A View on the Synthesis and Characterization of Porous Microspheres Containing Pyrrolidone Units
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Direct suspension copolymerization of NVP with ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA) under varying monomer ratios and diluent systems to explore the influence on morphology, porosity, and thermal stability.
- Post-polymerization modification of poly(GMA-co-EGDMA) copolymers via reaction with pyrrolidone to evaluate the functionalization efficiency and preservation of the porous architecture.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Syntheses of the Porous Microspheres
2.3. Measurement Techniques
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghosh Dastidar, D.; Saha, S.; Chowdhury, M. Porous microspheres: Synthesis, characterisation and applications in pharmaceutical & medical fields. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 548, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grochowicz, M. Poly (glycidyl methacrylate-co-1,4-dimethacryloyloxybenzene) monodisperse microspheres—Synthesis, characterization and application as chromatographic packings in RP-HPLC. React. Funct. Polym. 2019, 137, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Peng, Q.; Wang, S.; Guo, L.; Cong, H.; Shen, Y.; Yu, B. Preparation of poly (KH570-co-DVB) microspheres and application in HPLC for separation of benzene and benzene homologs. Ferroelectrics 2020, 562, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lengyel, M.; Kállai-Szabó, N.; Antal, V.; Laki, A.J.; Antal, I. Microparticles, Microspheres, and Microcapsules for Advanced Drug Delivery. Sci. Pharm. 2019, 87, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankala, R.K.; Zhao, J.; Liu, C.; Song, X.; Yang, D.; Zhu, K.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.S.; Chen, A. Highly porous microcarriers for minimally invasive in situ skeletal muscle cell delivery. Small 2019, 15, e1901397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edward, D.A.; Hanes, J.; Caponetti, G.; Hrkach, J.; Ben-Jebria, A.; Eskew, M.L.; Mintzes, J.; Deaver, D.; Lotan, N.; Langer, R. Large porous particles for pulmonary drug delivery. Science 1997, 276, 1868–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokmen, M.T.; Du Prez, F.E. Porous polymer particles—A comprehensive guide to synthesis, characterization, functionalization and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 365–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wu, H.; Peng, C.; He, J.; Pu, Z.; Lin, Z.; Wang, J.; Hu, Y.; Su, Q.; Zhou, B.; et al. From the microspheres to scaffolds: Advances in polymer microsphere scaffolds for bone regeneration applications. Biomater. Transl. 2024, 5, 274–299. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, L.; Tan, B. Hypercrosslinked porous polymer materials: Design, synthesis, and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 3322–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germain, J.; Frechet, J.M.; Svec, F. Hypercrosslinked Polyanilines with Nanoporous Structure and High Surface Area: Potential Adsorbents for Hydrogen Storage. J. Mat. Chem. 2007, 17, 4989–4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, R.T.; Kessler, M.; Lima, S.; Rinaldi, R. Hypercrosslinked MicroporousPolymer Sorbents for the Efficient Recycling of a Soluble Acid Catalyst in Cellulose Hydrolysis. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 2374–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Z.; Wang, P.; Yan, Y.; Ran, J. Adsorption Materials for Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) and the Key Factors for VOCs Adsorption Process: A Review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 235, 116213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Yao, J.; Yang, Z.; Sun, H.; Liu, W. Silane-Based Hyper-Cross-Linked PorousPolymers and Their Applications in Gas Storage and Water Treatment. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 10469–10478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, A.; Baig, N.; Ullah, N.; Falath, W. Removal of Hazardous Dyes, Toxic Metal Ions and Organic Pollutants from Wastewater by Using Porous Hyper-Cross-Linked Polymeric Materials: A Review of Recent Advances. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 287, 112360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Turner, S.R. Hypercrosslinked Polymers: A Review. Polym. Rev. 2017, 58, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzyszczak-Turczyn, A.; Grochowicz, M.; Jonik, I.; Sadok, I. Removal of polyphenols from anthocyanin-rich extracts using 4-vinylpyridine crosslinked copolymers. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunin, R. The use of macroreticular polymeric adsorbents for the treatment of waste effluents. Pure Appl. Chem. 1976, 46, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azanova, V.V.; Hradil, J. Sorption properties of macroporous and hypercrosslinked copolymers. React. Funct. Polym. 1999, 41, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusler, G.M.; Browne, T.E.; Cohen, Y. Sorption of organics from aqueous solution onto polymeric resins. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1993, 32, 2727–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvazinia, M. Atmospheric water harvesting using sulfonated macroporous and hypercrosslinked polystyrene-divinylbenzene beads in a prototype system. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 360, 131096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podkościelna, B.; Wawrzkiewicz, M.; Klapiszewski, Ł. Synthesis, Characterization and Sorption Ability of Epoxy Resin-Based Sorbents with Amine Groups. Polymers 2021, 13, 4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grochowicz, M.; Szajnecki, Ł.; Rogulska, M. Crosslinked 4-vinylpyridine monodisperse functional microspheres for sorption of ibuprofen and ketoprofen. Polymers 2022, 14, 2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Cao, K.; Tang, H.; Li, C. Synthesis and characterization of poly(St-co-DVB)/montmorillonite nanocomposites by suspension polymerization. e-Polymers 2012, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podkościelna, B.; Kołodyńska, D.; Podkościelny, P. Chemical modification of commercial St-DVB microspheres and their application for metal ions removal. Adsorption 2019, 25, 529–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šálek, P.; Horák, D.; Hromádková, J. Novel Preparation of Monodisperse Poly(styrene-co-divinylbenzene) Microspheres by Controlled Dispersion Polymerization. Polym. Sci. Ser. B 2018, 60, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Xu, T.; Cong, H.; Peng, Q.; Usman, M. Preparation of Porous Poly (Styrene-Divinylbenzene) Microspheres and Their Modification with Diazoresin for Mix-Mode HPLC Separations. Materials 2017, 10, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, L.; Xiao, A.; Yu, H.; Ding, J.; Tan, Q.; Huo, J. Preparation of poly(divinylbenzene) microspheres with controllable pore structure using poly (propylene)/toluene as coporogen. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 113, 2997–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Chen, H.; Qu, R.; Wang, C.; Sun, C.; Zhou, W.; Yu, M.; Jiang, H. Highly crosslinked poly (styrene-co-divinylbenzene) microspheres prepared by precipitation polymerization: Effects of the polymerization parameters on the characteristics of the particles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 111, 3144–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejewska, M.; Gawdzik, J. Preparation and Characterization of Sorption Properties of Porous Microspheres of 1-Vinyl-2-Pyrrolidone-Divinylbenzene. J. Liq. Chrom. Relat. Tech. 2008, 31, 950–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ye, Y.; Li, W.; Pan, F.; Xia, D.; Li, A. The efficient adsorption of tetracycline from aqueous solutions onto polymers with different N-vinylpyrrolidone contents: Equilibrium, kinetic and dynamic adsorption. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 15158–15169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejewska, M.; Osypiuk-Tomasik, J. Sorption on porous copolymers of 1-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone-divinylbenzene. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2013, 114, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Malgar Puttaiahgowda, Y. N-vinylpyrrolidone antimicrobial polymers: Current trends and emerging perspectives. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 180, 111590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurmaz, S.V.; Fadeeva, N.V.; Ignat’ev, V.M.; Kurmaz, V.A.; Kurochkin, S.A.; Emel’yanova, N.S. Structure and State of Water in Branched N-Vinylpyrrolidone Copolymers as Carriers of a Hydrophilic Biologically Active Compound. Molecules 2020, 25, 6015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Lu, Q.; Cong, H.; Shen, Y.; Yu, B. Microporous Poly (glycidyl methacrylate-co-ethylene glycol dimethyl acrylate) Microspheres: Synthesis, Functionalization and Applications. Polym. Chem. 2021, 12, 6050–6070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.; Vermeeren, P.; Haim, A.; van Dorp, M.J.; Codée, J.D.; Bickelhaupt, F.M.; Hamlin, T.A. Regioselectivity of Epoxide Ring-Openings via SN2 Reactions Under Basic and Acidic Conditions. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 2020, 3822–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wawrzkiewicz, M.; Podkoscielna, B.; Podkoscielny, P. Application of functionalized DVB-co-GMA polymeric microspheres in the enhanced sorption process of hazardous dyes from dyeing baths. Molecules 2020, 25, 5247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejewska, M.; Kołodyńska, D. Synthesis and characterization of porous microspheres bearing pyrrolidone units. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 149–150, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejewska, M. Characterization of thermal properties of porous microspheres bearing pyrrolidone units. J. Therm. Anal Calorim. 2015, 119, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejewska, M.; Rogulska, M. Porous Copolymers of 3-(Trimethoxysilyl)propyl Methacrylate with Trimethylpropane Trimethacrylate Preparation: Structural Characterization and Thermal Degradation. Materials 2024, 17, 4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, K.; Everett, D.H.; Haul, R.A.; Moscou, L.; Pierotti, R.A.; Rouquerol, J.; Siemieniewska, T. Reporting Physisorption Data for Gas/Solid Systems with Special Reference to the Determination of Surface Area and Porosity. Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 57, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejewska, M. Characterization of macroporous 1-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone copolymers obtained by suspension polymerization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 124, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://webbook.nist.gov/cgi/inchi?ID=C106912&Mask=80 (accessed on 28 March 2025).
- Maciejewska, M.; Łastawiecka, E.; Grochowicz, M. Thermal Characterization of Crosslinked Polymeric Microspheres Bearing Thiol Groups Studied by TG/FTIR/DSC under Non-Oxidative Conditions. Materials 2024, 17, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
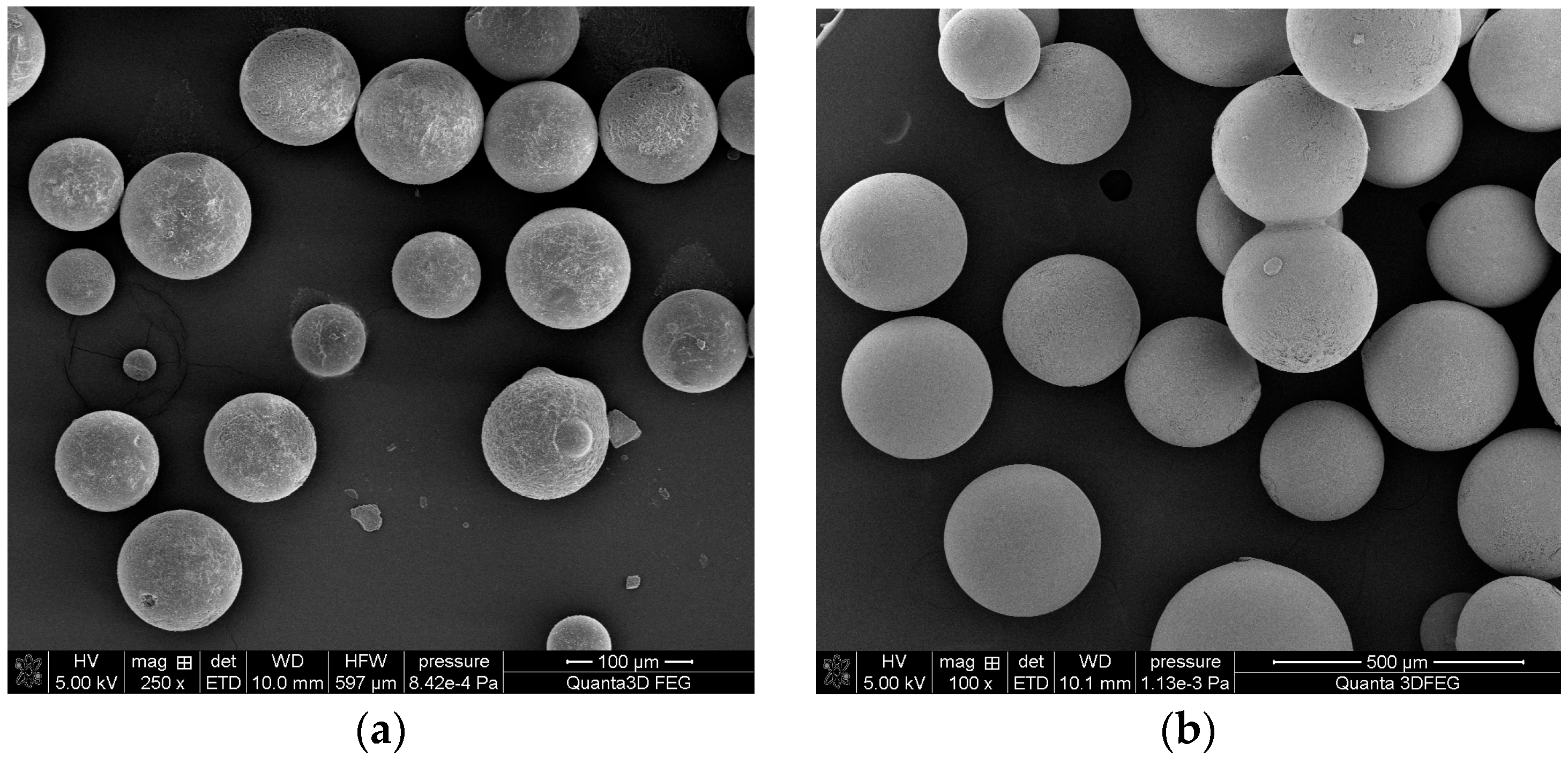
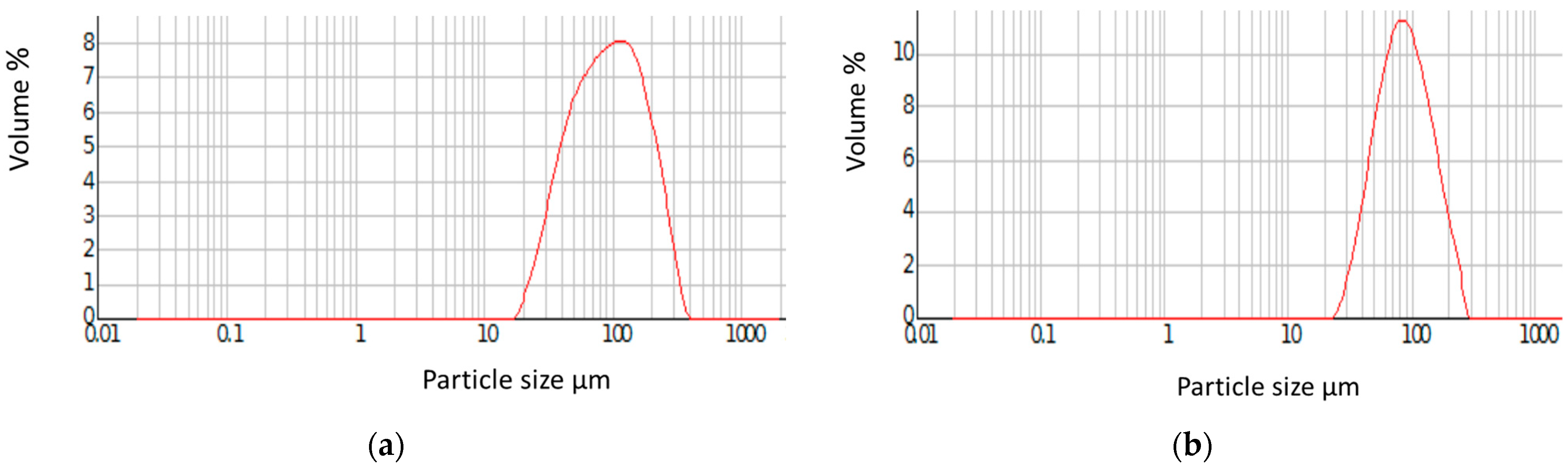

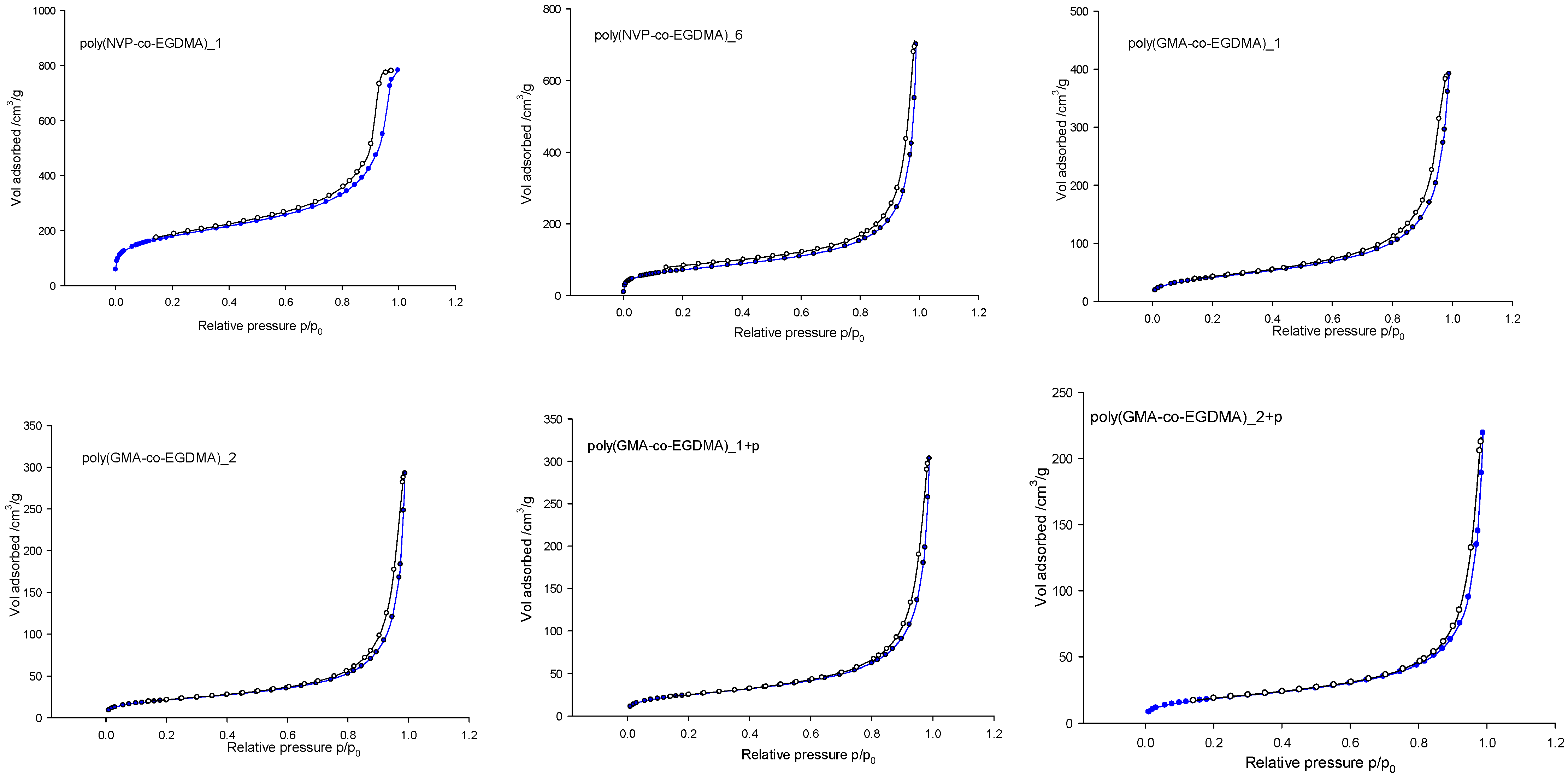
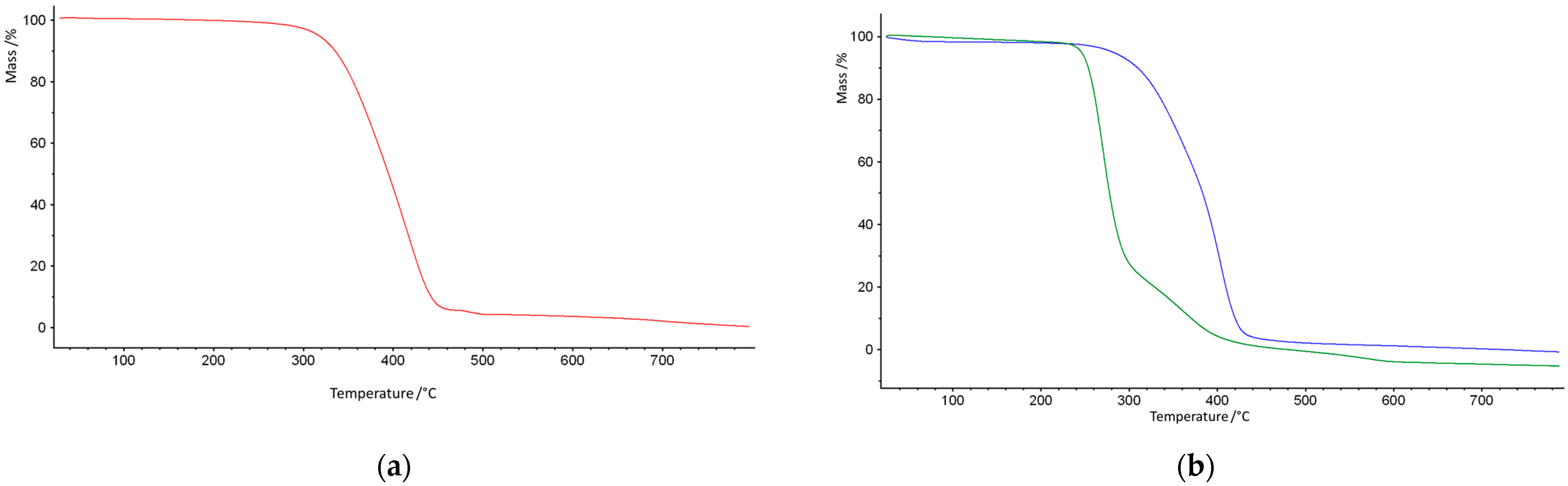
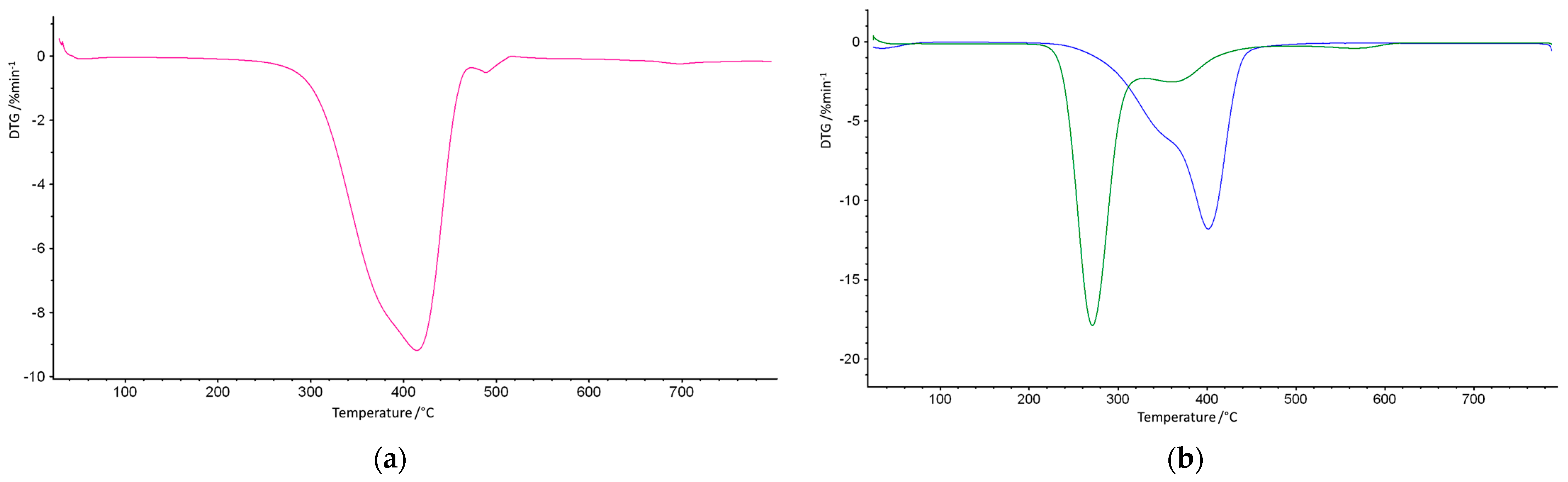
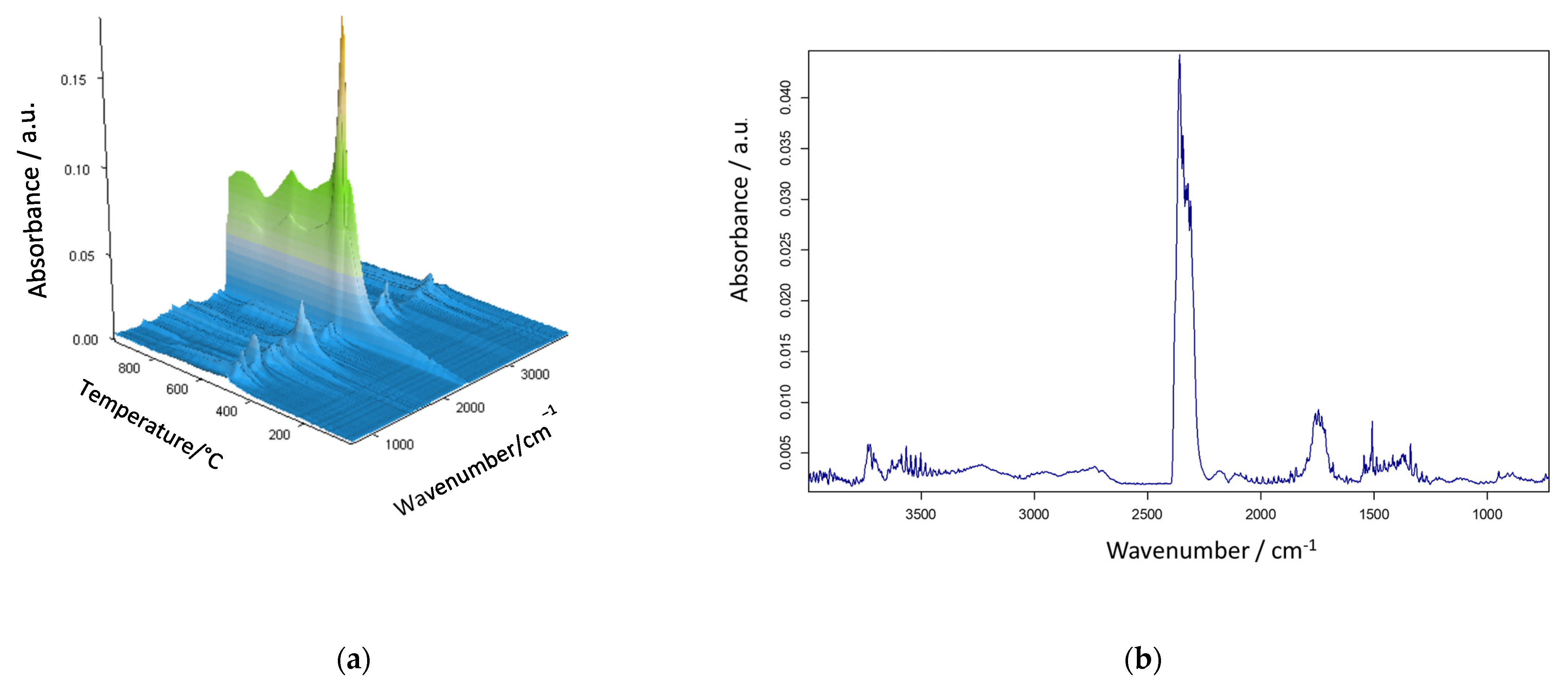

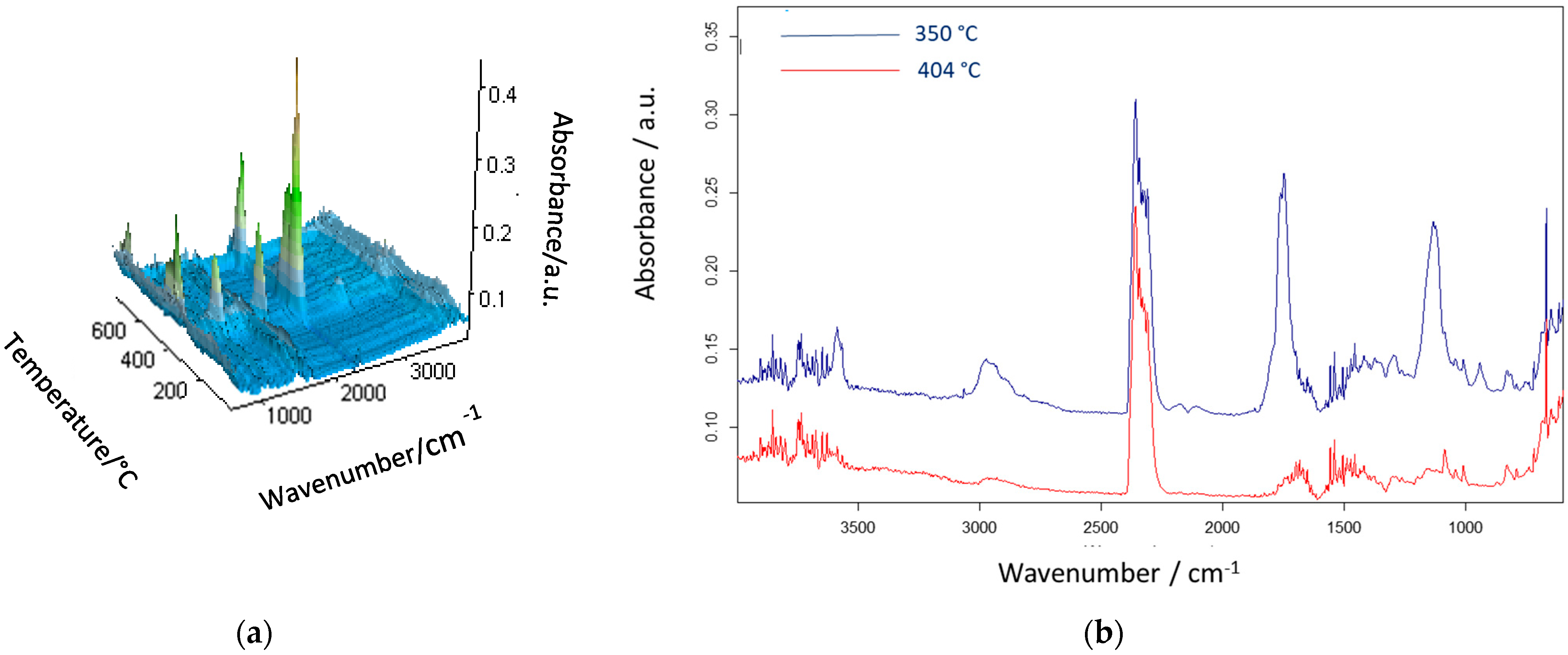
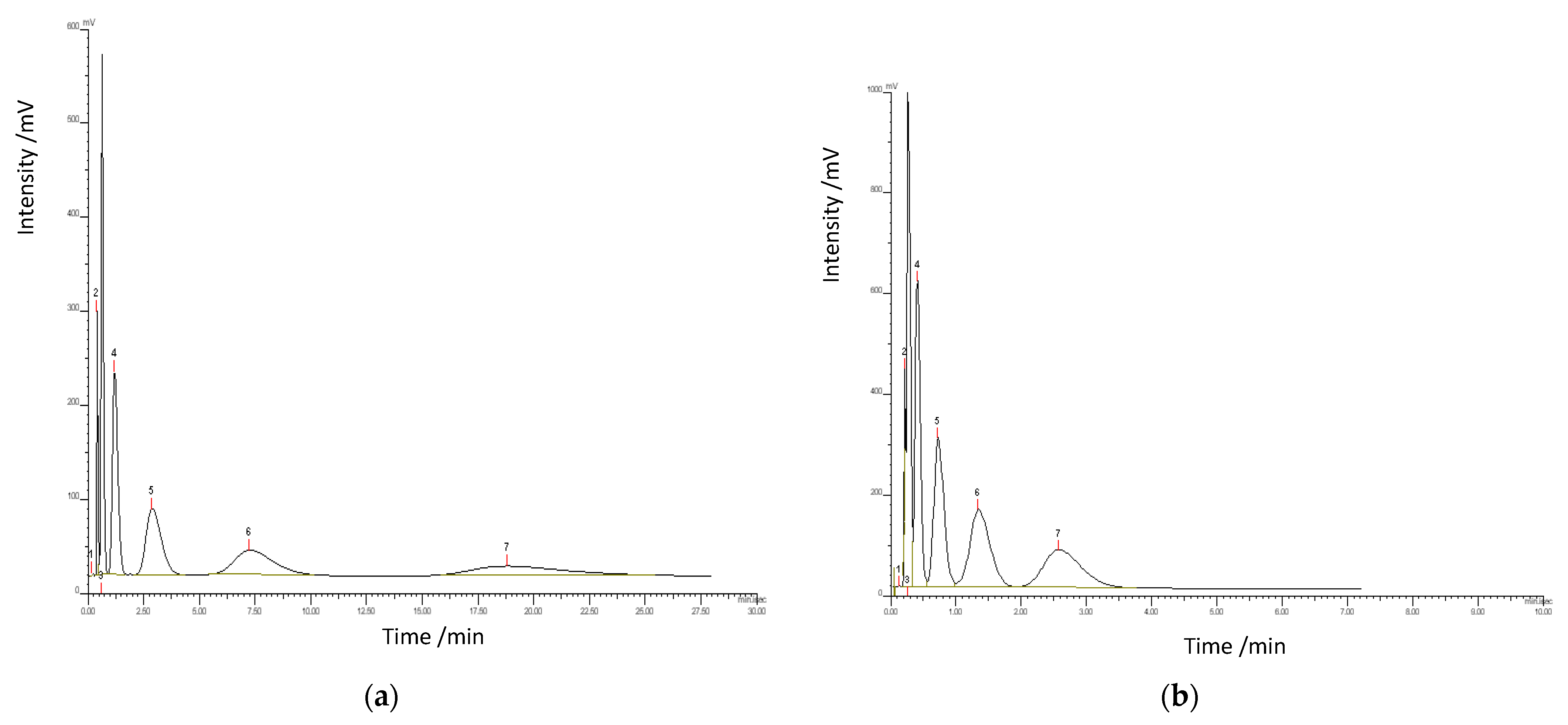
| Copolymer | Molar Ratio of Monomers | Diluents/mL | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EGDMA | VP | GMA | Toluene | Decan-1-ol | Dodecane | |
| poly(NVP-co-EGDMA)_1 | 1 | 1 | - | 22.5 | - | - |
| poly(NVP-co-EGDMA)_2 | 1 | 1 | - | 19.1 | 3.4 | - |
| poly(NVP-co-EGDMA)_3 | 1 | 1 | - | 11.25 | 11.25 | - |
| poly(NVP-co-EGDMA)_4 | 1 | 1 | - | 19.1 | - | 3.4 |
| poly(NVP-co-EGDMA)_5 | 1 | 1 | - | 11.25 | - | 11.25 |
| poly(NVP-co-EGDMA)_6 | 1 | 2 | - | 22.5 | - | |
| poly(NVP-co-EGDMA)_7 | 1 | 3 | - | 22.5 | - | - |
| poly(NVP-co-EGDMA)_8 | 1 | 4 | - | 22.5 | - | - |
| poly(GMA-co-EGDMA)_1 | 1 | - | 1 | 22.5 | - | - |
| poly(GMA-co-EGDMA)_2 | 2 | - | 1 | 22.5 | - | - |
| Copolymer | Specific Surface Area SBET (m2/g) | Pore Volume V (cm3/g) | Pore Diameter DBJH (nm) | N % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| poly(NVP-co-EGDMA)_1 | 456 | 0.675 | 31 | 3.01 |
| poly(NVP-co-EGDMA)_2 | 88 | 0.624 | 31 | 3.45 |
| poly(NVP-co-EGDMA)_3 | 76 | 0.313 | 50 | 3.60 |
| poly(NVP-co-EGDMA)_4 | 267 | 0.566 | 37 | 2.80 |
| poly(NVP-co-EGDMA)_5 | 190 | 0.275 | 40 | 2.97 |
| poly(NVP-co-EGDMA)_6 | 101 | 0.215 | 37 | 3.80 |
| poly(NVP-co-EGDMA)_7 | 81 | 0.284 | 38 | 4.40 |
| poly(NVP-co-EGDMA)_8 | 59 | 0.319 | 47 | 6.40 |
| poly(GMA-co-EGDMA)_1 | 109 | 0.483 | 39 | - |
| poly(GMA-co-EGDMA)_2 | 72 | 0.280 | 52 | - |
| poly(GMA-co-EGDMA)_1+p | 101 | 0.378 | 38 | 1.51 |
| poly(GMA-co-EGDMA)_2+p | 68 | 0.210 | 51 | 2.50 |
| Copolymer | T5% (°C) | T20% (°C) | T50% (°C) | T1max (°C) | T2max (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| poly(NVP-co-EGDMA)_1 | 317 | 355 | 394 | 417 | - |
| poly(GMA-co-EGDMA)_1 | 251 | 265 | 288 | 272 | 369 |
| poly(GMA-co-EGDMA)_2 | 245 | 257 | 276 | 265 | 367 |
| poly(GMA-co-EGDMA)_1+p | 283 | 337 | 385 | 350 | 404 |
| poly(GMA-co-EGDMA)_2+p | 277 | 301 | 348 | 334 | 370 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maciejewska, M. A View on the Synthesis and Characterization of Porous Microspheres Containing Pyrrolidone Units. Materials 2025, 18, 2432. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112432
Maciejewska M. A View on the Synthesis and Characterization of Porous Microspheres Containing Pyrrolidone Units. Materials. 2025; 18(11):2432. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112432
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaciejewska, Małgorzata. 2025. "A View on the Synthesis and Characterization of Porous Microspheres Containing Pyrrolidone Units" Materials 18, no. 11: 2432. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112432
APA StyleMaciejewska, M. (2025). A View on the Synthesis and Characterization of Porous Microspheres Containing Pyrrolidone Units. Materials, 18(11), 2432. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112432






