Micromodification Mechanism and High-Temperature Rheological Properties of Activated Rubber/Styrene–Butadiene–Styrene Compound-Modified Asphalt
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Base Asphalt
2.1.2. Activated Rubber
2.1.3. Conventional Rubber
2.1.4. SBS Modifiers
2.1.5. Stabilizer
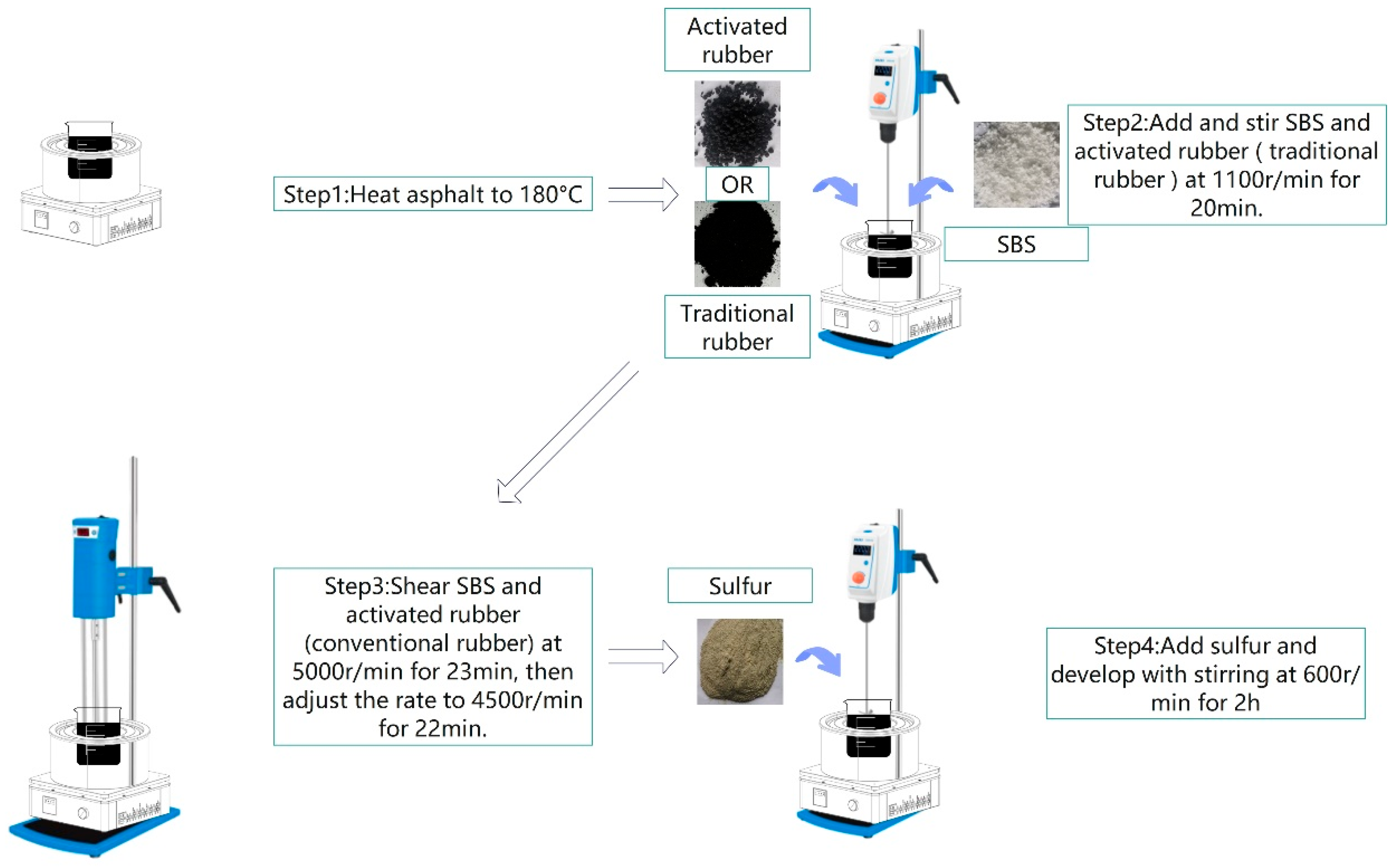
2.1.6. Composite-Modified Asphalt Preparation Process
2.2. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
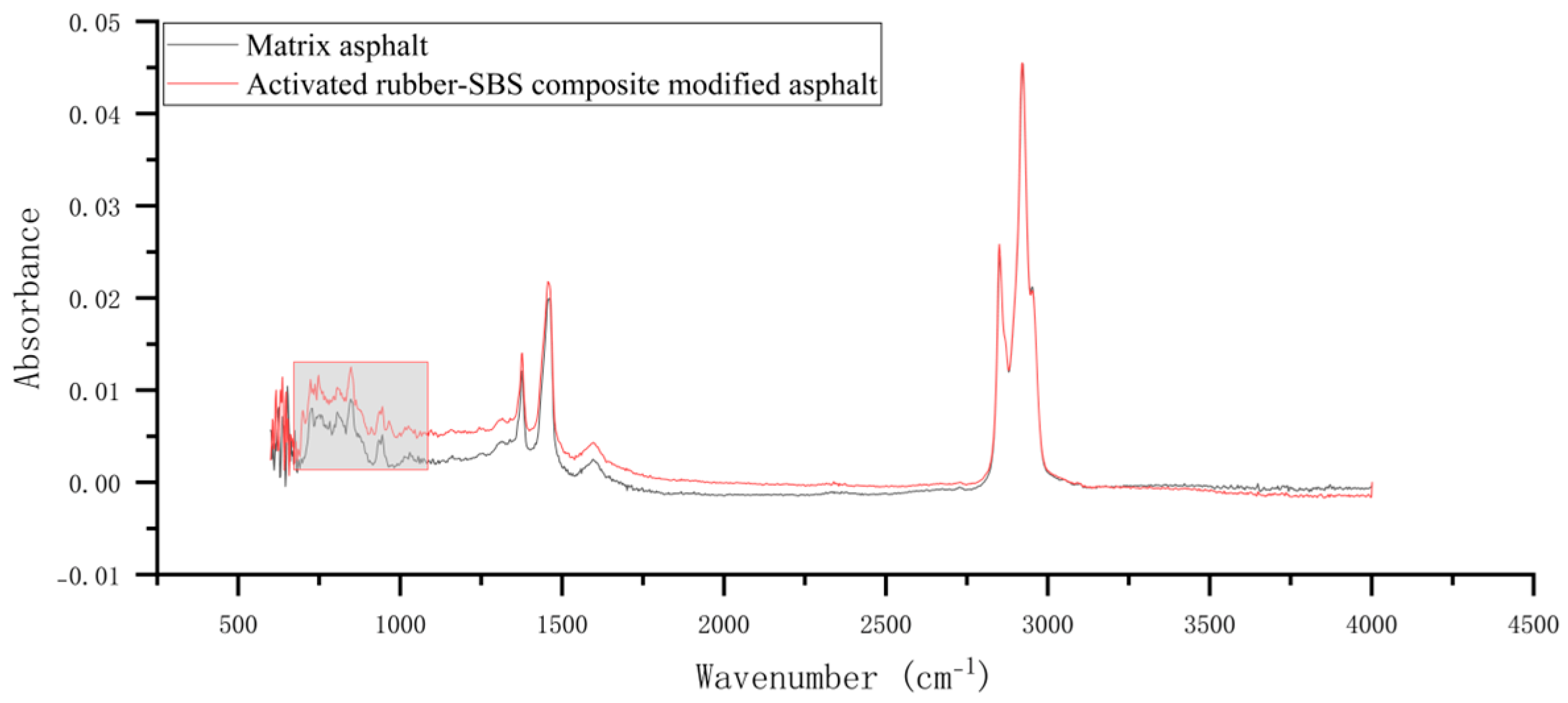
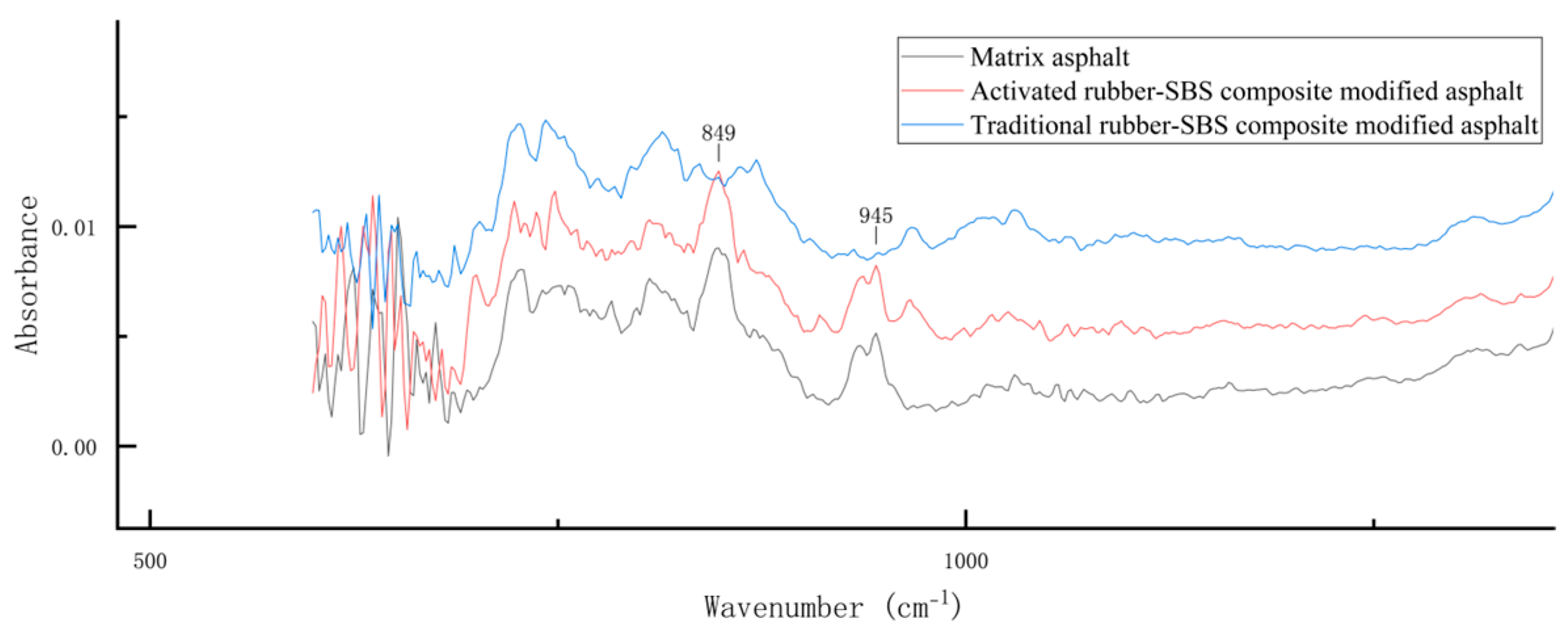
3.1. Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis
3.1.1. Base Asphalt
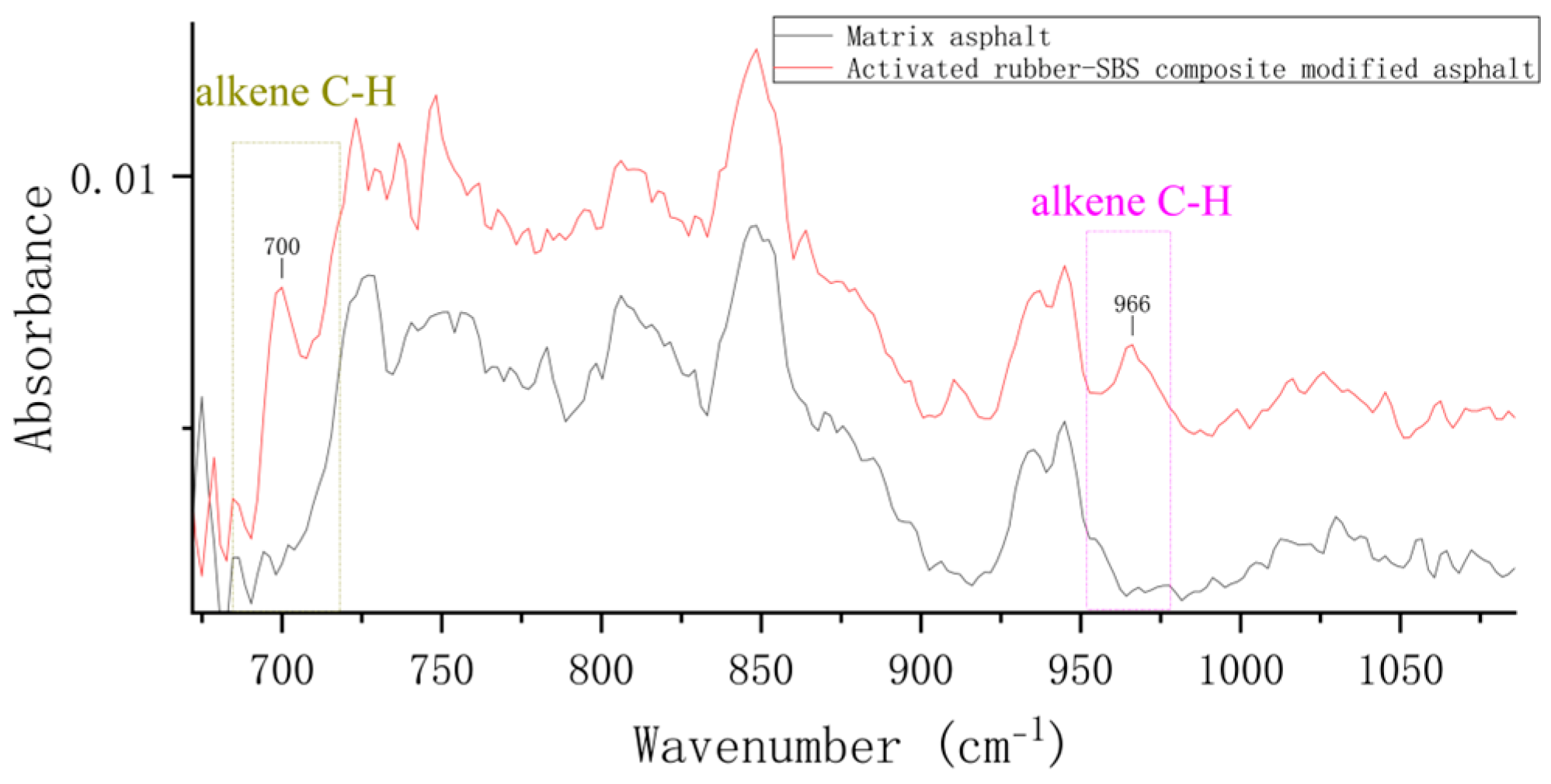
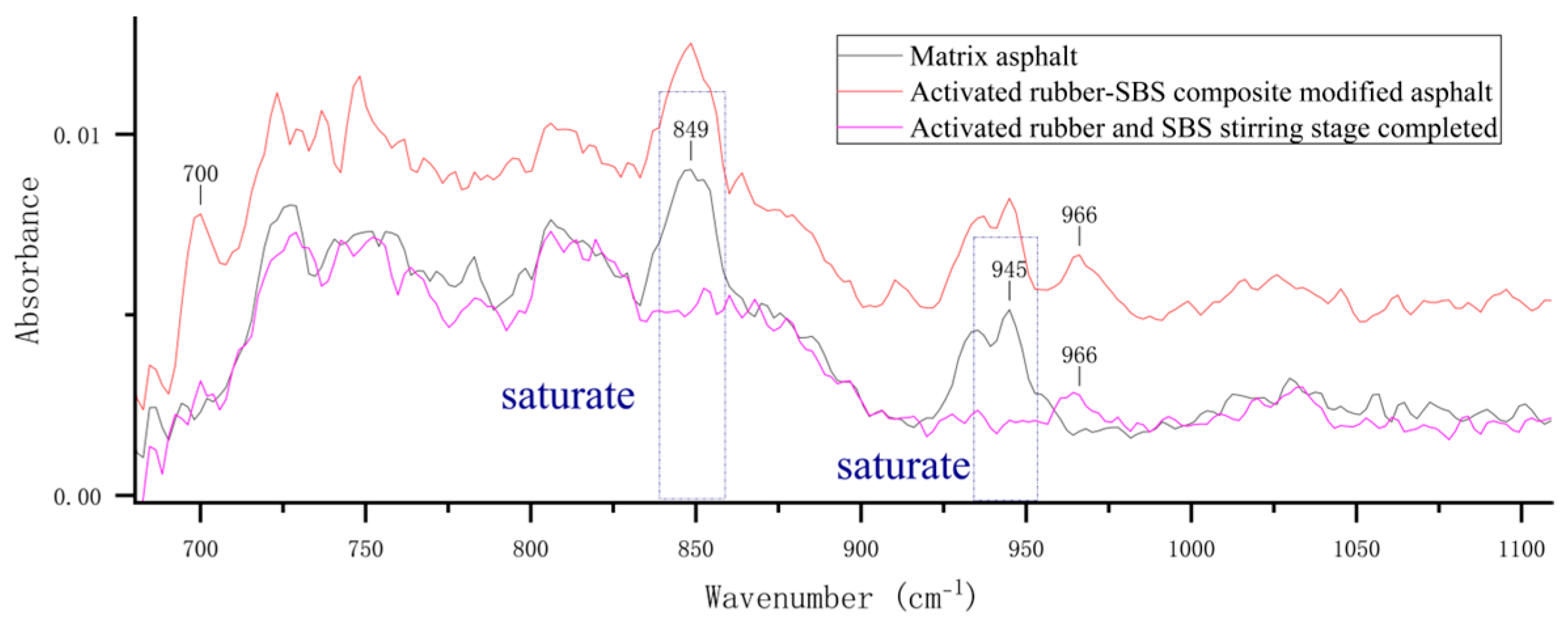
3.1.2. Activated Rubber/SBS Composite Modified Asphalt
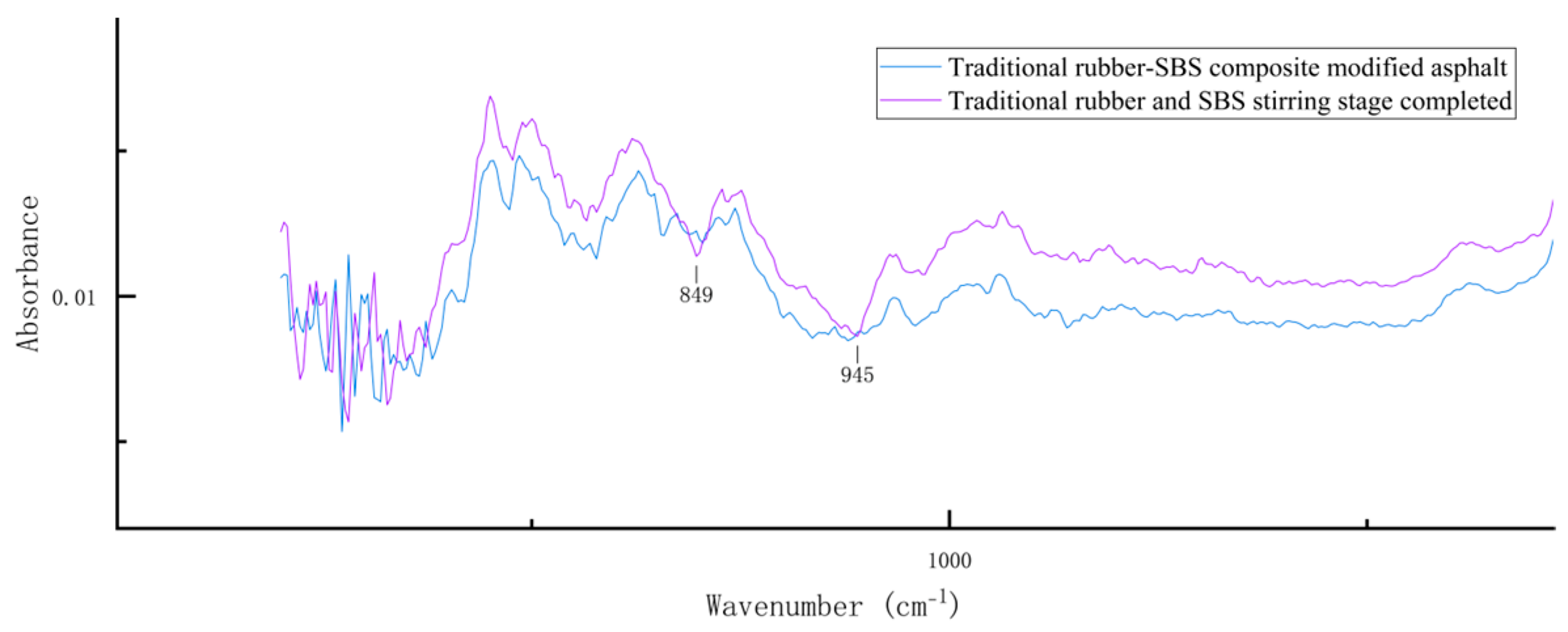
3.1.3. Conventional Rubber/SBS Composite-Modified Asphalt
3.2. SEM Scanning Analysis
3.2.1. Activated Rubber/SBS Composite Modified Asphalt
3.2.2. Conventional Rubber/SBS Composite Modified Asphalt
3.3. Analysis of High-Temperature Rheological Properties of Asphalt
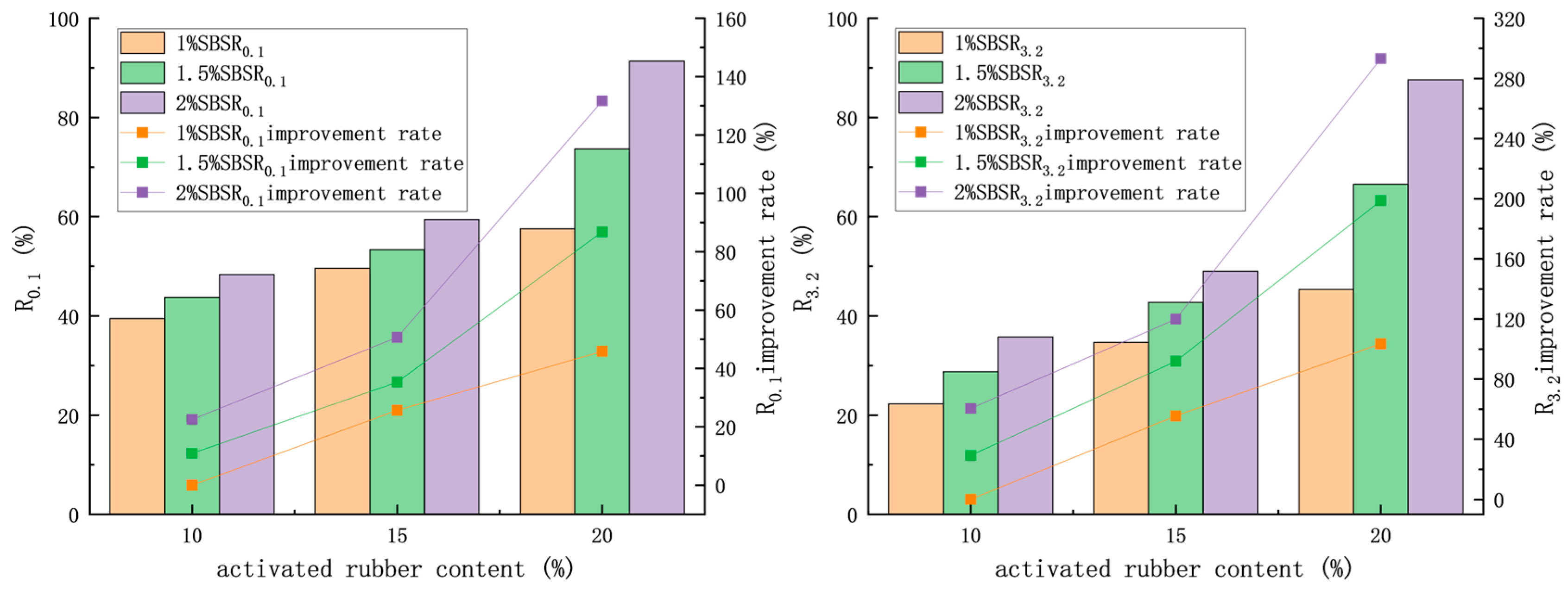
3.3.1. Frequency Scanning
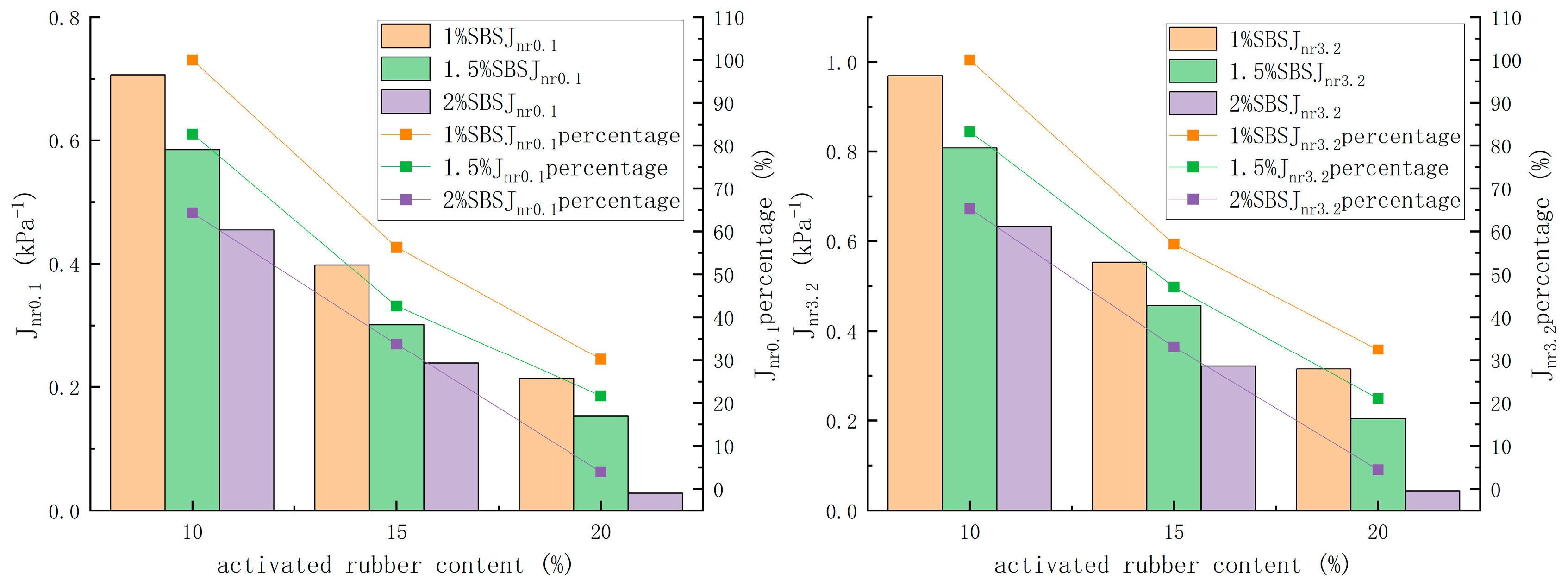
3.3.2. Multiple Stress Creep Recovery Test
4. Conclusions
4.1. Conclusions
4.2. Limitations and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bamigboye, G.O.; Bassey, D.E.; Olukanni, D.O.; Ngene, B.U.; Adegoke, D.; Odetoyan, A.O.; Kareem, M.A.; Enabulele, D.O.; Nworgu, A.T. Waste Materials in Highway Applications: An Overview on Generation and Utilization Implications on Sustainability. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 283, 124581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, X.; Polaczyk, P.; Huang, B. Weather Aging Effects on Modified Asphalt with Rubber-Polyethylene Composites. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 865, 161089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, D.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Yin, L.; Liu, S.; Li, L. Enhancing Shear Resistance in Pavement Structures with Crumb Rubber Modified Asphalt Gravel as A Bonding Layer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 426, 136184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Xie, Y.; Yao, H.; Wang, S. Excellent Low Temperature Performance for Modified Asphalt by Finely Dispersed Sidewall Tire Rubber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 392, 131939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y.; Yu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, R. Conventional Properties, Rheological Characteristics, and Thermal Performance of Waste Polyurethane Modified Asphalt with Butyl Rubber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, K.; Wang, C.; Liu, J.; Song, L.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Y. Research Progress and Performance Evaluation of Crumb-Rubber-Modified Asphalts and Their Mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 361, 129687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhu, H.; Tan, Q.; Yang, X.; Chen, Y.; Lei, L. Application of TOR as A Secondary Modifier for the Preparation of Crumb Rubber Modified Asphalt with Excellent Storage Stability. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 428, 135863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M.A.; Wang, J. Investigation of the Effects of Nano-Al2O3 Addition on Compatibility, Rutting and Fatigue Properties of Styrene-Butadiene-Rubber Modified Asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 416, 135267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, G.; Qi, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Wang, Z. Effects of Tetraethyl Orthosilicate on Rheological Behaviors of Crumb Rubber Modified Asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 325, 126807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Yu, X.; Dong, F.; Wang, S.; Jiang, Y.; Lu, J. The Improvement of Various Polyethylene on the High-Temperature Performance of Degraded Ground Tire Rubber Modified Asphalt and the Compatibility Enhancement Mechanism of Compatibilizer for Composite Modified Asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 427, 136255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Long, G.; Zeng, L. Ultraviolet Irradiation of Crumb Rubber on Mechanical Performance and Mechanism of Rubberised Asphalt. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2019, 20, 1624–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinnezhad, S.; Kabir, S.F.; Oldham, D.; Mousavi, M.; Fini, E.H. Surface functionalization of rubber particles to reduce phase separation in rubberized asphalt for sustainable construction. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 225, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Liang, H.; Dai, Z. Rheological properties and microscopic mechanism of waste cooking oil activated waste crumb rubber modified asphalt. J. Road Eng. 2022, 2, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M.A.; Wang, J. Enhancement of Rheological Performance and Compatibility of Tire Rubber-Modified Asphalt Binder with the Addition of Graphene. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 402, 133038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, M.; Leng, B.; Wu, S.; Chen, D.; Zhao, Z. Investigation on Storage Stability, H2S Emission and Rheological Properties of Modified Asphalt with Different Pretreated Waste Rubber Powder. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 456, 142469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Kabir, S.F.; Cao, L.; Luan, H.; Dong, Z.; Fini, E.H. Comparing Effects of Physisorption and Chemisorption of Bio-Oil onto Rubber Particles in Asphalt. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 273, 123112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, J.; Yu, B.; Zhang, J.; Pei, J. Evaluation and Optimization of Asphalt Binder and Mixture Modified with High Activated Crumb Rubber Content. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 314, 125676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Jiang, W.; Xiao, J.; Yuan, D.; Wang, T.; Xing, C. Analysis of Thermal Susceptibility and Rheological Properties of Asphalt Binder Modified with Microwave Activated Crumb Rubber. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 377, 134488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Yang, X.; Shen, A.; Wu, H.; Wu, H.; Lyu, Z.; Li, B. Mechanical Properties and Reaction Mechanism of Microwave-Activated Crumb Rubber-Modified Asphalt before and after Thermal Aging. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 267, 120773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, M.; Hosseinnezhad, S.; Kabir, S.F.; Burnett, D.J.; Fini, E.H. Reaction Pathways for Surface Activated Rubber Particles. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 149, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Xu, G.; Chen, X.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, H. Evaluation of Aging Resistance for High-Performance Crumb Tire Rubber Compound Modified Asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 218, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Gao, Y.; Yan, K.; You, L.; Jia, Y.; Dai, X.; Chen, M.; Diab, A. Effect of Long-Term Aging on Waste Tire Rubber and Amorphous Poly Alpha Olefin Compound Modified Asphalt Binder and Its Mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 272, 121667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, N.; Peng, X.; He, Y.; Lei, W.; Pu, C.; Meng, H.; Ma, H.; Tan, L.; Zhao, P. Investigation on Performance and Durability of Bone Glue and Crumb Rubber Compound Modified Asphalt and Its Mixture. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 19, e02437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Ge, D.; Lv, S.; Duan, D.; Deng, Y. Evaluation of Asphalt Modified with Bio-Oil and High Rubber Content: Low Temperature and Short Mixing Time Production Condition. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 408, 133656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Fan, W.; Liang, M.; He, Y.; Ren, S.; Lv, X.; Nan, G.; Luo, H. Rheological Properties, Storage Stability and Morphology of CR/SBS Composite Modified Asphalt by High-Cured Method. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 193, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Choudhary, R. Effect of Microwave Pretreatment on Characteristics of Asphalt Binders Modified with Scrap Non-Tire Automotive Rubber and Waste Derived Pyrolytic Oils After Prolonged Thermal Storage. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 419, 135558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, R.; Song, P.; Wang, S. Thermal Analysis on the Interactions Among Asphalt Modified with SBS and Different Degraded Tire Rubber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 182, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JTG E20-2011; Standard Test Methods of Bitumen and Bituminous Mixtures for Highway Engineering. Ministry of Transport: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Xu, O.; Rangaraju, P.R.; Wang, S.; Xiao, F. Comparison of Rheological Properties and Hot Storage Characteristics of Asphalt Binders Modified with Devulcanized Ground Tire Rubber and Other Modifiers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 154, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wu, S.; Xie, J.; Yang, C.; Yang, X.; Wang, F.; Liu, Q. Utilization of High Contents Desulfurized Crumb Rubber in Developing an Asphalt Rubber Pellets Modified Asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 402, 133043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, G.; Leng, Z.; Kong, P.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Qiu, W.; Xu, Z.; Chen, X. Investigation on Storage Stability and Rheological Properties of Environment-Friendly Devulcanized Rubber Modified Asphalt. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2022, 129, 103332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AASHTO-T315; Standard Method of Test for Determining the Rheological Properties of Asphalt Binder Using a Dynamic Shear Rheometer (DSR). ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- AASHTO-T350-19; Standard Method of Test for Multiple Stress Creep Recovery(MSCR) Test of Asphalt Binder Using a Dynamic Shear Rheometer (DSR). ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2023.








| Pilot Projects | Unit | Test Values |
|---|---|---|
| Penetration (25 °C) | 0.1 mm | 71.6 |
| Softening point | °C | 49.6 |
| Ductility (25 °C) | cm | >100 |
| Ductility (5 °C) | cm | 5.6 |
| Sample Number | Dosage of Activated Rubber (%) | Dosage of SBS (%) |
|---|---|---|
| D10-S1 | 10 | 1.0 |
| D15-S1 | 15 | 1.0 |
| D20-S1 | 20 | 1.0 |
| D10-S1.5 | 10 | 1.5 |
| D15-S1.5 | 15 | 1.5 |
| D20-S1.5 | 20 | 1.5 |
| D10-S2 | 10 | 2.0 |
| D15-S2 | 15 | 2.0 |
| D20-S2 | 20 | 2.0 |
| Wavenumber (cm−1) | The Peak of a Telescope | Characterizing Component |
|---|---|---|
| 2922 | Alkane CH2 antisymmetric stretching peaks | saturate |
| 2852 | Alkane CH2 symmetric stretching peaks | saturate |
| 1597 | Aromatic C=C stretching peaks | aromatic |
| 1460 | Aliphatic CH3 asymmetric variant angles | aliphatic compound |
| 1377 | Aliphatic CH3 symmetry variant | aliphatic compound |
| Wavenumber (cm−1) | The Peak of a Telescope | Characterizing Component |
|---|---|---|
| 966 | trans-olefin CH peak | polybutadiene |
| 700 | cis-olefin CH peak | polystyrene |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, K.; Zhong, X.; Huang, X.; Wan, W.; Zhou, H.; Liu, B. Micromodification Mechanism and High-Temperature Rheological Properties of Activated Rubber/Styrene–Butadiene–Styrene Compound-Modified Asphalt. Materials 2025, 18, 2643. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112643
Zhang K, Zhong X, Huang X, Wan W, Zhou H, Liu B. Micromodification Mechanism and High-Temperature Rheological Properties of Activated Rubber/Styrene–Butadiene–Styrene Compound-Modified Asphalt. Materials. 2025; 18(11):2643. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112643
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Kai, Xuwen Zhong, Xukun Huang, Weihua Wan, Hai Zhou, and Bin Liu. 2025. "Micromodification Mechanism and High-Temperature Rheological Properties of Activated Rubber/Styrene–Butadiene–Styrene Compound-Modified Asphalt" Materials 18, no. 11: 2643. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112643
APA StyleZhang, K., Zhong, X., Huang, X., Wan, W., Zhou, H., & Liu, B. (2025). Micromodification Mechanism and High-Temperature Rheological Properties of Activated Rubber/Styrene–Butadiene–Styrene Compound-Modified Asphalt. Materials, 18(11), 2643. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112643






