Co-Intercalation of Sericite by Cationic and Anionic Surfactants and the Mechanical Properties of Sericite/Epoxy Resin Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. The Intercalation Process of Sericite by Anionic–Cationic Surfactants CTAB and SDS
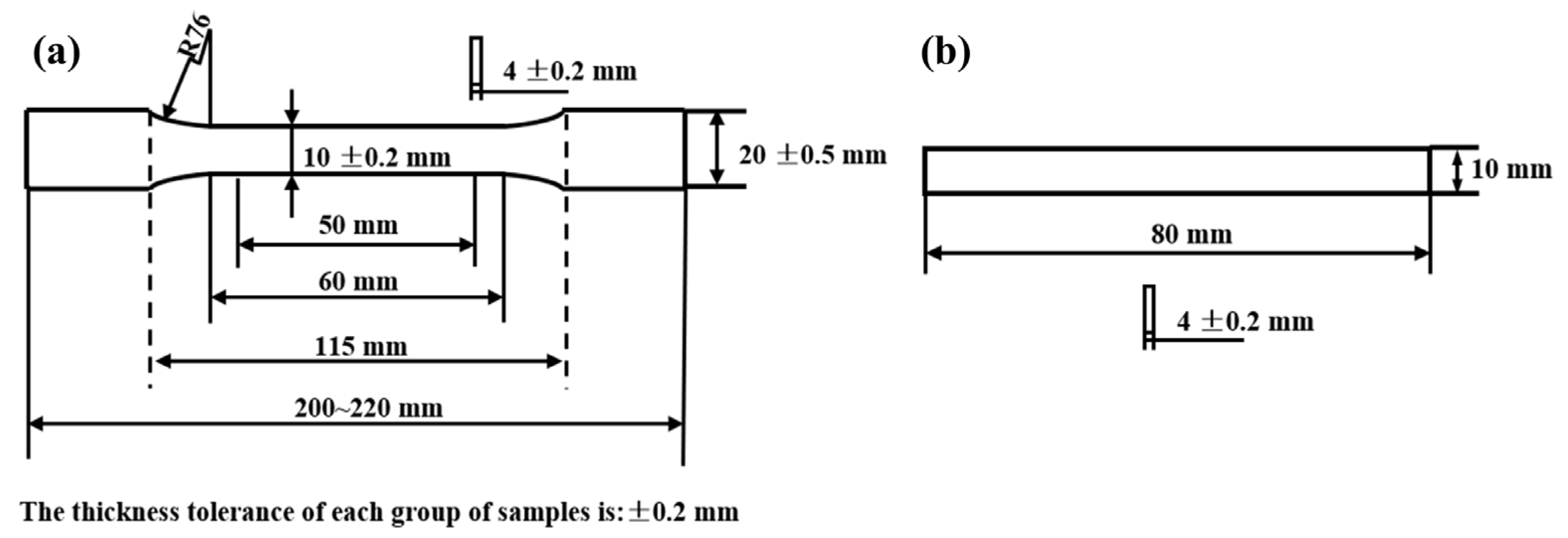
2.3. The Preparation Process of Sericite/Epoxy Composites
2.4. Characterization Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Effects of Co-Intercalation Conditions
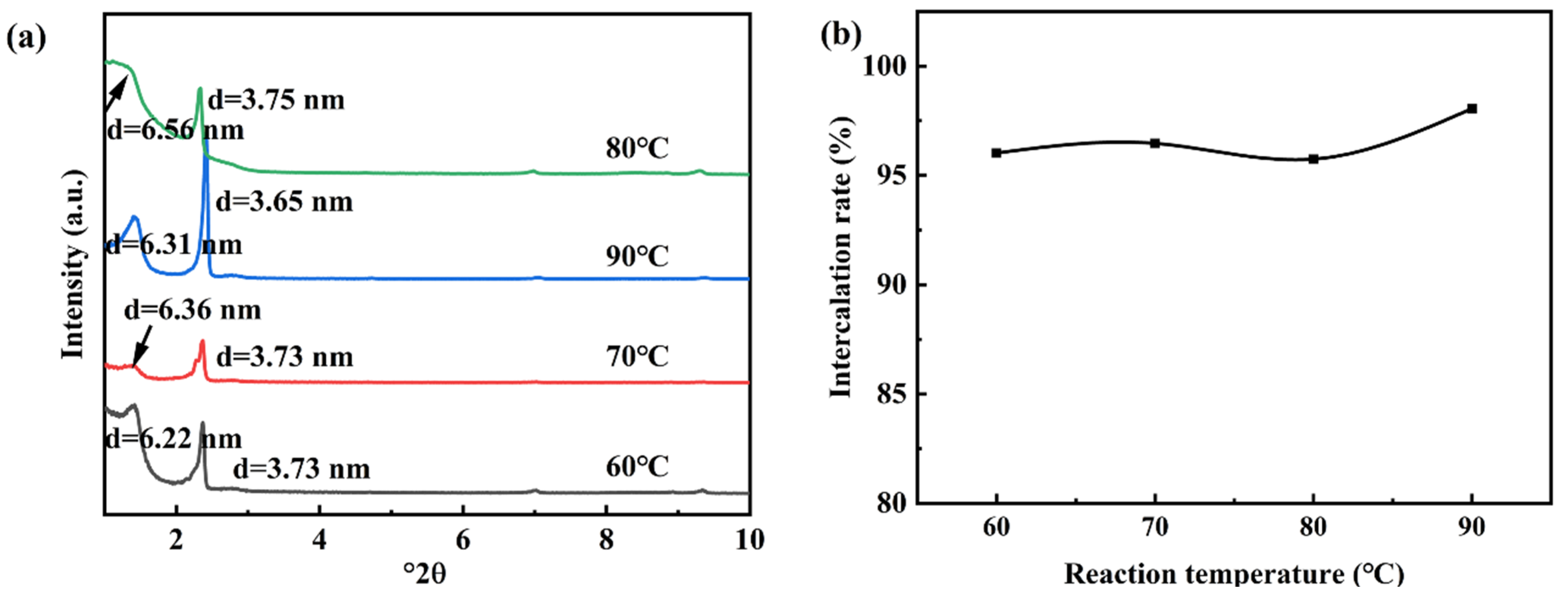
3.1.1. The Effects of Co-Intercalation Temperature
3.1.2. The Effects of Co-Intercalation Time
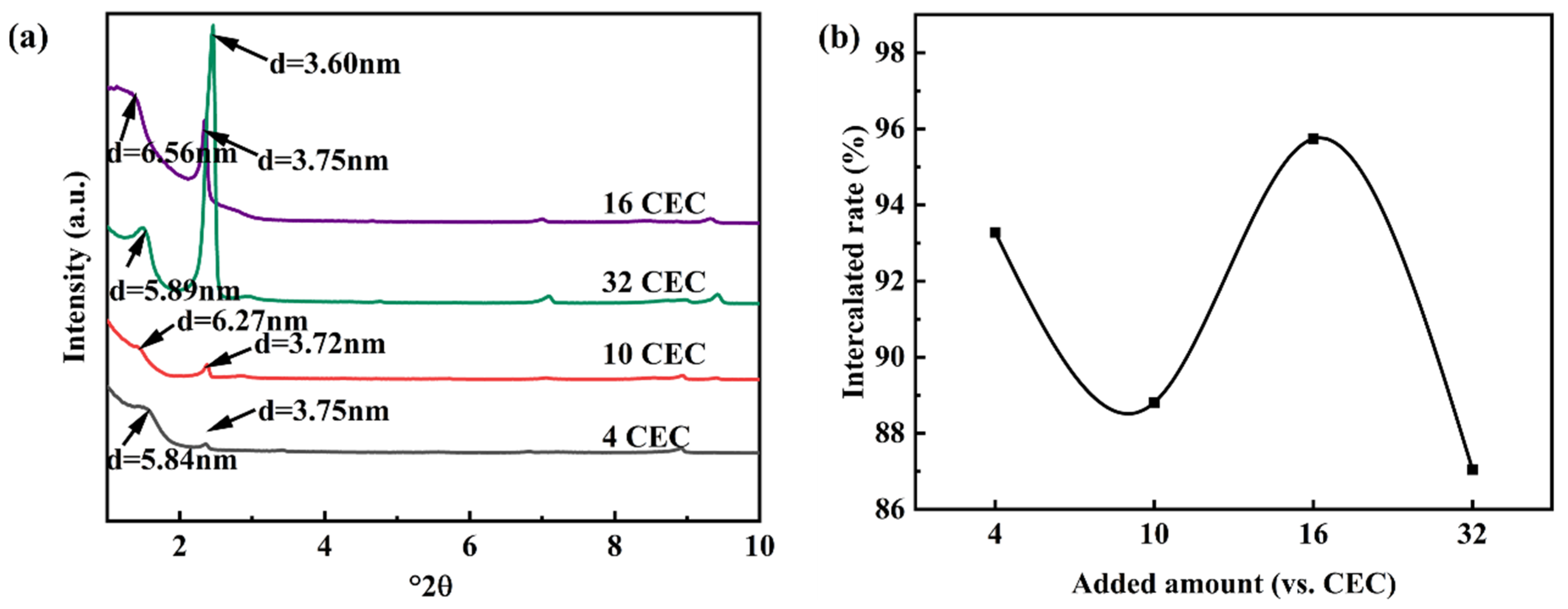
3.1.3. The Effects of Co-Intercalation Agent Dosage
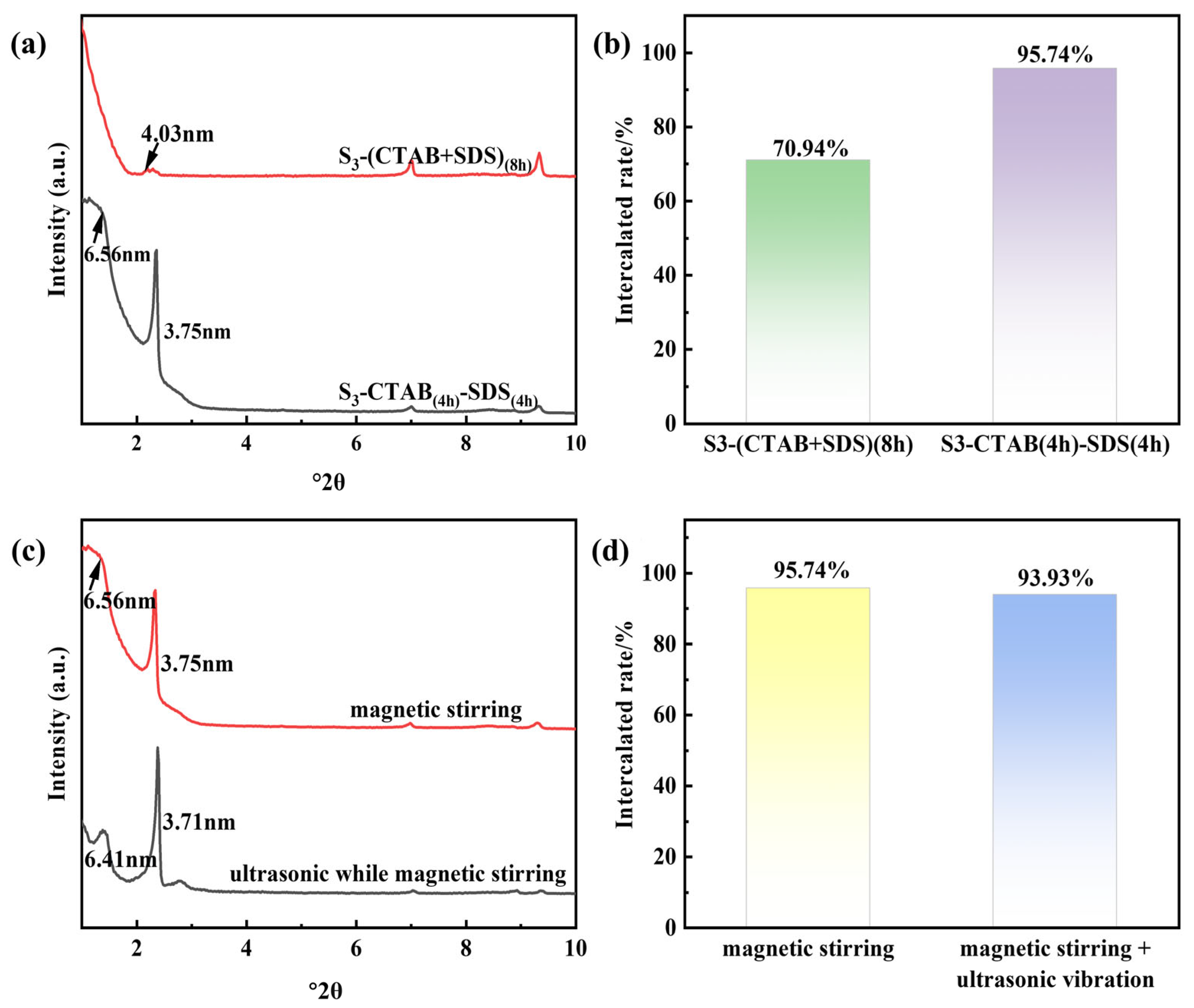
3.1.4. The Effects of Various Feeding Sequences and Mixing Methods
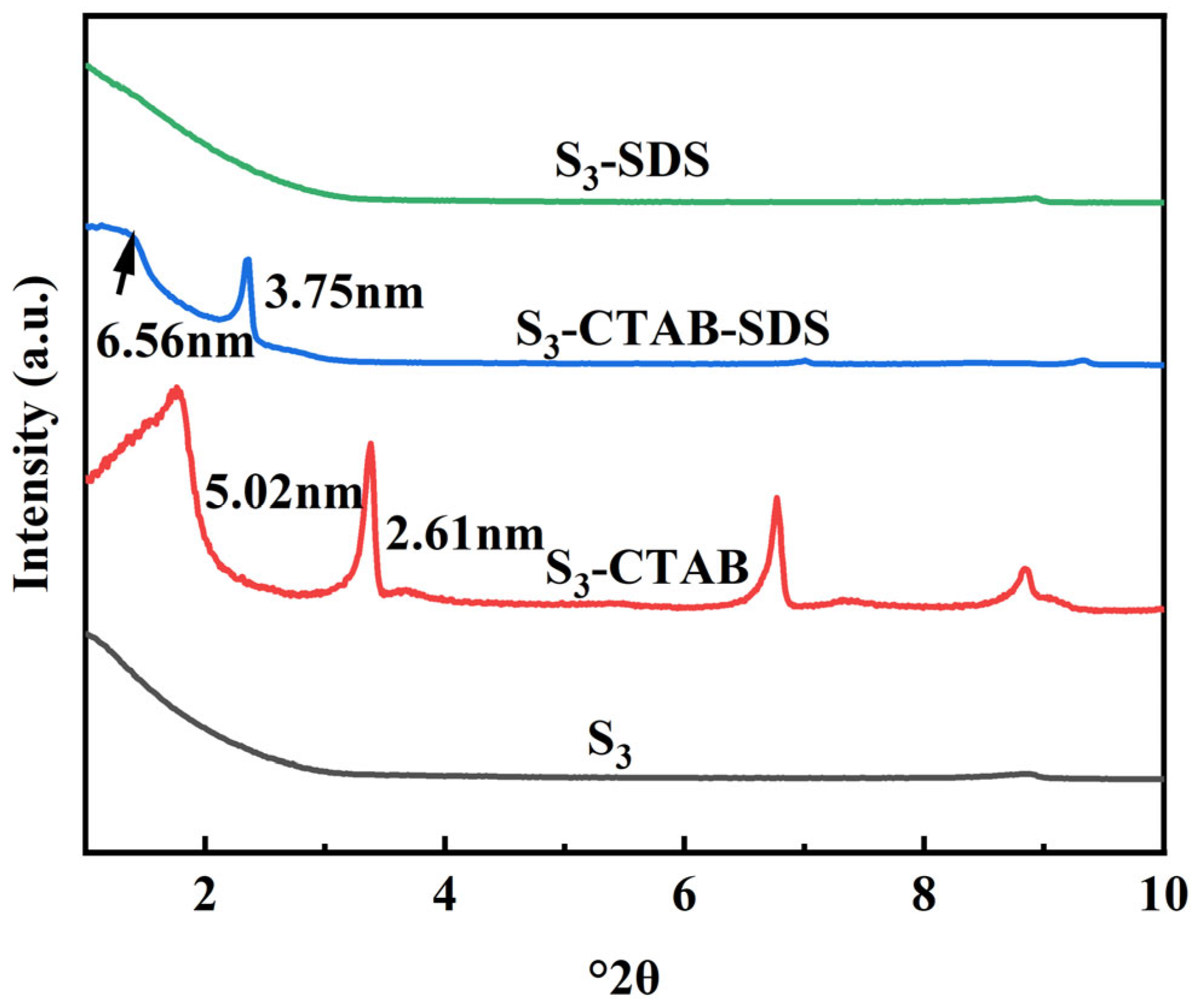
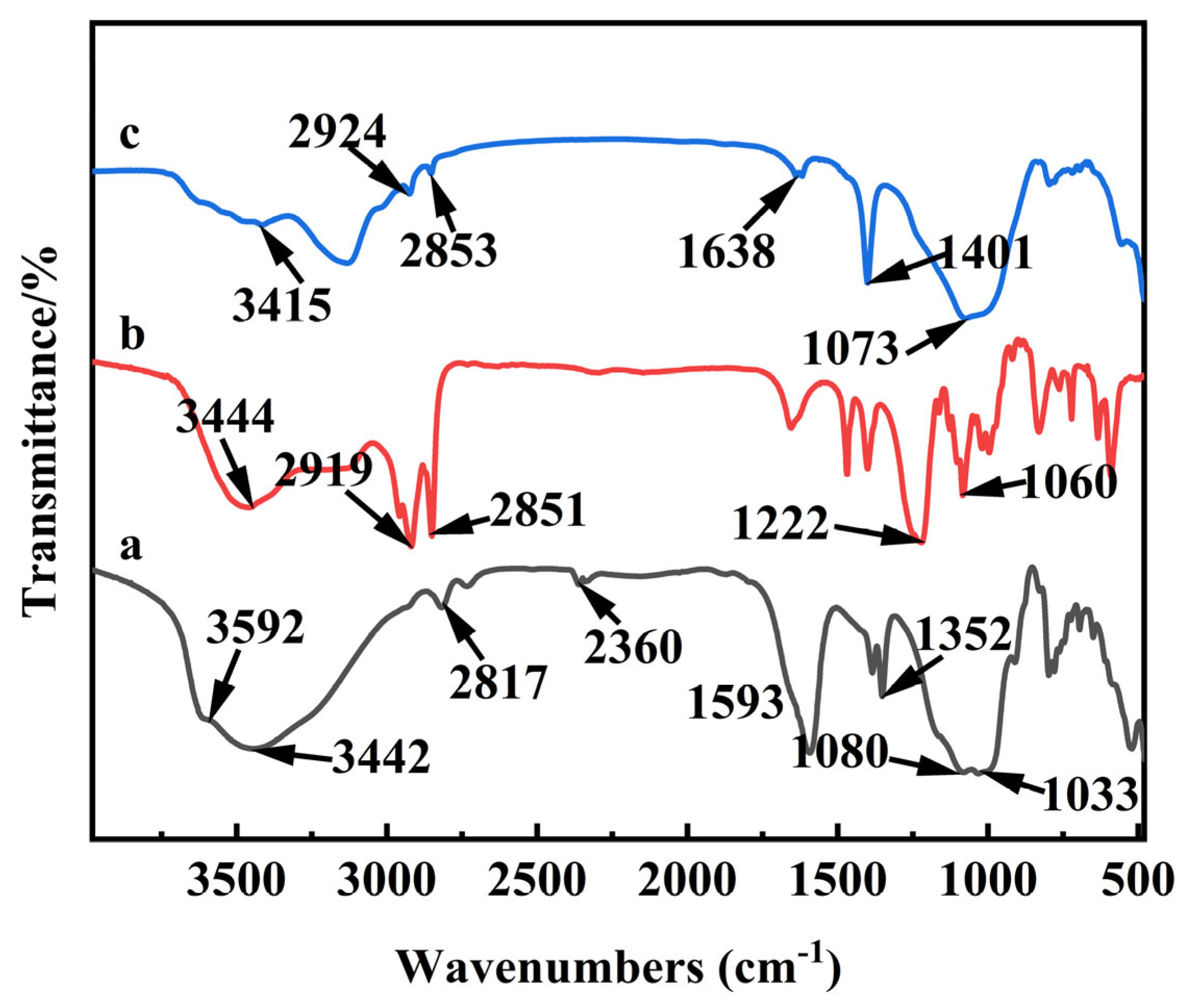
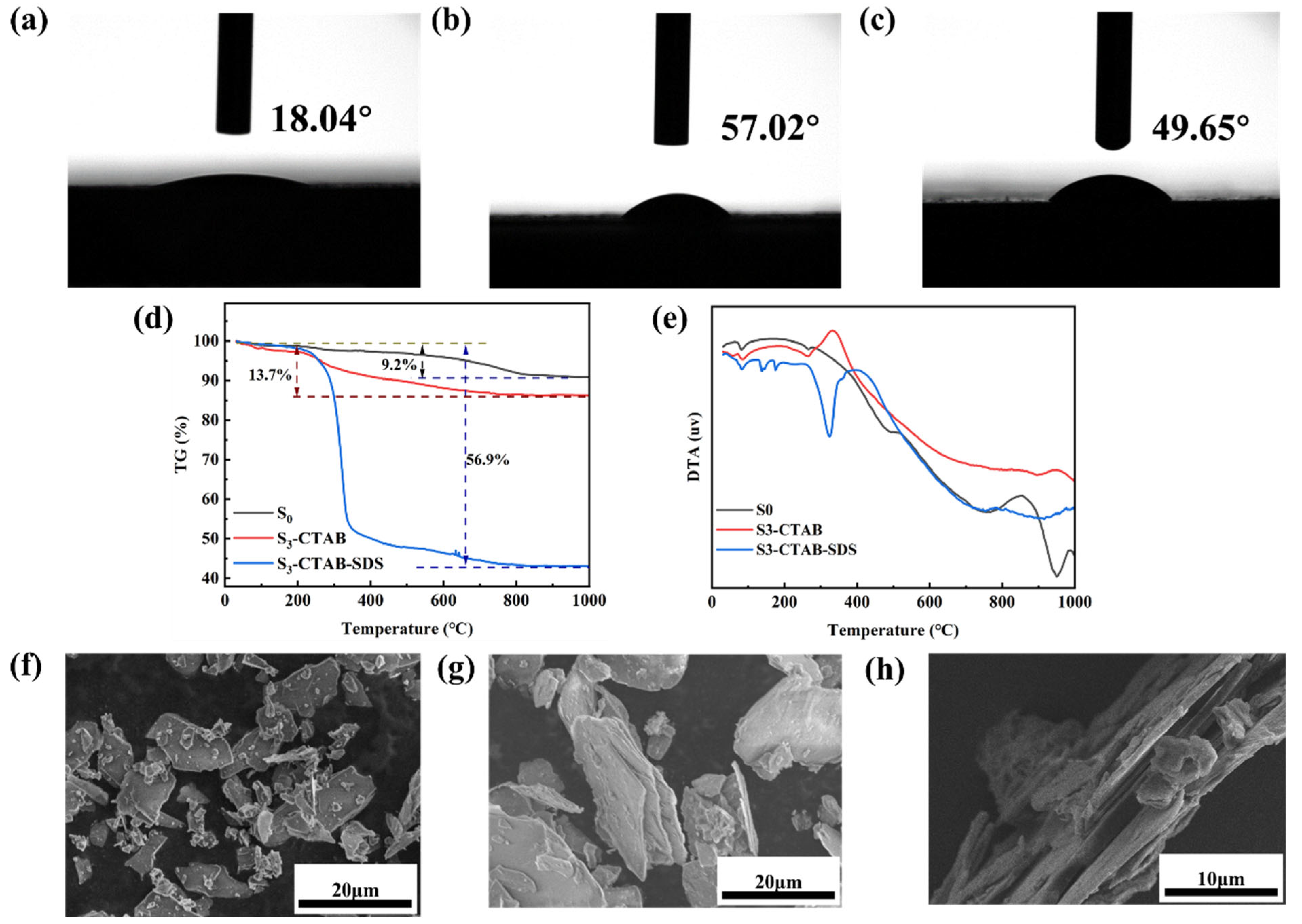
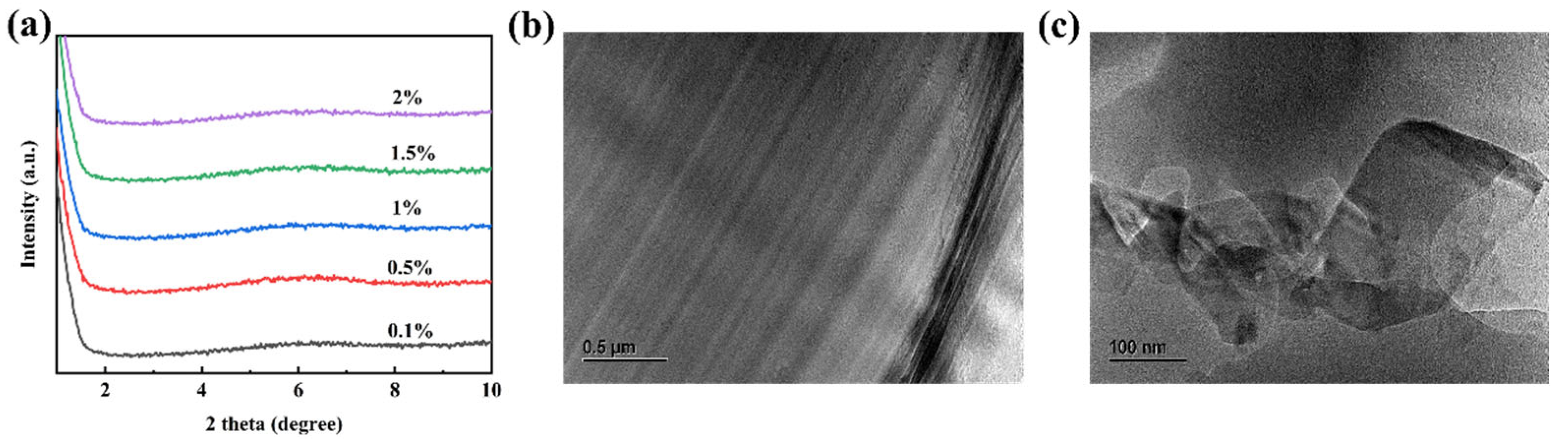
3.2. Characterization of the Obtained Anionic–Cationic Surfactants Co-Intercalated Sericite
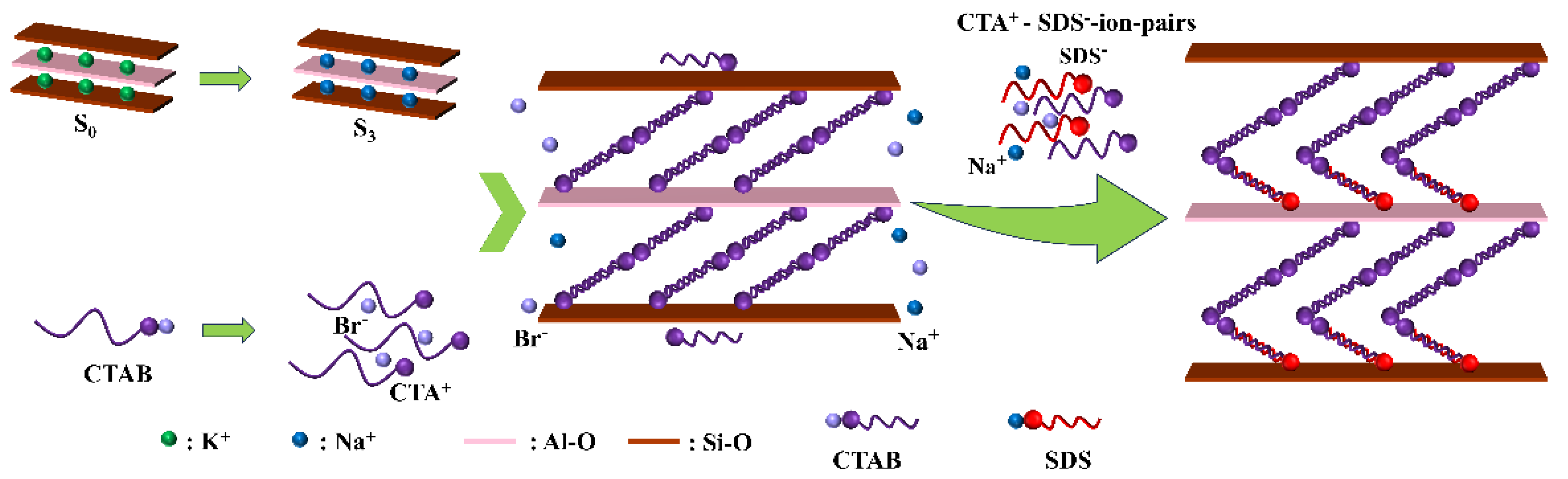
3.3. Mechanism for Cationic–Anionic Surfactants Intercalated Sericite
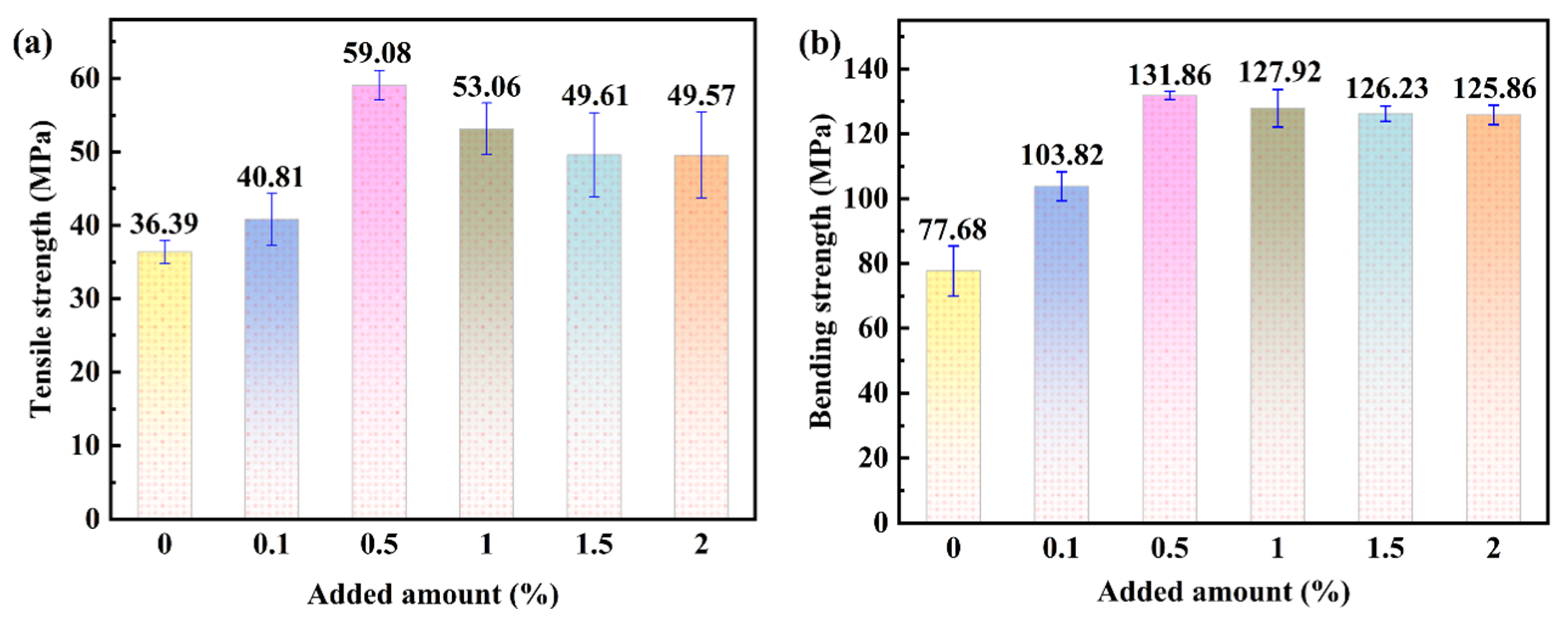
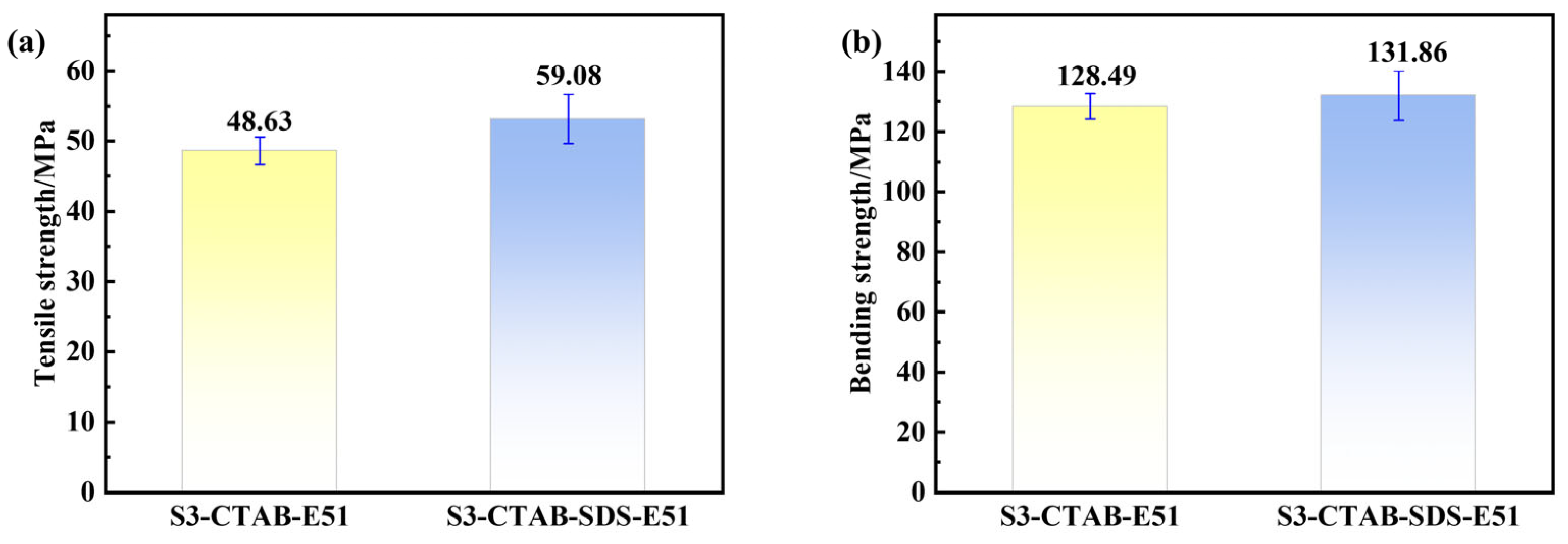
3.4. Mechanical Properties of Sericite/Epoxy Resin Composites
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jia, F.F.; Su, J.; Song, S.X. Can Natural Muscovite be Expanded? Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 471, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Ding, H.; Wang, Y.; Liang, N.; Wang, G. Intercalation of cetyl trimethylammonium ion into sericite in the solvent of dimethyl sulfoxide. Appl. Clay Sci. 2013, 74, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Sun, Y.; Chu, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, M. Crystalline structure variation within phlogopite, muscovite and talc under 0–1000 kGy γ ray irradiation: A clear dependence on intrinsic characteristic. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 187, 105475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Ding, H.; Sun, S.; Chen, Y. Microstructural Modification and Characterization of Sericite. Materials 2017, 10, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Sun, J.; Chen, H.; Wang, X.; Bai, X.; Zhang, H.; Ding, H.; Xue, C. Preparation of TiO2/sericite composite by mechano-chemical method and calcination with favorable pigment properties and photocatalytic properties. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2024, 170, 113353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Li, W.; Bei, B.; Li, C.; He, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhou, R.; Ding, H.; Li, S. Composites of TiO2 pillared sericite: Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange. Appl. Clay Sci. 2023, 242, 107044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.Y.; Pan, Z.D.; Zhang, T.; Lu, Y.J.; Wang, Y.M. Preparation of high near-infrared reflectance mica/(Ni, Sb)-co-doped rutile yellow composite pigment via mechanochemical pretreatment and sintering. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 6015–6029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.F.; Gao, H.L.; Lu, Y.; Wu, C.Y.; Wu, Y.D.; Wang, X.Y.; Pan, Z.Q.; Dong, L.; Song, Y.H.; Cong, H.P.; et al. Transforming ground mica into high-performance biomimetic polymeric mica film. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ding, J.H.; Chu, Q.C.; Zhao, H.R.; Zhu, J.; Wang, J.G. Strong and tough bio-based biomimetic-multiphase composite polyesters with superior barrier and chemically closed-loop performances. Green Chem. 2025, 27, 743–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, P.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, T. All-inorganic flexible high-temperature strain sensor based on SrRuO3/muscovite heteroepitaxy. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 105, 2038–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Liu, Y.N.; Lei, Y.S.; Qian, H.Y.; Li, Y.Z.; Yan, W.J.; Zhou, C.J.; Wen, H.M.; Xia, S.J.; Mao, P.; et al. Innovative Thermocatalytic H2 Sensor with Double-Sided Pd Nanocluster Films on an Ultrathin Mica Substrate. ACS Sens. 2024, 9, 2529–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-J.; Chen, J.-W.; Lai, Y.-H.; Shao, P.-W.; Bitla, Y.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chu, Y.-H. Flexible magnetoelectric complex oxide heterostructures on muscovite for proximity sensor. npj Flex. Electron. 2023, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, P.W.; Siao, Y.S.; Lai, Y.H.; Hsieh, P.Y.; Tsao, C.W.; Lu, Y.J.; Chen, Y.C.; Hsu, Y.J.; Chu, Y.H. Flexible BiVO4/WO3/ITO/muscovite heterostructure for visible-light photoelectrochemical photoelectrode. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 21186–21193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Yokoyama, S.; Pascua, C.S.; Yamada, H. New age of polymer nanocomposites containing dispersed high-aspect-ratio silicate nanolayers. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 2242–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Yang, D.; Yang, T.; Liang, N.; Ding, H. The Stability of Intercalated Sericite by Cetyl Trimethylammonium Ion under Different Conditions and the Preparation of Sericite/Polymer Nanocomposites. Polymers 2019, 11, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, H.; Tamura, K.; Yamada, H.; Umeyama, K.; Hatta, T.; Moriyoshi, Y. Preparation and mechanical properties of exfoliated mica-polyamide 6 nanocomposites using sericite mica. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 46, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.P.; Wang, I.C.; Perng, Y.S. Enhanced thermal behavior, mechanical properties and UV shielding of polylactic acid (PLA) composites reinforces with nanocrystalline cellulose and filled with nanosericite. Cellul. Chem. Technol. 2013, 47, 111–123. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, N.H.C.; Akil, H.M. Effects of organomodified muscovite on the properties of acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Lang, F.; Liu, F.; Wei, M.L.; Li, D.X.; You, Y.L. Structure and properties of polyimide/sericite composite adhesive prepared by polyamide acid salt method. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2022, 36, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Wang, F.K.; Wang, J.; Li, J.F. Surface modification of sericite and preparation of sericite/polystyrene with enhanced thermal-insulating performance. Polym. Bull. 2024, 81, 773–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.; Komarneni, S. Cation exchange equilibria of cesium and strontium with K-depleted biotite and muscovite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 44, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Weerasinghe, P.V.T.; Wu, P. Fostering mica exfoliation through biaxial straining strategy with monovalent cation substitution. Flatchem 2023, 42, 100565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X. The preparation and characterization of cetyltrimethylammonium intercalated muscovite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2007, 98, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, D.X.; Lai, D.W.; You, Y.L.; Ou, B.L.; Lei, T. Preparation and characterization of polyimide/sericite mica composites. Acta Polym. Sin. 2014, 3, 369–377. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, V. High CEC generation and surface modification in mica and vermiculite minerals. Philos. Mag. 2013, 93, 777–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liao, L.; Xia, Z. Synergistic effect of cationic and anionic surfactants for the modification of Ca-montmorillonite. Mater. Res. Bull. 2013, 48, 1811–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Davarpanah, A. Impact of anionic and cationic surfactants interfacial tension on the oil recovery enhancement. Powder Technol. 2020, 373, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massarweh, O.; Abushaikha, A.S. The use of surfactants in enhanced oil recovery: A review of recent advances. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 3150–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 2567-2021; Test Methods for Properties of Resin Casting Body. National Standards of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Fu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, L.; Zhuang, G.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, J.; Liao, L. Investigation on the co-modification process of montmorillonite by anionic and cationic surfactants. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 132–133, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloprogge, J.T.; Frost, R.L.; Hickey, L. Infrared absorption and emission study of synthetic mica-montmorillonite in comparison to rectorite, beidellite and paragonite. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1999, 18, 1921–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ding, H.; Sun, S.; Wang, Y.; Bai, X.; Li, S. Amorphous silica: Prepared by byproduct microsilica in the ferrosilicon production and applied in amorphous silica-TiO2 composite with favorable pigment properties. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.H.; Ren, Q.Q.; Tong, D.S.; Zhou, C.H.; Wang, H. Clean production of CTAB-montmorillonite: Formation mechanism and swelling behavior in xylene. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 97–98, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshmiri-Naqab, R.; Taghavijeloudar, M. Could organoclay be used as a promising natural adsorbent for efficient and cost-effective dye wastewater treatment? J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 342, 118322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayram, T.; Bucak, S.; Ozturk, D. BR13 dye removal using sodium dodecyl sulfate modified montmorillonite: Equilibrium, thermodynamic, kinetic and reusability studies. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process. Intensif. 2020, 158, 108186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahmirzaee, M.; Hemmati-Sarapardeh, A.; Husein, M.M.; Schaffie, M.; Ranjbar, M. ZIF-8/carbon fiber for continuous adsorption of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) from aqueous solutions: Kinetics and equilibrium studies. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 44, 102437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, J.; Liao, L.; Zhao, J. A new ball milling method to produce organo-montmorillonite from anionic and nonionic surfactants. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 104, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, D.; Lai, D.; You, Y.; Ou, B. Preparation, microstructure, mechanical, and thermal properties of in situ polymerized polyimide/organically modified sericite mica composites. Polym. Compos. 2015, 37, 2243–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani Moghaddam, F.; Ghanbari, H.; Mirkazemi, S.M.; Ahmadi, F. Purification of Iranian bentonite for organoclay synthesis for use in clay–polymer composites. Clay Miner. 2024, 59, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, L.; Ding, H. Co-Intercalation of Sericite by Cationic and Anionic Surfactants and the Mechanical Properties of Sericite/Epoxy Resin Composites. Materials 2025, 18, 2486. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112486
Liang Y, Xu Y, Jiang Y, Yu L, Ding H. Co-Intercalation of Sericite by Cationic and Anionic Surfactants and the Mechanical Properties of Sericite/Epoxy Resin Composites. Materials. 2025; 18(11):2486. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112486
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Yu, Yajuan Xu, Yiman Jiang, Lingfeng Yu, and Hao Ding. 2025. "Co-Intercalation of Sericite by Cationic and Anionic Surfactants and the Mechanical Properties of Sericite/Epoxy Resin Composites" Materials 18, no. 11: 2486. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112486
APA StyleLiang, Y., Xu, Y., Jiang, Y., Yu, L., & Ding, H. (2025). Co-Intercalation of Sericite by Cationic and Anionic Surfactants and the Mechanical Properties of Sericite/Epoxy Resin Composites. Materials, 18(11), 2486. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112486






