Understanding the Effect of IM-5 Zeolite Treated with Hexafluorosilicic Acid for the Methanol Alkylation of Pseudocumene
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis and Modification of IM-5 Zeolites
- Primary crystallization: 48 h at 140 °C;
- Secondary crystallization: 96 h at 175 °C.
2.3. The Charaterization of Samples
2.4. Catalyst Testing
3. Results
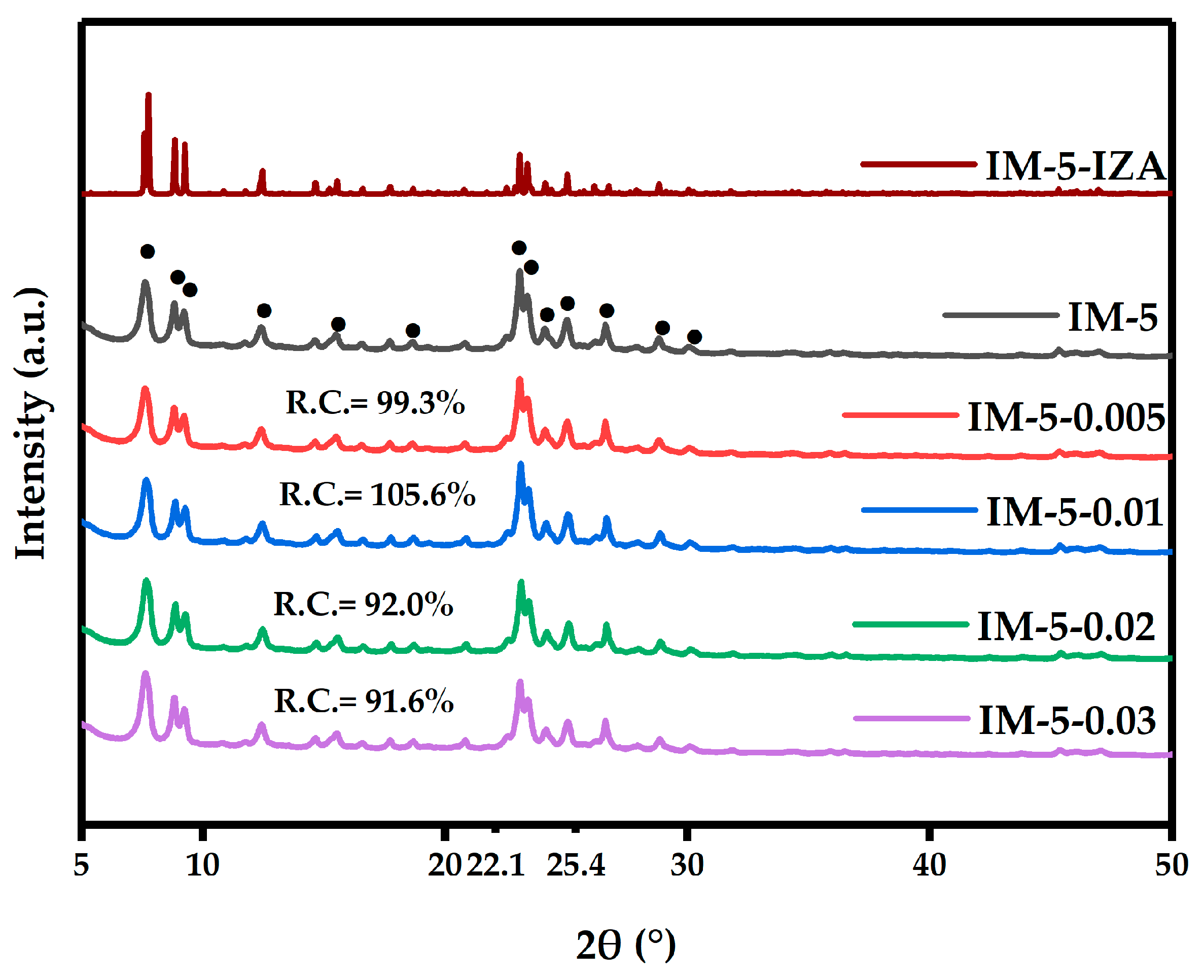
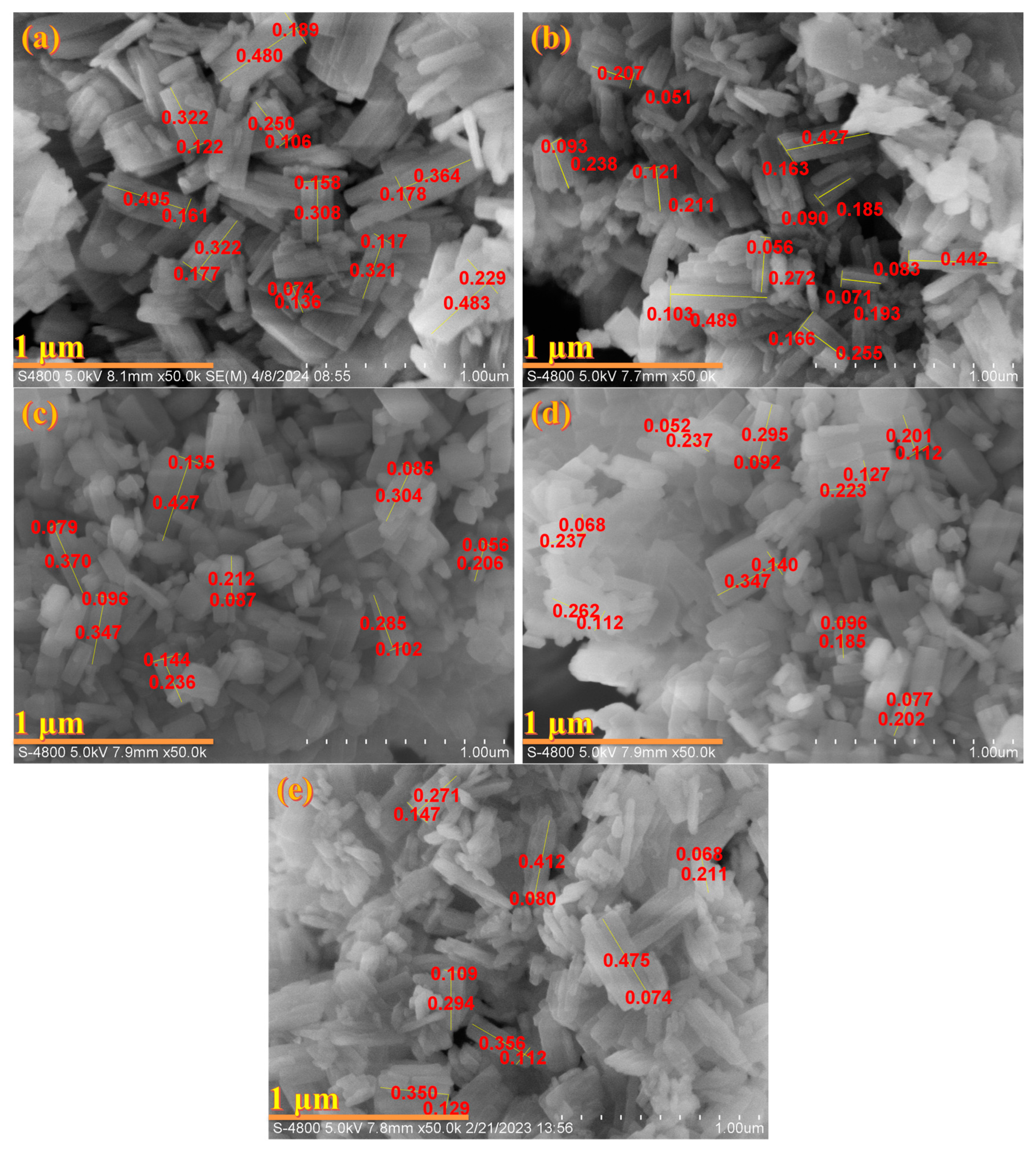
3.1. The Phase, Morphology and Textural Properties of IM-5 Zeolites
3.1.1. Phase
3.1.2. Morphology
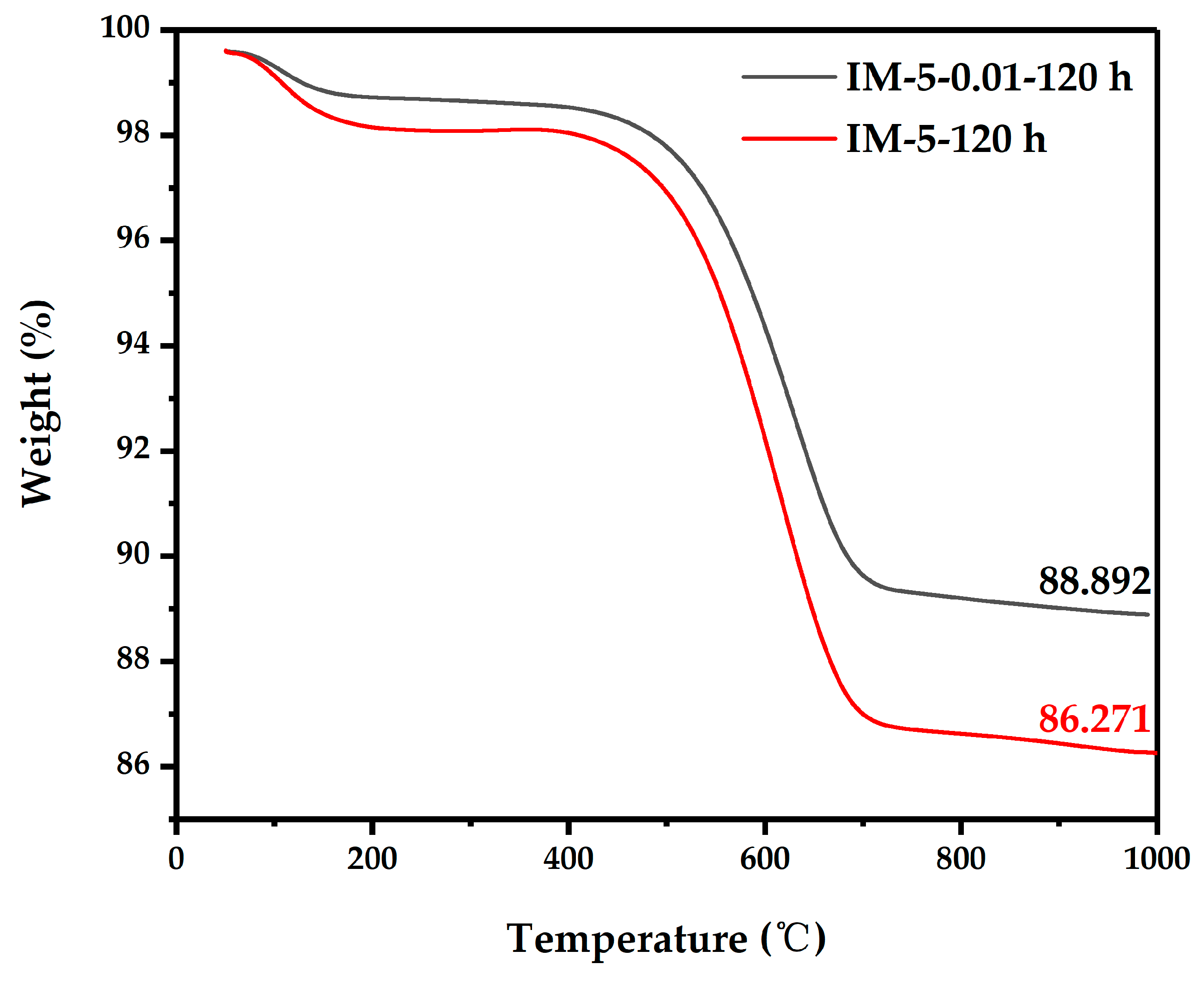
3.1.3. Textural Properties
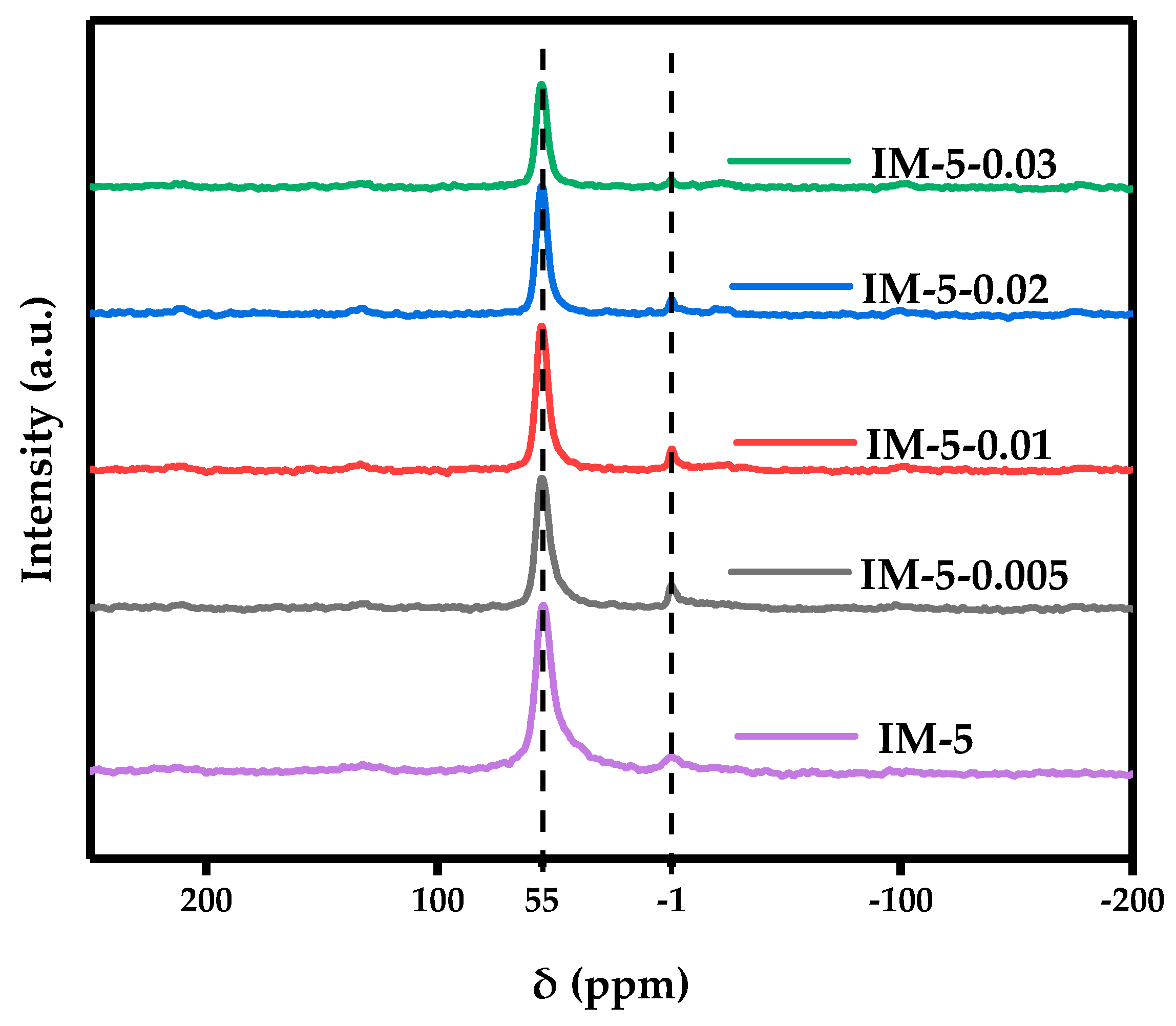
3.2. The Coordination Structure of IM-5 Zeolites
3.2.1. 27 Al MAS NMR
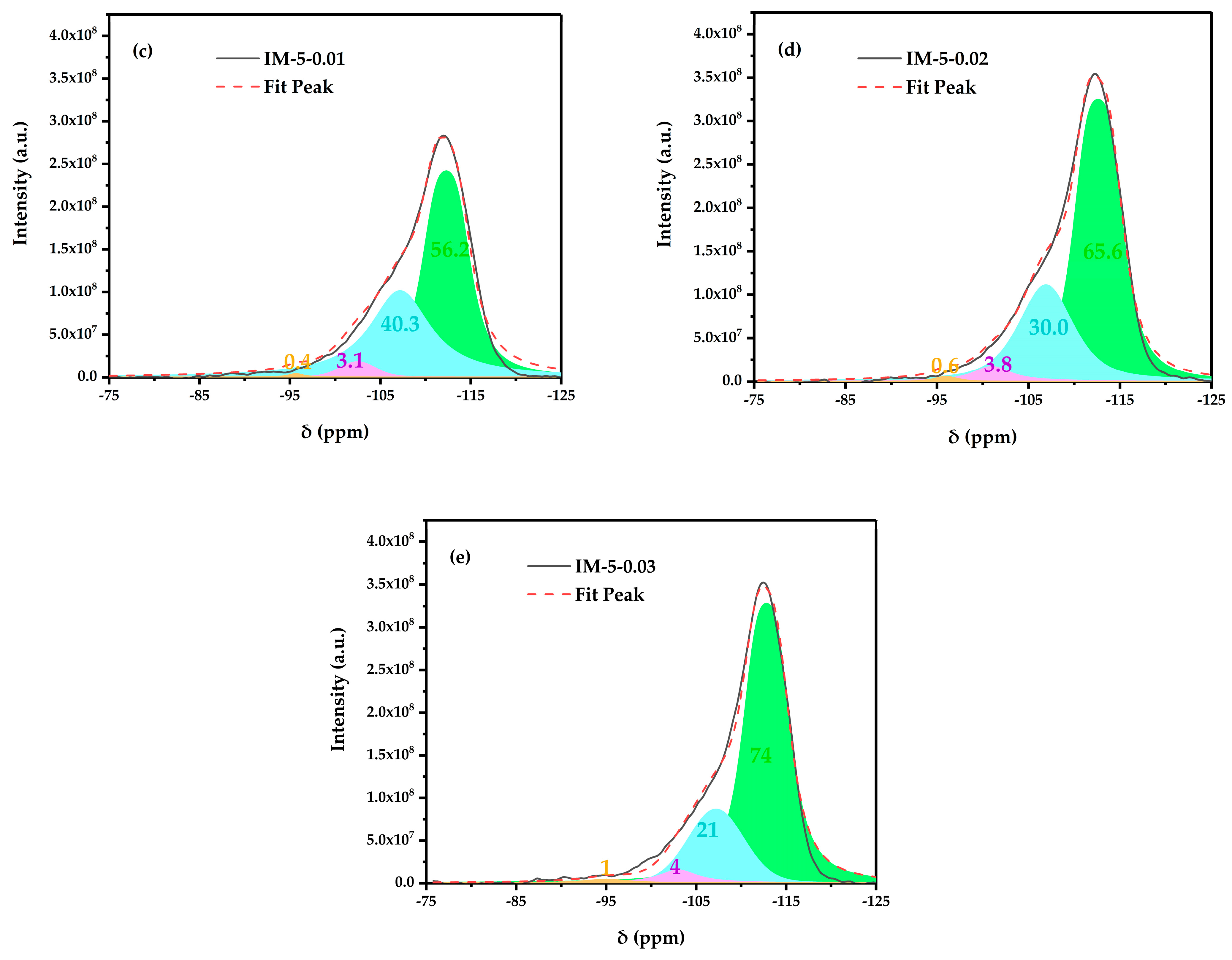
3.2.2. 29 Si MAS NMR
3.2.3. 1 H MAS NMR
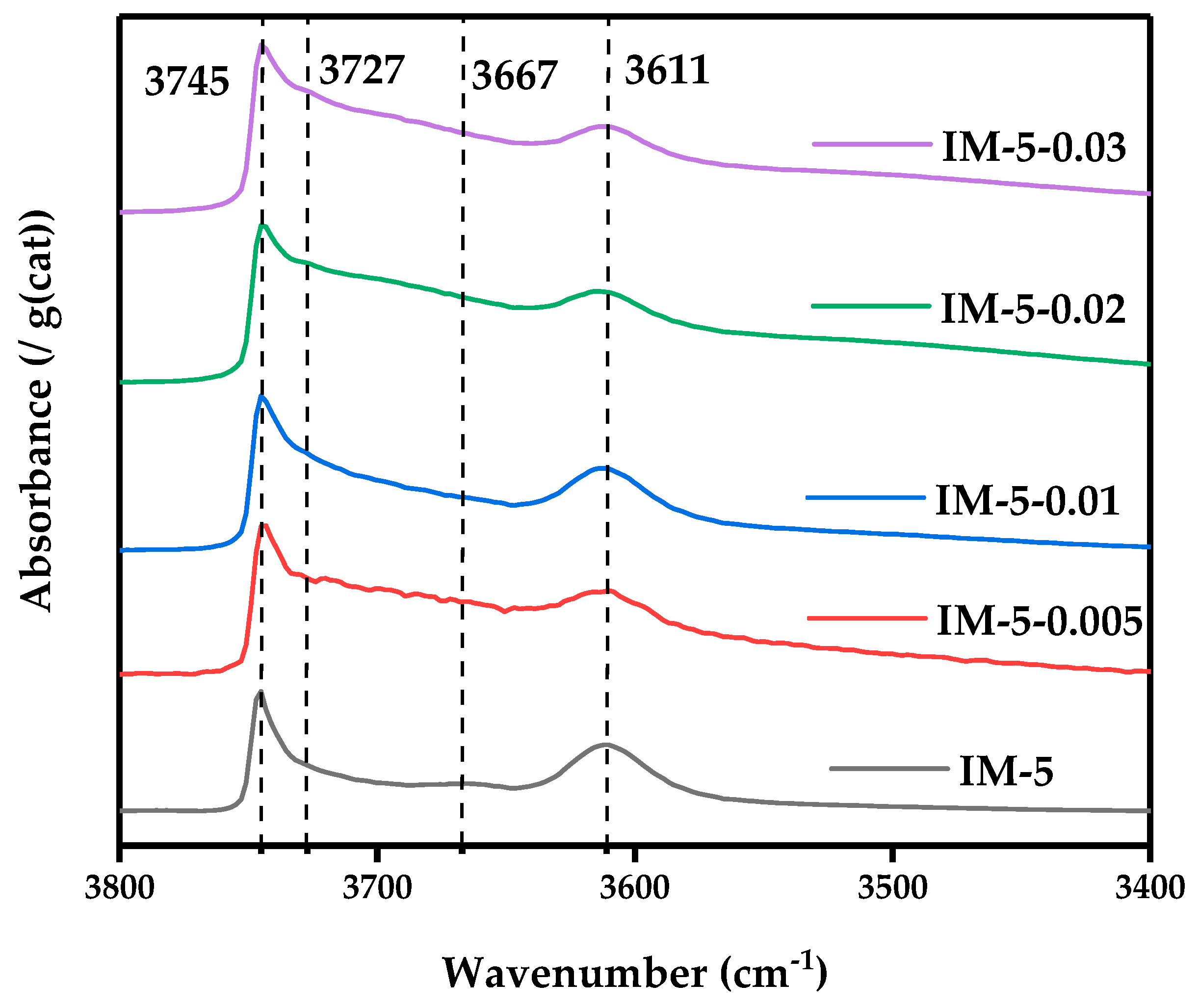
3.2.4. OH-IR
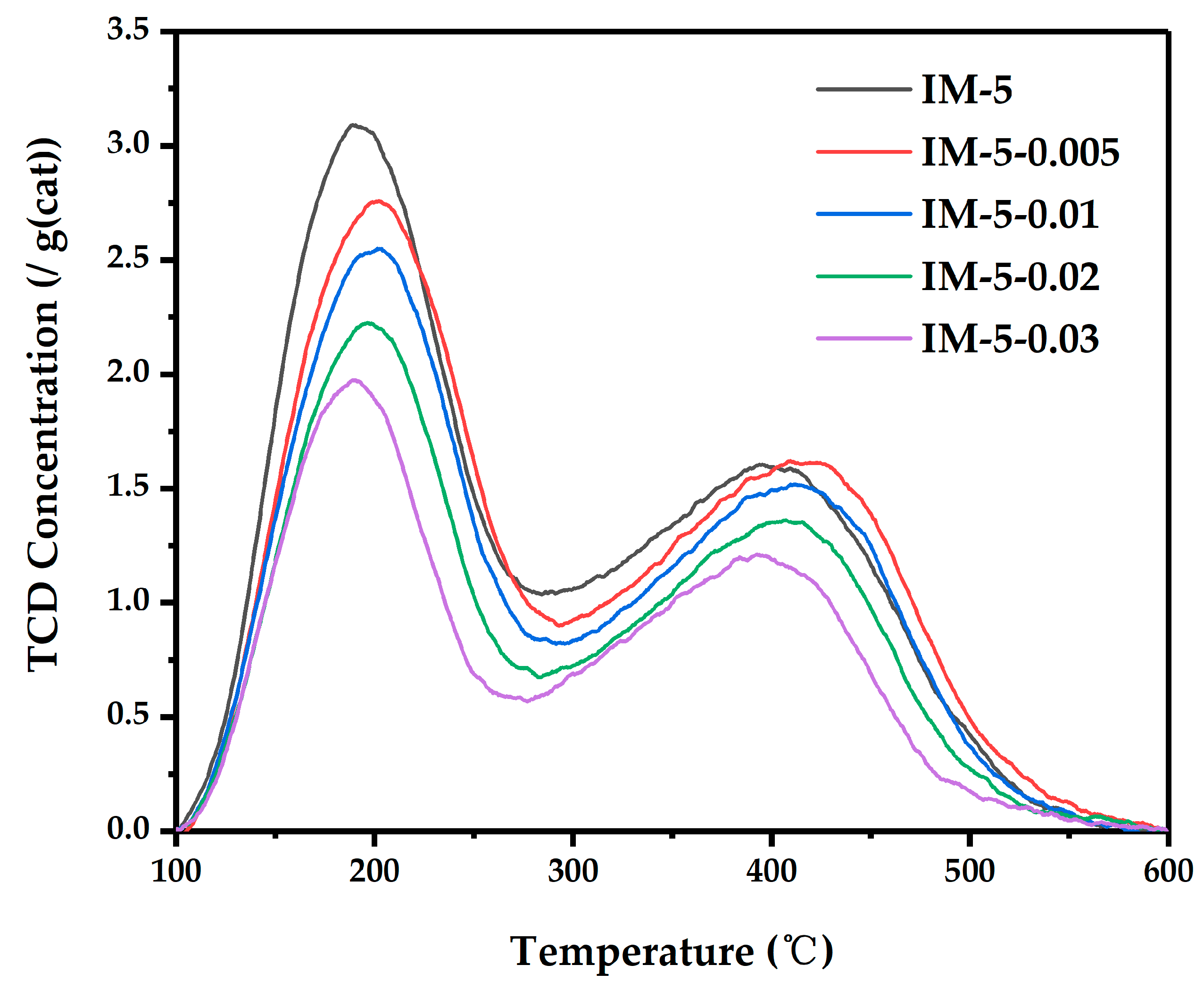
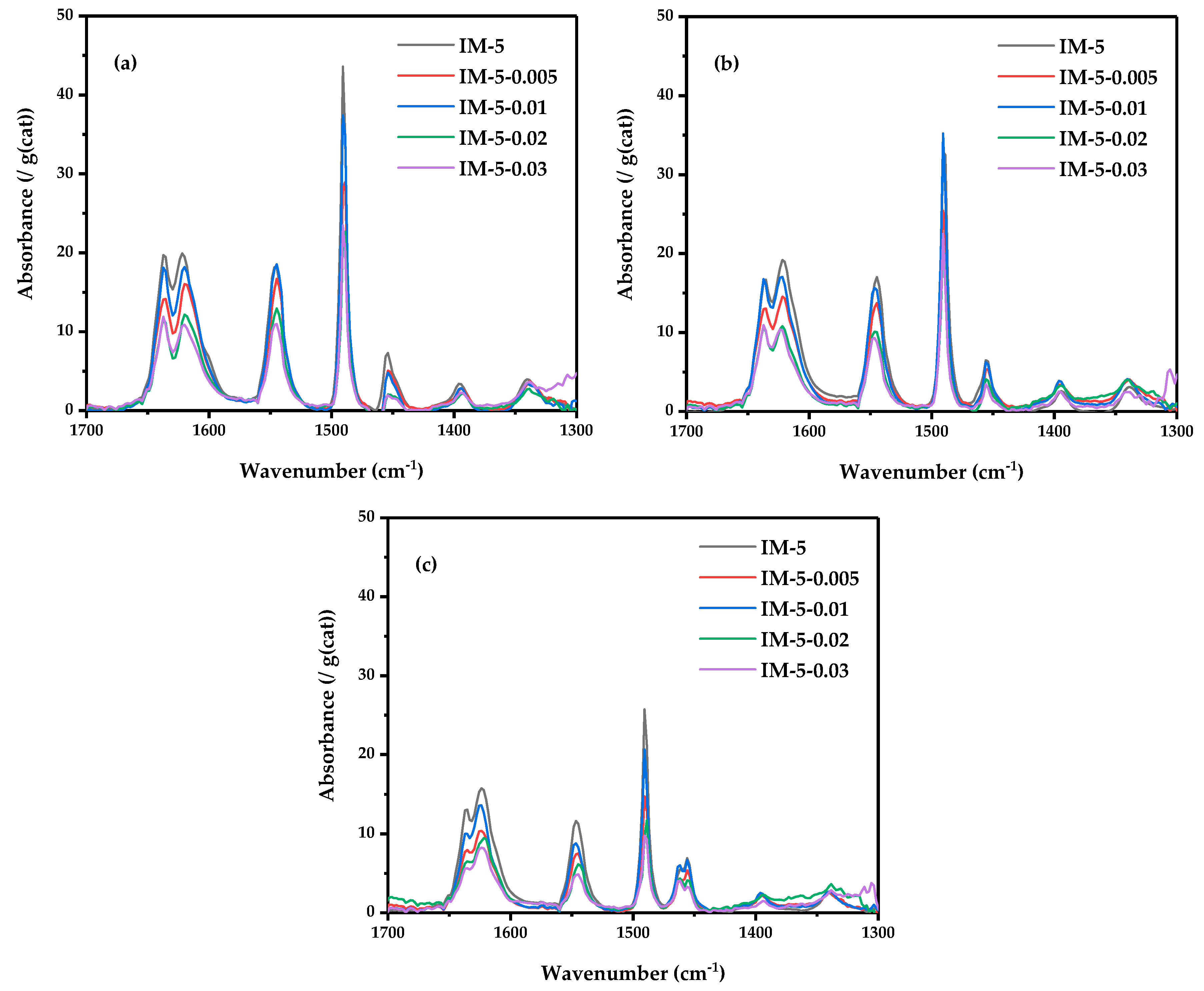
3.3. The Acidity of IM-5 Zeolites
3.4. Catalytic Property Test
- Initial stage: Strong acid sites in the parent zeolite accelerated alkylation but concurrently drove side reactions (e.g., polyalkylation, coking), boosting early durene selectivity. IM-5-0.01’s reduced acidity slowed the main reaction slightly, suppressing side reactions and yielding temporarily lower selectivity.
- Middle stage: Parent zeolite deactivated rapidly due to coke-covered strong acid sites, reducing main reaction rates and increasing isomerization dominance—lowering durene selectivity. IM-5-0.01’s stable acid sites sustained the main reaction, maintaining durene formation and driving selectivity past the parent.
- Later stage: While both samples approach equilibrium selectivity, the modified zeolite achieved a higher plateau and stability, attributed to superior diffusion and acid-site resilience.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ke, D.; Wang, M.J.; Ruan, J.C.; Chen, X.Z.; Zhou, S.D. Efficient, continuous oxidation of durene to pyromellitic dianhydride mediated by a V-Ti-P ternary catalyst: The remarkable doping effect. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2023, 55, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.H.; Liu, J.W.; Li, Z.Z.; An, X. Research progress on synthesis strategy on pyromellitic dianhydride. Petrochem. Technol. 2020, 49, 398–402. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.H.; Li, S.S.; Chen, Z.H.; Jiang, Q.S.; Liu, D.H. Efficient synthesis of durene from syngas utilizing composite catalyst of Zr/Al activity-regulated CuZn oxides and alkali-treated HZSM-5-PEG. Fuel 2024, 378, 132800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, M.T.; Qureshi, B.A.; Gilani, S.A.; Cai, D.; Ma, Y.; Usman, M.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Wei, F. Single-Step Conversion of H2-Deficient Syngas into High Yield of Tetramethylbenzene. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 2203–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Cheng, K.; Kang, J.C.; Zhou, C.; Vijayanand, S.; Zhang, Q.H.; Wang, Y. New horizon in C1 chemistry: Breaking the selectivity limitation in transformation of syngas and hydrogenation of CO2 into hydrocarbon chemicals and fuels. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, D.L.; Zuo, J.C.; Han, X.Q.; Liu, J.; Ye, L.M.; Yuan, Y.Z. Synthesis of durene by methylation of 1,2,4- trimethylbenzene with syngas over bifunctional CuZnZrOx –HZSM-5 catalysts. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2022, 12, 2555–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.J.; Hong, B.L.; Zhou, W.; Wen, D.L.; Xie, Y.F.; Luo, F.; Ye, L.M.; Zuo, J.C.; Yuan, Y.Z. Upgrading Trimethylbenzene to Durene by CO2-Mediated Methylation over Cu-Boosted ZnZrOx Integrated with HZSM-5. ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 11780–11793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Z.; Jiao, L.K.; Muhammad, A.N.; Cheng, L.K.; Meng, C.; Yang, T.H.; Muhammad, T.; Liu, D.H. A one-step synthesis method of durene directly from syngas using integrated catalyst of Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 and Co-Nb/HZSM-5. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 200, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Asano, T.; Koju, K.; Sato, S. Synthesis of Durene by Condensation of 1, 2, 4-Trimethylbenzene and Methanol over Ag-Silica-Alumina Catalyst. J. Jpn. Petrol. Inst. 1970, 13, 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolenko, I.P.; Korenskii, V.I.; Skobeleva, V.D.; Soboleva, A.A. The methylation of pseudocumene by methyl alcohol on aluminum phosphate. Russ. Chem. B+ 1979, 28, 1361–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, T.; Matsukata, M.; Kikuchi, E.; Morita, Y. Reaction of pseudocumene and methanol on montmorillonite catalysts pillared by aluminium hydroxyl complexes. Appl. Catal. 1986, 21, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsuaki, Y.; Akira, I.; Seitaro, N.; Nobuyoshi, H. Selective Formation of 1, 2, 4, 5-Tetra methyl benzene by the Alkylation of 1, 2, 4-Trimethylbenzene with Methanol on HZSM-5 Type Zeolite Catalysts. J. Jpn. Petrol. Inst. 1985, 28, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Tatsuaki, Y.; Akira, I.; Seitaro, N. Selective Alkylation of pseudocumene with Methanol on Modified HZSM-5 Type Zeolite Catalysts. J. Jpn. Petrol. Inst. 1985, 28, 498–502. [Google Scholar]
- Tatsuaki, Y. Shape selective alkylation of methylbenzenes with methanol on ZSM-5 type zeolite catalysts. J. Jpn. Petrol. Inst. 1988, 31, 185–193. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, S.M.; Wang, Y.R.; Xing, E.H.; Mu, X.H. Improved catalytic performance of IM-5 zeolite in pseudocumene methylation with methanol superior to ZSM-5 zeolite. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2025; submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Benazzi, E.; Guth, J.L.; Roulean, L. IM-5 Zeolite, a Process for Its Preparation and Catalytic Applications Thereof. U.S. Patent US6136290A, 24 October 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Christian, B.; Fabian, G.; Lars, M.; Lynne, B.M.; He, Z.B.; Sven, H.; Zou, X.D. Structure of the Polycrystalline Zeolite Catalyst IM-5 Solved by Enhanced Charge Flipping. Science 2007, 315, 1113–1116. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.; Yi, D.Z.; Shi, L.; Liu, N.W. Catalytic performance of IM-5 zeolite with high xylene selectivity in benzene alkylation with methanol. An alternative to ZSM-5 zeolite. Petrol. Sci. Technol. 2020, 38, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.Q.; Huang, Z.G.; Sun, H.X.; Li, L.; Zhu, X.C.; Ren, S.Y.; Shen, B.J. Investigation on n-Alkane Hydroisomerization, a Comparison of IM-5 to ZSM-5 Zeolites. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 14448–14459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babatunde, O.; Abdullah, A.; Jiří, Č.; Martin, K.; Sulaiman, A.K. The effect of alkylation route on ethyltoluene production over different structural types of zeolites. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 306, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar]
- Karolina, A.T.; Joaquin, M.T.; Susana, V.; Kamila, W.; Fernando, R.; Kinga, G.M. Hierarchical zeolites TNU-9 and IM-5 as the catalysts for cracking processes. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. Energy 2023, 338, 123066. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Q.J.; Wei, L.S.; Hou, R.F.; Zhang, L.; Hao, K.; Hu, C.X.; Wen, X.D.; Xiang, H.W.; Tao, Z.C.; Yang, Y.; et al. Insight into performance over IM-5, ZSM-5 and ZSM-11 zeolites for n-heptane cracking to light olefins in the absence & presence of steam. Fuel 2023, 353, 129255. [Google Scholar]
- Deependra, P.; Seung, H.C.; Huang, C.F.; Chiang, H.; Seth, W.; Lars, C.G.; Jeffrey, D.R. Impact of medium-pore zeolite topology on para-xylene production from toluene alkylation with methanol. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2023, 13, 5227. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.H.; Lee, D.K.; Shin, C.H.; Park, Y.K.; Paul, A.W.; Lee, W.M.; Hong, S.B. Synthesis, characterization, and catalytic properties of zeolites IM-5 and NU-88. J. Catal. 2003, 215, 151–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q.J.; Wei, L.S.; Zhang, L.; Qin, Z.X.; Hao, K.; Hu, C.X.; Wen, X.D.; Shen, B.J.; Tao, Z.C.; Yang, Y.; et al. Insight into stepwise dealumination in acid-treatment of IM-5 for catalytic cracking of n-heptane and Fischer-Tropsch naphtha. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2022, 342, 112117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.P.; Chen, J.W.; Wang, Y.R.; Luo, Y.B.; Shu, X.T. Effect of H 2 SiF 6 modification of IM-5 on catalytic performance in benzene alkylation with ethylene. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 18288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.P.; Li, M.G.; Chen, J.W.; Xing, E.H.; Luo, Y.B.; Shu, X.T. Effects of Modification of Acidity and Pore Structure of IM-5 Zeolite on the Catalytic Performance in Methanol to Propylene Reaction. Acta Pet. Sin. (Pet. Process. Sect.) 2020, 36, 17–27. [Google Scholar]
- Zang, Y.R.; Tao, K.Y.; Qiu, P.; Li, H.X. Modification of Zeolite Catalysts with Organic Chlorofluoro-compound I. Modification of HZSM-5 Zeolite with CCl2 F2. Chin. J. Catal. 1989, 10, 171–178. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, K.Y.; Zang, Y.R.; Jia, T.W.; Liu, R.H.; Li, H.X. Alkylation of pseudocumene with Methanol on HZSM-5 Zeolite Catalysts to Form 1,2,4,5- Tetramethylbenzene. Acta Pet. Sin. (Pet. Process. Sect.) 1989, 5, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Yang, W.Y.; Ling, F.X.; Shen, Z.Q.; Yang, R.C.; Sun, W.F.; Fang, X.C.; Ji, H.H. A facile method for the fabrication of IM-5 hollow zeolite sphere in emulsion system. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2012, 163, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ma, B.; Yang, W.Y.; Ling, F.X.; Shen, Z.Q.; Hou, Y.X. Green Synthesis and Characterization of IM -5 Zeolite. Petro Chem. Technol. 2014, 43, 897–902. [Google Scholar]
- Hanene, N.; Mongia, S.Z.; Abdelhamid, G. Study of the effect of the acid dealumination on the physico-chemical properties of Y zeolite. Reac. Kinet Mech. Cat. 2010, 100, 385–398. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, Y.D.; Li, G.C.; Lin, Z.Z.; Xu, Z.H.; Huang, H.T.; Zhu, Y.; Tsang, S.C.E.; Li, M.M.J. In situ hierarchical pore engineering in small pore zeolite via methanol-mediated NH 4 F etching. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 14058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kencana, K.S.; Choi, H.J.; Kemp, K.C.; Hong, S.B. Enhancing the CO2 adsorption kinetics on Na-RHO and Cs-MER zeolites by NH4F/H2O2 etching induced mesoporosity. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploychanok, I.; Anittha, P.; Mutjalin, L.; Jungkyu, C.; Heon, E.P.; Chularat, W.; Alex, C.K.Y. Modification of Zeolite Morphology via NH4F Etching for Catalytic Bioalcohol Conversion. Chemcatchem 2024, 16, e202301208. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.G.; Li, C.Y.; Min, E.Z. A Mechanism Study of Framework Si-Al Substitution in Y Zeolite During Aqueous Fluorosilicate Treatment. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 1989, 49, 189–197. [Google Scholar]
- Onfroy, T.; Qin, Z.; Casale, S.; Valtchev, V. Optimization of ammonium fluoride route to hierarchical ZSM-5 zeolites. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2023, 362, 112760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.B.; Ding, X.F.; Chen, J.; Wang, H.Y.; Wang, H. Preparation of hierarchical EU-1 zeolite via NH 4 F etching and the catalytic activity in cracking of n-hexane. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2024, 286, 119694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, F.H.; John, B.N.; Xu, T.; Larry, W.B.; David, B.F. Physical Organic Chemistry of Solid Acids: Lessons from in Situ NMR and Theoretical Chemistry. Acc. Chem. Res. 2003, 29, 259–267. [Google Scholar]
- Philip, M.K.; Jerry, T.C.; Li, S.C.; William, F.S.; Rajamani, G. Effects of Brønsted acid site proximity in chabazite zeolites on OH infrared spectra and protolytic propane cracking kinetics. J. Catal. 2021, 395, 210–226. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, S.H.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.X.; Chu, Y.Y.; Deng, F.; Hong, S.B. Identifying Crystallographically Different Si−OH−Al Brønsted Acid Sites in LTA Zeolites. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2022, 61, e202203603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; Wang, Q.; Xu, J.; Xia, Q.H.; Deng, F. The Effects of Ammonium Hexafluorosilicate Post-Treatment on the Acidity of H-ZSM-5 Zeolite Studied by Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy. Chin. J. Magn. Reson. 2021, 38, 514–522. [Google Scholar]
- Mykela, D.; David, H. Predicting diffusion barriers and diffusivities of C6–C12 methylbenzenes in MFI zeolites. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2022, 333, 111705. [Google Scholar]
- Röger, H.P.; Möller, K.P.; O’Connor, C.T. The transformation of pseudocumene A probe reaction to monitor external surface modifications of HZSM-5? Microporous Mater. 1997, 8, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röger, H.P.; Böhringer, W.; Möller, K.P.; Connor, C.T.O. Rediscovery of the Paring Reaction: The Conversion of 1,2,4-Trimethylbenzene over HZSM5 at Elevated Temperature. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 2000, 130, 281–286. [Google Scholar]
- Seung, H.C.; Young, C.B.; Hyung, K.M.; Suk, B.H. 1,2,4-Trimethylbenzene disproportionation over large-pore zeolites: An experimental and theoretical study. J. Catal. 2015, 323, 145–157. [Google Scholar]
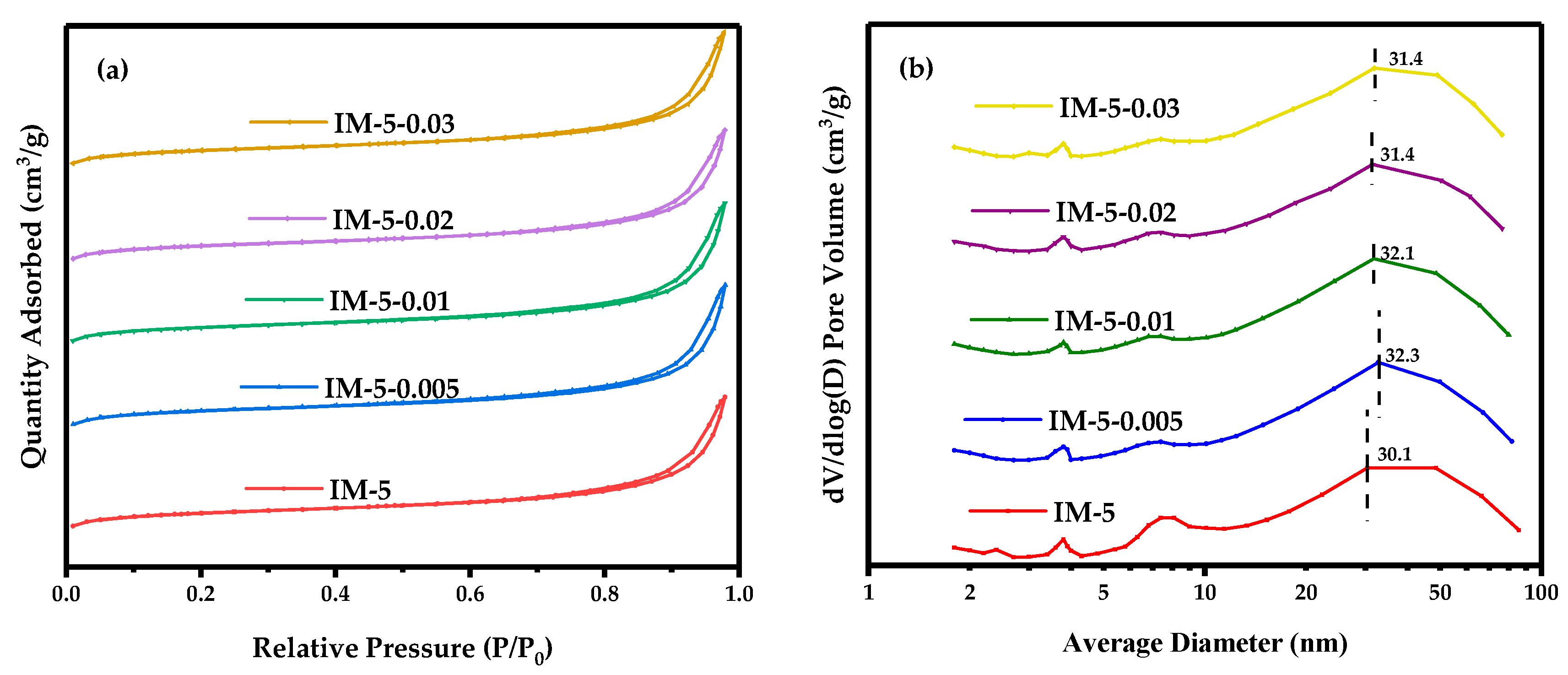





| Samples | SBET a/ (m2·g−1) | Smicro b/ (m2·g−1) | Sext b/ (m2·g−1) | Vtotal c/ (cm3·g−1) | Vmicro b/ (cm3·g−1) | Vmeso d/ (cm3·g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IM-5 | 372 | 332 | 40 | 0.32 | 0.15 | 0.17 |
| IM-5-0.005 | 369 | 310 | 59 | 0.38 | 0.14 | 0.24 |
| IM-5-0.01 | 365 | 307 | 58 | 0.38 | 0.14 | 0.24 |
| IM-5-0.02 | 364 | 308 | 56 | 0.36 | 0.14 | 0.22 |
| IM-5-0.03 | 359 | 303 | 56 | 0.37 | 0.14 | 0.23 |
| Samples | n(SiO2)/n(Al2O3) | Acidity | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bulk a | Framework b | Total | Weak Sites | Medium Sites | Strong Sites | |||||||
| Amounts c | Percents | T d | Amounts c | Percents | T d | Amounts c | Percents | T d | ||||
| IM-5 | 31 | 18 | 1463 | 629 | 43 | 188 | 278 | 19 | 270 | 556 | 38 | 403 |
| IM-5-0.005 | 35 | 18 | 1366 | 628 | 46 | 198 | 342 | 25 | 328 | 396 | 29 | 428 |
| IM-5-0.01 | 36 | 17 | 1249 | 587 | 47 | 197 | 475 | 38 | 363 | 187 | 15 | 431 |
| IM-5-0.02 | 45 | 20 | 1036 | 487 | 47 | 195 | 186 | 18 | 314 | 363 | 35 | 412 |
| IM-5-0.03 | 58 | 25 | 931 | 419 | 45 | 187 | 168 | 18 | 302 | 344 | 37 | 401 |
| Samples | Brønsted Acid μmol/g | Lewis Acid μmol/g | B/L a | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 190 °C | 310 °C | 410 °C | 190 °C | 310 °C | 410 °C | 190 °C | 310 °C | 410 °C | |
| IM-5 | 206 | 180 | 132 | 49 | 47 | 36 | 4.2 | 3.8 | 3.6 |
| IM-5-0.005 | 182 | 149 | 86 | 50 | 36 | 29 | 3.7 | 4.1 | 2.9 |
| IM-5-0.01 | 206 | 176 | 100 | 50 | 45 | 35 | 4.1 | 3.9 | 2.8 |
| IM-5-0.02 | 137 | 116 | 63 | 33 | 32 | 27 | 4.1 | 3.6 | 2.3 |
| IM-5-0.03 | 118 | 102 | 50 | 23 | 25 | 23 | 5.2 | 4.1 | 2.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hao, S.; Wang, Y.; Xing, E.; Mu, X. Understanding the Effect of IM-5 Zeolite Treated with Hexafluorosilicic Acid for the Methanol Alkylation of Pseudocumene. Materials 2025, 18, 2252. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102252
Hao S, Wang Y, Xing E, Mu X. Understanding the Effect of IM-5 Zeolite Treated with Hexafluorosilicic Acid for the Methanol Alkylation of Pseudocumene. Materials. 2025; 18(10):2252. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102252
Chicago/Turabian StyleHao, Shumin, Yongrui Wang, Enhui Xing, and Xuhong Mu. 2025. "Understanding the Effect of IM-5 Zeolite Treated with Hexafluorosilicic Acid for the Methanol Alkylation of Pseudocumene" Materials 18, no. 10: 2252. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102252
APA StyleHao, S., Wang, Y., Xing, E., & Mu, X. (2025). Understanding the Effect of IM-5 Zeolite Treated with Hexafluorosilicic Acid for the Methanol Alkylation of Pseudocumene. Materials, 18(10), 2252. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102252






