Evaluation of NDT Methods for In Situ Documentation of Concrete for Reuse: Laboratory Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Casting of Test Specimens
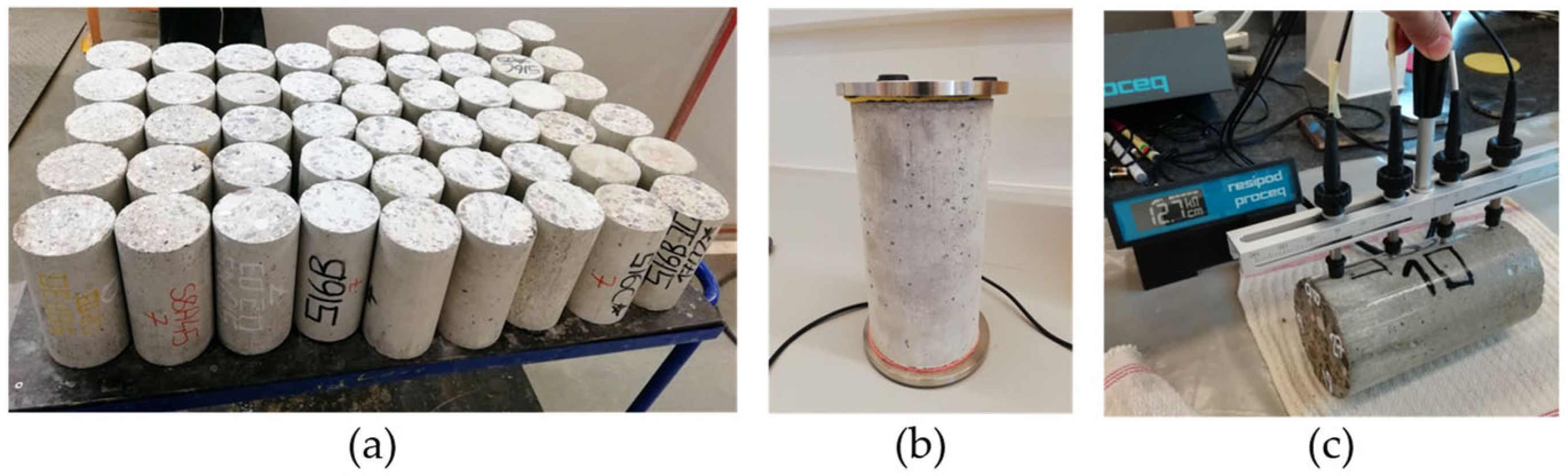
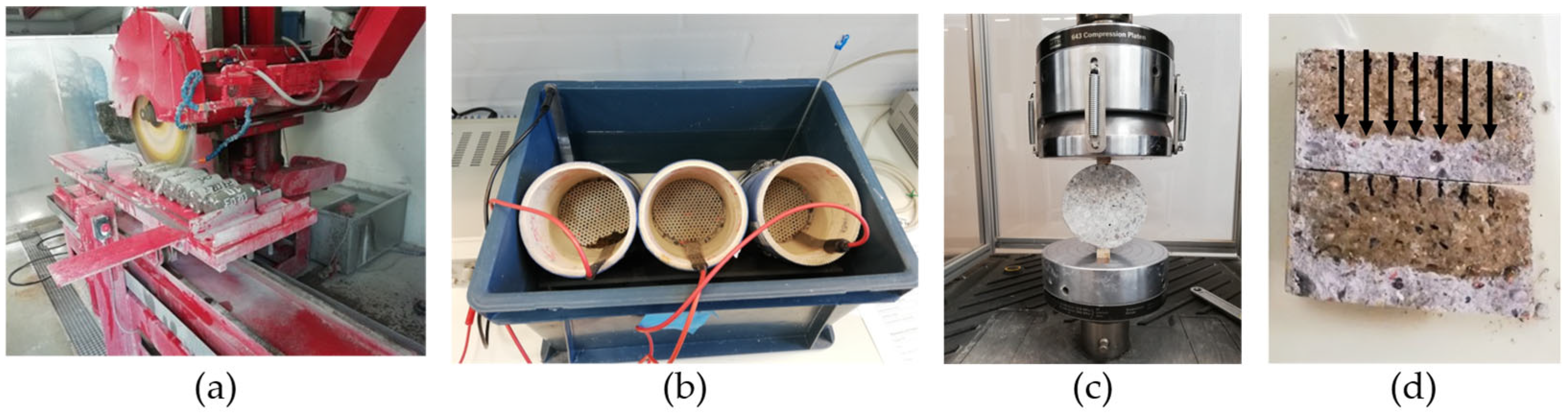
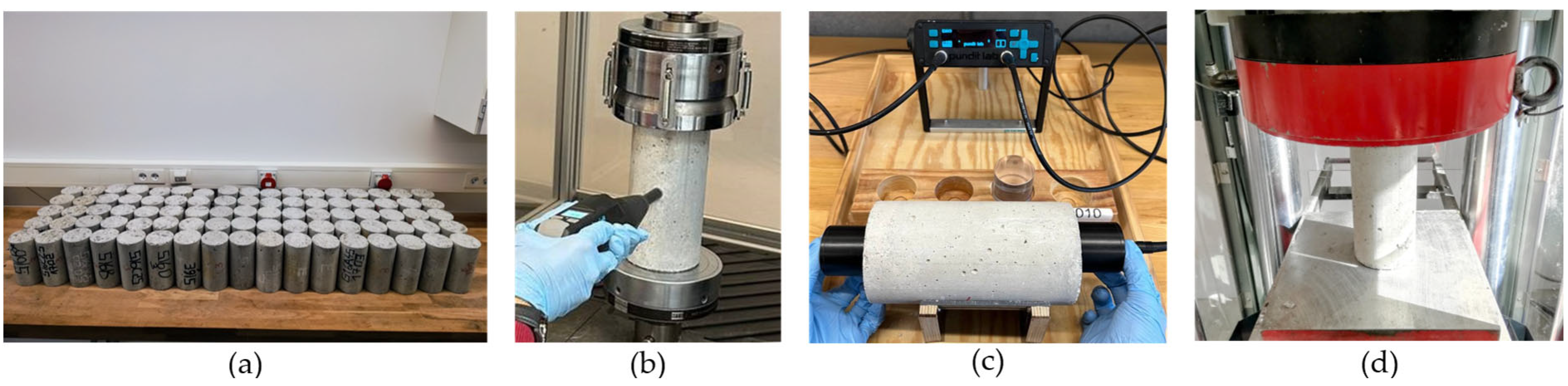
2.2. NDT Methods
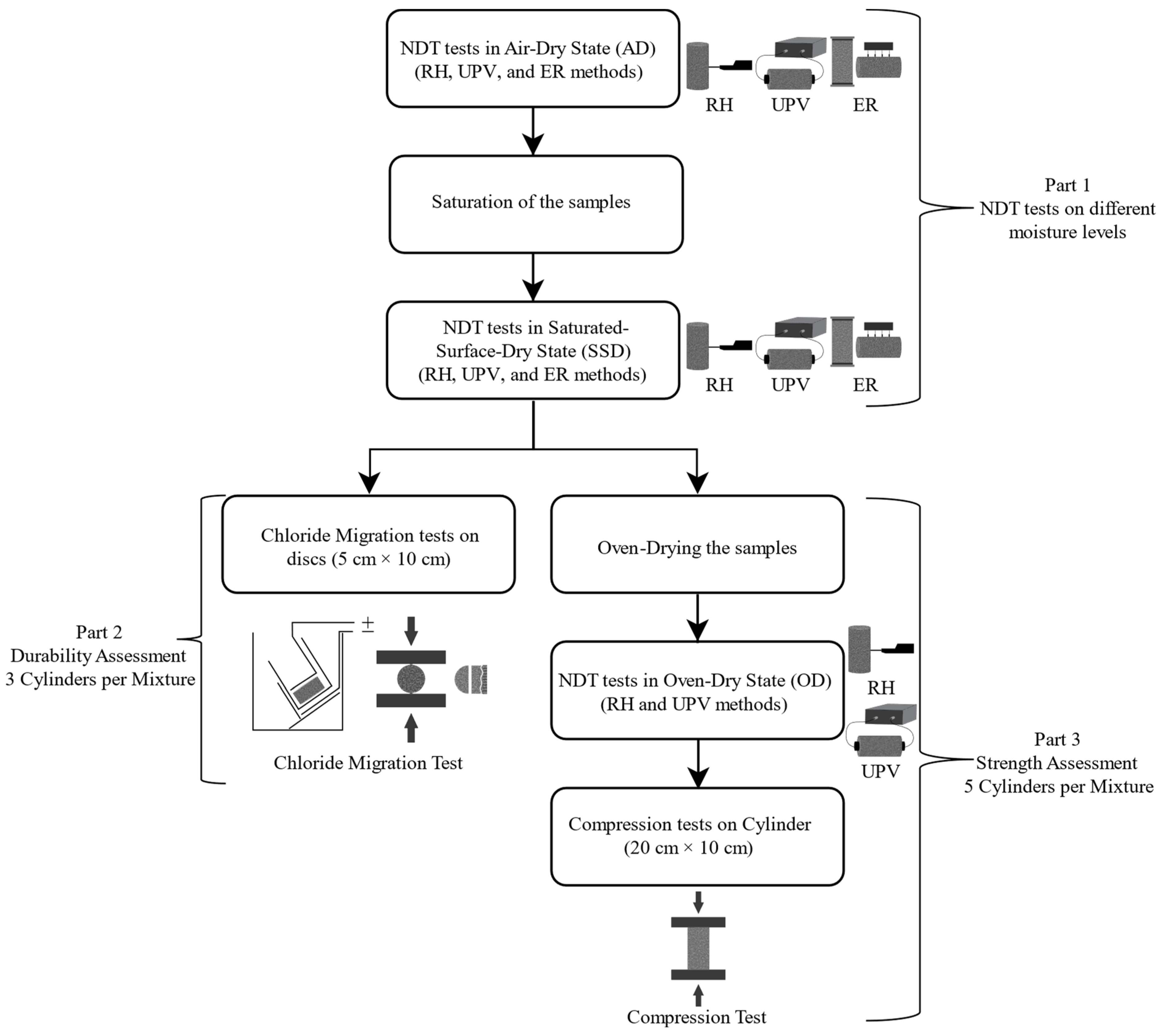
2.3. Test Methodology
2.4. Statistical Data Analysis
3. Results
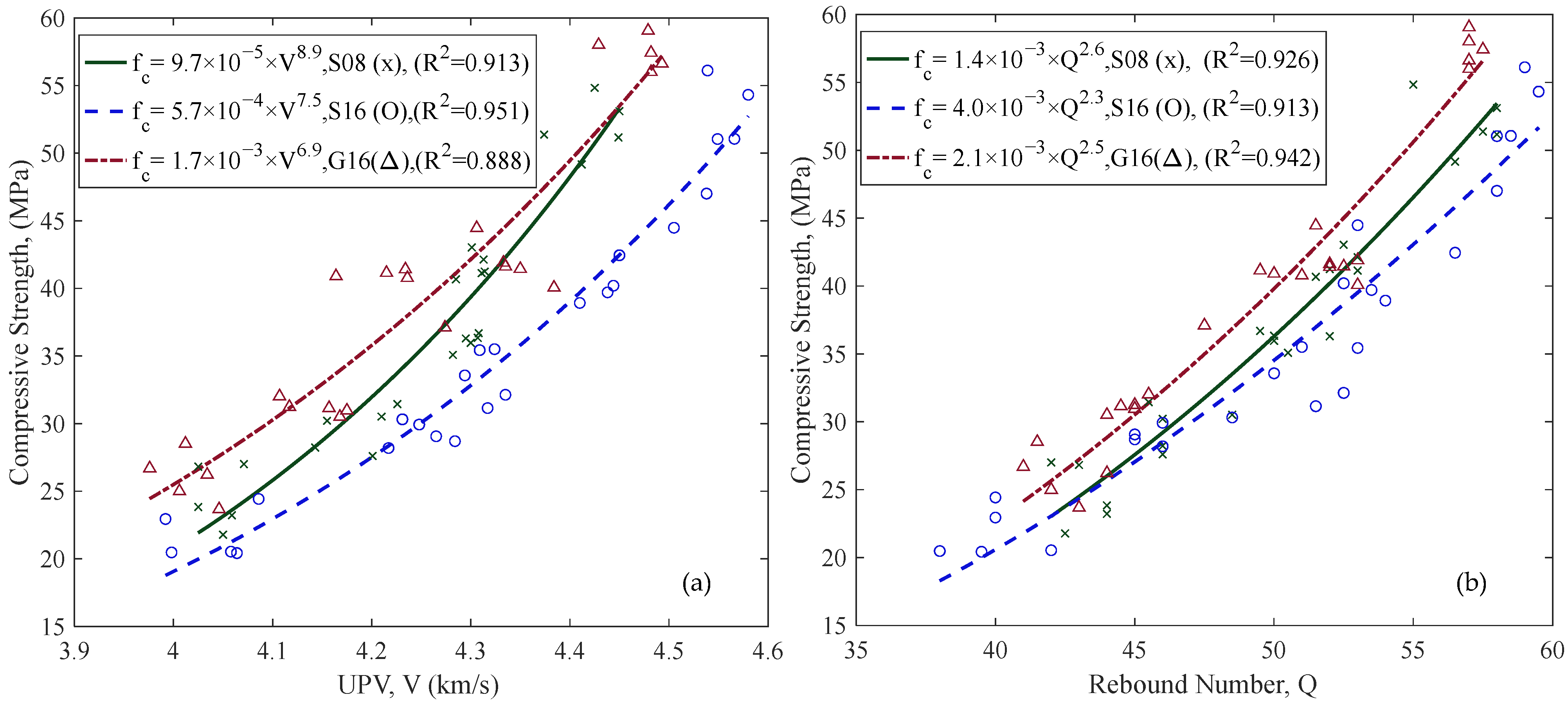
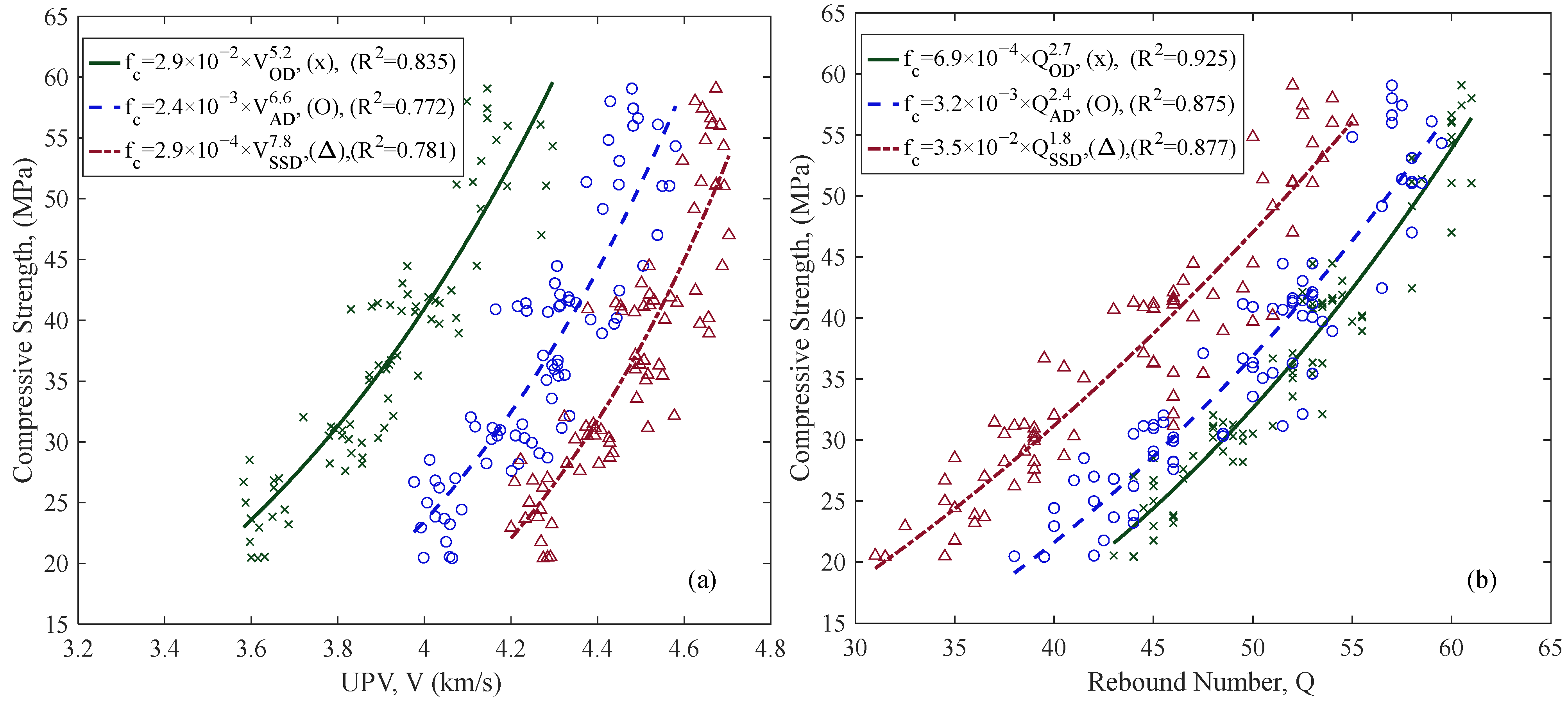
3.1. Correlation of Compressive Strength with UPV and RH
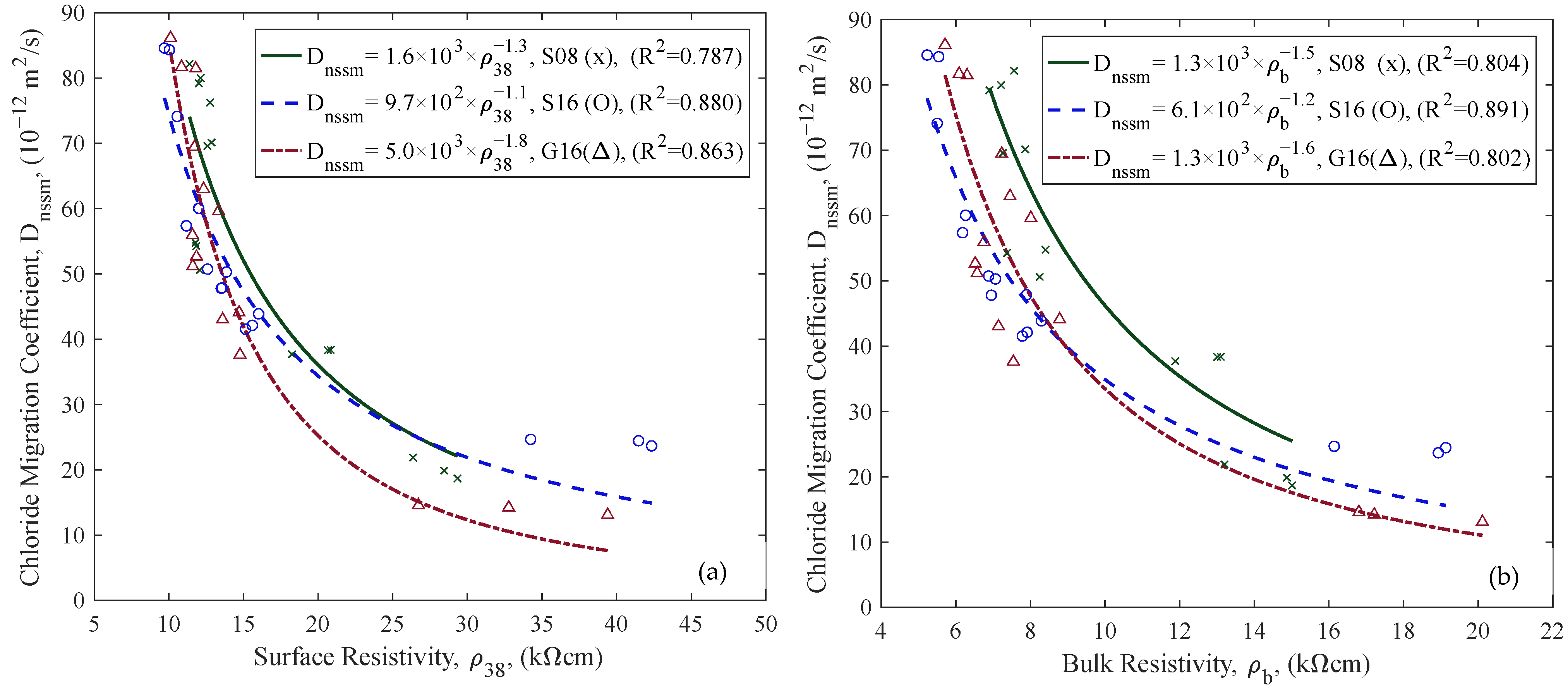
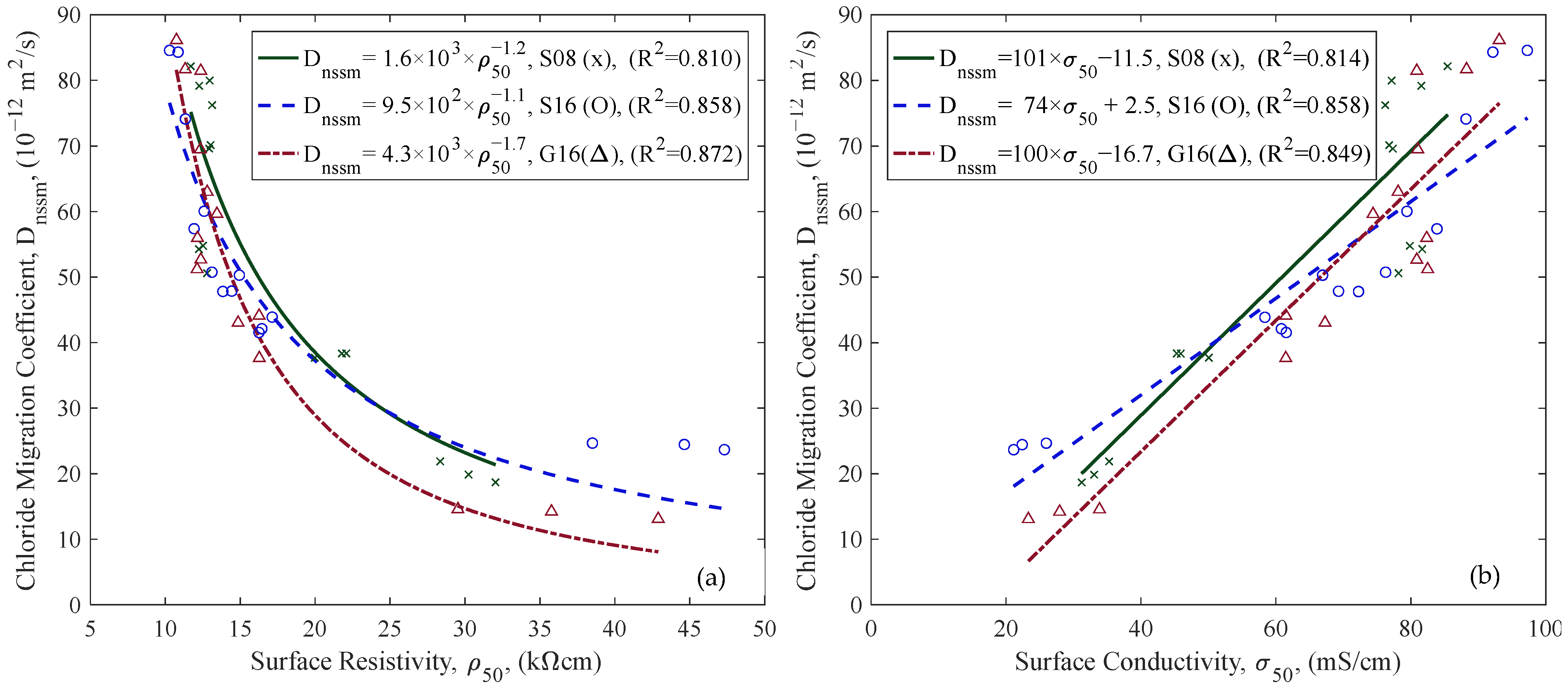
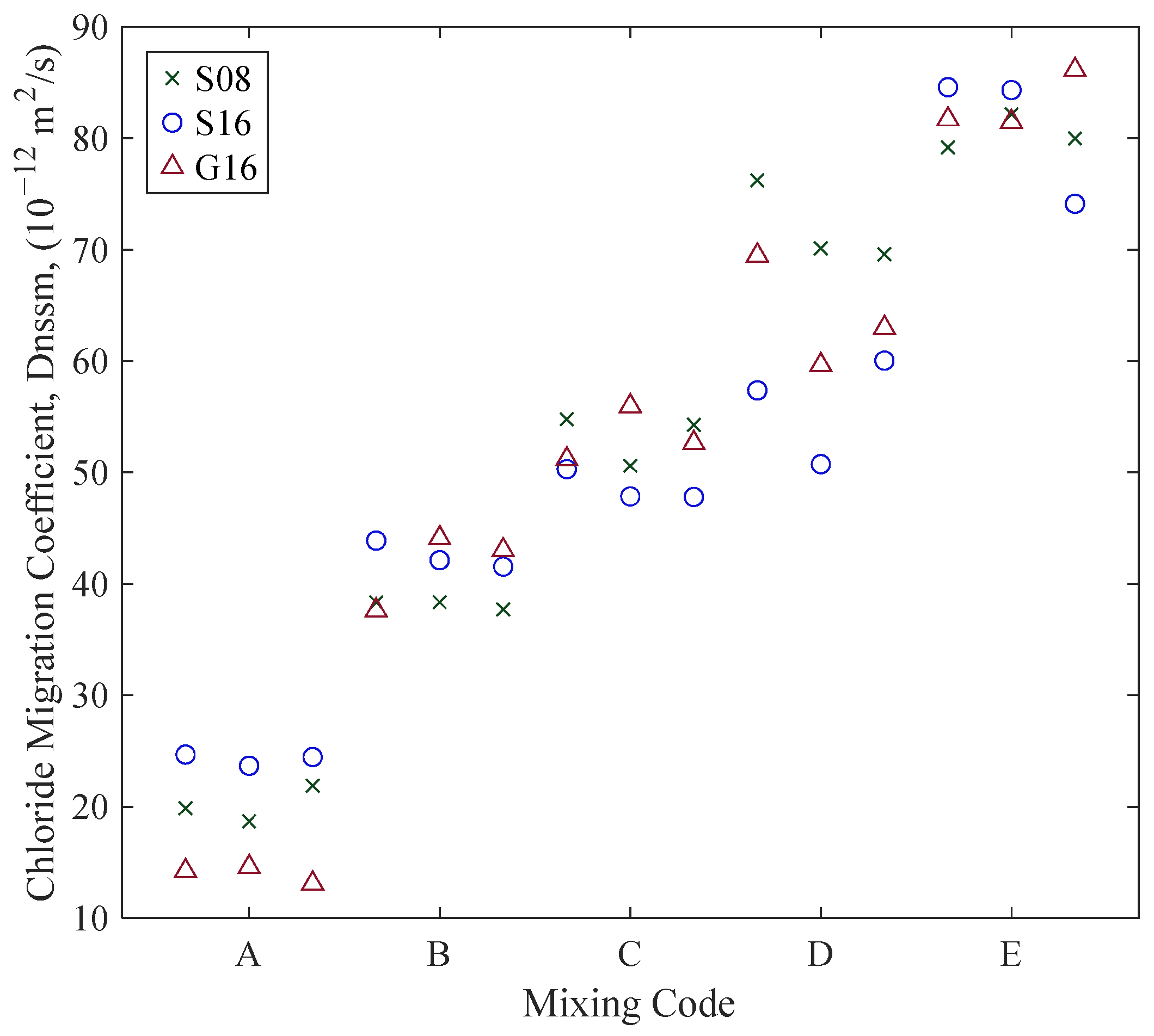
3.2. Correlation of Chloride Migration Coefficients with ER
- is the electrical resistivity,
- σ is the electrical conductivity.
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Aggregate Size and Type
4.2. Effect of Saturation Level
4.3. Combined (SonReb) or Single Methods
4.4. Electrical Resistivity and In Situ Measurement
4.5. Scaling the Findings to Use in Full Scale
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UNEP. 2021 Global Status Report for Buildings and Construction: Towards a Zero-emission. In Efficient and Resilient Buildings and Construction Sector; UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 2021; pp. 1–105. [Google Scholar]
- Cancio Díaz, Y.; Sánchez Berriel, S.; Heierli, U.; Favier, A.R.; Machado, I.R.S.; Scrivener, K.L.; Hernández, J.F.M.; Habert, G. Limestone calcined clay cement as a low-carbon solution to meet expanding cement demand in emerging economies. Dev. Eng. 2017, 2, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP. Global Resources Outlook 2024 Bend the Trend—Pathways to a Liveable Planet as Resource Use Spikes; UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- UNEP. 2023 Global Status Report for Buildings and Construction: Beyond Foundations—Mainstreaming Sustainable Solutions to Cut Emissions from the Buildings Sector; UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, P.J.M.; Miller, S.A.; Horvath, A. Towards sustainable concrete. Nat. Mater. 2017, 16, 698–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbabi, M.S.; Carrigan, C.; McKenna, S. Trends and developments in green cement and concrete technology. Int. J. Sustain. Built Environ. 2012, 1, 194–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhardt, L.C.M.; Birgisdottir, H.; Birkved, M. Potential of Circular Economy in Sustainable Buildings. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 471, 092051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oluleye, B.I.; Chan, D.W.M.; Saka, A.B.; Olawumi, T.O. Circular economy research on building construction and demolition waste: A review of current trends and future research directions. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 357, 131927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López Ruiz, L.A.; Roca Ramón, X.; Gassó Domingo, S. The circular economy in the construction and demolition waste sector—A review and an integrative model approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 248, 119238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addis, B. Building with Reclaimed Components and Materials; Routledge: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.T.; Kirkelund, G.M.; Lu, Z.; Mao, R.; Kunther, W.; Rode, C.; Slabik, S.; Hafner, A.; Sameer, H.; Dürr, H.H.; et al. Mapping circular economy practices for steel, cement, glass, brick, insulation, and wood—A review for climate mitigation modeling. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 202, 114697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küpfer, C.; Bastien-Masse, M.; Fivet, C. Reuse of concrete components in new construction projects: Critical review of 77 circular precedents. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 383, 135235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küpfer, C.; Bastien-Masse, M.; Devènes, J.; Fivet, C. Environmental and economic analysis of new construction techniques reusing existing concrete elements: Two case studies. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1078, 012013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devènes, J.; Brütting, J.; Küpfer, C.; Bastien-Masse, M.; Fivet, C. Re:Crete—Reuse of concrete blocks from cast-in-place building to arch footbridge. Structures 2022, 43, 1854–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission; Joint Research Centre; Jenet, A.; Lamperti Tornaghi, M.; Tsionis, G.; Sejersen, A.; Moseley, P.; De La Fuente Nuno, A.; Wrobel, M.; Hobbs, G.; et al. Circular Technologies in Construction—Putting Science into Standards; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottosen, L.M.; Gustafsson, K.F. Enabling reuse of structural components through documentation of quality. In Building A Circular Future—Insights from Interdisciplinary Reseach; BLOXHUB: Kobenhavn, Denmark, 2024; pp. 153–155. [Google Scholar]
- Anastasiades, K.; Dockx, J.; van den Berg, M.; Rinke, M.; Blom, J.; Audenaert, A. Stakeholder perceptions on implementing design for disassembly and standardisation for heterogeneous construction components. Waste Manag. Res. 2023, 41, 1372–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottosen, L.M.; Kunther, W.; Ingeman-Nielsen, T.; Karatosun, S. Non-Destructive Testing for Documenting Properties of Structural Concrete for Reuse in New Buildings: A Review. Materials 2024, 17, 3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breysse, D.; Balayssac, J.P. {Non-Destructive} In Situ Strength Assessment of Concrete: Practical Application of the {RILEM} {TC} {249-ISC} Recommendations; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Schabowicz, K. Non-destructive testing of materials in civil engineering. Materials 2019, 12, 3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederleithinger, E. NDE 4.0 in Civil Engineering BT—Handbook of Nondestructive Evaluation 4.0; Meyendorf, N., Ida, N., Singh, R., Vrana, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 937–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helal, J.; Sofi, M.; Mendis, P. Non-destructive testing of concrete: A review of methods. Electron. J. Struct. Eng. 2015, 14, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarsa, P.; Gupta, R. Electrical Resistivity of Concrete for Durability Evaluation: A Review. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 2017, 8453095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushpakumara, B.H.J.; De Silva, S.; De Silva, G.H.M.J.S. Visual inspection and non-destructive tests-based rating method for concrete bridges. Int. J. Struct. Eng. 2017, 8, 74–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kog, Y.C. Estimating In Situ Compressive Strength of Existing Concrete Structures. Pract. Period. Struct. Des. Constr. 2018, 23, 04018013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breccolotti, M.; Bonfigli, M.F. I-SonReb: An improved NDT method to evaluate the in situ strength of carbonated concrete. Nondestruct. Test. Eval. 2015, 30, 327–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JGJ/T 23; Technical Specification for Inspecting of Concrete Compressive Strength by Rebound Method. China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Craeye, B.; van de Laar, H.; van der Eijk, J.; Gijbels, W.; Lauriks, L. On-site strength assessment of limestone based concrete slabs by combining non-destructive techniques. J. Build. Eng. 2017, 13, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucinotti, R. In situ concrete strength assessment: Part I—The use of multiple combined nondestructive testing. Int. J. Microstruct. Mater. Prop. 2009, 4, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha Araújo, E.; Macioski, G.; Henrique Farias de Medeiros, M. Concrete surface electrical resistivity: Effects of sample size, geometry, probe spacing and SCMs. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 324, 126659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breysse, D. Nondestructive evaluation of concrete strength: An historical review and a new perspective by combining NDT methods. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 33, 139–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.T.; Sbartaï, Z.M.; Lataste, J.F.; Breysse, D.; Bos, F. Assessing the spatial variability of concrete structures using NDT techniques—Laboratory tests and case study. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 49, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, E.V.; Kristensen, L.F. Sea Dredged Gravel versus Crushed Granite as Coarse Aggregate for Self Compacting Concrete in Aggressive Environment. Nord. Concr. Res. 2007, 36, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- International Atomic Energy Agency. Guidebook on non-destructive testing of concrete structures. Ind. Appl. Chem. Sect. IAEA 2002, 17, 231. [Google Scholar]
- Naik, T.R.; Malhotra, V.M.; Popovics, J.S. The ultrasonic pulse velocity method. In Handbook on Nondestructive Testing of Concrete, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- EN 12504-4:2021; Testing Concrete in Structures—Part 4: Determination of Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2021.
- Malhotra, V.M. Surface Hardness Methods. In Handbook on Nondestructive Testing of Concrete; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 12504-2:2021; Testing Concrete in Structures—Part 2: Non-Destructive Testing—Determination of Rebound Number. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2021.
- Lauer, K.R. Magnetic/Electrical Methods. In Handbook on Nondestructive Testing of Concrete; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carino, N.J. Methods to evaluate corrosion of reinforcement. In Handbook on Nondestructive Testing of Concrete; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; Volume 11. [Google Scholar]
- Proceq. Resipod Family Operating Instructions—Concrete Durability Testing; Proceq: Schwerzenbach, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- NT Build 492; Concrete, Mortar and Cement-Based Repair Materials: Chloride Migration Coefficient from Non-Steady-State Migration Experiments. Nordtest: Espoo, Finland, 1999; pp. 1–8.
- Breysse, D.; Balayssac, J.P.; Biondi, S.; Corbett, D.; Goncalves, A.; Grantham, M.; Luprano, V.A.M.; Masi, A.; Monteiro, A.V.; Sbartai, Z.M. Recommendation of RILEM TC249-ISC on non destructive in situ strength assessment of concrete. Mater. Struct./Mater. Constr. 2019, 52, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali-Benyahia, K.; Sbartaï, Z.M.; Breysse, D.; Ghrici, M.; Kenai, S. Improvement of nondestructive assessment of on-site concrete strength: Influence of the selection process of cores location on the assessment quality for single and combined NDT techniques. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 195, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breysse, D.; Balayssac, J.-P.; Alwash, M.; Biondi, S.; Chiauzzi, L.; Corbett, D.; Garnier, V.; Gonçalves, A.; Grantham, M.; Gunes, O.; et al. In-Situ Strength Assessment of Concrete: Detailed Guidelines. In Non-Destructive In Situ Strength Assessment of Concrete; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 3–56. [Google Scholar]
- Rui, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Qiu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, W.; Fan, J. A robust triaxial localization method of AE source using refraction path. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2024, 34, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Rui, Y.; Pu, Y. Joint Inversion of AE/MS Sources and Velocity with Full Measurements and Residual Estimation. Rock. Mech. Rock. Eng. 2024, 57, 7371–7386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balayssac, J.P.; Laurens, S.; Arliguie, G.; Breysse, D.; Garnier, V.; Dérobert, X.; Piwakowski, B. Description of the general outlines of the French project SENSO—Quality assessment and limits of different NDT methods. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 35, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Maio, A.A.; Zega, C.J.; Traversa, L.P. Estimation of compressive strength of recycled concretes with the ultrasonic method. J. ASTM Int. 2005, 2, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maio AADi Traversa, L.P.; Giovambattista, A. Nondestructive Combined Methods Applied to Structural Concrete Members. Cem. Concr. Aggreg. 1985, 7, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengul, O. Use of electrical resistivity as an indicator for durability. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 73, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candelaria, M.D.E.; Kee, S.H.; Yee, J.J.; Lee, J.W. Effects of saturation levels on the ultrasonic pulse velocities and mechanical properties of concrete. Materials 2021, 14, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohdaira, E.; Masuzawa, N. Water content and its effect on ultrasound propagation in concrete—The possibility of NDE. Ultrasonics 2000, 38, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brencich, A.; Cassini, G.; Pera, D.; Riotto, G. Calibration and Reliability of the Rebound (Schmidt) Hammer Test. Civil Eng. Archit. 2013, 1, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.T.; Chang, J.J.; Yeih, W.C. The effects of specimen parameters on the resistivity of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 71, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaswari, H.Y. Concrete strength by combined nondestructive methods simply and reliably predicted. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 739–746. [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs, B.; Tchoketch Kebir, M. Non-destructive testing techniques for the forensic engineering investigation of reinforced concrete buildings. Forensic Sci. Int. 2007, 167, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, K.; Waqas, R. Compressive strength evaluation by non-destructive techniques: An automated approach in construction industry. J. Build. Eng. 2017, 12, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaze, P.; Beno, P. The use of combined non-destructive testing methods to determine the compressive strength of concrete. Matériaux Constr. 1984, 17, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbartaï, Z.M.; Luprano, V.A.M.; Vasanelli, E. Evaluation of Concrete Strength by Combined NDT Techniques: Practice, Possibilities and Recommendations. In Non-Destructive In Situ Strength Assessment of Concrete; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 101–116. [Google Scholar]
- Hannachi, S.; Guetteche, M.N. Application of the Combined Method for Evaluating the Compressive Strength of Concrete on Site. Open J. Civil Eng. 2012, 02, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengul, O.; Gjørv, O.E. Effect of embedded steel on electrical resistivity measurements on concrete structures. ACI Mater. J. 2009, 106, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengul, O.; Gjørv, O.E. Electrical resistivity measurements for quality control during concrete construction. ACI Mater. J. 2008, 105, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, P.; Tran, Q. Correlation Between Bulk and Surface Resistivity of Concrete. Int. J. Concr. Struct. Mater. 2015, 9, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layssi, H.; Ghods, P.; Alizadeh, A.R.; Salehi, M. Electrical resistivity of concrete: Concepts, applications, and measurement techniques. Concr. Int. 2015, 37, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, R.; Gaboreau, S.; Gance, J.; Ignatiadis, I.; Betelu, S. Reinforced concrete structures: A review of corrosion mechanisms and advances in electrical methods for corrosion monitoring. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 269, 121240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouteiller, V.; Marie-Victoire, E.; Cremona, C. Mathematical relation of steel thickness loss with time related to reinforced concrete contaminated by chlorides. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 124, 764–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- EN 13791:2019; Assessment of In-Situ Compressive Strength in Structures and Precast Concrete Components. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2019.




| Batch No. | Mixing Code | Concrete Constituent (kg/m3) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cement | Water | w/c | Sand 0–4 | Sea Stone 4–8 | Sea Stone 8–16 | Granite 4–8 | Granite 8–16 | SP * | ||
| 1 | S16A | 363 | 163 | 0.45 | 850 | 380 | 600 | - | - | 3.1 |
| 2 | S16B | 310 | 183 | 0.59 | 850 | 380 | 600 | - | - | 2.2 |
| 3 | S16C | 287 | 187 | 0.65 | 850 | 380 | 600 | - | - | 1.6 |
| 4 | S16D | 265 | 195 | 0.74 | 850 | 380 | 600 | - | - | 0.6 |
| 5 | S16E | 241 | 202 | 0.84 | 850 | 380 | 600 | - | - | 0.0 |
| 6 | S08A | 363 | 163 | 0.45 | 730 | 1100 | - | - | - | 3.4 |
| 7 | S08B | 310 | 183 | 0.59 | 730 | 1100 | - | - | - | 2.2 |
| 8 | S08C | 287 | 187 | 0.65 | 730 | 1100 | - | - | - | 1.6 |
| 9 | S08D | 265 | 195 | 0.74 | 730 | 1100 | - | - | - | 1.3 |
| 10 | S08E | 241 | 202 | 0.84 | 730 | 1100 | - | - | - | 0.9 |
| 11 | G16A | 413 | 185 | 0.45 | 810 | - | - | 380 | 560 | 3.4 |
| 12 | G16B | 349 | 206 | 0.59 | 810 | - | - | 380 | 560 | 2.2 |
| 13 | G16C | 327 | 213 | 0.65 | 810 | - | - | 380 | 560 | 1.6 |
| 14 | G16D | 301 | 221 | 0.74 | 810 | - | - | 380 | 560 | 0.9 |
| 15 | G16E | 274 | 230 | 0.84 | 810 | - | - | 380 | 560 | 0.0 |
| Test | Parameter | Sample Size (n) | Min. | Mean | Median | Max. | Std Dev. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ultrasonic velocity (UPV) | VOD (km/s) | 75 | 3.582 | 3.908 | 3.912 | 4.296 | 0.192 |
| VAD (km/s) | 75 | 3.976 | 4.271 | 4.294 | 4.580 | 0.162 | |
| VSSD (km/s) | 75 | 4.200 | 4.474 | 4.490 | 4.703 | 0.148 | |
| Rebound hammer (RH) | QOD (-) | 75 | 43.0 | 52.0 | 52.5 | 61.0 | 5.2 |
| QAD (-) | 75 | 38.0 | 49.7 | 50.5 | 59.5 | 5.7 | |
| QSSD (-) | 75 | 31.0 | 43.6 | 45.0 | 55.0 | 6.5 | |
| Compressive Strength | fc (MPa) | 75 | 20.43 | 37.21 | 36.30 | 59.06 | 10.54 |
| Electrical Resistivity (ER) | (kΩcm) | 45 | 10.28 | 18.37 | 13.12 | 47.30 | 10.02 |
| (kΩcm) | 45 | 9.70 | 17.16 | 12.85 | 42.34 | 8.97 | |
| (kΩcm) | 45 | 5.23 | 9.43 | 7.56 | 20.11 | 4.18 | |
| Chloride Migration | Dnssm (×10−12 m2/s) | 45 | 13.09 | 51.49 | 50.74 | 86.14 | 21.69 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karatosun, S.; Ingeman-Nielsen, T.; Ottosen, L.M. Evaluation of NDT Methods for In Situ Documentation of Concrete for Reuse: Laboratory Studies. Materials 2025, 18, 2470. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112470
Karatosun S, Ingeman-Nielsen T, Ottosen LM. Evaluation of NDT Methods for In Situ Documentation of Concrete for Reuse: Laboratory Studies. Materials. 2025; 18(11):2470. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112470
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaratosun, Serkan, Thomas Ingeman-Nielsen, and Lisbeth M. Ottosen. 2025. "Evaluation of NDT Methods for In Situ Documentation of Concrete for Reuse: Laboratory Studies" Materials 18, no. 11: 2470. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112470
APA StyleKaratosun, S., Ingeman-Nielsen, T., & Ottosen, L. M. (2025). Evaluation of NDT Methods for In Situ Documentation of Concrete for Reuse: Laboratory Studies. Materials, 18(11), 2470. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112470









