Abstract
Carbon dioxide (CO2) capture is a pivotal technology for achieving the goal of carbon neutrality. This paper proposes a novel process, SBS + SI, which integrates Solution Blow Spinning (SBS) and Solution Impregnation Method (SI), using polyamide 66 (PA66) as the carrier material and high-purity tetraethylenepentamine (TEPA) as the modifier, to fabricate nanofiber adsorption membranes with varying carrier structures and modifier component loadings. The CO2 adsorption performance and pore structure of the adsorbents were investigated using characterization techniques, such as Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA), Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) surface area and pore size analysis, and Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR). The results indicate that as the mass fraction of TEPA increases, the pores in the nanofiber membranes gradually decrease, while the CO2 adsorption capacity significantly increases. The PA66 nanofiber membrane achieves peak CO2 capture performance (44.7 mg/g at 25 °C) at 15% TEPA loading. Meanwhile, the composite nanofiber membranes also exhibit outstanding CO2/N2 selectivity with a separation factor reaching 28. Thermal regeneration tests at 90 °C confirm the composite’s outstanding cyclic stability and regenerability, demonstrating its potential for practical carbon capture applications. These findings suggest that the nanofiber adsorbents prepared by the SBS + SI process have broad application prospects in the field of CO2 capture.
1. Introduction
Carbon dioxide (CO2), a key greenhouse gas, is widely recognized as the main driver of global warming and climate change [1]. The combustion of fossil fuels is the leading source of excessive CO2 emissions. With carbon neutrality goals in mind, there is an urgent need for effective CO2 capture and separation technologies. Currently, pre-combustion, oxy-fuel combustion, and post-combustion capture are the primary methods. Among these, post-combustion capture has gained attention for its flexible systems, broad applicability, and compatibility with existing power plants [2]. Various separation techniques, including solid adsorption, liquid absorption, cryogenic distillation, and membrane separation, are widely used [3]. Liquid amine solutions, a common liquid absorption method, have proven effective in industrial applications but face challenges such as toxicity, corrosiveness, and high energy consumption during regeneration [4,5,6]. Thus, there is a need for new CO2 capture materials that are easy to process, environmentally friendly, cost-effective, and require less energy for regeneration [7,8,9].
Porous carbon-based materials have emerged as leading candidates for CO2 capture applications, owing to their exceptional structural tunability, high surface area, and robust chemical stability under operational conditions [10,11,12,13]. However, their inherent brittleness severely limits their practical applications. Therefore, the development of new materials with both high CO2 capture efficiency, good flexibility, and sufficient mechanical strength has become a key research focus. Polymer nanocomposites have emerged as a potential alternative with their unique combination of properties [14,15,16]. Zhang et al. [17] developed amine-modified porous nanofiber membranes mimicking balsam-pear skin morphology for CO2 capture. They prepared PAN/PVP composite fibers via electrospinning, followed by PVP removal through hydrolysis. The resulting PAN nanofibers were then grafted with polyethyleneimine (PEI), which introduced CO2 adsorption sites while maintaining the original porous structure. The PEI-functionalized membranes achieved a CO2 adsorption capacity of 1.23 mmol/g at 40 °C. Wang et al. [18] investigated the effects of nitric acid (HNO₃) and TEPA treatments on the physicochemical properties of modified and activated polyacrylonitrile (PAN)-based nanofibers. The results demonstrated that the final CO2 adsorption capacity was significantly enhanced, showing increases of 39% at 0.3 vol% CO2 concentration and 57% under pure CO2 conditions. Moreover, by introducing specific functional groups, the material’s selectivity and adsorption efficiency for CO2 can be further enhanced [19,20,21,22], opening up broader application prospects. Among various amine-based modifiers, polyethylenepolyamine compounds (e.g., DETA, TETA, and MEA) have attracted significant attention due to their abundant amine functional groups that enable efficient CO2 chemisorption [18,23,24]. However, these conventional amines suffer from limitations including volatility and poor thermal stability, which restrict their practical applications and lead to performance degradation after repeated adsorption-desorption cycles [25]. In contrast, tetraethylenepentamine (TEPA) demonstrates superior characteristics, maintaining high CO2 capture capacity even at low concentrations while exhibiting excellent adaptability across wide temperature/pressure ranges. Furthermore, TEPA-modified adsorbents can be regenerated through either thermal desorption or pressure swing processes for cyclic utilization [26].
Electrospinning is a commonly used method for preparing polymer nanofibers, but it has limitations, including a dependence on high voltage and high dielectric constant of the solution [27]. In recent years, solution blow spinning (SBS) has attracted significant attention in both academia and industry as an emerging fiber manufacturing technology due to its economic efficiency, wide applicability of raw materials, and suitability for batch production [28].
In this study, polyamide 66 (PA66) was used as the matrix material, and high-purity TEPA was used as the modifier. A novel process combining SBS and solution impregnation (SI) was proposed to prepare nanofiber membranes with various carrier structures and modification component loadings. PA66 not only exhibits excellent spinnability, mechanical properties, and thermal stability but also contains abundant repeating amide groups (CO-NH) in its molecular chain [29,30]. Due to the strong polarity of its amide groups, PA66 offers advantages over other polymers for CO2 capture. Using solution blow spinning, nanofiber mats with diameters smaller than 0.60 μm were fabricated. This porous structure exhibits a high surface area, superior flexibility, and moderate mechanical strength, making it highly efficient for CO2 adsorption. The incorporation of TEPA not only creates additional active sites for CO2 binding but also boosts the membrane’s selectivity and affinity toward CO2. Furthermore, TEPA reinforcement enhances the composite’s mechanical durability, underscoring its suitability for CO2 capture and other potential applications.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Fabrication Methods
2.1.1. Materials
Polyamide 66 (PA66, viscosity: 135 g/mL) and formic acid (98%) were purchased from Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China), while tetraethylenepentamine (TEPA) (99%) was obtained from Shanghai Linen Technology Development Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). All chemicals, including anhydrous ethanol, were used without further purification.
2.1.2. Preparation of PA66-TEPA Nanofiber Membranes via SBS + SI Method
The fabrication of PA66-TEPA nanofiber membranes comprises two sequential steps (Figure 1): (1) solution blow spinning of PA66 fibrous scaffolds, followed by (2) surface functionalization through TEPA solution impregnation.
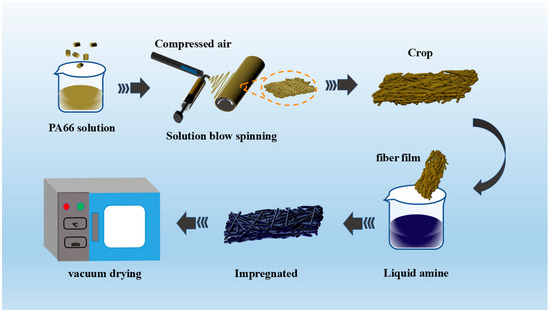
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the SBS + SI preparation process of PA66-TEPA.
The preparation of PA66 nanofibers via solution blow spinning (SBS) involves dissolving 2.6 g PA66 microspheres in 10 g formic acid (26 wt%) under continuous stirring for 6 h at room temperature. The resulting homogeneous solution was loaded into a 20 mL syringe and used with an injection pump at a constant feed rate of 4.5 mL/h under 175 kPa air pressure. Nanofibers were collected on a rotating drum (250 rpm, 5 cm/s reciprocal motion) covered with tin foil, positioned 50 cm from the needle tip to facilitate fiber deposition and subsequent membrane formation
The amine impregnation method involves a solution-based process where amine compounds are adsorbed onto a support material via non-covalent interactions [31]. The amine modification of PA66 nanofiber membranes was performed through solution impregnation as follows: The thinner edges of the fiber membrane are trimmed and placed at the bottom of a beaker. A TEPA solution is prepared by mixing TEPA with anhydrous ethanol in specified proportions and stirring until homogeneous. The solution is then added to the beaker containing the fiber membrane, and the beaker is subjected to ultrasonic-assisted impregnation for 30 min. After impregnation, the composite fiber membrane is transferred to a vacuum drying oven set at 90 °C and dried for 8 h. The resulting samples are designated as PA66-TEPA-xx, where “xx” refers to the TEPA concentration in the solution. The concentrations used are 0%, 5%, 15%, and 20%, yielding samples PA66-TEPA-0, PA66-TEPA-5, PA66-TEPA-10, PA66-TEPA-15, and PA66-TEPA-20, respectively.
2.2. Performance Evaluation
2.2.1. CO2 Adsorption Performance of PA66 Composite Nanofiber Membranes
The CO2 capture performance was assessed via TGA using 10 mg of membrane samples. Following moisture removal (N2 purge, 200 mL/min, 90 °C, 60 min), adsorption was measured at 25 °C under CO2 flow (200 mL/min) until mass stabilization. Subsequent desorption at 90 °C (N2 atmosphere) completed one cycle, with six repeats demonstrating membrane stability. Adsorption capacities were derived from mass differentials.
2.2.2. Mechanical Properties of PA66 Composite Nanofiber Membranes
The complete membrane was removed from the aluminum foil and cut into strips with dimensions of 40 mm in length and 30 mm in width. The thickness of the membrane was measured using a micrometer, and the average value was taken. The tensile properties, including the breaking stress and breaking elongation, of the composite nanofiber membrane were tested using a tensile testing machine (PT-305; Guangdong Beidou Precision Instrument Corporation; Dongwan, China) under the following conditions: a clamp distance of 30 mm and a testing speed of 5 mm/min. The breaking stress and breaking elongation were calculated as follows:
where σ is the breaking stress (N/m2), P is the breaking force (N), S is the cross-sectional area (m2), ε is the breaking elongation (%), L₀ is the length of the fiber after applying pre-tension and straightening (mm), and L is the length of the fiber at the point of fracture (mm).
2.2.3. Calculation of CO2/N2 Adsorption Selectivity
It is essential to analyze the CO2/N2 selectivity of the synthesized samples to evaluate the feasibility of CO2 capture under practical conditions. Adsorption selectivity is a crucial characteristic of an adsorbent, equally important as its adsorption capacity. High selectivity indicates the ability of the adsorbent to effectively distinguish CO2 from other coexisting gases, thereby enhancing separation efficiency.
The CO2 and N2 adsorption isotherms were fitted with a virial-type equation to calculate the Henry’s law selectivity of CO2 over N2 at 25 °C for PA66-TEPA [32,33]:
where p (Pa) is the pressure and n (mol/g) is the gas adsorbed amount, Ai (i = 1, 2, 3 ···) is a virial coefficient. The first virial coefficient (A0) is associated with the energy of adsorbate-adsorbent interactions, while the second (A1) is associated with the energy of adsorbate-adsorbate interactions. At low surface coverage, Ai (i = 2, 3, 4 ···) could be negligible, allowing the equation to be reduced to:
At low surface coverage, ln(n/p) shows a linear dependence on the adsorbed amount n. The values of A0 and A1 could thus be obtained from the slope and the intercept. The Henry’s constant (KH) can be extracted from the value of the first coefficient using the following expression:
The Henry’s law selectivity for CO2 over N2 can be determined based on the ratio of their Henry’s constant and , respectively:
By applying this approach, the selective adsorption performance of the PA66-TEPA composite membrane toward CO2 can be accurately assessed, providing valuable insights into its potential application in industrial flue gas separation.
2.3. Characterization
The morphology of PA66 nanofibers and PA66-TEPA nanocomposite membranes was examined using scanning electron microscopy (SEM5000, Guoyi Quantum Technology Corporation, Hefei, China). The samples were sputter-coated with gold before imaging to enhance fiber conductivity. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (VERTE70, Bruker Corporation, Berlin, Germany) was used to analyze the materials’ functional groups. The membranes were characterized for their physicochemical properties using multiple analytical techniques. Surface area and pore structure analysis were conducted via nitrogen physisorption measurements (ASAP 2020 PLUS, Micromeritics Instrument Corporation, Norcross, GA, USA) based on the Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) method. Thermal stability and CO2 adsorption performance were evaluated by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA-550, TA Instruments, New Castle, DE, USA) under controlled atmospheric conditions.
3. Results
3.1. Morphological Characterization of Composite Nanofiber Membranes
Figure 2 displays the images of three key stages in the fabrication process of the PA66-TEPA composite nanofiber membrane. Figure 2a shows the pristine PA66 nanofiber membrane prepared via solution blow spinning. The membrane exhibits a uniform fibrous network structure with a smooth surface, demonstrating excellent film-forming properties. Figure 2b presents the trimmed pristine PA66 nanofiber membrane, where the thinner edges were removed. The cropped membrane has neat edges, facilitating subsequent experimental procedures. The trimming process did not significantly affect the microstructure, and the fibrous network remained intact. Figure 2c illustrates the PA66-TEPA composite nanofiber membrane after liquid amine impregnation. Through these three consecutive processing stages, a functionalized PA66-TEPA composite nanofiber membrane was successfully prepared, laying a solid foundation for further performance testing and application research.

Figure 2.
Fabrication process stages: (a) Initial collection, (b) After cropping, and (c) impregnation.
Figure 3 presents the morphological evolution of composite membranes with varying TEPA concentrations. The unmodified PA66 nanofibers (Figure 3a), fabricated by solution blow spinning (SBS), display smooth surfaces and uniform diameters (590 nm), forming an interconnected porous network. This pristine fibrous architecture provides an ideal substrate for subsequent amine functionalization. The pore size and structure of porous carriers play a selective role in CO2 adsorption, enabling preferential adsorption of smaller CO2 molecules while exhibiting weaker adsorption capacity for larger molecules, such as nitrogen, thus further enhancing the selectivity for CO2 [34]. Figure 3b–f show the morphology of PA66-TEPA-0 to PA66-TEPA-20. It can be observed that as the PA66 nanofiber membrane, prepared by SBS, is impregnated with TEPA solutions of varying concentrations, the average fiber diameter increases significantly with higher TEPA concentration (Figure 3b–f), indicating successful deposition of TEPA onto the membrane. Figure 3c,d clearly show that as the TEPA concentration rises, the TEPA layer thickens, covering most fibers and forming adhesive structures between adjacent fibers. When the TEPA concentration exceeds a critical threshold, a much thicker polymer membrane forms, covering most of the fiber surface and blocking the pores both between and inside the fibers. At a concentration of 20 wt%, the pores between the nanofibers are nearly completely filled with polymer, resulting in a continuous membrane (Figure 3f), primarily due to the high molecular weight of the TEPA solution.
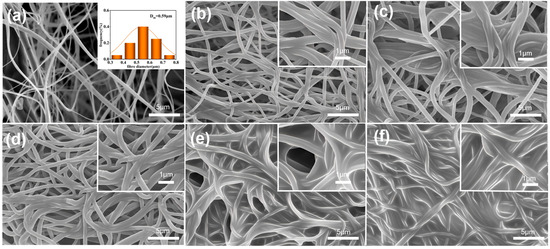
Figure 3.
The SEM images of composite fiber membranes modified with varying TEPA concentrations: (a) PA66, (b) PA66-TEPA-0, (c) PA66-TEPA-5, (d) PA66-TEPA-10, (e) PA66-TEPA-15, and (f) PA66-TEPA-20.
3.2. Molecular Structure Analysis of Composite Nanofiber Membranes
Figure 4 shows the FTIR spectra of the original PA66 membrane and the TEPA-impregnated membrane. It can be observed that both membranes exhibit similar spectra, with distinct absorption bands corresponding to the methylene and amide groups. The infrared characteristic peaks of PA66’s amide linkages (-CO-NH-) are as follows: 3298 cm⁻1 corresponds to the N-H stretching vibration of the amine group (-NH2); 1631 cm⁻1 is the main characteristic absorption peak of the amide I band, corresponding to the C=O stretching vibration of the carbonyl group in the amide; and 1534 cm⁻1 corresponds to the N-H bending vibration of the amine group (-NH2) in the amide. The methylene (-CH2-) groups’ peaks are as follows: 2932 cm⁻1 corresponds to the C-H stretching vibration of the methyl group (-CH₃), and 2858 cm⁻1 corresponds to the C-H stretching vibration of the methylene group (-CH2-) [35]. For TEPA, characteristic peaks appear at 1453 cm⁻1 and 1123 cm⁻1, with the former corresponding to the C-H bending vibration of the methylene group (-CH2-) and the latter corresponding to the C-N bending vibration in the TEPA molecule [36,37]. Additionally, the peak changes in the 1300–1700 cm⁻1 range further confirm the successful loading of TEPA onto the membrane.
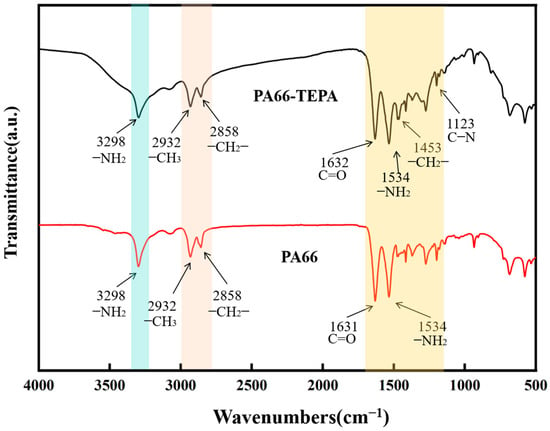
Figure 4.
FT-IR spectra of PA66 and PA66-TEPA composite nanofiber membranes.
3.3. Pore Structure Analysis of Composite Nanofiber Membranes
Porosity plays a crucial role in determining the CO2 adsorption efficiency of membranes. The pore structure of the PA66-TEPA composite nanofiber membranes was characterized using the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) method at −196 °C. The nitrogen adsorption/desorption isotherms obtained can be used to analyze the porosity and structural characteristics of the composite nanofiber membranes, as shown in Figure 5a. All nanofiber membranes exhibit typical Type IV isotherms [38], indicating the presence of mesopores, and the composite nanofiber membranes retain a porous fiber structure after TEPA treatment. The adsorption curve of the original PA66 nanofiber membrane shows a rapid increase in nitrogen adsorption at relatively low pressures (0–0.1 p/p₀), corresponding to monolayer adsorption, which suggests the presence of micropores. Subsequently, the adsorption increases slowly until 0.9 p/p₀, corresponding to multilayer adsorption. Finally, at higher relative pressures (0.9–1 p/p₀), the adsorption increases sharply due to capillary condensation, indicating the presence of mesopores. By observing the nitrogen adsorption/desorption isotherms of PA66-TEPA-5, PA66-TEPA-10, PA66-TEPA-15, and PA66-TEPA-20, it can be seen that the composite nanofiber membranes and the original PA66 nanofiber membrane exhibit similar isotherms, with the presence of mesopores, indicating the potential for CO2 adsorption applications. However, compared to the original PA66 nanofiber membrane, the isotherms of the composite nanofiber membranes show lower initial nitrogen adsorption, and the isotherms at higher relative pressures also exhibit smaller slopes. This suggests that as the TEPA concentration increases, the pore sizes of the micropores and mesopores in the composite nanofiber membranes decrease, which is also evident in the pore size distribution plot and SEM images shown in Figure 3. Additionally, the presence of TEPA blocks the pores between and inside the fibers, leading to a significant reduction in specific surface area and total pore volume (Table 1). The specific surface areas of pure PA66, PA66-TEPA-5, PA66-TEPA-10, PA66-TEPA-15, and PA66-TEPA-20 were 17.31 m2/g, 7.51 m2/g, 5.21 m2/g, 3.75 m2/g, and 1.56 m2/g, respectively. It can be observed that the original PA66 nanofiber membrane has the highest BET surface area, and the unobstructed pores between and inside the fibers ensure a higher BET surface area. Figure 5b presents the Barrett-Joyner-Halenda (BJH) plot, which is used to analyze the pore structure, including pore size and volume. It is clear from the plot that the original PA66 nanofibers contain a notable amount of micropores and mesopores, with a pore volume of 0.23 cm3/g. The pore volume of the composite nanofiber membranes decreases with increasing TEPA impregnation concentration. Since the specific surface area, pore size, and TEPA loading are key factors influencing the CO2 adsorption performance of the composite membrane, optimal CO2 adsorption can only be achieved when these factors are balanced. These results demonstrate that the successful incorporation of TEPA, as confirmed by FTIR, directly influences the membrane’s porous structure. The BET measurements show a clear trend of decreasing specific surface area and pore volume with increasing TEPA loading, which is attributed to physical occupation of pores by TEPA molecules. The agreement between these characterization techniques confirms the controlled modification of membrane properties through TEPA incorporation.
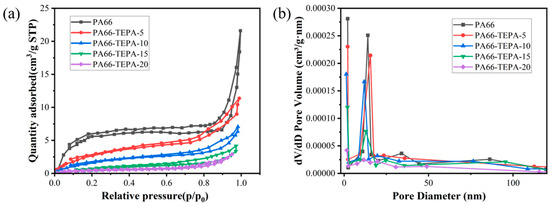
Figure 5.
(a) N2 adsorption/desorption isotherms and (b) pore size distribution of the composite nanofiber membranes.

Table 1.
Pore volumes, average pore sizes, and specific surface areas (SBET) of PA66, PA66-TEPA-5, PA66-TEPA-10, and PA66-TEPA-20.
3.4. Mechanical Properties of Composite Nanofiber Membranes
The mechanical properties of the composite nanofiber membranes obtained with different TEPA impregnation concentrations are shown in Figure 6. Compared with the original PA66 membrane, the synthesized composite nanofiber membranes exhibit excellent flexibility and enhanced mechanical properties. Figure 6a presents the stress-strain characteristics of pure PA66 membranes and composite nanofiber membranes with varying TEPA impregnation concentrations. It can be observed that the flexibility and stress strength of the composite nanofiber membranes impregnated with TEPA are significantly improved compared to the pure PA66 nanofiber membrane. As the TEPA concentration increases, the mechanical strength of the material increases significantly from 2.5 MPa to 11.3 MPa, which is attributed to the successful attachment of TEPA to the original PA66 nanofiber membrane, with the thickness of the attached layer increasing as the TEPA impregnation concentration rises.
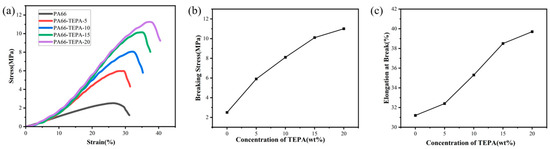
Figure 6.
Stress-strain characteristics of composite nanofiber membranes with different TEPA impregnation concentrations: (a) Stress-strain curves, (b) Fracture elongation, and (c) Fracture stress.
Figure 6b,c show that as the TEPA impregnation concentration increases from 0 wt% to 15 wt%, the fracture stress of the composite nanofiber membranes exhibits a steady increase. However, when the concentration increases from 15 wt% to 20 wt%, the rate of increase in fracture stress slows down, and a similar trend is observed in the fracture elongation. This behavior can be attributed to the TEPA layer, which strengthens the cross-linking force between the nanofibers attached to the original PA66 membrane [39]. As a result, the diameter of individual nanofibers increases, and thus, when a single nanofiber breaks, it has to withstand a larger tensile load, thereby improving both the fracture stress and fracture elongation of the composite nanofiber membranes.
3.5. CO2 Adsorption Performance of Composite Nanofiber Membranes
Figure 7a presents the CO2 adsorption performance of pure PA66 and TEPA-impregnated composite nanofiber membranes, as tested by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). It can be observed that the original PA66 nanofiber membrane exhibits almost negligible CO2 adsorption. However, after impregnation with TEPA solution, the CO2 adsorption capacity of the composite nanofiber membrane significantly increased, with adsorption amounts ranging from 10 to 44.7 mg/g. This enhancement is attributed to the abundant amine groups (-NH2) present in TEPA, which can react with CO2 in a dry environment to form carbamate salts, thereby increasing the CO2 adsorption.
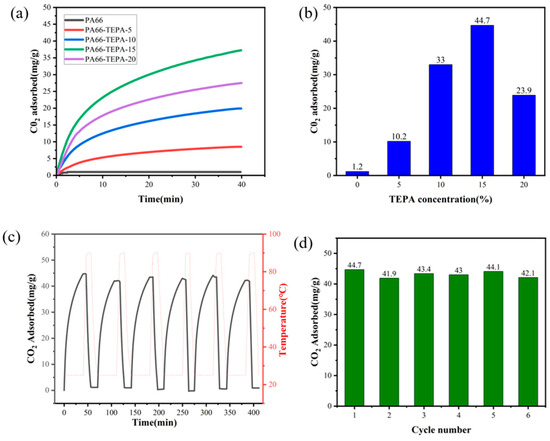
Figure 7.
(a) CO2 adsorption isotherms of nanofiber membranes at 25 °C; (b) Effect of TEPA concentration on CO2 adsorption; (c) CO2 adsorption/desorption cycles; (d) Cycling CO2 adsorption capacity of composite nanofiber membranes.
Figure 7b demonstrates the effect of different TEPA concentrations on CO2 adsorption. As the TEPA concentration increases, the CO2 adsorption capacity of the composite nanofiber membranes steadily improves. However, when the TEPA concentration reaches 20%, the CO2 adsorption performance declines by 20.8 mg/g. This decrease is attributed to the complete blockage of the fiber pores when the TEPA concentration reaches 20 wt%, thereby decreasing the available space for CO2 adsorption in the fibers [40]. This is also confirmed by the scanning electron microscope (SEM) images (Figure 3c–f), which show the pore-blocking effect.
Further studies were conducted on the optimized TEPA-impregnated composite membranes to assess the adsorption stability of the composite nanofiber membranes after multiple cycles. The CO2 adsorption performance was evaluated through multiple adsorption cycles, with the results shown in Figure 7c. Throughout the testing process, the adsorption capacity of the composite nanofiber membrane showed only slight fluctuations, confirming the stable cycling performance of the TEPA-impregnated PA66 nanofiber composite membrane. Figure 7d displays the adsorption amount in each cycle. The cyclic adsorption-desorption tests revealed excellent recyclability of the PA66-TEPA membranes. While the first cycle showed the highest CO2 uptake, subsequent cycles exhibited a marginal decrease (~2.6 mg/g after 6 cycles), retaining 94% of the initial capacity (Figure 7d). This minor reduction likely stems from residual CO2 remaining after the 10-min desorption phase (90 °C, N2), suggesting that slightly longer regeneration times or higher temperatures may further improve reversibility. This demonstrates exceptional regenerability for practical carbon capture applications. The consistent cycle-to-cycle reproducibility further confirms the structural integrity and amine stability of the PA66-TEPA composite under operational conditions.
Table 2 presents the adsorption temperatures and capacities of some previously reported adsorbents. It can be seen that PA66-TEPA exhibits a good adsorption capacity at room temperature (25 °C), and due to the excellent flexibility and mechanical properties of the PA66 nanofiber matrix, it can be applied in a wider range of environments.

Table 2.
Comparison of our optimized sample’s CO2 adsorption capacity with the literature-reported sorbents.
3.6. Selective CO2/N2 Adsorption Performance of Composite Nanofiber Membranes
Moreover, an excellent CO2 capture material must not only exhibit high and stable CO2 adsorption capacity with superior regeneration performance but also demonstrate high selectivity for CO2 molecules in flue gas. Since CO2 and N2 are the two primary components of flue gas, where CO2 accounts for only 12–15% while N2 makes up 70–75%, the designed adsorbent must possess a strong affinity for CO2 in a mixed gas environment to achieve effective separation.
Figure 8a presents the CO2 and N2 adsorption isotherms of the optimized composite nanofiber membrane PA66-TEPA-15 at 25 °C. At 1 bar and 25 °C, PA66-TEPA-15 exhibits a CO2 uptake of 2.67 mmol/g, significantly higher than its N2 adsorption capacity (0.15 mmol/g). The adsorption isotherms of CO2 and N2 were fitted using Henry’s law to evaluate the CO2/N2 selectivity of the composite nanofibers [33,47]. Figure 8b,c display the Henry’s law characteristic curves for CO2 and N2 adsorption on PA66-TEPA-15, while Table 3 summarizes the corresponding Henry’s constants and fitting results. As calculated from the ratio of their Henry’s constants using Equation (6), the Henry’s law selectivity (S) for CO2 over N2 reached 28, demonstrating its outstanding CO2/N2 selective adsorption capability. These findings highlight the great potential of the PA66-TEPA composite membrane for efficient CO2 separation in industrial flue gas applications.
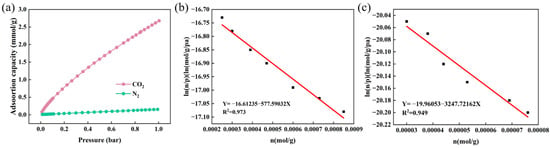
Figure 8.
(a) CO2 and N2 adsorption isotherms at 25 °C; The virial characteristic curves of (b) CO2 and (c) N2 for PA66-TEPA-15 at 0 °C.

Table 3.
Henry’s constants and virial fitting results for PA66-TEPA-15 at 25 °C.
3.7. CO2 Adsorption Mechanism
The adsorption mechanism of CO2 in different materials can generally be classified into two categories: physisorption and chemisorption. Physisorption is governed by van der Waals forces, where CO2 molecules are adsorbed onto the porous structure of the adsorbent with relatively weak interactions [48]. In contrast, chemisorption involves the formation of chemical bonds between CO2 molecules and active functional groups, significantly enhancing the binding strength and improving CO2 capture efficiency [49].
The CO2 saturation adsorption capacity of porous materials is primarily determined by two key parameters: the number of active adsorption sites and the structural characteristics of the material’s porosity. The PA66-TEPA composite nanofiber membrane, developed in this study, exhibits enhanced CO2 adsorption performance due to the synergistic effect between the porous PA66 nanofiber structure and the amine functional groups in TEPA.
Experimental results indicate that when CO2 molecules reach the modified composite membrane’s surface, they are effectively trapped within the membrane via a combination of physisorption on the PA66 nanofiber framework and chemisorption by TEPA. The hierarchical porous structure of the PA66 nanofiber framework provides efficient transport pathways for CO2 molecules, while the amine groups in TEPA react with CO2 to form stable carbamate structures through neutralization reactions [23], as described below:
This coupled mechanism of physisorption and chemisorption significantly enhances the CO2 adsorption capacity of PA66-TEPA. In the adsorption process, most of the amine groups originate from TEPA, which contains two primary amines and three secondary amines, enabling 1 mol of CO2 to react with 2 mol of TEPA. Once the reaction reaches completion, CO2 molecules diffuse into the composite membrane’s porous network until saturation is achieved. These findings confirm that the number of active functional sites and the porous structure play a crucial role in regulating the CO2 adsorption capacity of the composite membrane. The CO2 adsorption process of the amine-modified PA66-TEPA composite nanofiber membrane is exothermic and reversible. Therefore, increasing temperature reverses the reaction and reduces adsorption capacity by promoting the decomposition of carbamate (RNHCOO⁻) formed between amine groups and CO2, thereby releasing CO2 and regenerating amine groups [50,51,52]. As the temperature rises, the average kinetic energy of CO2 gas molecules increases significantly, leading to more vigorous molecular motion. When the molecular kinetic energy exceeds the van der Waals binding energy on the material surface, adsorbed CO2 molecules detach from the surface. Moreover, elevated temperatures may cause microstructural changes in the PA66-TEPA composite, such as pore structure deformation or reduced activity of adsorption sites [53], which further diminishes the material’s CO2 adsorption capacity at high temperatures.
4. Conclusions
In this work, an SBS + SI method was proposed to successfully anchor TEPA onto the surface of PA66 nanofiber membranes, resulting in the preparation of PA66-TEPA composite nanofiber membranes. The pore structure of the membranes could be effectively tuned by adjusting the TEPA impregnation concentration. It was found that a 15 wt% TEPA impregnation concentration provided the optimal CO2 adsorption performance, with an impressive tensile strength of up to 10.1 MPa. The PA66-TEPA exhibited a BET surface area of 3.75 m2/g and a rich porous structure, with a significant amount of mesopores. Meanwhile, the composite nanofiber membranes also exhibit outstanding CO2/N2 selectivity with a separation factor reaching 28. After TEPA impregnation, the composite membrane was able to adsorb up to 44.7 mg of CO2 per gram. Furthermore, the membrane demonstrated excellent performance stability, as evidenced by the CO2 adsorption/desorption cycle test, which showed that it could be reused multiple times as a CO2 adsorbent.
Throughout the adsorption process, the introduction of TEPA played a critical role in enhancing the adsorption performance. On the one hand, TEPA improved the flexibility and tensile strength of the nanofiber membrane, enabling its application in a broader range of environments. On the other hand, TEPA provided a substantial number of amine groups, creating additional CO2 capture sites and enhancing the membrane’s affinity and selectivity toward CO2. This makes the PA66-TEPA composite membrane a promising candidate for CO2 capture and related applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.Y.; Methodology, Y.W. and K.Y.; Resources, X.F.; Data curation, C.Z. and W.W.; Writing—original draft, K.Y. and X.F.; Writing—review and editing, Y.W. and W.W.; Supervision, Y.W. and C.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51575245), Zhenjiang Key Research and Development Program (GY2023013), and Yangzhou Science and Technology Program (YZ2023028).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Xuefei Fan was employed by the company Zhenjiang Sanwei Conveying Equipment Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Chao, C.; Deng, Y.; Dewil, R.; Baeyens, J.; Fan, X. Post-combustion carbon capture. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 138, 110490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boot-Handford, M.E.; Abanades, J.C.; Anthony, E.J.; Blunt, M.J.; Brandani, S.; Mac Dowell, N.; Fernández, J.R.; Ferrari, M.-C.; Gross, R.; Hallett, J.P. Carbon capture and storage update. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 130–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, D.Y.; Caramanna, G.; Maroto-Valer, M.M. An overview of current status of carbon dioxide capture and storage technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 39, 426–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Lawal, A.; Stephenson, P.; Sidders, J.; Ramshaw, C. Post-combustion CO2 capture with chemical absorption: A state-of-the-art review. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2011, 89, 1609–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Otto, A.; Robinius, M.; Stolten, D. A review of post-combustion CO2 capture technologies from coal-fired power plants. Energy Procedia 2017, 114, 650–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feron, P.H.; Cousins, A.; Jiang, K.; Zhai, R.; Garcia, M. An update of the benchmark post-combustion CO2-capture technology. Fuel 2020, 273, 117776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Li, W.-C.; Ren, Z.-X.; Guo, L.-P.; Lu, A.-H. Synthesis of mechanically robust porous carbon monoliths for CO2 adsorption and separation. J. Energy Chem. 2020, 42, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.; Feng, B.; Su, S. Effect of monolithic structure on CO2 adsorption performance of activated carbon fiber–phenolic resin composite: A simulation study. Fuel 2013, 103, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, M.; Yang, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Tang, A. Amine-impregnated mesoporous silica nanotube as an emerging nanocomposite for CO2 capture. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 17312–17320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevilla, M.; Valle-Vigón, P.; Fuertes, A.B. N-doped polypyrrole-based porous carbons for CO2 capture. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 2781–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.; Feng, B.; Su, S. CO2 capture by electrothermal swing adsorption with activated carbon fibre materials. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2011, 5, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, T.-T.; Liu, X.-H.; Zou, K.; Deng, W.-Q. Capture and conversion of CO2 at ambient conditions by a conjugated microporous polymer. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.-H.; Li, P.; Yuan, H.; Huang, W.; Hu, Z.; Yang, R.T. CO2 capture by ZSM-5 with varied Si/Al molar ratios: Isothermal adsorption capacity of CO2 vs dynamic CO2 adsorption capacity. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 129304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Song, C.; Miller, B.G.; Scaroni, A.W. Adsorption separation of carbon dioxide from flue gas of natural gas-fired boiler by a novel nanoporous “molecular basket” adsorbent. Fuel Process. Technol. 2005, 86, 1457–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, A.; Nasef, M.M.; Kheawhom, S.; Faridi-Majidi, R.; Takeshi, M.; Abouzari-Lotf, E.; Choong, T. Amine functionalized radiation induced grafted polyolefin nanofibers for CO2 adsorption. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2019, 156, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, Y.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Rhee, K.Y.; Park, S.-J. Synthesis of PAN/PVDF nanofiber composites-based carbon adsorbents for CO2 capture. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 156, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guan, J.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Balsam-pear-skin-like porous polyacrylonitrile nanofibrous membranes grafted with polyethyleneimine for postcombustion CO2 capture. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 41087–41098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Adelodun, A.A.; Oh, J.M.; Jo, Y.M. TEPA impregnation of electrospun carbon nanofibers for enhanced low-level CO2 adsorption. Nano Converg. 2020, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, R.; Peng, K.; Zhao, K.; Bai, M.; Li, H.; Gao, W.; Gong, Z. Amine-impregnated porous carbon–silica sheets derived from vermiculite with superior adsorption capability and cyclic stability for CO2 capture. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 464, 142662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Meikap, B. Role of amine-impregnated activated carbon in carbon dioxide capture. Indian Chem. Eng. 2021, 63, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ding, L.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, X.; Sui, X.; Li, J.-R. Porous sorbents for direct capture of carbon dioxide from ambient air. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2025, 36, 109676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surkatti, R.; Abdullatif, Y.M.; Muhammad, R.; Sodiq, A.; Mroue, K.; Al-Ansari, T.; Amhamed, A.I. Comparative analysis of amine-functionalized silica for direct air capture (DAC): Material characterization, performance, and thermodynamic efficiency. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 128641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Jiang, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Pan, H.; Shi, Y. Adsorption of low-concentration carbon dioxide on amine-modified carbon nanotubes at ambient temperature. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 2497–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, A.M.; Karanikolos, G.N. CO2 capture adsorbents functionalized by amine–bearing polymers: A review. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2020, 96, 103005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Liu, Q.; Chen, D.; Wen, S.; Wang, T. CO2 adsorption on amine-modified mesoporous silicas. J. Porous Mater. 2014, 21, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouikhi, N.; Cecilia, J.A.; Vilarrasa-García, E.; Besghaier, S.; Chlendi, M.; Franco Duro, F.I.; Rodriguez Castellon, E.; Bagane, M. CO2 adsorption of materials synthesized from clay minerals: A review. Minerals 2019, 9, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Ang, B.C.; Andriyana, A.; Afifi, A.M. A review on fabrication of nanofibers via electrospinning and their applications. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atif, R.; Khaliq, J.; Combrinck, M.; Hassanin, A.H.; Shehata, N.; Elnabawy, E.; Shyha, I. Solution blow spinning of polyvinylidene fluoride based fibers for energy harvesting applications: A review. Polymers 2020, 12, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Zheng, G.; Dai, K.; Liu, C.; Yan, X.; Shen, C.; Guo, Z. Carbon nanotubes-adsorbed electrospun PA66 nanofiber bundles with improved conductivity and robust flexibility. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 14150–14159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cao, X.; Wu, P.; Ye, G.; Fu, Y.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Zheng, K.; Ma, Y. High heat resistance and good melt spinnability of a polyamide 66 containing benzene structure. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 6647–6654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza, M.; Pevida, C.; Arenillas, A.; Rubiera, F.; Pis, J. CO2 capture by adsorption with nitrogen enriched carbons. Fuel 2007, 86, 2204–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czepirski, L.; JagieŁŁo, J. Virial-type thermal equation of gas—Solid adsorption. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1989, 44, 797–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Wang, X.-F.; Li, L.; Jin, L.; Zhang, Y.-G.; Song, S.-L.; Liu, R.-P. Nitrogen-enriched porous carbon fiber as a CO2 adsorbent with superior CO2 selectivity by air activation. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 12558–12567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Deng, S.; Hu, B.; Chen, Z.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Yu, G. Granular bamboo-derived activated carbon for high CO2 adsorption: The dominant role of narrow micropores. ChemSusChem 2012, 5, 2354–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Zhou, T.; Su, G.; Li, Y.; Zhang, A. Understanding the crystallization behavior of polyamide 6/polyamide 66 alloys from the perspective of hydrogen bonds: Projection moving-window 2D correlation FTIR spectroscopy and the enthalpy. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 87405–87415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Zhang, H.; Qi, G.; Lu, W.; Wang, M. Preparation and CO2 adsorption properties of TEPA-functionalized multi-level porous particles based on solid waste. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 653, 130004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq, A.; Mukhtar, H.B.; Shariff, A.M. Research article FTIR study of enhanced polymeric blend membrane with amines. Res. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2014, 7, 1811–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainab, G.; Iqbal, N.; Babar, A.A.; Huang, C.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Free-standing, spider-web-like polyamide/carbon nanotube composite nanofibrous membrane impregnated with polyethyleneimine for CO2 capture. Compos. Commun. 2017, 6, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; He, X.; Li, P.; Li, L.; Wang, M.; Li, Y.; Xu, Q.; Sun, Y.; Hai, C.; Dong, S. Dynamic performance of TEPA-impregnated carbon nanofibers composites for direct air carbon capture in fixed bed columns. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 115747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquino, C.C.; Richner, G.; Chee Kimling, M.; Chen, D.; Puxty, G.; Feron, P.H.; Caruso, R.A. Amine-functionalized titania-based porous structures for carbon dioxide postcombustion capture. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 9747–9757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillerm, V.; Weseliński, Ł.J.; Alkordi, M.; Mohideen, M.I.H.; Belmabkhout, Y.; Cairns, A.J.; Eddaoudi, M. Porous organic polymers with anchored aldehydes: A new platform for post-synthetic amine functionalization en route for enhanced CO2 adsorption properties. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 1937–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Zhu, B.; Wang, L.; Yu, J. Triethanolamine-modified layered double oxide for efficient CO2 capture with low regeneration energy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 659, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.; Xin, H.; Wang, M.; Xu, S.; Zhai, W.; Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Lu, X. Functionalized 3D Covalent Organic Frameworks for High-Performance CO2 Capture and Separation over N2. Adv. Theory Simul. 2022, 5, 2200588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, W.; Chen, B.; Zhou, H.; Yao, Q.; Shen, X.; Pan, Y.; Wu, D.; Cao, Y.; Shen, Z. In situ rapid synthesis of ionic liquid/ionic covalent organic framework composites for CO2 fixation. Chem. Commun. 2023, 59, 14435–14438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Liu, N.; Wang, L.; Sang, Y.; Wan, H.a.; Zhan, P.; Zhang, L.; Huang, J.; Chen, J. Facile preparation of oxygen-rich porous polymer microspheres from lignin-derived phenols for selective CO2 adsorption and iodine vapor capture. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, L.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, X.; Zhang, L.; Shen, Q.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Sun, N.; Wei, W. Potassium tethered carbons with unparalleled adsorption capacity and selectivity for low-cost carbon dioxide capture from flue gas. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 3495–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zainab, G.; Babar, A.A.; Iqbal, N.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Amine-impregnated porous nanofiber membranes for CO2 capture. Compos. Commun. 2018, 10, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollini, P.; Didas, S.A.; Jones, C.W. Amine-oxide hybrid materials for acid gas separations. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 15100–15120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; He, Z.; Zhu, X.; Izikowitz, D.; Li, J. Operating temperatures affect direct air capture of CO2 in polyamine-loaded mesoporous silica. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 131875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suba, M.; Verdeș, O.; Borcănescu, S.; Popa, A. Effect of temperature on CO2 adsorption onto amine-functionalized KIT-6 adsorbents. Molecules 2024, 29, 3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irani, M.; Jacobson, A.T.; Gasem, K.A.; Fan, M. Modified carbon nanotubes/tetraethylenepentamine for CO2 capture. Fuel 2017, 206, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Kim, I.Y.; Lakhi, K.S.; Srivastava, P.; Naidu, R.; Vinu, A. Single step synthesis of activated bio-carbons with a high surface area and their excellent CO2 adsorption capacity. Carbon 2017, 116, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).