Preparation and Properties of Na2HPO4∙12H2O/Silica Aerogel Composite Phase Change Materials for Building Energy Conservation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Materials
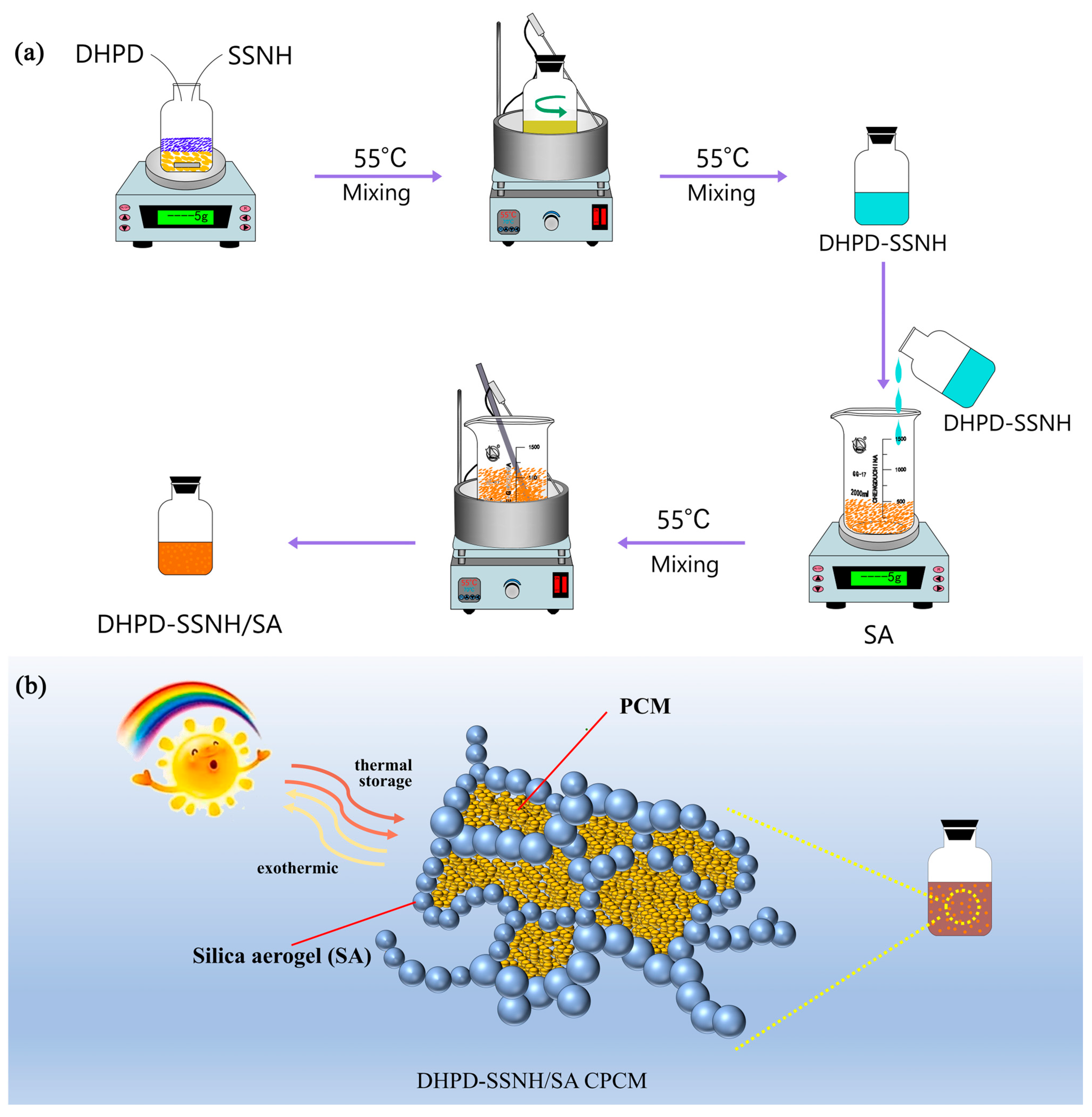
2.2. Preparation of DHPD-SSNH/SA CPCM
2.3. Characterization
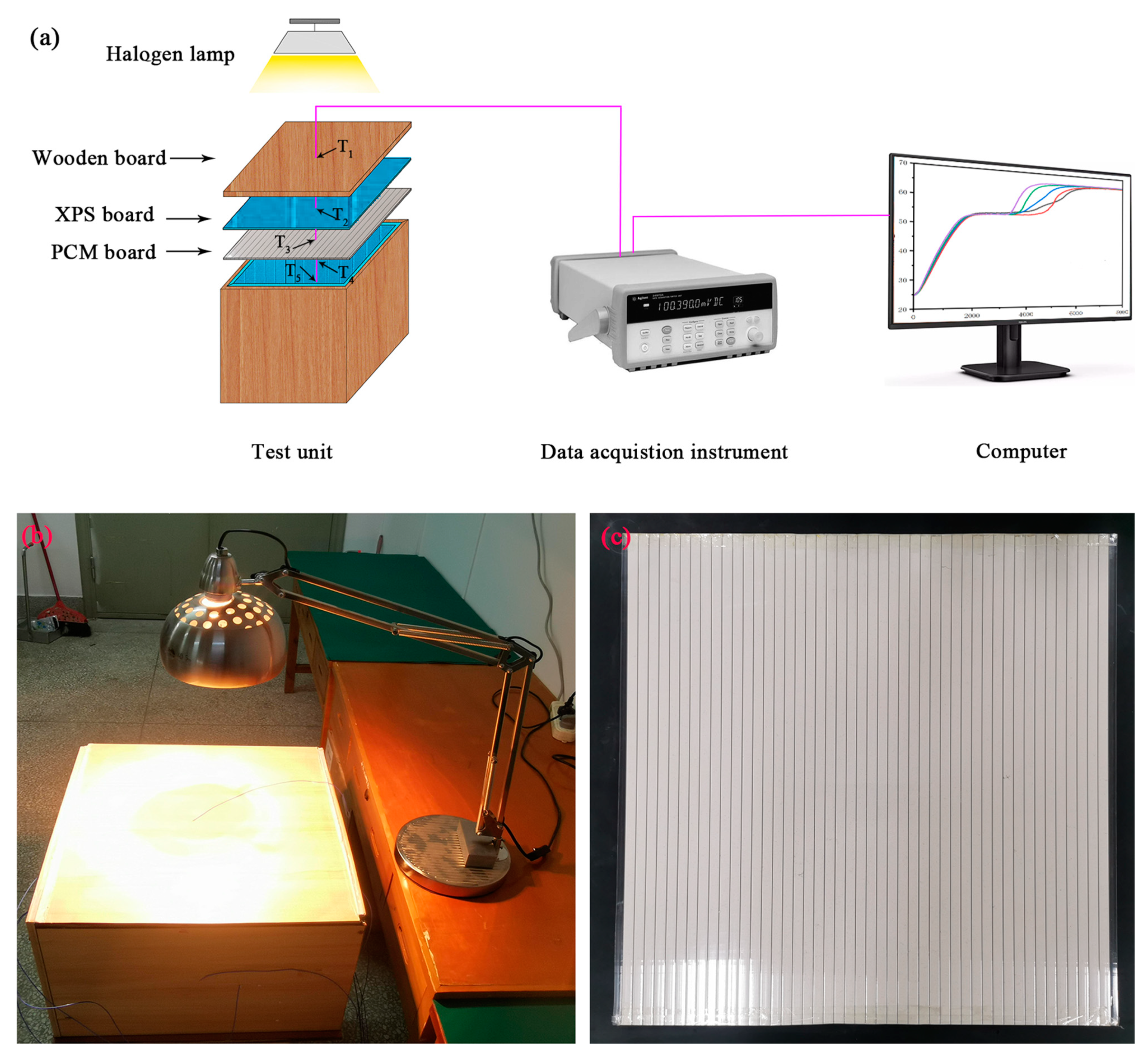
2.4. Effect of DHPD-SSNH/SA CPCM on Thermal Performance of Buildings
3. Results and Discussion
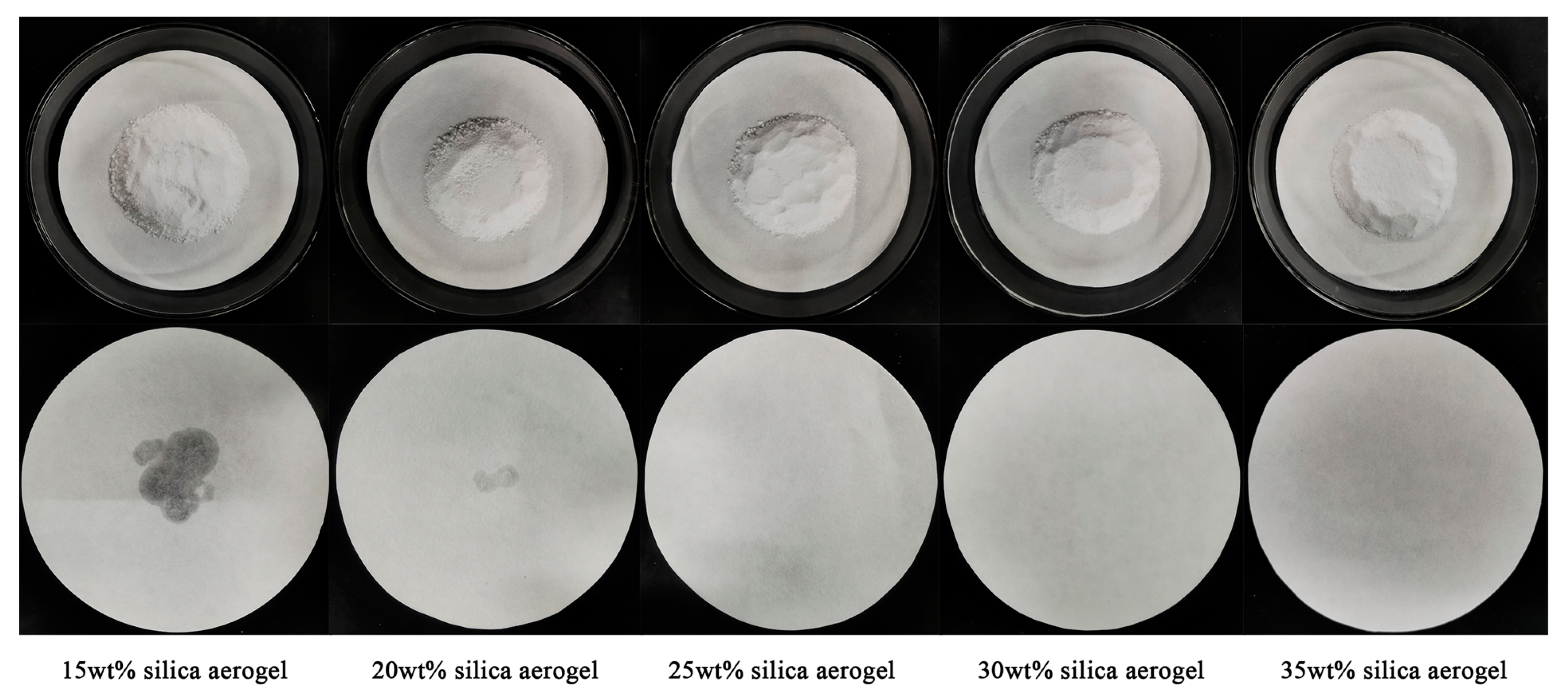
3.1. Optimal Loading of DHPD-SSNH PCM with SA
3.2. Effect of SA Mass Fraction on Thermal Properties
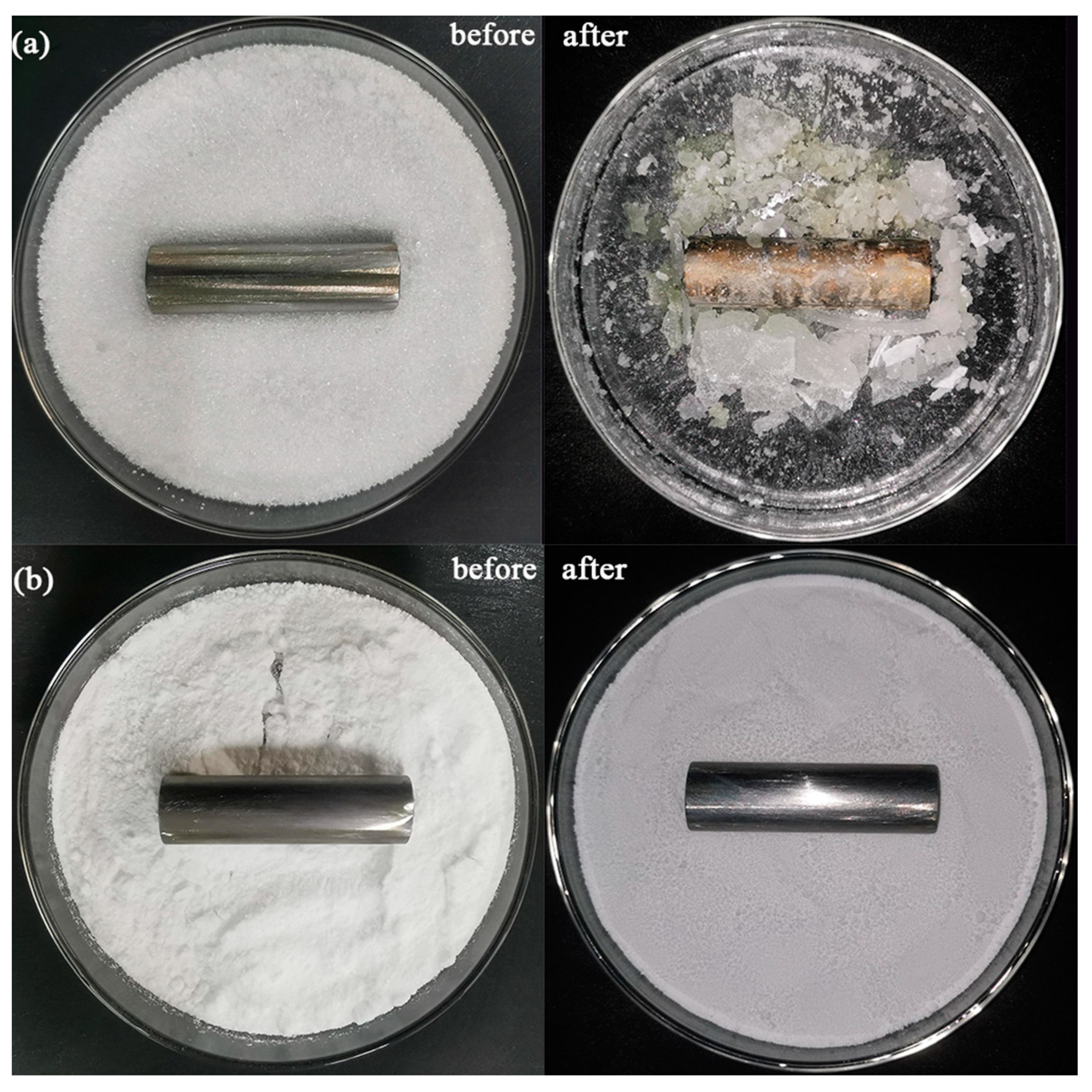
3.3. Corrosion Analysis of DHPD-SSNH/SA CPCM on Reinforcing Bars
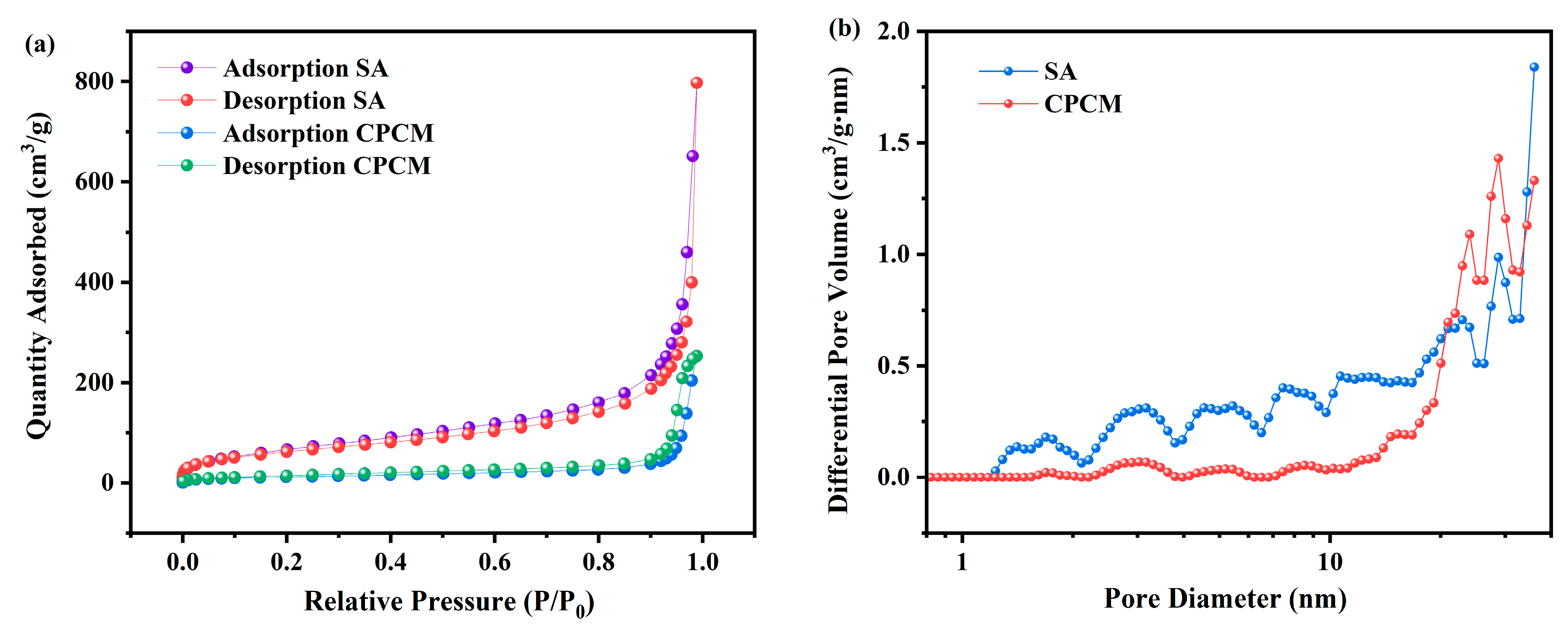
3.4. Pore Structure Analysis
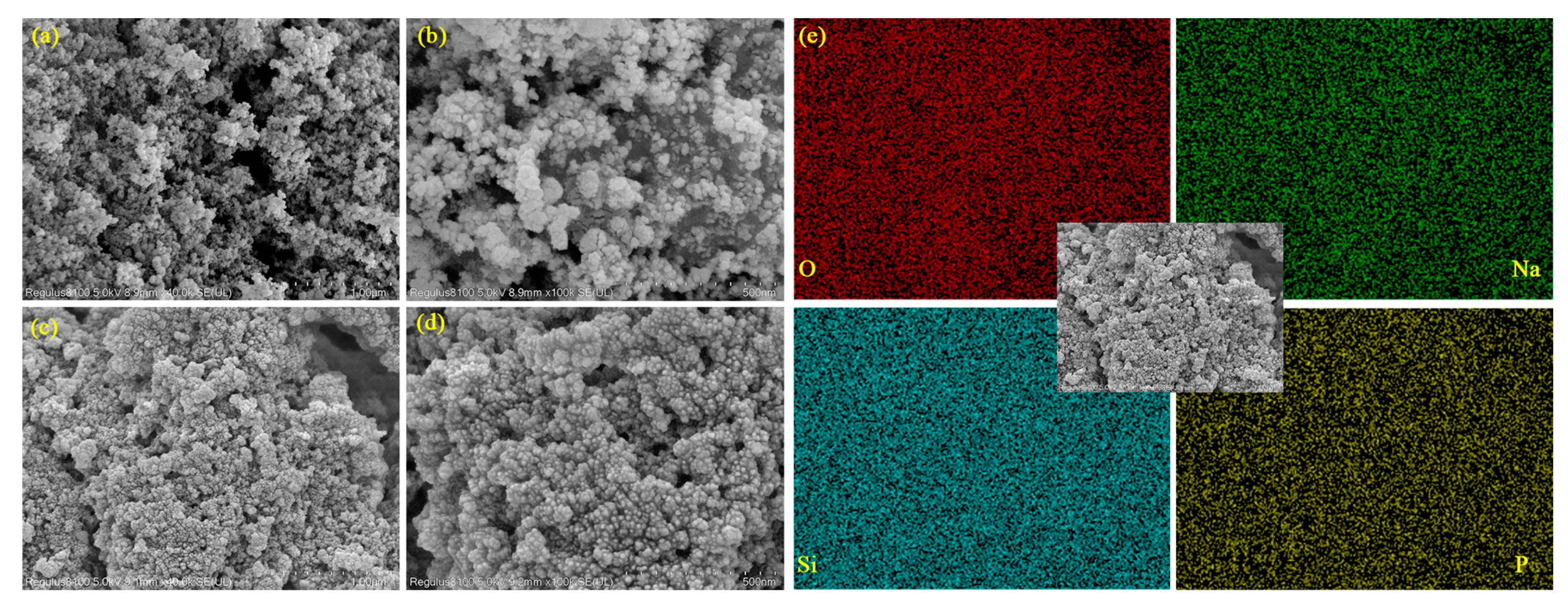
3.5. Micromorphology Analysis
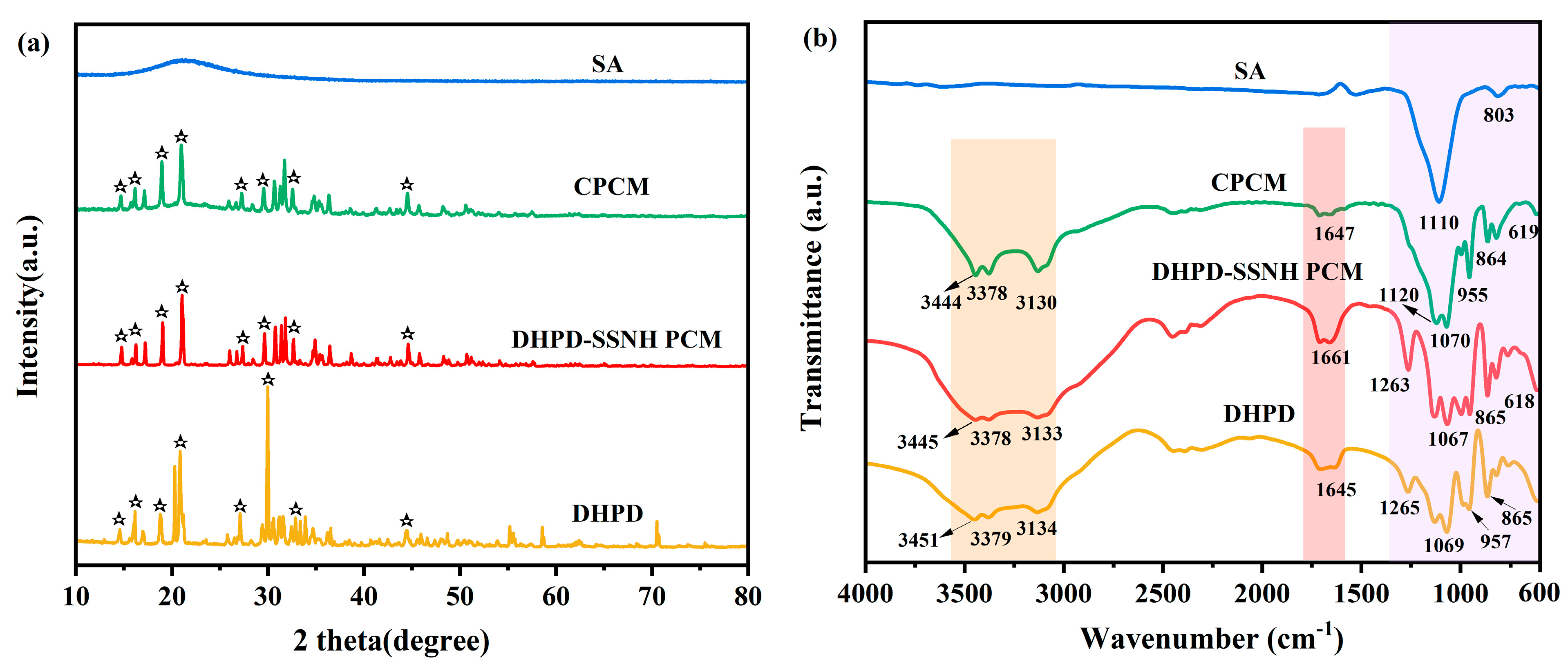
3.6. Chemical Composition and Crystal Structure
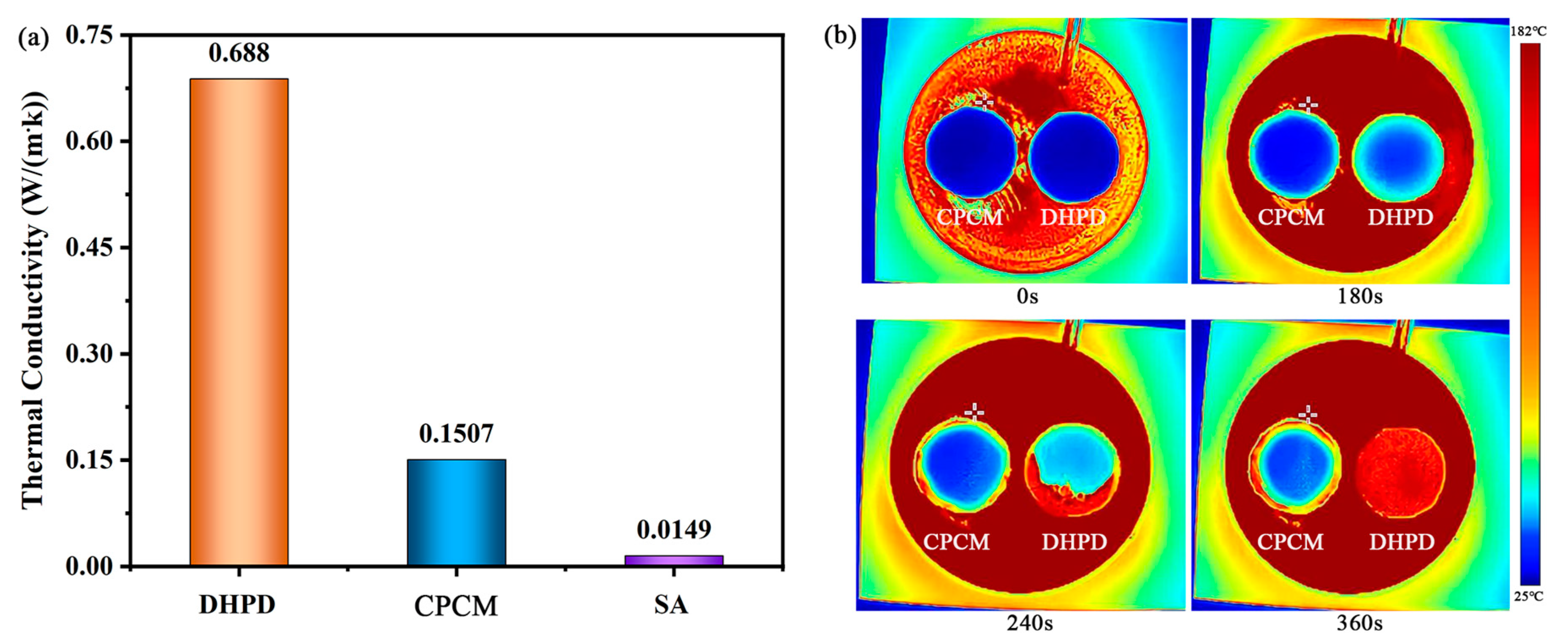
3.7. Thermal Conductivity
3.8. Thermal Reliability
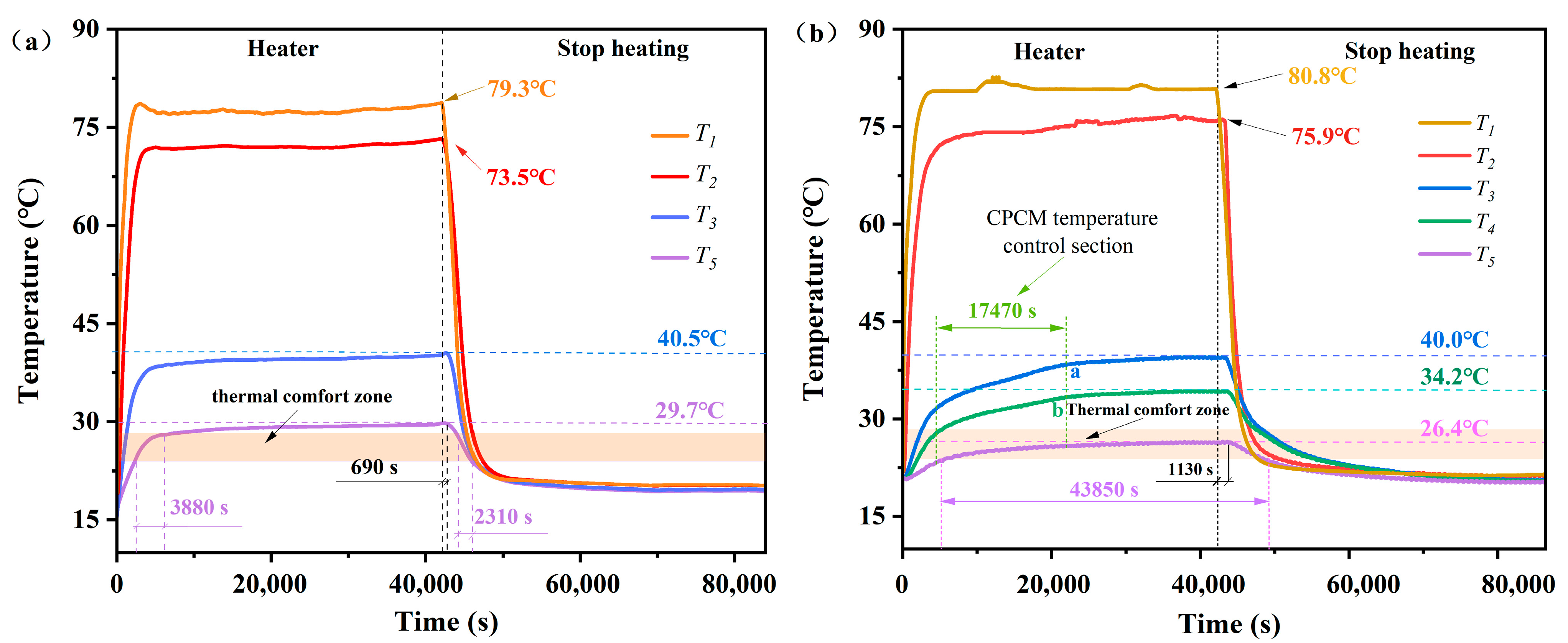
3.9. Assessment of Impact of CPCM on Thermal Performance of Buildings
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- When adding 25% SA, the prepared DHPD-SSNH/SA CPCM had good shape stability, with a Tm of 30.4 °C, a ∆Hm of 163.4 J/g, thermal conductivity of 0.1507 W/(m·K), and a low supercooling degree of 1.3 °C.
- (2)
- The SEM and pore structure analysis results show that the DHPD-SSNH PCM was confined in the three-dimensional mesh structure of SA, which could effectively inhibit the leakage of PCMs. The FT-IR and XRD results indicated that the SA and PCM in the DHPD-SSNH/SA CPCM were physically bonded and did not involve chemical reactions.
- (3)
- Corrosion experiments showed that the DHPD-SSNH/SA CPCM with 25% SA could effectively solve the corrosion problem of hydrated, salt-based PCMs in reinforcing bars in practical applications.
- (4)
- After 200 cold-heat cycles, the Tm of CPCM was almost unchanged, and the loss of ∆Hm was only 4.8%, with the unchanged crystal structure and chemical composition possessing good thermal reliability.
- (5)
- The thermal performance evaluation showed that the PCM board was equipped with an excellent energy-saving effect by increasing the thermal comfort time in the center of the test unit room by 43.38%.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Parameters | |
| Tm | Phase change temperature (°C) |
| ∆Hm | Measured phase change enthalpy (J/g) |
| ∆Hm,theory | Theoretical phase change enthalpy (J/g) |
| ∆T | Supercooling degree (°C) |
| T1 | Temperature of the outer surface of the test unit (°C) |
| T2 | XPS outer surface or wood plate inner surface temperature (°C) |
| T3 | PCM outer surface or XPS inner surface temperature (°C) |
| T4 | PCM plate internal surface temperature (°C) |
| T5 | Room center temperature (°C) |
| SBET | Surface area (m2/g) |
| V | Pore volume (cm3/g) |
| Abbreviations | |
| PCM | Phase change material |
| CPCM | Composite phase change materials |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| FT-IR | Fourier transform infrared |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
| DSC | Differential scanning calorimetry |
| BET | Brunauer–Emmett–Teller |
| DFT | Density functional theory |
References
- Abu-Jdayil, B.; Mourad, A.-H.; Hittini, W.; Hassan, M.; Hameedi, S. Traditional, state-of-the-art and renewable thermal building insulation materials: An overview. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 214, 709–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, N.; Niu, J.; Zhong, Y.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, Y. Development of polyurethane acrylate coated salt hydrate/diatomite form-stable phase change material with enhanced thermal stability for building energy storage. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 259, 119714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templeman, S.; Dun, T.; McKenzie, M. Matias Fabricio Var-Gas Masias, Clancy Walker-Fitzgerald, Chris Williams, State of the Tropics (2022) COVID-19 in the Tropics; Technical report; James Cook University: Townsville, Australia, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Sudarsanam, N.; Kannamma, D. Investigation of summertime thermal comfort at the residences of elderly people in the warm and humid climate of India. Energy Build. 2023, 291, 113151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, P.; Cheong, D.; Sekhar, C. A review of occupancy-based building energy and IEQ controls and its future post-COVID. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 804, 150249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.J.; Ghazali, M.F.; Kumarasamy, S. Advancements in phase change materials for energy-efficient building construction: A comprehensive review. J. Energy Storage 2024, 81, 110494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’neill, P.; Fischer, L.; Haberschill, P.; Revellin, R.; Bonjour, J. Heat transfer and rheological performance of a phase change dispersion during crystallisation. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 225, 120139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahon, H.; O’Connor, D.; Friedrich, D.; Hughes, B. A review of thermal energy storage technologies for seasonal loops. Energy 2022, 239, 122207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abden, J.; Tao, Z.; Alim, M.A.; Pan, Z.; George, L.; Wuhrer, R. Combined use of phase change material and thermal insulation to improve energy efficiency of residential buildings. J. Energy Storage 2022, 56, 105880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasiri, Q.A.; Szab, M. Building envelope-combined phase change material and thermal insulation for energy-effective buildings during harsh summer: Simulation-based analysis. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2023, 72, 326–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Feng, J.; Ling, Z.; Fang, X.; Zhang, Z. A sodium acetate trihydrate-formamide/expanded perlite composite with high latent heat and suitable phase change temperatures for use in building roof. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 226, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Huang, D.; Zhang, L. An innovative modified calcium chloride hexahydrate–based composite phase change material for thermal energy storage and indoor temperature regulation. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2023, 6, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.W.; Lao, J.Y.; Chen, L.W.; Ma, J.; Peng, H.; Fang, T. Design of Na2HPO4·12H2O/diatomite composite phase change materials with low supercooling degree, excellent thermal properties and corrosion resistance for building energy conservation. J. Energy Storage 2024, 84, 110922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Zou, T.; Liang, X.; Wang, S.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, Y. Preparation and properties of phase change temperature-tuned composite phase change material based on sodium acetate trihydrate–urea/fumed silica for radiant floor heating system. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 162, 114253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Lin, L.; Shi, J. A Review of Composite Phase Change Materials Based on Biomass Materials. Polymers 2022, 14, 4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goryunova, K.; Gahramanli, Y.; Gurbanova, R. Adsorption properties of silica aerogel-based materials. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 18207–18216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikam, L.; Arthi, P.; Senthil, B.; Shanmugam, M. A review on exfoliated graphite: Synthesis and applications. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 152, 110685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namvar, M.; Mahinroosta, M.; Allahverdi, A.; Mohammadzadeh, K. Preparation of monolithic amorphous silica aerogel through promising valorization of silicomanganese slag. J. Non-Crystalline Solids 2022, 586, 121561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, F.; Soomro, S.A.; Inglezakis, V.J. Silica aerogels; a review of synthesis, applications and fabrication of hybrid composites. J. Porous Mater. 2021, 28, 1387–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Xiao, Q.; Chen, C.; Li, L.; Yuan, W. Developing a heat-insulating composite phase change material with light-to-thermal conversion performance from graphene oxide/silica hybrid aerogel. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2020, 174, 115303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, S.; Tang, B. Silica-based aerogels encapsulate organic/inorganic composite phase change materials for building thermal management. J. Energy Storage 2024, 97, 112858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Tan, H.; Yang, Y.; He, W. Preparation and characteristics of paraffin/silica aerogel composite phase-change materials and their application to cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 387, 131609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, A.; Roy, A.; Mallick, T.K.; Tahir, A.A. Shape-Stabilized PEGylated Silica Aerogel-Composite as an Energy Saving Building Material. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 20236–20250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lao, J.; Fu, W.; Chen, L.; Ma, J.; Xiang, J.; Liu, J.; Peng, H.; Luo, Y. Adjustable temperature and high thermal conductivity composite phase change material based on sodium acetate trihydrate–alanine/expanded graphite for thermal management of electronic devices. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 497, 154867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, P.; Yan, R.H.; Wu, Z.G.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Sheng, X. Thermal performance of novel form-stable disodium hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate-based composite phase change materials for building thermal energy storage. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2023, 74, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, X.; Ji, J.; Yan, H. Review of research progress on corrosion and anti-corrosion of phase change materials in thermal energy storage systems. J. Energy Storage 2023, 63, 107005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, T.; Fu, W.; Liang, X.; Wang, S.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, Y. Hydrophilic modification of expanded graphite to develop form-stable composite phase change material based on modified CaCl2·6H2O. Energy 2019, 190, 116473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Fu, W.; Lv, G.; Liu, J.; Peng, H.; Fang, T.; Tan, X.; Chen, Z. Preparation and properties of CaCl2·6H2O/silica aerogel composite phase change material for building energy conservation. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 382, 121986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. GB50736-2012 design code for heating ventilation and air conditioning of civil buildings. China Archit. Build. 2012, 1, 1–224. [Google Scholar]

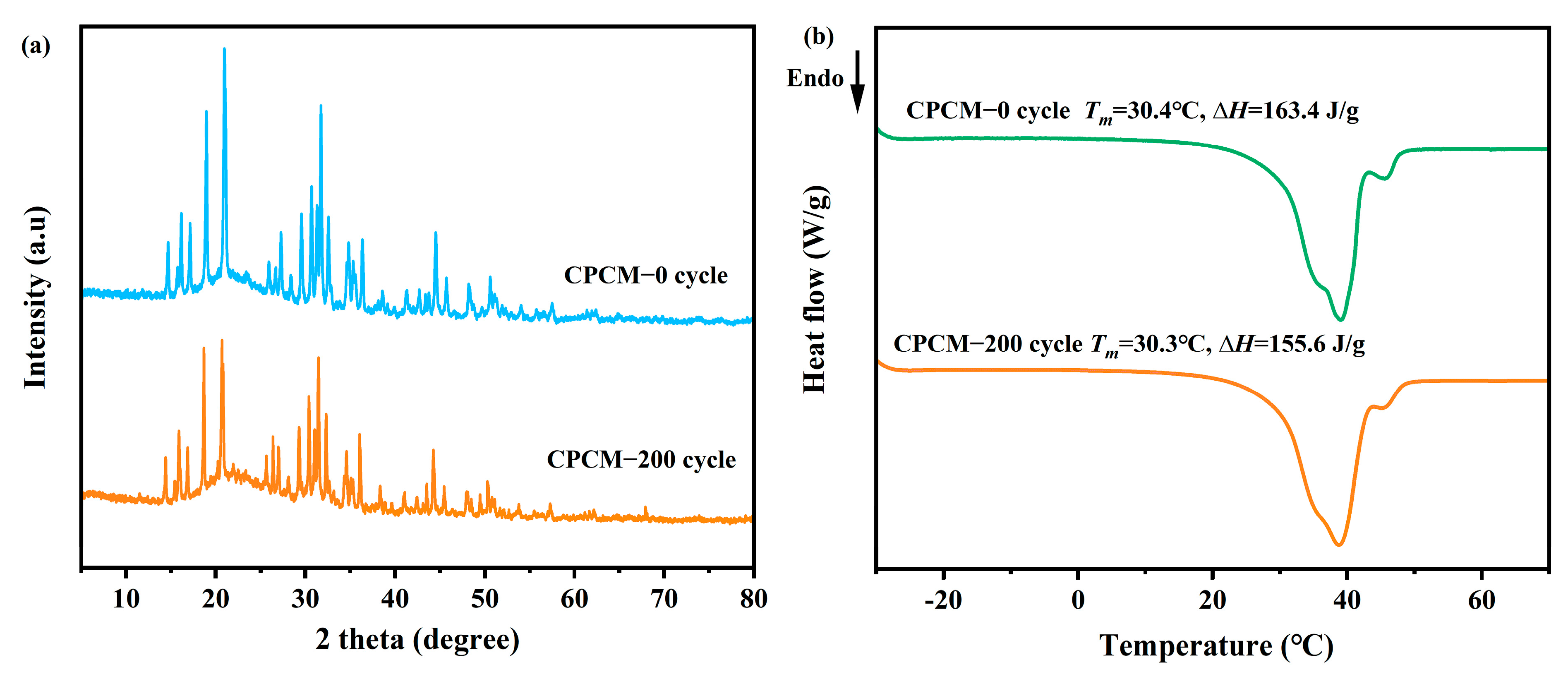
| Mass Fraction of SA (%) | Tm (°C) | ∆Hm (J/g) | ∆Hm,theory (J/g) | Relative Errors (%) | ∆T (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 35.3 | 215.3 | - | - | 0.3 |
| 25 | 30.4 | 163.4 | 161.5 | −1.18 | 1.3 |
| 30 | 30.0 | 150.2 | 150.7 | 0.33 | 2.8 |
| 35 | 30.6 | 139.3 | 139.9 | 0.43 | 9.5 |
| Sample | SBET (m2/g) | V (cm3/g) |
|---|---|---|
| SA | 224.508 | 0.395 |
| DHPD-SSNH/SA CPCM | 43.650 | 0.108 |
| Sample | Thermal Conductivity (W/(m·K)) | Thermal Comfort Time (s) | Percentage of Thermal Comfort Time (%) | Energy-Saving Effect (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference group | - | 6190 | 7.37 | - |
| DHPD-SSNH/diatomite CPCM [13] | 0.2400 | 39,870 | 47.46 | 40.09 |
| DHPD-SSNH/SA CPCM | 0.1507 | 43,850 | 50.75 | 43.38 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lao, J.; Ma, J.; Zhao, Z.; Xia, N.; Liu, J.; Peng, H.; Fang, T.; Fu, W. Preparation and Properties of Na2HPO4∙12H2O/Silica Aerogel Composite Phase Change Materials for Building Energy Conservation. Materials 2024, 17, 5350. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17215350
Lao J, Ma J, Zhao Z, Xia N, Liu J, Peng H, Fang T, Fu W. Preparation and Properties of Na2HPO4∙12H2O/Silica Aerogel Composite Phase Change Materials for Building Energy Conservation. Materials. 2024; 17(21):5350. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17215350
Chicago/Turabian StyleLao, Jiayue, Jintao Ma, Zhili Zhao, Ning Xia, Jiesheng Liu, Hao Peng, Tao Fang, and Wanwan Fu. 2024. "Preparation and Properties of Na2HPO4∙12H2O/Silica Aerogel Composite Phase Change Materials for Building Energy Conservation" Materials 17, no. 21: 5350. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17215350
APA StyleLao, J., Ma, J., Zhao, Z., Xia, N., Liu, J., Peng, H., Fang, T., & Fu, W. (2024). Preparation and Properties of Na2HPO4∙12H2O/Silica Aerogel Composite Phase Change Materials for Building Energy Conservation. Materials, 17(21), 5350. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17215350





