Hot Workability and Microstructure Evolution of Homogenized 2050 Al-Cu-Li Alloy during Hot Deformation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. True Stress–Strain Curves
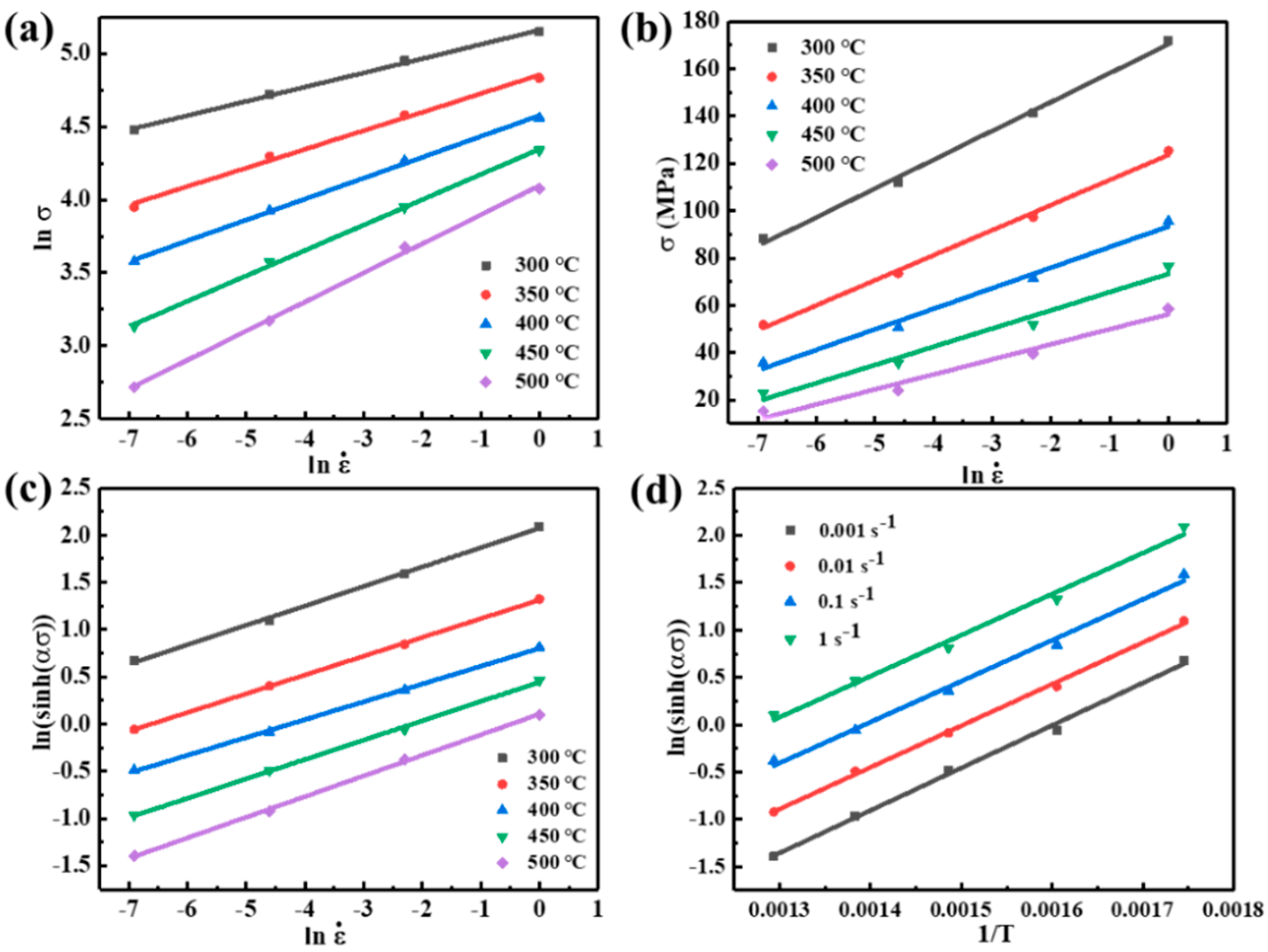
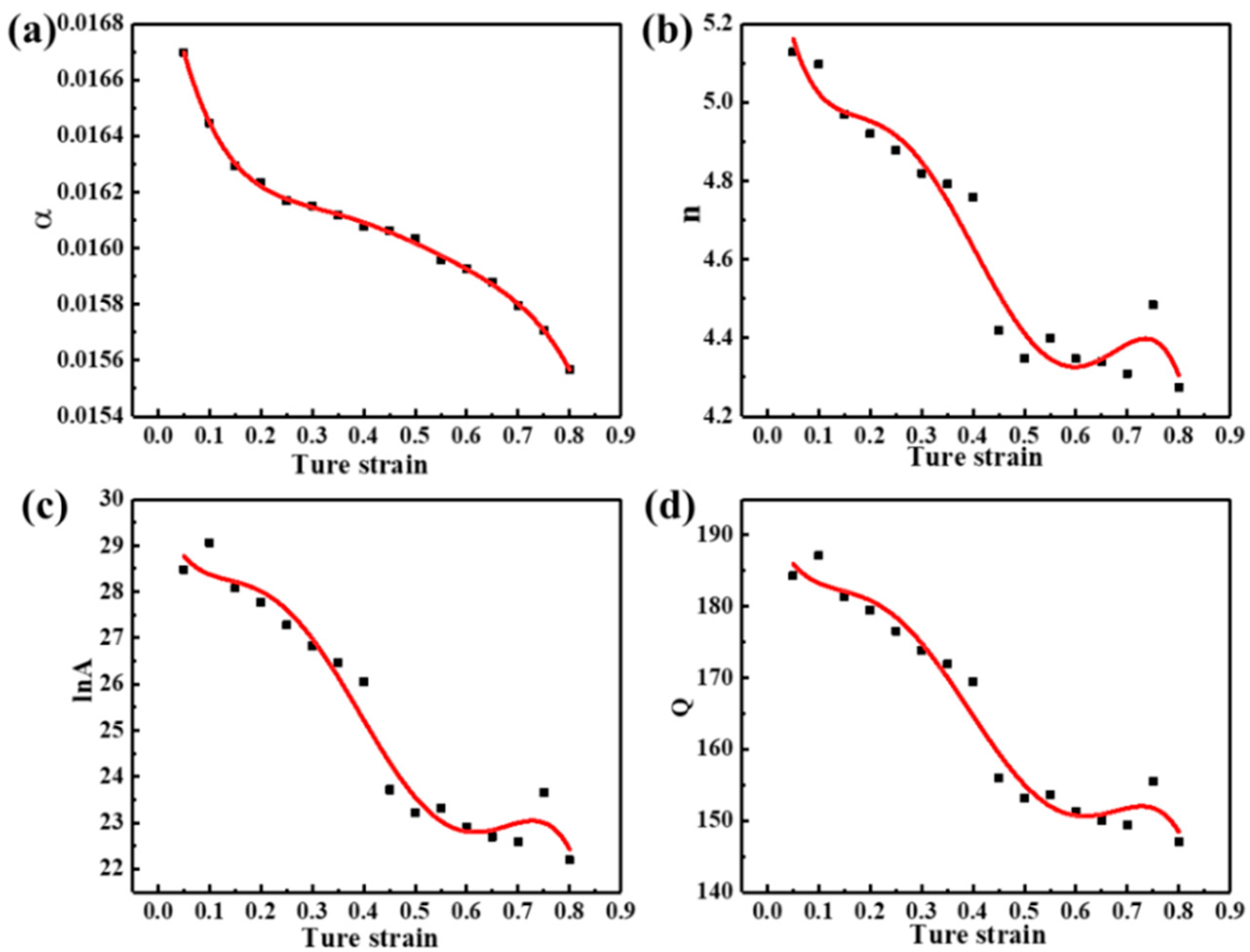
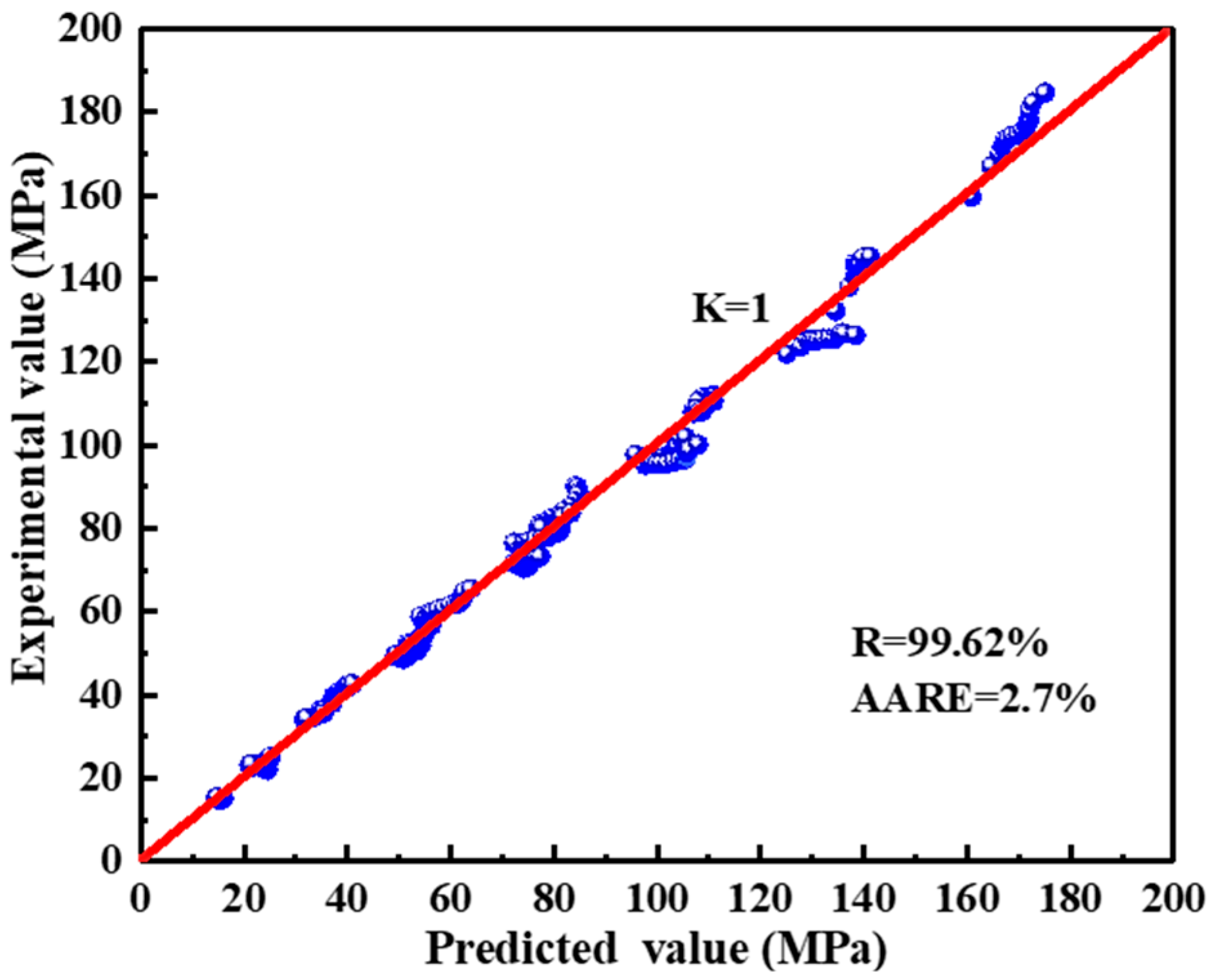
3.2. Constitutive Model with Compensation of Strain
3.3. Processing Map
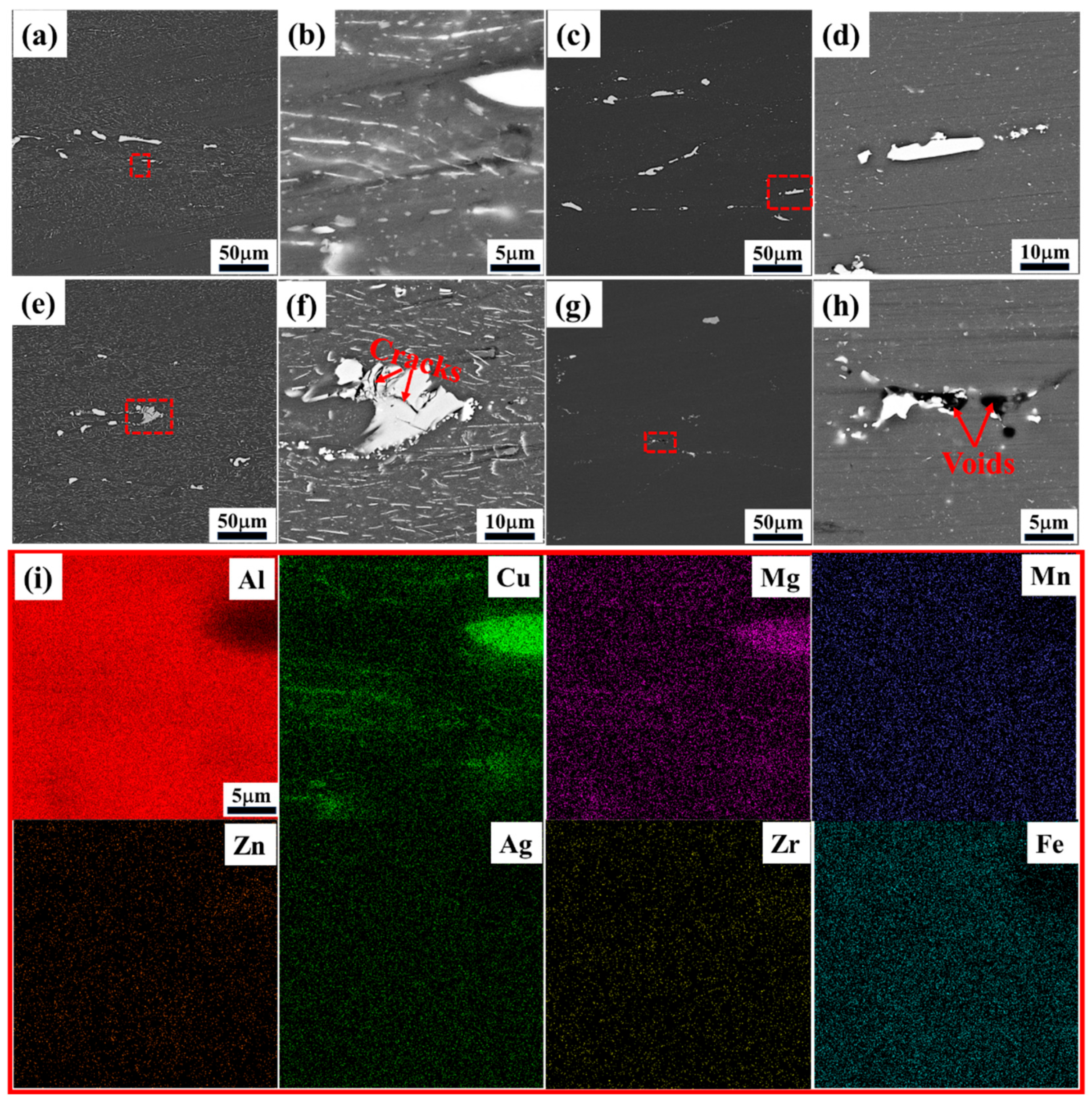
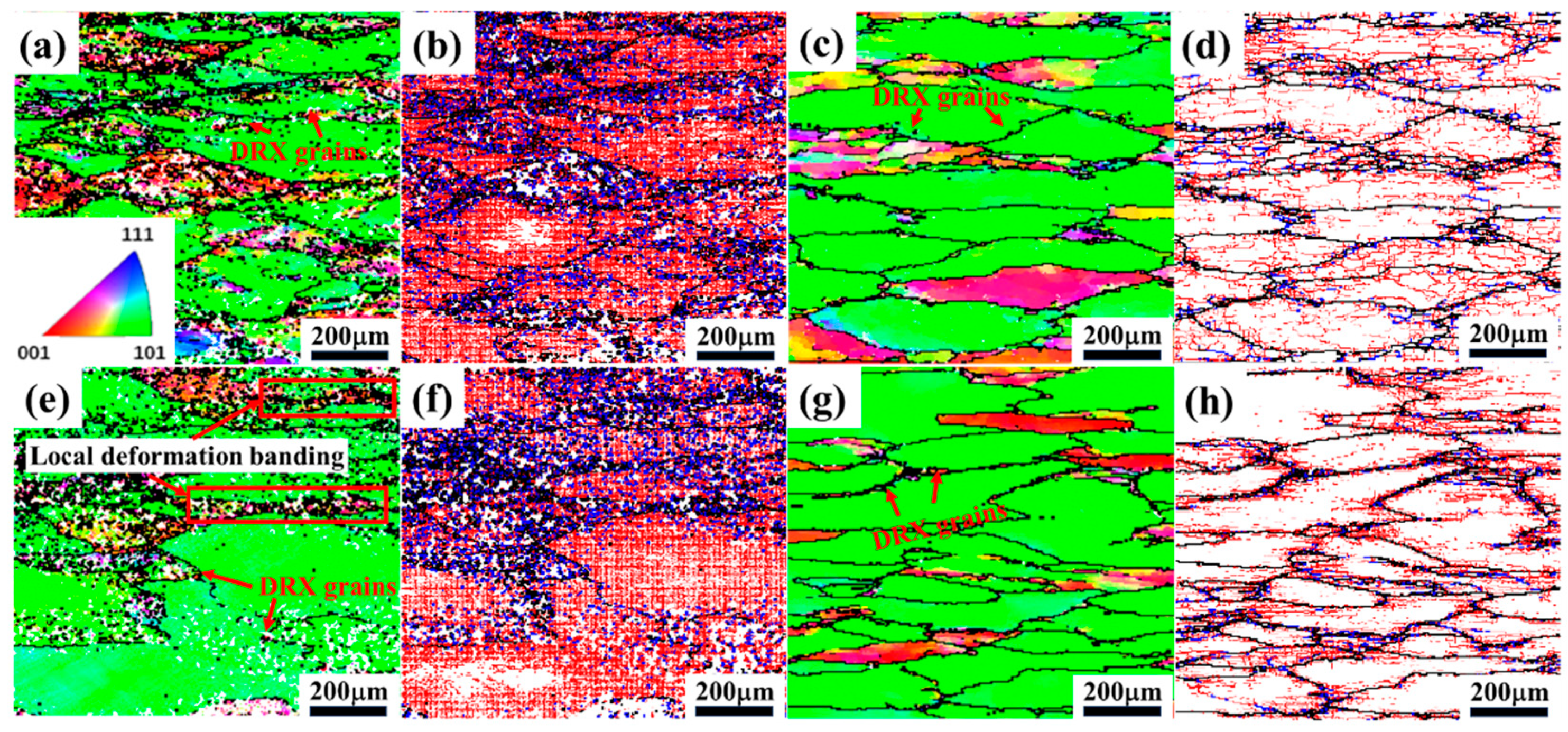
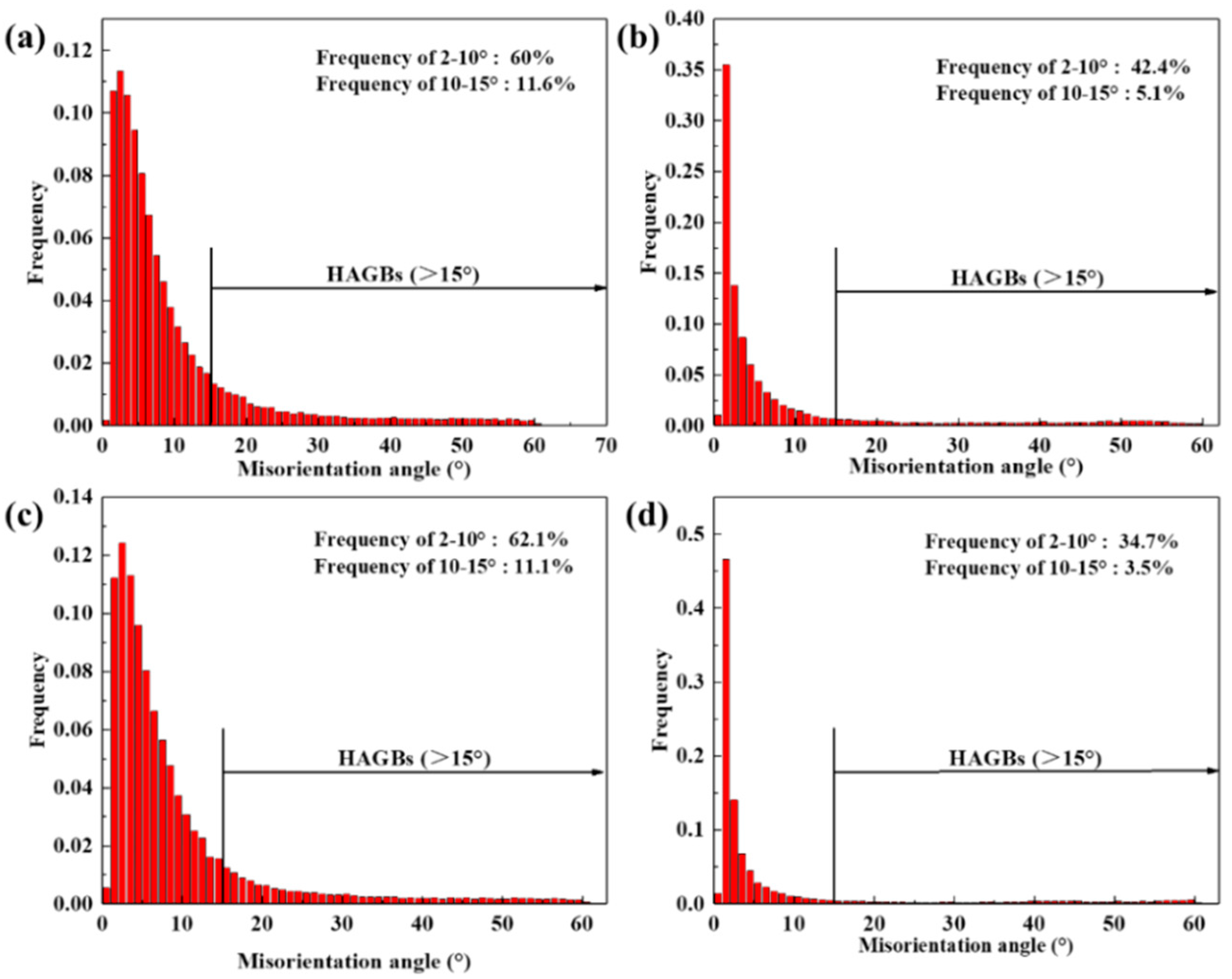
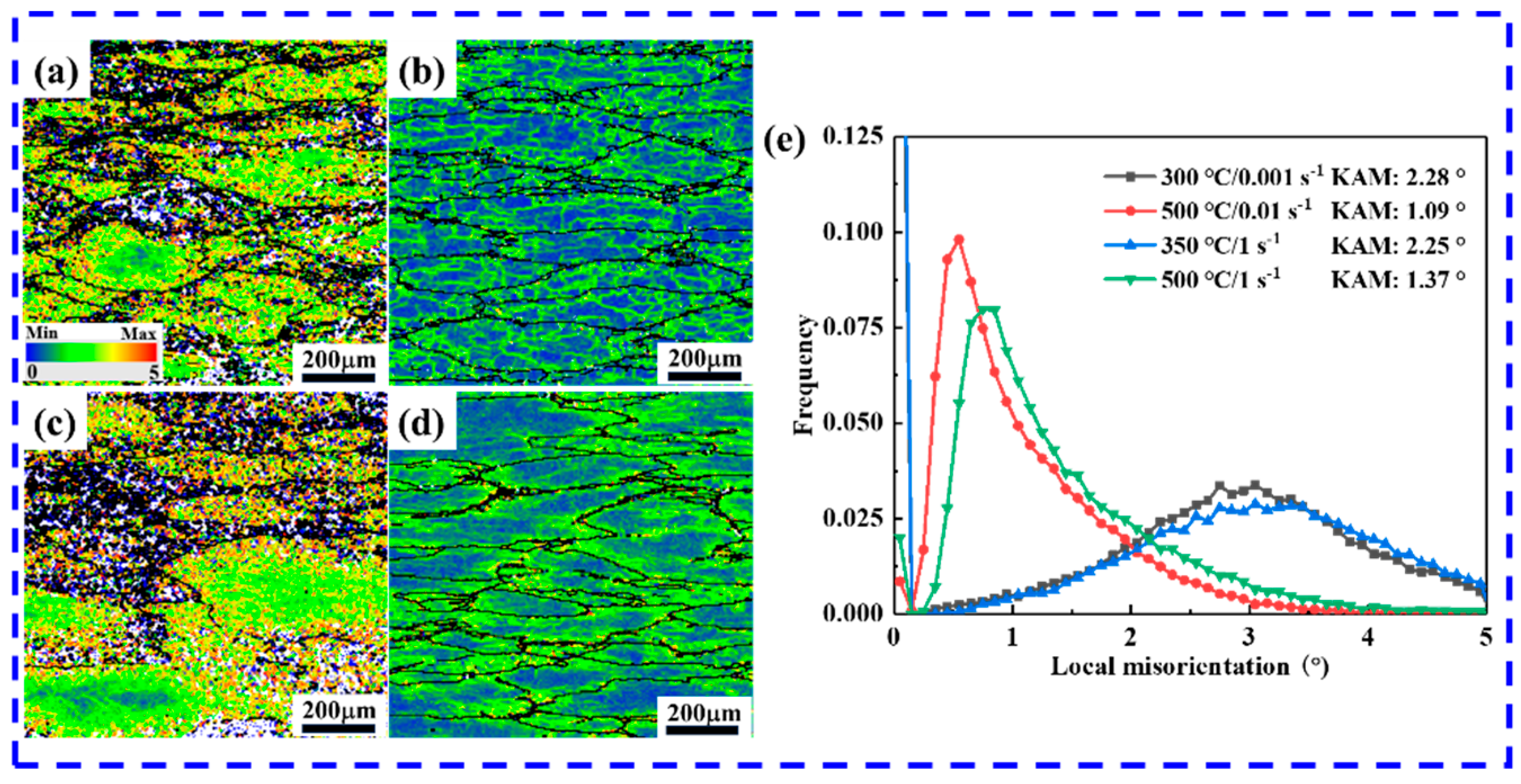
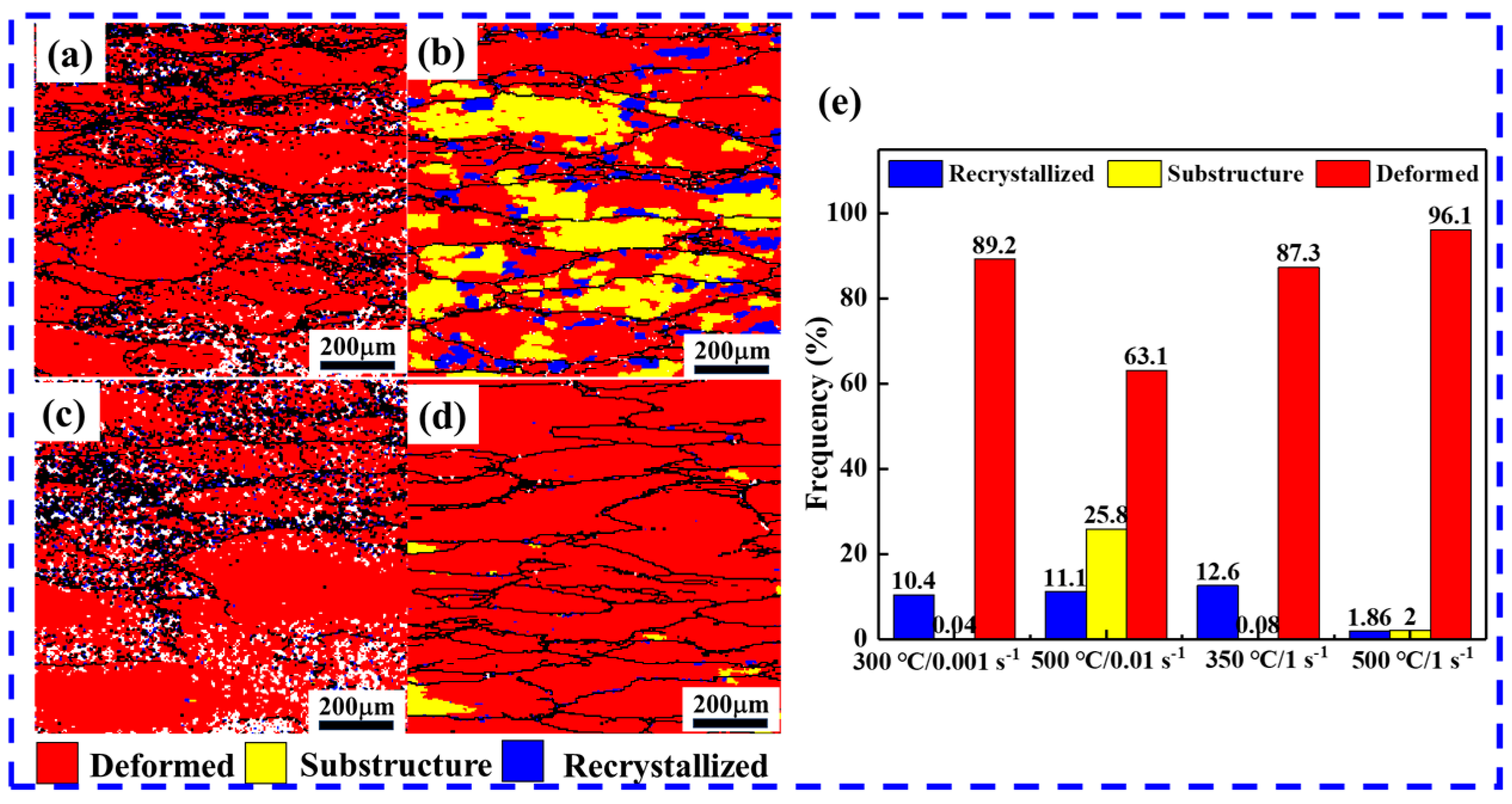
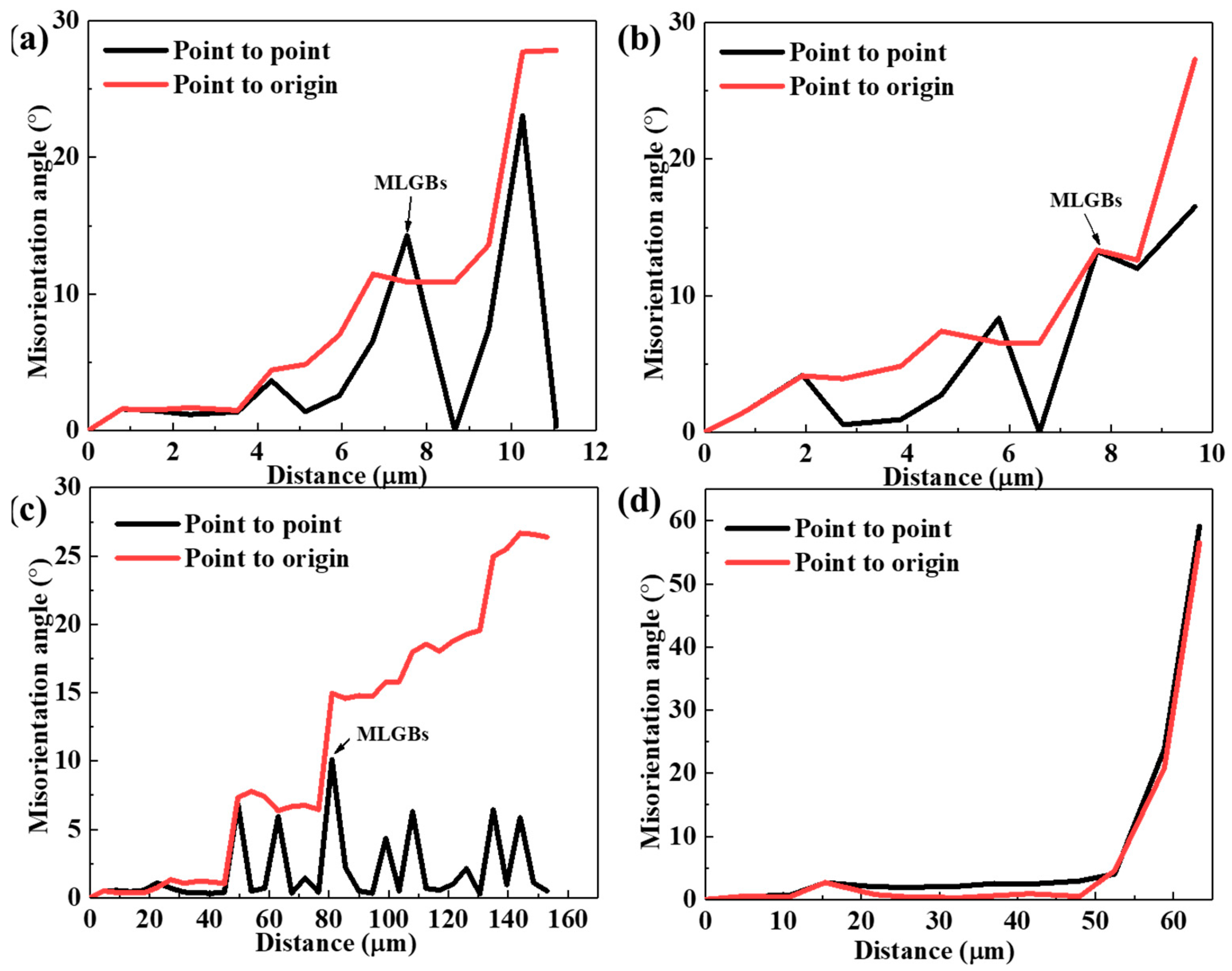
3.4. Microstructure Characterization
4. Conclusions
- The flow stress of 2050 Al-Li alloy increases significantly with true strain (true strain of less than 0.05) in the early compression process and then stabilizes. The highest flow stresses occur at high strain rates and low temperatures, and the flow stress for various deformation conditions can be accurately described by the established strain-compensated Arrhenius model.
- The appropriate conditions for the hot working of 2050 Al-Li alloys have been identified as 430 °C–500 °C and 0.1 s−1–0.001 s−1, where the dynamic softening mechanisms are dynamic recovery (DRV) and dynamic recrystallization (DRX), and the DRX mechanisms are dominated by DDRX and CDRX, which exhibit a large dissipation efficiency (> 30%).
- The processing parameter regions C (300 °C–400 °C, 0.1–1 s−1) and D (440 °C–500 °C, 0.1–1 s−1) are undesirable for 2050 Al-Li alloys, due to their inhomogeneous microstructure and the occurrence of flow instability, in which local deformation banding and secondary phase cracking are mainly observed in region C, while micro-voids are formed in region D.
- The microstructure of the compressed specimens consists of abundant pancake-like grains with an orientation concentrated in the <101>CD direction, along with some equiaxed DRX grains with a random orientation. Compared to samples under high-temperature conditions, a considerable population of DRX grains with smaller sizes was observed at low temperatures, accompanied by a higher number of LAGBs and HAGBs, which finding is related to the PSN mechanism induced by dynamic precipitation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abd El-Aty, A.; Xu, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhang, S.H.; Ma, Y.; Chen, D. Strengthening mechanisms, deformation behavior, and anisotropic mechanical properties of Al-Li alloys: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 10, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.; Wu, D.-X.; Wang, S.-Y.; Jiang, Y.-P.; Xia, R.-Z.; Li, S.-S.; Zhou, Y.-T.; Peng, P.; Dai, Q.-W. An optimized constitutive model and microstructure characterization of a homogenized Al-Cu-Li alloy during hot deformation. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 929, 167290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, H. Microstructure evolution and mechanical responses of Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloys during hot deformation process. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 13429–13478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.; Sutton, S.; Luo, A.A. Deformation microstructure and thermomechanical processing maps of homogenized AA2070 aluminum alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 834, 142619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, G.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, C. Constitutive modeling and microstructure characterization of 2196 Al-Li alloy in various hot deformation conditions. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 59, 326–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Sun, Y.; He, J.; Li, C.; Li, H.; Yu, L.; Liu, Y. Hot deformation behaviour and microstructure evolution of Al-3%Mg2Si alloy. Mater. Charact. 2022, 183, 111623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, G.; Xu, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, C. Constitutive modeling, processing map establishment and microstructure analysis of spray deposited Al-Cu-Li alloy 2195. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 779, 735–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Pan, Q.; Yin, Z. Microstructural evolution and constitutive relationship of Al–Zn–Mg alloy containing small amount of Sc and Zr during hot deformation based on Arrhenius-type and artificial neural network models. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 584, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Nayan, N.; Narayana Murty, S.V.S.; Yadava, M.; Bajargan, G.; Mohan, M. Hot deformation behavior of Sc/Nb modified AA2195 Al–Li–Cu alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 844, 143169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareem, S.A.; Anaele, J.U.; Aikulola, E.O.; Olarewaju, O.F.; Omiyale, B.O.; Bodunrin, M.O.; Alaneme, K.K. Hot deformation behaviour, constitutive model description, and processing map analysis of superalloys: An overview of nascent developments. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 8624–8669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Logé, R.E. A review of dynamic recrystallization phenomena in metallic materials. Mater. Des. 2016, 111, 548–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQueen, H.J. Development of dynamic recrystallization theory. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 387–389, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Wang, R.; Feng, Y.; Peng, C.; Cai, Z. Hot deformation behavior and microstructural evolution of as-quenched 7055 Al alloy fabricated by powder hot extrusion. Mater. Charact. 2019, 156, 109833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.-W.; Li, H.-Z.; Huang, L.; Liang, X.-P.; Zhu, Z.-X. Characterization of hot deformation behavior of AA2014 forging aluminum alloy using processing map. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2017, 27, 1677–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourdet, S.; Montheillet, F. An experimental study of the recrystallization mechanism during hot deformation of aluminium. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2000, 283, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.S.S.; Raghu, T.; Bhattacharjee, P.P.; Rao, G.A.; Borah, U. Strain rate dependent microstructural evolution during hot deformation of a hot isostatically processed nickel base superalloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 681, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Liu, Q.; Li, J.; Xiang, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X. Dynamic restoration mechanism and physically based constitutive model of 2050 Al–Li alloy during hot compression. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 650, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yi, Y.; Huang, S.; Mao, X.; He, H.; Tang, J.; Guo, W.; Dong, F. Dynamic recrystallization mechanisms of 2195 aluminum alloy during medium/high temperature compression deformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 804, 140650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-Y.; Jiang, J.-T.; Li, G.-A.; Wang, X.-M.; Sun, J.; Zhen, L. Effects of coarse Al2CuLi phase on the hot deformation behavior of Al–Li alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 815, 152469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, J.D.; Henry, D.; Davis, B. Particle effects on recrystallization in magnesium–manganese alloys: Particle-stimulated nucleation. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 2739–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Xu, W.; Jin, X.; Wang, Z.; Shan, D.; Guo, B. Hot deformation behavior and microstructure evolution of the spray deposited and secondary hot extruded 2195 Al–Li alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 20, 2784–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Gao, W.; Feng, Z.; Lu, Z.; Zhu, C. Hot deformation characterization of as-homogenized Al-Cu-Li X2A66 alloy through processing maps and microstructural evolution. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 2409–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Lin, T.; Luo, T.; Zhao, Y.; Hou, H.; Yang, Y. Hot compression deformation behavior of Mg-5Zn-3.5 Sn-1Mn-0.5Ca-0.5Cu alloy. Mater. Charact. 2019, 157, 109896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Chen, M. Progress in characterization methods for thermoplastic deforming constitutive models of Al–Li alloys: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 9828–9847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, H. Microstructural Evolution and Dynamic Recrystallization Behavior of the Homogenized 2195 Al–Li Alloy During Hot Deformation. Met. Mater. Int. 2023, 29, 2605–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, L.; Zhou, P.; Song, Y.; Sun, Q. Characterization of strain rate sensitivity of 7075 aluminum alloy at different solution temperatures by novel kinetic models. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2022, 282, 115751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamanfar, A.; Alamoudi, M.T.; Nanninga, N.E.; Misiolek, W.Z. Analysis of flow stress and microstructure during hot compression of 6099 aluminum alloy (AA6099). Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 743, 684–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, X.; Liao, B.; Cao, L. Simulation of dynamic recrystallization in an Al-Mg-Si alloy during inhomogeneous hot deformation. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 29, 102810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, N.; Daniel, B. Microstructural evolution of Al-7.3Zn-2.2Mg-2Cu (Al7068) alloy in T6 condition during isothermal compression using 3-dimensional processing map. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 902, 163690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, L.; Senthilvelan, T. Constitutive equation and microstructure evaluation of an extruded aluminum alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2016, 5, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zener, C.; Hollomon, J.H. Effect of strain rate upon plastic flow of steel. J. Appl. Phys. 1944, 15, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, C.; Peng, Y.; Xia, X.; Li, J.; Ding, J.; Liu, C.; Chen, X.; Dong, J.; Liu, Y. Hot compression deformation behavior and processing maps of ATI 718Plus superalloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 835, 155195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Pan, Q.; Li, H.; Huang, Z.; Li, K.; He, X.; Li, X. Characterization of hot deformation behavior and constitutive modeling of Al–Mg–Si–Mn–Cr alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 4366–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Pan, Q.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; He, X.; Li, X.; Peng, Z.; Lai, J. Microstructure evolution and physical-based diffusion constitutive analysis of Al-Mg-Si alloy during hot deformation. Mater. Des. 2019, 184, 108181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, Y.; Gegel, H.; Doraivelu, S.; Malas, J.; Morgan, J.; Lark, K.; Barker, D. Modeling of dynamic material behavior in hot deformation: Forging of Ti-6242. Metall. Trans. A 1984, 15, 1883–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, Y.; Seshacharyulu, T. Processing maps for hot working of titanium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1998, 243, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qin, J.; Nagaumi, H.; Wu, R.; Li, Q. The Effect of α-Al(MnCr)Si Dispersoids on Activation Energy and Workability of Al-Mg-Si-Cu Alloys during Hot Deformation. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 2020, 3471410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Li, H. Dynamic precipitation and its effect on microstructure of 2195 Al–Li alloy during medium/high temperature deformation. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 27, 3259–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Prameela, S.E.; Yi, P.; Fernandez, M.; Krywopusk, N.M.; Kecskes, L.J.; Sano, T.; Falk, M.L.; Weihs, T.P. Dynamic Precipitation and Recrystallization in Mg-9wt.%Al During Equal-Channel Angular Extrusion: A Comparative Study to Conventional Aging. Acta Mater. 2019, 172, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatemi, S.; Aliyari, S.; Miresmaeili, S. Dynamic precipitation and dynamic recrystallization during hot deformation of a solutionized WE43 magnesium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 762, 138076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Xiao, D.; Huang, L.; You, R.; Zhao, X.; Lin, N.; Ma, Y.; Liu, W. Dynamic microstructural evolution of Al-Cu-Li alloys during hot deformation. Mater. Charact. 2022, 191, 112135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, Z.; Zhao, H.; Meng, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhao, G. Dynamic evolution of the T1 phase and its effect on continuous dynamic recrystallization in Al–Cu–Li alloys. Int. J. Plast. 2024, 175, 103948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.D.; Li, J.F.; Guo, Y.J.; Wang, G.; Wu, R.; Ma, P.C.; Chen, Y.L.; Zhang, X.H.; You, W.; Zhang, R.F. T1 precipitate bands and particle stimulated nucleation in 2195 Al-Cu-Li alloy during hot deformation. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 909, 164716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, S.M.; Glavatskikh, M.V.; Barkov, R.Y.; Churyumov, A.Y.; Loginova, I.S.; Khomutov, M.G.; Pozdniakov, A.V. Comprehensive Analysis of Microstructure and Hot Deformation Behavior of Al-Cu-Y-Mg-Cr-Zr-Ti-Fe-Si Alloy. Metals 2023, 13, 1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Huang, W.; Pan, J.; Wang, H.; Weng, M. A high-performance Mg-4.9 Gd-3.2 Y-1.1 Zn-0.5 Zr alloy via multidirectional forging after analyzing its compression behavior. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 70, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babout, L.; Brechet, Y.; Maire, E.; Fougères, R. On the competition between particle fracture and particle decohesion in metal matrix composites. Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 4517–4525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H. Texture of metals. Texture Stress Microstruct. 1974, 1, 233–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiamiyu, A.A.; Odeshi, A.G.; Szpunar, J.A. Crash-worthiness of a recently-developed AA 2624 aluminum alloy: Experimental studies. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 766, 138389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Q.; Yu, H.; Lee, Y.-S.; Kim, M.-S.; Kim, H.-W. Hot deformation behavior and microstructure evolution of annealed Al-7.9Zn-2.7Mg-2.0Cu (wt%) alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 763, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Li, H.; Du, R.; You, W.; Zhao, M.; Wang, Z.-A. Characteristic constitution model and microstructure of an Al-3.5Cu-1.5Li alloy subjected to thermal deformation. Mater. Charact. 2018, 145, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mofarrehi, M.; Javidani, M.; Chen, X.-G. Effect of Mn content on the hot deformation behavior and microstructure evolution of Al–Mg–Mn 5xxx alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 845, 143217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zribi, Z.; Ktari, H.H.; Herbst, F.; Optasanu, V.; Njah, N. EBSD, XRD and SRS characterization of a casting Al-7wt%Si alloy processed by equal channel angular extrusion: Dislocation density evaluation. Mater. Charact. 2019, 153, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, Z.; Meng, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhao, G. Deformation mechanism of as-extruded Al–Cu–Li alloy with heterogeneous fiber structure. Mater. Des. 2023, 229, 111872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murty, S.V.S.N.; Sarkar, A.; Narayanan, P.R.; Venkitakrishnan, P.V.; Mukhopadhyay, J. Microstructure and micro-texture evolution during large strain deformation of aluminium alloy AA 2219. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 677, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
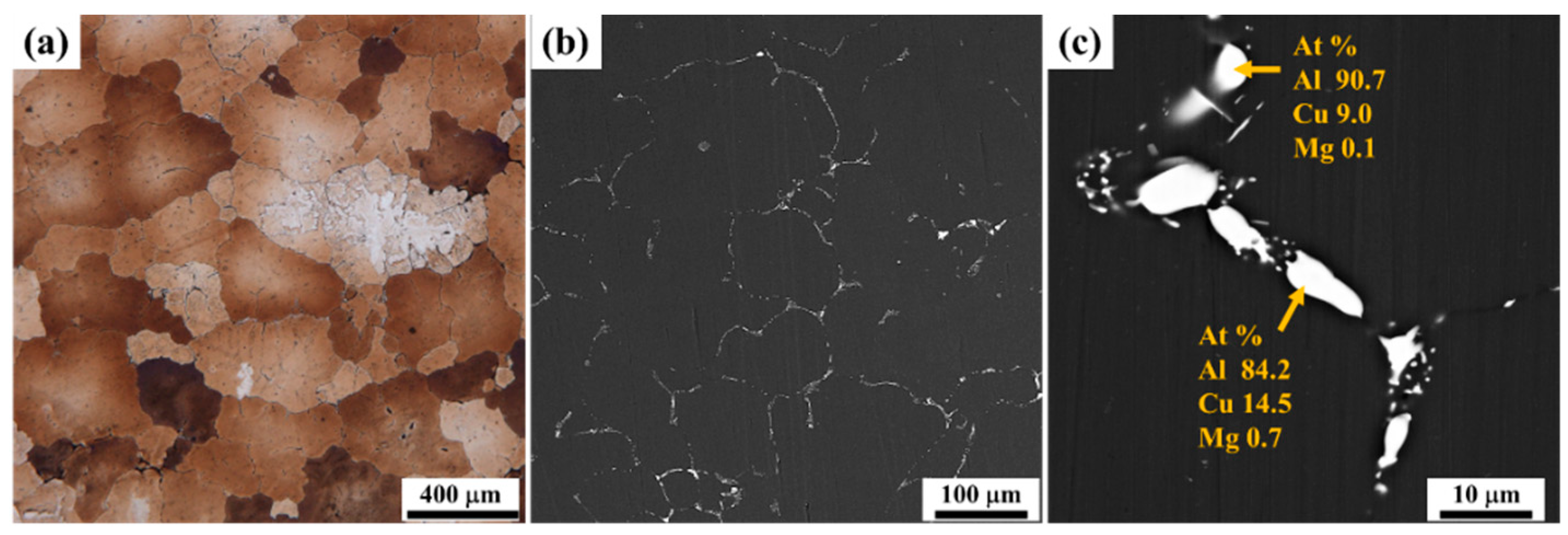





| Cu | Li | Mg | Mn | Ag | Zn | Zr | Fe | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.30 | 0.77 | 0.54 | 0.31 | 0.26 | 0.19 | 0.13 | 0.01 | Bal |
| α | n | lnA | Q | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B0 | 0.0171 | C0 | 5.48541 | D0 | 29.86473 | E0 | 192.91543 |
| B1 | −0.01008 | C1 | −9.17561 | D1 | −32.47934 | E1 | −203.7002 |
| B2 | 0.04411 | C2 | 63.24509 | D2 | 260.26328 | E2 | 1572.6177 |
| B3 | −0.09778 | C3 | −203.4514 | D3 | −979.0298 | E3 | −5796.022 |
| B4 | 0.10441 | C4 | 276.17689 | D4 | 1431.5919 | E4 | 8405.2129 |
| B5 | −0.04396 | C5 | −132.0563 | D5 | −711.4815 | E5 | −4160.178 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sheng, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Fu, R.; Wang, X.; Fan, X.; Wu, F. Hot Workability and Microstructure Evolution of Homogenized 2050 Al-Cu-Li Alloy during Hot Deformation. Materials 2024, 17, 4236. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174236
Sheng Z, Huang Y, Zhao Y, Fu R, Wang X, Fan X, Wu F. Hot Workability and Microstructure Evolution of Homogenized 2050 Al-Cu-Li Alloy during Hot Deformation. Materials. 2024; 17(17):4236. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174236
Chicago/Turabian StyleSheng, Zhiyong, Yuanchun Huang, Yongxing Zhao, Rong Fu, Xucheng Wang, Xi Fan, and Fan Wu. 2024. "Hot Workability and Microstructure Evolution of Homogenized 2050 Al-Cu-Li Alloy during Hot Deformation" Materials 17, no. 17: 4236. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174236
APA StyleSheng, Z., Huang, Y., Zhao, Y., Fu, R., Wang, X., Fan, X., & Wu, F. (2024). Hot Workability and Microstructure Evolution of Homogenized 2050 Al-Cu-Li Alloy during Hot Deformation. Materials, 17(17), 4236. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174236






