Plastic Workability and Rheological Stress Model Based on an Artificial Neural Network of SiCp/Al-7.75Fe-1.04V-1.95Si Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
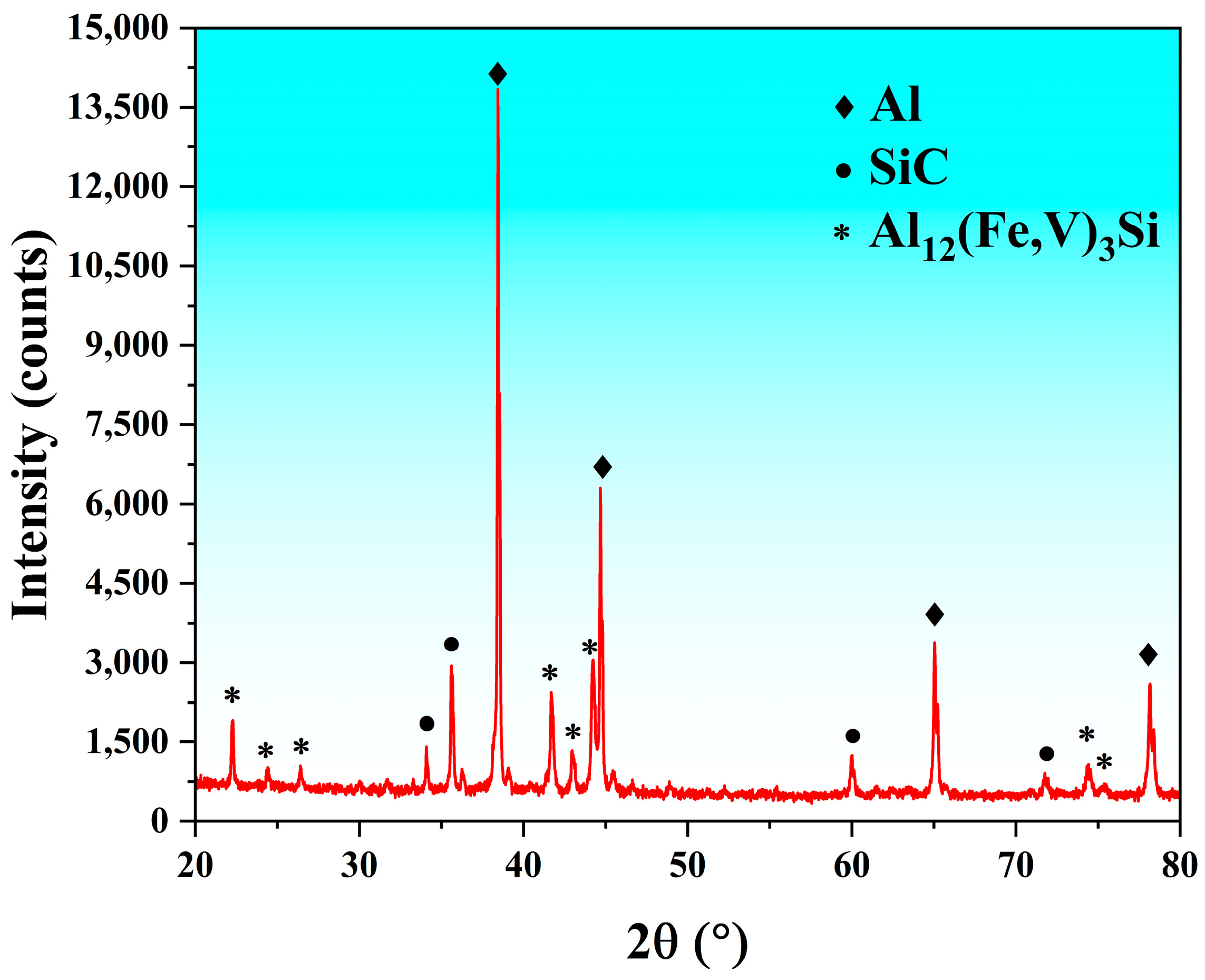
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Flow Stress
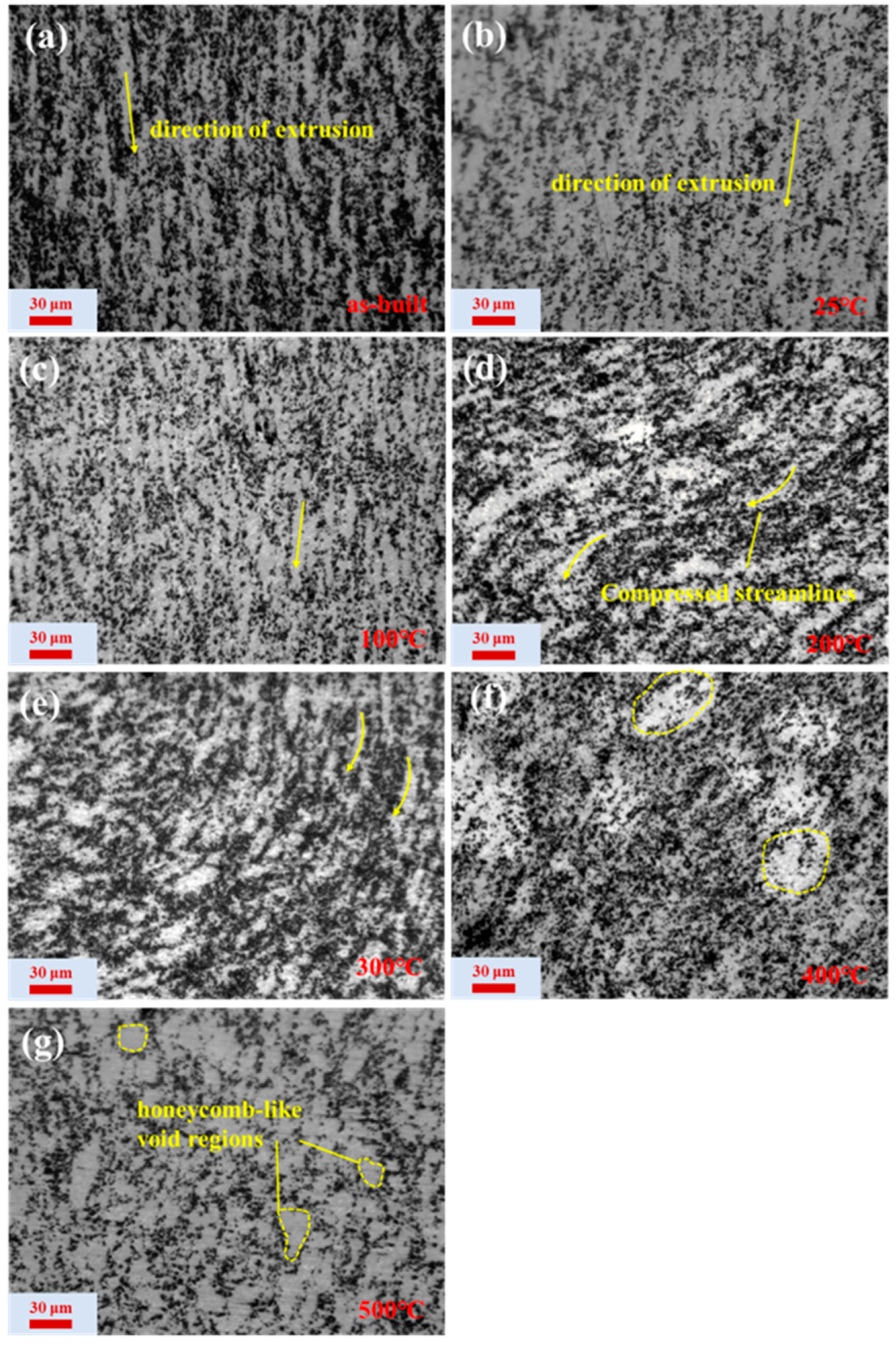
3.2. Microstructure Evolution
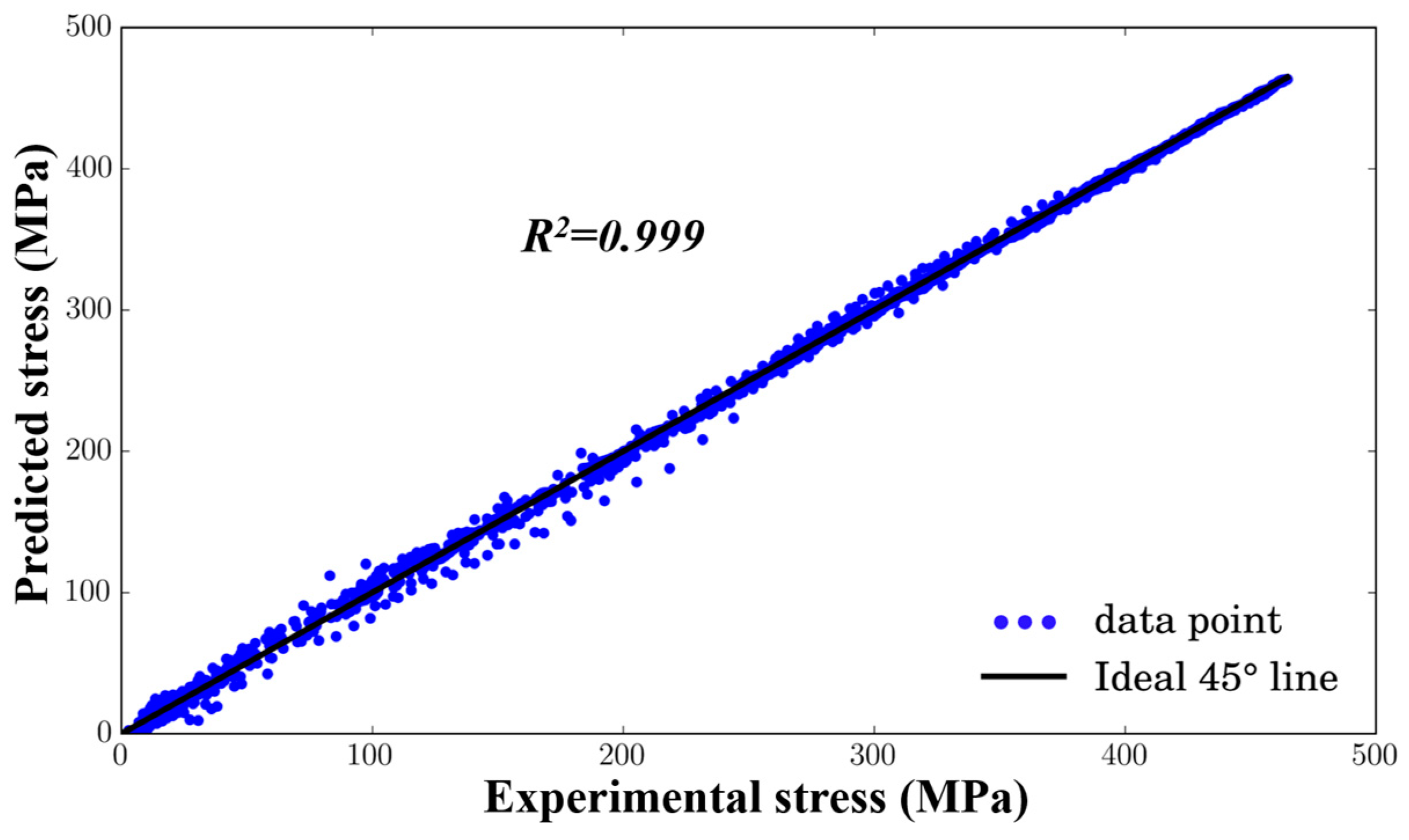
3.3. Artificial Neural Network Model
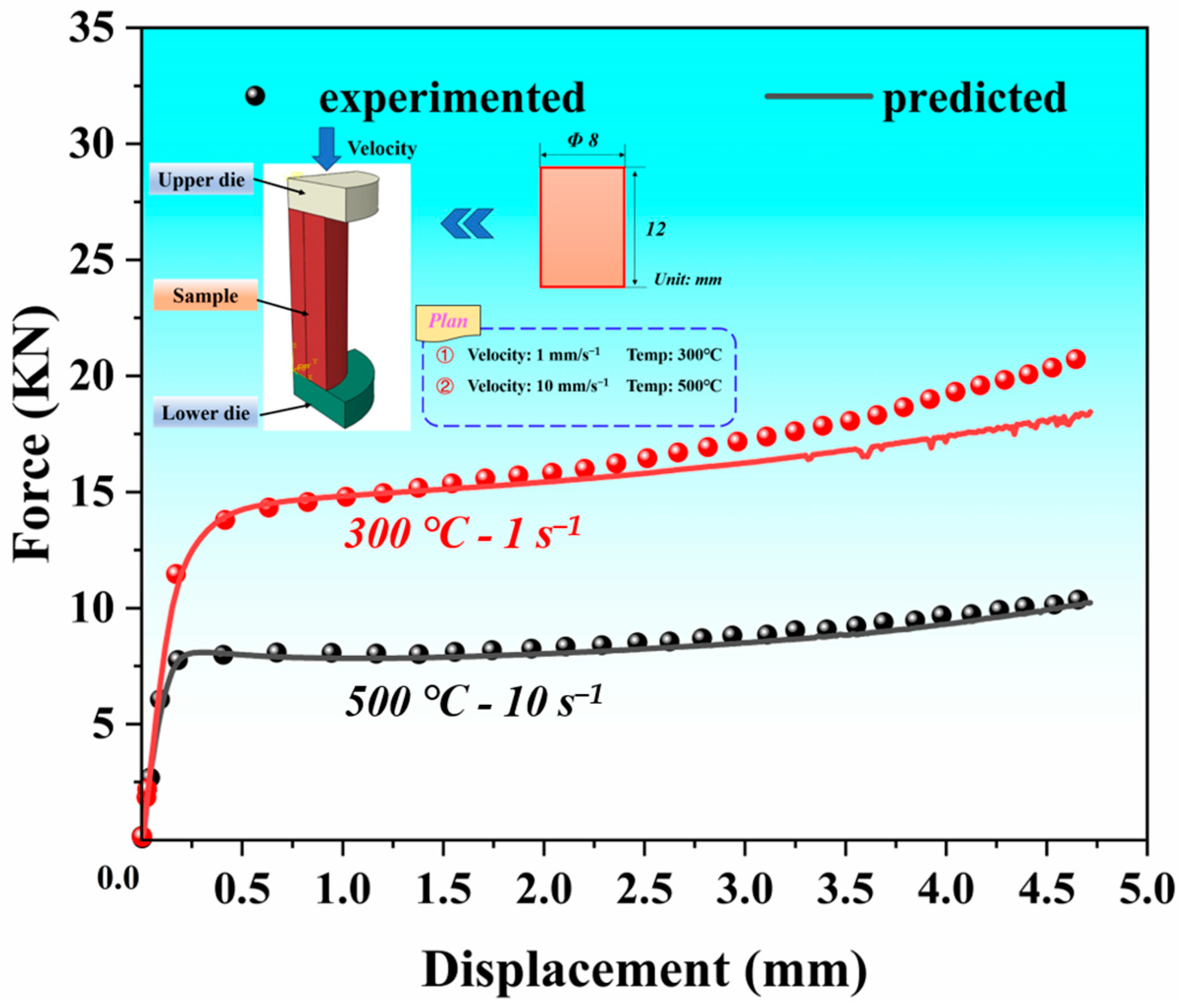
3.4. Finite Element Analysis
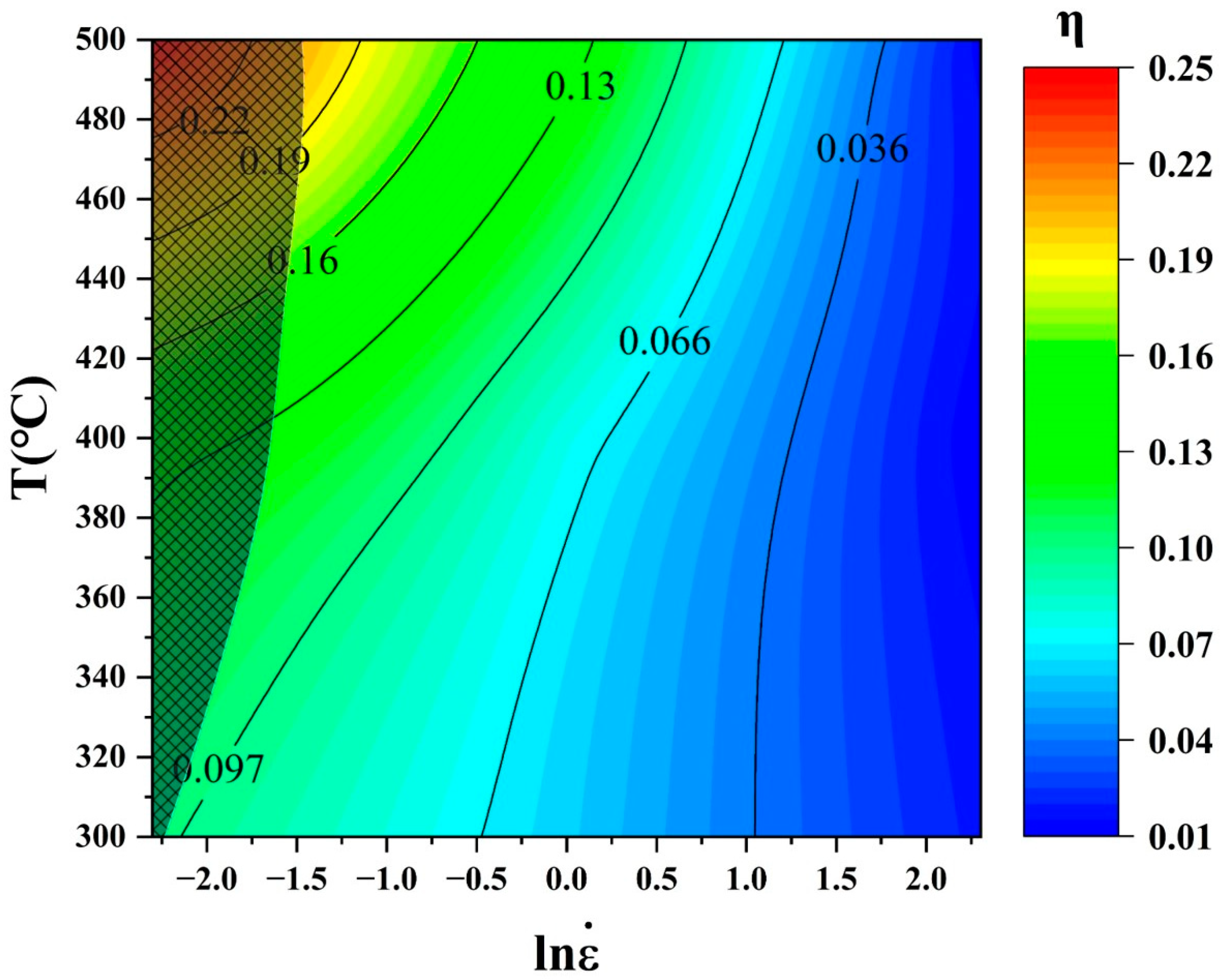
3.5. Thermomechanical Processing Diagram
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Idusuyi, N.; Olayinka, J.I. Dry sliding wear characteristics of aluminium metal matrix composites: A brief overview. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 3338–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chak, V.; Chattopadhyay, H.; Dora, T.L. A review on fabrication methods, reinforcements and mechanical properties of aluminum matrix composites. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 56, 1059–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Yuan, L.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Xu, F.; Zheng, Z.; Shan, D.; Guo, B. Research on the Secondary Forgeability of High Volume Fraction Whisker Reinforced Aluminum Matrix Composites of Original Squeeze Casting. Materials 2021, 14, 7261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, X.; Yan, H.; Chen, X. Compression deformation behavior of semisolid Al2O3np reinforced 7075 aluminum matrix composites with high solid fraction. J. Mater. Res. 2016, 31, 3981–3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghdadi, N.; Zarei-Hanzaki, A.; Abedi, H.R. The flow behavior modeling of cast A356 aluminum alloy at elevated temperatures considering the effect of strain. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 535, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seif, C.Y.; Hage, I.S.; Hamade, R.F. Incorporating dual BCC/FCC Zerilli-Armstrong and blue brittleness constitutive material models into Oxley’s machining shear zone theory. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 50, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Cheng, X.-W.; Liu, X.-P.; Zhang, S.-Z.; He, J.-Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, L.-J. The investigation on Johnson-Cook model and dynamic mechanical behaviors of ultra-high strength steel M54. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 835, 142693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chen, S.; Tang, J.; Fu, D.; Teng, J.; Jiang, F. Hot Workability of the Multi-Size SiC Particle-Reinforced 6013 Aluminum Matrix Composites. Materials 2023, 16, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Wang, F.; Shang, C.; Wu, H.; Wu, G.; Gao, J.; Wang, S.; Gao, Z.; Zhou, X.; Mao, X. Advances in machine learning- and artificial intelligence-assisted material design of steels. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2023, 30, 1003–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghdadi, N.; Zarei-Hanzaki, A.; Khalesian, A.R.; Abedi, H.R. Artificial neural network modeling to predict the hot deformation behavior of an A356 aluminum alloy. Mater. Des. 2013, 49, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Jia, X.; Zhang, Z. A Modified Back Propagation Artificial Neural Network Model Based on Genetic Algorithm to Predict the Flow Behavior of 5754 Aluminum Alloy. Materials 2018, 11, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, D.J.; Bye, R.L.; Raybould, D.; Brown, A.M. Dispersion strengthened Al-Fe-V-Si alloys. Scr. Metall. 1986, 20, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakata, I.; Langenbeck, S.L. Elevated Temperature Aluminum Alloys for Aerospace Applications; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Diao, E.; Fan, J.; Yang, Z.; Lv, Z.; Gao, H.; Nie, J. Hot Deformation Behavior and Mechanisms of SiC Particle Reinforced Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloy Matrix Composites. Materials 2023, 16, 7430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Geng, H.; Ji, X.; Xu, P.; Li, X.; Zhang, H. Investigation of the hot deformation behavior and microstructure evolution of TiB2 +TiAl3/2024Al composite. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 933, 167765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Teng, J.; Luo, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H. Hot deformation characteristics and mechanism of PM 8009Al/SiC particle reinforced composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 697, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, Z.; Dang, X.; Ma, Y.; Cai, J.; Wang, K. Hot deformation behavior of multilayered Ti/Ni composites during isothermal compression. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 18, 4903–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, G.R.; Cook, W.H.J.E.F.M. A constitutive model and data for metals subjected to large strains, high strain rates and high temperatures. In Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Ballistics, The Hague, The Netherlands, 19–21 April 1983; Volume 21, pp. 541–548. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, N.; Fang, X.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, K. Wire arc additive manufacturing of Inconel 718: Constitutive modelling and its microstructure basis. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 75, 1134–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Gao, G.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, H.; Xiang, D.; Zhao, B. Research on dynamic mechanical properties and plastic constitutive relation of Ti3Al intermetallic compounds under mechanical-thermal coupling. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 19, 4154–4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Mao, P.; Kuang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ju, Y.; Xu, X. The modified temperature term on Johnson-Cook constitutive model of AZ31 magnesium alloy with {0002} texture. J. Magnes. Alloys 2020, 8, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Li, M.; Bu, H.; Lu, X.; Yang, H.; Qian, Z. Modeling of Flow Stress of As-Rolled 7075 Aluminum Alloy during Hot Deformation by Artificial Neural Network and Application. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2022, 32, 5666–5677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Pan, Q.; Xiong, S.; Liu, L. Prediction on hot deformation behavior of spray formed ultra-high strength aluminum alloy—A comparative study using constitutive models. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 735, 1931–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoudi Nejad, R.; Sina, N.; Ma, W.; Song, W.; Zhu, S.P.; Branco, R.; Macek, W.; Gholami, A. Artificial neural network based fatigue life assessment of riveted joints in AA2024 aluminum alloy plates and optimization of riveted joints parameters. Int. J. Fatigue 2024, 178, 107997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Shao, Z.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, X. Modeling the Mechanical Properties of Heat-Treated Mg-Zn-RE-Zr-Ca-Sr Alloys with the Artificial Neural Network and the Regression Model. Crystals 2022, 12, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantalé, O.; Tize Mha, P.; Tongne, A. Efficient implementation of non-linear flow law using neural network into the Abaqus Explicit FEM code. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 2022, 198, 103647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, Y.V.R.K. Processing Maps: A Status Report. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2003, 12, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Element | Si | Fe | V | Mg | Mn | Cu | Ti | Zn | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.95 | 7.75 | 1.04 | 0.013 | 0.031 | 0.0041 | 0.074 | 0.18 | Bal. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, P.; Chen, S.; Tang, J.; Liu, H.; Fu, D.; Teng, J.; Jiang, F. Plastic Workability and Rheological Stress Model Based on an Artificial Neural Network of SiCp/Al-7.75Fe-1.04V-1.95Si Composites. Materials 2024, 17, 5317. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17215317
Feng P, Chen S, Tang J, Liu H, Fu D, Teng J, Jiang F. Plastic Workability and Rheological Stress Model Based on an Artificial Neural Network of SiCp/Al-7.75Fe-1.04V-1.95Si Composites. Materials. 2024; 17(21):5317. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17215317
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Pinming, Shuang Chen, Jie Tang, Haiyang Liu, Dingfa Fu, Jie Teng, and Fulin Jiang. 2024. "Plastic Workability and Rheological Stress Model Based on an Artificial Neural Network of SiCp/Al-7.75Fe-1.04V-1.95Si Composites" Materials 17, no. 21: 5317. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17215317
APA StyleFeng, P., Chen, S., Tang, J., Liu, H., Fu, D., Teng, J., & Jiang, F. (2024). Plastic Workability and Rheological Stress Model Based on an Artificial Neural Network of SiCp/Al-7.75Fe-1.04V-1.95Si Composites. Materials, 17(21), 5317. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17215317






