The Effect of Waste Low-Density Polyethylene/Plasticizer Diisononyl Phthalate on the Performance of Asphalt Binder
Abstract
1. Introduction
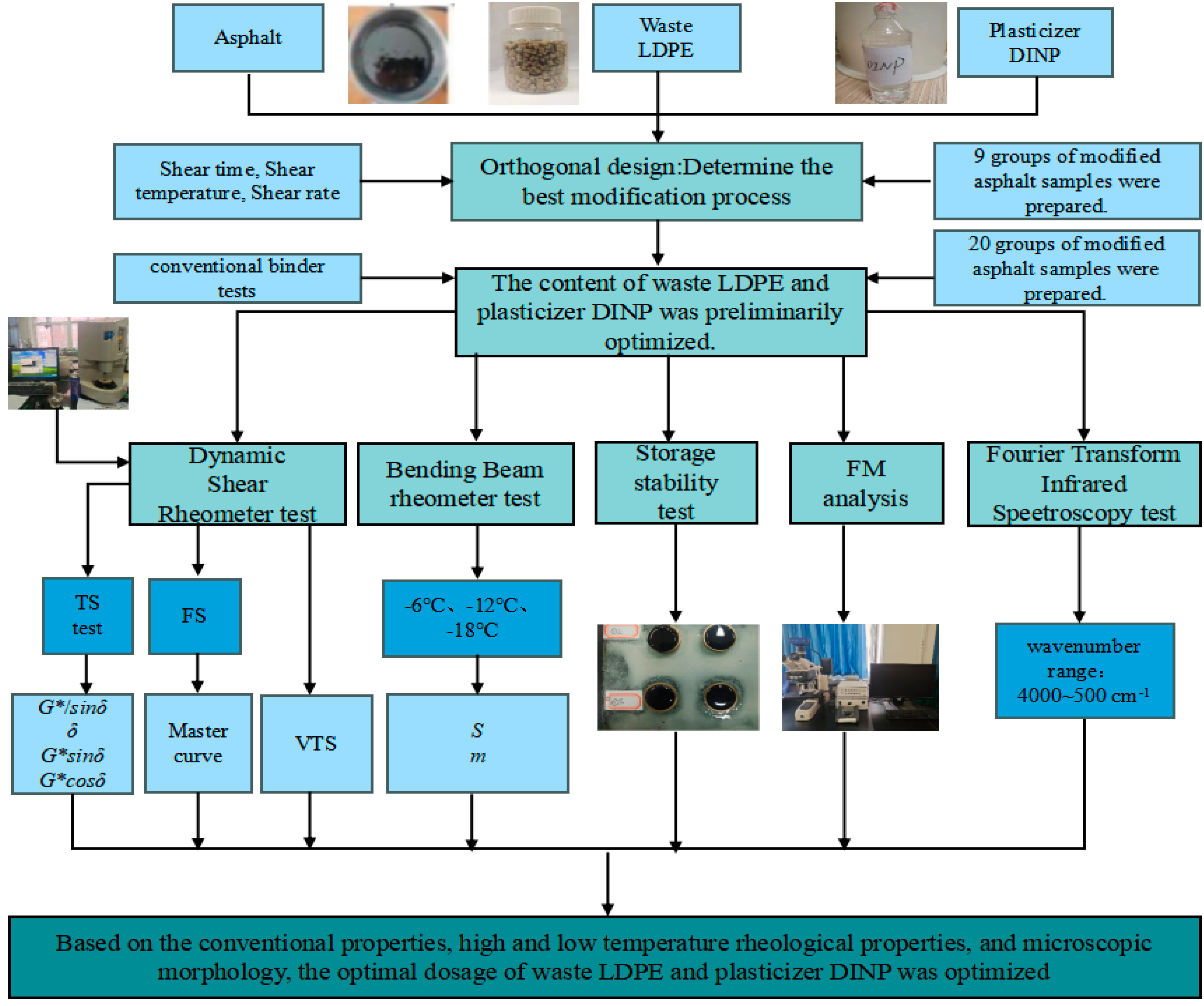
2. Materials and Sample Preparation
2.1. Asphalt
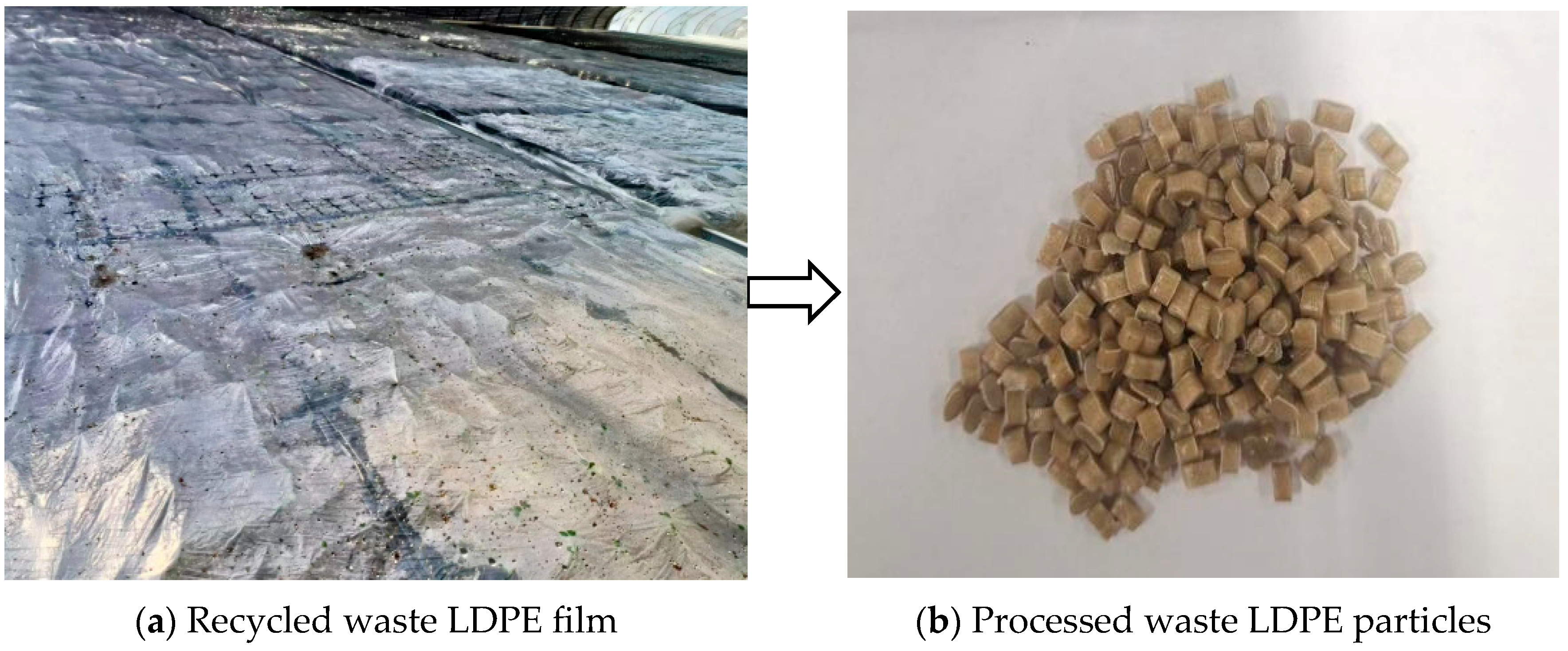
2.2. Waste LDPE
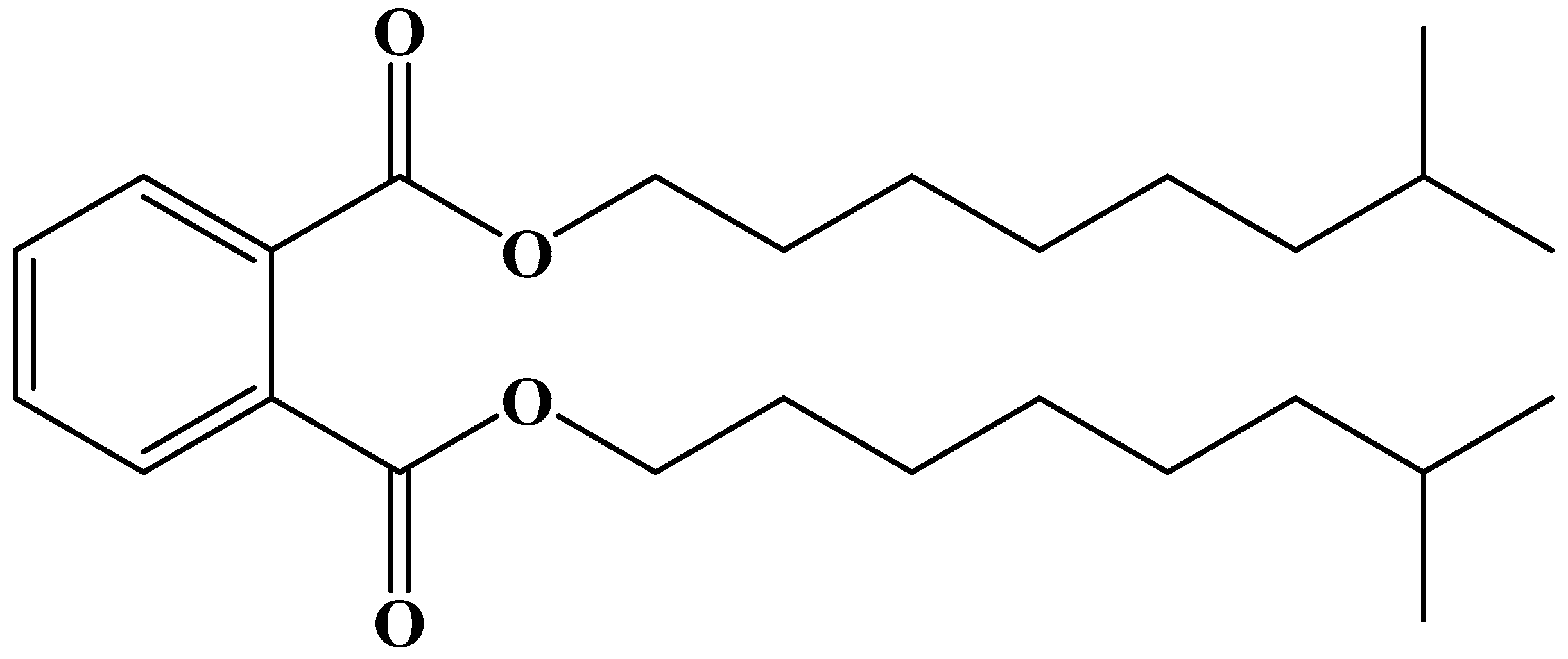
2.3. Plasticizer DINP
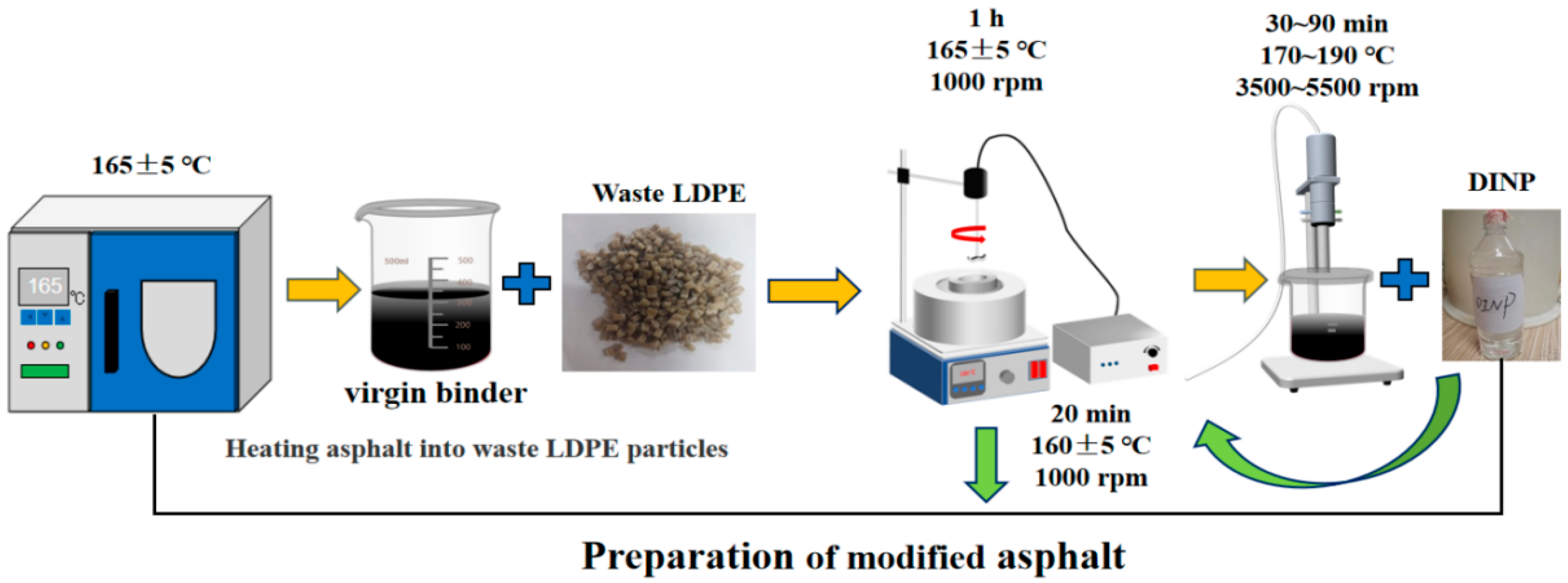
2.4. Sample Preparation
3. Test Methods
3.1. Orthogonal Experiment
3.2. Conventional Tests
3.3. Temperature Scanning Test
3.4. Viscosity-Temperature Susceptibility Test (VTS)
3.5. Frequency Sweep Test
3.6. Bending Beam Rheometer Test
3.7. Storage Stability Test
3.8. Fluorescence Microscopy (FM)
3.9. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Orthogonal Test Analysis
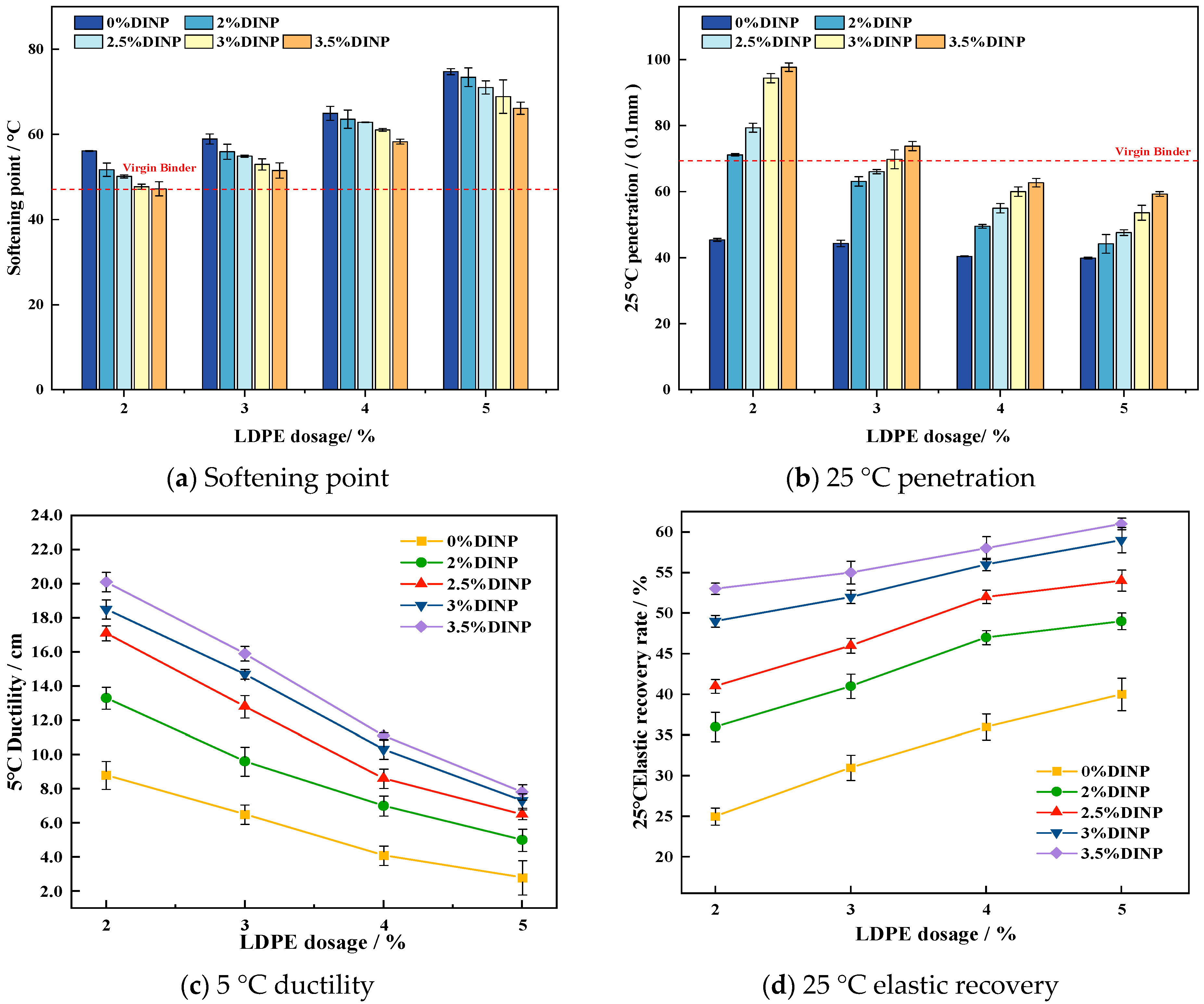
4.2. Conventional Physical Properties
4.3. Rheological Property Analysis
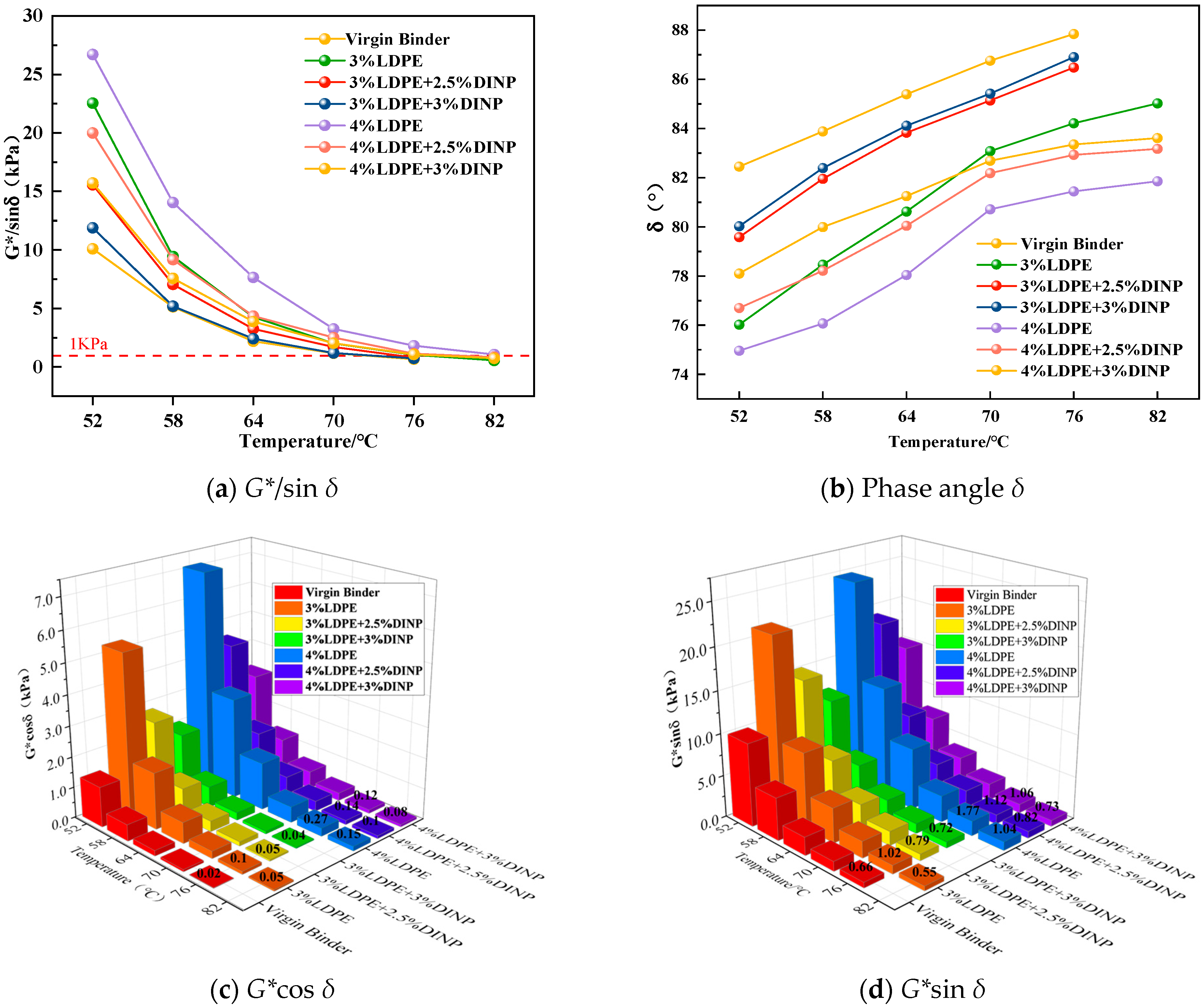
4.3.1. G*/sin δ, Phase Angle δ, G*sin δ and G*cos δ
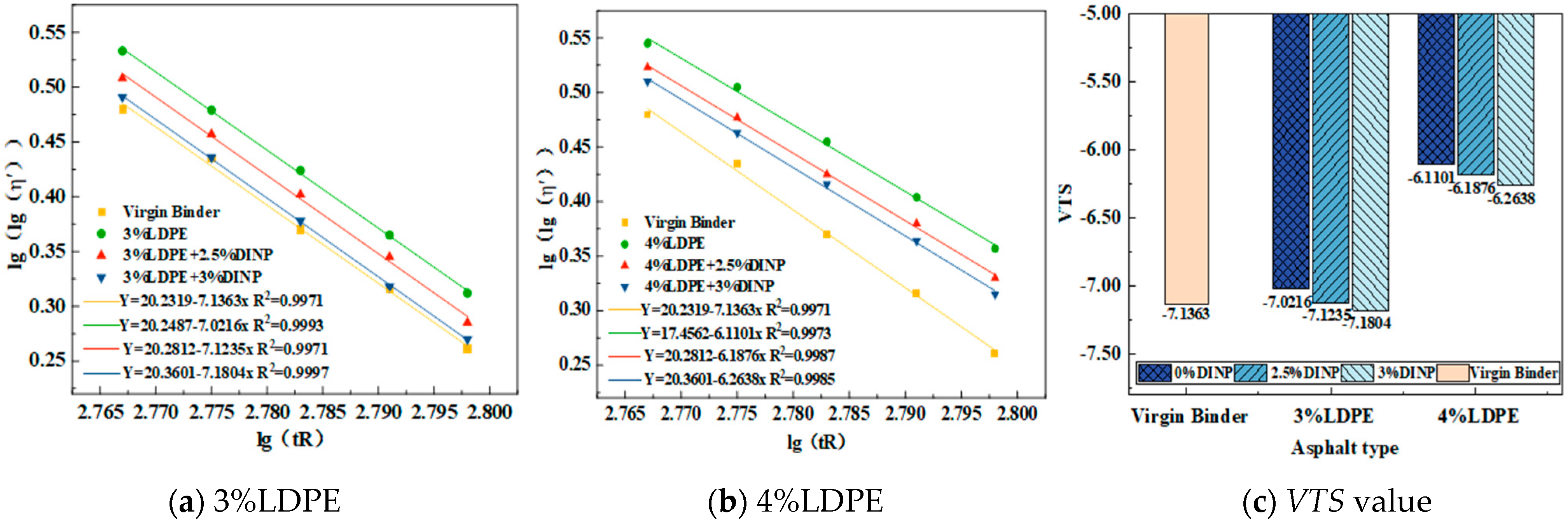
4.3.2. VTS Analysis
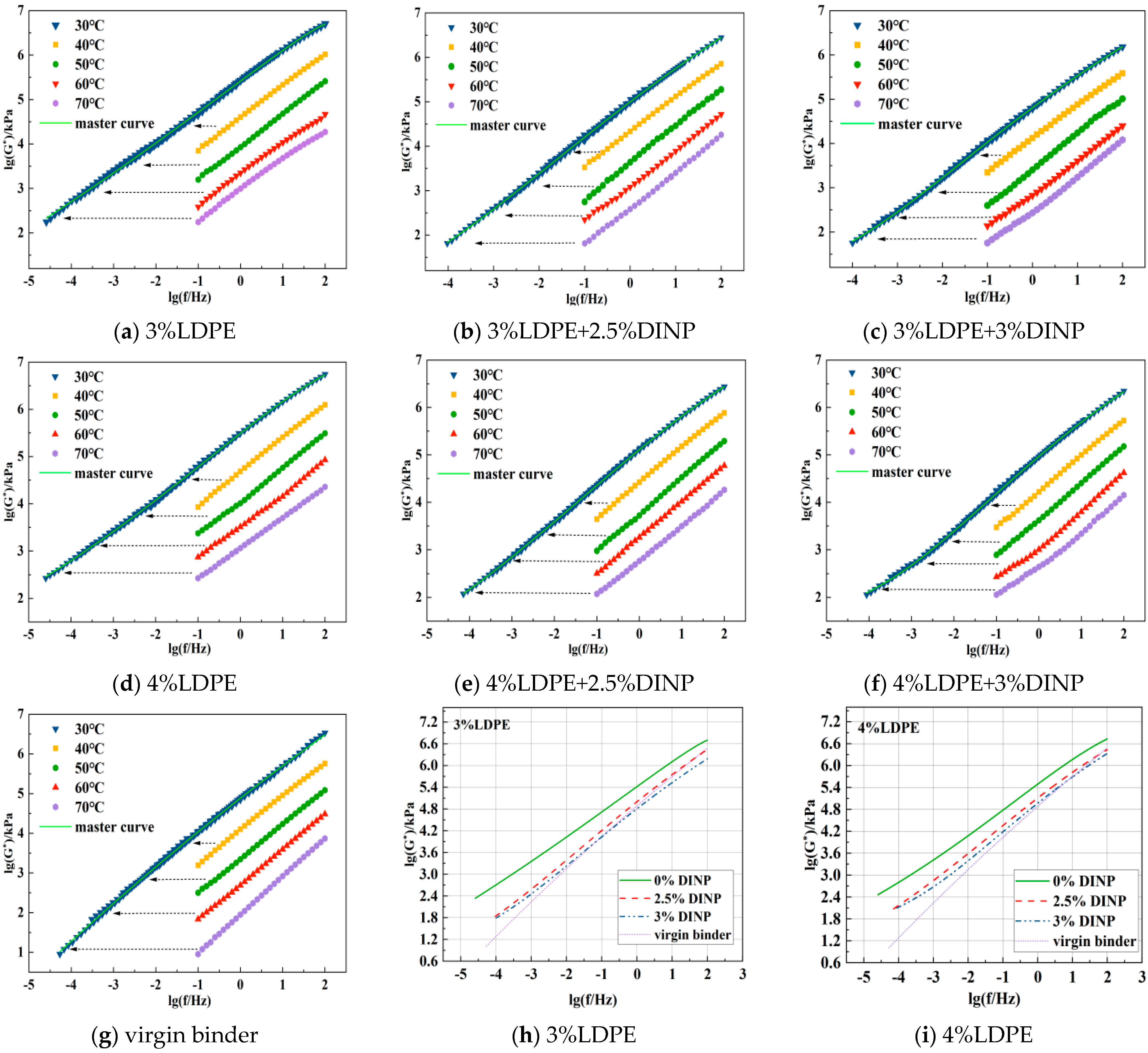
4.3.3. Analysis of the Frequency Sweep Test Results
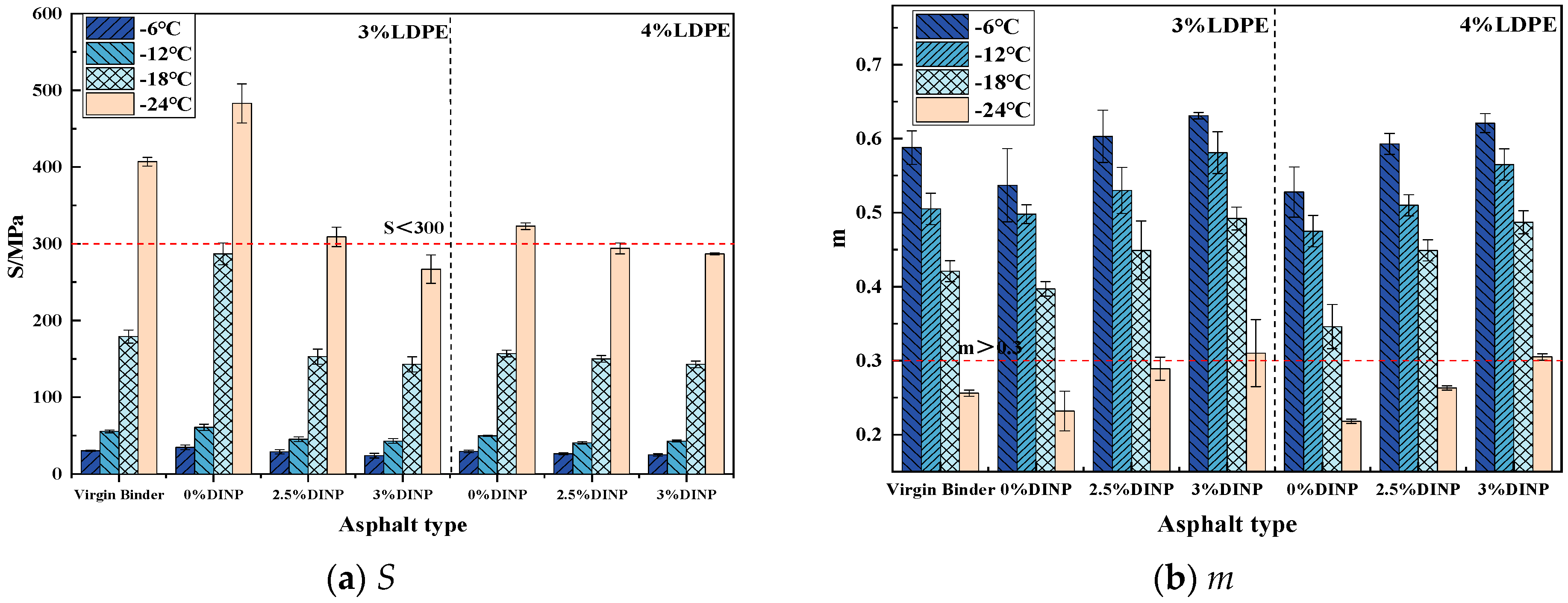
4.3.4. BBR Results Analysis
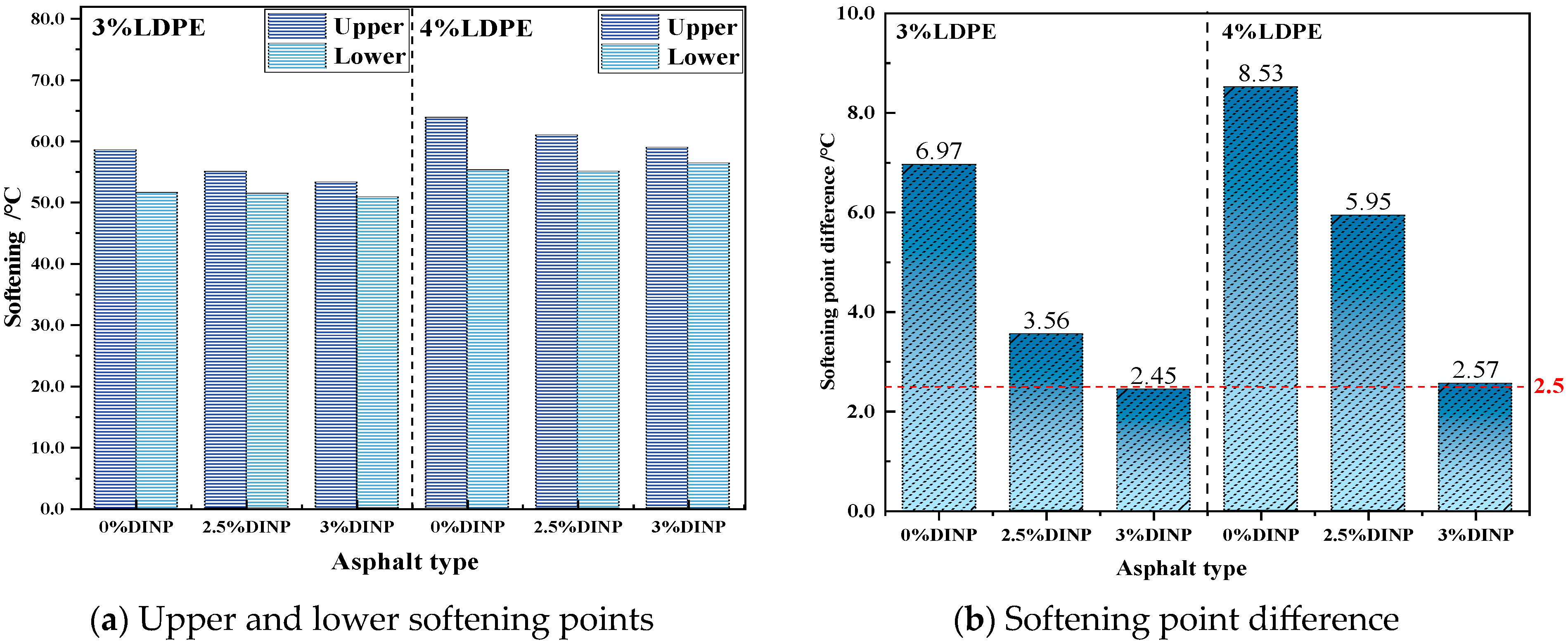
4.4. Storage Stability Results Analysis
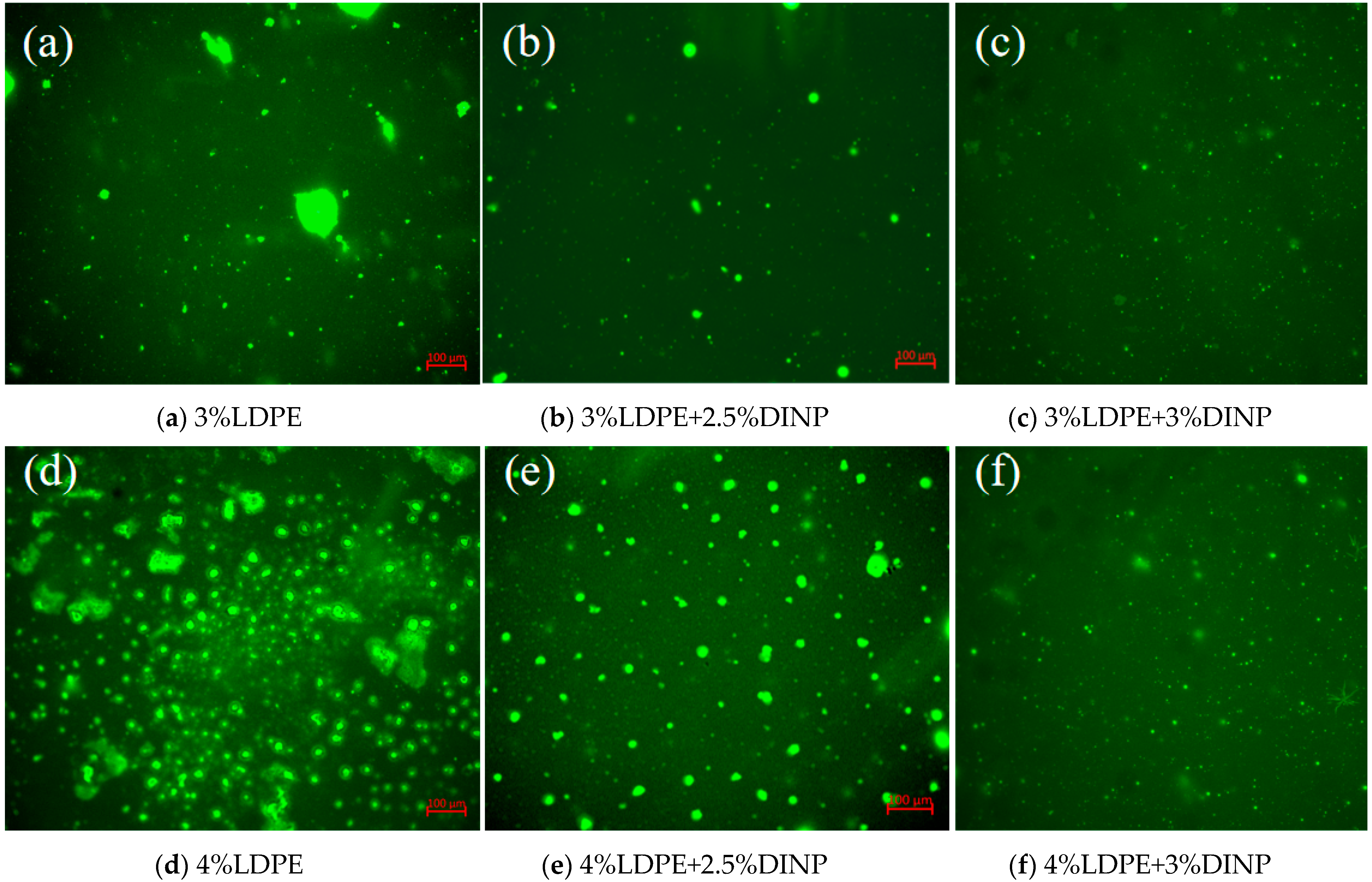
4.5. FM Results Analysis
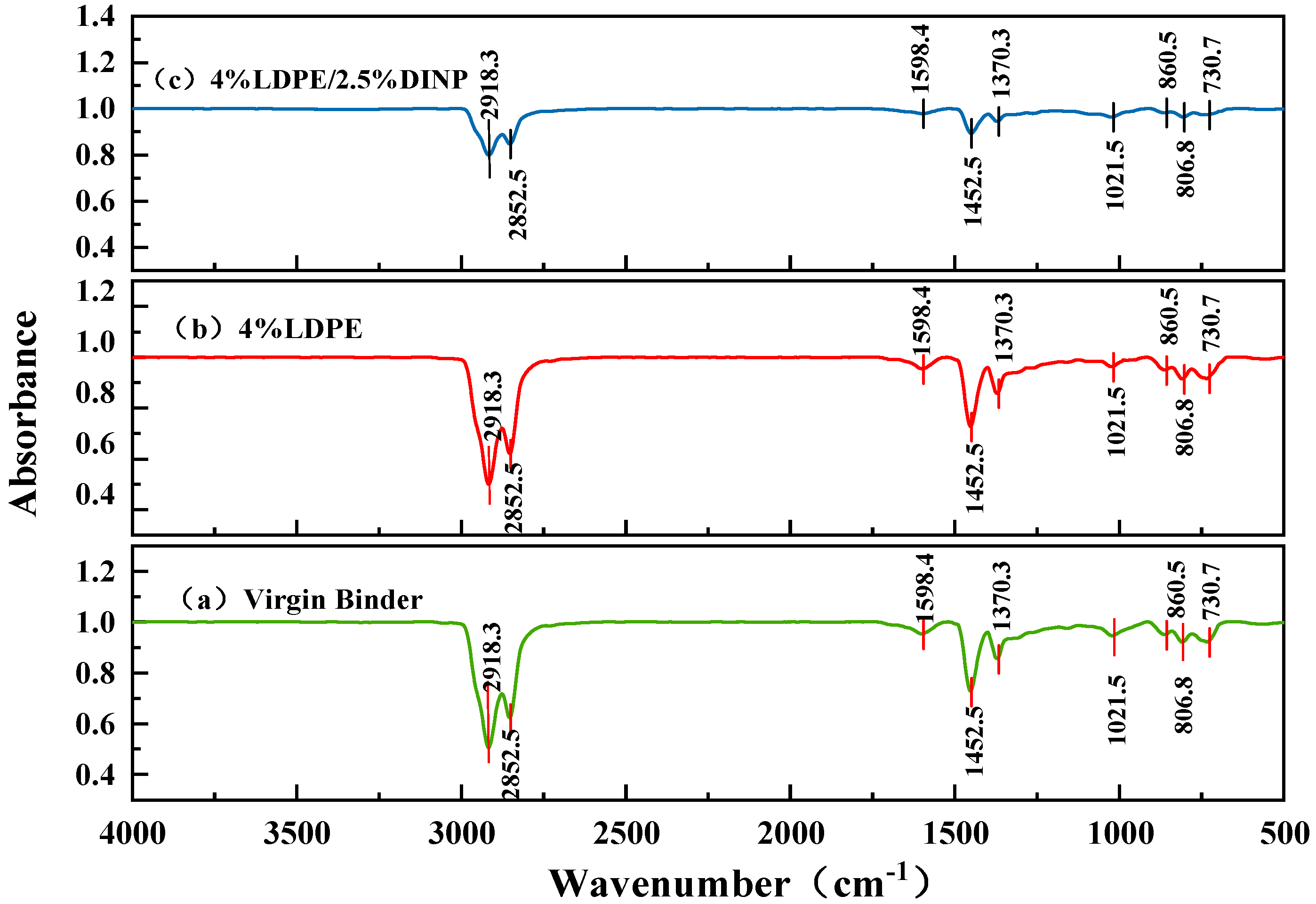
4.6. FTIR Results Analysis
5. Conclusions
- Temperature scanning tests and frequency scanning master curve analysis indicated that the waste LDPE/plasticizer DINP-modified asphalt had increasing high-temperature resistance as the dosage of waste LDPE increased. The low-temperature properties of the asphalt improved when the content of plasticizer DINP exceeded 2.5%;
- The BBR test results indicated that the addition of 3% plasticizer DINP can increase the resistance of waste LDPE/plasticizer DINP-modified asphalt to low-temperature cracking;
- Storage stability and fluorescence microscopy tests indicated that the addition of 2.5% and 3% plasticizer DINP significantly improved the storage stability of waste LDPE/plasticizer DINP-modified asphalt;
- When the dosage of waste LDPE was 4% and the dosage of plasticizer DINP was 2.5%, the rheological and storage stability properties of the asphalt binder clearly improved.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elnaml, I.; Liu, J.; Mohammad, L.; Dylla, H.; Wasiuddin, N.; Cooper, S.; Cooper, S. Recycling waste plastics in asphalt mixture: Engineering performance and environmental assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 453, 142180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Ge, M.Z.; Zhu, H.K.; Qing, L.Y.; Liu, S.X.; Chen, H.Y.; Li, Z.F. Impacts of plastic pollution on soil–plant properties and greenhouse gas emissions in wetlands: A meta-analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naga, A.I.; Ragab, M. Benefits of utilization the recycle polyethylene terephthalate waste plastic materials as a modifier to asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 219, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranowska, W.; Rzepna, M.; Ostrowski, P.; Lewandowska, H. Radiation and Radical Grafting Compatibilization of Polymers for Improved Bituminous Binders—A Review. Materials 2024, 17, 1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julián, J.R.; Battista, N.; Adrián, O.; Rebollo, O.R.; Ignacio, Z.F.; Fensel, E.A.; Luis, D.H.; Martínez, A.H. Cold mix asphalt with polymeric stone for low traffic volume roads. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 401, 132714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.P.; Xue, C.Y.; Hao, G.R.; Huang, W.D.; Zhu, H.Z.; Li, R. Sustainable production of eco-friendly rubberized asphalt binders through chemically crosslinking with polymer modifier. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 422, 138633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, U.; Javed, M.F. Optimizing plastic waste inclusion in paver blocks: Balancing performance, environmental impact, and cost through LCA and economic analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 478, 143901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.; Church, R.; Klassen, K.; Law, B.; MacLeod, D.; Zanzotto, L. Study of recycled polyethylene materials as asphalt modifiers. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2006, 33, 968–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Jing, H.; Luo, C.; Luo, C.; Li, M.; Deng, J.; Yan, L. Modification of epoxy asphalt by low-doping PE—GMA and PE—MAH. J. Appl. Polym. 2023, 141, e55143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, L.C.; Mivehchi, M.; Wen, H. Towards a use of waste polyethylene in asphalt mixture as a compaction aid. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 440, 140989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasim, N.; Mohammad, M.S.; Vivek. Study on optimal preparation and rheological characteristics of waste low density polyethylene (LDPE)/styrene butadiene styrene (SBS) composite modified asphalt binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 407, 133459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin, A.; Hasan, T. Investigating the properties of asphalt binder modified by high- and low-density polyethylene polymer and nano-silica. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2024, 25, 838–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedy, H.; Sofyan, M.S.; Yaminc, R.A.; Sri, A. Utilization of LDPE plastic waste on the quality of pyrolysis oil as an asphalt solvent alternative. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2021, 23, 100872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, G.; Bakht, Z.; Muhammad, B.T.; Mahmood, A.; Sabri, M.M.; Suraparb, K. Comprehensive Study on the Performance of Waste HDPE and LDPE Modified Asphalt Binders for Construction of Asphalt Pavements Application. Polymers 2022, 14, 3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlotte, A.; Yuqing, Z.; Jiawei, W.; Yang, Y.; Ignacio, A.; Bob, A. Pyrolysis of polyolefin plastic waste and potential applications in asphalt road construction: A technical review. Resour. Conserv. Recy. 2022, 180, 106213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelo, F.; Satyavati, K.; Lakshmi, R.K.; Anand, S.; Amit, B.; Eyad, M. A comprehensive evaluation of mixture and binder properties to explore the use of low-density polyethylene (LDPE) as an asphalt modifier and co-modifier. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2023, 24, 2120988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghrafy, Y.M.; Sayed, M.A.A.E.; Sherif, M.E.B. Rheological properties and aging performance of sulfur extended asphalt modified with recycled polyethylene waste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 273, 121771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birlie, G.M.; Bantie, S.Z.; Lemessa, J.A. Investigation and optimization of waste LDPE plastic as a modifier of asphalt mix for highway asphalt: Case of Ethiopian roads. Case Stud. Chem Environ. Eng. 2021, 4, 100150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalhat, M.A.; Wahhab, H.I.A.A. Performance of recycled plastic waste modified asphalt binder in Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2015, 18, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, L.; Xue, X.; Fan, W.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, H.; Yao, Z. Comparison of rheological properties and compatibility of asphalt modified with various polyethylene. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2019, 22, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhou, B.S.; Peng, A.; Xuan, W.; Li, W. Analysis of the performance and mechanism of desulfurized rubber and low-density polyethylene compound-modified asphalt. J. Appl. Polym. 2019, 136, 48194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celauro, C.; Bosurgi, G.; Sollazzo, G.; Ranieri, M. Laboratory and in-situ tests for estimating improvements in asphalt concrete with the addition of an LDPE and EVA polymeric compound. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 196, 714–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhe, H.; Yan, K.; Wang, M.; You, L.; Ge, D. Low-density polyethylene/ethylene–vinyl acetate compound modified asphalt: Optimal preparation process and high-temperature rheological properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 314, 125688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.P.; Ren, S.S.; Qiu, Y.J. Balancing the sustainable component of ethylene-vinyl acetate for achieved better compatibility improvement of wax-based warm mix additives in bitumen. Colloid. Surface A 2023, 675, 132054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Feng, M.; Zhen, F.; Dai, J.; Wen, Y.; Shi, K. Using Cereclor plasticizer to modify the virgin asphalt binder: A case of rheological properties improvement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 318, 126039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.K.; Zhang, H.T.; Gu, Y.; Gao, M.; Shan, Z. Rheological properties of composite DTDM/DOP/SBS modified asphalt and its effect on high and low temperature performance. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 18, e02031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.L.; Tian, W.W.; Li, Y.L.; Zhu, J.; Liao, M.; Xie, Y. Study on compatibility mechanism of plasticizer and asphalt based on molecular dynamics. Mater. Des. 2023, 228, 111827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.W.; Gao, Y.L.; Li, Y.L.; Zhu, J.; Zhan, M.; Wang, S. Molecular dynamics study on the effect of rheological performance of asphalt with different plasticizers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 400, 132791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, W.; Andrea, B.; Lily, P.; Kamilla, V.; Rafiq, M.K.; Gaspare, G.; Emiliano, P.; Laurent, P.; Marjan, T.; Chiara, R.; et al. Rheological properties of asphalt binder modified with waste polyethylene: An interlaboratory research from the RILEM TC WMR. RCR Adv. 2022, 186, 106564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basheet, H.B.; Latief, H.R. Asphalt Binder Modification with High-Density Polyethylene Polymer and Low-Density Polyethylene Polymer-Efficiency of Conducting Semi-Wet Mixing Process. J. Ecol. Eng. 2024, 25, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Su, Q.; Yang, X.; Lin, S.; Wang, H.; Hou, R.; Cao, D. Research on the Performance and Application of High-Performance PE Composite Modified Asphalt. Polymers 2025, 17, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akkenzheyeva, A.; Haritonovs, V.; Bussurmanova, A.; Meri, R.M.; Imanbayev, Y.; Serikbayeva, A.; Sydykov, S.; Ayapbergenov, Y.; Jankauskas, M.; Trumpels, A.; et al. The Use of Rubber-Polymer Composites in Bitumen Modification for the Disposal of Rubber and Polymer Waste. Polymers 2024, 16, 3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D5/D5M-20; Standard Test Method for Penetration of Bituminous Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- ASTM D36/D36M-1 4(2020) e1; Standard Test Method for Softening Point of Bitumen (Ring-and-Ball Apparatus). ASTM International: Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- ASTM D113/D113M-17; Standard Test Method for Ductility of Bituminous Materials. ASTM International: Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- Hay, A. CPC bans di-isononyl phthalate in toys, care items. ICIS Chem. Bus. 2017, 292, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.H.; Xia, T.; Zhao, L.; Bo, Y.; Yang, M. Correlation between phase separation and rheological behavior in bitumen/SBS/PE blends. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 41713–41721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Xia, S.; Xu, J.; Zhang, A.; Li, Y. Influence of shearing process on the property and microstructure of bitumen modified by polyethylene and ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer. Mater. Struct. 2023, 56, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haibin, L.; Lichang, Z.; Jianmei, S.; Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Hu, Y.; Abdulakeem, T.A. Analysis of the Influence of Production Method, Plastic Content on the Basic Performance of Waste Plastic Modified Asphalt. Polymers 2022, 14, 4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Yi, J.; Feng, D.; Kasbergen, C.; Scarpas, A.; Zhu, Y. Preparation of bio-bitumen by bio-oil based on free radical polymerization and production process optimization. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 189, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.Q.; Qiao, X.T.; Yu, R.E.; Xin, Y.; Liu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Xia, R. Influence of modification process parameters on the properties of crumb rubber/EVA modified asphalt. J. Appl. Polym. 2016, 133, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richmond, C.; Adey, B.T. A-VTS model of bitumen viscosity transformed and made continuous across families of grades. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2021, 22, 664–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, O.R.; Lytton, L.R.; Chang, K.G. Method to Predict Temperature Susceptibility of an Asphalt Binder. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2002, 14, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AASHTO T315-23; Standard Method of Test for Determining the Rheological Properties of Asphalt Binder Using a Dynamic Shear Rheometer (DSR). AASHTO: Washington, DC, USA, 2023.
- Cuciniello, G.; Leandri, P.; Polacco, G.; Airey, G.; Losa, M. Applicability of time-temperature superposition for laboratory-aged neat and SBS-modified bitumens. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 263, 120964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellinen, T.K.; Witczak, M.W.; Marasteanu, M.; Chehab, G.; Alavi, S.; Dongre, R. Stress dependent master curve construction for dynamic (complex)modulus. J. Assoc. Asphalt. Paving Technol. 2002, 71, 281–309. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Z.; Yan, K.Z.; Wang, M.; Ge, D.; Chen, J. Laboratory performance evaluation of waste tire rubber (WTR) and ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA)-modified asphalt mixtures. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2023, 24, 2224914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AASHTO. Determining the Flexural Creep Stiffness of Asphalt Binder Using the Bending Beam Rheometer (BBR) Method; American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
| Density (g/cm3) | Melt Flow Rate (g/10 min) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Softening Point (°C) | Elongation at Break (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.9244 | 1.83 | 1.83 | 95 | 620 |
| Levels | Factor | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| A Shear Time/min | B Shear Temperature/°C | C Shear Rate/(r/pm) | |
| 1 | 30 | 170 | 3500 |
| 2 | 60 | 180 | 4500 |
| 3 | 90 | 190 | 5500 |
| Test Number | Test Scheme | A | B | C | Softening Point/°C | Penetration (25 °C)/0.1 mm | Ductility (5 °C)/cm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A1B1C1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 57.7 | 62.5 | 6.7 |
| 2 | A1B2C2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 58.8 | 62.6 | 9.3 |
| 3 | A1B3C3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 59.2 | 62.3 | 12.3 |
| 4 | A2B2C3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 60.2 | 61.0 | 8.8 |
| 5 | A2B3C1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 57.8 | 59.5 | 6.0 |
| 6 | A2B1C2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 57.5 | 61.8 | 13.4 |
| 7 | A3B3C2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 59.0 | 62.1 | 7.5 |
| 8 | A3B1C3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 56.2 | 59.8 | 7.9 |
| 9 | A3B2C1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 57.9 | 62.3 | 6.6 |
| Indicator | Factor | A | B | C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Softening point/°C | K1 | 175.7 | 171.4 | 173.4 |
| K2 | 175.5 | 176.9 | 175.4 | |
| K3 | 173.1 | 176.0 | 175.5 | |
| k1 | 58.55 | 57.12 | 57.80 | |
| k2 | 58.51 | 58.98 | 58.45 | |
| k3 | 57.70 | 58.66 | 58.51 | |
| R | 0.85 | 1.86 | 0.71 | |
| Ranking of factors | RB > RA > RC | |||
| Optimal blending parameter | A1B2C3 |
| Indicator | Factor | A | B | C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration/0.1 mm | K1 | 187.37 | 184.1 | 184.3 |
| K2 | 182.31 | 185.9 | 186.5 | |
| K3 | 184.21 | 183.9 | 183.1 | |
| k1 | 62.46 | 61.37 | 61.44 | |
| k2 | 60.77 | 61.97 | 62.17 | |
| k3 | 61.40 | 61.29 | 61.02 | |
| R | 1.69 | 0.68 | 1.15 | |
| Ranking of factors | RA > RC > RB | |||
| Optimal blending parameter | A1B2C2 |
| Indicator | Factor | A | B | C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ductility/cm | K1 | 28.30 | 28.00 | 19.30 |
| K2 | 28.20 | 24.70 | 30.20 | |
| K3 | 22.00 | 25.80 | 29.00 | |
| k1 | 9.43 | 9.33 | 6.43 | |
| k2 | 9.40 | 8.23 | 10.07 | |
| k3 | 7.33 | 8.60 | 9.67 | |
| R | 2.10 | 1.10 | 3.63 | |
| Ranking of factors | RC > RA > RB | |||
| Optimal blending parameter | A1B1C2 |
| Type of Asphalt | δ | α | λ | β | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| virgin binder | 7.121 | −9.926 | 0.323 | 0.431 | 0.9996 |
| 3%LDPE | 10.276 | −11.386 | 0.287 | 0.428 | 0.9993 |
| 3%LDPE + 2.5%DINP | 8.165 | −9.181 | 0.349 | 0.458 | 0.9995 |
| 3%LDPE + 3%DINP | 7.901 | −7.292 | 0.397 | 0.439 | 0.9998 |
| 4%LDPE | 12.125 | −15.253 | 0.451 | 0.529 | 0.9991 |
| 4%LDPE + 2.5%DINP | 9.155 | −8.772 | 0.324 | 0.381 | 0.9992 |
| 4%LDPE + 3%DINP | 8.424 | −9.403 | 0.286 | 0.370 | 0.9996 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, P.; Shao, X.; Wang, K.; Jia, H.; Chen, L. The Effect of Waste Low-Density Polyethylene/Plasticizer Diisononyl Phthalate on the Performance of Asphalt Binder. Materials 2025, 18, 2580. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112580
Hu P, Shao X, Wang K, Jia H, Chen L. The Effect of Waste Low-Density Polyethylene/Plasticizer Diisononyl Phthalate on the Performance of Asphalt Binder. Materials. 2025; 18(11):2580. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112580
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Peng, Xiao Shao, Kun Wang, Haichuan Jia, and Long Chen. 2025. "The Effect of Waste Low-Density Polyethylene/Plasticizer Diisononyl Phthalate on the Performance of Asphalt Binder" Materials 18, no. 11: 2580. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112580
APA StyleHu, P., Shao, X., Wang, K., Jia, H., & Chen, L. (2025). The Effect of Waste Low-Density Polyethylene/Plasticizer Diisononyl Phthalate on the Performance of Asphalt Binder. Materials, 18(11), 2580. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112580






