6. J. Bio. Tribo-Corros. 2016, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qiu, H.; Zhang, X.F.; Yu, H.L.; Yang, J.J.; Tu, X.H.; Li, W. Effects of (Ti, Mo) C particles on the abrasive wear-corrosion of low alloy martensitic steel. Wear 2022, 496, 204288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Gao, M.; Yu, Y.; Lu, X.; Blawert, C.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, J.; et al. Improving corrosion resistance of Ti alloy in hydrochloric acid by embedding TiC/TiB and Y2O3 ceramic nano-particles. Corros. Sci. 2023, 215, 111013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Thomas, S.; Gibson, M.A.; Fraser, H.L.; Pohl, K.; Birbilis, N. Microstructure and corrosion properties of the low-density single-phase compositionally complex alloy AlTiVCr. Corros Sci. 2018, 133, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, A.; Inoue, A. Classification of bulk metallic glasses by atomic size difference, heat of mixing and period of constituent elements and its application to characterization of the main alloying element. Mater. Trans. 2005, 46, 2817–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.X.; Wang, S.Q.; Chen, K.M.; Cui, X.H. Relations between oxidative wear and Cr content of steels. Wear 2011, 272, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Wilks, G.B.; Miracle, D.B.; Chuang, C.P.; Liaw, P.K. Refractory high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2010, 18, 1758–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Perevoshchikova, N.; Sha, Y.; Wu, X. The effects of selective laser melting process parameters on relative density of the AlSi10Mg parts and suitable procedures of the archimedes method. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, C.G. X-ray diffraction and the Bragg equation. J. Chem. Educ. 1997, 74, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.J.; Lin, J.P.; Chen, G.L.; Liaw, P.K. Solid-solution phase formation rules for multi-component alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2008, 10, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.T. Atomic-size effect and solid solubility of multicomponent alloys. Scr. Mater. 2015, 94, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ningshen, S.; Sakairi, M.; Suzuki, K.; Ukai, S. The corrosion resistance and passive film compositions of 12% Cr and 15% Cr oxide dispersion strengthened steels in nitric acid media. Corros. Sci. 2014, 78, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Qian, Y.; Xu, J.; Zuo, J.; Li, M. Effect of annealing on microstructure evolution and corrosion resistance of an amorphous Cr-Al-C coating. Corros. Sci. 2021, 178, 109062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, H.Y.; Kim, K.W.; Park, S.J.; Lee, T.H.; Park, H.; Moon, J.; Hong, H.; Lee, C. Effects of Cr on pitting corrosion resistance and passive film properties of austenitic Fe–19Mn–12Al–1.5C lightweight steel. Corros. Sci. 2022, 206, 110529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.H.; Yue, T.M.; Guo, Z.N.; Lin, X. Microstructure and corrosion properties of AlCoCrFeNi high entropy alloy coatings deposited on AISI 1045 steel by the electrospark process. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2013, 44, 1767–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Luo, D.W.; Hua, D.P.; Ye, W.T.; Li, S.; Zou, Q.G.; Chen, Z.Q.; Wang, H.F. Design and characterization of metallic glass/graphene multilayer with excellent nanowear properties. Friction 2022, 10, 1913–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Qiu, H.; Cao, L.; Tu, X.; Cui, J.; Yu, H.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Yang, J.; Li, W.; et al. Effect of TiC on the impact abrasive wear resistance of low alloy martensitic steel. Tribol. Int. 2022, 175, 107866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Hua, D.; Huang, Z.; Li, Y.; Jia, Q.; Gumbsch, P.; Greiner, C.; Wang, H.; Liu, W. Wear-resistant CoCrNi multi-principal element alloy at cryogenic temperature. Sci. Bull. 2024, 69, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Stack, M.M.; Neville, A. Modelling the tribo-corrosion interaction in aqueous sliding conditions. Tribol. Int. 2002, 35, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Yang, J.S.; Jin, J.S.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.Y.; Li, B.; Hu, J.G.; Gong, P. Effect of Grain Size on the Tribological Behavior of CoCrFeMnNi High Entropy Alloy. Materials 2023, 16, 1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
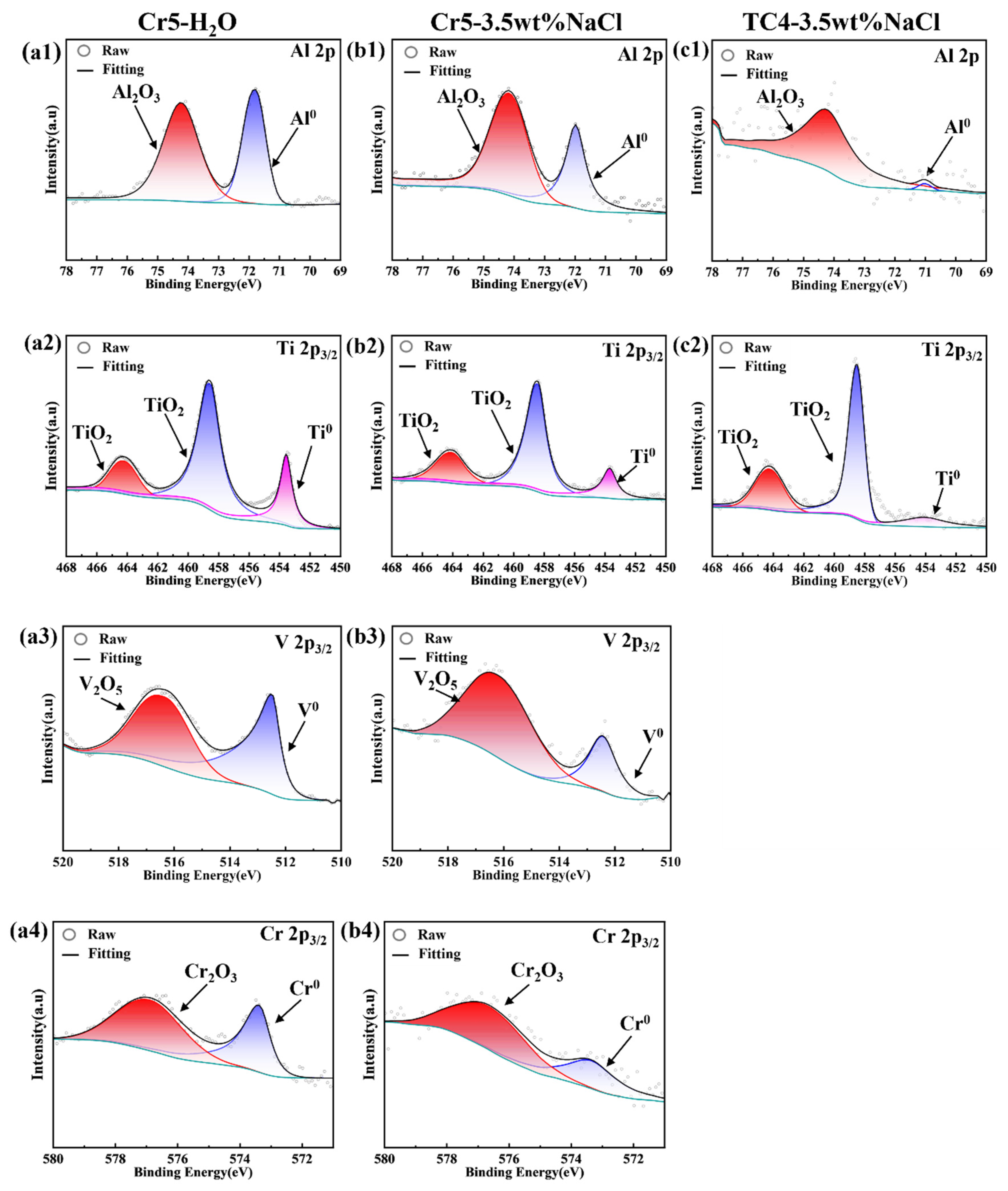
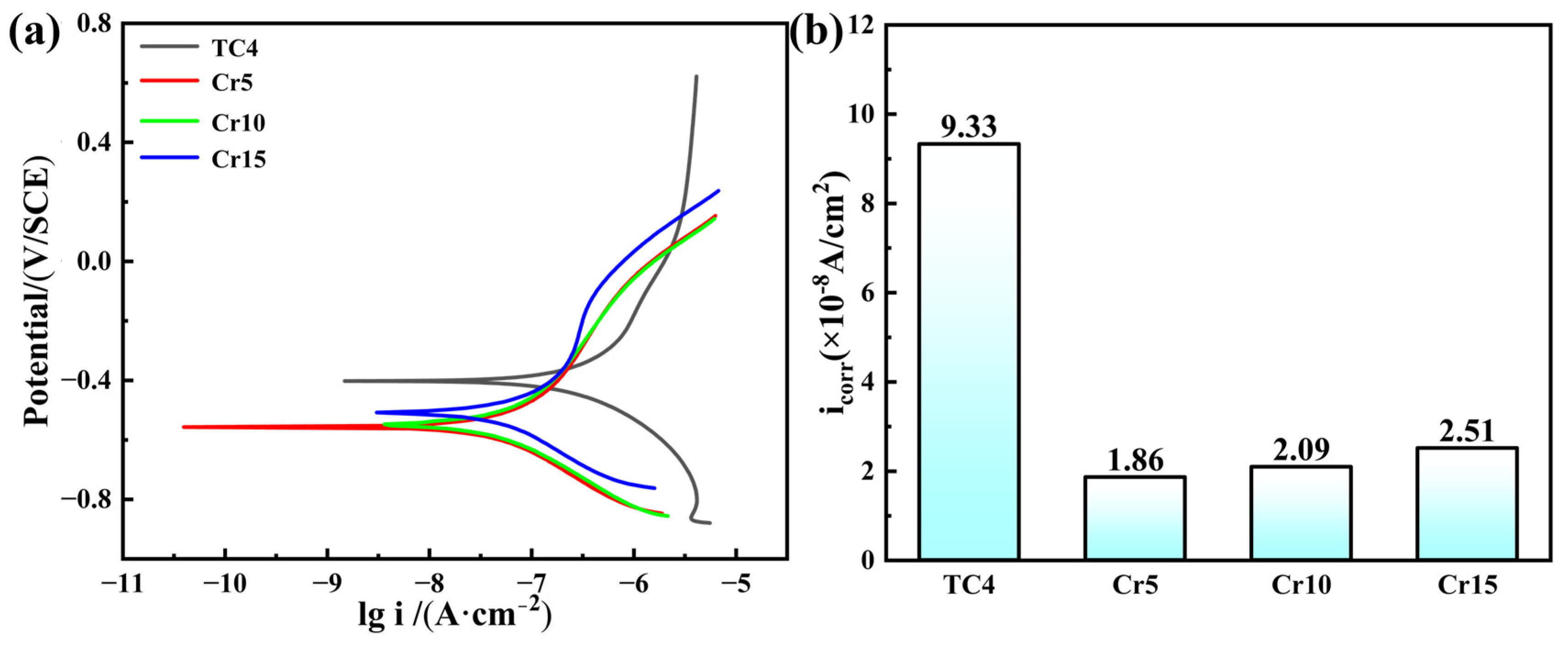
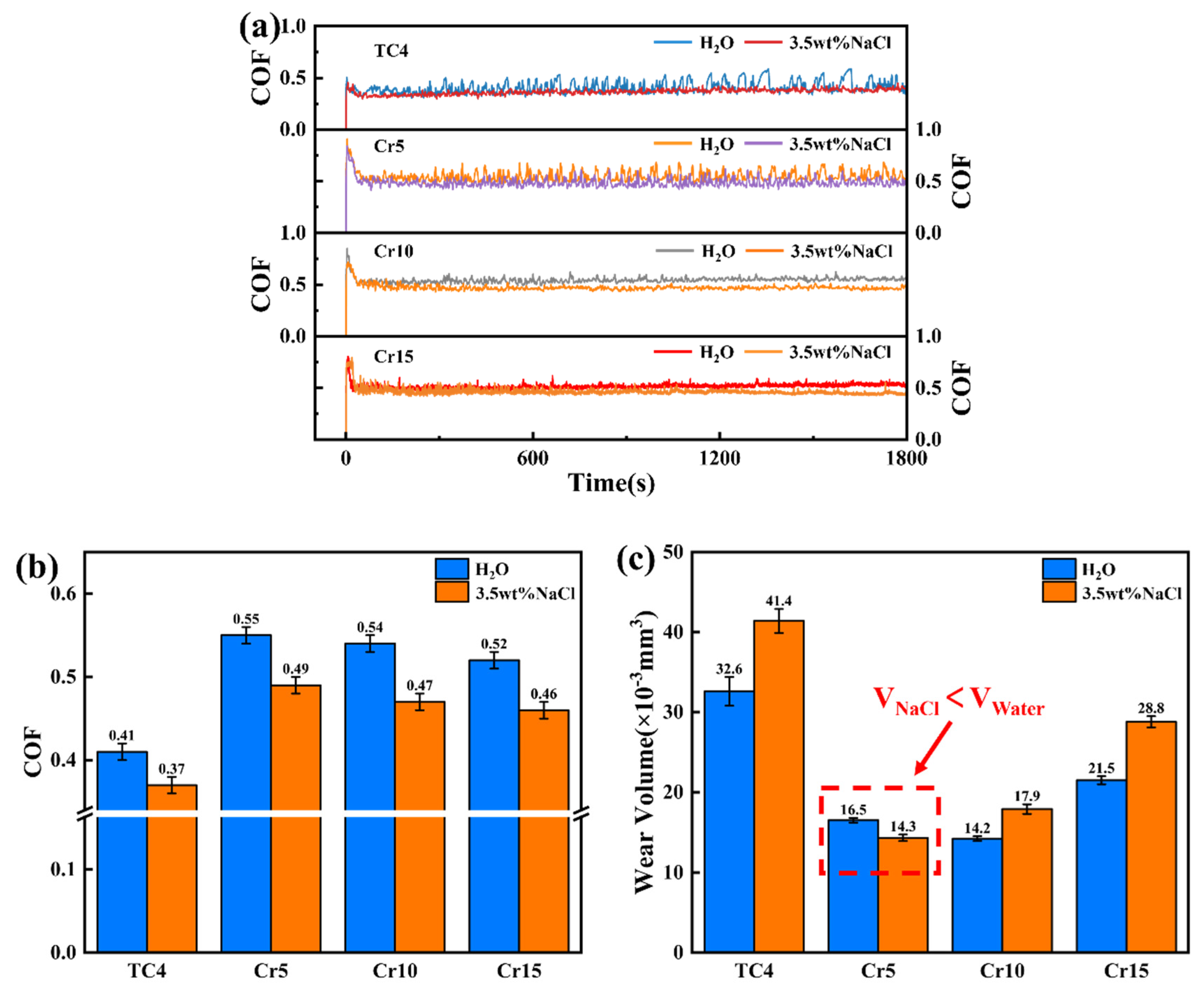

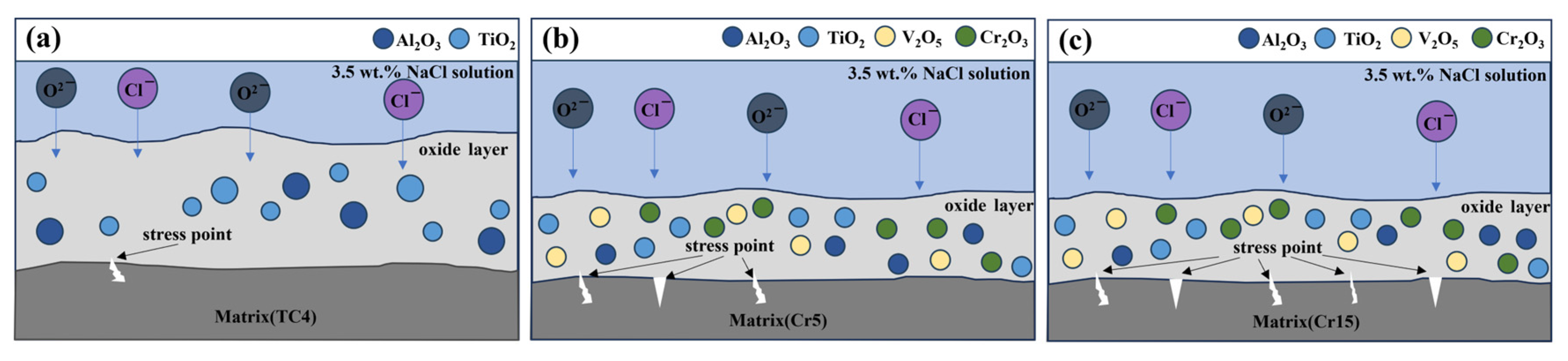
| Alloys | Al (at.%) | Ti (at.%) | V (at.%) | Cr (at.%) | Ρ (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr5 | 35.00 | 35.00 | 25.00 | 5.00 | 4.29 ± 0.02 |
| Cr10 | 33.33 | 33.33 | 23.34 | 10.00 | 4.40 ± 0.04 |
| Cr15 | 31.67 | 31.67 | 21.66 | 15.00 | 4.52 ± 0.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, J.; Zhang, P.; Yang, J.; Li, W.; Wang, Q.; Li, J. Corrosion-Wear Mechanism of (AlTiV)100−xCrx Lightweight High-Entropy Alloy in the 3.5 wt.% NaCl Solution. Materials 2025, 18, 2670. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112670
Huang J, Zhang P, Yang J, Li W, Wang Q, Li J. Corrosion-Wear Mechanism of (AlTiV)100−xCrx Lightweight High-Entropy Alloy in the 3.5 wt.% NaCl Solution. Materials. 2025; 18(11):2670. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112670
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Jiakai, Peng Zhang, Junjie Yang, Wei Li, Qiwei Wang, and Jie Li. 2025. "Corrosion-Wear Mechanism of (AlTiV)100−xCrx Lightweight High-Entropy Alloy in the 3.5 wt.% NaCl Solution" Materials 18, no. 11: 2670. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112670
APA StyleHuang, J., Zhang, P., Yang, J., Li, W., Wang, Q., & Li, J. (2025). Corrosion-Wear Mechanism of (AlTiV)100−xCrx Lightweight High-Entropy Alloy in the 3.5 wt.% NaCl Solution. Materials, 18(11), 2670. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112670






