Ion Beam-Induced Luminescence (IBIL) for Studying Manufacturing Conditions in Ceramics: An Application to Ceramic Body Tiles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
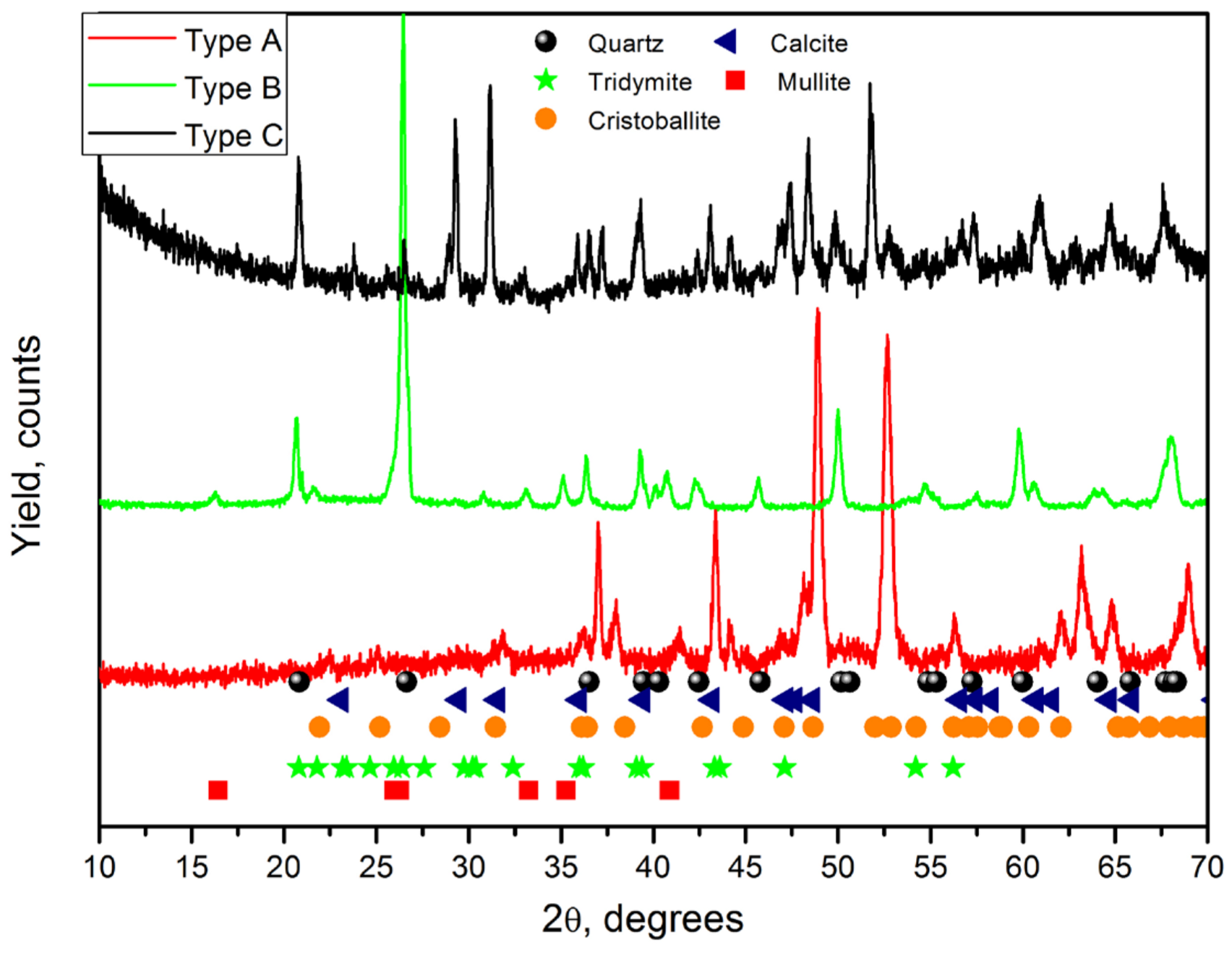
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johansson, S.A.E.; Campbell, J.L. PIXE: A Novel Technique for Elemental Analysis; Wiley Company: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Nastasi, M.A. Handbook of Modern Ion Beam Materials Analysis; Materials Research Society: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Huddle, J.R.; Grant, P.G.; Ludington, A.R.; Foster, R.L. Ion beam-induced luminescence. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2007, 261, 475–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, P.; Crespillo, M. An Ideal System for Analysis and Interpretation of Ion Beam Induced Luminescence. Phys. Procedia 2015, 66, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Wang, G.; Zheng, L.; Qiu, M.; Yin, P.; Xu, M. In-situ luminescence studies of silica glass during low energy H+, He+ and O+ irradiation. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2018, 348, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dran, J.-C.; Salomon, J.; Calligaro, T.; Walter, P. Ion beam analysis of art works: 14 years of use in the Louvre. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2004, 219, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corregidor, V.; Oliveira, A.; Rodrigues, P.; Alves, L. Paintings on copper by the Flemish artist Frans Francken II: PIXE characterization by external microbeam. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2015, 348, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiari, M.; Barone, S.; Bombini, A.; Calzolai, G.; Carraresi, L.; Castelli, L.; Czelusniak, C.; Fedi, M.E.; Gelli, N.; Giambi, F.; et al. LABEC, the INFN ion beam laboratory of nuclear techniques for environment and cultural heritage. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2021, 136, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeynes, C. Chapter 10—Ion Beam Analysis for Cultural Heritage. In Spectroscopy, Diffraction and Tomography in Art and Heritage Science; Adriaens, M., Dowsett, M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 335–364. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Morón, M.A.; Palomar, T.; Alves, L.C.; Ortiz, P.; Vilarigues, M.; Schibille, N. Christian-Muslim contacts across the Mediterranean: Byzantine glass mosaics in the Great Umayyad Mosque of Córdoba (Spain). J. Archaeol. Sci. 2021, 129, 105370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiari, M. External Beam IBA Measurements for Cultural Heritage. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corregidor, V.; Viegas, R.; Ferreira, L.M.; Alves, L.C. Study of Iron Gall Inks, Ingredients and Paper Composition Using Non-Destructive Techniques. Heritage 2019, 2, 2691–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, J.; Manso, M.; Corregidor, V.; Silva, R.J.C.; Figueiredo, E.; Carvalho, M.; Alves, L.C. Surface analysis of corroded XV–XVI century copper coins by μ-XRF and μ-PIXE/μ-EBS self-consistent analysis. Mater. Charact. 2020, 161, 110170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, P.N.; Moser, M.; Bubb, I.F.; Bouanani, M.E.; Stannard, W.B.; Short, R.C. Elemental Analyisis of Artefacts in Air. AICCM Bull. 1997, 22, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demortier, G.; Ruvalcaba Sil, J.L. Quantitative ion beam analysis of complex gold-based artefacts. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2005, 239, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calligaro, T.; Dran, J.C.; Salomon, J.; Walter, P. Review of accelerator gadgets for art and archaeology. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2004, 226, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giudice, A.L.; Re, A.; Calusi, S.; Giuntini, L.; Massi, M.; Olivero, P.; Pratesi, G.; Albonico, M.; Conz, E. Multitechnique characterization of lapis lazuli for provenance study. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 2211–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calligaro, T.; Coquinot, Y.; Pichon, L.; Pierrat-Bonnefois, G.; de Campos, P.; Re, A.; Angelici, D. Characterization of the lapis lazuli from the Egyptian treasure of Tôd and its alteration using external μ-PIXE and μ-IBIL. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2014, 318, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruvalcaba-Sil, J.L.; Manzanilla, L.; Melgar, E.; Cruz, R.L.S. PIXE and ionoluminescence for Mesoamerican jadeite characterization. X Ray Spectrom. 2008, 37, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viggiano, A.M.; Sil, J.L.R.; Ortega, M.D.M.; Berdasco, V.C. Non-Destructive Micro-Chemical and Micro-Luminescence Characterization of Jadeite. Microsc. Microanal. 2016, 22, 1304–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czelusniak, C.; Palla, L.; Massi, M.; Carraresi, L.; Giuntini, L.; Re, A.; Giudice, A.L.; Pratesi, G.; Mazzinghi, A.; Ruberto, C.; et al. Preliminary results on time-resolved ion beam induced luminescence applied to the provenance study of lapis lazuli. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2015, 371, 336–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giudice, A.L.; Angelici, D.; Re, A.; Gariani, G.; Borghi, A.; Calusi, S.; Giuntini, L.; Massi, M.; Castelli, L.; Taccetti, F.; et al. Protocol for lapis lazuli provenance determination: Evidence for an Afghan origin of the stones used for ancient carved artefacts kept at the Egyptian Museum of Florence (Italy). Archaeol. Anthr. Sci. 2017, 9, 637–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidorzi, L.; Re, A.; Magalini, M.; Angelici, D.; Borghi, A.; Vaggelli, G.; Fantino, F.; Rigato, V.; La Torre, L.; Lemasson, Q.; et al. Micro-PIXE and micro-IBIL characterization of lapis lazuli samples from Myanmar mines and implications for provenance study. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2023, 138, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Castillo, H.C.; Ruvalcaba, J.L.; Calderón, T. Some new trends in the ionoluminescence of minerals. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 387, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Castillo, H.C.; Ruvalcaba-Sil, J.; Barboza-Flores, M.; Belmont, E.; Calderón, T. Ionoluminescence of diamond, synthetic diamond and simulants. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2007, 580, 400–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaranta, A.; Salomon, J.; Dran, J.C.; Tonezzer, M.; Della Mea, G. Ion beam induced luminescence analysis of painting pigments. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2007, 254, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enguita, O.; Calderón, T.; Fernández-Jiménez, M.; Beneitez, P.; Millan, A.; García, G. Damage induced by proton irradiation in carbonate based natural painting pigments. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2004, 219, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisboa, J.V.; Carvalho, J.F.; Cunha, P.; Oliveira, Á. Typological classification of clayey raw materials for ceramics manufacture, in the Tábua region (central Portugal). Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2013, 72, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sugita, T.; Yoshida, H.; Kodama, H.; Ishigaki, T.; Oba, Y. Evaluation of the effect of composition and firing temperature on pore size distribution of ceramics by SANS measurement. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2024, 132, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molera, J.; Pradell, T.; Vendrell-Saz, M. The colours of Ca-rich ceramic pastes: Origin and characterization. Appl. Clay Sci. 1998, 13, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasić, M.V.; Radovanović, L.; Pezo, L.; Radojević, Z. Raw kaolinitic-illitic clays as high-mechanical-performance hydraulically pressed refractories. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2022, 148, 1783–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botto, A.; Campanella, B.; Legnaioli, S.; Lezzerini, M.; Lorenzetti, G.; Pagnotta, S.; Poggialini, F.; Palleschi, V. Applications of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy in cultural heritage and archaeology: A critical review. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2018, 34, 81–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazic, V.; Vadrucci, M.; Fantoni, R.; Chiari, M.; Mazzinghi, A.; Gorghinian, A. Applications of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for cultural heritage: A comparison with X-ray Fluorescence and Particle Induced X-ray Emission techniques. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2018, 149, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.F.V.; Machado, I.F.; Gonzalez, A.; Pereira, M.F.C.; Casimiro, T.M. A new fifteenth-to-sixteenth-century pottery kiln on the Tagus basin, Portugal. Appl. Phys. A 2018, 124, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira Ferreira, L.F.; Casimiro, T.M.; Boavida, C.; Costa Pereira, M.F.; Ferreira Machado, I. An Archaeometric Study of Lead-Glazed Medieval Ceramics (13th–14th Century) from Santarém, Portugal. Heritage 2024, 7, 2217–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, G.; Crupi, V.; Longo, F.; Majolino, D.; Mazzoleni, P.; Venuti, V. Characterisation of archaeological pottery: The case of Ionian Cups. J. Mol. Struct. 2011, 993, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crupi, V.; Interdonato, M.; Longo, F.; Maisano, G.; Majolino, D.; Rossi, B.; Venuti, V. Coulometry for the detection of water content in ar-chaeological findings. Atti. Accad. Peloritana Pericolanti Cl. Sci. Fis. Mat. Nat. 2016, 94, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götze, J. Application of Cathodoluminescence Microscopy and Spectroscopy in Geosciences. Microsc. Microanal. 2012, 18, 1270–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, R.J.; Finch, A.A.; Hole, D.E.; Townsend, P.D.; Wu, Z.-L. The red to near-infrared luminescence in alkali feldspar. Contrib. Miner. Pet. 2002, 143, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Castillo, H.C.; Sil, J.R.; Álvarez, M.; Beneitez, P.; Millán, M.; Calderón, T. Relationship between ionoluminescence emission and bond distance (M–O) in carbonates. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2006, 249, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Malmqvist, K.; Elfman, M.; Kristiansson, P.; Pallon, J.; Sjöland, A.; Utui, R. Ionoluminescence and PIXE study of inorganic materials. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 1997, 130, 746–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayama, M.; Nishido, H.; Ninagawa, K. Cathodoluminescence characterization of tridymite and cristobalite: Effects of electron irradiation and sample temperature. Am. Mineral. 2009, 94, 1018–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, H. Cathodoluminescence study of SiO2. J. Appl. Phys. 1980, 51, 2228–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coroado, J.; Gomes, E.C. Physical and chemical characterization of ceramic wall tiles, dated to the 17th century, from the Convento de Cristo in Tomar, Portugal. In Proceedings of the 7th European Meeting on Ancient Ceramics, Lisabon, Portugal, 27–31 October 2003; pp. 33–39. [Google Scholar]
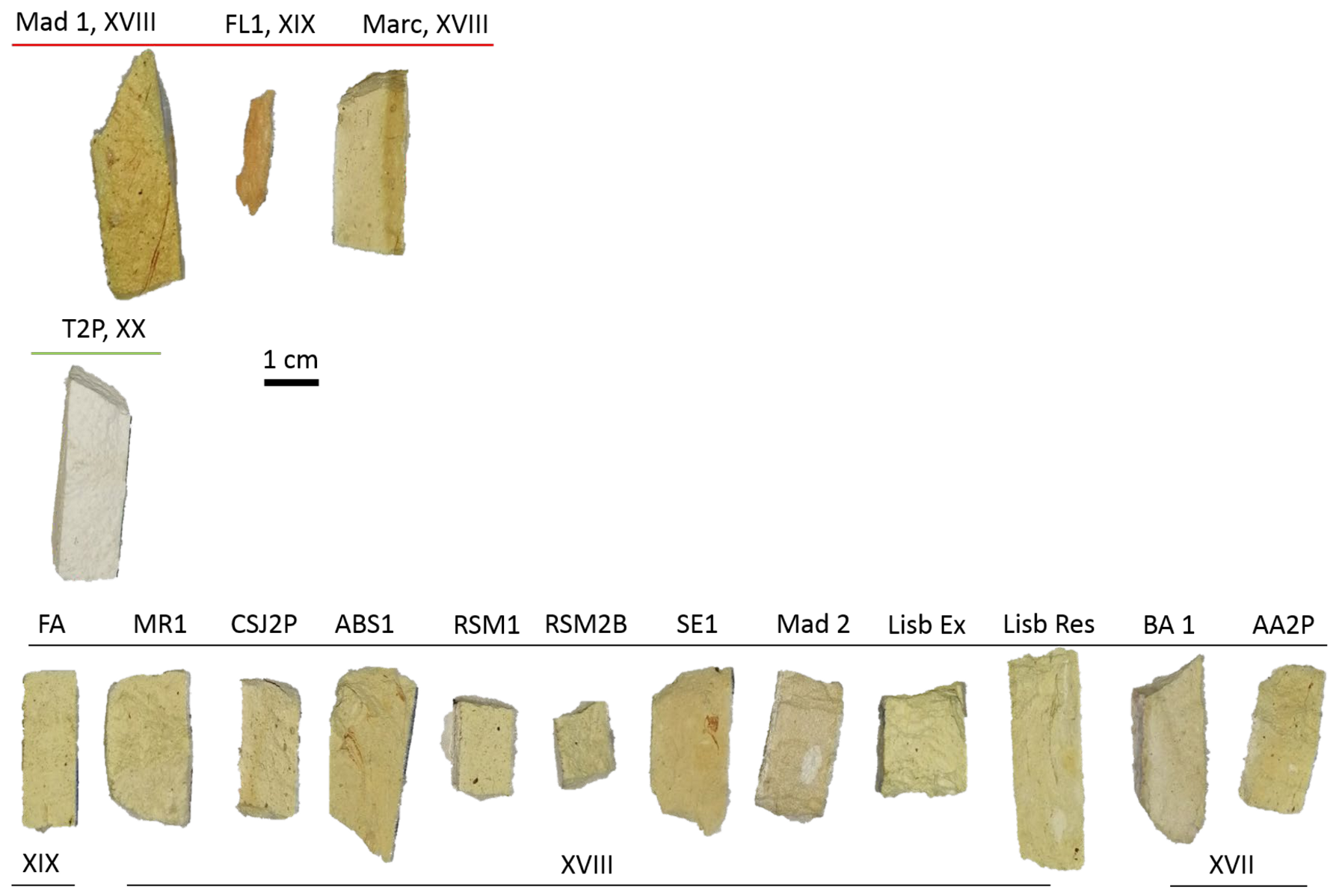

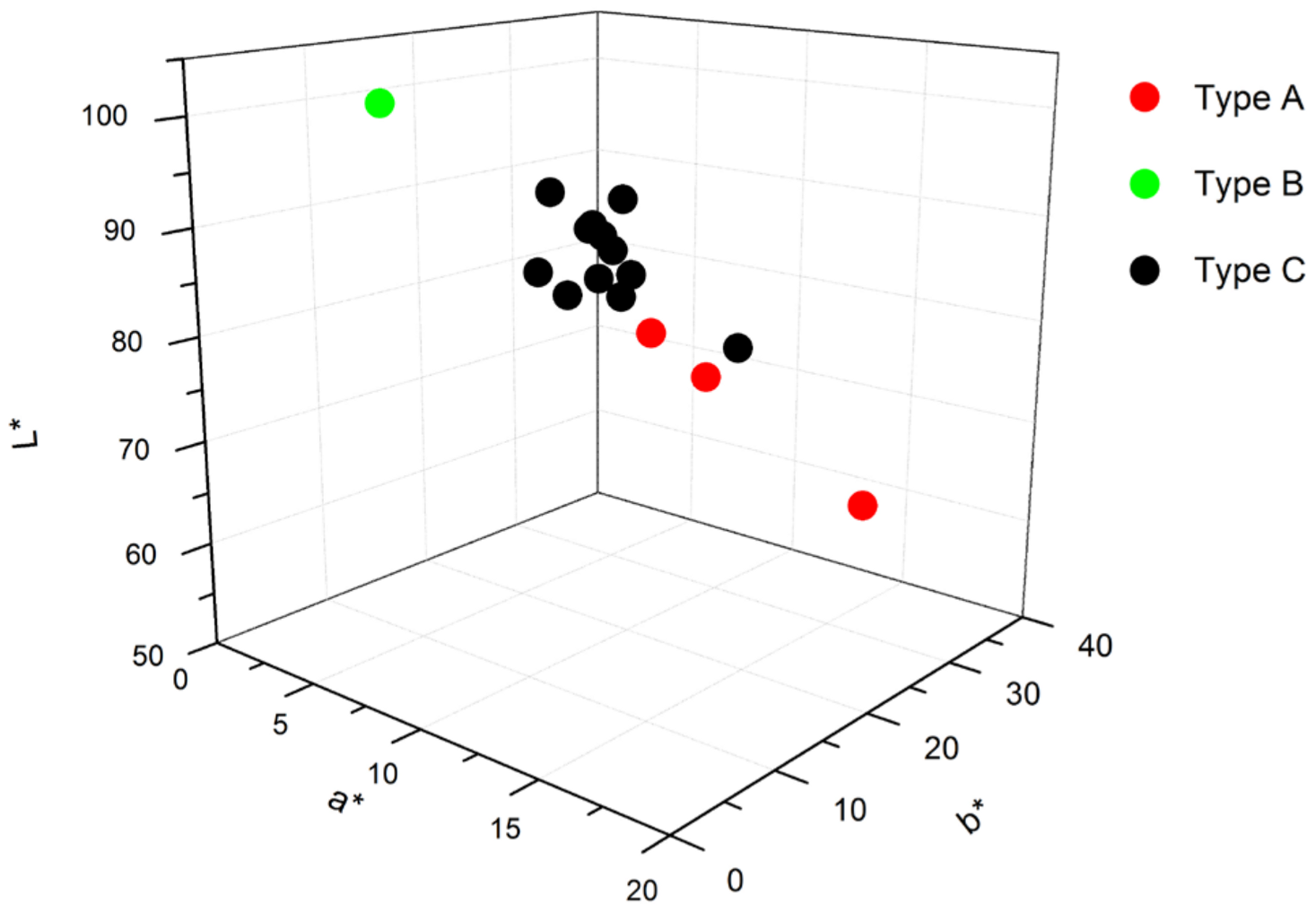
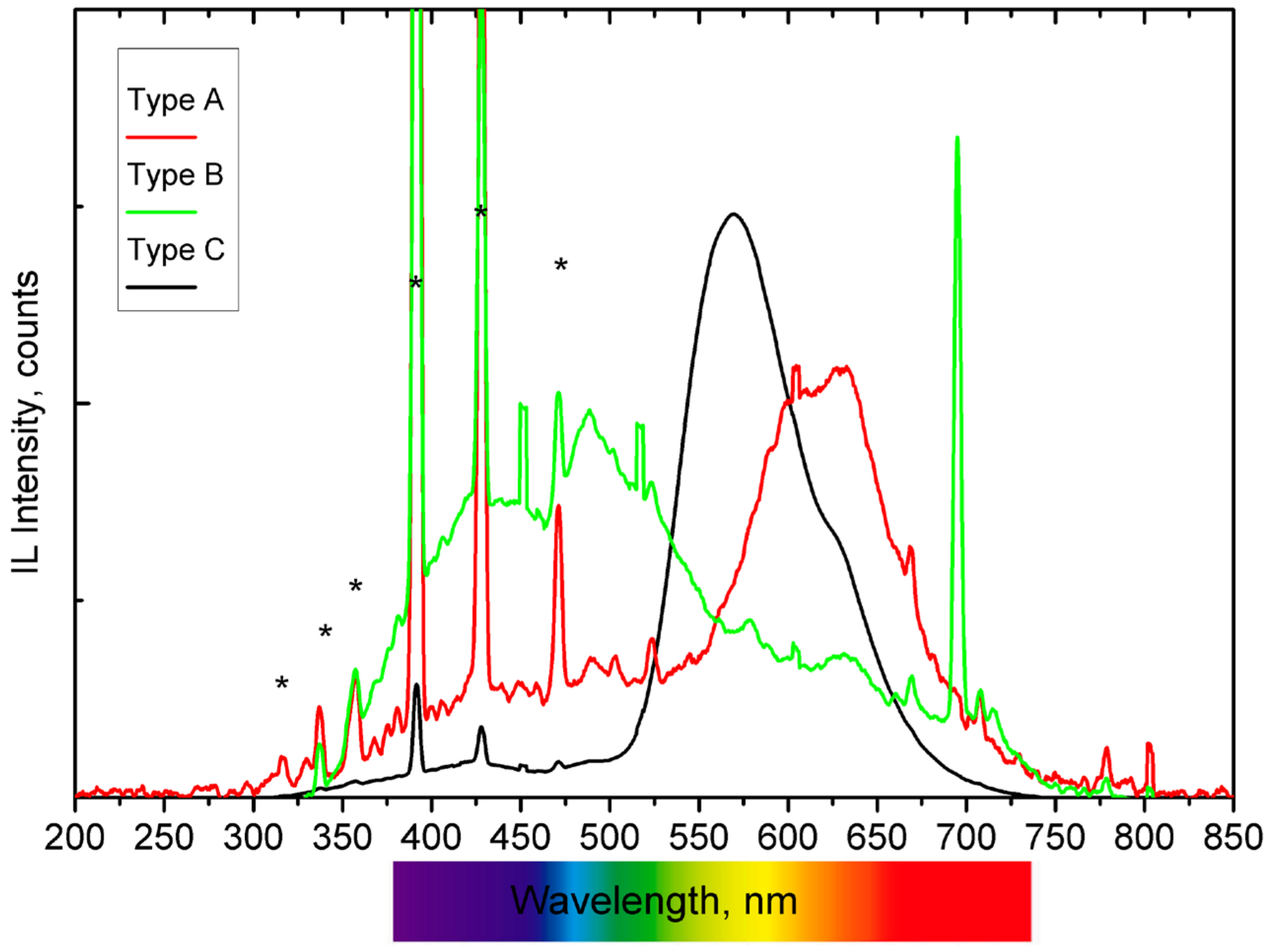
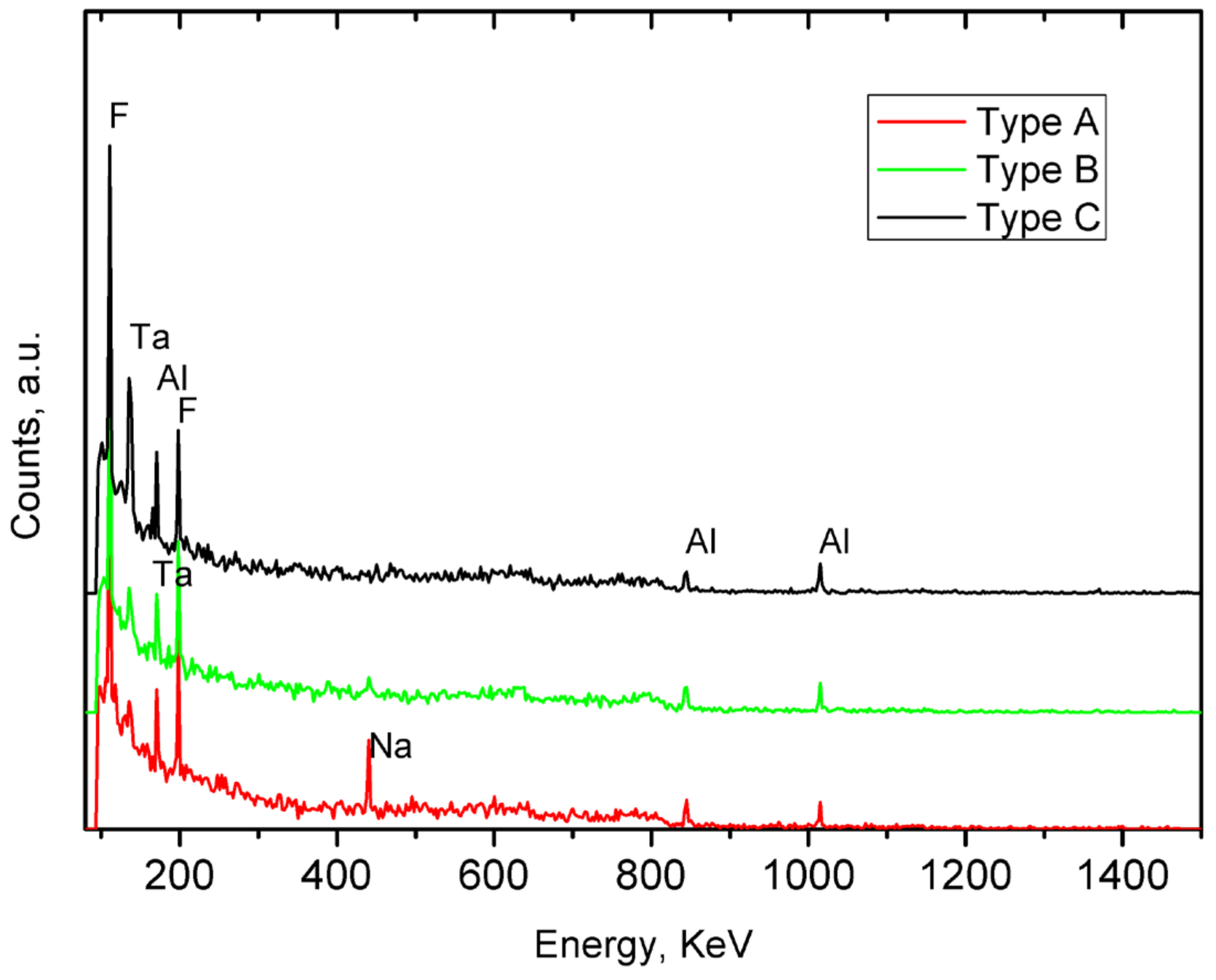
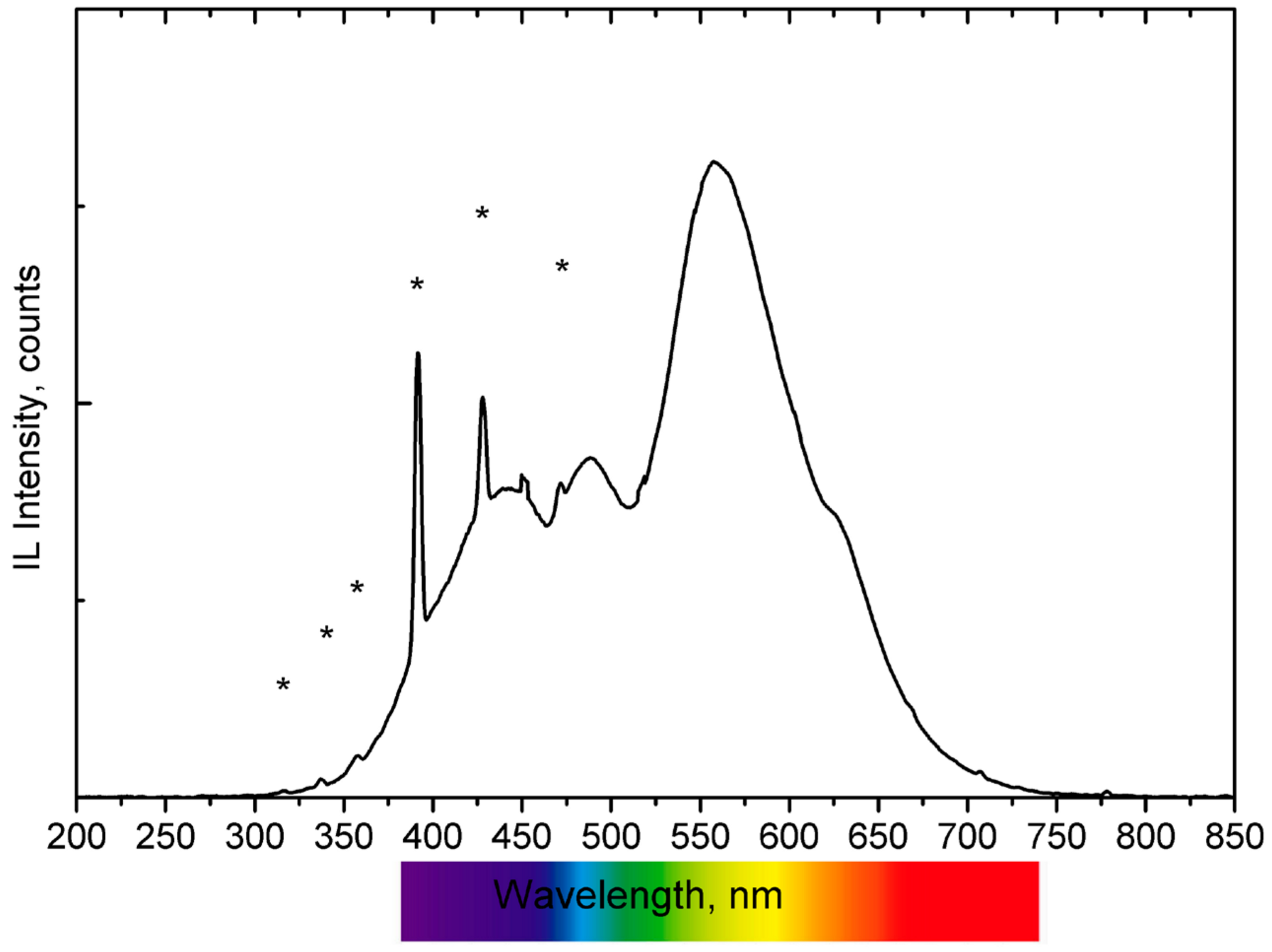
| Na | Al2O3 | SiO2 | P2O5 | S | Cl | K2O | CaO | Cr2O3 | Fe2O3 | TiO2 | MnO | SrO | PbO | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | D | 36.70 | 51.21 | 1.04 | 0.047 | 1.08 | 1.09 | 7.53 | 0.01 | 1.17 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.09 |
| B | - | 43.52 | 55.56 | 0.28 | - | 0.02 | 0.43 | 0.08 | - | 0.10 | 0.01 | - | - | - |
| C | D * | 37.89 | 49.24 | 0.57 | 0.09 | 0.13 | 0.66 | 10.33 | 0.01 | 0.99 | - | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.08 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Corregidor, V.; Ruvalcaba-Sil, J.L.; Prudêncio, M.I.; Dias, M.I.; Alves, L.C. Ion Beam-Induced Luminescence (IBIL) for Studying Manufacturing Conditions in Ceramics: An Application to Ceramic Body Tiles. Materials 2024, 17, 5075. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17205075
Corregidor V, Ruvalcaba-Sil JL, Prudêncio MI, Dias MI, Alves LC. Ion Beam-Induced Luminescence (IBIL) for Studying Manufacturing Conditions in Ceramics: An Application to Ceramic Body Tiles. Materials. 2024; 17(20):5075. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17205075
Chicago/Turabian StyleCorregidor, Victoria, José Luis Ruvalcaba-Sil, Maria Isabel Prudêncio, Maria Isabel Dias, and Luís C. Alves. 2024. "Ion Beam-Induced Luminescence (IBIL) for Studying Manufacturing Conditions in Ceramics: An Application to Ceramic Body Tiles" Materials 17, no. 20: 5075. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17205075
APA StyleCorregidor, V., Ruvalcaba-Sil, J. L., Prudêncio, M. I., Dias, M. I., & Alves, L. C. (2024). Ion Beam-Induced Luminescence (IBIL) for Studying Manufacturing Conditions in Ceramics: An Application to Ceramic Body Tiles. Materials, 17(20), 5075. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17205075







