Dimensional Accuracy of Novel Vinyl Polysiloxane Compared with Polyether Impression Materials: An In Vitro Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- VPS and PE impression materials have adequate accuracy for all clinical applications.
- The dual-phase impression technique may give a more accurate impression.
- Short distances are displayed more accurately than long distances regardless of the impression material.
- Inlay preparations are less accurate than full crown preparations, regardless of the impression material used.
- The choice of impression material and impression technique lies with the treating clinician and is not only dependent on the accuracy of the impression material.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuzbasioglu, E.; Kurt, H.; Turunc, R.; Bilir, H. Comparison of digital and conventional impression techniques: Evaluation of patients’ perception, treatment comfort, effectiveness and clinical outcomes. BMC Oral Health 2014, 14, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepke, U.; Meijer, H.J.; Kerdijk, W.; Cune, M.S. Digital versus analog complete-arch impressions for single-unit premolar implant crowns: Operating time and patient preference. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2015, 114, 403–406.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chochlidakis, K.M.; Papaspyridakos, P.; Geminiani, A.; Chen, C.J.; Feng, I.J.; Ercoli, C. Digital versus conventional impressions for fixed prosthodontics: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2016, 116, 184–190.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldecker, M.; Rues, S.; Behnisch, R.; Rammelsberg, P.; Bomicke, W. Effect of scan-path length on the scanning accuracy of completely dentate and partially edentulous maxillae. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2024, 131, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldecker, M.; Bömicke, W.; Behnisch, R.; Rammelsberg, P.; Rues, S. In-vitro accuracy of complete arch scans of the fully dentate and the partially edentulous maxilla. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2021, 66, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldecker, M.; Rues, S.; Rammelsberg, P.; Bömicke, W. Accuracy of complete-arch intraoral scans based on confocal microscopy versus optical triangulation: A comparative in vitro study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2020, 126, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldecker, M.; Rues, S.; Awounvo Awounvo, J.S.; Rammelsberg, P.; Bömicke, W. In vitro accuracy of digital and conventional impressions in the partially edentulous maxilla. Clin. Oral Investig. 2022, 26, 6491–6502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, A.B.; Evans, J.L.; Robb, N.D. A technical and clinical digital approach to the altered cast technique with an intraoral scanner and polyvinyl siloxane impression material. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2022, 132, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebib, N.; Imamura, Y.; El Osta, N.; Srinivasan, M.; Muller, F.; Maniewicz, S. Fit and retention of complete denture bases: Part II—Conventional impressions versus digital scans: A clinical controlled crossover study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2022, 131, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamalian, T.A.; Nasr, E.; Chidiac, J.J. Impression materials in fixed prosthodontics: Influence of choice on clinical procedure. J. Prosthodont. 2011, 20, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraman, S.; Singh, B.P.; Ramanathan, B.; Pazhaniappan Pillai, M.; MacDonald, L.; Kirubakaran, R. Final-impression techniques and materials for making complete and removable partial dentures. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 4, CD012256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.Q.; Ma, Y.; Cai, S.N.; Yu, H. Optimal impression materials for implant-supported fixed complete dentures: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2023; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hüttig, F.; Klink, A.; Kohler, A.; Mutschler, M.; Rupp, F. Flowability, Tear Strength, and Hydrophilicity of Current Elastomers for Dental Impressions. Materials 2021, 14, 2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, M.P.; Rondeau, M.; Petrie, C.; Tasca, A.; Williams, K. Surface quality and long-term dimensional stability of current elastomeric impression materials after disinfection. J. Prosthodont. 2007, 16, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsiomiti, E.; Tzialla, A.; Hatjivasiliou, K. Accuracy and stability of impression materials subjected to chemical disinfection—A literature review. J. Oral Rehabil. 2008, 35, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtan, J.R.; Olin, P.S.; Rudney, J.D. Dimensional stability of a polyvinylsiloxane impression material following ethylene oxide and steam autoclave sterilization. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1991, 65, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaziz, K.M.; Hassan, A.M.; Hodges, J.S. Reproducibility of sterilized rubber impressions. Braz. Dent. J. 2004, 15, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ishida, H.; Nahara, Y.; Tamamoto, M.; Hamada, T. The fungicidal effect of ultraviolet light on impression materials. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1991, 65, 532–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, T.; Fiehn, N.E.; Peutzfeldt, A.; Owall, B. Disinfection of dental impressions and occlusal records by ultraviolet radiation. Eur. J. Prosthodont. Restor. Dent. 2000, 8, 71–74. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanovski, S.; Savage, N.W.; Brockhurst, P.J.; Bird, P.S. Disinfection of dental stone casts: Antimicrobial effects and physical property alterations. Dent. Mater. 1995, 11, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, M.A.; Johnson, G.H.; Toolson, L.B. An evaluation of dental stones after repeated exposure to spray disinfectants. Part I: Abrasion and compressive strength. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1991, 65, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahuja, B.M.; Pawashe, K.G.; Sanyal, P.K.; Al-Qarni, M.A.; Alqahtani, N.M.; Alqahtani, S.M.; Ahmed, A.R.; Abdul Khader, M.; Elmahdi, A.E.; Chaturvedi, S. Assessment of dimensional stability of novel VPES impression material at different time intervals with standard disinfectants. BMC Oral Health 2024, 24, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardan, L.; Bourgi, R.; Cuevas-Suarez, C.E.; Lukomska-Szymanska, M.; Cornejo-Rios, E.; Tosco, V.; Monterubbianesi, R.; Mancino, S.; Eid, A.; Mancino, D.; et al. Disinfection Procedures and Their Effect on the Microorganism Colonization of Dental Impression Materials: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of In Vitro Studies. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chidambaram, S.R.; George, A.M.; Muralidharan, N.P.; Prasanna Arvind, T.R.; Subramanian, A.; Rahaman, F. Current overview for chemical disinfection of dental impressions and models based on its criteria of usage: A microbiological study. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2022, 33, 30–36. [Google Scholar]
- Vrbova, R.; Bradna, P.; Bartos, M.; Roubickova, A. The effect of disinfectants on the accuracy, quality and surface structure of impression materials and gypsum casts: A comparative study using light microscopy, scanning electron microscopy and micro computed tomography. Dent. Mater. J. 2020, 39, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepe, X.; Johnson, G.H. Accuracy of polyether and addition silicone after long-term immersion disinfection. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1997, 78, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awod Bin Hassan, S.; Ali, F.A.A.; Ibrahim, N.A.L.; Heboyan, A.; Ravinder, S.S. Effect of chemical disinfection on the dimensional stability of polyvinyl ether siloxane impression material: A systemic review and meta-analysis. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soganci, G.; Cinar, D.; Caglar, A.; Yagiz, A. 3D evaluation of the effect of disinfectants on dimensional accuracy and stability of two elastomeric impression materials. Dent. Mater. J. 2018, 37, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputi, S.; Varvara, G. Dimensional accuracy of resultant casts made by a monophase, one-step and two-step, and a novel two-step putty/light-body impression technique: An in vitro study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2008, 99, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoods-Moonsammy, V.J.; Owen, P.; Howes, D.G. A comparison of the accuracy of polyether, polyvinyl siloxane, and plaster impressions for long-span implant-supported prostheses. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2014, 27, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stober, T.; Johnson, G.H.; Schmitter, M. Accuracy of the newly formulated vinyl siloxanether elastomeric impression material. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2010, 103, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, G.H.; Lepe, X.; Aw, T.C. The effect of surface moisture on detail reproduction of elastomeric impressions. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2003, 90, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zenthöfer, A.; Rues, S.; Rammelsberg, P.; Ruckes, D.; Stober, T. Accuracy of a New Fast-Setting Polyether Impression Material. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2020, 33, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sydiskis, R.J.; Gerhardt, D.E. Cytotoxicity of impression materials. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1993, 69, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberta, T.; Federico, M.; Federica, B.; Antonietta, C.M.; Sergio, B.; Ugo, C. Study of the potential cytotoxicity of dental impression materials. Toxicol. Vitro. 2003, 17, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Chen, C.C.; Kuo, H.W. Cytotoxicity of dental impression materials. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2002, 69, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehm, S.; Rues, S.; Balzer, A.; Rammelsberg, P.; Waldecker, M. Effect of a calibration aid and the intraoral scanner on the registration of a partially edentulous maxilla: An in vitro study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rues, S.; Stober, T.; Bargum, T.; Rammelsberg, P.; Zenthöfer, A. Disposable plastic trays and their effect on polyether and vinyl polysiloxane impression accuracy-an in vitro study. Clin. Oral Investig. 2021, 25, 1475–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Distances between Precision Balls | Distances between Prepared Teeth | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [mm] | ||||||||
| P1P2 | P1P3 | P2P3 | LPLM | LMRP | LPRP | |||
| Margin level | Surface level | Margin level | Surface level | Margin level | Surface level | |||
| 40.338 | 35.916 | 31.927 | 15.400 | 15.359 | 41.515 | 41.500 | 36.578 | 36.498 |
| Test Group | Impression Material/Material Combinations | Material Class | Impression Technique |
|---|---|---|---|
| VPS-MP | Aquasil Ultra+ Medium | Vinyl polysiloxane | Mono-phase |
| PE-MP | Impregum Penta Soft | Polyether | Mono-phase |
| VPS-DP | Aquasil Ultra+ Heavy/XLV | Vinyl polysiloxane | Dual-phase |
| PE-DP | Impregum Penta H Duo Soft/Garant L Duo Soft | Polyether | Dual-phase |
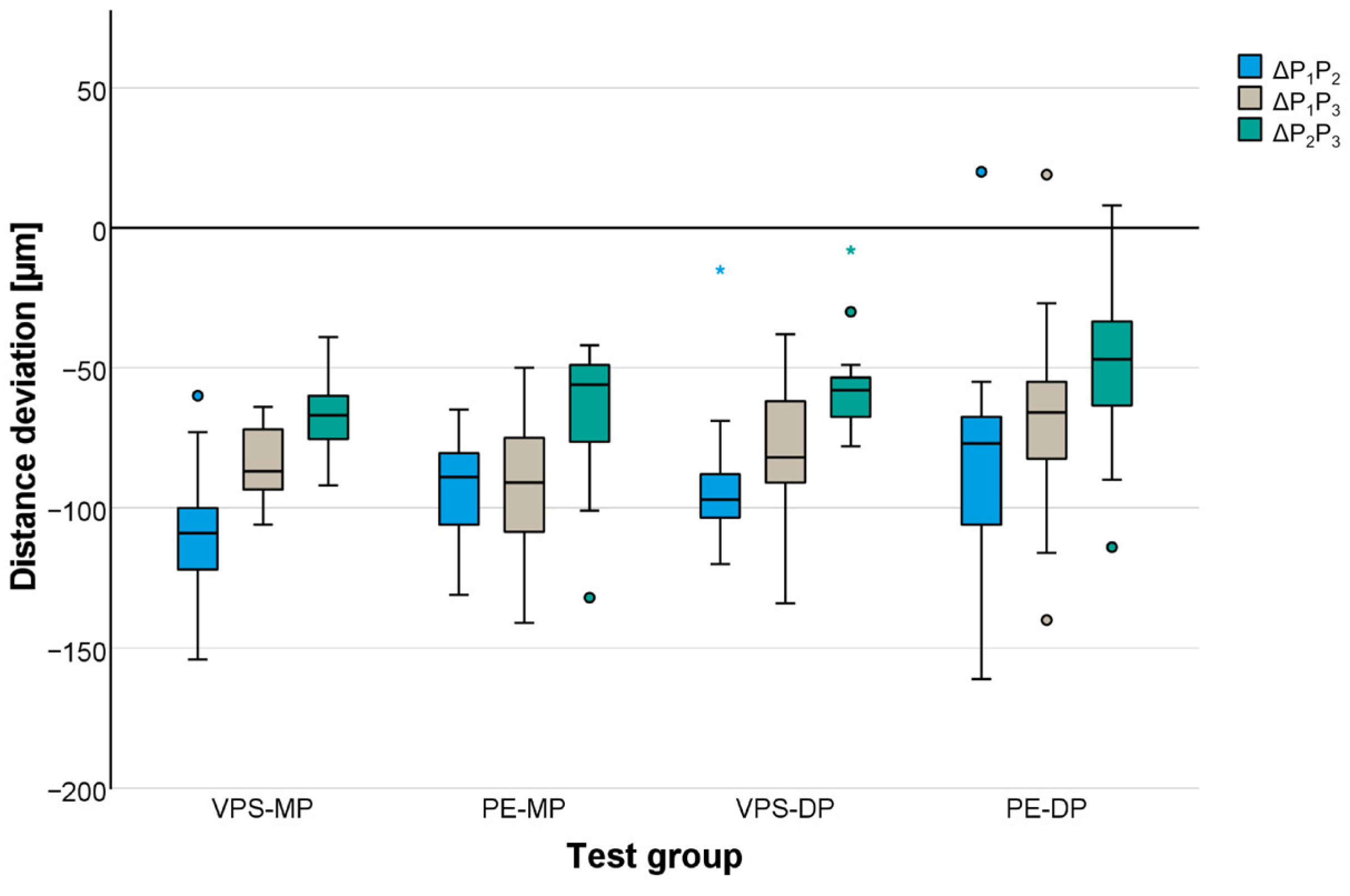
| Test group | Distance | Level | Distance Deviations [µm] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Value | Standard Deviation | Minimum | Median | Maximum | |||
| VPS-MP | P1P2 | - | −109 | 24 | −154 | −109 | −60 |
| P1P3 | - | −83 | 14 | −106 | −87 | −64 | |
| P2P3 | - | −66 | 15 | −92 | −67 | −39 | |
| LMLP | Margin | −13 | 11 | −32 | −13 | 4 | |
| Surface | −16 | 13 | 39 | −16 | 5 | ||
| LMRP | Margin | −58 | 21 | −109 | −53 | −28 | |
| Surface | −84 | 17 | −123 | −82 | −59 | ||
| LPRP | Margin | −58 | 23 | −109 | −53 | −23 | |
| Surface | −84 | 17 | −114 | −80 | −47 | ||
| PE-MP | P1P2 | - | −94 | 20 | −131 | −89 | −65 |
| P1P3 | - | −93 | 25 | −141 | −91 | −50 | |
| P2P3 | - | −66 | 26 | −132 | −56 | −42 | |
| LMLP | Margin | −18 | 14 | −36 | −23 | 6 | |
| Surface | −16 | 16 | −38 | −23 | 17 | ||
| LMRP | Margin | −49 | 12 | −69 | −45 | −33 | |
| Surface | −69 | 15 | −96 | −72 | −48 | ||
| LPRP | Margin | −48 | 19 | −80 | −42 | −23 | |
| Surface | −69 | 20 | −96 | −66 | −37 | ||
| VPS-DP | P1P2 | - | −91 | 25 | −120 | −97 | −15 |
| P1P3 | - | −80 | 27 | −134 | −82 | −38 | |
| P2P3 | - | −56 | 18 | −78 | −58 | −8 | |
| LMLP | Margin | −13 | 11 | −37 | −13 | 7 | |
| Surface | −16 | 14 | −46 | −13 | 4 | ||
| LMRP | Margin | −63 | 28 | −107 | −61 | −10 | |
| Surface | −83 | 28 | −125 | −89 | −19 | ||
| LPRP | Margin | −59 | 27 | −104 | −58 | −21 | |
| Surface | −79 | 26 | −127 | −76 | −45 | ||
| PE-DP | P1P2 | - | −82 | 40 | −161 | −77 | 20 |
| P1P3 | - | −68 | 36 | −140 | −66 | 19 | |
| P2P3 | - | −47 | 32 | −114 | −47 | 8 | |
| LMLP | Margin | −12 | 16 | −43 | −10 | 18 | |
| Surface | −9 | 19 | −42 | −10 | 36 | ||
| LMRP | Margin | −36 | 31 | −88 | −43 | 35 | |
| Surface | −53 | 37 | −111 | −63 | 34 | ||
| LPRP | Margin | −34 | 29 | −74 | −40 | 20 | |
| Surface | −56 | 29 | −101 | −60 | −5 | ||
| Angular Deviation | Test Group | Mean Value | Standard Deviation | Minimum | Median | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [°] | ||||||
| Δα | VPS-MP | 1.0 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 1.3 |
| PE-MP | 1.0 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 1.0 | 1.8 | |
| VPS-DP | 1.0 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 1.0 | 1.2 | |
| PE-DP | 1.1 | 0.3 | 0.8 | 1.1 | 1.9 | |
| Δβ | VPS-MP | 1.1 | 0.1 | 0.9 | 1.1 | 1.2 |
| PE-MP | 1.1 | 0.2 | 1.0 | 1.1 | 1.7 | |
| VPS-DP | 1.0 | 0.1 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 1.2 | |
| PE-DP | 1.2 | 0.2 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 2.0 | |
| Δγ | VPS-MP | 0.8 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 1.0 |
| PE-MP | 0.8 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 1.1 | |
| VPS-DP | 0.8 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 | |
| PE-DP | 0.9 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 1.1 | |
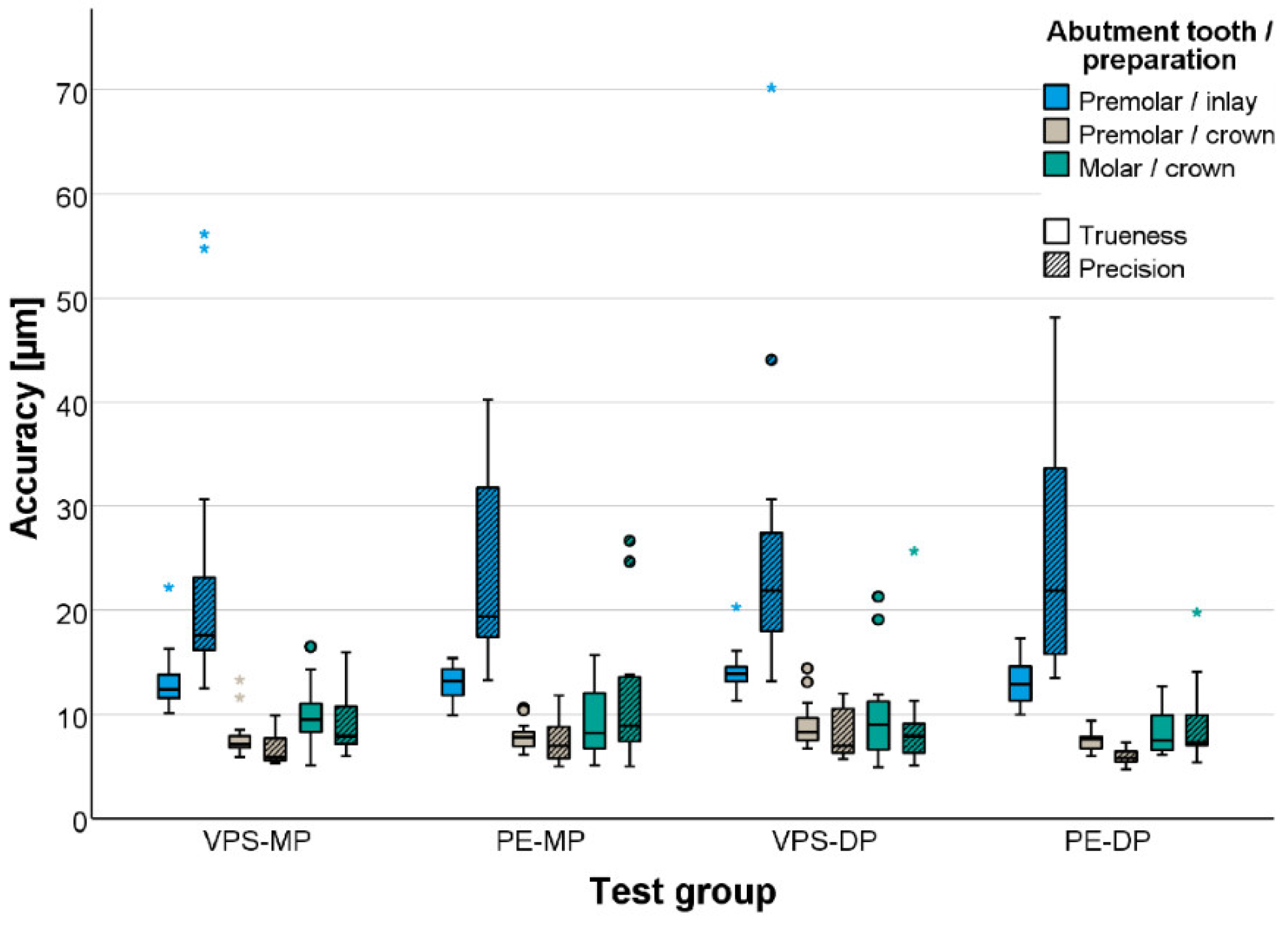
| Tooth | Test Group | Mean Value | Standard Deviation | Minimum | Median | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [µm] | ||||||
| LP | VPS-MP | 8 (7) | 2 (2) | 6 (5) | 7 (6) | 13 (10) |
| PE-MP | 8 (7) | 1 (2) | 6 (5) | 8 (7) | 11 (12) | |
| VPS-DP | 9 (10) | 2 (2) | 7 (6) | 8 (7) | 14 (39) | |
| PE-DP | 7 (6) | 1 (1) | 6 (5) | 8 (6) | 9 (7) | |
| LM | VPS-MP | 10 (9) | 3 (3) | 5 (6) | 10 (8) | 17 (16) |
| PE-MP | 9 (11) | 4 (6) | 5 (5) | 8 (9) | 16 (27) | |
| VPS-DP | 10 (9) | 5 (5) | 5 (5) | 9 (8) | 21 (26) | |
| PE-DP | 8 (9) | 2 (4) | 6 (5) | 8 (7) | 13 (20) | |
| RP | VPS-MP | 13 (23) | 3 (14) | 10 (13) | 12 (18) | 22 (56) |
| PE-MP | 13 (24) | 2 (9) | 10 (13) | 13 (19) | 15 (40) | |
| VPS-DP | 14 (26) | 2 (14) | 11 (13) | 14 (22) | 20 (70) | |
| PE-DP | 13 (25) | 2 (11) | 10 (14) | 13 (22) | 17 (48) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Waldecker, M.; Rues, S.; Rammelsberg, P.; Bömicke, W. Dimensional Accuracy of Novel Vinyl Polysiloxane Compared with Polyether Impression Materials: An In Vitro Study. Materials 2024, 17, 4221. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174221
Waldecker M, Rues S, Rammelsberg P, Bömicke W. Dimensional Accuracy of Novel Vinyl Polysiloxane Compared with Polyether Impression Materials: An In Vitro Study. Materials. 2024; 17(17):4221. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174221
Chicago/Turabian StyleWaldecker, Moritz, Stefan Rues, Peter Rammelsberg, and Wolfgang Bömicke. 2024. "Dimensional Accuracy of Novel Vinyl Polysiloxane Compared with Polyether Impression Materials: An In Vitro Study" Materials 17, no. 17: 4221. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174221
APA StyleWaldecker, M., Rues, S., Rammelsberg, P., & Bömicke, W. (2024). Dimensional Accuracy of Novel Vinyl Polysiloxane Compared with Polyether Impression Materials: An In Vitro Study. Materials, 17(17), 4221. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174221







