Valorization of Steel Slag and Fly Ash in Mortar: Modeling Age-Dependent Strength with Response Surface Methodology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Mortar Preparation and Testing
2.3. Mathematical Model Development
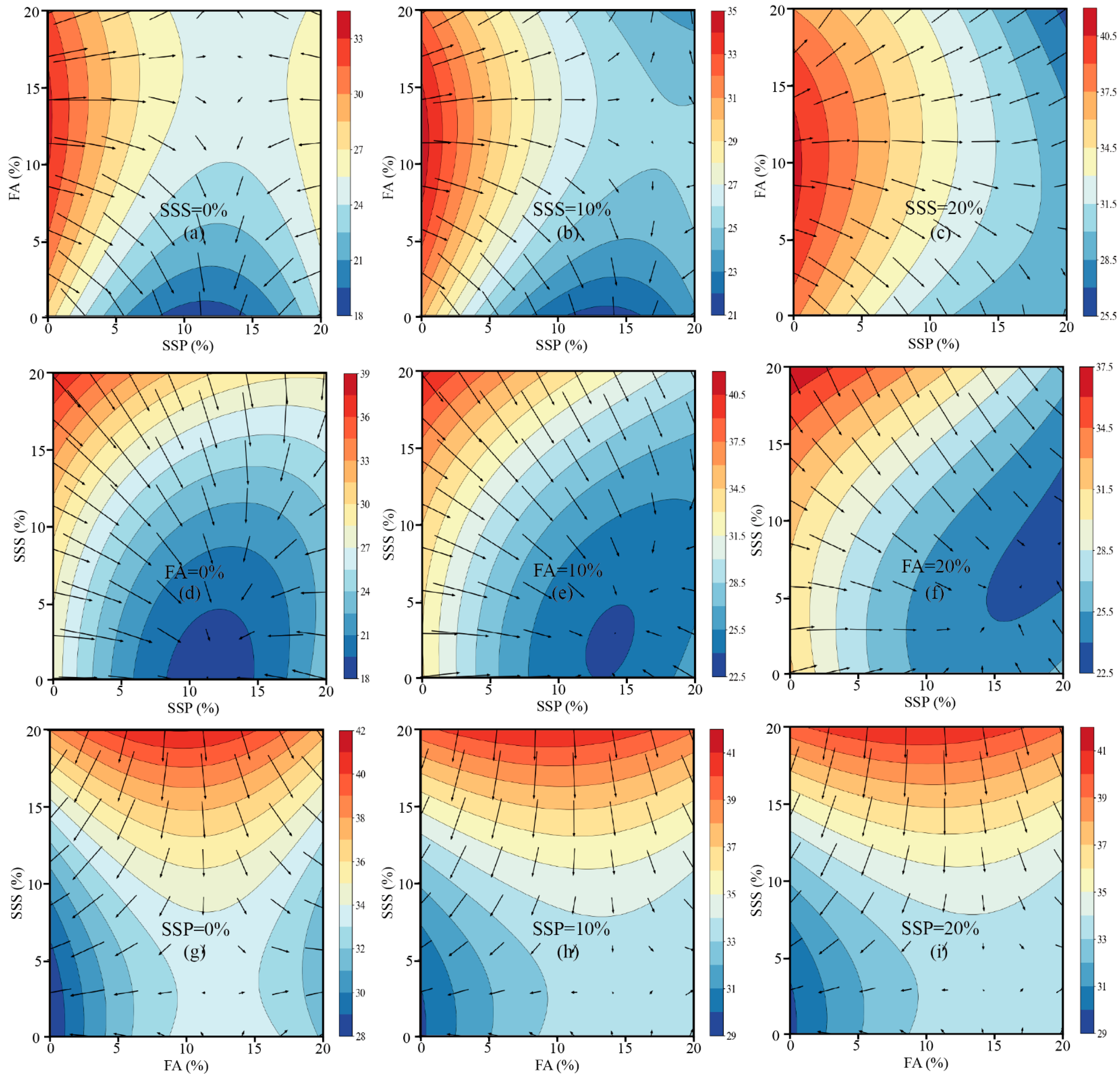
2.4. Gradient Vector Calculation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Compressive Strength of Mortar
3.2. RSM Analysis
3.2.1. Analysis of Variance
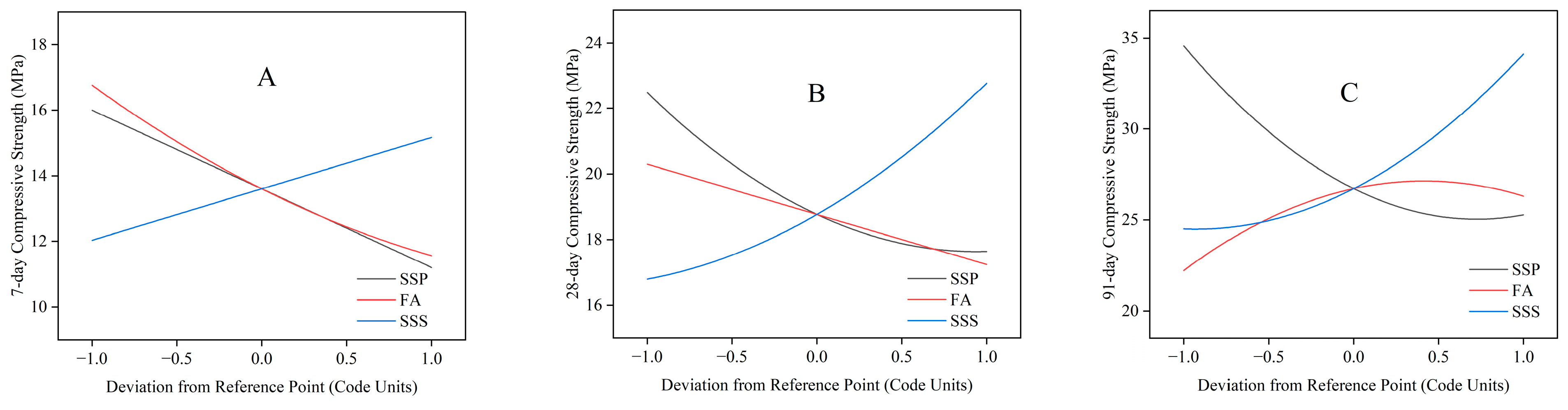
3.2.2. Strength Development Analysis
3.2.3. Main Effect Analysis
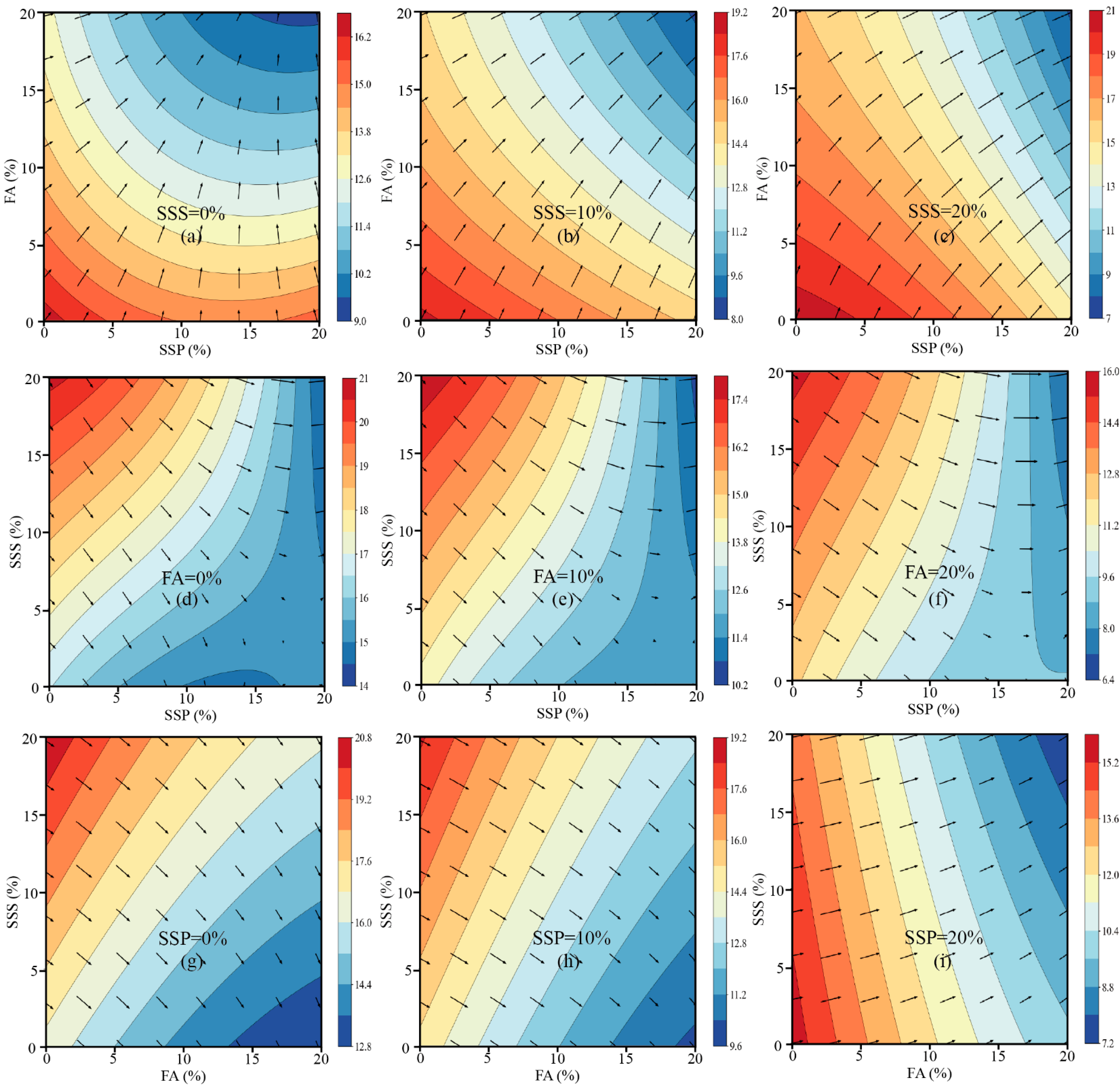
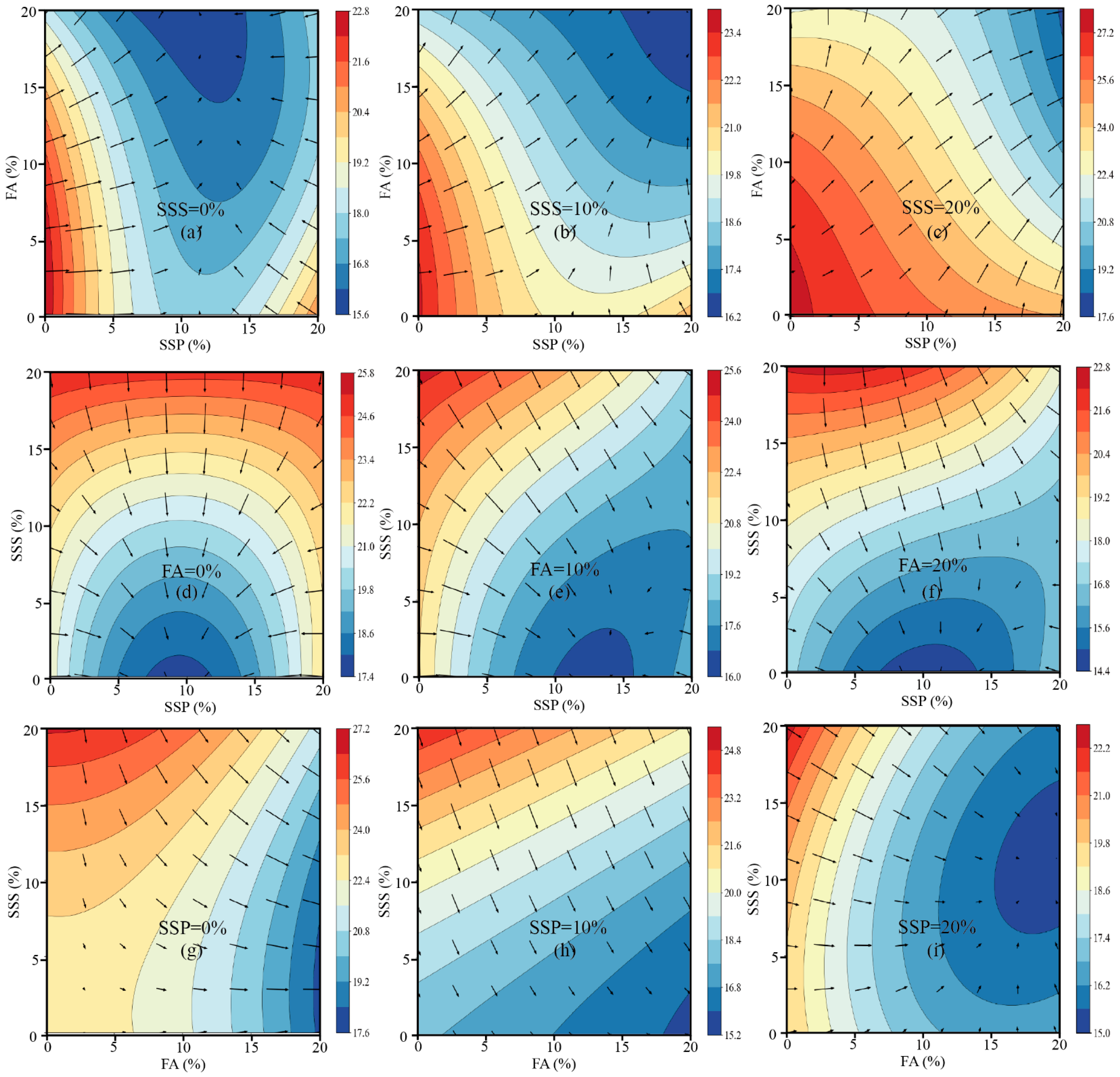
3.2.4. Interaction Analysis Among SSP, FA, and SSS
4. Recommendations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- USGS mineral review. In Mineral Commodity Summaries; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2025.
- Panagoda, S.S.; Ranasinghe, H.; Perera, V.; Sandunika, I.; Tilanka, G.; Alwis, S.; Dilka, S. Cement manufacturing process and its environmental impact. J. Res. Technol. Eng. 2023, 4, 161–168. [Google Scholar]
- Hasanbeigi, A. Carbon emissions mitigation methods for cement industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2010, 18, 1509–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, R.M. Global CO2 emissions from cement production. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2018, 10, 195–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Energy Agency (IEA). Cement Technology Roadmap: Carbon Emissions Reductions up to 2050; International Energy Agency (IEA): Paris, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Althoey, F.; Ansari, W.S.; Sufian, M.; Deifalla, A.F. Advancements in low-carbon concrete as a construction material for the sustainable built environment. Dev. Built Environ. 2023, 16, 100284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, F.; Pan, Z.; Li, H.; Wu, Z.; Li, L.; Xiong, Z. Use of supplementary cementitious materials in seawater-sea sand concrete: State-of-the-art review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 425, 136009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Hu, X.; Alengaram, U.J.; Chen, W.; Shi, C. Use of carbonated recycled cement paste powder as a new supplementary cementitious material: A critical review. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2024, 154, 105783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Lujan, V.A.; Ramirez-Arellanes, S.; Gomez-Sanchez, A.; Perez-Ramos, A.E.; Cruz-Garcia, E.S.; Cruz-Martinez, H. Properties of fresh and hardened cement-based materials with waste glass as supplementary cementitious material: A review. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 95, 110137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Yu, Q.; van der Laan, S.R.; Chen, Y. Dipotassium hydrogen phosphate activated Al-rich steel slag: The role of layered double hydroxides and aluminum hydrate gel. Cem. Concr. Res. 2025, 189, 107783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.F.; Doh, S.I.; Feng, W.Y.; Albtoosh, J.f.A.A.; Wei, C.B. The mechanical properties of concrete incorporating steel slag as supplementary cementitious material. Key Eng. Mater. 2021, 879, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.M.; Doh, S.I.; Chin, S.C.; Li, X. The effect of particle sizes of steel slag as cement replacement in high strength concrete under elevated temperatures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juenger, M.; Winnefeld, F.; Provis, J.L.; Ideker, J. Advances in alternative cementitious binders. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 1232–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrivener, K.; Snellings, R.; Lothenbach, B. A Practical Guide to Microstructural Analysis of Cementitious Materials; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; Volume 540. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez, R.; Martirena, F.; Scrivener, K.L. The origin of the pozzolanic activity of calcined clay minerals: A comparison between kaolinite, illite and montmorillonite. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, N.; Guo, W.; Cao, H.; Wang, Y. Study on the hydration characteristics of steel slag cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 420, 135605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skibsted, J.; Snellings, R. Reactivity of supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs) in cement blends. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 124, 105799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Hu, M.; Yao, J.; Wang, K.; Tang, S.; Zuo, Y. Calcium sulfoaluminate cementitious materials with steel slag and calcined phosphogypsum: Hydration and physico-mechanical properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 460, 139795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzoubaa, N.; Zhang, M.-H.; Malhotra, V.M.; Golden, D.M. Blended fly ash cements—A review. ACI Mater. J. 1999, 96, 641–650. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, S.; Kwon, E.E.; Lee, J. Upcycling steel slag into construction materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 444, 137882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, F.; Yu, F.; Du, T. A review of the application of steel slag in concrete. Structures 2024, 63, 106352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahmani, H.; Mostafaei, H.; Santos, P.; Fallah Chamasemani, N. Enhancing the mechanical properties of Ultra-High-Performance Concrete (UHPC) through silica sand replacement with steel slag. Buildings 2024, 14, 3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, D.; Yan, P. Hydration heat evolution and kinetics of blended cement containing steel slag at different temperatures. Thermochim. Acta 2015, 605, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, G.; Li, Z.; Sun, T.; Ye, Z.; Deng, Y.; Li, W. Greener phosphogypsum-based all-solid-waste cementitious binder with steel slag activation: Hydration, mechanical properties and durability. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 443, 140996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, Z.; Sun, Y.; Qiu, J.; Zheng, P. Mechanical activation of steel slag to prepare supplementary cementitious materials: A comparative research based on the particle size distribution, hydration, toxicity assessment and carbon dioxide emission. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 60, 105200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.M.; Doh, S.I.; Al-Btoush, A.M.; Li, X.; Chin, S.C. The impact of alkali activator dosage on the compressive strength and water absorption of steel slag concrete. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 51, 1323–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Yang, Z.; Yan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, S.; Li, K.; Briseghella, B.; Marano, G.C. Mechanical properties and microstructure of engineered cementitious composites with high volume steel slag and GGBFS. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 398, 132512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheen, Y.-N.; Le, D.-H.; Lam, M.N.-T. Performance of self-compacting concrete with stainless steel slag versus fly ash as fillers: A comparative study. Period. Polytech. Civ. Eng. 2021, 65, 1050–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, P.; Hu, C.; Xia, H.; Liang, Z. Study on the Mechanical Properties and Hydration Behavior of Steel Slag-Red Mud-Electrolytic Manganese Residue Based Composite Mortar. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharathi, K.; Adari, S.; Pallepamula, U. Mechanical properties of self-compacting concrete using steel slag and glass powder. J. Build. Pathol. Rehabil. 2022, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Hou, S.; Guo, Y.; Cao, X.; Zhang, D. Feasibility of Preparing Steel Slag–Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag Cementitious Materials: Synergistic Hydration, Fresh, and Hardened Properties. Buildings 2024, 14, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, T. In-depth insight into the cementitious synergistic effect of steel slag and red mud on the properties of composite cementitious materials. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 52, 104449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gao, Z.; Jin, Q.; Zhang, X.; Ruan, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, S. Synergistic effect of waste glass and steel slag on mechanical property and microstructure of cement-based materials. Powder Technol. 2025, 451, 120479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Wan, Y.; Li, H.; Jiao, X. Rheology, mechanics, microstructure and durability of low-carbon cementitious materials based on circulating fluidized bed fly ash: A comprehensive review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemalatha, T.; Ramaswamy, A. A review on fly ash characteristics—Towards promoting high volume utilization in developing sustainable concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 147, 546–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, D.; Wang, H.; Gao, W. A review on fly ash high-value synthesis utilization and its prospect. Green Energy Resour. 2024, 2, 100062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wei, L.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, J. Study on the Inhibition Effect of Fly Ash on Alkali–Silica Reaction and Its Influence on Building Energy Performance. Buildings 2025, 15, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, B.; Maghfouri, M.; Alimohammadi, V.; Asadi, I.; Roychand, R. The acid and chloride permeability resistance of masonry cement plaster mortar incorporating high-volume fly ash content. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 86, 108783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-X.; Liu, R.-A.; Liu, L.-Y.; Zhuo, K.-Y.; Chen, Z.-B.; Guo, Y.-C. High-strength and high-toughness alkali-activated composite materials: Optimizing mechanical properties through synergistic utilization of steel slag, ground granulated blast furnace slag, and fly ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 422, 135811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, G.; Alengaram, U.J.; Ibrahim, S.; Ibrahim, M.S.I. Effect of Fly Ash characteristics, sodium-based alkaline activators, and process variables on the compressive strength of siliceous Fly Ash geopolymers with microstructural properties: A comprehensive review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 437, 136808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, A.K.A.; Bouaziz, I.; Jaber, L.; Abushawish, A.; Almanassra, I.W.; Ali Abdelkareem, M.; Ali Atieh, M. Fly ash as zero cost material for water treatment applications: A state of the art review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 129104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rentier, E.S.; Cammeraat, L.H. The environmental impacts of river sand mining. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 155877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirthika, S.; Singh, S.; Chourasia, A. Alternative fine aggregates in production of sustainable concrete—A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 268, 122089. [Google Scholar]
- Rashad, A.M. Behavior of steel slag aggregate in mortar and concrete-A comprehensive overview. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 53, 104536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.; Li, X. Hydration behavior and cementitious properties of steel slag: From an early age to a long-term. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e03066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, W.; Jiang, J.; Ding, S.; Duan, P. Hydration and Microstructure of Steel Slag as Cementitious Material and Fine Aggregate in Mortar. Molecules 2020, 25, 4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Box, G.E.P.; Wilson, K.B. On the Experimental Attainment of Optimum Conditions. In Breakthroughs in Statistics: Methodology and Distribution; Kotz, S., Johnson, N.L., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 270–310. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, D.C. Design and Analysis of Experiments, 9th ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Ho, C.M.; Doh, S.I.; Al Biajawi, M.I.; Ma, Q.; Zhao, D.; Liu, R. Strength Characteristics and Prediction of Ternary Blended Cement Building Material Using RSM and ANN. Buildings 2025, 15, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kursuncu, B.; Gencel, O.; Bayraktar, O.Y.; Shi, J.; Nematzadeh, M.; Kaplan, G. Optimization of foam concrete characteristics using response surface methodology and artificial neural networks. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 337, 127575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BS EN 197-1:2011; Methods of testing Composition, Specifications and Conformity Criteria for Common Cements. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2011.
- Huo, B.; Yanglin, L.; Baoliang, L.; Chun, C.; and Zhang, Y. Influence of particle size on the reactivity of chemical modified steel slag powder. J. Sustain. Cem.-Based Mater. 2023, 12, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BS EN 450-1:2012; Fly ash for concrete—Definition, specifications and conformity criteria. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2012.
- BS EN 12620:2013; Aggregates for Concrete. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2013.
- BS EN 12390-3:2019; Testing hardened concrete—Compressive strength of test specimens. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2019.
- Nguyen, H.-A.; Chang, T.-P.; Shih, J.-Y.; Chen, C.-T. Influence of low calcium fly ash on compressive strength and hydration product of low energy super sulfated cement paste. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 99, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.H.J.; Winnefeld, F.; Tschopp, E.; Müller, C.J.; Lothenbach, B. Influence of fly ash on the hydration of calcium sulfoaluminate cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 95, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, K.; Aguayo, M.; Oey, T.; Sant, G.; Neithalath, N. Hydration and strength development in ternary portland cement blends containing limestone and fly ash or metakaolin. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2013, 39, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschner, F.; Winnefeld, F.; Lothenbach, B.; Seufert, S.; Schwesig, P.; Dittrich, S.; Goetz-Neunhoeffer, F.; Neubauer, J. Hydration of Portland cement with high replacement by siliceous fly ash. Cem. Concr. Res. 2012, 42, 1389–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yan, P. Hydration properties of basic oxygen furnace steel slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 1134–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Mi, G.; Wang, Q. A comparison of early hydration properties of cement-steel slag binder and cement-limestone powder binder. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2014, 115, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, A.A.; Puffer, S.M.; Ahadisarkani, S.; Ahmadi, F.; Naderpour, H. Steel Slag as Sand Replacement in Concrete: A Systematic Review of Fresh, Mechanical, and Durability Properties. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2025, 2025, 3901578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alterary, S.S.; Marei, N.H. Fly ash properties, characterization, and applications: A review. J. King Saud Univ.—Sci. 2021, 33, 101536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Gao, Z.; Wang, J.; Guo, J.; Hu, S.; Ling, Y. Properties of fresh and hardened fly ash/slag based geopolymer concrete: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 270, 122389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Ren, X.; Ye, J.; Luan, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, W. Performance of a steel slag-based supplementary cementitious material via the synergistic modification of binary fly ash and gypsum system. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 405, 133186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lothenbach, B.; Scrivener, K.; Hooton, R.D. Supplementary cementitious materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 1244–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Shi, X. Characteristics and applications of fly ash as a sustainable construction material: A state-of-the-art review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 136, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Binder | CaO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | SO3 | K2O | Na2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | |
| Error | ±0.1% | ±0.1% | ±0.1% | ±0.1% | ±0.2% | ±0.2% | ±0.2% | ±0.2% |
| OPC | 63.37 | 19.26 | 3.64 | 4.22 | 1.49 | 1.71 | 0.25 | 0.18 |
| SSP | 39.12 | 13.34 | 8.41 | 24.31 | 3.53 | 1.22 | 0.46 | 0.27 |
| FA | 4.7 | 48.5 | 25.4 | 7.8 | 2.2 | 0.5 | 3.4 | 1.1 |
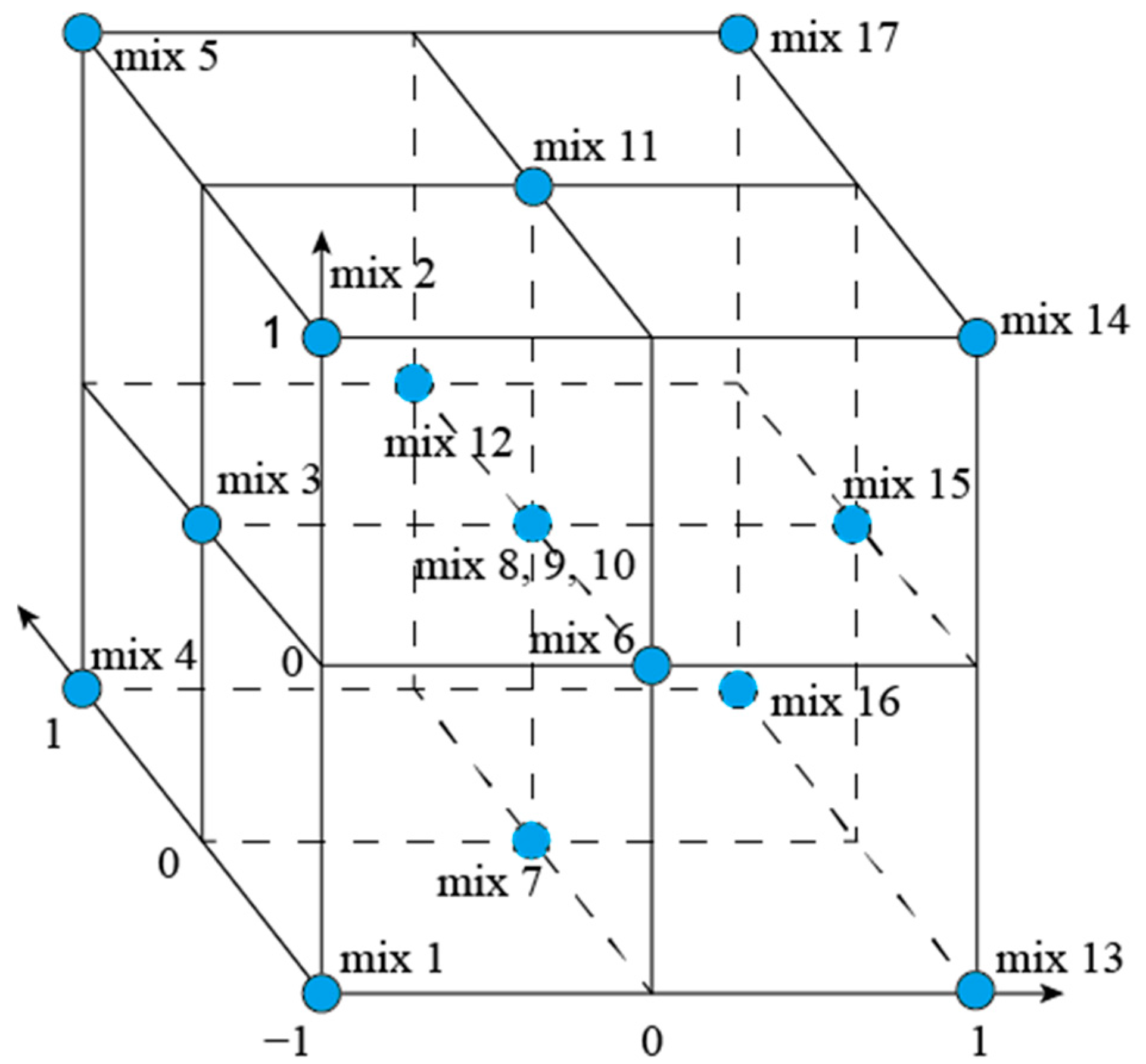
| Mix | SSP% | FA% | SSS% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 20 |
| 3 | 0 | 10 | 10 |
| 4 | 0 | 20 | 0 |
| 5 | 0 | 20 | 20 |
| 6 | 10 | 0 | 10 |
| 7 | 10 | 10 | 0 |
| 8 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| 9 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| 11 | 10 | 10 | 20 |
| 12 | 10 | 20 | 10 |
| 13 | 20 | 0 | 0 |
| 14 | 20 | 0 | 20 |
| 15 | 20 | 10 | 10 |
| 16 | 20 | 20 | 0 |
| 17 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Variables | Symbol | Unit | Coded Factor Levels | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0 | 1 | |||
| SSP | x | % | 0 | 10 | 20 |
| FA | y | % | 0 | 10 | 20 |
| SSS | z | % | 0 | 10 | 20 |
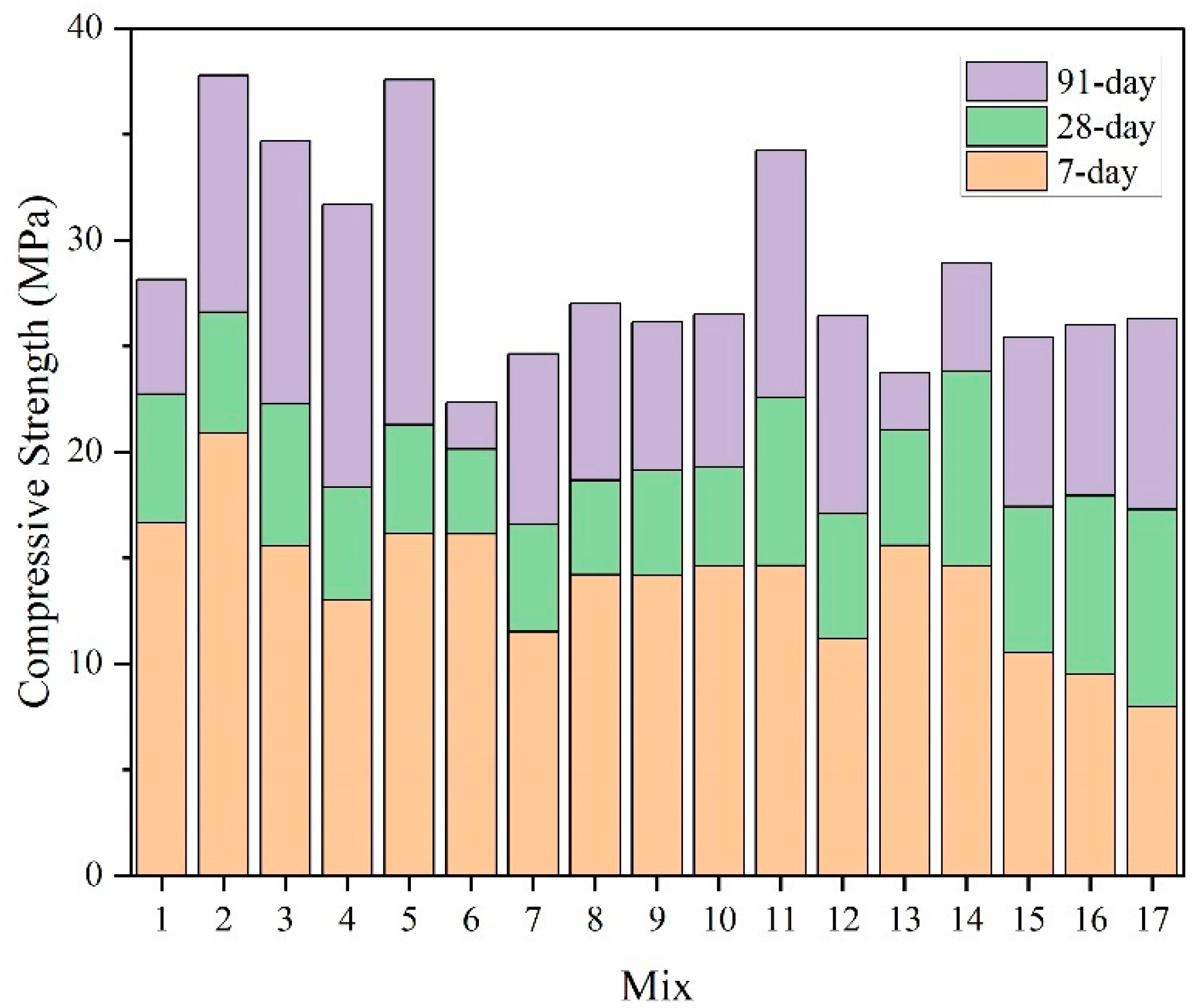
| Mix | SSP% | FA% | SSS% | 7 Days | 28 Days | 91 Days | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental | Predicted | Experimental | Predicted | Experimental | Predicted | ||||
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 16.64 | 16.56 | 22.73 | 22.67 | 28.15 | 28.04 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 20.87 | 20.68 | 26.59 | 26.53 | 37.77 | 37.96 |
| 3 | 0 | 10 | 10 | 15.56 | 16 | 22.26 | 22.48 | 34.68 | 34.56 |
| 4 | 0 | 20 | 0 | 13.00 | 12.86 | 18.34 | 18.27 | 31.7 | 31.86 |
| 5 | 0 | 20 | 20 | 16.14 | 16.14 | 21.29 | 21.25 | 37.57 | 37.46 |
| 6 | 10 | 0 | 10 | 16.12 | 16.76 | 20.13 | 20.3 | 22.34 | 22.22 |
| 7 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 11.50 | 12.03 | 16.57 | 16.79 | 24.63 | 24.51 |
| 8 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 14.21 | 13.6 | 18.65 | 18.77 | 27.02 | 26.72 |
| 9 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 14.15 | 13.6 | 19.13 | 18.77 | 26.15 | 26.72 |
| 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 14.62 | 13.6 | 19.3 | 18.77 | 26.51 | 26.72 |
| 11 | 10 | 10 | 20 | 14.63 | 15.17 | 22.55 | 22.77 | 34.23 | 34.11 |
| 12 | 10 | 20 | 10 | 11.18 | 11.56 | 17.07 | 17.24 | 26.43 | 26.3 |
| 13 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 15.58 | 15.32 | 21.04 | 20.99 | 23.73 | 23.92 |
| 14 | 20 | 0 | 20 | 14.60 | 14.48 | 23.82 | 23.77 | 28.9 | 28.8 |
| 15 | 20 | 10 | 10 | 10.53 | 11.2 | 17.41 | 17.64 | 25.4 | 25.28 |
| 16 | 20 | 20 | 0 | 9.52 | 9.46 | 17.93 | 17.87 | 26.01 | 25.9 |
| 17 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 7.95 | 7.78 | 17.27 | 17.21 | 26.28 | 26.46 |
| 7 Days | 28 Days | 91 Days | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ss | Df | F-Value | p-Value | Ss | Df | F-Value | p-Value | Ss | Df | F-Value | p-Value | |
| Model | 149.55 | 8 | 40.86 | <0.0001 | 123.51 | 11 | 79.51 | <0.0001 | 360.87 | 12 | 165.77 | <0.0001 |
| x | 57.74 | 1 | 126.22 | <0.0001 | 11.76 | 1 | 83.28 | 0.0003 | 43.06 | 1 | 237.36 | 0.0001 |
| y | 67.70 | 1 | 147.99 | <0.0001 | 4.68 | 1 | 33.15 | 0.0022 | 8.36 | 1 | 46.11 | 0.0025 |
| z | 4.90 | 1 | 10.71 | 0.0113 | 17.88 | 1 | 126.61 | <0.0001 | 46.08 | 1 | 254.01 | <0.0001 |
| xy | 2.35 | 1 | 5.15 | 0.053 | 2.75 | 1 | 19.47 | 0.0069 | 1.71 | 1 | 9.43 | 0.0372 |
| xz | 12.30 | 1 | 26.89 | 0.0008 | 12.60 | 1 | 69.46 | 0.0011 | ||||
| yz | 0.35 | 1 | 0.77 | 0.4055 | 2.37 | 1 | 16.75 | 0.0094 | 9.37 | 1 | 51.68 | 0.002 |
| x2 | 5.03 | 1 | 35.65 | 0.0019 | 27.37 | 1 | 150.86 | 0.0003 | ||||
| y2 | 1.29 | 1 | 2.82 | 0.1315 | 16.20 | 1 | 89.30 | 0.0007 | ||||
| z2 | 3.12 | 1 | 22.06 | 0.0054 | 17.92 | 1 | 98.77 | 0.0006 | ||||
| xyz | 0.80 | 1 | 5.67 | 0.0631 | ||||||||
| x2y | 1.26 | 1 | 8.95 | 0.0304 | 4.46 | 1 | 24.60 | 0.0077 | ||||
| x2z | 1.48 | 1 | 3.24 | 0.1096 | 5.62 | 1 | 39.78 | 0.0015 | 7.62 | 1 | 42.01 | 0.0029 |
| xy2 | 2.76 | 1 | 19.55 | 0.0069 | 1.18 | 1 | 6.49 | 0.0635 | ||||
| Residual | 3.66 | 8 | 0.7061 | 5 | 0.7256 | 4 | ||||||
| Lack of Fit | 3.53 | 6 | 8.99 | 0.1035 | 0.4788 | 3 | 1.40 | 0.4416 | 0.3434 | 2 | 0.90 | 0.5267 |
| Pure Error | 0.1309 | 2 | 0.2273 | 2 | 0.3822 | 2 | ||||||
| Cor Total | 153.21 | 16 | 124.21 | 16 | 361.59 | 16 | ||||||
| R2 | 0.9761 | 0.9943 | 0.9980 | |||||||||
| Adjusted R2 | 0.9522 | 0.9818 | 0.9920 | |||||||||
| Predicted R2 | 0.9137 | 0.9358 | 0.9351 | |||||||||
| Adeq pre | 26.2324 | 30.8467 | 42.2253 | |||||||||
| MSE | 0.2153 | 0.0416 | 0.0426 | |||||||||
| RMSE | 0.4640 | 0.2039 | 0.2064 | |||||||||
| MAE | 0.3765 | 0.1582 | 0.1741 | |||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Ho, C.-M.; Li, H.; Guo, H.; Wang, D.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, K. Valorization of Steel Slag and Fly Ash in Mortar: Modeling Age-Dependent Strength with Response Surface Methodology. Materials 2025, 18, 2203. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102203
Li X, Ho C-M, Li H, Guo H, Wang D, Zhao D, Zhang K. Valorization of Steel Slag and Fly Ash in Mortar: Modeling Age-Dependent Strength with Response Surface Methodology. Materials. 2025; 18(10):2203. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102203
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiaofeng, Chia-Min Ho, Huawei Li, Huaming Guo, Deliang Wang, Dan Zhao, and Kun Zhang. 2025. "Valorization of Steel Slag and Fly Ash in Mortar: Modeling Age-Dependent Strength with Response Surface Methodology" Materials 18, no. 10: 2203. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102203
APA StyleLi, X., Ho, C.-M., Li, H., Guo, H., Wang, D., Zhao, D., & Zhang, K. (2025). Valorization of Steel Slag and Fly Ash in Mortar: Modeling Age-Dependent Strength with Response Surface Methodology. Materials, 18(10), 2203. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102203






