Sea Sand as a Silica Source to Hydrothermally Synthesize Analcime
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
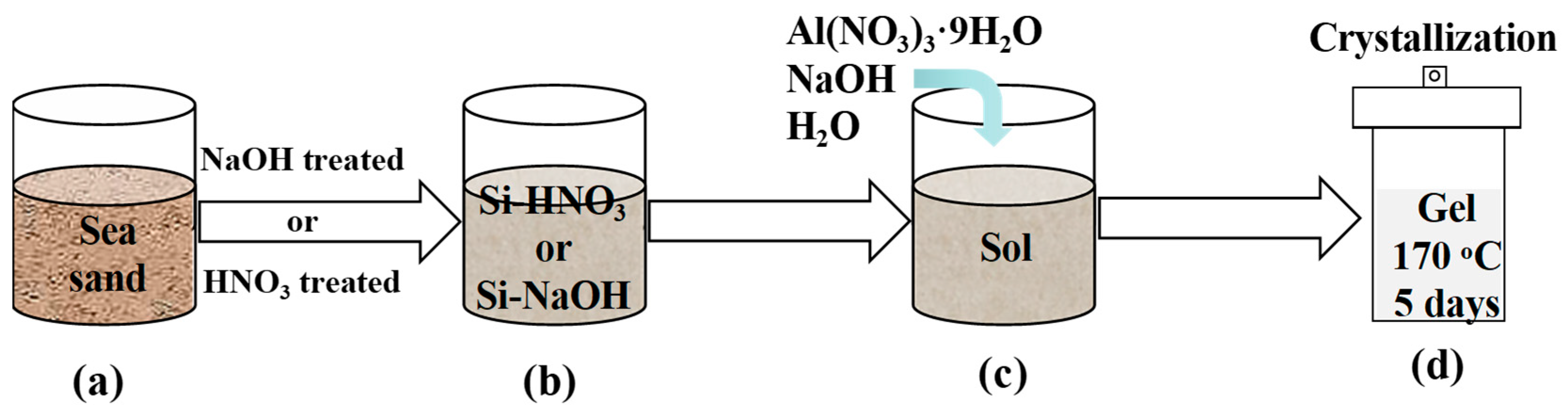
2.1. Sea Sand Pretreatment
2.2. Preparation of Analcime
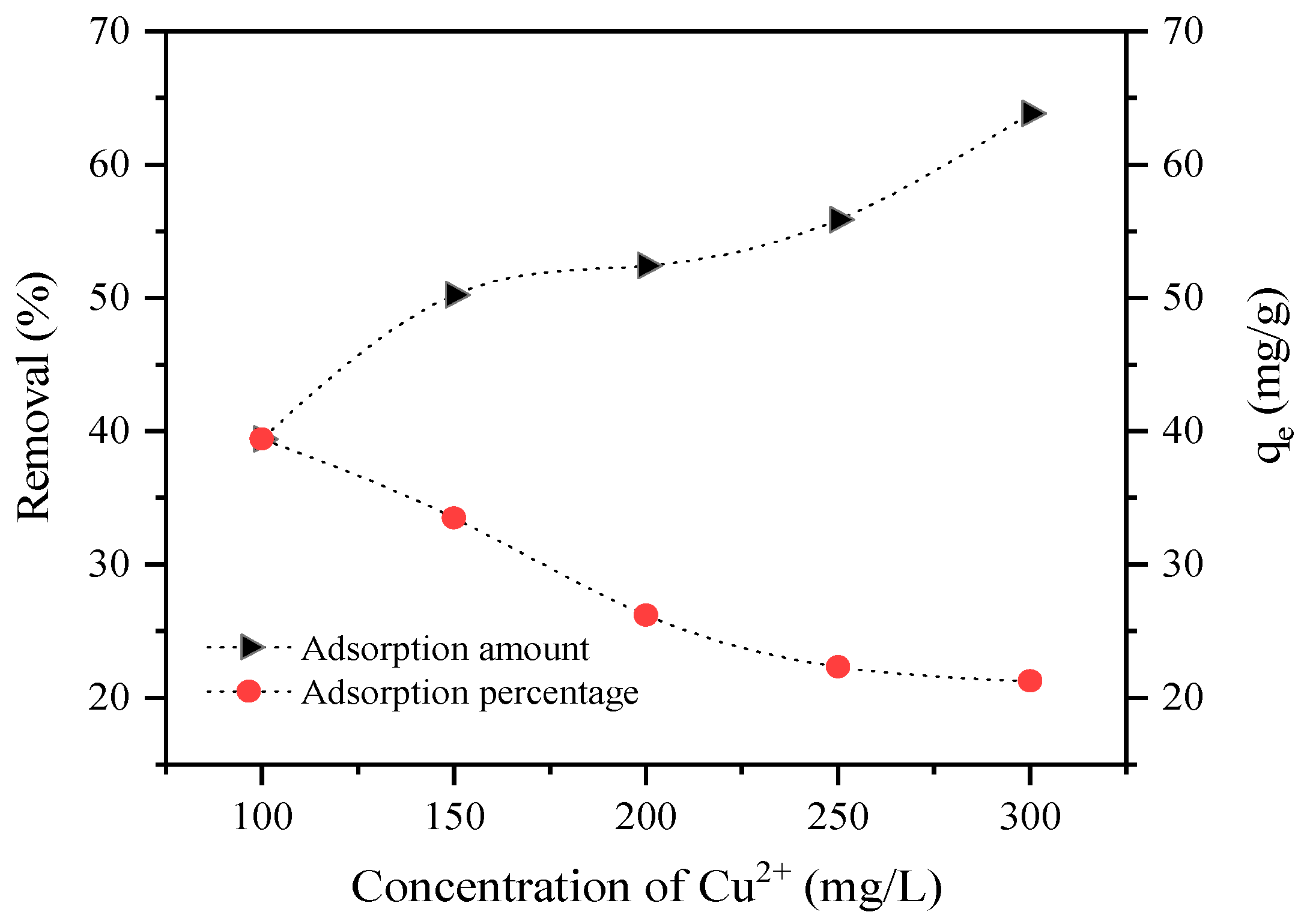
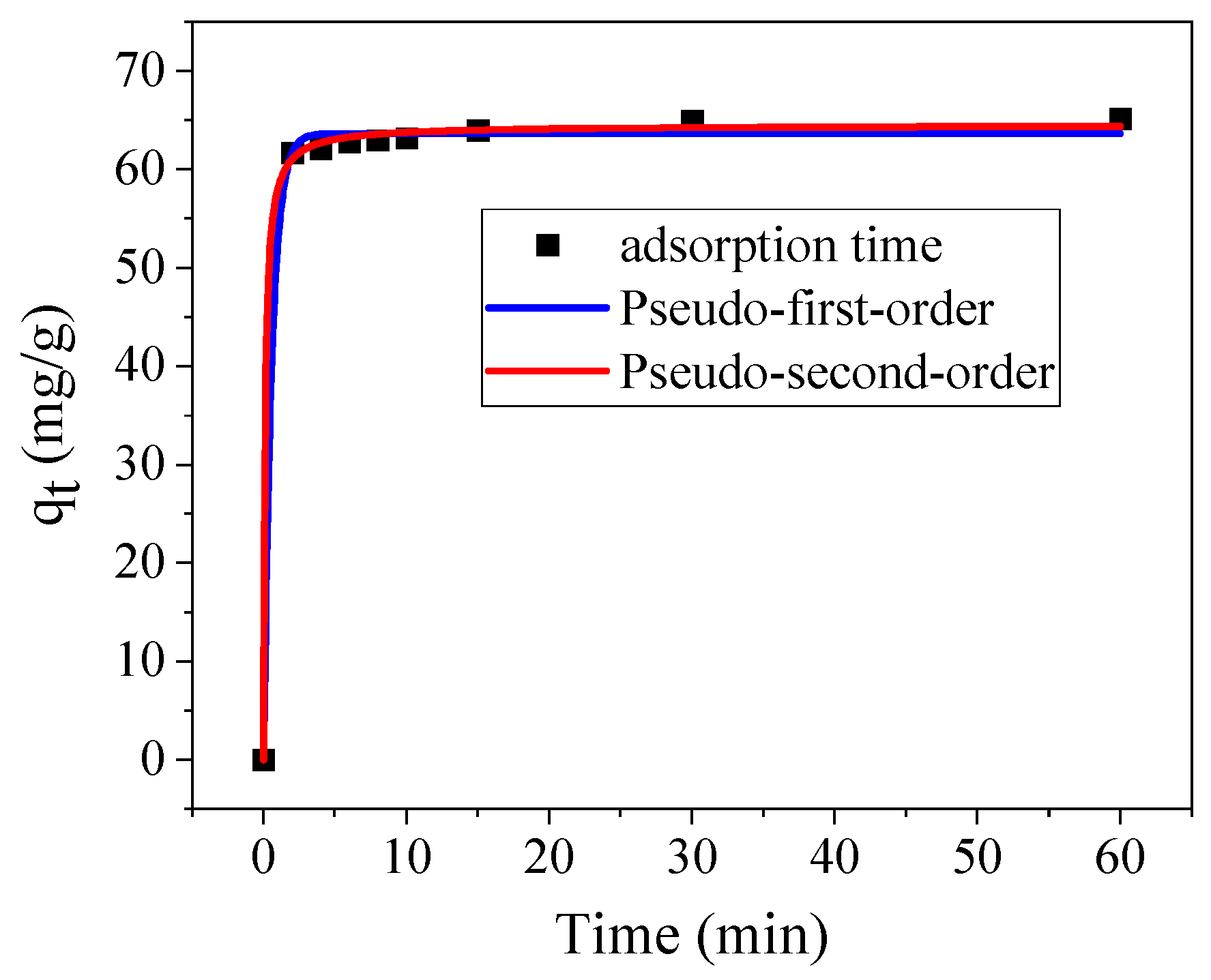
2.3. Adsorption Experiments
2.4. Characterization Techniques
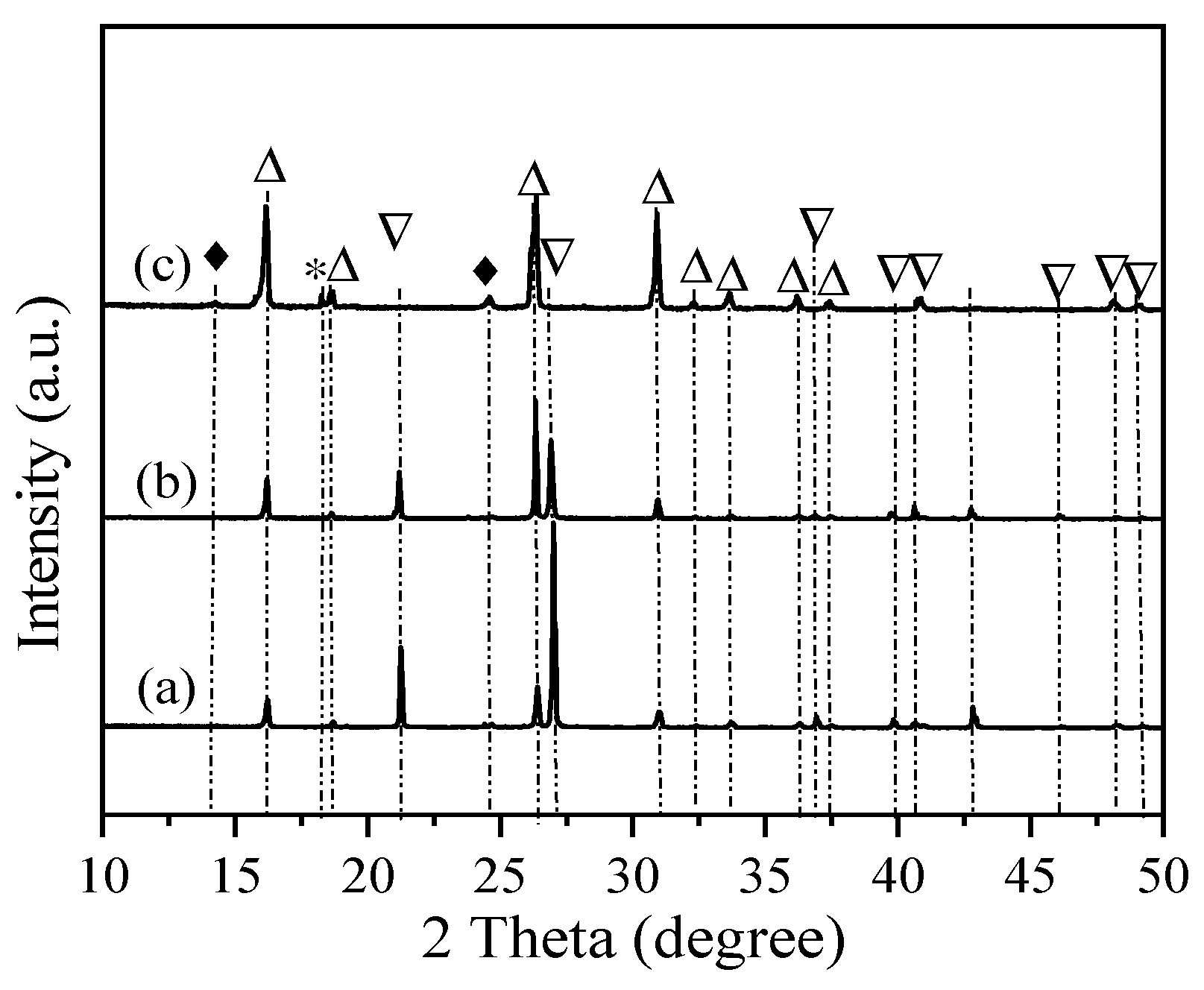
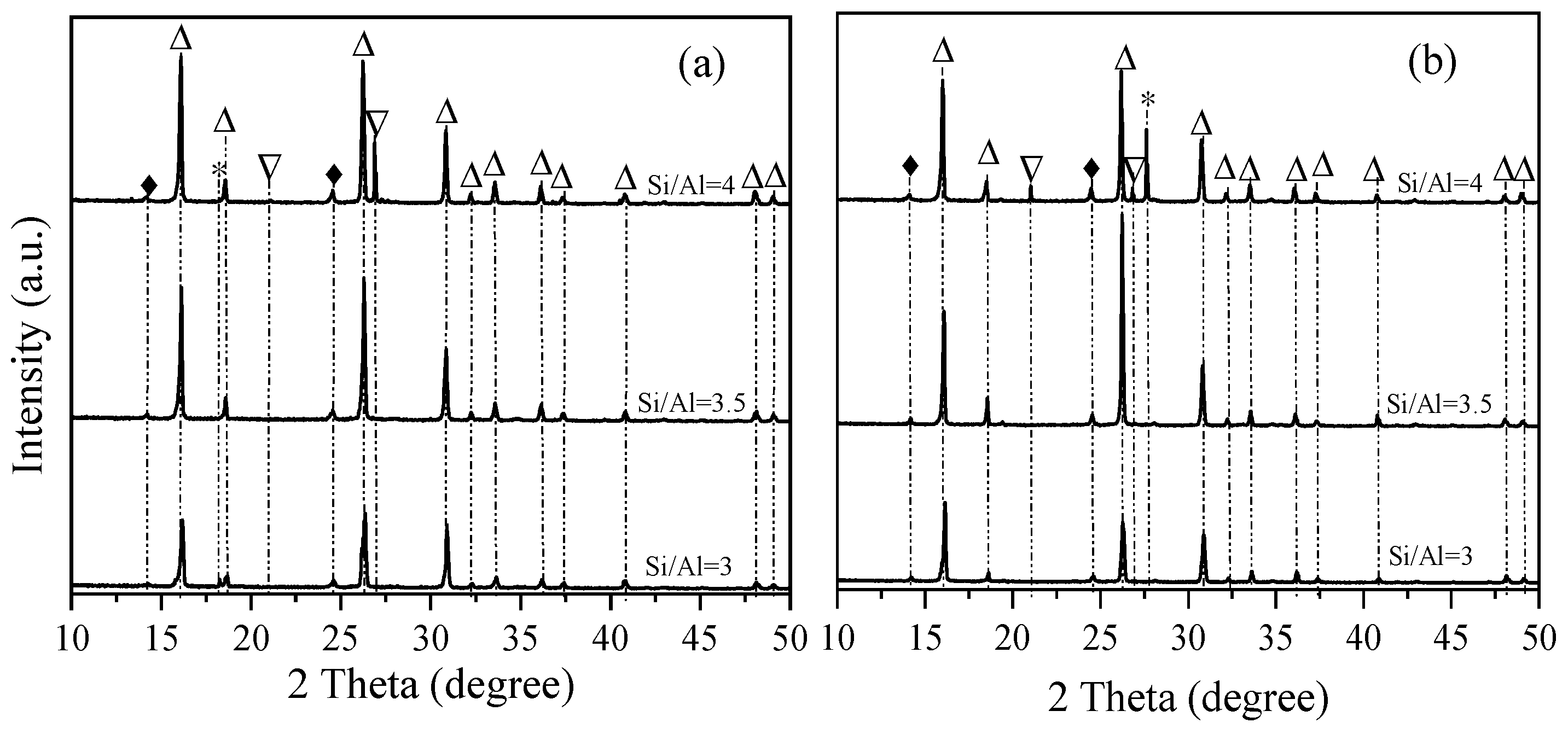
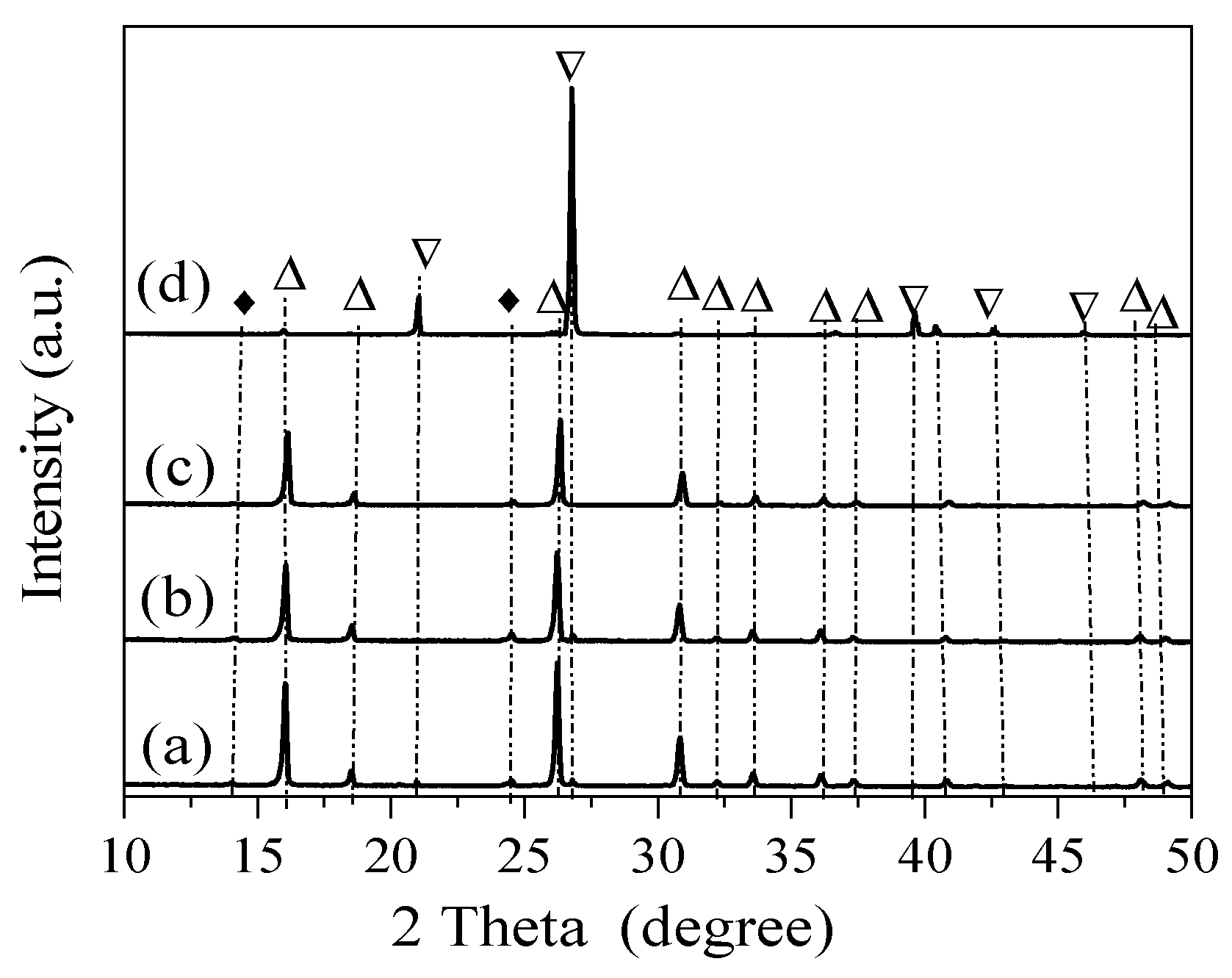
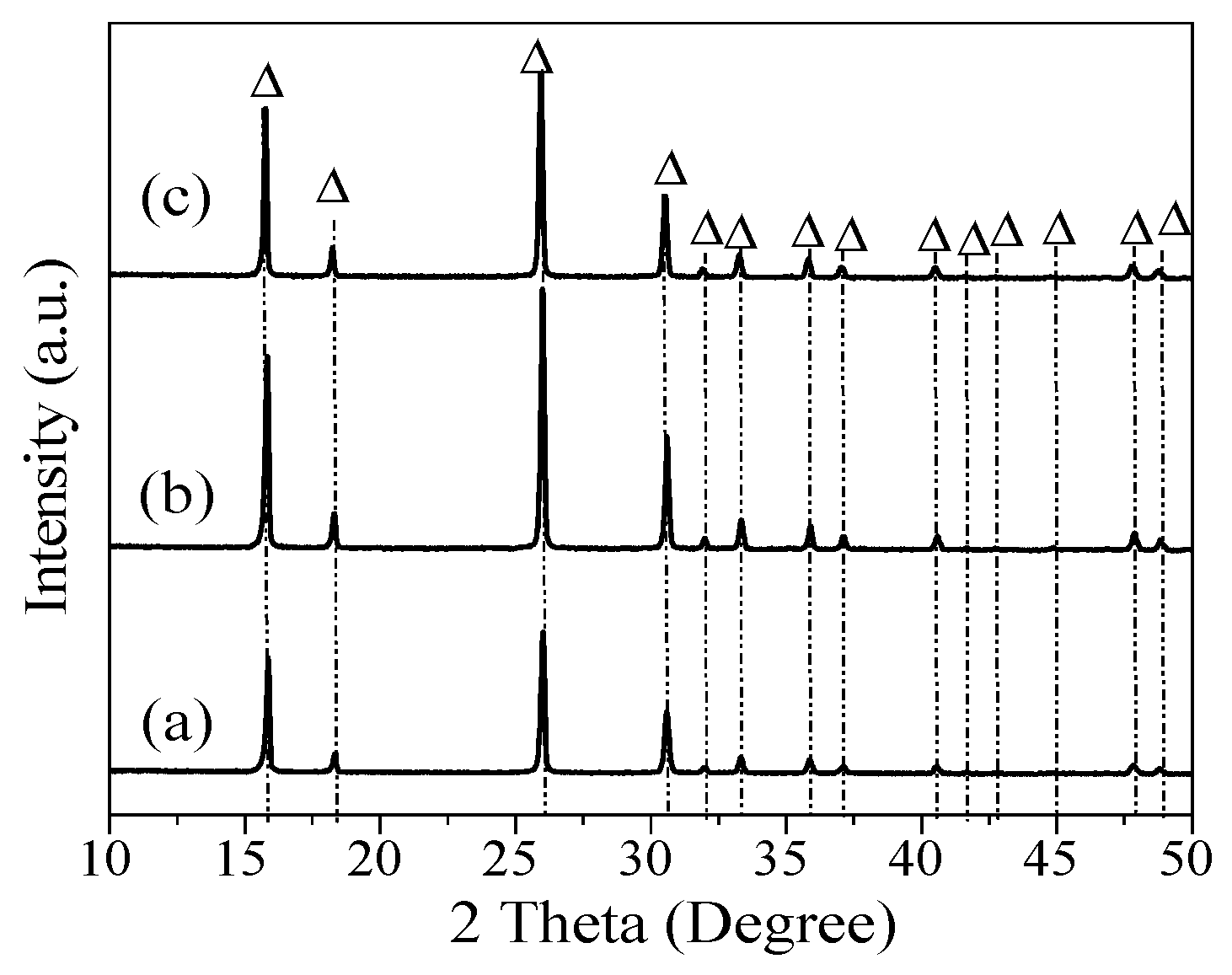
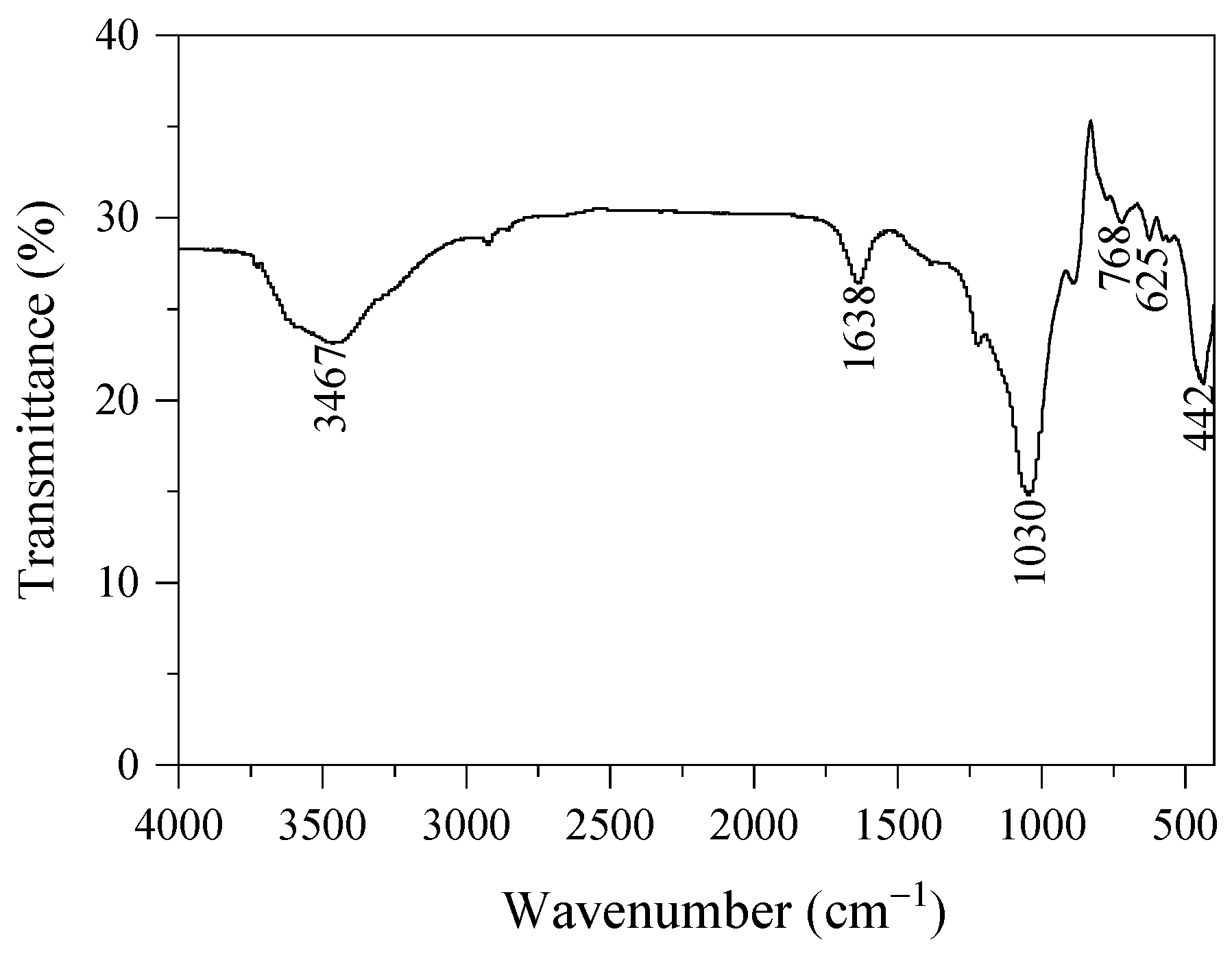
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balandis, A.; Traidaraitė, A. The influence of Al containing component on synthesis of analcime of various crystallographic systems. Mater. Sci. Pol. 2007, 25, 637–647. [Google Scholar]
- Tangkawanit, S.; Rangsriwatananon, K.; Dyer, A. Ion exchange of Cu2+, Ni2+, Pb2+ and Zn2+ in analcime (ANA) synthesized from Thai perlite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2005, 79, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, E.Z.; Maksod, I.H.A.E.; Enin, R.M.M.A.E. Preparation and characterization of Ti and V modified analcime from local kaolin. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 49, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.Z.; Kameda, T.; Yoshioka, T. Hydrothermal synthesis of hardened diatomite-based adsorbents with analcime formation for methylene blue adsorption. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 26765–26774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colella, C. Natural zeolites. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 2005, 157, 13–40. [Google Scholar]
- Neuhoff, P. Natural Zeolites: Occurrence, Properties, Applications. Am. Mineral. 2002, 87, 1737–1738. [Google Scholar]
- Barrer, R.M. Hydrothermal Chemistry of Zeolites; Academic Press: London, UK, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Mintova, S.V.V. Effect of the silica source on the formation of nanosized silicalite-1: An in situ dynamic light scattering study. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2002, 55, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, A.Y.; Jibril, B.Y.; Aderemi, B.O.; Adefila, S.S. Preparation of analcime from local kaolin and rice husk ash. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 61, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, S.N.; Yousefpour, M. Synthesis of zeolites NaA and analcime using rice husk ash as silica source without using organic template. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 5692–5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, M.V.; Henao, J.A.; Rios, C.A.; Williams, C.D.; Apperley, D.C. Synthesis and characterization of zeotype ANA framework by hydrothermal reaction of natural clinker. Fuel 2009, 88, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, A.; Tangkawanit, S.; Rangsriwatananon, K. Exchange diffusion of Cu2+, Ni2+, Pb2+ and Zn2+ into analcime synthesized from perlite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2004, 75, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolini, H.R.; Lima, D.S.; Perez-Lopez, O.W. Hydrothermal synthesis of analcime without template. J. Cryst. Growth 2019, 532, 125424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Liu, Z.; Han, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Zhu, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, D. Synthesis of coal-analcime composite from coal gangue and its adsorption performance on heavy metal ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.T.; Wu, X.; Xu, W. Porous analcime composite synthesized from solid waste:A cost-effective and superb adsorbent for efficient removal of Cu(II)and cationic dye. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. Trans. Inst. Chem. Eng. 2023, 189, 474–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, L.; Shao, N.; Hu, T.; Han, L.; Wang, D. Geopolymerization enhanced hydrothermal synthesis of analcime from steel slag and CFBC fly ash and heavy metal adsorption on analcime. Environ. Technol. 2018, 41, 1753–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocaoba, S.; Orhan, Y.; Akyüz, T.l. Kinetic and equilibrium studies of heavy metal ions removal by use on natural zeolite. Desalination 2007, 214, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotova, O.B.; Shabalin, I.L.; Shushkov, D.A.; Kocheva, L.S. Hydrothermal synthesis of zeolites from coal fly ash. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 2016, 115, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Yang, J.; Ma, H.; Liu, C.; Zhang, P. Synthesis and characterization of analcime using quartz syenite powder by alkali-hydrothermal treatment. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 201, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, Y.H.; Ho, T.Y.; Shen, Y.H.; Ray, D. Synthesis of analcime from sericite and pyrophyllite by microwave-assisted hydrothermal processes. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 143, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraris, G.; Jones, D.W.; Terkess, J. A neutron-diffraction study of the crystal structure of analcime, NaAlSi2O6·H2O. Z. Krist.-Cryst. Mater. 1972, 135, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buamah, R.; Kwakye-Awuah, B.; Von-Kiti, E.; Nkrumah, I.; Williams, C. Effect of crystallization time on the hydrothermal synthesis of zeolites from kaolin and bauxite. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2014, 5, 734–741. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelmoneim, A.A.; Abdul-Moneim, M.; Geies, A.A.; Farghaly, S.O. Synthesis, characterization and application of analcime to control nitrate ions from the ground water samples from Wadi El-Assiuti—Egypt as a low-cost and locally available adsorbent. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 975, 012013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esaifan, M.; Al Daboubi, F.; Hourani, M.K. Preparation of Mesoporous Analcime/Sodalite Composite from Natural Jordanian Kaolin. Materials 2024, 17, 4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-nayili, A.; Rzoqy, M. Local silica sand as a silica source in the synthesis of Y zeolite. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 17, 2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Palomares, A.; Ángeles-García, E.; Maldonado, Y.; Coutino-Gonzalez, E.; Espejel-Ayala, F. Synthesis of industrially appealing low-silica zeolites using aluminum scraps and sand. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2024, 307, 117508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.Z.; Qiang, C.B.; Nanni, A.; Zhang, K.J. Use of sea-sand and seawater in concrete construction: Current status and future opportunities. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 155, 1101–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Xu, D.; Ma, H.; Li, B.; Howard, A. Synthesis of NaA zeolite from foundry dust and its adsorption capacity of ammonia. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 331, 117297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Xiao, L.; Qu, R.; Liu, S.; Ye, D.; Song, H.; Wu, W.; Zheng, C.; Wu, X.; Gao, X. Synthesis and characterization of a single phase zeolite A using coal fly ash. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 42200–42209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treacy, M.M.J.; Higgins, J.B. Collection of Simulated XRD Powder Patterns for Zeolites; Elsevier, B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 373–379. [Google Scholar]
- Sakizci, M. Investigation of thermal and structural properties of natural and ion exchanged analcime. Anadolu Univ. J. Sci. Technol. A-Appl. Sci. Eng. 2016, 17, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bouzón, N.; Payá, J.; Borrachero, M.V.; Soriano, L.; Tashima, M.M.; Monzó, J. Refluxed rice husk ash/NaOH suspension for preparing alkali activated binders. Mater. Lett. 2014, 115, 72–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Cui, X.-M.; Liu, X.-D.; Wang, Y.-P.; Zhang, J.; Liu, K. Preparation of self-supporting NaA zeolite membranes using geopolymers. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 447, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; He, Y.; Wang, Y.-p.; Mao, J.; Cui, X.-m. Synthesis of a self-supporting faujasite zeolite membrane using geopolymer gel for separation of alcohol/water mixture. Mater. Lett. 2014, 116, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohoutkova, M.; Kloužková, A.; Maixner, J.; Mrazova, M. Preparation and characterization of analcime powders by x-ray and sem analyses. Ceram. Silik. 2007, 51, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Novembre, D.; Gimeno, D.; Del Vecchio, A. Synthesis and characterization of Na-P1 (GIS) zeolite using a kaolinitic rock. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, S.K.; Kumar, S. Role of particle fineness on engineering properties and microstructure of fly ash derived geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 233, 117294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adil, K.; Abdellah, A.; Abdelaziz, D.; Fahoul, Y.; Iboustaten, E.; Abdelali, E.G.; Karim, T.; Abdelhak, K. Kinetic, equilibrium, and thermodynamic studies of heavy metal removal from aqueous solutions by natural material from Morocco. Euro-Mediterr. J. Environ. Integr. 2022, 7, 141–153. [Google Scholar]
- Bejar, A.; Ben Chaabene, S.; Jaber, M.; Lambert, J.F.; Bergaoui, L. Mn-analcime: Synthesis, characterization and application to cyclohexene oxidation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 196, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Specialty Zeolite Market, Share, and Trends Analysis Report. Available online: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-specialty-zeolite-market (accessed on 19 February 2025).
- Belver, C.; Vicente, M.A. Easy synthesis of K-F zeolite from kaolin, and characterization of this zeolite. J. Chem. Educ. 2006, 83, 1541–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, S.; Premada, P.N. Investigation on synthesis of zeolite NaX from Kerala kaolin. J. Porous Mater. 1999, 6, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, S.; Premada, P.N. Kaolin based zeolite Y, a precursor cordierite ceramics. Appl. Clay Sci. 2004, 27, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

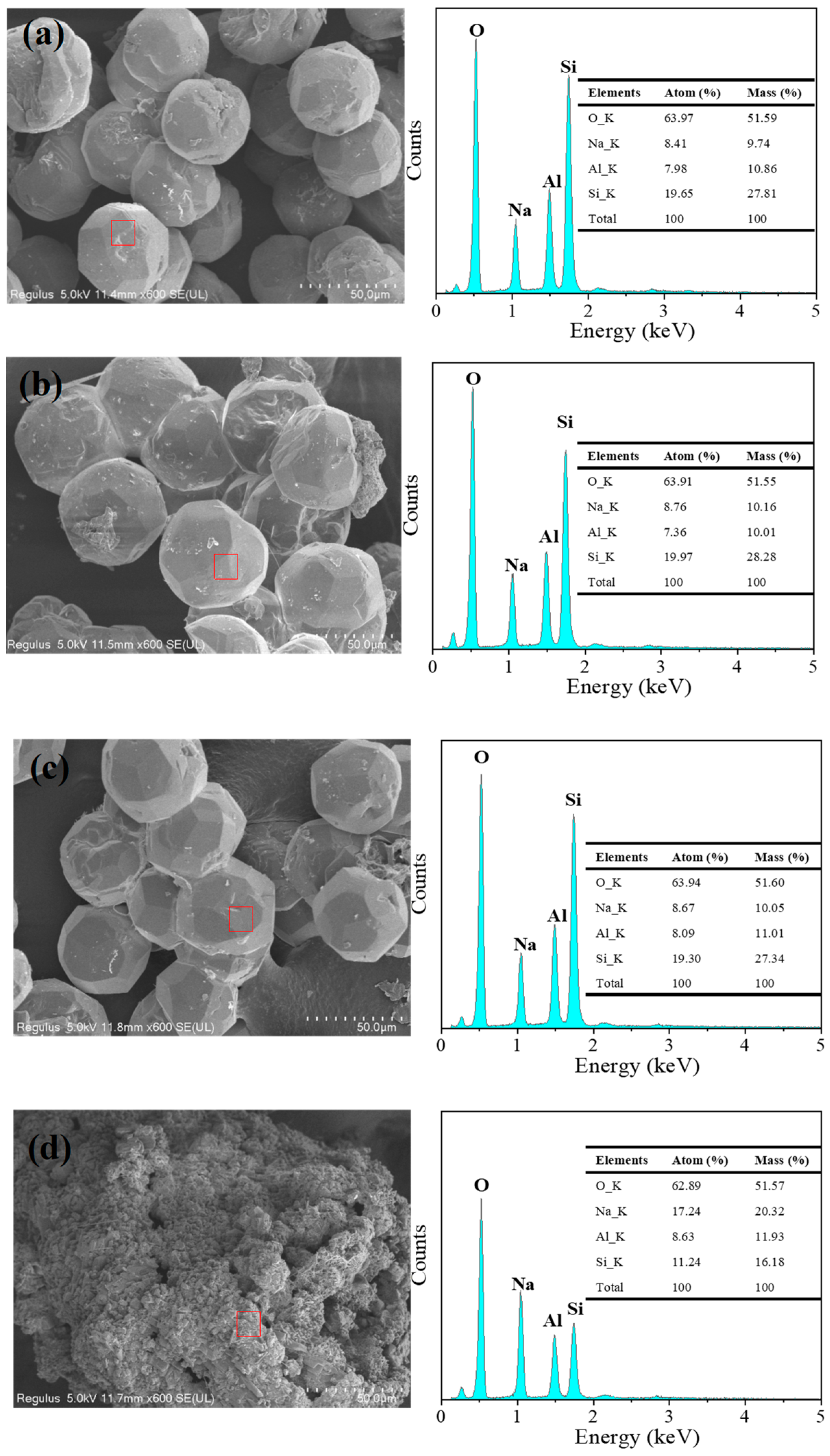


| Element | Sea Sand | Acid-Treated | Alkali-Treated |
|---|---|---|---|
| O | 42.03 | 42.56 | 50.54 |
| Si | 22.59 | 32.27 | 33.46 |
| Cl | 18.30 | 14.80 | 4.96 |
| Na | 14.41 | 8.72 | 8.24 |
| Al | 1.37 | 1.05 | 2.08 |
| K | 1.15 | 0.60 | 0.72 |
| Fe | 0.15 | 0 | 0 |
| Sample | Si/Al Ratio | Specific Surface Area (m2/g) |
|---|---|---|
| Analcime, prepared from alkali-treated sea sand as silica source | 3 | 0.69 |
| 3.5 | 0.71 | |
| 4 | 0.67 |
| pseudo-First-Order | pseudo-Second-Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 (1/min) | R12 | Qe (mg/g) | K1 (1/min) | R22 | Qe (mg/g) |
| 1.7215 | 99.558 | 63.64 | 0.1353 | 99.832 | 64.50 |
| Acid Treatment | Alkali Treatment | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dosage | Unit Cost (USD) | Total (USD) | Dosage | Unit Cost (USD) | Total (USD) | |
| Sea sand | 1.1 kg | 0.02 | 0.022 | 1.1 kg | 0.02 | 0.022 |
| HNO3 (65 wt.%) | 19.3 kg | 0.2 | 3.86 | - | - | - |
| NaOH | 0.7 kg | 0.38 | 0.76 | 1.3 kg | 0.38 | 1.064 |
| Al(NO3)3 | 2.08 kg | 8 | 16.64 | 2.08 kg | 8 | 16.64 |
| Total | - | - | 21.282 | - | - | 17.726 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, W.; Ma, H.; Cao, C.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Teng, J.; Li, N.; Yue, C. Sea Sand as a Silica Source to Hydrothermally Synthesize Analcime. Materials 2025, 18, 2818. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122818
Xie W, Ma H, Cao C, Wang Y, Qiao Y, Teng J, Li N, Yue C. Sea Sand as a Silica Source to Hydrothermally Synthesize Analcime. Materials. 2025; 18(12):2818. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122818
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Wei, Hao Ma, Chuangguang Cao, Yating Wang, Yanhui Qiao, Junjiang Teng, Ning Li, and Chaochao Yue. 2025. "Sea Sand as a Silica Source to Hydrothermally Synthesize Analcime" Materials 18, no. 12: 2818. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122818
APA StyleXie, W., Ma, H., Cao, C., Wang, Y., Qiao, Y., Teng, J., Li, N., & Yue, C. (2025). Sea Sand as a Silica Source to Hydrothermally Synthesize Analcime. Materials, 18(12), 2818. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122818






