Realization of Joints of Aluminosilicate Glass and 6061 Aluminum Alloy via Picosecond Laser Welding without Optical Contact
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Typical Macroscopic Morphology and Microstructure
3.2. Effect of Single-Pulse Energy on Aluminosilicate Glass/6061 Al ps Laser Welding
3.2.1. Effect of Single-Pulse Energy on Macroscopic and Cross-Sectional Morphology of Aluminosilicate Glass/6061 Al ps Laser Welding Joint
3.2.2. Effect of Single-Pulse Energy on Mechanical Properties of Aluminosilicate Glass/6061 Al ps Laser Welding Joint
3.3. Effect of Linear Energy Density on Aluminosilicate Glass/6061 Al ps Laser Welding
3.3.1. Effect of Linear Energy Density on Macroscopic and Cross-Sectional Morphology of Aluminosilicate Glass/6061 Al ps Laser Welding Joint
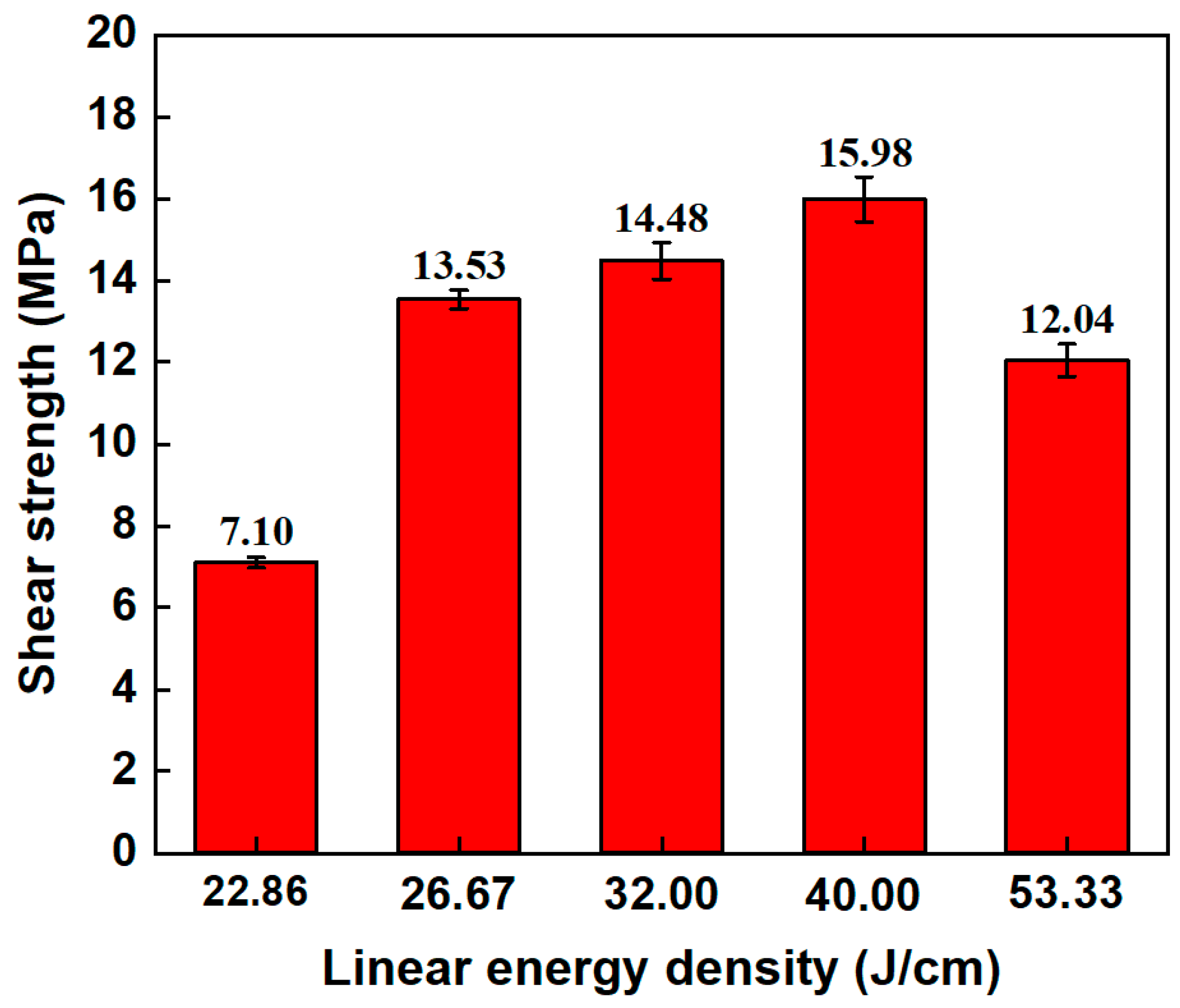
3.3.2. Effect of Linear Energy Density on Mechanical Properties Aluminosilicate Glass/6061 Al ps Laser Welding Joint
3.4. Student’s t Test and the Comparison between This Study and Previous Studies
3.4.1. Student’s t Test
3.4.2. The Comparison between This Study and Previous Studies
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Aluminosilicate glass and 6061 Al were successfully welded with a ps laser at a gap of 30 ± 5 μm. The main reason for the formation of the connection is the diffusion mixing of molten glass and metal at the interface, consisting of the Al–Si–O compound and Al. The glass will collapse after melting and caulking, resulting in an approximately arc-shaped microcrack between the modified glass and the unmodified glass or the weakly modified glass due to the relatively large gap between glass and metal caused by the rough surface of material;
- (2)
- Single-pulse energy and linear energy density affect the shape of the glass modification zone and thermal accumulation. The Student’s t-test, with a t-value of 0.022, indicates a statistically significant difference in shear strength when adjusting the two parameters. By properly adjusting these two parameters, the shear strength of the aluminosilicate glass/6061 Al joint reaches the maximum value of 15.98 MPa, which is excellent under the conditions of simple cleaning of the material surface only;
- (3)
- By analyzing the morphologies of the fracture surfaces, three fracture patterns can be identified: fracture pattern I in which the fractures occur partly on the glass side and partly at the interface; fracture pattern II, where the fractures occur entirely on the glass side; and fracture pattern III, where the fractures occur entirely at the interface. Fracture pattern III exhibits the better joint macroscopic morphology and cross-sectional morphology, as well as the maximum joint shear strength.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Robert, E.L.; Steven, L.; Frankie, M.; Stephen, L. Ultrafast laser bonding of glasses and crystals to metals for epoxy-free optical instruments. In Components and Packaging for Laser Systems VI; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2020; p. 1126103. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, M.H.; Yoshihara, K.; Mercelis, B.; Van Landuyt, K.; Peumans, M.; Van Meerbeek, B. Quick bonding using a universal adhesive. Clin. Oral Investig. 2020, 24, 2837–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Ma, C.; Hou, B.; Liu, H. Rational design of adhesives for effective underwater bonding. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 1007212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overend, M.; Jin, Q.; Watson, J. The selection and performance of adhesives for a steel–glass connection. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2011, 31, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Chen, C. Research on mechanical clinching process for dissimilar aluminum alloy sheets with inclined surface. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 89, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temiz, Y.; Lovchik, R.D.; Kaigala, G.V.; Delamarche, E. Lab-on-a-chip devices: How to close and plug the lab? Microelectron. Eng. 2015, 132, 156–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfait, W.J.; Klemenčič, R.; Lang, B.; Rist, T.; Klučka, M.; Zajacz, Z.; Koebel, M.M. Optimized solder alloy for glass-to-metal joints by simultaneous soldering and anodic bonding. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2016, 236, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, R.; Wei, H.; Lin, T.; He, P.; Sekulic, D.P.; Wang, Q.; Duan, X. Homogenization of the zirconium carbide–titanium interface domain. Scr. Mater. 2016, 112, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, L.-X.; Feng, J.-C.; Liu, H.-B.; He, P. Microstructure and fracture behavior of SiO2 glass ceramic and TC4 alloy joint brazed with TiZrNiCu alloy. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 2009, 16, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.B.; Zhang, L.X.; Wu, L.Z.; Liu, D.; Feng, J.C. Vacuum brazing of SiO2 glass ceramic and Ti–6Al–4V alloy using AgCuTi filler foil. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 498, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Stoian, R.; Zhao, W.; Cheng, G. Femtosecond laser Bessel beam welding of transparent to non-transparent materials with large focal-position tolerant zone. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 917–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, L. New application of a new generation femtosecond laser in hyperfine cold processing. Met. Work. 2013, 1, 29–32. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, W.; Onda, S.; Tamaki, T.; Itoh, K.; Nishii, J. Space-selective laser joining of dissimilar transparent materials using femtosecond laser pulses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 021106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, R.M.; Chen, J.; Shephard, J.D.; Thomson, R.R.; Hand, D.P. Picosecond laser welding of similar and dissimilar materials. Appl. Opt. 2014, 53, 4233–4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.-H.; Huang, Y.-J.; Chen, X.; Jiang, J.-Y.; Guo, Z.-J.; Long, Y. Direct microwelding of dissimilar glass and Kovar alloy without optical contact using femtosecond laser pulses. J. Cent. South Univ. 2022, 29, 3422–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, J.; Gao, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhu, W.; Wang, S.; Jiang, L.; Li, X. Mechanism and optimization of femtosecond laser welding fused silica and aluminum. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 640, 158327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Pan, R.; Zhou, T.; Dong, Z.; Yan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, P.; Chen, S. Direct joining of quartz glass and copper by nanosecond laser. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 36056–36070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaki, T.; Watanabe, W.; Nishii, J.; Itoh, K. Welding of Transparent Materials Using Femtosecond Laser Pulses. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 44, L687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Carter, R.M.; Thomson, R.R.; Hand, D.P. Avoiding the requirement for pre-existing optical contact during picosecond laser glass-to-glass welding. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 18645–18657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, S.; Zimmermann, F.; Eberhardt, R.; Tünnermann, A.; Nolte, S. Toward laser welding of glasses without optical contacting. Appl. Phys. A 2015, 121, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, R.M.; Troughton, M.; Chen, J.; Elder, I.; Thomson, R.R.; Daniel Esser, M.J.; Lamb, R.A.; Hand, D.P. Towards industrial ultrafast laser microwelding: SiO2 and BK7 to aluminum alloy. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 4873–4881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuyoshi, S.; Mizuguchi, Y.; Muratsugu, A.; Yamada, H.; Tamaki, T.; Watanabe, W. Welding of Glass and Copper with a Rough Surface using Femtosecond Fiber Laser Pulses. J. Laser Micro/Nanoeng. 2018, 13, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Cheng, G. Direct welding of glass and metal by 1 kHz femtosecond laser pulses. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 8957–8961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fermann, M.E.; Galvanauskas, A.; Sucha, G. Ultrafast Lasers Technology and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; Volume 80. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, U. Recent developments in compact ultrafast lasers. Nature 2003, 424, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Z.; Yu, S.; Song, K.; Zhou, X.; Yin, X. Fabrication of a leaf-like superhydrophobic CuO coating on 6061Al with good self-cleaning, mechanical and chemical stability. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 14872–14883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Su, J.; Feng, Z.; Liu, H.; Xia, H.; Zhang, Z.; Tan, C.; Chen, B.; Song, X. Effect of laser textured patterns on the interfacial characteristics and mechanical properties of 6061Al/GFRTP joints via hot-pressing. Thin-Walled Struct. 2023, 189, 110916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.; Pan, R.; Zhong, M. Ultrafast Laser Enabling Hierarchical Structures for Versatile Superhydrophobicity with Enhanced Cassie–Baxter Stability and Durability. Langmuir 2019, 35, 16693–16711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wang, H.; Rinker, T.; Tan, W. Investigation of metal mixing in laser keyhole welding of dissimilar metals. Mater. Des. 2020, 195, 109056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, M.T.; Tian, K.V.; Dobó-Nagy, C.; Chass, G.A.; Neville Greaves, G.; Yue, Y. Phase separation in an ionomer glass: Insight from calorimetry and phase transitions. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2015, 415, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Z.; Yufei, C.; Changjun, C.; Zhaoling, Q. A new sealing technology for ultra-thin glass to aluminum alloy by laser transmission welding method. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 115, 2017–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



















| Element | Si | Na | Ca | O | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content | 34.55–42.61 | 9.21 | 1.38 | 35.61–39.95 | 10.80–15.30 |
| Element | Si | Fe | Cu | Mn | Mg | Cr | Zn | Ti | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content | 0.4–0.8 | 0.7 | 0.15–0.4 | 0.15 | 0.8–1.2 | 0.04–0.35 | 0.25 | 0.15 | Bal |
| Material | Melting Point/°C | Density/g·cm−3 | Thermal Conductivity/Wm−1k−1 | Thermal Expansion Coefficient/10−6k−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminosilicate glass | 1425 | 2.42 | 1.67 | 8.69 |
| 6061 Al | 650 | 2.75 | 168 | 23.5 |
| Number | Scanning Speed (mm/s) | Frequency (kHz) | Power (W) | Linear Energy Density (J/cm) | Single-Pulse Energy (μJ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 25 | 1100 | 40 | 32.00 | 36.37 |
| 2 | 25 | 1000 | 40 | 32.00 | 40.00 |
| 3 | 25 | 900 | 40 | 32.00 | 44.44 |
| 4 | 25 | 800 | 40 | 32.00 | 50.00 |
| 5 | 25 | 700 | 40 | 32.00 | 57.14 |
| 6 | 35 | 1000 | 40 | 22.86 | 40.00 |
| 7 | 30 | 1000 | 40 | 26.67 | 40.00 |
| 8 | 25 | 1000 | 40 | 32.00 | 40.00 |
| 9 | 20 | 1000 | 40 | 40.00 | 40.00 |
| 10 | 15 | 1000 | 40 | 53.33 | 40.00 |
| Element (at%) | Si | O | Al | Possible Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Region C | 7.35 | 29.38 | 57.00 | Al2O3-SiO2, Al |
| Region D | 4.70 | 0.77 | 91.14 | Base Al metal |
| Region E | 21.20 | 51.77 | 12.66 | Al2O3-SiO2, Al |
| Region F | 7.27 | 16.33 | 65.67 | Al2O3-SiO2, Al |
| Region G | 5.50 | 22.42 | 64.03 | Al2O3-SiO2, Al |
| Region H | 0.90 | 0.67 | 91.40 | Base Al metal |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, C.; Lu, X.; Liu, F.; Song, W.; Guo, G.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y.; Su, J.; Song, X. Realization of Joints of Aluminosilicate Glass and 6061 Aluminum Alloy via Picosecond Laser Welding without Optical Contact. Materials 2024, 17, 4299. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174299
Tan C, Lu X, Liu F, Song W, Guo G, Li Q, Liu Y, Su J, Song X. Realization of Joints of Aluminosilicate Glass and 6061 Aluminum Alloy via Picosecond Laser Welding without Optical Contact. Materials. 2024; 17(17):4299. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174299
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Caiwang, Xing Lu, Fuyun Liu, Wei Song, Guanghui Guo, Qige Li, Yuhang Liu, Jianhui Su, and Xiaoguo Song. 2024. "Realization of Joints of Aluminosilicate Glass and 6061 Aluminum Alloy via Picosecond Laser Welding without Optical Contact" Materials 17, no. 17: 4299. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174299
APA StyleTan, C., Lu, X., Liu, F., Song, W., Guo, G., Li, Q., Liu, Y., Su, J., & Song, X. (2024). Realization of Joints of Aluminosilicate Glass and 6061 Aluminum Alloy via Picosecond Laser Welding without Optical Contact. Materials, 17(17), 4299. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174299







