Effect of Bio-Oils and Wastewater Sludge on the Performance of Binders and Hot Mix Asphalt with High Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement Content
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Plan
2.2. Material Selection
2.3. Binder Test Design and Effect on HMA Mixes
2.4. RAP Binder Extraction and Binder Testing
2.5. Mix Design, Specimen Preparation, and Tests
2.6. Mixing and Preparation
2.7. Mix Testing
3. Results and Discussions
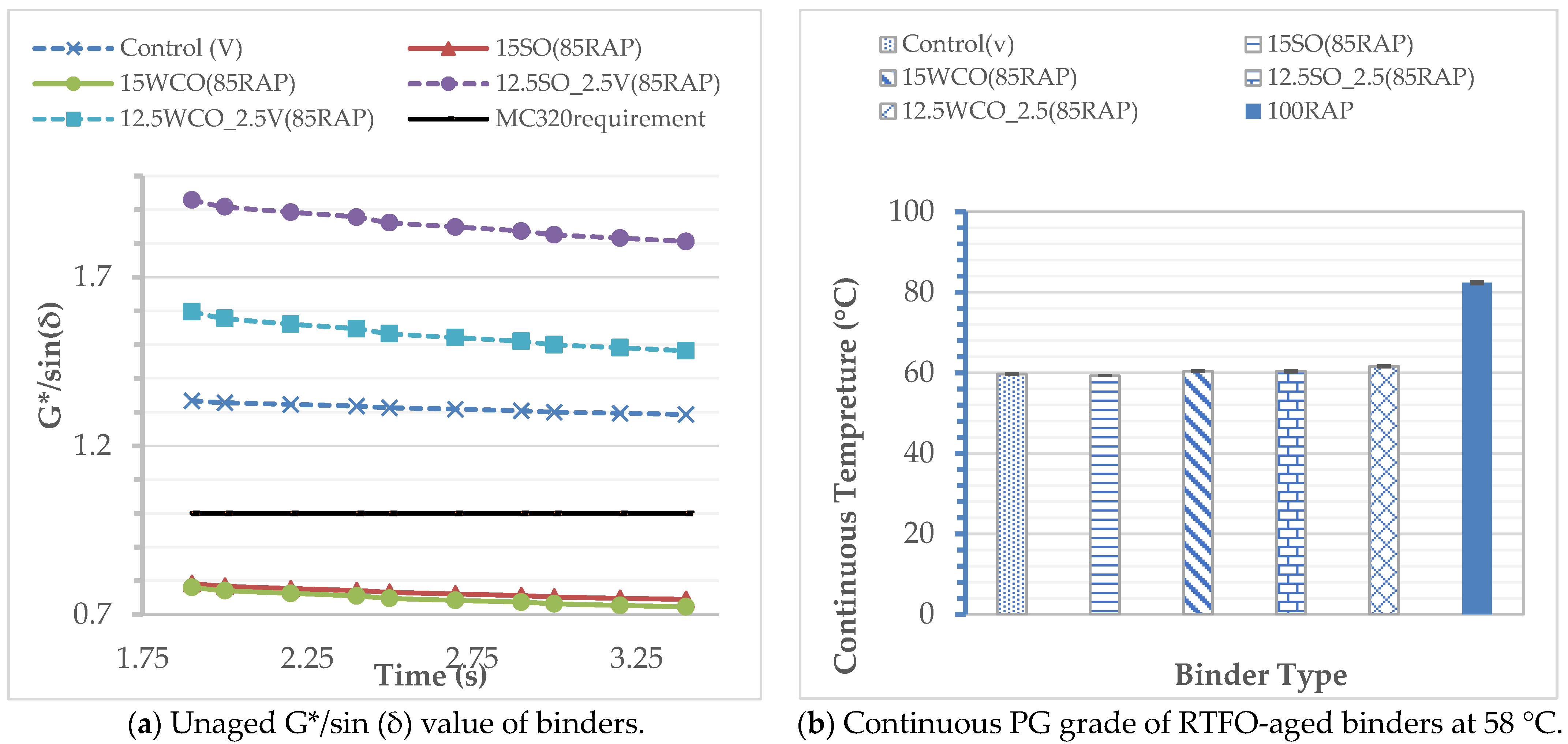
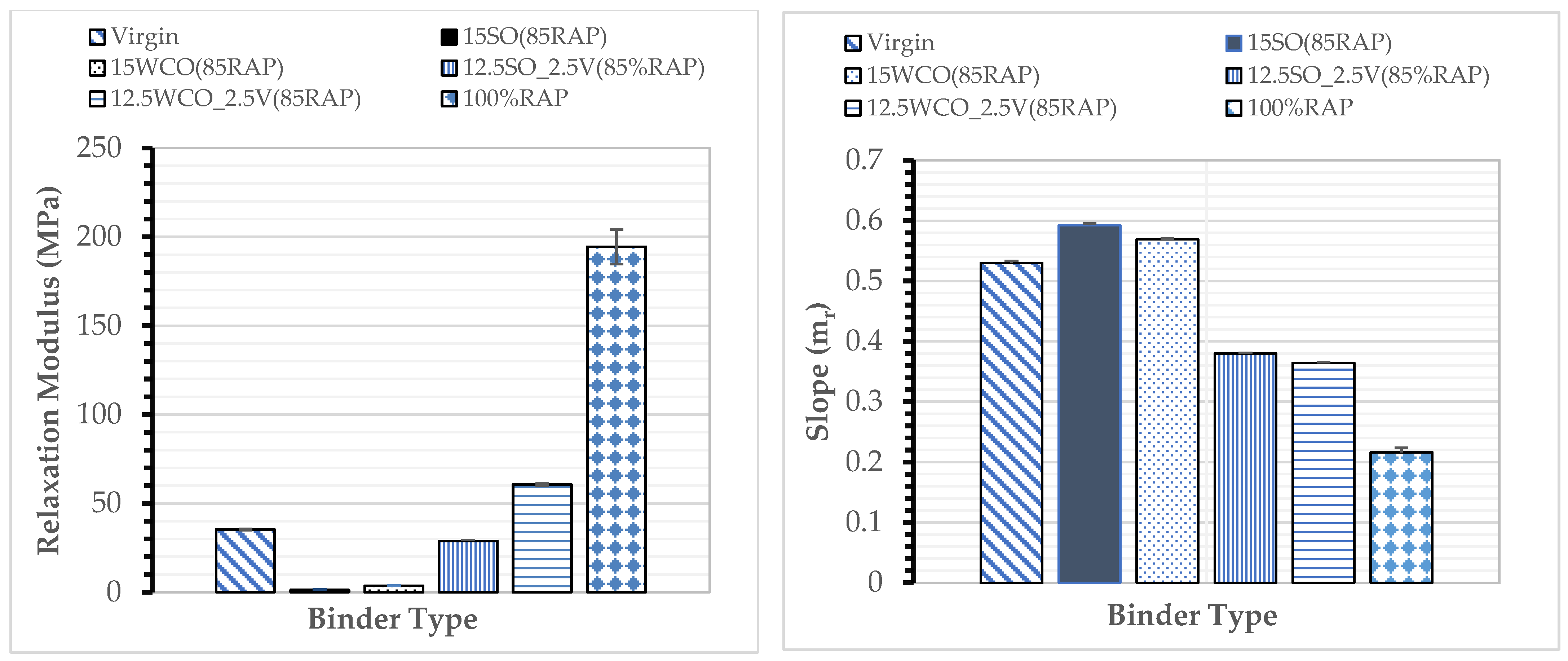
3.1. Effect of Bio-Oils on Binder Rheology
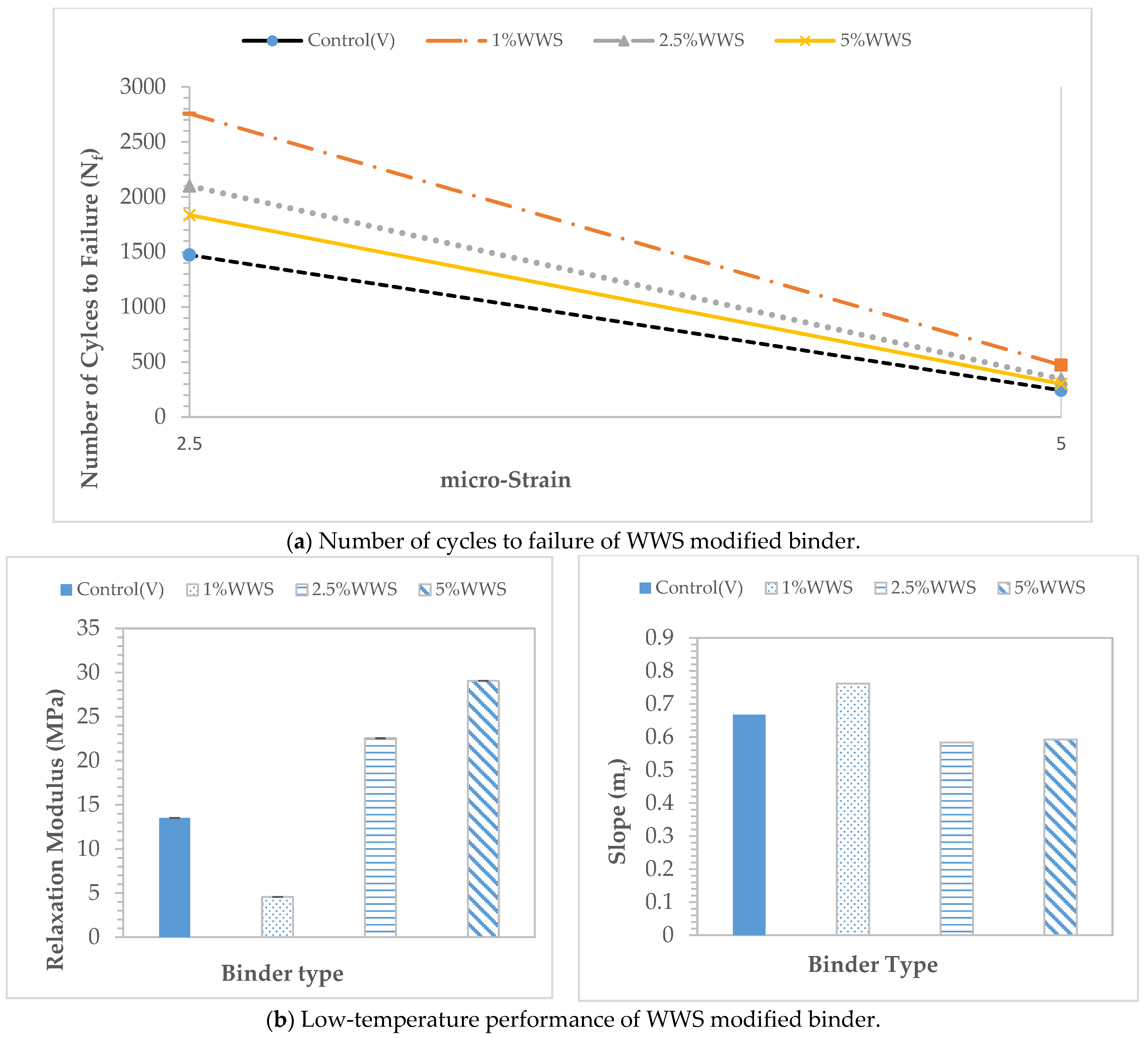
3.2. Effect of WWS on Binder Performance
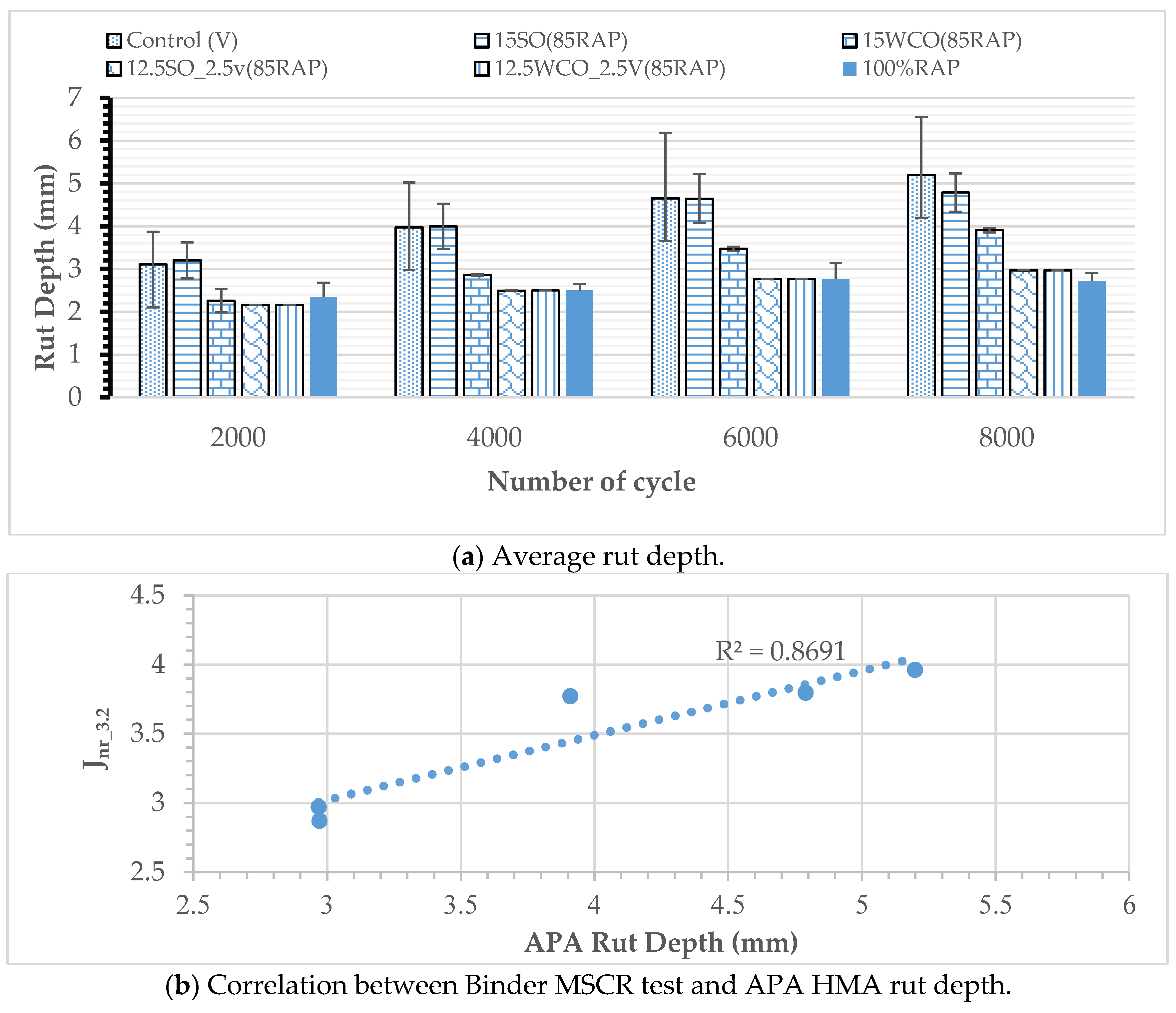
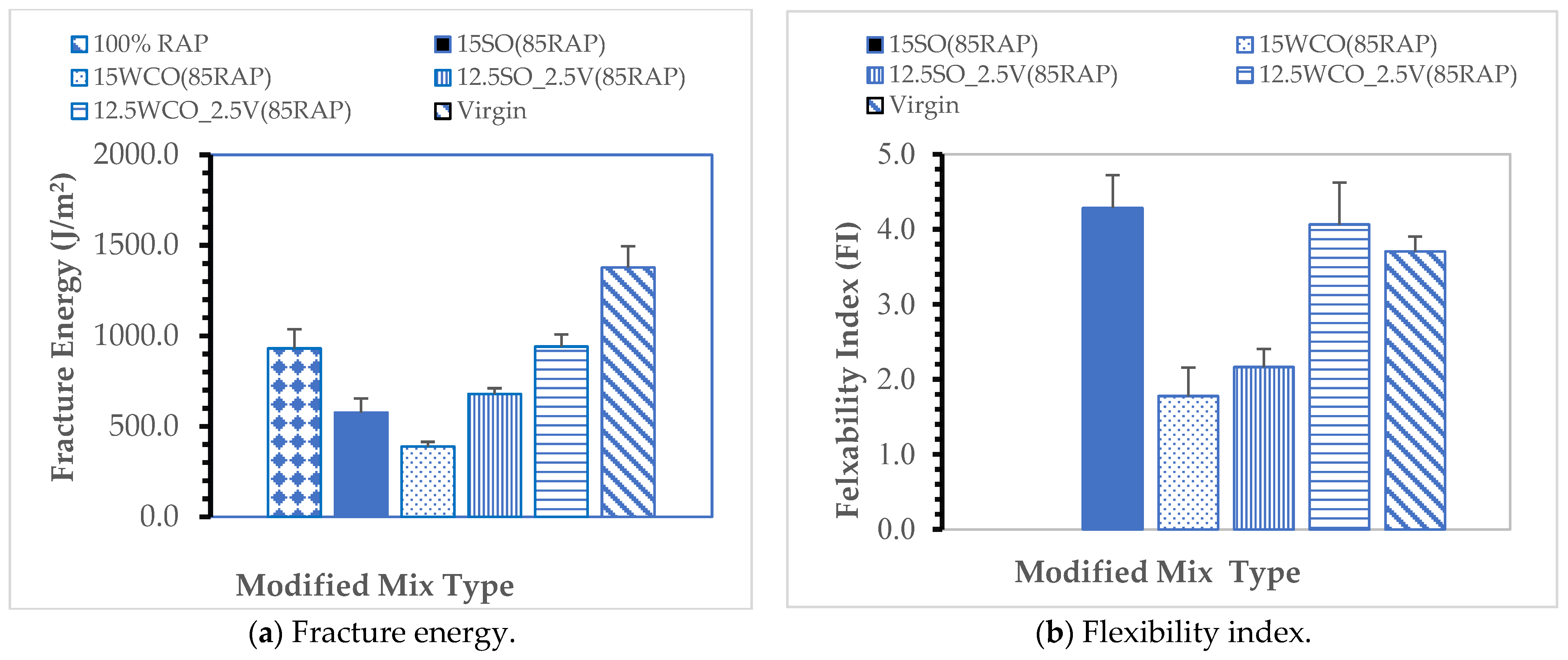
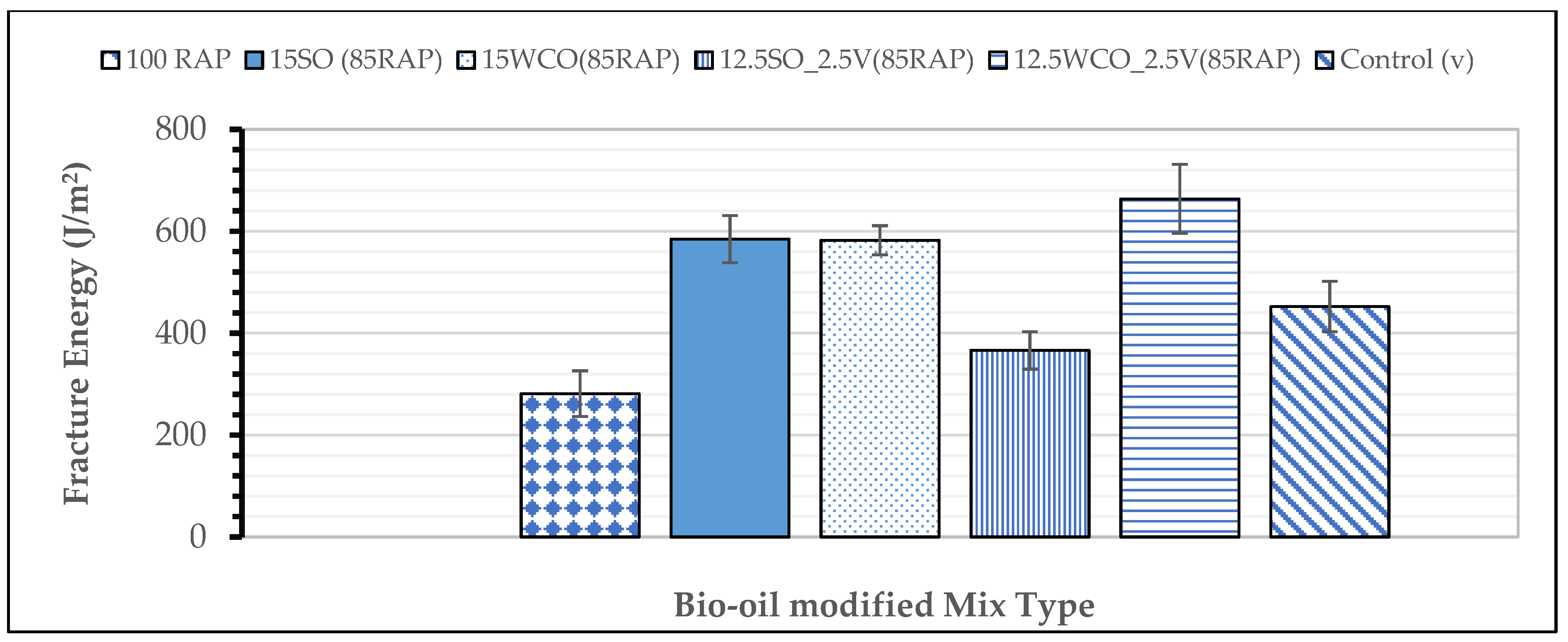
3.3. Effect of Bio-Oils on HMA
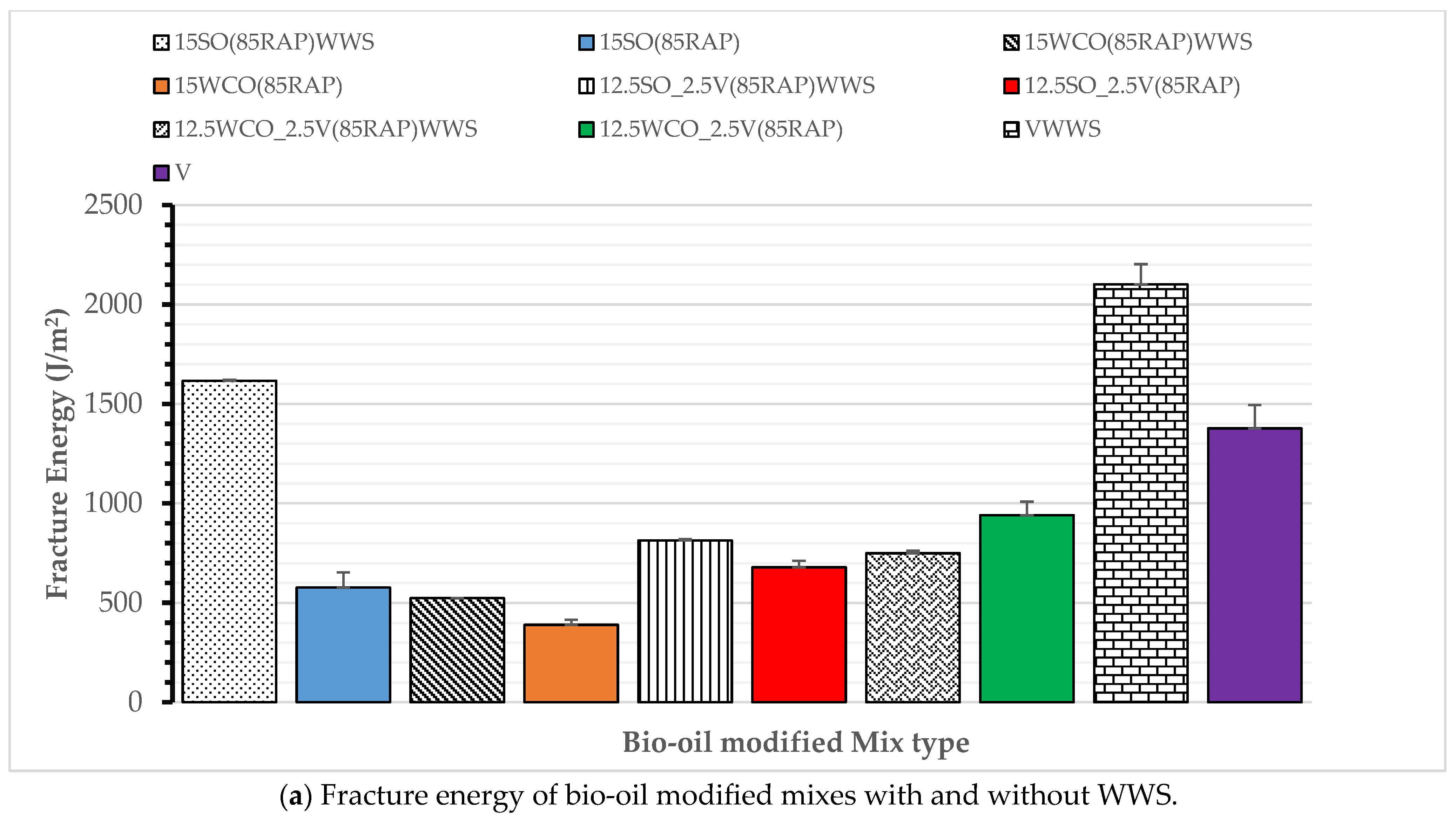
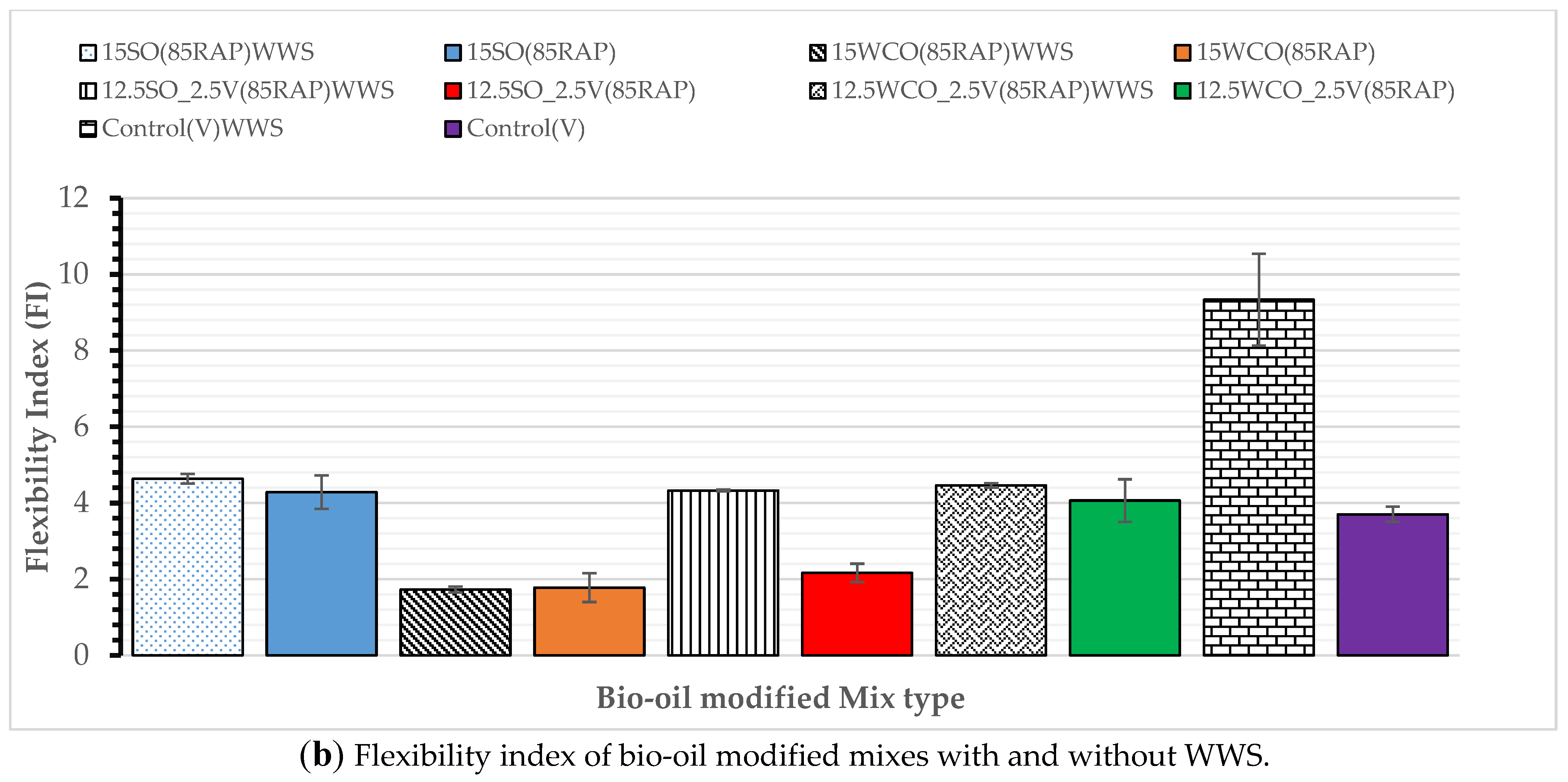
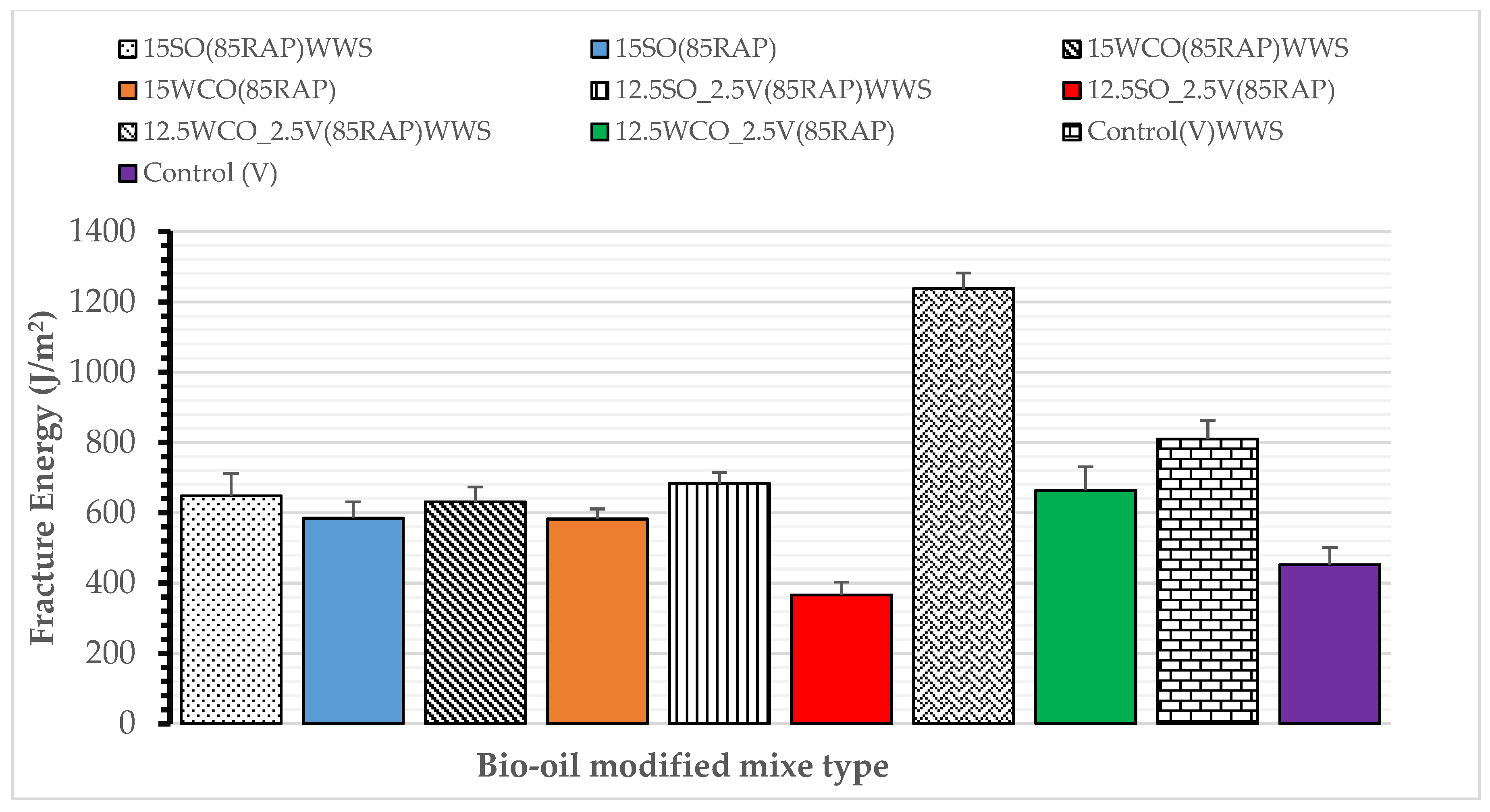
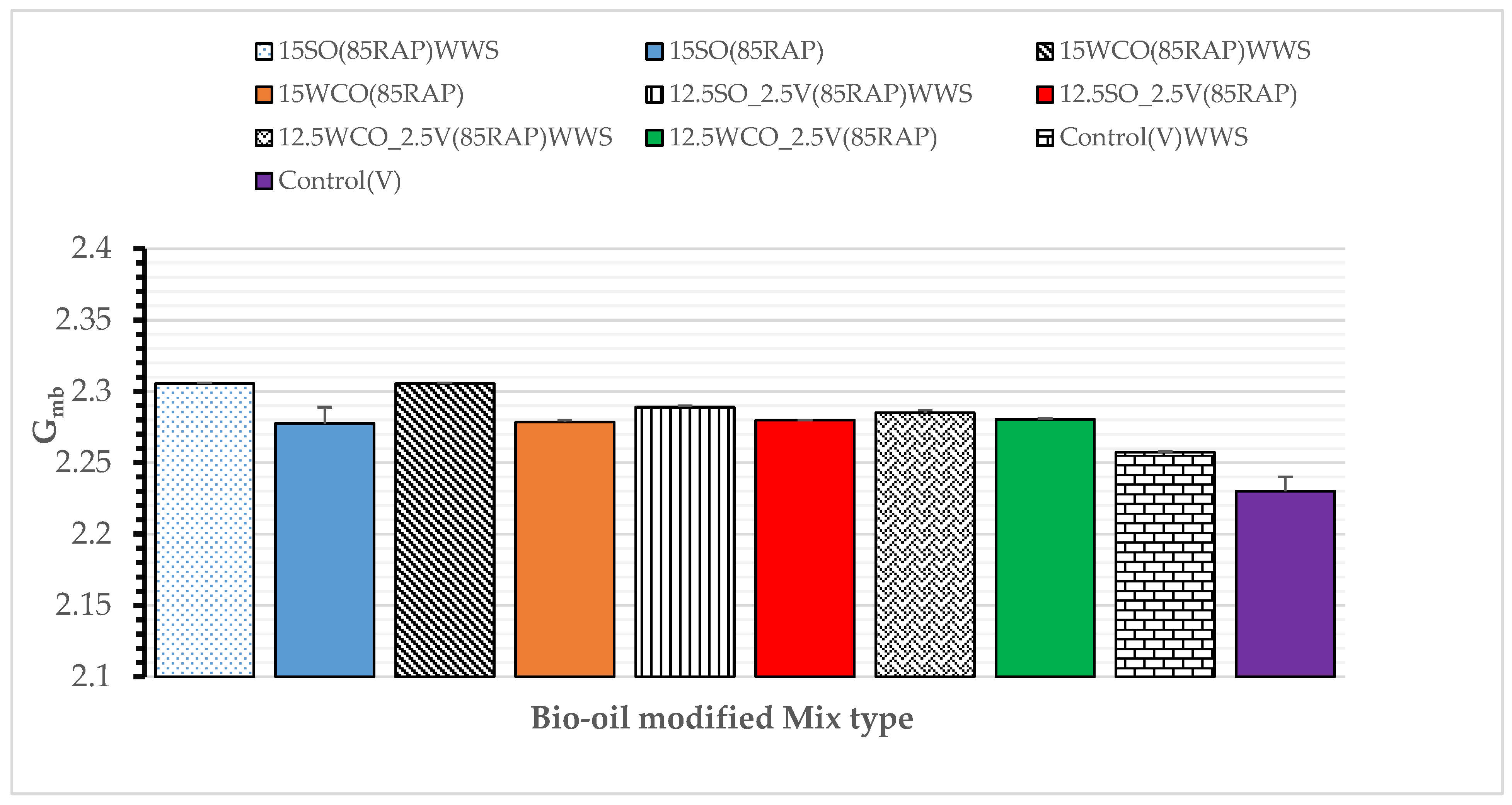
3.4. Effect of WWS on Cracking Performance and Compaction Effort
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Williams, B.A.; Copeland, A.; Ross, T.C. Asphalt Pavement Industry Survey on Recycled Materials and Warm-Mix Asphalt Usage: 2017 (No. IS 138 (8e)); National Asphalt Pavement Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, K.R.; Copeland, A. Asphalt Pavement Industry Survey on Recycled Materials and Warm-Mix Asphalt Usage: 2014 (No. Information Series 138); National Asphalt Pavement Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- NAPA. 2024. Available online: https://www.asphaltpavement.org/expertise/sustainability/sustainability-resources/recycling (accessed on 8 August 2024).
- Kingery, W.R. Laboratory Study of Fatigue Characteristics of HMA Surface Mixtures Containing Recycled Asphalt Pavement (RAP); University of Tennessee: Knoxville, TN, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- McDaniel, R.S.; Anderson, R.M. Recommended Use of Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement in the Superpave Mix Design Method: Technician’s Manual (No. Project D9-12 FY’97); National Research Council (US), Transportation Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hajj, E.Y.; Sebaaly, P.E.; Shrestha, R. Laboratory evaluation of mixes containing recycled asphalt pavement (RAP). Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2009, 10, 495–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, R.C.; Willis, J.R.; Marasteanu, M.O. Improved Mix Design, Evaluation, and Materials Management Practices for Hot Mix Asphalt with High Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement Content; Transportation Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; Volume 752. [Google Scholar]
- Vukosavljevic, D. Fatigue Characteristics of Field HMA Surface Mixtures Containing Recycled Asphalt Pavement (RAP); University of Tennessee: Knoxville, TN, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Valdés, G.; Pérez-Jiménez, F.; Miró, R.; Martínez, A.; Botella, R. Experimental study of recycled asphalt mixtures with high percentages of reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP). Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, R.; Kvasnak, A.; Tran, N.; Powell, B.; Turner, P. Testing of moderate and high reclaimed asphalt pavement content mixes: Laboratory and accelerated field performance testing at the national center for asphalt technology test track. Transp. Res. Rec. 2009, 2126, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, J.S.; Pochily, J.L.; Boisvert, D.M. Can more reclaimed asphalt pavement be added? Study of extracted binder properties from plant-produced mixtures with up to 25% reclaimed asphalt pavement. Transp. Res. Rec. 2010, 2180, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, D.R. Bioasphalt and Biochar from Pyrolysis of Urban Yard Waste. Ph.D. Thesis, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, R.; Melaku, R.S.; Karki, B.; Berg, A.; Gedafa, D.S. Effect of Bio-Oils on Binder and Mix Properties with High RAP Binder Content. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2020, 32, 04020007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Bhusal, S.; Wen, B. Laboratory Evaluation of Waste Cooking Oil-Based Bioasphalt as an Alternative Binder for Hot Mix Asphalt. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2013, 25, 1432–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargar, M.; Ahmadinia, E.; Asli, H.; Karim, M.R. Investigation of the possibility of using waste cooking oil as a rejuvenating agent for aged bitumen. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 233, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asli, H.; Ahmadinia, E.; Zargar, M.; Karim, M.R. Investigation on physical properties of waste cooking oil—Rejuvenated bitumen binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 37, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkashef, M.; Podolsky, J.; Williams, R.C.; Cochran, E. Preliminary examination of soybean oil derived material as a potential rejuvenator through Superpave criteria and asphalt bitumen rheology. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 149, 826–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkashef, M.; Williams, R.C.; Cochran, E. Investigation of fatigue and thermal cracking behavior of rejuvenated reclaimed asphalt pavement binders and mixtures. Int. J. Fatigue 2018, 108, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesner, W.H.; Collins, R.J.; MacKay, M.H.; Emery, J. User Guidelines for Waste and By-Product Materials in Pavement Construction (No. FHWA-RD-97-148, Guideline Manual, Rept No. 480017); Recycled Materials Resource Center: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Suárez-Iglesias, O.; Urrea, J.L.; Oulego, P.; Collado, S.; Díaz, M. Valuable compounds from sewage sludge by thermal hydrolysis and wet oxidation. A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584, 921–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woszuk, A.; Franus, W. Properties of the Warm Mix Asphalt involving clinoptilolite and Na-P1 zeolite additives. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 114, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengoz, B.; Topal, A.; Gorkem, C. Evaluation of natural zeolite as warm mix asphalt additive and its comparison with other warm mix additives. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 43, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FHWA, Warm Mix Asphalt Technologies and Research. 2018. Available online: https://www.fhwa.dot.gov/pavement/asphalt/wma.cfm (accessed on 12 February 2024).
- Rubio, M.C.; Martínez, G.; Baena, L.; Moreno, F. Warm mix asphalt: An overview. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 24, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melaku, R.S.; Gedafa, D.S. Impact of Wastewater Treatment Sludge on Cracking Resistance of Hot Mix Asphalt Mixes at Lower Mixing Temperature. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2020, 32, 05020009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, R.; Karki, B.; Berg, A.; Melaku, R.S.; Gedafa, D.S. Effect of RAP on cracking and rutting resistance of HMA mixes. In Airfield and Highway Pavements 2017; ASCE Library: Reston, VA, USA, 2017; pp. 86–94. [Google Scholar]
- AASHTO M 320; Standard Specification for Performance-Graded Asphalt Binder. AASHTO: Washington, DC, USA, 2023.
- ASTM D 2172/D 2172M; Standard Test Methods for Quantitative Extraction of Bitumen from Bituminous Paving Mixtures. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011.
- ASTM D 1856; Standard Test Method for Recovery of Asphalt from Solution by Abson Method. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015.
- AASHTO T 350; Standard Method of Test for Multiple Stress Creep Recovery (MSCR) Test of Asphalt Binder Using a Dynamic Shear Rheometer (DSR). AASHTO: Washington, DC, USA, 2023.
- AASHTO M 332; Standard Specification for Performance-Graded Asphalt Binder Using Multiple Stress Creep Recovery (MSCR) Test. AASHTO: Washington, DC, USA, 2023.
- D‘Angelo, J.; Kluttz, R.; Dongre, R.N.; Stephens, K.; Zanzotto, L. Revision of the superpave high temperature binder specification: The multiple stress creep recovery test (with discussion). J. Assoc. Asph. Paving Technol. 2007, 76, 123–162. [Google Scholar]
- AASHTO TP 101; Standard Method of Test for Estimating Fatigue Resistance of Asphalt Binders Using the Linear Amplitude Sweep. AASHTO: Washington, DC, USA, 2018.
- Hintz, C.; Velasquez, R.; Johnson, C.; Bahia, H. Modification and Validation of Linear Amplitude Sweep Test for Binder Fatigue Specification. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2011, 2207, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, C.; Farrar, M.J.; Harnsberger, P.M.; Tuminello, W.H.; Turner, T.F. New low-temperature performance-grading method: Using 4-mm parallel plates on a dynamic shear rheometer. Transp. Res. Rec. 2011, 2207, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FHWA. Four-mm Dynamic Shear Rheometer, Federal Highway Administration; FHWA: Washinton, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- AASHTO T308-16; Standard Method of Test for Determining the Asphalt Binder Content of Asphalt Mixtures by the Ignition Method. AASHTO: Washington, DC, USA, 2022.
- AASHTO T 340; Standard Method of Test for Determining Rutting Susceptibility of Asphalt Mixtures Using the Asphalt Pavement Analyzer (APA). AASHTO: Washington, DC, USA, 2023.
- Suleiman, N. Evaluation of North Dakota’s Aggregate Characteristics and Performance in Locally Produced HMA Mixtures Using the Asphalt Pavement Analyzer; North Dakota Department of Transportation: Bismarck, ND, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D7313; Standard Test Method for Determining Fracture Energy of Asphalt Mixtures Using the Disk-Shaped Compact Tension Geometry. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- Al-Qadi, I.L.; Ozer, H.; Lambros, J.; Khatib, A.E.; Singhvi, P.; Khan, T.; Rivera-Perez, J.; Doll, B. Testing Protocols to Ensure Performance of High Asphalt Binder Replacement Mixes Using RAP and RAS (No. FHWA-ICT-15-017); Illinois Center for Transportation: Rantoul, IL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bahia, H.; Teymourpour, P.; Swiertz, D.; Ling, C.; Varma, R.; Mandal, T.; Chaturabong, P.; Lyngdal, E.; Hanz, A. Analysis and Feasibility of Asphalt Pavement Performance-Based Specifications for WisDOT (No. 0092-15-04); Wisconsin Department of Transportation: Madison, WI, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gedafa, D.S.; Berg, A.; Karki, B.; Saha, R.; Melaku, R.S. Cracking and Rutting Performance of Field and Laboratory HMA Mixes. In Proceedings of the International Airfield and Highway Pavements Conference, Chicago, IL, USA, 21–24 July 2019; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2019; pp. 12–19. [Google Scholar]
- Gedafa, D.S.; Karki, B.; Berg, A.; Saha, R.; Melaku, R.S. Effect of nanomaterials on cracking and rutting resistance of HMA. In Proceedings of the International Airfield and Highway Pavements Conference, Chicago, IL, USA, 21–24 July 2019; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2019; pp. 88–95. [Google Scholar]
- Melaku, R.S. Performance Evaluation of Sustainable Pavement Materials. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of North Dakota, Grand Forks, ND, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]


| Bio-Oil Type | SO | WCO | WWS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Viscosity (Stokes) | 0.32–0.5 | 0.782 | 0.04–0.11 |
| Specific Gravity at 25 °C | 0.925 | 0.914–0.917 | 1–1.1 |
| Acidic Value | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1–0.2 |
| Flash Point (°C) | 260 | 220–230 | 250 |
| Types of Binders and Mixes | Test on Binders | Test on Mixes | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rutting (MSCR) at 58 °C | Fatigue Cracking (LAS) at 19 °C | Low-Temperature Cracking (4mmDSR) at −18 °C | APA at 58 °C | SCB at 25 °C | DCT at −18 °C | |
| V | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 15SO | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 15WCO | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 12.5SO_2.5V | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 12.5WCO_2.5V | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 100R | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 15SO_(1%)WWS | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| V_ (1%)WWS | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| 15WCO_ (1%)WWS | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| 12.5SO_2.5V_ (1%)WWS | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| 12.5WCO_2.5V_ (1%)WWS | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Virgin PG 58–28 HMA | SO and WCO Modified HMA | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | Percent (%) | Materials | Percent (%) |
| Optimum Binder content (OBC) | 6.4 | Optimum Binder content (OBC) | 6.4 |
| Bio-oil modifiers as a % of OBC | 0 | Bio-oil modifiers as a % of OBC | 12.5/15 |
| Virgin binder as %of (OBC) | 100 | Virgin binder as a % of OBC | 2.5/0 |
| Binder from the dry RAP aggregate as % of OBC | 0 | Binder from the RAP as % of OBC | 85 |
| Crushed Rock | 29 | Crushed Rock | 8 |
| Crushed Fines | 37 | Crushed Fines | 10 |
| Washed Dust | 13 | Washed Dust | 3.5 |
| Washed Sand | 21 | Washed Sand | 6 |
| RAP | 0 | RAP | 72.5 |
| Sieve | Bio-Oil Modified & Control HMA | Unmodified 100%RAP | Lower | Upper |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gradation | Gradation | Control Pt | Control Pt | |
| 5/8” | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 1/2” | 93.35 | 97.50 | 90 | 100 |
| 3/8” | 81.03 | 87.65 | ||
| #4 | 59.44 | 68.41 | 40 | 70 |
| #8 | 41.37 | 47.88 | ||
| #16 | 30.27 | 34.48 | ||
| #30 | 20.23 | 23.19 | 15 | 35 |
| #50 | 11.19 | 13.89 | ||
| #100 | 6.32 | 9.01 | ||
| #200 | 3.48 | 5.58 | 2 | 7 |
| Binder Type | Control (V) | 15SO (85RAP) | 15WCO (85RAP) | 12.5SO_2.5V (85RAP) | 12.5WCO_2.5 (85RAP) | 100RAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. avg | 12,353.3 | 70,966.7 | 39,766.7 | 31,442.8 | 39,248.4 | 30,407.6 |
| St. D. | 859.8 | 2263.8 | 5655.8 | 3943.5 | 4766.7 | 10,447.6 |
| COV (%) | 6.96 | 3.19 | 14.22 | 12.54 | 12.15 | 34.36 |
| Bavg. | −2.4760 | −2.8873 | −2.8570 | −3.0137 | −3.0606 | −3.8520 |
| St. D. | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.19 |
| COV (%) | 0.39 | 0.76 | 0.88 | 0.42 | 2.05 | 4.96 |
| Nf_2.5avg | 1279 | 5052 | 2908 | 1985 | 2384 | 854 |
| St. D. | 100.05 | 56.36 | 474.06 | 228.13 | 344.25 | 127.58 |
| COV (%) | 7.82 | 1.12 | 16.30 | 11.50 | 14.44 | 14.93 |
| Nf_5avg | 230 | 656 | 402 | 245 | 287 | 59 |
| St. D. | 19.47 | 52.16 | 72.00 | 26.27 | 49.05 | 0.62 |
| COV (%) | 8.47 | 7.95 | 17.91 | 10.70 | 17.08 | 1.06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Melaku, R.S.; Liu, J.; Gedafa, D.S. Effect of Bio-Oils and Wastewater Sludge on the Performance of Binders and Hot Mix Asphalt with High Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement Content. Materials 2024, 17, 4276. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174276
Melaku RS, Liu J, Gedafa DS. Effect of Bio-Oils and Wastewater Sludge on the Performance of Binders and Hot Mix Asphalt with High Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement Content. Materials. 2024; 17(17):4276. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174276
Chicago/Turabian StyleMelaku, Robeam S., Jun Liu, and Daba S. Gedafa. 2024. "Effect of Bio-Oils and Wastewater Sludge on the Performance of Binders and Hot Mix Asphalt with High Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement Content" Materials 17, no. 17: 4276. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174276
APA StyleMelaku, R. S., Liu, J., & Gedafa, D. S. (2024). Effect of Bio-Oils and Wastewater Sludge on the Performance of Binders and Hot Mix Asphalt with High Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement Content. Materials, 17(17), 4276. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174276






