Effects of Sn Addition and Fe Content Adjustment on the Decolorization Performance of Fe-Si-B Amorphous Alloys for Azo Dyes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, S.; Xue, H.; Feng, X.; Pyo, S.-H. Electrostimulation for promoted microbial community and enhanced biodegradation of refractory azo dyes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, X.; Xia, S.; Ding, Q.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H. Au/Boron organic frameworks for efficient removal and degradation of azo dye pollutants. Colloids Surf. A 2022, 646, 128884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; You, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yao, R.; Liu, G.; Lu, J.; Zhao, S. Research progress on high entropy alloys and high entropy derivatives as OER catalysts. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, S.; Mandal, A.K.; Behera, A.K.; Patra, S.; Nayak, R.; Behera, C.; Jena, M. A comprehensive review on phycoremediation of azo dye to combat industrial wastewater pollution. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 70, 107088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhong, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, F.; Guo, J.; Xu, M. Molecular mechanism of zero valent iron-enhanced microbial azo reduction. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 290, 118046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Yao, G.; Cheng, Q.; Yu, S.; Liu, M.; Gao, C. Positively charged thin-film composite hollow fiber nanofiltration membrane for the removal of cationic dyes through submerged filtration. Desalination 2013, 328, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Zhang, C.; Wang, H. Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution using Mg-Fe, Zn-Fe, Mn-Fe layered double hydroxide. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 81, 2522–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, V.; Swarna Karthika, T.; Mansiya, C.; Alagar, M. An over review on recently developed techniques, mechanisms and intermediate involved in the advanced azo dye degradation for industrial applications. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1224, 129195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunez, J.; Yeber, M.; Cisternas, N.; Thibaut, R.; Medina, P.; Carrasco, C. Application of electrocoagulation for the efficient pollutants removal to reuse the treated wastewater in the dyeing process of the textile industry. J. Hazard Mater. 2019, 371, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, F.; Wang, Q.; Zeng, Q.; Hou, L.; Liang, T.; Cui, Z.; Shen, B. Excellent reusability of FeBC amorphous ribbons induced by progressive formation of through-pore structure during acid orange 7 degradation. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 38, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Peng, S.Y.; Zheng, Z.G.; Zuo, J.L.; Zeng, D.C.; Qiu, Z.G.; Xiao, M.; Chen, J.W.; Yu, H.Y. The degradation performance of the Fe78Si13B9 and (FeCoNi)78Si13B9 high-entropy amorphous alloy ribbons. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 815, 152347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, J.; Pan, J.; Zhang, G.; Liu, S.; Sun, C.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Guan, S. Efficient degradation capability of the FePCB amorphous alloy in acid orange 7 dye solution. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 6842–6856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-Q.; Liu, Y.-H.; Chen, M.-W.; Xie, G.-Q.; Louzguine-Luzgin, D.V.; Inoue, A.; Perepezko, J.H. Rapid Degradation of Azo Dye by Fe-Based Metallic Glass Powder. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 2567–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zheng, Z.; Zhao, L.; Qiu, Z.; Zeng, D. Synergistic effect between pyrite and Fe-based metallic glass for the removal of azo dyes in wastewater. Colloids Surf. A 2023, 666, 131227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-C.; Jia, Z.; Lyu, F.; Liang, S.-X.; Lu, J. A review of catalytic performance of metallic glasses in wastewater treatment: Recent progress and prospects. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 105, 100576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, F.; Wang, Q.; Di, S.; Yun, L.; Zhou, J.; Shen, B. Enhanced dye degradation capability and reusability of Fe-based amorphous ribbons by surface activation. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 53, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Li, X.; Sun, H.; Song, K.; Wang, L. Comparative study on the corrosion and self-cleaning behavior of Fe-B-C and Fe-B-P amorphous alloys in methylene blue dye solution degradation. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2022, 575, 121212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.; Dan, Z.; Qin, F.; Chang, H. Adsorption-enhanced reductive degradation of methyl orange by Fe73.3Co10Si4B8P4Cu0.7 amorphous alloys. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 242, 122307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.C.; Ma, H.; Wang, W.; Wang, W. High MB Solution Degradation Efficiency of FeSiBZr Amorphous Ribbon with Surface Tunnels. Materials 2020, 13, 3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, Y. Pd nanoparticles immobilized on aniline-functionalized MXene as an effective catalyst for hydrogen production from formic acid. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 33098–33106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, X.; Liu, H.; Yang, W.; Xiong, X.; Chen, C.; Xie, Y. Ultrafast degradation of azo dye using surface-activated Fe-based metallic glass. Surf. Interfaces 2025, 59, 105938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zheng, Z.; Huang, L.; Qiu, Z.; Xia, Q.; Zhou, S.; Tong, X.; Zeng, D. Effective removal of Orange II dye by porous Fe-base amorphous/Cu bimetallic composite. Colloids Surf. A 2023, 656, 130388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-J.; Qian, T.-T.; Jiang, H. Bimetallic Fe nanoparticles: Recent advances in synthesis and application in catalytic elimination of environmental pollutants. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 236, 448–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Xia, F.; Wang, B.; Lv, X.; Ye, W.; Yang, G. Hydrogen production by Co-based bimetallic nano-catalysts and their performance in methane steam reforming. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2020, 38, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-Q.; Hui, K.-Z.; Dong, L.-Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Q.-h.; Gu, L.; Zhao, W.; Lan, S.; Ke, Y.; Shao, Y.; et al. Excellent long-term reactivity of inhomogeneous nanoscale Fe-based metallic glass in wastewater purification. Sci. China Mater. 2019, 63, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zheng, Z.; Zhao, L.; Qiu, Z.; Zeng, D. Oxalic acid modification enables high efficiency and proton conductive of Fe-base amorphous toward acid orange II in wastewater removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 332, 125768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Chen, J.W.; Zheng, Z.G.; Qiu, Z.G.; Peng, S.Y.; Zhou, S.H.; Zeng, D.C. Excellent degradation performance of the Fe78Si11B9P2 metallic glass in azo dye treatment. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2020, 145, 109546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liang, S.X.; Jia, L.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tao, P. Breaking the pH limitation by Mo modulated amorphous medium-entropy alloys as efficient advanced oxidation catalysts. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 116151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Wang, K.; Yao, K. Maintaining high saturation magnetic flux density and reducing coercivity of Fe-based amorphous alloys by addition of Sn. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2020, 528, 119710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.G.; Chen, Y.B.; Wei, J.; Wang, X.; Qiu, Z.G.; Zeng, D.C. Enhanced Ms of Fe-rich Fe-B-Cu amorphous/nanocrystalline alloys achieved by annealing treatments. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 939, 168621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, M.; Ji, Q.; Feng, T.; Lan, S.; Yao, K. Effect of the chloride ion on advanced oxidation processes catalyzed by Fe-based metallic glass for wastewater treatment. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 117, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, M.; Yi, S.; Choi, J. Excellent dye degradation performance of FeSiBP amorphous alloys by Fenton-like process. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 105, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Q.; Xie, L.; Zhang, G.; Mu, B.; Chang, C.; Ma, X. Development of novel Fe-based bulk metallic glasses with excellent wear and corrosion resistance by adjusting the Cr and Mo contents. Intermetallics 2023, 153, 107801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yang, G.; Luo, S.; Yin, S.; Jia, J.; Li, Z.; Gao, S.; Shao, Y.; Yao, K. Unexpected high performance of Fe-based nanocrystallized ribbons for azo dye decomposition. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 14230–14240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Zhang, W.C.; Wang, W.M.; Habibi, D.; Zhang, L.C. Amorphous Fe78Si9B13 alloy: An efficient and reusable photo-enhanced Fenton-like catalyst in degradation of cibacron brilliant red 3B-A dye under UV–vis light. Appl. Catal. B 2016, 192, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Chen, N.; Cheng, M.; Luo, S.; Shao, Y.; Yao, K. Multi-phase nanocrystallization induced fast degradation of methyl orange by annealing Fe-based amorphous ribbons. Intermetallics 2017, 90, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Hu, Z. Rapid reductive degradation of azo dyes by a unique structure of amorphous alloys. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2011, 56, 3988–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, H.; Lv, M.; Hu, Z. Decolorization of azo dye solution by Fe–Mo–Si–B amorphous alloy. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2010, 356, 1703–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Choi, W. Visible light and Fe(III)-mediated degradation of Acid Orange 7 in the absence of H2O2. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2003, 159, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stylidi, M.; Kondarides, D.I.; Verykios, X.E. Pathways of solar light-induced photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes in aqueous TiO2 suspensions. Appl. Catal. B 2003, 40, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



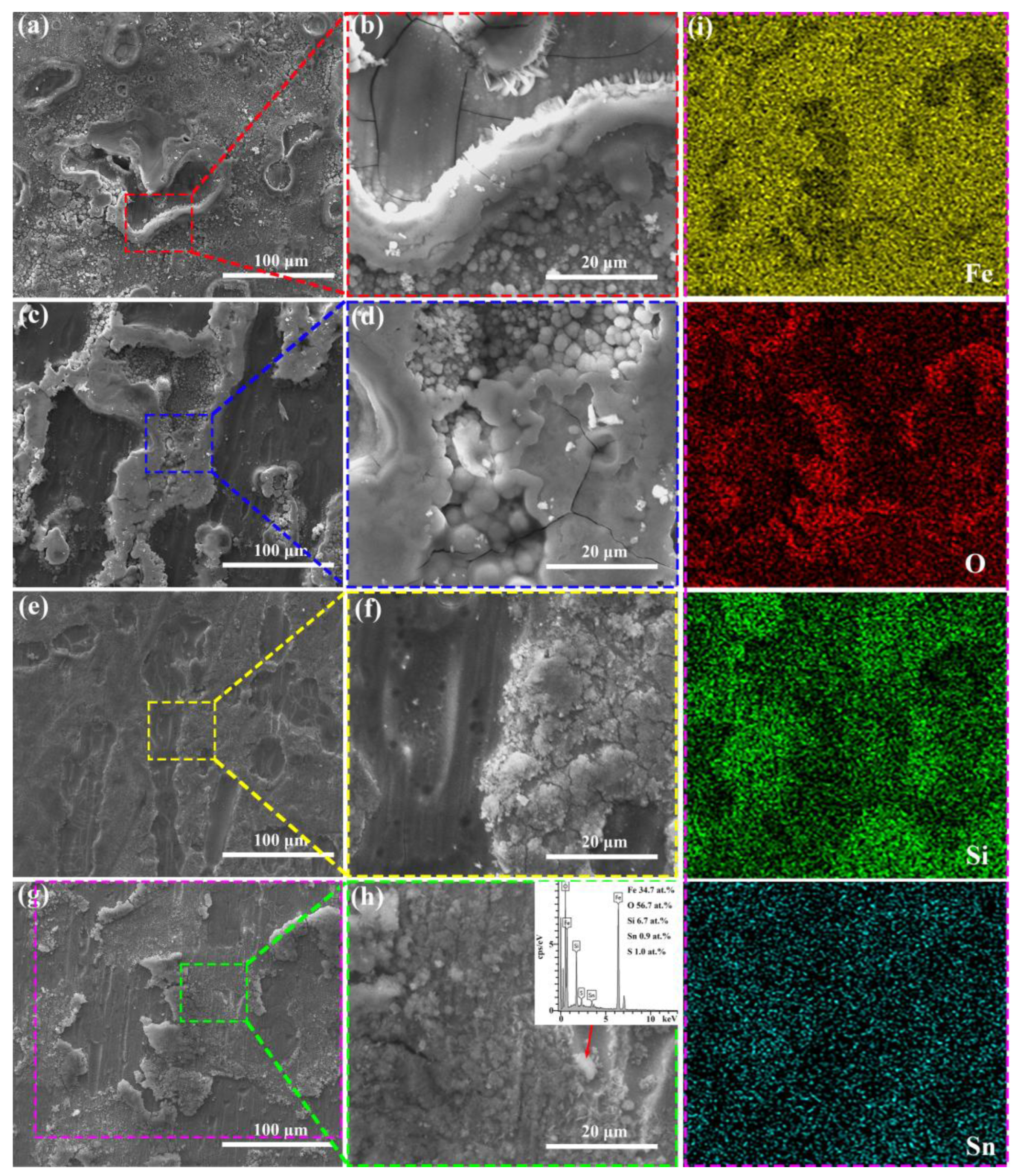


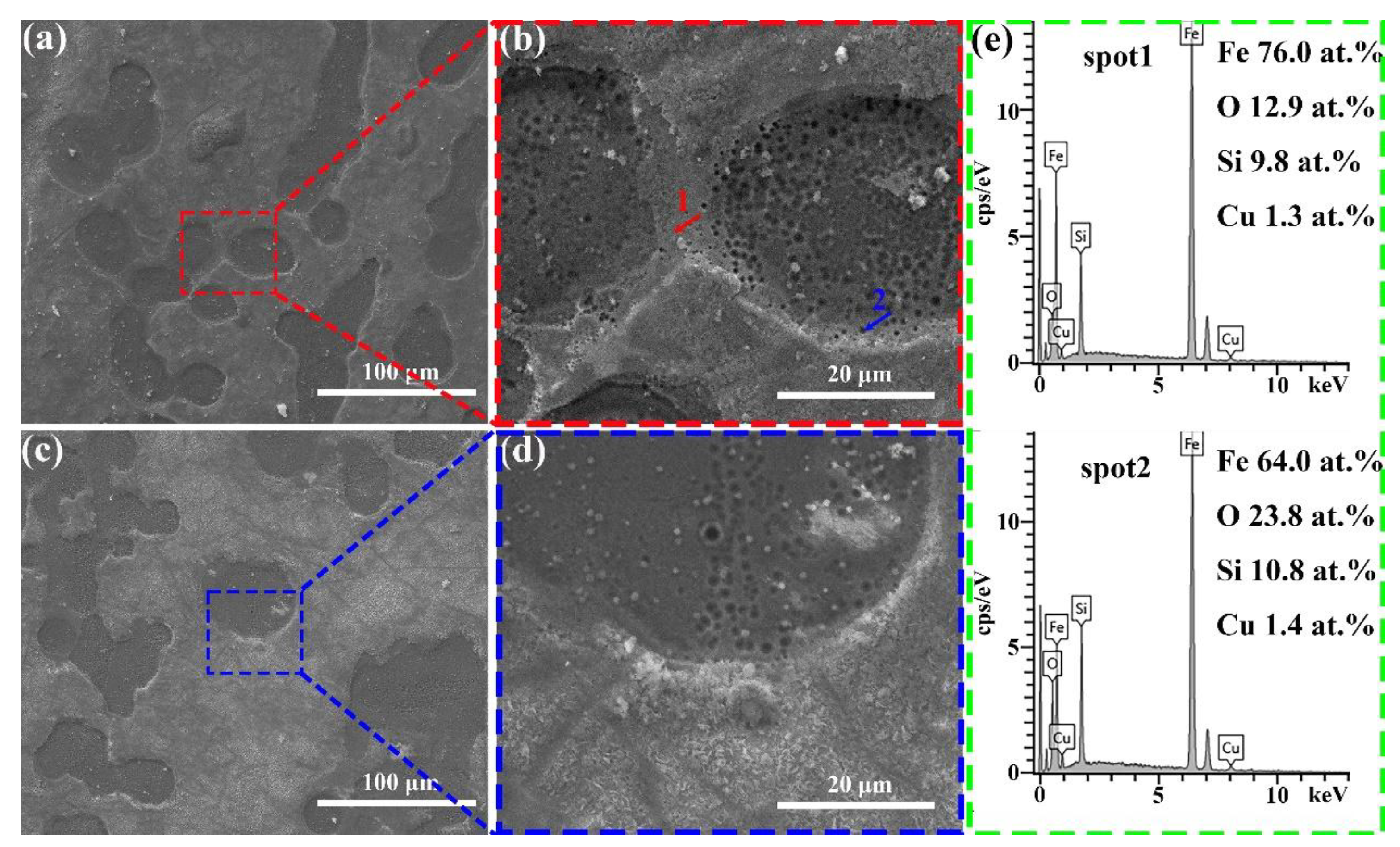

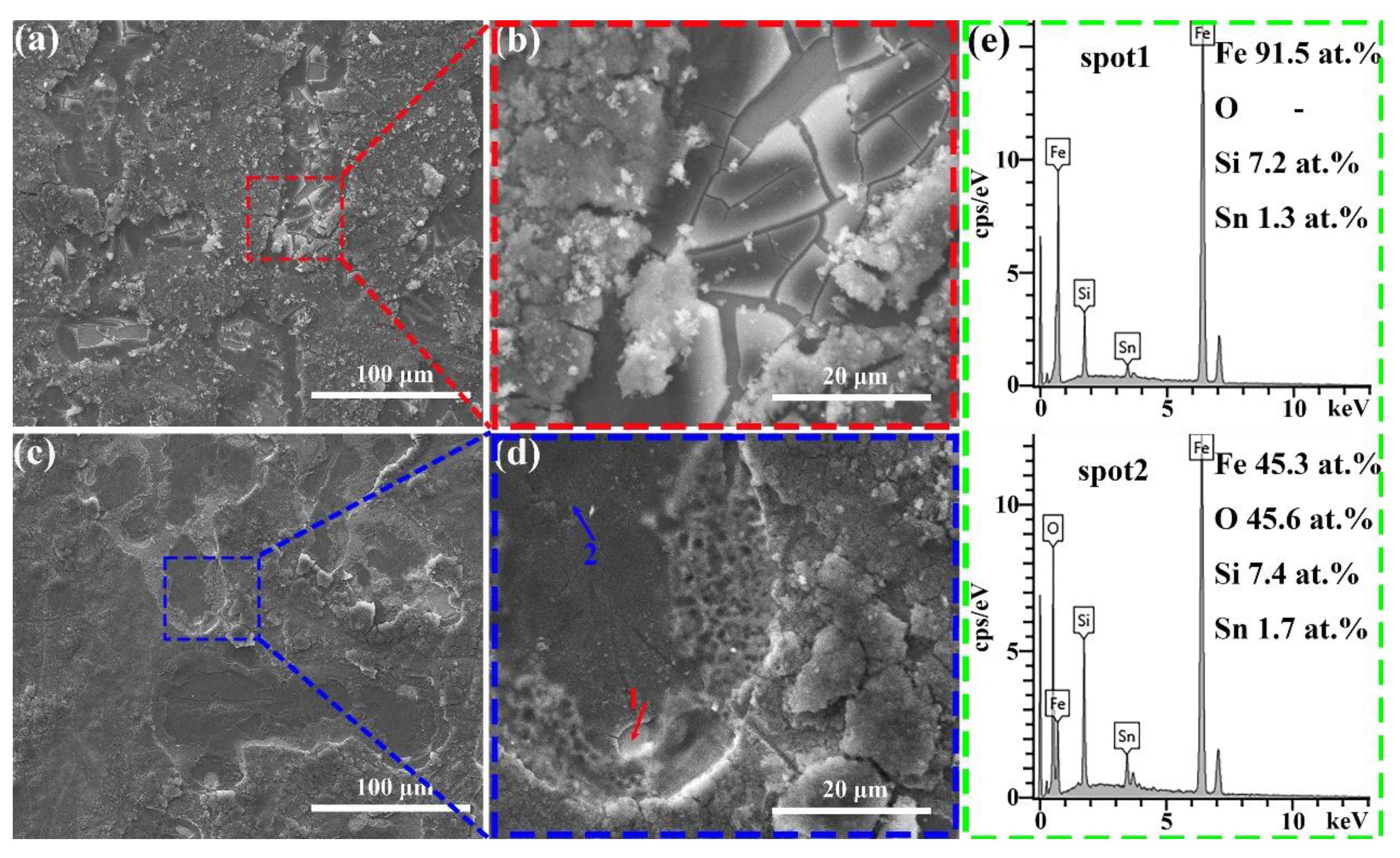

| Sample | Fe | Si | Cu | Sn |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe77Si13B9Cu1 | 86.8 | 11.6 | 1.6 | - |
| Fe79Si11B9Cu1 | 89.0 | 9.7 | 1.3 | - |
| Fe81Si9B9Cu1 | 90.8 | 7.9 | 1.3 | - |
| Fe77Si13B9Sn1 | 87.3 | 11.5 | - | 1.2 |
| Fe79Si11B9Sn1 | 89.3 | 9.4 | - | 1.3 |
| Fe81Si9B9Sn1 | 91.5 | 7.3 | - | 1.2 |
| Composition | Dye | C0 (mg/L) | pH | Mass Dosage (g/L) | Temp. (°C) | Kobs (min−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe78(Si,B)22 | Orange II | 100 | 6 | 9-12 | Room | 0.125 | [37] |
| (Fe0.99Mo0.01)78Si9B13 | Direct blue 2B | 200 | 7 | 13.3 | 60 | 0.136 | [38] |
| Fe78Si13B9 | Orange II | 40 | 7 | 2 | 35 | 0.071 | [11] |
| Fe80B13C7 | acid orange 7 | 20 | 3 | 2 | 25 | 0.08 | [10] |
| Fe85P11C2B2 | acid orange 7 | 20 | 3 | 2 | 35 | 0.0118 | [12] |
| Fe78Si11B9P2 | Orange II | 40 | 7 | 2 | 35 | 0.082 | [27] |
| Fe81Si9B9Sn1 | Orange II | 40 | 7 | 2 | 35 | 0.094 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, J.; Zheng, Z.; Qiu, Z.; Xu, W.; Xiao, M.; Zeng, D. Effects of Sn Addition and Fe Content Adjustment on the Decolorization Performance of Fe-Si-B Amorphous Alloys for Azo Dyes. Materials 2025, 18, 2240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102240
Wei J, Zheng Z, Qiu Z, Xu W, Xiao M, Zeng D. Effects of Sn Addition and Fe Content Adjustment on the Decolorization Performance of Fe-Si-B Amorphous Alloys for Azo Dyes. Materials. 2025; 18(10):2240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102240
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Jing, Zhigang Zheng, Zhaoguo Qiu, Wanghui Xu, Meng Xiao, and Dechang Zeng. 2025. "Effects of Sn Addition and Fe Content Adjustment on the Decolorization Performance of Fe-Si-B Amorphous Alloys for Azo Dyes" Materials 18, no. 10: 2240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102240
APA StyleWei, J., Zheng, Z., Qiu, Z., Xu, W., Xiao, M., & Zeng, D. (2025). Effects of Sn Addition and Fe Content Adjustment on the Decolorization Performance of Fe-Si-B Amorphous Alloys for Azo Dyes. Materials, 18(10), 2240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102240






