Influence of Connector Design on Displacement and Micromotion in Tooth-Implant Fixed Partial Dentures Using Different Lengths and Diameters: A Three-Dimensional Finite Element Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
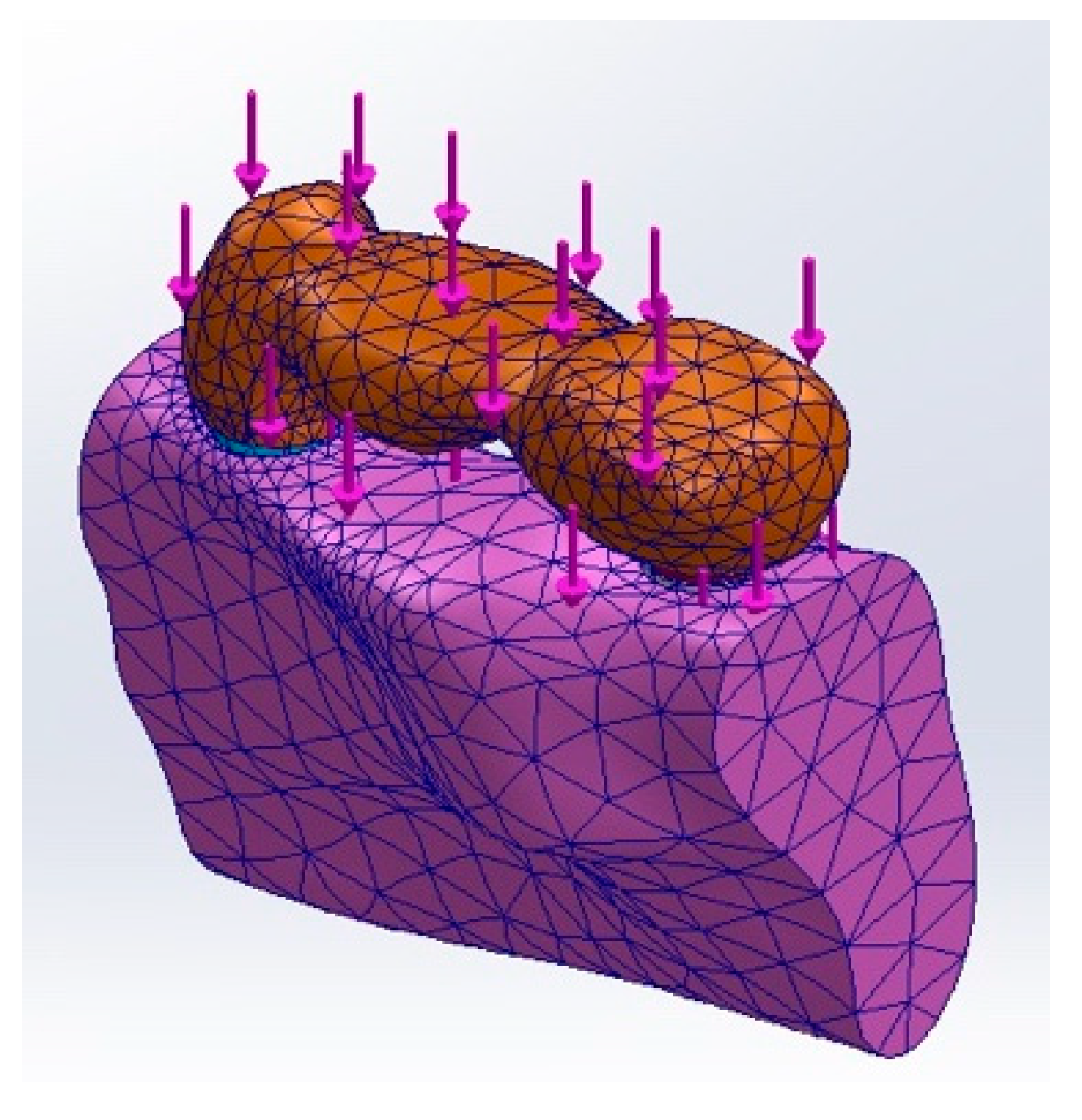
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Displacement at the FPD Bridge
3.2. Displacement at the Mandible
3.3. Displacement at the Dentin
3.4. Displacement at the Cementum
3.5. Displacement at the PDL
3.6. Displacement at the Implant
3.7. Influence of Implant Length and Diameter
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FPD | Fixed partial dentures |
| PDL | Periodontal ligament |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| ROI | Region of interest |
| DICOM | Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine |
| Ni-Cr | Nickel–chromium |
| TRIPOD | Transparent reporting of a multivariable prediction model for Individual Prognosis or Diagnosis |
| FDP | Fixed dental prosthesis |
| p-value “p” | Probability value of significance |
References
- Adell, R.; Lekholm, U.; Rockler, B.; Branemark, P.-I. A 15-year study of osseointegrated implants in the treatment of the edentulous jaw. Int. J. Oral Surg. 1981, 10, 387–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns, R.; Jemt, T.; Heath, M.; Hutton, J.; McKenna, S.; McNamara, D.; van Steenberghe, D.; Taylor, R.; Watson, R.; Herrmann, I. A multicenter study of overdentures supported by Branemark implants. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1992, 7, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukunoor, S.; Savadi, R.C.; Venkata Krishnam Raju, K.; Kumar, S. A viable treatment alternative in distal extension cases: A case report. J. Indian Prosthodont. Soc. 2014, 14, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buser, D.; Janner, S.; Wittneben, J.; Bragger, U.; Ramseier, C.; Salvi, G. 10-year survival and success rates of 511 titanium implants with a sandblasted and acid-etched surface: A retrospective study in 303 partially edentulous patients. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2012, 14, 839–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglundh, T.; Persson, L.; Klinge, B. A systematic review of the incidence of biological and technical complications in implant dentistry reported in prospective longitudinal studies of at least 5 years. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2002, 29, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pjetursson, B.; Thoma, D.; Jung, R.; Zwahlen, M.; Zembic, A. A systematic review of the survival and complication rates of implant-supported fixed dental prostheses (FDPs) after a mean observation period of at least 5 years. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2012, 23, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayaraghavan, V.; Sabane, A.V.; Tejas, K. Hypersensitivity to titanium: A less explored area of research. J. Indian Prosthodont. Soc. 2012, 12, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.R.; Denry, I. Stabilized zirconia as a structural ceramic: An overview. Dent. Mater. 2008, 24, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Wang, L.; Lu, Q.; Fan, Z. Changes in the esthetic, physical, and biological properties of a titanium alloy abutment treated by anodic oxidation. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019, 121, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.; Campbell, S.D.; Viana, M.A.; Knoernschild, K.L. Abutment Material Effect on Peri-implant Soft Tissue Color and Perceived Esthetics. J. Prosthodont. 2016, 25, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoma, D.S.; Ioannidis, A.; Cathomen, E.; Hämmerle, C.H.; Hüsler, J.; Jung, R.E. Discoloration of the Peri-implant Mucosa Caused by Zirconia and Titanium Implants. Int. J. Periodontol. Restor. Dent. 2016, 36, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, D.; Cionca, N.; Courvoisier, D.S.; Mombelli, A. A systematic review of the clinical survival of zirconia implants. Clin. Oral Investig. 2016, 20, 1403–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covacci, V.; Bruzzese, N.; Maccauro, G.; Andreassi, C.; Ricci, G.A.; Piconi, C.; Marmo, E.; Burger, W.; Cittadini, A. In vitro evaluation of the mutagenic and carcinogenic power of high purity zirconia ceramic. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivaraman, K.; Chopra, A.; Narayan, A.I.; Balakrishnan, D. Is zirconia a viable alternative to titanium for oral implant? A critical review. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2018, 62, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lughi, V.; Sergo, V. Low temperature degradation—Aging—of zirconia: A critical review of the relevant aspects in dentistry. Dent. Mater. 2010, 26, 807–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webber, L.P.; Chan, H.-L.; Wang, H.-L. Will Zirconia Implants Replace Titanium Implants? Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, M.T.; Mously, H.A.; Hashem, A.B.H.; Naguib, G.H. Clinical concerns regarding dentition and connections to osseointegrated implants: A systematic review of implant restoration trends and treatment of partial edentulism. J. Long Term Eff. Med. Implant. 2019, 29, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, M.T.; Mously, H.A. Investigating Economic and Clinical Implications of Tooth Implant Supported Prosthesis among Patients and Practitioners. Int. J. Pharm. Res. Allied Sci. 2019, 8, 116–121. [Google Scholar]
- Von Stein-Lausnitz, M.; Nickenig, H.-J.; Wolfart, S.; Neumann, K.; Von Stein-Lausnitz, A.; Spies, B.C.; Beuer, F. Survival rates and complica-tion behaviour of tooth implant–supported, fixed dental prostheses: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Dent. 2019, 88, 103167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Monaca, G.; Pranno, N.; Annibali, S.; Massimo, C.; Polimeni, A.; Patini, R.; Cristalli, M.P. Survival and complication rates of tooth-implant versus freestanding implant supporting fixed partial prosthesis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2021, 65, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskitascioglu, G.; Usumez, A.; Sevimay, M.; Soykan, E.; Unsal, E. The influence of occlusal loading location on stresses transferred to implant-supported prostheses and supporting bone: A three-dimensional finite element study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2004, 91, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevimay, M.; Turhan, F.; Kiliçarslan, M.A.; Eskitascioglu, G. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the effect of different bone quality on stress distribution in an implant-supported crown. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2005, 93, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soncini, M.; Rodriguez, Y.; Baena, R.; Pietrabissa, R.; Quaglini, V.; Rizzo, S.; Zaffe, D. Experimental procedure for the evaluation of the mechanical properties of the bone surrounding dental implants. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamed, M.T.; Mously, H.A. A Clinical Study Assessing the Surrounding Bone Levels and Bone Density of Implant-borne and Implant-tooth-fixed Partial Dentures. World J. Dent. 2019, 10, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, P.M.; Dalstra, M.; Melsen, B. Strains in periodontal ligament and alveolar bone associated with orthodontic tooth movement analyzed by finite element. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2009, 12, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunski, J.B. In vivo bone response to biomechanical loading at the bone/dental-implant interface. Adv. Dent. Res. 1999, 13, 99–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.P.; Tan, K.B.C.; Liu, G.R. Application of finite element analysis in implant dentistry: A review of the literature. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2001, 85, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, M.S.; Sundram, R.; Abdemagyd, H.A.E. Application of finite element model in implant dentistry: A systematic review. J. Pharm. Bio. Allied Sci. 2019, 11, S85–S91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, F.R.; Bitencourt, S.B.; Rosa, C.D.D.R.D.; Vieira, A.B.; Dos Santos, D.M.; Goiato, M.C. Influence of different restoring materials on stress distribution in prosthesis on implants: A review of finite element studies. Eur. J. Dent. 2023, 17, 001–006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, S.; Wakabayashi, N.; Shiota, M.; Ohyama, T. The influence of implant location and length on stress distribution for three-unit implant- supported posterior cantilever fixed partial dentures. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2004, 91, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohyama, T.; Yasuda, H.; Shibuya, N.; Tadokoro, S.; Nakabayashi, S.; Namaki, S.; Hara, Y.; Ogawa, T.; Ishigami, T. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the effects of implant diameter and photofunctionalization on peri-implant stress. J. Oral Sci. 2017, 59, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.L.; Chang, S.H.; Chang, W.J.; Kuo, Y.C. Factorial analysis of variables influencing mechanical characteristics of a single tooth implant placed in the maxilla using finite element analysis and the statistics-based Taguchi method. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2007, 115, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsouknidas, A.; Giannopoulos, D.; Savvakis, S.; Michailidis, N.; Lympoudi, E.; Fytanidis, D.; Pissiotis, A.; Michalakis, K. The influence of bone quality on the biomechanical behaviour of a tooth-implant fixed partial denture: A three-dimensional finite element analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2016, 31, e143–e154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, P.K.; Chen, Y.C.; Huang, C.C.; Lu, W.H.; Chen, Y.C.; Tsai, H.H. Distribution of micromotion in implants and alveolar bone with different thread profiles in immediate loading: A finite element study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2012, 27, e96–e101. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.L.; Fuh, L.J.; Hsu, J.T.; Tu, M.G.; Shen, Y.W.; Wu, C.L. Effects of implant surface roughness and stiffness of grafted bone on an immediately loaded maxillary implant: A 3D numerical analysis. J. Oral Rehabil. 2008, 35, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, A.C., Jr.; Bonfante, E.A.; Giro, G.; Janal, M.N.; Coelho, P.G. The effect of implant design on insertion torque and immediate micromotion. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2012, 23, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, W.; Klein, D.; Karl, M. Effect of model parameters on finite element analysis of micromotions in implant dentistry. J. Oral Implant. 2013, 39, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, H.C.; Gung, Y.W.; Chung, T.F.; Hsu, M.L. The influence of abutment angulation on micromotion level for immediately loaded dental implants: A 3-D finite element analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2008, 23, 623–630. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, M.G.; Hsu, J.T.; Fuh, L.J.; Lin, D.J.; Huang, H.L. Effects of cortical bone thickness and implant length on bone strain and interfacial micromotion in an immediately loaded implant. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2010, 25, 706–714. [Google Scholar]
- Trisi, P.; Perfetti, G.; Baldoni, E.; Berardi, D.; Colagiovanni, M.; Scogna, G. Implant micromotion is related to peak insertion torque and bone density. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2009, 20, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goellner, M.; Schmitt, J.; Karl, M.; Wichmann, M.; Holst, S. The effect of axial and oblique loading on the micromovement of dental implants. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2011, 26, 257–264. [Google Scholar]
- Mish, C.E. Stress treatmant Theorem. In Contemporary Implant Dentistry, 3rd ed.; Mosby: Maryland Heights, MO, USA, 2008; p. 69. [Google Scholar]
- Özçelik, T.B.; Ersoy, E.; Yilmaz, B. Biomechanical evaluation of tooth-and implant-supported fixed dental prostheses with various nonrigid connector positions: A finite element analysis. J. Prosthodont. 2011, 20, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Omiri, M.K.; Al-Masri, M.; Alhijawi, M.M.; Lynch, E. Combined implant and tooth support: An up-to-date comprehensive overview. Int. J. Dent. 2017, 2017, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özçelik, T.B.; Ersoy, A.E. An investigation of tooth/implant-supported fixed prosthesis designs with two different stress analysis methods: An in vitro study. J. Prosthodont. 2007, 16, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naguib, G.H.; Hashem, A.B.H.; Abougazia, A.; Mously, H.A.; Qutub, O.A.; Hamed, M.T. Effect of non-rigid connector on the stress distribution of tooth-implant supported fixed prostheses using different implant length and diameter: A comparative 3D finite element study. J. Prosthodont. 2023, 32, e129–e138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moons, K.G.M.; Altman, D.G.; Reitsma, J.B.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Macaskill, P.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Vickers, A.J.; Ransohoff, D.F.; Collins, G.S. Transparent reporting of a multivariable prediction model for Individual Prognosis or Diagnosis (TRIPOD): Explanation and elaboration. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, W1–W73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.H.; Nien, C.Y.; Chen, Y.L.; Hsu, K.W. The prevalence and associated factors of proximal contact loss between implant restoration and adjacent tooth after function: A retrospective study. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2020, 22, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfield, W. Elasticity and viscoelasticity of cortical bone. In Natural and Living Biomaterials; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 43–60. [Google Scholar]
- Middleton, J.; Jones, M.; Wilson, A. The role of the periodontal ligament in bone modeling: The initial development of a time- dependent finite element model. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthopedics. 1996, 109, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, C.C.; Chu, C.S.; Chung, K.H.; Lee, M.C. Effect of posts on dentin stress distribution in pulpless teeth. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1992, 67, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegaroiu, R.; Kusakari, H.; Nishiyama, S.; Miyakawa, O. Influence of prosthesis material on stress distribution in bone and implant: A 3-dimensional finite element analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1998, 13, 781–790. [Google Scholar]
- Merz, B.R.; Hunenbart, S.; Belser, U.C. Mechanics of the implant-abutment connection: An 8-degree taper compared to a butt joint connection. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2000, 15, 519. [Google Scholar]
- Hamed, M.T.; Mously, H.A.; Hashem, A.B.H.; Naguib, G.H. Stresses Induced in Dental Implant Retaining Screw before Tightening. J. Res. Med. Dent. Sci. 2019, 7, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Hamed, M.T.; Mously, H.A.; Hashem, A.B.H.; Naguib, G.H. Influence of Coefficient of Friction on Stress Distribution in Implant Components and Surrounding Bone. J. Res. Med. Dent. Sci. 2019, 7, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Soares, C.J.; Pizi, E.C.G.; Fonseca, R.B.; Martins, L.R.M. Influence of root embedment material and periodontal ligament simulation on fracture resistance tests. Braz. Oral. Res. 2005, 19, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picton, D.C.A.; Wills, D.J. Viscoelastic properties of the periodontal ligament and mucous membrane. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1978, 40, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-L.; Wang, J.-C.; Chang, S.-H.; Chen, S.-T. Evaluation of stress induced by implant type, number of splinted teeth, and variations in periodontal support in tooth-implant–supported fixed partial dentures: A non-linear finite element analysis. J. Periodontol. 2010, 81, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Akbari, A.; Jiang, F.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J. The effects of different types of periodontal ligament material models on stresses computed using finite element models. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2022, 162, e328–e336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khraisat, A.; Hashimoto, A.; Nomura, S.; Miyakawa, O. Effect of lateral cyclic loading on abutment screw loosening of an external hexagon implant system. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2004, 91, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, J.F., Jr.; Verri, F.R.; Almeida, D.A.; de Souza Batista, V.E.; Lemos, C.A.; Pellizzer, E.P. Finite element analysis on influence of implant surface treatments, connection and bone types. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 63, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spies, B.C.; Sauter, C.; Wolkewitz, M.; Kohal, R.J. Alumina reinforced zirconia implants: Effects of cyclic loading and abutment modification on fracture resistance. Dent. Mater. 2015, 31, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lofaj, F.; Kučera, J.; Németh, D.; Kvetková, L. Finite element analysis of stress distributions in mono- and bi-cortical dental implants. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2015, 50, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeganni, N.; Abulaban, R.; Naguib, G.; Tharwat, M.; Nassar, H.M. Anterior provisional fixed partial dentures: A finite element analysis. J. Prosthodont. 2024, 33, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamed, M.T.; Mously, H.A. Stress Analysis for Different Designs of Implant-borne and Tooth-implant Fixed Partial Dentures in Mandibular Posterior Region. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2019, 20, 1375–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsaousoglou, P.; Michalakis, K.; Kang, K.; Weber, H.P.; Sculean, A. The effect of rigid and nonrigid connections between implants and teeth on biological and technical complications: A systematic review and a metaanalysis. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2017, 28, 849–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrecillas-Martinez, L.; Monje, A.; Lin, G.; Suarez, F.; Ortega-Oiler, I.; Galindo-Moreno, P.; Wang, H. Effect of cantilevers for implant-supported prostheses on marginal bone loss and prosthetic complications: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2014, 29, 1315–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naert, I.; Duyck, J.; Hosny, M.; Quirynen, M.; van Steenberghe, D. Freestanding and tooth-implant connected prostheses in the treatment of partially edentulous patients Part II: An up to 15-years radiographic evaluation. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2001, 12, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Block, M.; Lirette, D.; Gardiner, D.; Li, L.; Finger, I.; Hochstedler, J.; Evans, G.; Kent, J.; Misiek, D.; Mendez, A.; et al. Prospective evaluation of implants connected to teeth. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2002, 17, 473–487. [Google Scholar]
- Cordaro, L.; Ercoli, C.; Rossini, C.; Torsello, F.; Feng, C. Retrospective evaluation of complete-arch fixed partial dentures connecting teeth and implant abutments in patients with normal and reduced periodontal support. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2005, 94, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanishi, Y.; Yamaguchi, S.; Imazato, S.; Nakano, T.; Yatani, H. Influences of implant neck design and implant-abutment joint type on peri-implant bone stress and abutment micromovement: Three-dimensional finite element analysis. Dent. Mater. 2012, 28, 1126–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, S.; Yamanishi, Y.; Machado, L.S.; Matsumoto, S.; Tovar, N.; Coelho, P.G.; Thompson, V.P.; Imazato, S. In vitro fatigue tests and in silico finite element analysis of dental implants with different fixture/abutment joint types using computer-aided design models. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2018, 62, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Mondragon, M.; Urriolagoitia-Sosa, G.; Romero-Ángeles, B.; García-Laguna, M.A.; Laguna-Canales, A.S.; Pérez-Partida, J.C.; Mireles-Hernández, J.; Carrasco-Hernández, F.; Urriolagoitia-Calderón, G.M. Biomechanical Fatigue Behavior of a Dental Implant Due to Chewing Forces: A Finite Element Analysis. Materials 2024, 17, 1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, O.; Zafiropoulos, G.G. Tooth-implant connection: A review. J. Oral Implantol. 2012, 38, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, N.P.; Pjetursson, B.E.; Tan, K.; Brägger, U.; Egger, M.; Zwahlen, M. A systematic review of the survival and complication rates of fixed partial dentures (FPDs) after an observation period of at least 5 years: II. Combined tooth–implant-supported FPDs. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2004, 15, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamalis, A.; Markopoulou, K.; Kaloumenos, K.; Analitis, A. Splinting osseointegrated implants and natural teeth in partially edentulous patients: A systematic review of the literature. J. Oral Implantol. 2012, 38, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fobbe, H.; Rammelsberg, P.; Bermejo, J.L.; Kappel, S. The up-to-11–year survival and success of implants and abutment teeth under solely implant-supported and combined tooth-implant-supported double crown-retained removable dentures. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2019, 30, 1134–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, M.; Faulkner, R.J.; Donatelli, D.P.; Suzuki, J.B. Tooth-to-implant-supported fixed partial denture: A comprehensive overview of systematic reviews. Implant Dent. 2019, 28, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Száva, D.T.; Száva, A.; Száva, J.; Gálfi, B.; Vlase, S. Dental Implant and Natural Tooth Micro-Movements during Mastication-In Vivo Study with 3D VIC Method. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, M.; Laufer, B. Splinting osseointegrated implants and natural teeth in rehabilitation of partially edentulous patients. 1: Laboratory and clinical studies. J. Oral Rehabil. 1997, 24, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, D. Prosthetic considerations for the utilization of osseointegrated fixtures in the partially edentulous arch. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1986, 1, 39–45. [Google Scholar]
- Rygh, P. Hyalinization of the periodontal ligament incident to orthodontic tooth movement. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1976, 70, 459–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts-Harry, D.; Sandy, J. Orthodontics. Part 11: Orthodontic tooth movement. Br. Dent. J. 2004, 196, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Böhl, M.; Kuijpers-Jagtman, A.M. Hyalinization during orthodontic tooth movement: A systematic review on tissue reactions. Eur. J. Orthod. 2009, 31, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rammelsberg, P.; Schwarz, S.; Schroeder, C.; Bermejo, J.; Gabbert, O. Short-term complications of implant-supported and combined tooth-implant-supported fixed dental prostheses. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2013, 24, 758–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickenig, H.; Spiekermann, H.; Wichmann, M.; Andreas, S.; Eitner, S. Survival and complication rates of combined tooth-implant-supported fixed and removable partial dentures. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2008, 21, 131–137. [Google Scholar]
- Nickenig, H.; Schaefer, C.; Spiekermann, H. Survival and complication rates of combined tooth-implant-supported fixed partial dentures. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2006, 17, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misch, C. Contemporary Implant Dentistry, 3rd ed.; Mosby: Maryland Heights, MO, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Rangert, B.; Gunne, J.; Sullivan, D. Mechanical aspects of a branemark implant connected to a natural tooth an in vitro study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1991, 6, 177–186. [Google Scholar]
- Rangert, B.; Gunne, J.; Glantz, P.; Svensson, A. Vertical load distribution on a 3-unit prosthesis supported by a natural tooth and a single branemark implant-an in vitro study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 1995, 6, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesqueira, A.A.; Goiato, M.C.; Filho, H.G.; Monteiro, D.R.; dos Santos, D.M.; Haddad, M.F.; Pellizzer, E.P. Use of stress analysis methods to evaluate the biomechanics of oral rehabilitation with implants. J. Oral Implantol. 2014, 40, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenouth, M.J. The relationship between bruxism and temporo-mandibular joint dysfunction as shown by computer analysis of nocturnal tooth contacts. J. Oral Rehabil. 1979, 6, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spear, F.M. Fundamental occlusal therapy considerations. In Science and Practice of Occlusion, 1st ed.; Mc Neil, C., Ed.; Quintessence: Chicago, IL, USA, 1997; pp. 421–434. [Google Scholar]
- Rangert, B.; Jemt, T.; Jörneus, L. Forces and moments on Brånemark implants. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1989, 4, 241–247. [Google Scholar]
- Bragger, U.; Karoussis, I.; Persson, R.; Pjetursson, B.; Salvi, G.; Lang, N. Technical and biologicalcomplications/failures with single crowns and fixed partial dentures on implants: A 10-year prospective-cohort study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2005, 16, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, P.; Yu, H. Stress distribution and microgap formation in angulated zirconia abutments with a titanium base in narrow diameter implants: A 3D finite element analysis. Int. J. Numer. Methods Biomed. Eng. 2022, 38, e3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gratton, D.G.; Aquilino, S.A.; Stanford, C.M. Micromotion and dynamic fatigue properties of the dental implant–abutment interface. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2001, 85, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, M.; Abramovich, I.; Weiss, E.I. Microleakage at the abutment-implant interface of osseointegrated implants: A comparative study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1999, 14, 94–100. [Google Scholar]
- Coelho, A.L.; Suzuki, M.; Dibart, S.; N, D.S.; Coelho, P.G. Cross-sectional analysis of the implant–abutment interface. J. Oral Rehabil. 2007, 34, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibart, S.; Warbington, M.; Su, M.F.; Skobe, Z. In vitro evaluation of the implant-abutment bacterial seal: The locking taper system. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants. 2005, 20, 732–737. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, D.R.; Schwab, G.H.; Spengler, D.M. Tensile fracture of cancellous bone. Acta Orthop. Scand. 1980, 51, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, L.J.; Beaupre, G.S.; Hayes, W.C. Multiaxial strength characteristics of trabecular bone. J. Biomech. 1983, 16, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Røhl, L.; Larsen, E.; Linde, F.; Odgaard, A.; Jørgensen, J. Tensile and compressive properties of cancellous bone. J. Biomech. 1991, 24, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalakis, K.; Calvani, P.; Hirayama, H. Biomechanical considerations on tooth-implant supported fixed partial dentures. J. Dent. Biomech. 2012, 3, 1758736012462025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonas, J.E.; Riede, U.N. Reaction of oxytalan fibers in human periodontium to mechanical stress. A combined histochemical and morphometric analysis. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1980, 28, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.B.; Pylypas, S.P. A re-evaluation of the distribution of the elastic meshwork within the periodontal ligament of the mouse. J. Periodontal. Res. 1992, 27, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sloan, P.; Carter, D.H. Structural organization of the fibres of the periodontal ligament. In The Periodontal Ligament in Health and Disease; Berkovitz, B.K.B., Moxham, B.J., Newman, H.N., Eds.; Mosby-Wolfe: London, UK, 1995; pp. 35–53. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.C.; Ding, S.J.; Yuan, C.; Yan, M. Biomechanical analysis of rigid and non-rigid connection with implant abutment designs for tooth-implant supported prosthesis: A finite element analysis. J. Dent. Sci. 2022, 17, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowda, S.; Quadras, D.D.; Sesappa, R.S.; Katapadi, V. Evaluation of effect of connector designs in implant tooth-supported fixed partial denture: A two-dimensional finite element analysis. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2018, 19, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanojia, E.M.; Bhoyar, A.; Dubey, S.R.; Sathe, S.; Khubchandani, S.R.; Shinde, R. Shielding the Pier Abutment Using a Nonrigid Connector. Cureus 2024, 16, e52895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misch, C.E.; Wang, H.L.; Misch, C.M.; Sharawy, M.; Lemons, J.; Judy, K.W. Rationale for the application of immediate load in implant dentistry: Part I. Implant. Dent. 2004, 13, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosiakov, S.M.; Koroleva, A.A.; Rogosin, S.V.; Silberschmidt, V.V. Viscoelasticity of periodontal ligament: An analytical model. Mech. Adv. Mater. Mod. Process. 2015, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, W.E.; Stanford, C.M. Bone physiology, metabolism, and biomechanics in implant therapy. In Principles and Practice of Single Implant and Restorations; Torabinejad, M., Sabeti, M.A., Goodacre, C.J., Eds.; W.B. Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2014; pp. 53–73. [Google Scholar]
- Hamed, M.T.; Mously, H.A.; Ghulman, M.M.; Naguib, G.H. Impact of dental implant diameter on the efficiency of fatigue: A systematic review analysis. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2021, 71, 1648–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, P.; Cao, R.; Li, Z.; Fan, Z. A comprehensive biomechanical evaluation of length and diameter of dental implants using finite element analyses: A systematic review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, G.H.; Hashem, A.B.H.; Natto, Z.S.; Abougazia, A.O.; Mously, H.A.; Hamed, M.T. The Effect of Implant Length and Diameter on Stress Distribution of Tooth-Implant and Implant Supported Fixed Prostheses: An In Vitro Finite Element Analysis Study. J. Oral Implantol. 2023, 49, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, S.; Baghaei, K.; Fathi, A.; Aghadavoudi, N.; Hashemi, S.S.; Atash, R.; Khademi, S.S. Stress Analysis of Endodontically Treated Tooth-Implant Different Connectors Designs in Maxillary Posterior Region: A Finite Element Analysis. Eur. J. Dent. 2024, 18, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röhrle, O.; Saini, H.; Lee, P.V.S.; Ackland, D.C. A novel computa-tional method to determine subject-specific bite force and occlusal loading during mastication. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Engin. 2018, 21, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanford, C.M.; Brand, R.A. Toward an understanding of implant occlusion and strain adaptive bone modeling and remodeling. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1999, 81, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]













| Materials | Modulus of Elasticity (MPa) × 106 | Poisson’s Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Titanium implant | 110,000 [33,48] | 0.35 [33,48] |
| Cortical bone | 15,000 [33,49] | 0.30 [33,49] |
| Cancellous bone | 1500 [33,49] | 0.30 [33,49] |
| Dentin | 18,600 [50] | 0.31 [50] |
| Cementum | 16,000 [46] | 0.3 [46] |
| Periodontal ligament | 69 [48,51] | 0.45 [48,51] |
| Nickel–chromium | 185,000 [52] | 0.30 [52] |
| FPD Bridge | Mandible | Dentin | Cementum | PDL | Implant | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group A | ||||||
| 3.7–11.5 mm | 0.0086380 | 0.00205 | 0.00819 | 0.00816 | 0.00774 | 0.0041430 |
| 3.7–13 mm | 0.0066230 | 0.00178 | 0.00625 | 0.00623 | 0.00611 | 0.0032770 |
| 4.7–10 mm | 0.0103700 | 0.00162 | 0.00983 | 0.00976 | 0.00890 | 0.0045110 |
| 5.7–10 mm | 0.0079330 | 0.00198 | 0.00762 | 0.00759 | 0.00682 | 0.0034650 |
| Group B | ||||||
| 3.7–11.5 mm | 0.6640000 | 0.17150 | 0.63620 | 0.63300 | 0.63270 | 0.295800 |
| 3.7–13 mm | 0.0142900 | 0.00226 | 0.01022 | 0.01018 | 0.00923 | 0.0058260 |
| 4.7–10 mm | 0.9543000 | 0.15310 | 0.90940 | 0.90290 | 0.81100 | 0.388700 |
| 5.7–10 mm | 0.0120300 | 0.00215 | 0.00846 | 0.00841 | 0.00778 | 0.0040610 |
| Displacement Points | Group A (Rigid Connection) | Group B (Non-Rigid Connection) | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bridge | 0.0084 ± 0.002 | 0.4112 ± 0.237 | p value = 0.021 * |
| Percentage changes (%) | - | 4795.24% | |
| Mandible | 0.0019 ± 0.0002 | 0.39107 ± 0.455 | p value = 0.021 * |
| Percentage changes (%) | - | 20482.63% | |
| Dentin | 0.0080 ± 0.0015 | 0.39107 ± 0.455 | p value = 0.043 * |
| Percentage changes (%) | - | 4788.38% | |
| Cementum | 0.0079 ± 0.0014 | 0.38862 ± 0.4517 | p value = 0.043 * |
| Percentage changes (%) | - | 4819.24% | |
| PDL | 0.0074 ± 0.0012 | 0.36518 ± 0.4182 | p value = 0.043 * |
| Percentage changes (%) | - | 4834.86% | |
| Distal implant | 0.0038 ± 0.0006 | 0.17360 ± 0.1984 | p value = 0.083 |
| Percentage changes (%) | - | 4468.42% |
| Variable | Implant Diameter | Implant Length | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correlation Coefficient (r) | p-Value | Correlation Coefficient (r) | p-Value | |
| Displacement induced in Bridge | −0.180 | 0.670 | −0.259 | 0.535 |
| Displacement induced in Mandible | 0.026 | 0.952 | −0.185 | 0.660 |
| Displacement induced in Dentin | −0.180 | 0.670 | −0.309 | 0.457 |
| Displacement induced in Cementum | −0.180 | 0.670 | −0.309 | 0.457 |
| Displacement induced in PDL | −0.180 | 0.670 | −0.309 | 0.457 |
| Displacement induced in Distal implant | −0.103 | 0.808 | −0.272 | 0.515 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mously, H.A.; Naguib, G.H.; Hashem, A.B.H.; Abougazia, A.O.; Binmahfooz, A.M.; Hamed, M.T. Influence of Connector Design on Displacement and Micromotion in Tooth-Implant Fixed Partial Dentures Using Different Lengths and Diameters: A Three-Dimensional Finite Element Study. Materials 2024, 17, 4416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174416
Mously HA, Naguib GH, Hashem ABH, Abougazia AO, Binmahfooz AM, Hamed MT. Influence of Connector Design on Displacement and Micromotion in Tooth-Implant Fixed Partial Dentures Using Different Lengths and Diameters: A Three-Dimensional Finite Element Study. Materials. 2024; 17(17):4416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174416
Chicago/Turabian StyleMously, Hisham A., Ghada H. Naguib, Abou Bakr Hossam Hashem, Ahmed O. Abougazia, Abdulelah M. Binmahfooz, and Mohamed T. Hamed. 2024. "Influence of Connector Design on Displacement and Micromotion in Tooth-Implant Fixed Partial Dentures Using Different Lengths and Diameters: A Three-Dimensional Finite Element Study" Materials 17, no. 17: 4416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174416
APA StyleMously, H. A., Naguib, G. H., Hashem, A. B. H., Abougazia, A. O., Binmahfooz, A. M., & Hamed, M. T. (2024). Influence of Connector Design on Displacement and Micromotion in Tooth-Implant Fixed Partial Dentures Using Different Lengths and Diameters: A Three-Dimensional Finite Element Study. Materials, 17(17), 4416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174416







