Effect of Heat Treatments on the Microstructure and Properties of 18Ni300 Maraging Steel Produced by Selective Laser Melting
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
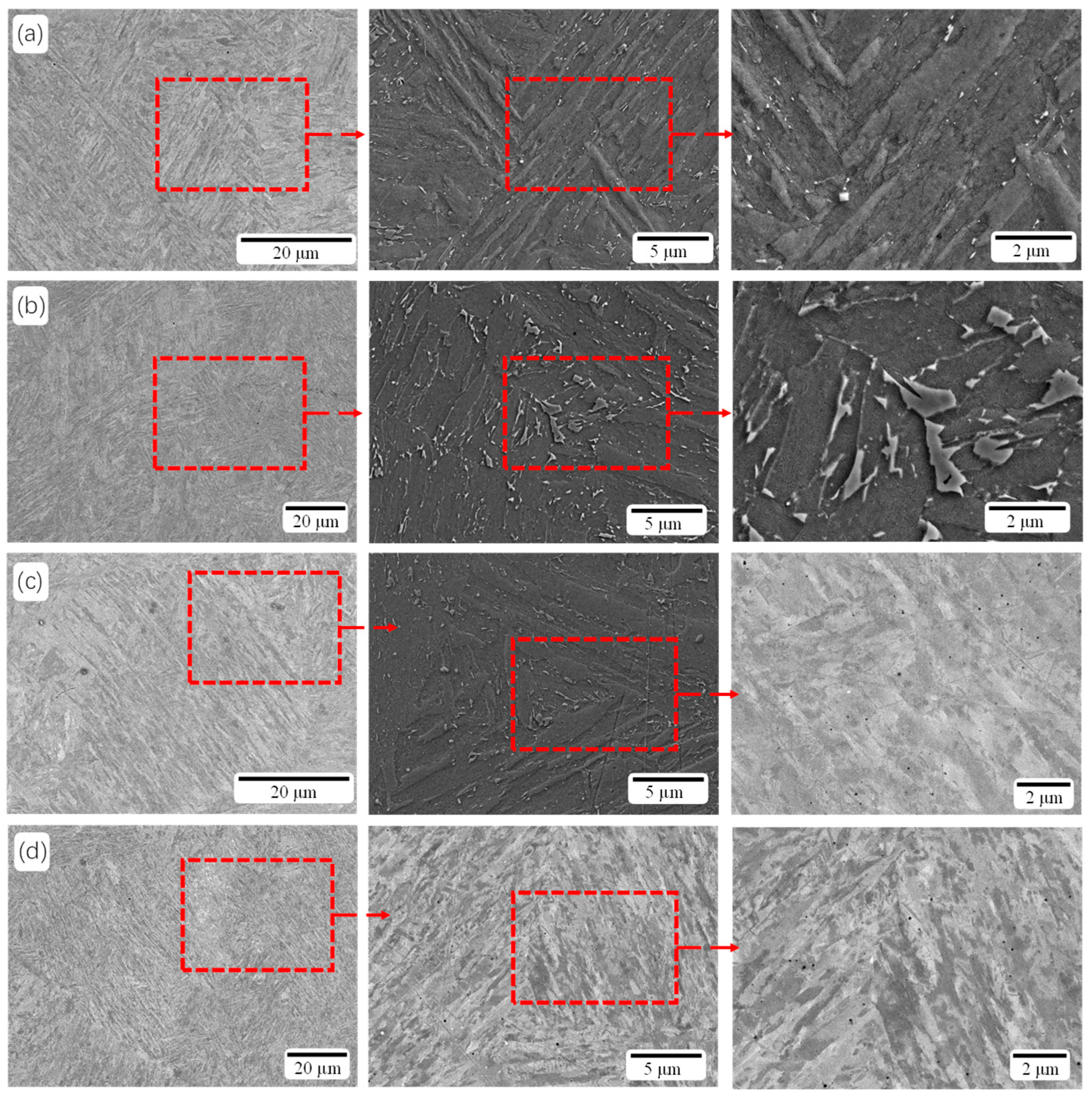
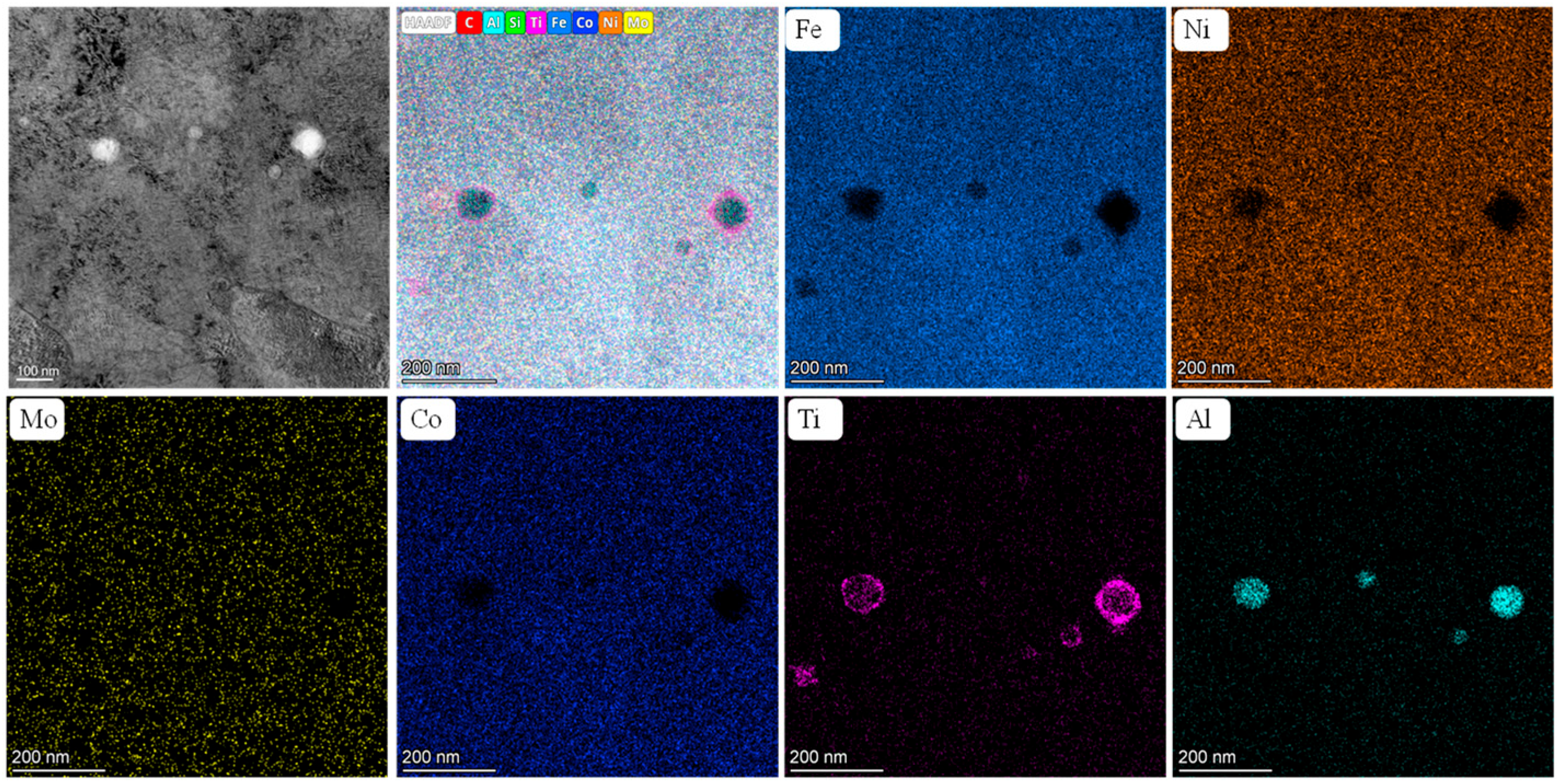
3.1. Microstructures
3.2. Tensile Properties and Hardness
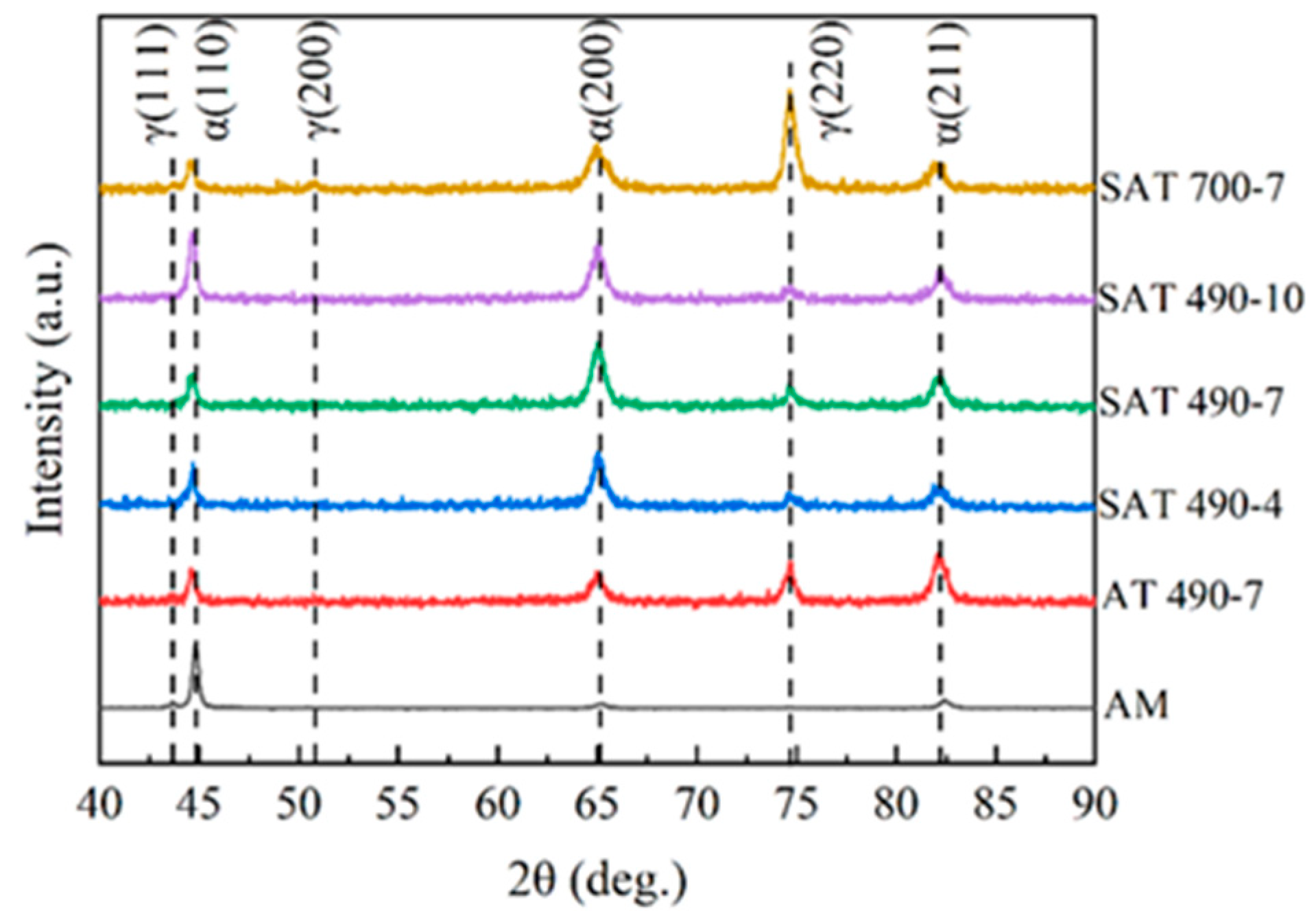
3.3. XRD Analyses
3.4. TEM Analyses
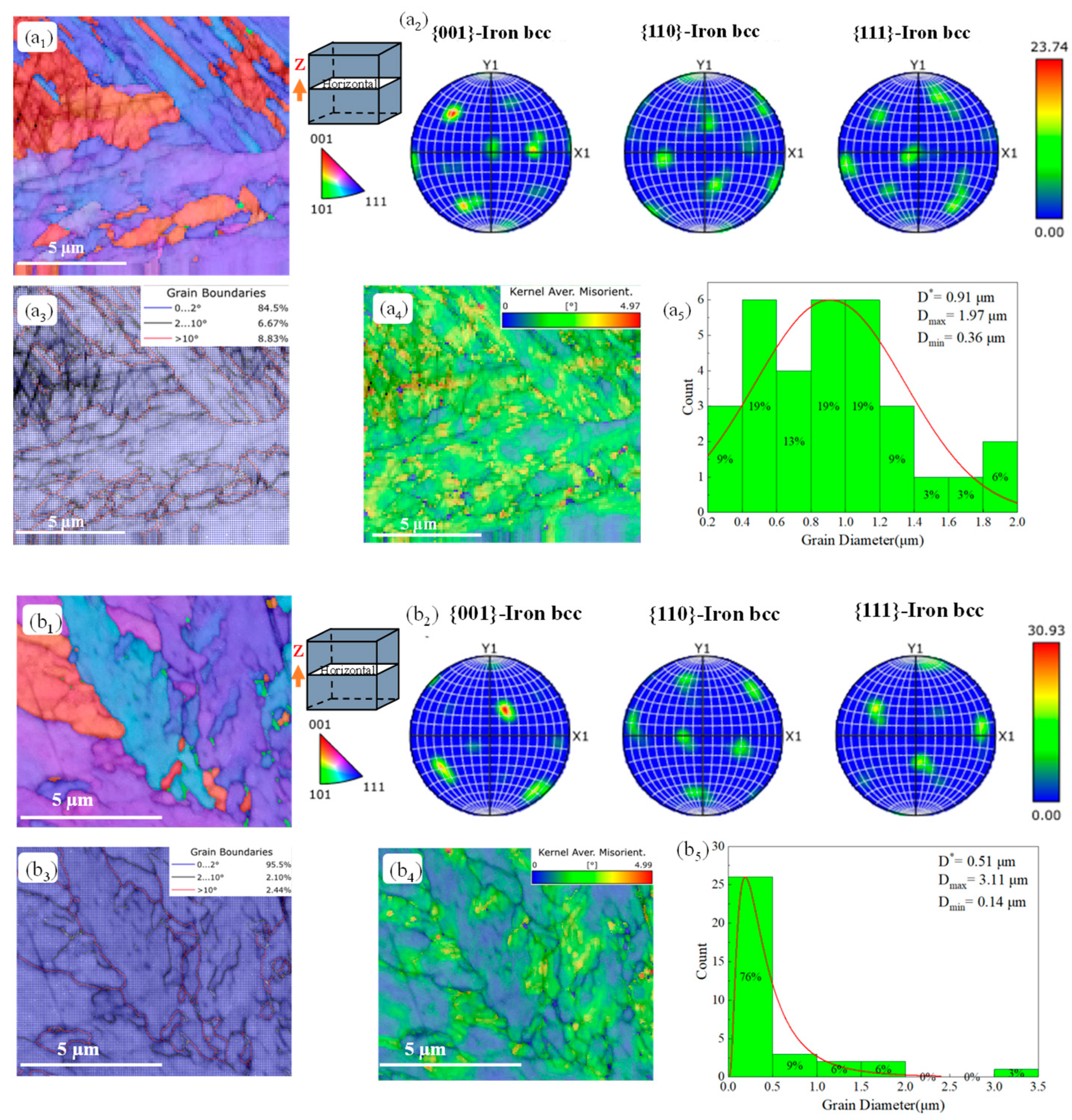
3.5. EBSD Analyses
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Heat treatment significantly alters the micromorphology of the original sample. The cross-sectional topography of the as-built specimen is characterized by long strips of laser tracks, while the longitudinal cross-sectional topography exhibits a fish scale-like molten pool pattern. After heat treatment, these topographical features are no longer visible. The microstructure of the original and aged samples reveals a cellular structure and long strip structure. Following solution aging heat treatment, both the cellular and long strip structures are completely eliminated, resulting in a bundle-like arrangement that is nearly parallel and of almost uniform length. Additionally, inverted austenite can be observed. For samples aged at 700 °C, white particles of Mo are present.
- (2)
- TEM and XRD results indicate that the structure of the martensitic steel transitions from a martensitic phase and austenite phase to a martensitic phase, inverted austenite phase, and Ni3(Ti, Al, Mo) precipitated phase after solution aging heat treatment.
- (3)
- Heat treatment improves the hardness and tensile strength of the sample. Prior to heat treatment, the specimen had a hardness of 310 HV, a tensile strength of 1002 MPa, and an elongation to fracture of 2.9%. After heat treatment, the samples subjected to solution treatment at 820 °C for 2 h followed by aging at 490 °C for 7 h exhibited the best overall properties, with a microhardness of 710 HV, a nanohardness of 7.7 GPa, a tensile strength of 2068 MPa, and an elongation at break of 4.5%.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bodziak, S.; Al-Rubaie, K.S.; Valentina, L.D.; Lafratta, F.H.; Santos, E.C.; Zanatta, A.M.; Chen, Y. Precipitation in 300 grade maraging steel built by selective laser melting: Aging at 510 C for 2 h. Mater. Charact. 2019, 151, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, C. Research on the SLM Forming Process of 18Ni300 Mold Steel. Sci. Technol. Inf. 2024, 22, 93–95. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Xiang, C.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, T.; Han, E. Effect of Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Tensile Properties of 18Ni300 Maraging Steel Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting. Acta Metall. Sin. 2024, 120, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.; Men, Z.; Su, Y.; Chen, C.; Ma, Y.; Yue, T.; Zhang, H. Effects of Aging Heat Treatment on Friction and Wear Behaviors of Selective Laser-melted 18Ni300. J. Netshape Form. Eng. 2023, 15, 164–172. [Google Scholar]
- Gorsse, S.; Hutchinson, C.; Gouné, M.; Banerjee, R. Additive manufacturing of metals: A brief review of the characteristic microstructures and properties of steels, Ti-6Al-4V and high-entropy alloys. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2017, 18, 584–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutua, J.; Nakata, S.; Onda, T.; Chen, Z.-C. Optimization of selective laser melting parameters and influence of post heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of maraging steel. Mater. Des. 2018, 139, 486–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A.; Nishida, R.; Takata, N.; Kobashi, M.; Kato, M. Design of laser parameters for selectively laser melted maraging steel based on deposited energy density. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 28, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, D. Selective laser melting of maraging steel: Mechanical properties development and its application in mold. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2018, 24, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Chen, C.; Yan, X.; Feng, X.; Jenkins, R.; O’Reilly, P.; Liu, M.; Li, H.; Lupoi, R. The influence of aging temperature and aging time on the mechanical and tribological properties of selective laser melted maraging 18Ni-300 steel. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 22, 592–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Ganguly, S.; Ding, J.; Guo, S.; Williams, S.; Martina, F. Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of maraging steel produced by wire + arc additive manufacture process. Mater. Charact. 2018, 143, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhang, L.; Andersson, J.; Ojo, O. Additive manufacturing of 18% nickel maraging steels: Defect, structure and mechanical properties: A review. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 120, 227–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Król, M.; Snopiński, P.; Czech, A. The phase transitions in selective laser-melted 18-Ni (300-grade) maraging steel. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 142, 1011–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, N.; Dabosi, F. Contribution to the study of the effect of molybdenum on the ageing kinetics of maraging steels. Cobalt 1972, 57, 192–201. [Google Scholar]
- Conde, F.F.; Escobar, J.D.; Oliveira, J.; Béreš, M.; Jardini, A.L.; Bose, W.W.; Avila, J.A. Effect of thermal cycling and aging stages on the microstructure and bending strength of a selective laser melted 300-grade maraging steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 758, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menapace, C.; Lonardelli, I.; Molinari, A. Phase transformation in a nanostructured M300 maraging steel obtained by SPS of mechanically alloyed powders. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2010, 101, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.Y.; Chen, W.Q.; Wan, J.F.; Huang, F.; Zhang, S.Q. Effect of aging temperature on microstructure and mechanical properties of SLM 18Ni300 maraging steel. Heat Treat. Met. 2023, 48, 144–150. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM E8; Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials. ASTM: West Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2021.
- Kimura, T.; Nakamoto, T. Microstructures and mechanical properties of A356 (AlSi7Mg0. 3) aluminum alloy fabricated by selective laser melting. Mater. Des. 2016, 89, 1294–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.C.; Attar, H. Selective laser melting of titanium alloys and titanium matrix composites for biomedical applications: A review. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2016, 18, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C. Selective Laser Melting of Maraging Steel and Its Composite, Gradient Materials. Bachelor’s Thesis, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X. Effect of Cobalt on Microstructure and Properties of Maraging Stainless Steel. Bachelor’s Thesis, Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology, Xi’an, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Men, Z.; Ma, Y.; Zhen, J.; Bai, J.; Zhang, H.; Yang, H.; Liu, J. Influence of heat treatment on friction and wear properties of 18Ni300 maraging steel by SLM. Forg. Stamp. Technol. 2022, 47, 228–234. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, L.N.; Martin, C.; Withers, P.J.; Attallah, M.M. The influence of the laser scan strategy on grain structure and cracking behaviour in SLM powder-bed fabricated nickel superalloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 615, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryawanshi, J.; Prashanth, K.G.; Ramamurty, U. Tensile, fracture, and fatigue crack growth properties of a 3D printed maraging steel through selective laser melting. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 725, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
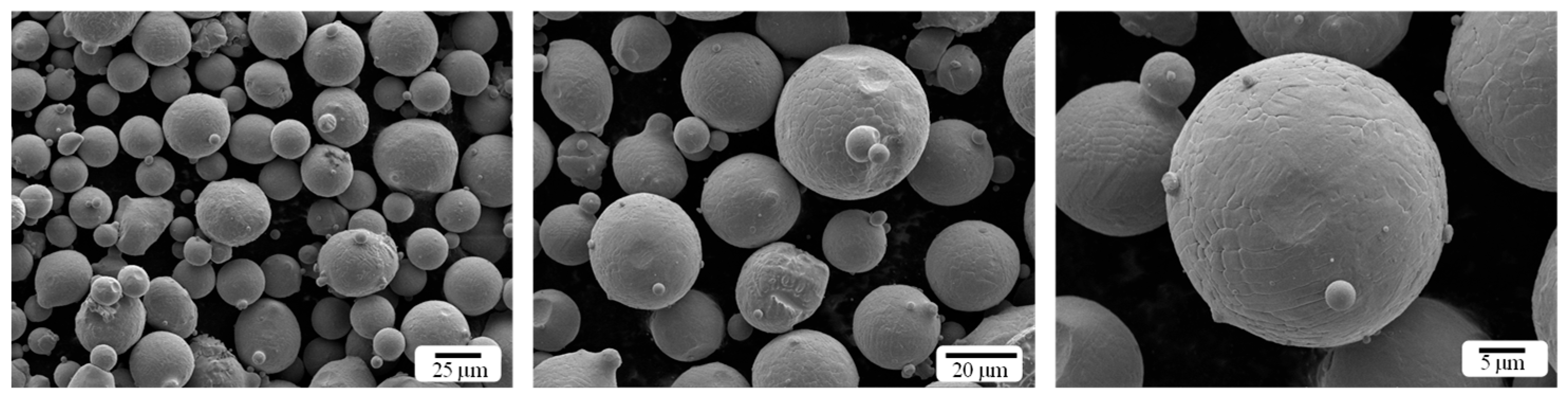
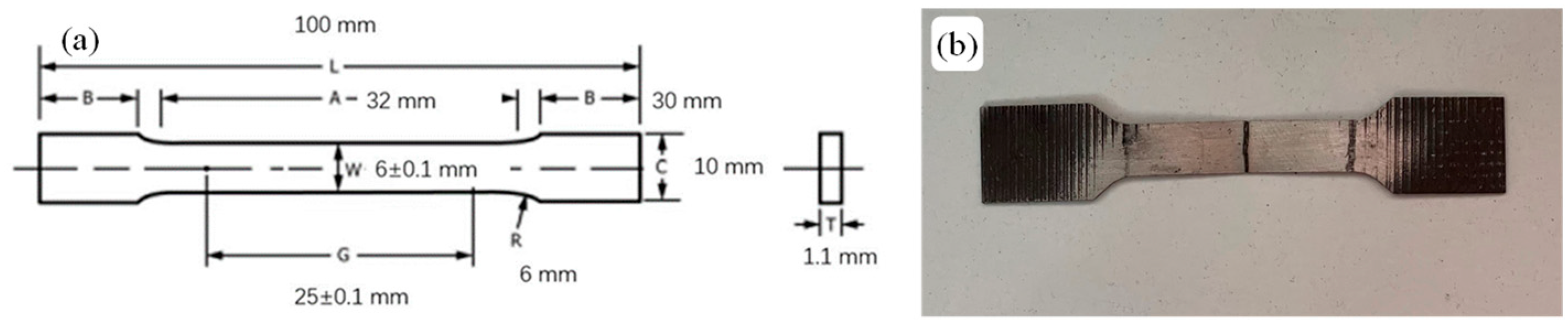






| Ni | Co | Mo | Ti | Al | Fe |
| 17.5–18.5 | 8.50–10.0 | 4.50–5.00 | 0.80–1.10 | 0.05–0.15 | Bal |
| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr |
| ≤0.03 | ≤0.10 | ≤0.15 | ≤0.010 | ≤0.010 | ≤0.60 |
| Heat Treatments | |
|---|---|
| / | No heat treatment after fabrication (AM) |
| Aging | 490 °C-7h (AT 490-7) |
| Solution+ Aging | 820 °C-2h-Water quench + 490 °C-4 h/7h/10 h, Air cooling (SAT 490-4/SAT 490-7/SAT 490-10) |
| 820 °C-2h-Water quench + 700 °C-7 h, Air cooling (SAT 700-7) |
| Specimens | UTS (MPa) | EL (%) |
|---|---|---|
| AM | 1002 | 2.9 |
| AT 490-7 | 1782 | 5.7 |
| SAT 490-4 | 1826 | 3.5 |
| SAT 490-7 | 1883 | 4.5 |
| SAT 490-10 | 1864 | 4.2 |
| SAT 700-7 | 1135 | 6.1 |
| Specimens | α (wt.%) | γ (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|
| AM | 93.4 | 6.6 |
| AT 490-7 | 48.2 | 51.8 |
| SAT 490-4 | 82.2 | 17.8 |
| SAT 490-7 | 73.8 | 19.5 |
| SAT 490-10 | 84.2 | 15.7 |
| SAT 700-7 | 26.7 | 73.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Lin, W.; Wei, P.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sun, K.; Yang, B.; Li, W. Effect of Heat Treatments on the Microstructure and Properties of 18Ni300 Maraging Steel Produced by Selective Laser Melting. Materials 2025, 18, 2284. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102284
Hu J, Zhang L, Wang X, Lin W, Wei P, Cao Y, Zhang J, Sun K, Yang B, Li W. Effect of Heat Treatments on the Microstructure and Properties of 18Ni300 Maraging Steel Produced by Selective Laser Melting. Materials. 2025; 18(10):2284. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102284
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Jun, Lei Zhang, Xuanzheng Wang, Wenzhao Lin, Pingang Wei, Yiwei Cao, Juanqi Zhang, Kai Sun, Bing Yang, and Wentao Li. 2025. "Effect of Heat Treatments on the Microstructure and Properties of 18Ni300 Maraging Steel Produced by Selective Laser Melting" Materials 18, no. 10: 2284. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102284
APA StyleHu, J., Zhang, L., Wang, X., Lin, W., Wei, P., Cao, Y., Zhang, J., Sun, K., Yang, B., & Li, W. (2025). Effect of Heat Treatments on the Microstructure and Properties of 18Ni300 Maraging Steel Produced by Selective Laser Melting. Materials, 18(10), 2284. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102284





