Study of Concrete Deterioration Damage by Landfill Leachate in Cold Regions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Concrete Specimen Preparation
2.2. Landfill Leachate
2.3. Test Design
3. Results and Discussion
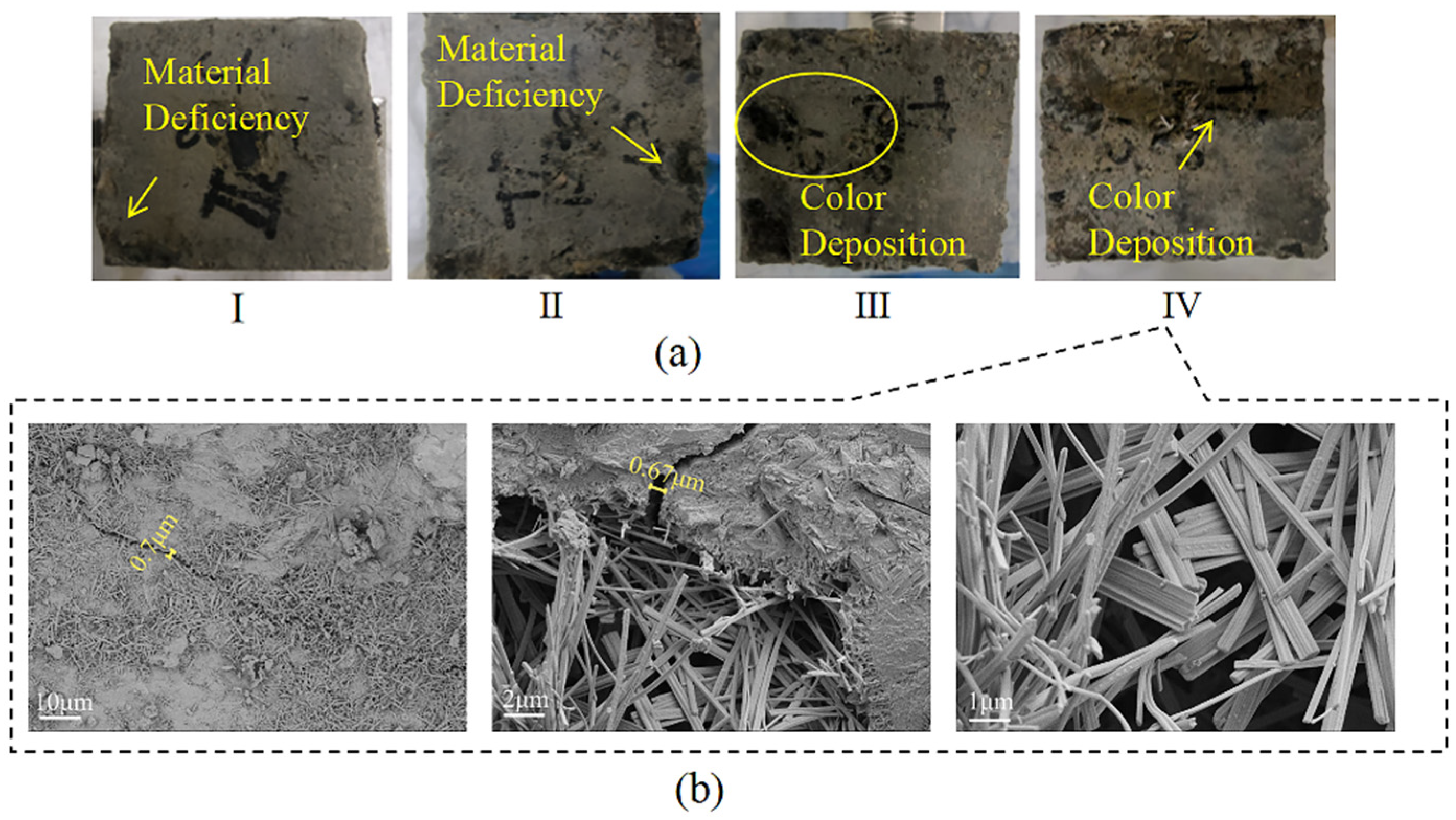
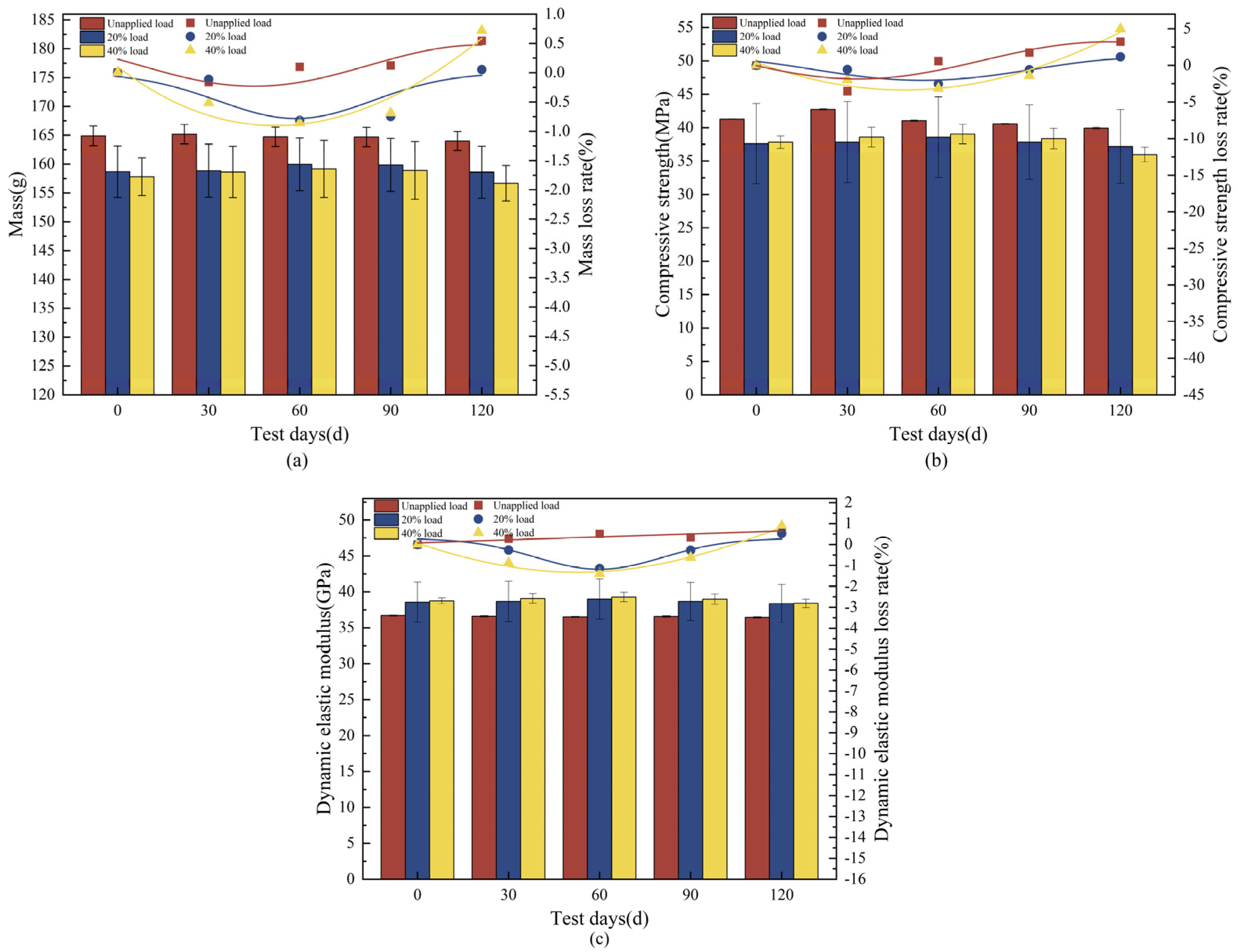
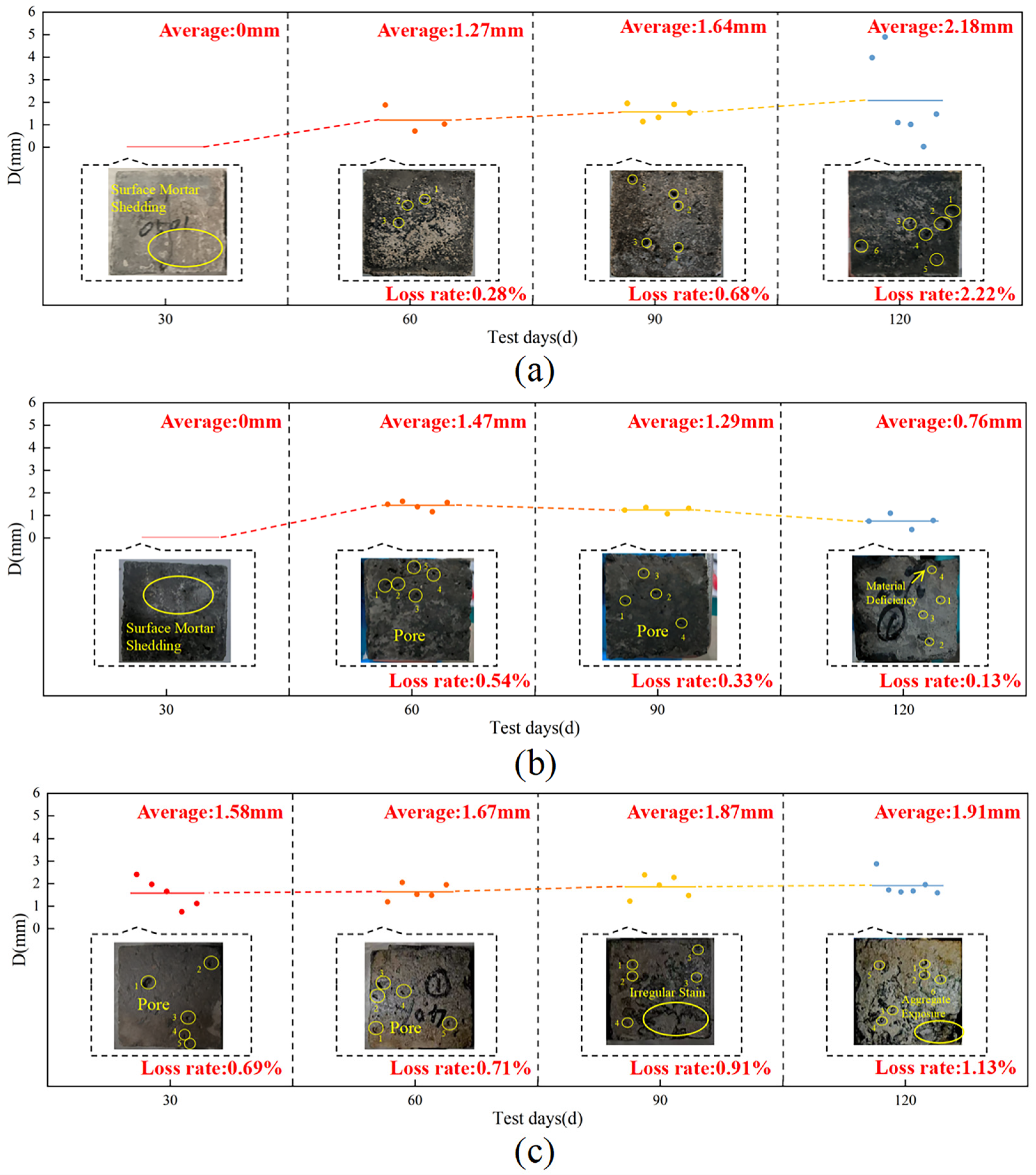
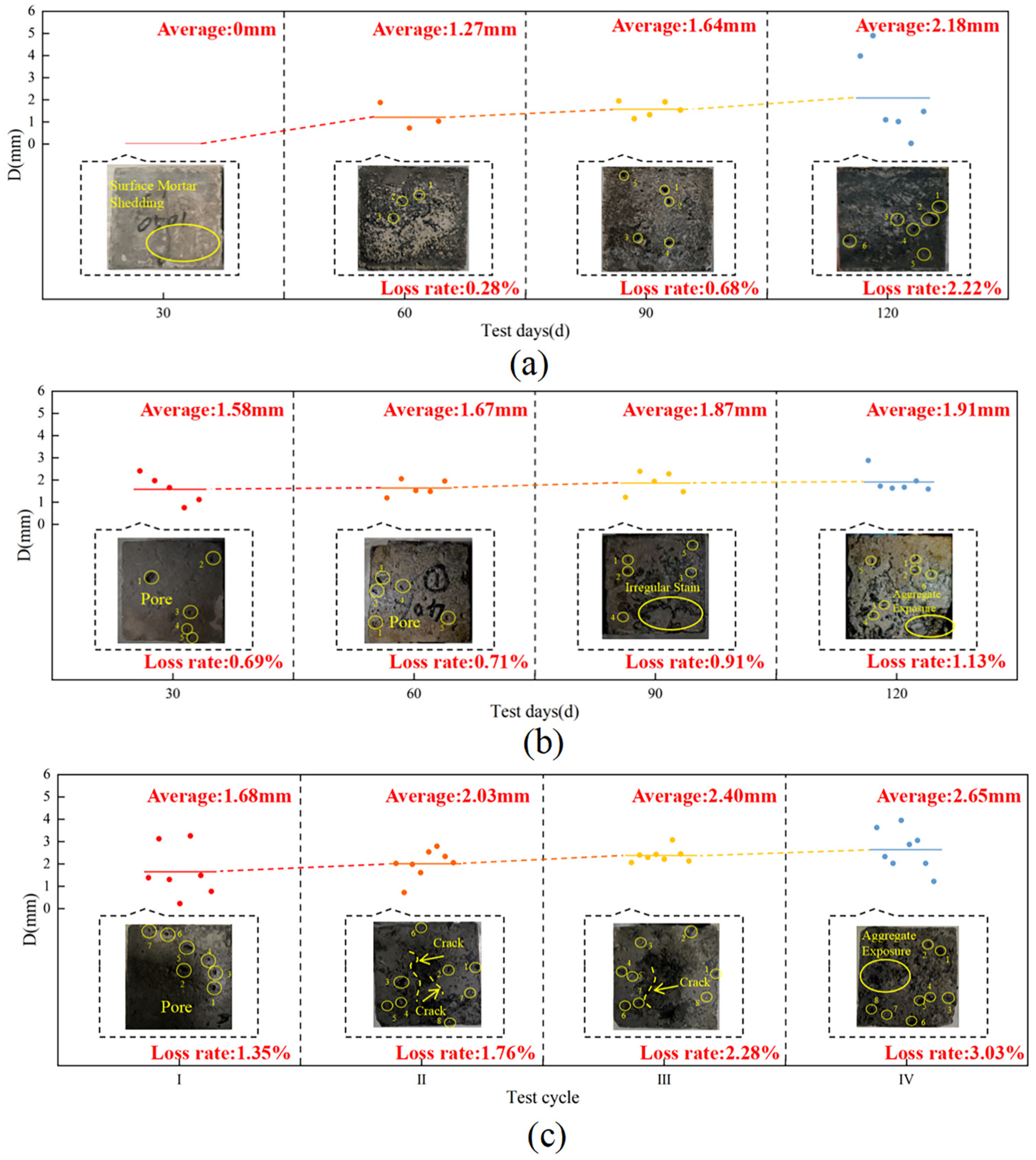
3.1. Concrete Deterioration Damage Under Loaded-Landfill Leachate Coupling
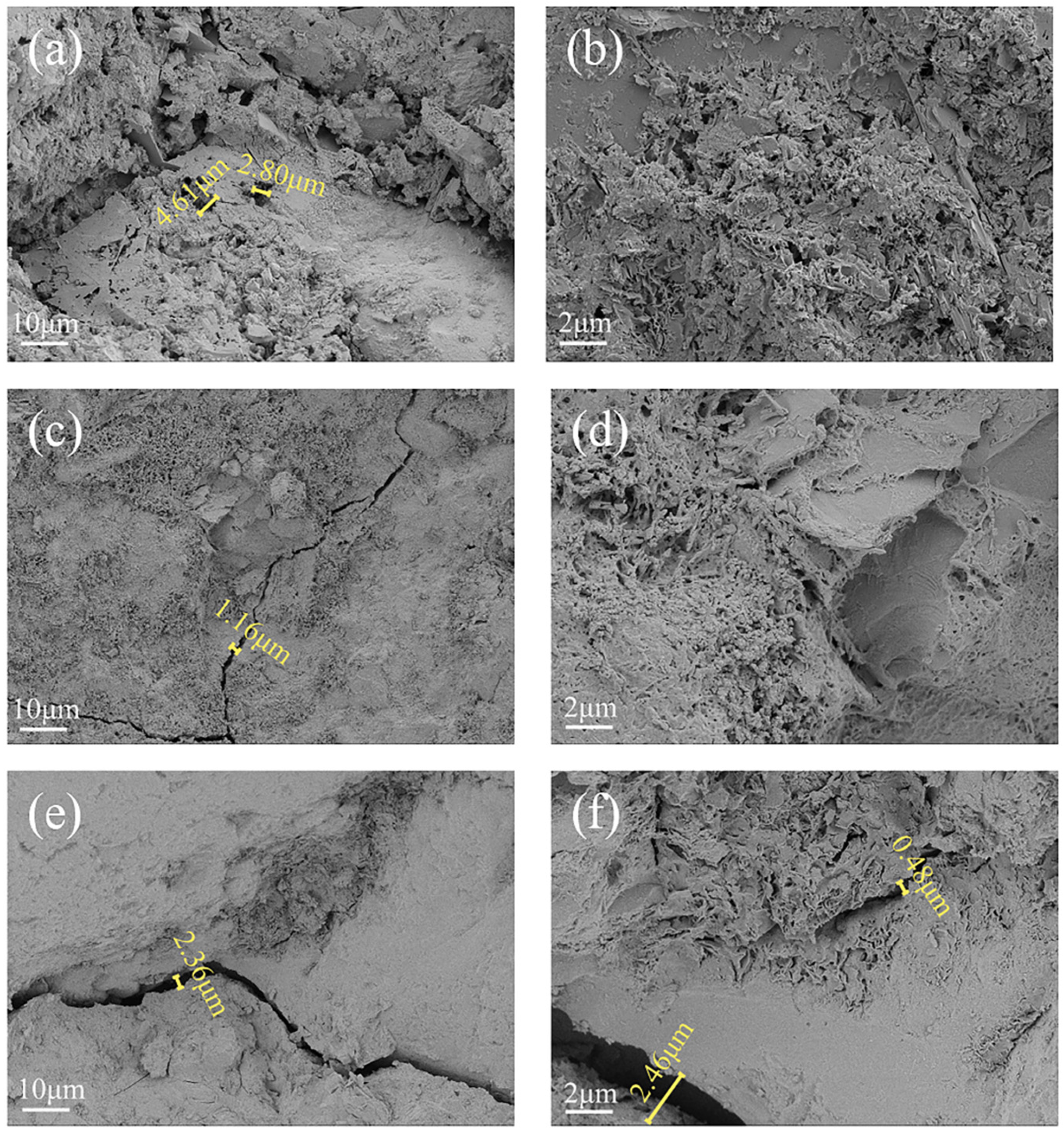
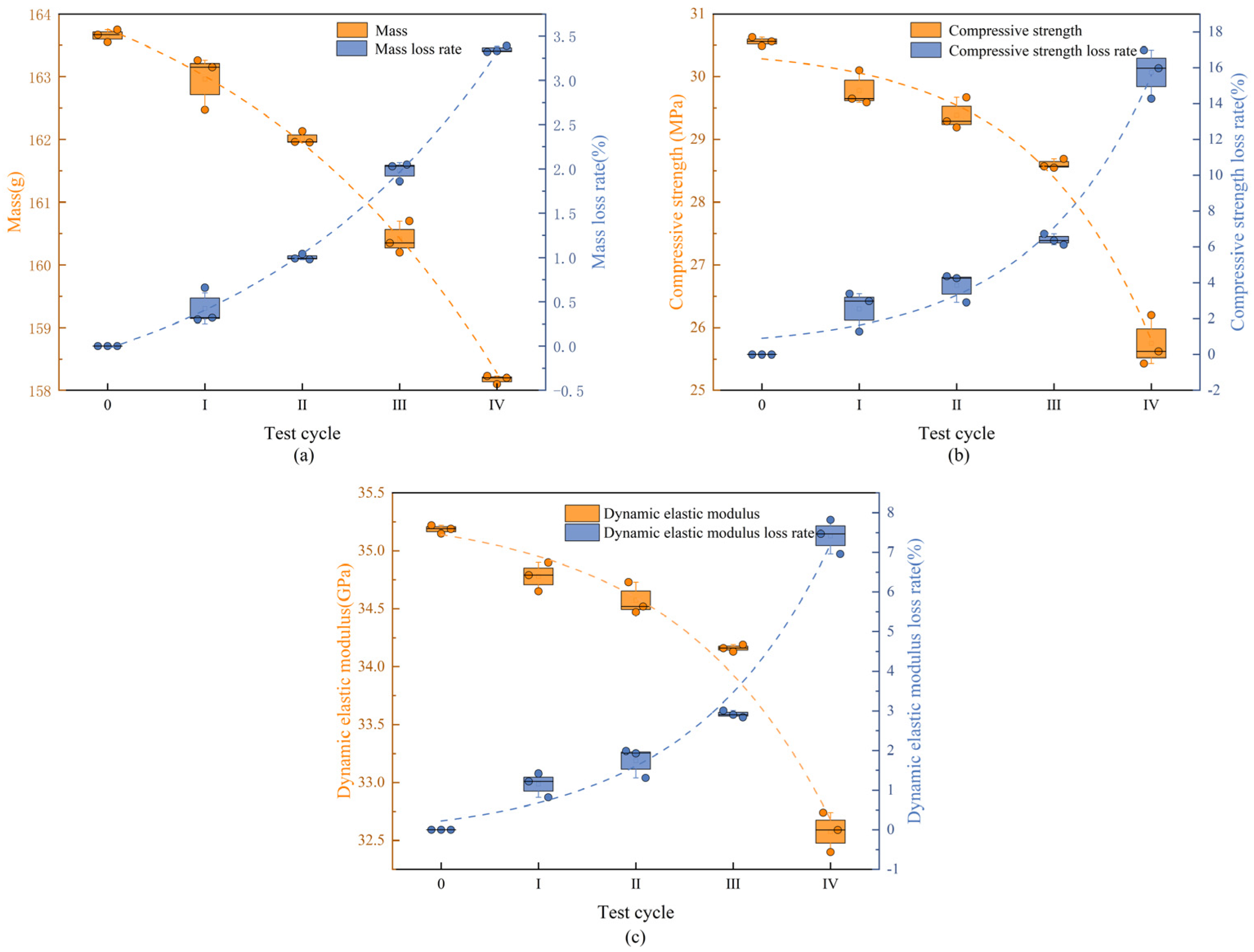
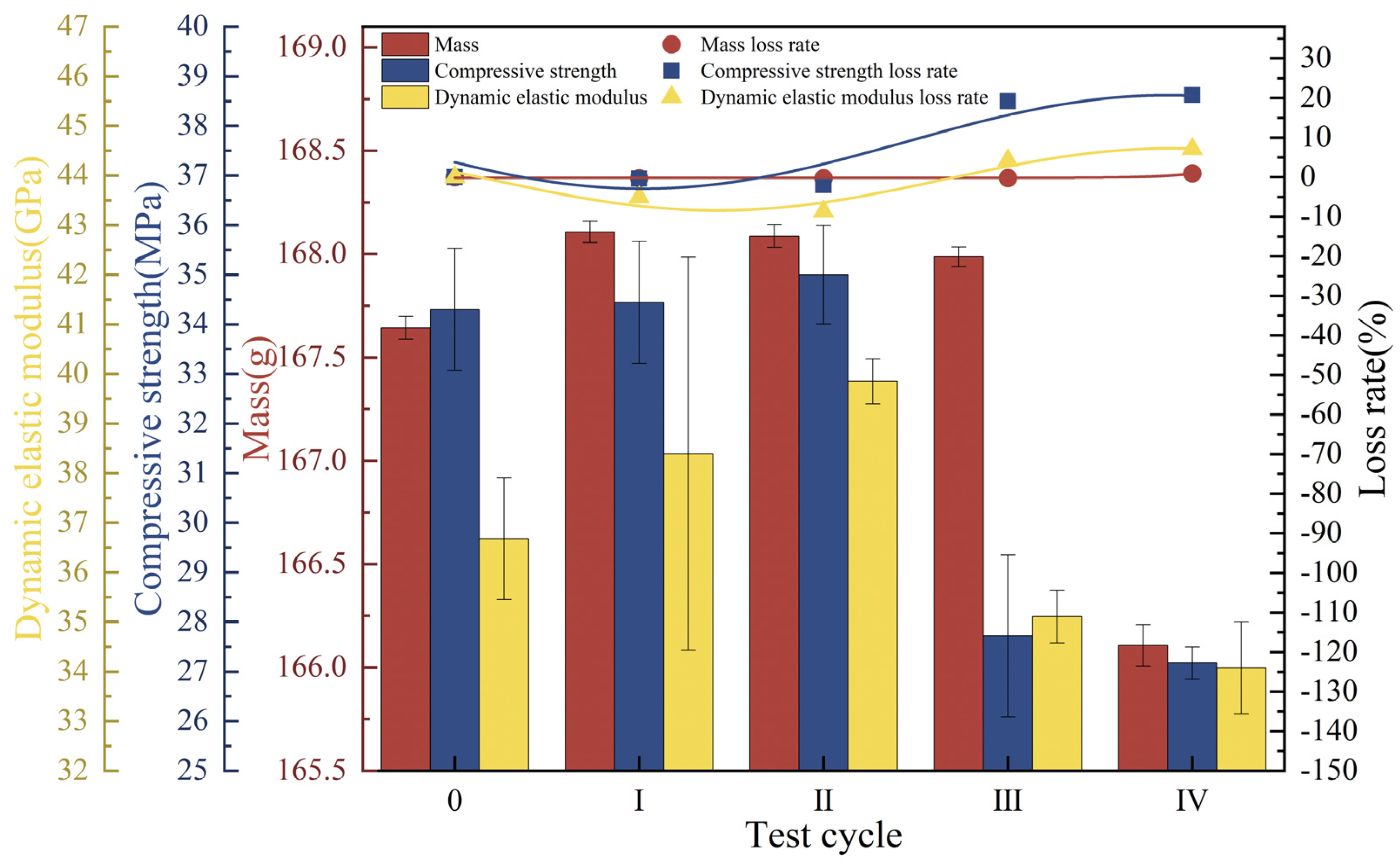
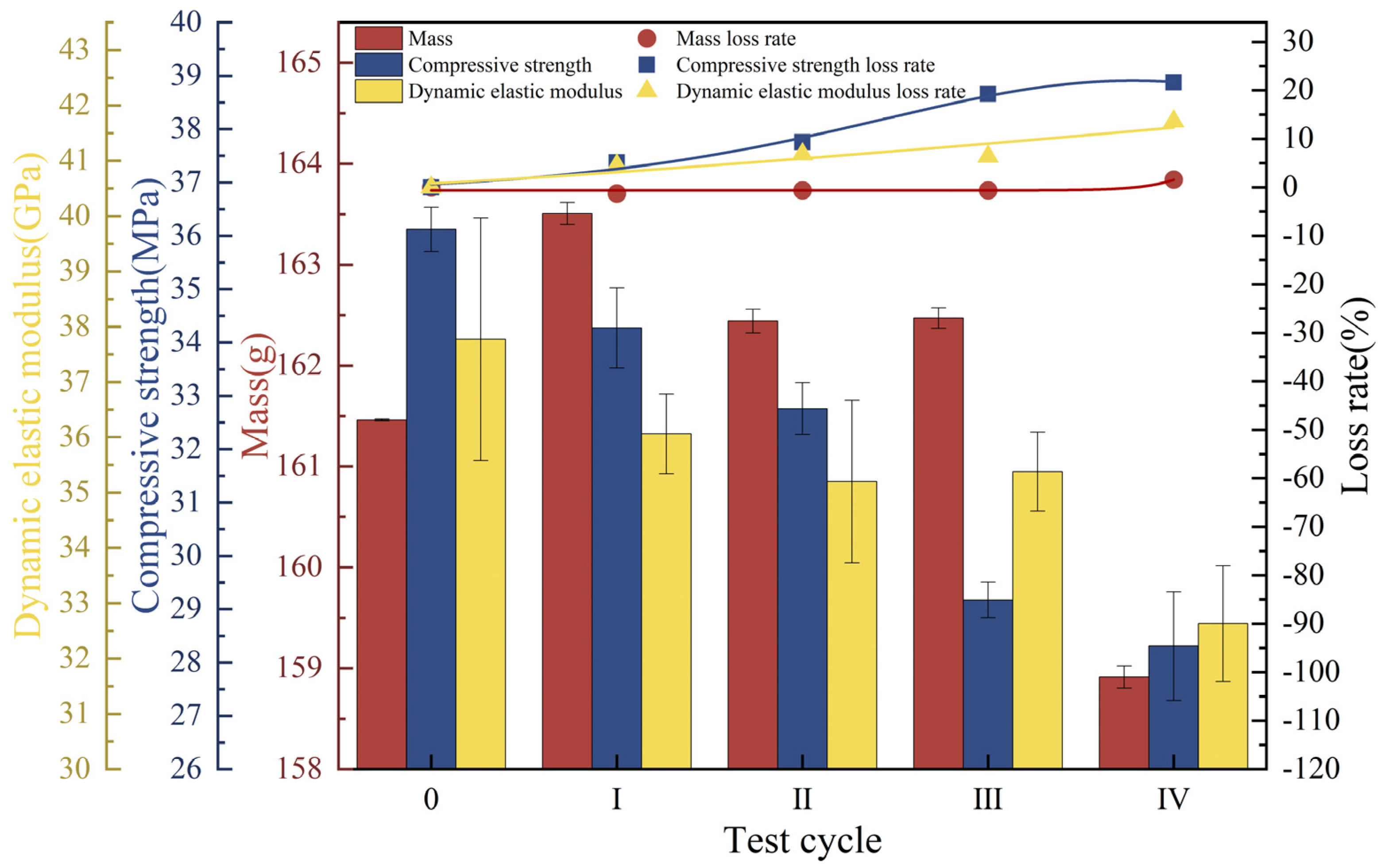
3.2. Concrete Deterioration Damage Under Freeze-Thaw Cycles-Loaded-Landfill Leachate Coupling
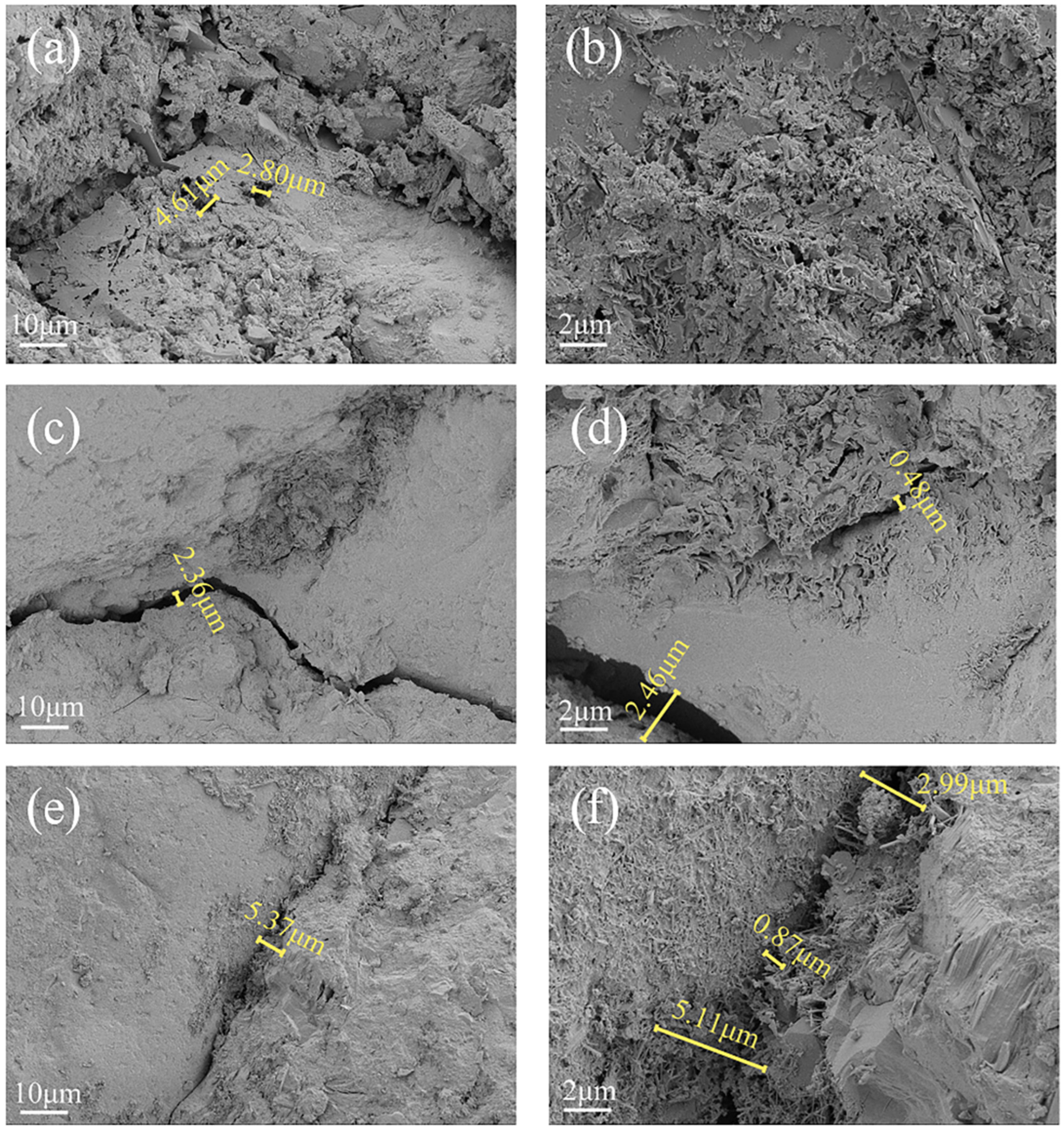
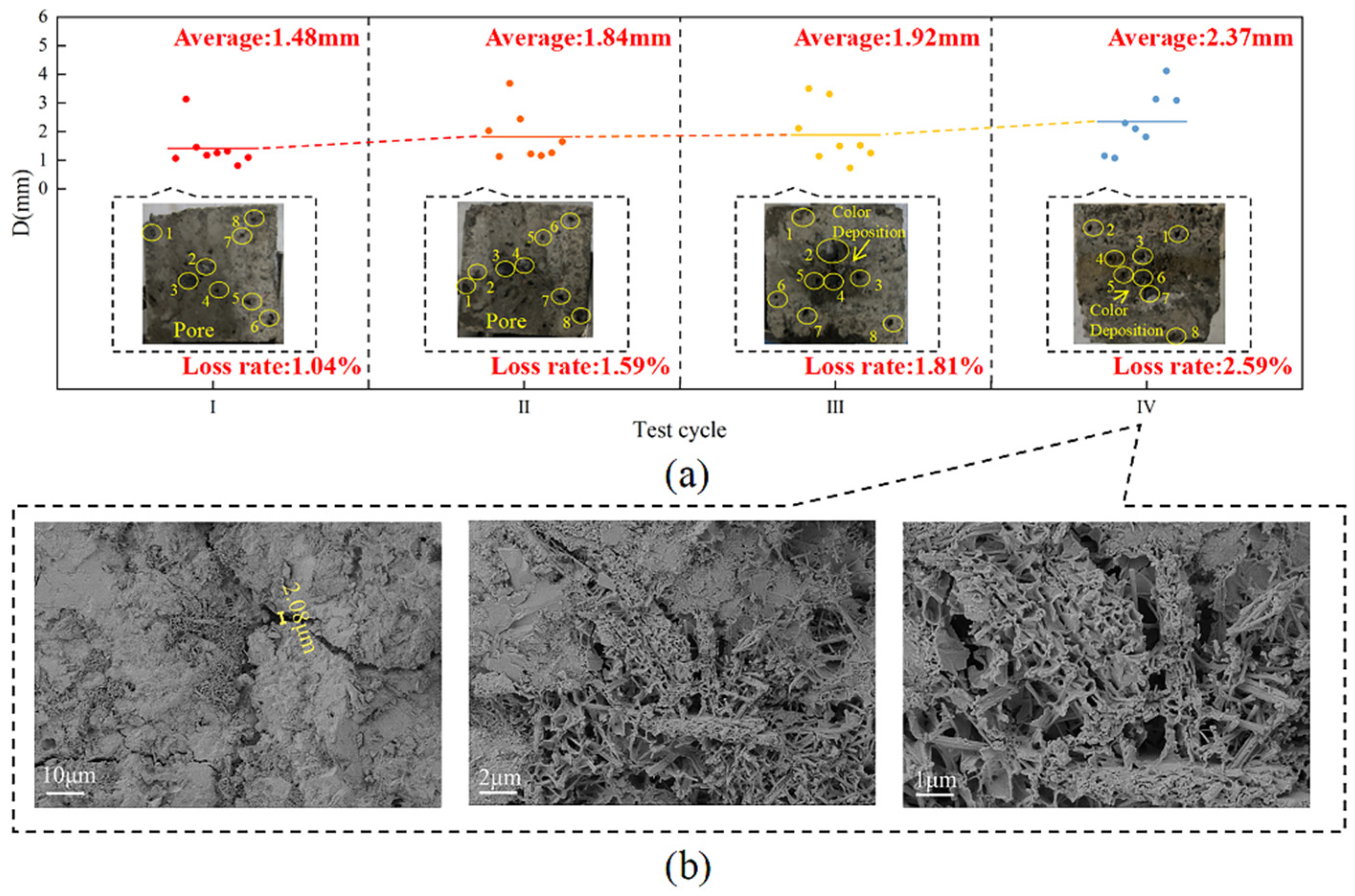
3.3. Concrete Deterioration Damage in Gas-Liquid Two-Phase Corrosion Scenarios
3.4. Concrete Deterioration Damage in Liquid-Solid Two-Phase Corrosion Scenarios
3.5. Concrete Deterioration Damage in Gas-Liquid-Solid Three-Phase Corrosion Scenarios
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhu, P.; Ma, Y. Interaction and coexistence characteristics of dissolved organic matter and toxic metals with per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in landfill leachate. Environ. Res. 2024, 260, 119680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente, E.; Domingues, E.; Quinta-Ferreira, R.M.; Leitão, A.; Martins, R.C. European and African landfilling practices: An overview on MSW management, leachate characterization and treatment technologies. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 66, 105931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistical Yearbook of Urban and Rural Construction in 2023. Available online: https://www.mohurd.gov.cn/gongkai/fdzdgknr/sjfb/tjxx/index.html (accessed on 3 February 2025).
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Lo, W.-H. Removal of refractory compounds from stabilized landfill leachate using an integrated H2O2 oxidation and granular activated carbon (GAC) adsorption treatment. Water Res. 2009, 43, 4079–4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebron, Y.A.R.; Moreira, V.R.; Brasil, Y.L.; Silva, A.F.R.; Souza Santos, L.V.; Lange, L.C.; Amaral, M.C.S. A survey on experiences in leachate treatment: Common practices, differences worldwide and future perspectives. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 288, 112475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, V.K.; Gautam, K.; Vishvakarma, R.; Sharma, P.; Pandey, U.; Srivastava, J.K.; Varjani, S.; Chang, J.-S.; Ngo, H.H.; Wong, J.W.C. Integrating advanced techniques and machine learning for landfill leachate treatment: Addressing limitations and environmental concerns. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 354, 124134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öman, C.B.; Junestedt, C. Chemical characterization of landfill leachates—400 parameters and compounds. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 1876–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woyciechowski, P.; Łukowski, P.; Szmigiera, E.; Adamczewski, G.; Chilmon, K.; Spodzieja, S. Concrete corrosion in a wastewater treatment plant—A comprehensive case study. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 303, 124388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Gao, X.; Xia, Y. Randomness and time-varying characteristics of chloride ion transport in existing harbor concrete structures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 412, 134839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Wang, H.; Xue, H.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Wei, L. Study on damage deterioration mechanism and service life prediction of hybrid fibre concrete under different salt freezing conditions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 435, 136688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Hu, D.W.; Ren, J.M.; Zhou, H.; Lu, J.J.; Liu, C.X. Influence of erosive environment on permeability and mechanical properties of underground structures. Rock Soil Mech. 2019, 40, 3457–3464. [Google Scholar]
- Val, D.V.; Andrade, C.; Sykora, M.; Stewart, M.G.; Bastidas-Arteaga, E.; Mlcoch, J.; Truong, Q.C.; El Soueidy, C.-P. Probabilistic modelling of deterioration of reinforced concrete structures. Struct. Saf. 2024, 133, 102454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y. Deterioration of concrete under the coupling effects of freeze–thaw cycles and other actions: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 319, 126045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uthaman, S.; Vishwakarma, V. Assessment of causes and consequences of concrete deterioration and its remediation. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 79, 107790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W. Evaluation of macro- and meso-mechanical properties of concrete under the aggressiveness of landfill leachate. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petryna, Y.S.; Pfanner, D.; Stangenberg, F.; Krätzig, W.B. Reliability of reinforced concrete structures under fatigue. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2002, 77, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Guo, W.; Wu, B.; Ye, T. Mesoscopic characteristics and spatiotemporal variability of chloride transport in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 415, 135081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.J.; Zuo, X.B.; Li, X.N.; Zou, Y.X. An integrated macro-microscopic model for concrete deterioration under external sulfate attack. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2020, 240, 107345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.H.; Cao, Z.Y.; Guan, X.; Li, Q.; Liu, X.L. Damage to recycled concrete with different aggregate substitution rates from the coupled action of freeze-thaw cycles and sulfate attack. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 221, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xie, M.; Zhang, J. Mechanical properties and damage model of modified recycled concrete under freeze-thaw cycles. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 78, 107680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Cao, J.; Gong, F.; Nie, D.; Li, W.; Lin, P.; Zhang, H. Multi-scale thermo-poro-mechanical simulation of the frost resistance of low-heat and moderate-heat hydraulic concrete considering the aging microstructure. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 453, 139062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, F.; Jacobsen, S.; Li, P.; Wang, Z.; Maekawa, K.; Koniorczyk, M. Modeling of path-dependent phase change in sorption and freezing of pore water for cementitious materials. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 57, 104969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Chen, X.; Chai, J.; Qin, Y. Correlation between mechanical properties and pore structure deterioration of recycled concrete under sulfate freeze-thaw cycles: An experimental study. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 412, 134794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; He, S.; Ou, Y.; Xiao, L.; Mei, G. Experimental and numerical analysis of chloride ion transportation in concrete under bending load with reverse seepage. Appl. Ocean Res. 2023, 137, 103617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Xin, D.; Zou, C. Damage evolution and plasticity development of concrete materials subjected to freeze-thaw during the load process. Mech. Mater. 2019, 139, 103192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, W.; Xiang, L.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, J. Transport behaviors of concrete under complex coupled effects of freeze-thaw, high-frequency load, and chloride attack: An experimental and numerical study. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 94, 109973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Deng, M.; Zhang, R.H.; Yu, X.M.; Xue, J.Z.; Zhang, J. Durability of Prestressed Piles in a Leachate Environment. Materials 2024, 17, 2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, J. Mechanism and dynamic evolution of leachate collection system clogging in MSW landfills in China. Waste Manag. 2021, 120, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Sun, W.; Lu, S.-F.; Li, M. Modeling the clogging process of leachate collection systems in municipal solid waste landfills: The role of temperature. Comput. Geotech. 2024, 175, 106670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Feng, S.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, Q.; Cao, B. Fully coupled hydromechanical study of tunnel excavation considering leachate leakage from a high water-level landfill. Comput. Geotech. 2024, 175, 106696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltazar-Zamora, M.A.; Mendoza-Rangel, J.M.; Croche, R.; Gaona-Tiburcio, C.; Hernández, C.; López, L.; Olguín, F.; Almeraya-Calderón, F. Corrosion Behavior of Galvanized Steel Embedded in Concrete Exposed to Soil Type MH Contaminated with Chlorides. Front. Mater. 2019, 6, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, R.; Xue, Y.; Wang, X.; Dou, X.; Song, Y. Damage evolution and life prediction of concrete in sulfate corrosion environments in Northwest China. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 97, 110909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Shi, J.; Liu, Z.; Wu, M.; Liu, C.; Chen, Y.; Liu, G.; Yang, Y.; et al. Degradation of mortar fully buried in saline soil containing sodium sulfate or magnesium sulfate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 369, 130620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Bi, S.; Ren, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J.; Huang, Y.; Ma, J. Characteristics of Concrete Corroded by Landfill Leachate in Extremely Cold Regions. J. Cold Reg. Eng. 2024, 38, 4024025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, T.; Ma, J.; Sun, Q.; Rong, G.; Ren, B. Corrosion characteristics of concrete by landfill leachates of different ages. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e03242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T50082-2024; Standard for Test Methods of Long-Term Performance and Durability of Concrete. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2024.
- Liu, K.; Fu, K.; Bao, J.; Chen, C.; Zhang, R.; Sang, Y. Damage mechanism and mechanical behavior of recycled aggregate concrete under the coupled compressive loading and sulfate erosion. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 99, 111664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, Z.; Lin, Z.; Pan, H.; Huang, Y.; Tang, F.; Jiang, L. Synergizing empirical and AI methods to examine nano-silica’s microscale contribution to epoxy coating corrosion resistance. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50 Pt B, 47172–47191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, F.; Chen, B.; Li, B.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, J.; Peng, C.; Lin, J. Investigation on the chloride ion erosion mechanism of cement mortar in coastal areas: From experiments to molecular dynamics simulation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 350, 128810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, J.; Yan, H.; Huang, J.; Li, Z.A.; Chen, B. Simulation of concrete cracking and chloride diffusion under uniaxial compression. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 96, 110329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Chu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Niu, D. Effect of external loads on chloride ingress into concrete: A state-of-the-art review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 450, 138657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Pellenq, R.J.M.; Poon, C.S. C-S-H decalcification in seawater: The view from the nanoscale. Cem. Concr. Res. 2024, 175, 107385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Yan, C.; Liu, S.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Z. Stress-strain constitutive model of concrete corroded by saline soil under uniaxial compression. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 213, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Gao, G.; Bao, J.; Zhang, P.; Song, Q.; Sun, J.; Qin, L.; Cui, Y. Salt frost damage evolution and transport properties of recycled aggregate concrete under sustained compressive loading. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 941, 173724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Cui, J.; Liu, K.; Sun, S. Study on the durability deterioration law of marine concrete with nano-particles under the coupled effects of freeze-thaw cycles, flexural fatigue load and Cl− erosion. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 87, 109039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Li, L.; Li, L.; Luan, X.; Guan, X.; Niu, G. Study on the deterioration characteristics and mechanisms of recycled brick-concrete aggregate concrete under load-freeze-thaw coupling. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 413, 134817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Zhang, B. Study on freeze-thaw deterioration model of new-to-old concrete based on pore surface fractal characteristics. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 421, 135757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, F.; Jacobsen, S. Modeling of water transport in highly saturated concrete with wet surface during freeze/thaw. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 115, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Li, F.; Niu, D. Study on the deterioration of concrete performance in saline soil area under the combined effect of high low temperatures, chloride and sulfate salts. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2024, 150, 105531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.-Y.; Xia, J.; Wang, S.-Q.; Wu, R.-J.; Min, W.-L.; Wei, J.-Y.; Hou, D.-S.; Mu, S. Insights on the chloride adsorption stability in cement mortar under current field and sulfate attack: From experiments to molecular dynamics simulation. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2024, 146, 105375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Akbar, M.; Wu, Q.; Hussain, Z.; Ansari, W.S. Microstructural Analysis of Corrosion Products of Steel Rebar in Coral Aggregate Seawater Concrete. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2023, 35, 4023470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. A coupled physical—Chemical model for mass transfer considering damage evolution: Sulfate ions transport in a cement-based material as an example. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 426, 136130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Hu, X.; Zhong, S.; Sun, J.; Peng, G. Macroscopic properties evolution and microstructural analysis of early-age concrete in sulfate saline soil. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 431, 136607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Material Dosage (kg/m3) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cement | Water | Fine Aggregate | Coarse Aggregate | Water-Reducing Agent |
| 409.32 | 184.19 | 767.48 | 1176.80 | 1.64 |
| pH | c(COD) (mg/L) | c(NH3-N) (mg/L) | c() (mg/L) | c(Cl−) (mg/L) | c(SS) (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.92–6.24 | 24,912.36–26,633.60 | 604.10–664.50 | 761.75–828.00 | 541.56–595.56 | 411.82–452.00 |
| Test Group | Tests | Continuous Axial Pressure Load + Landfill Leachate Immersion | Freeze-Thaw Cycles (120 d) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | III | IV | ||||
| 1 | Loaded-landfill leachate | 0 + immersion 120 d | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 20% load + immersion 120 d | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| 40% load + immersion 120 d | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| 2 | Freeze-thaw cycles-loaded-landfill leachate | 0 + immersion 120 d | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 40% load + immersion 120 d | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| 40% load + immersion 120 d | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | |||
| 3 | Corrosion scenario | Gas -Liquid | 40% load + immersion 120 d | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Liquid -Solid | 40% load + immersion 120 d | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | ||
| Gas-Liquid-Solid | 40% load + immersion 120 d | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Wang, M.; Xu, T.; Liu, J.; Zang, Z.; Li, S.; Jia, X.; Ma, J. Study of Concrete Deterioration Damage by Landfill Leachate in Cold Regions. Materials 2025, 18, 2361. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102361
Chen Y, Wang M, Xu T, Liu J, Zang Z, Li S, Jia X, Ma J. Study of Concrete Deterioration Damage by Landfill Leachate in Cold Regions. Materials. 2025; 18(10):2361. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102361
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yuejia, Mengya Wang, Tiefu Xu, Jinsuo Liu, Zijun Zang, Siru Li, Xuebin Jia, and Jialu Ma. 2025. "Study of Concrete Deterioration Damage by Landfill Leachate in Cold Regions" Materials 18, no. 10: 2361. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102361
APA StyleChen, Y., Wang, M., Xu, T., Liu, J., Zang, Z., Li, S., Jia, X., & Ma, J. (2025). Study of Concrete Deterioration Damage by Landfill Leachate in Cold Regions. Materials, 18(10), 2361. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102361







