Microstructure and Properties of Mg-Gd-Y-Zn-Mn High-Strength Alloy Welded by Friction Stir Welding
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Welding Experimental Procedure
2.3. Microstructural Observations
2.4. Mechanical Properties Test
3. Results
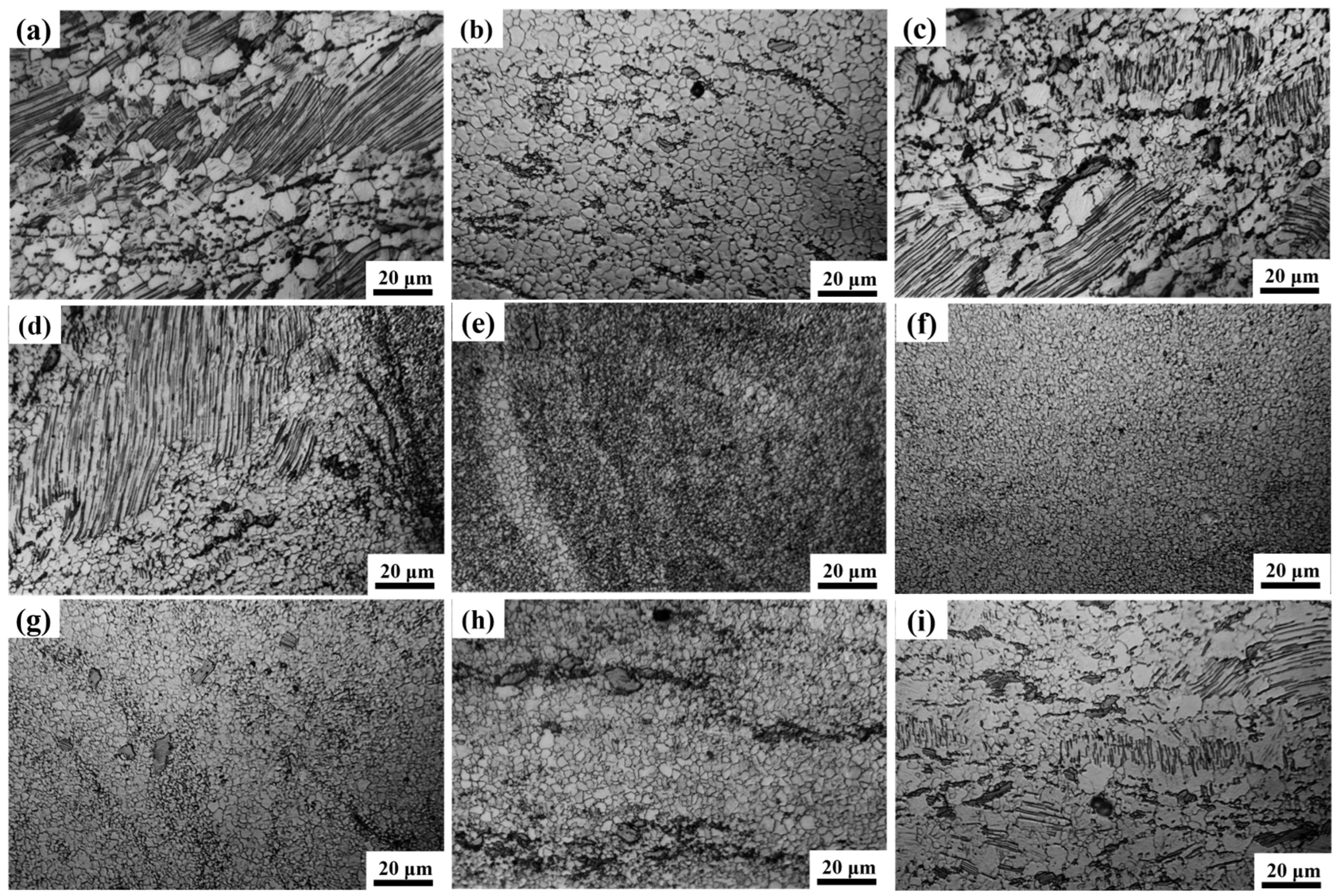
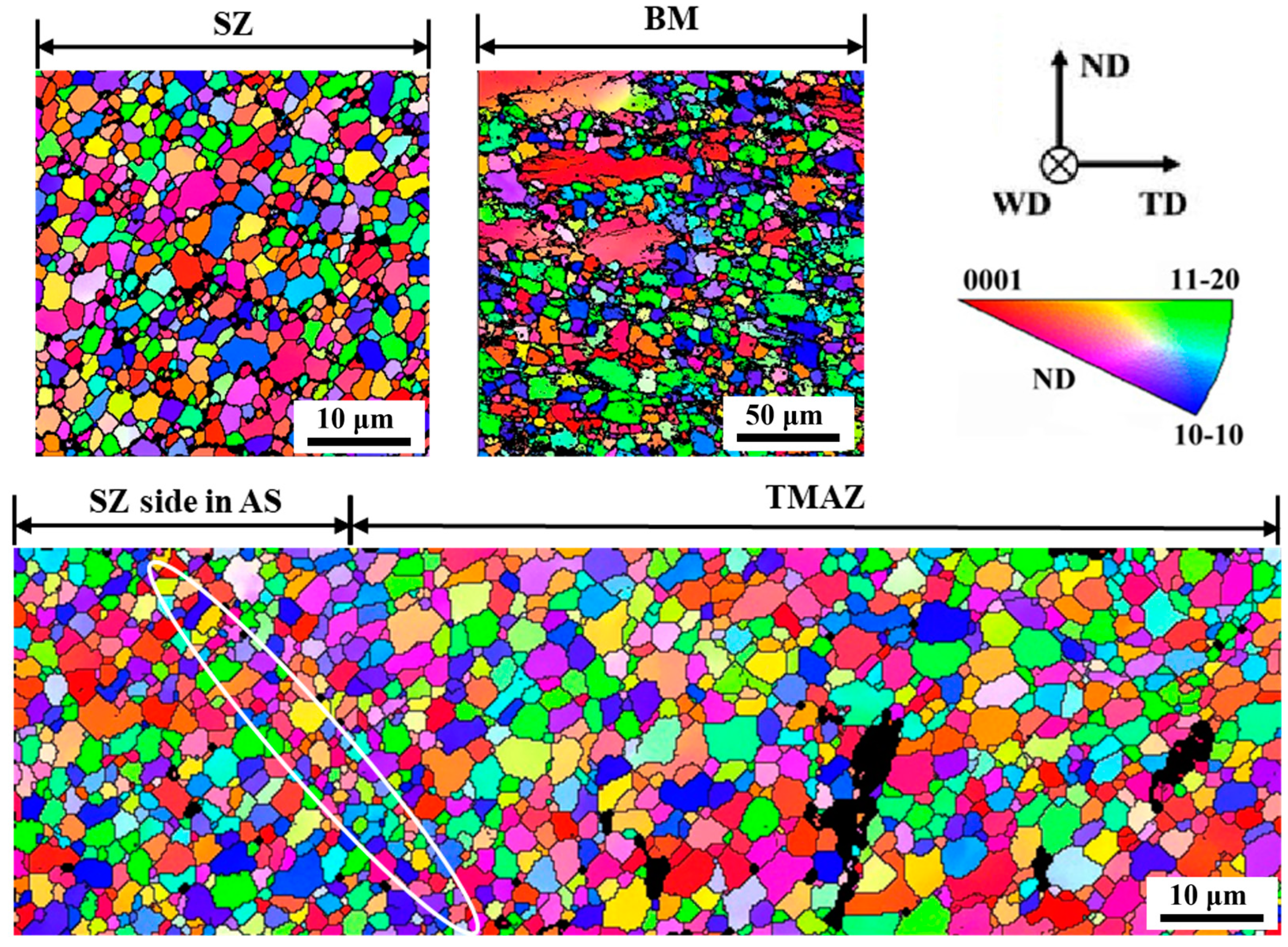
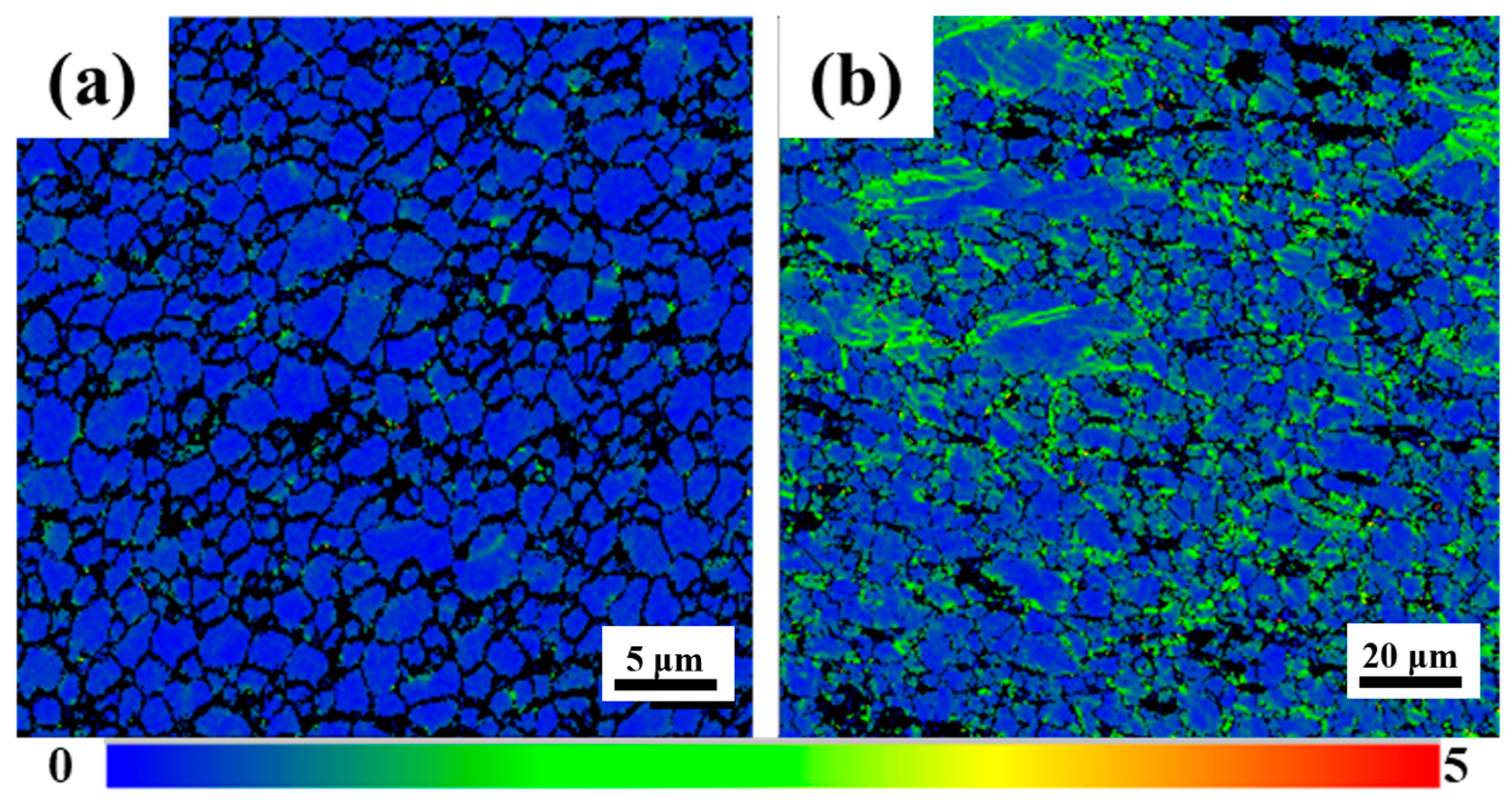
3.1. The Structure of the Joint
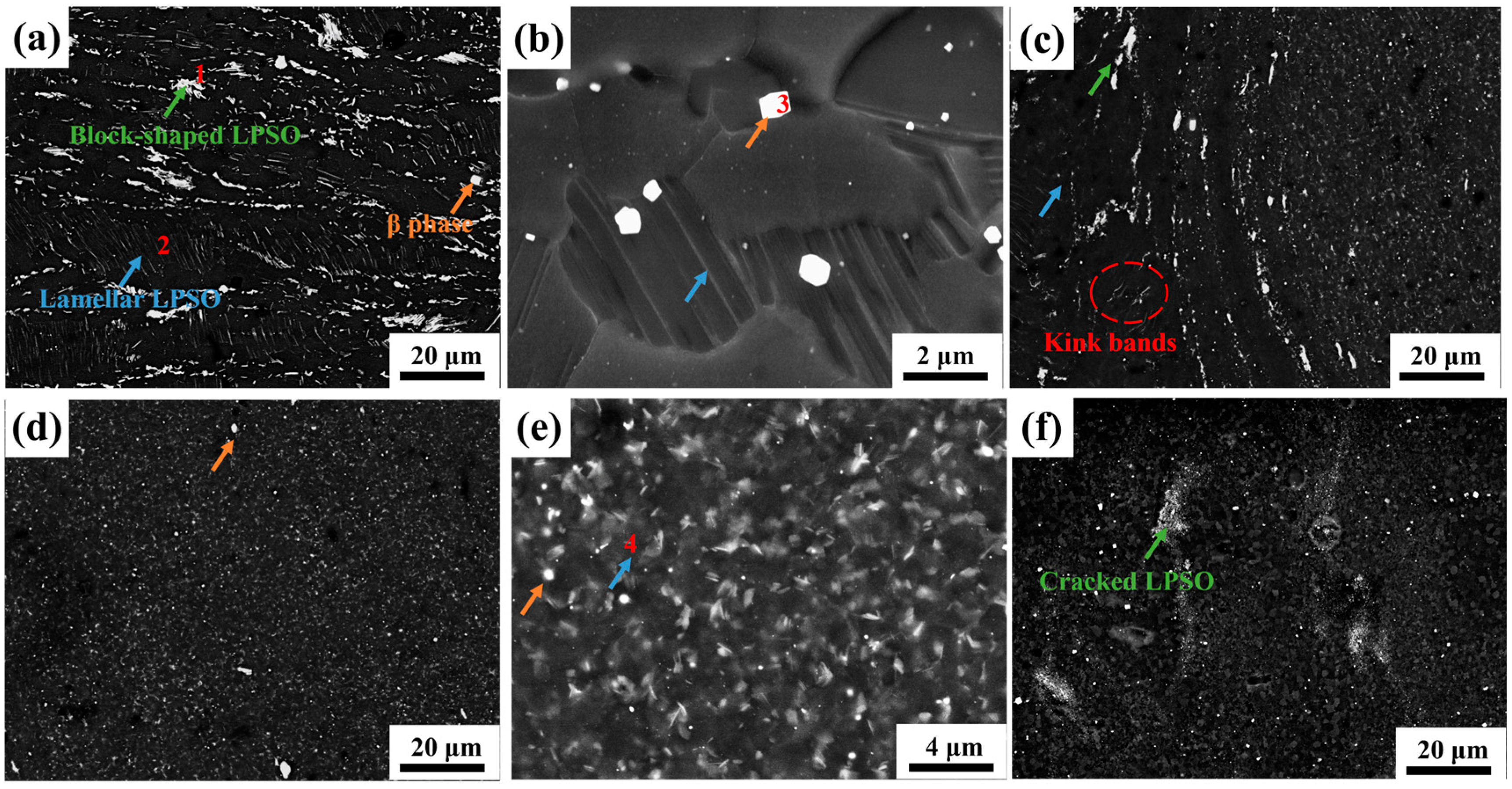
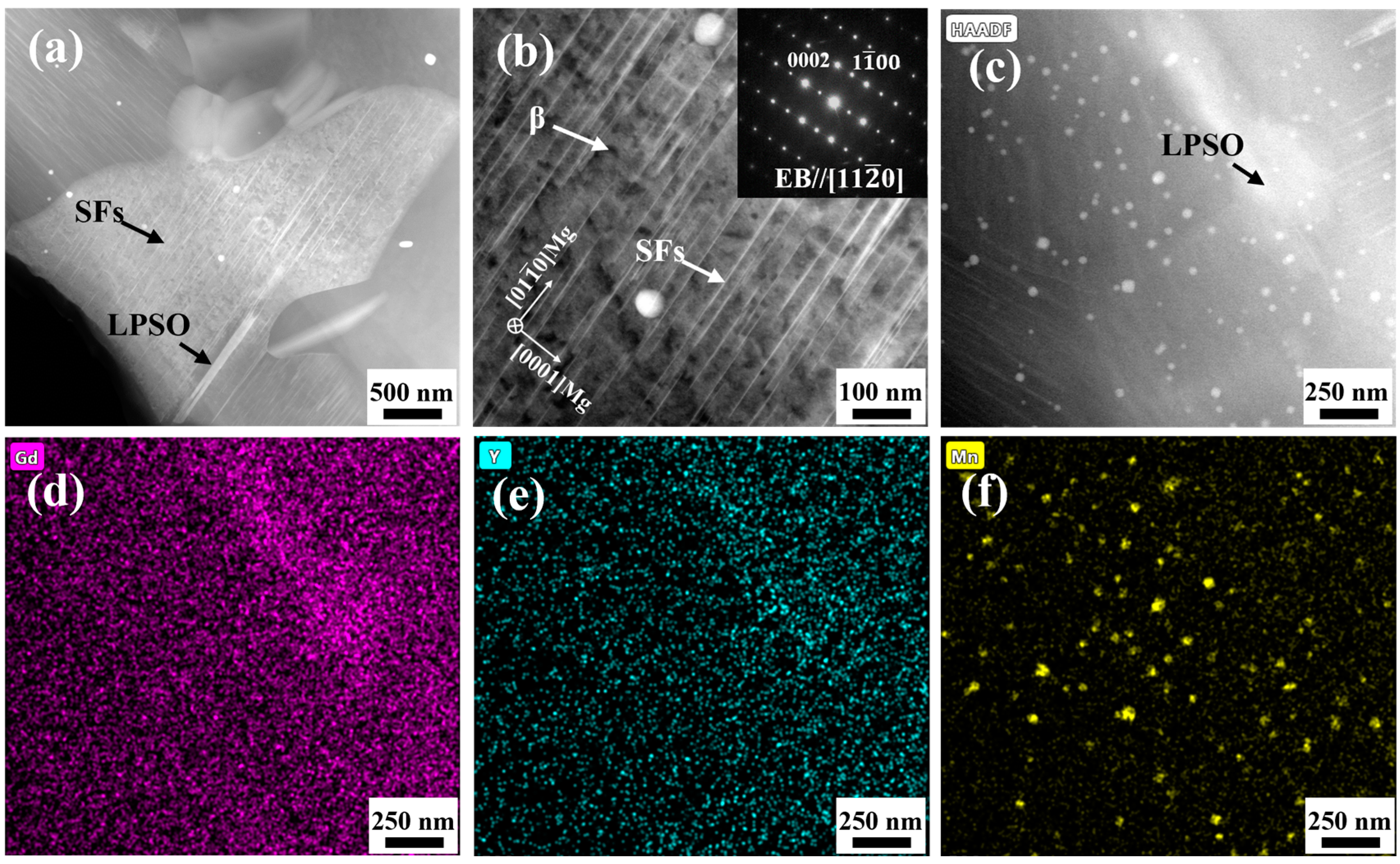
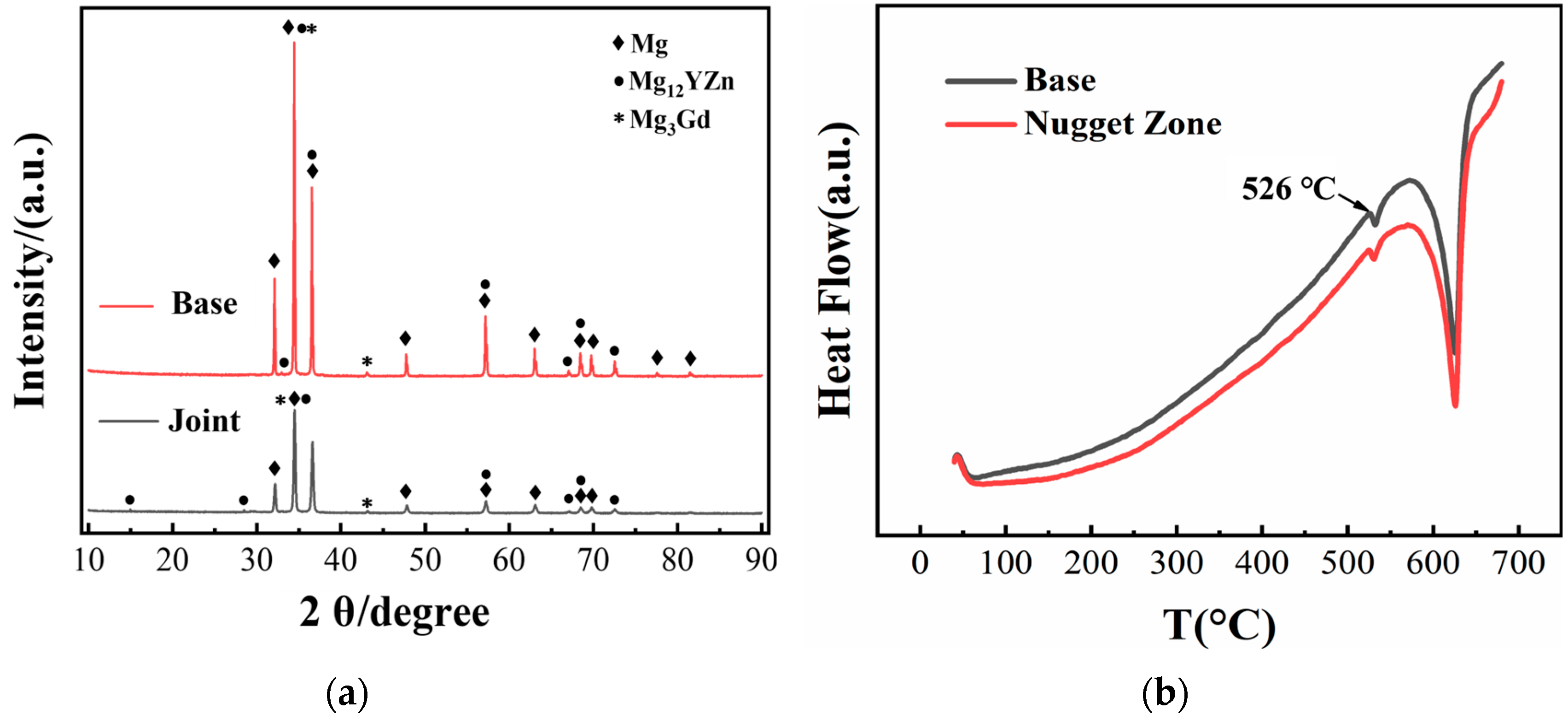
3.2. The Second Phase of Joint
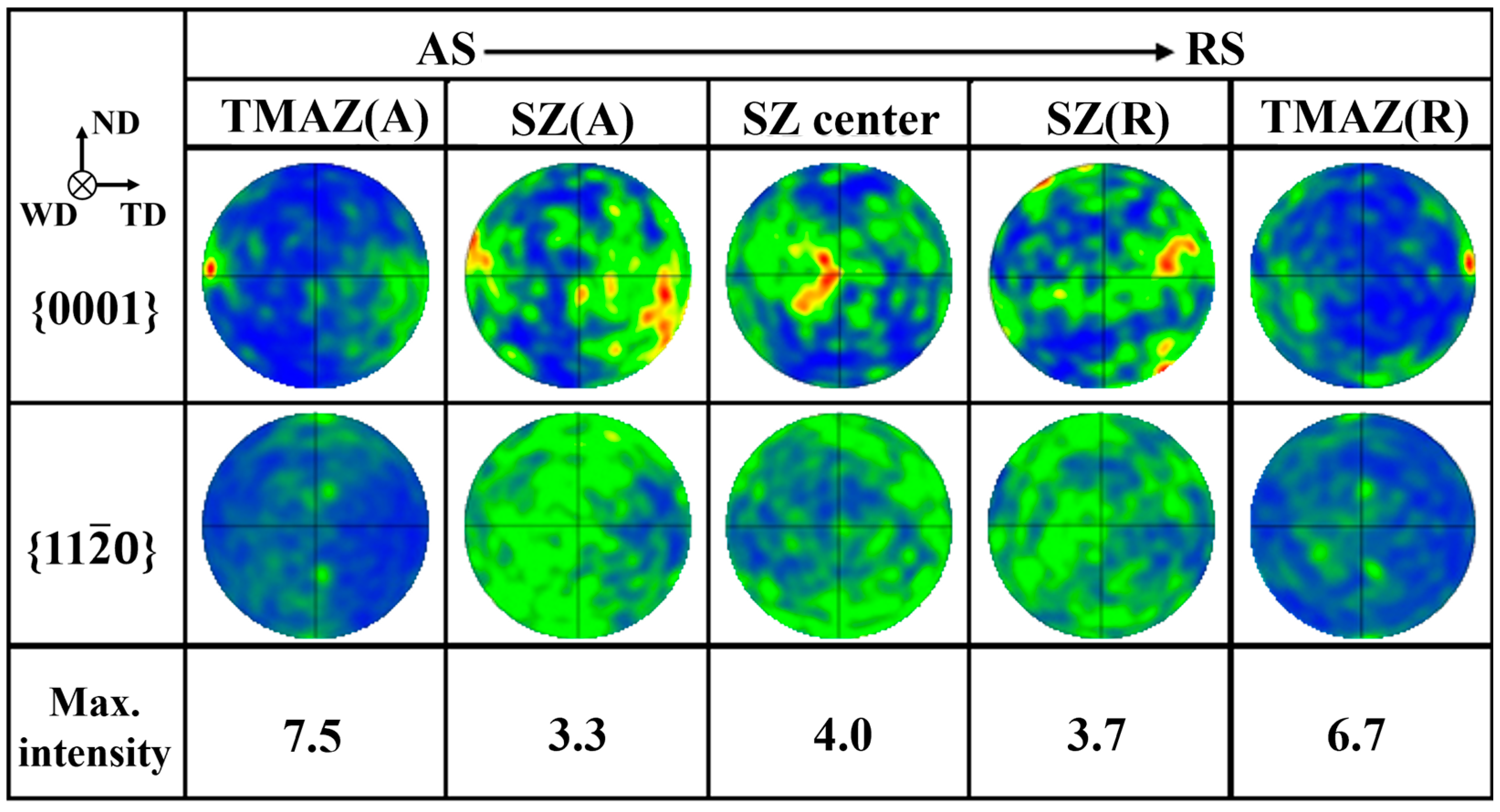
3.3. The Texture of the Joint
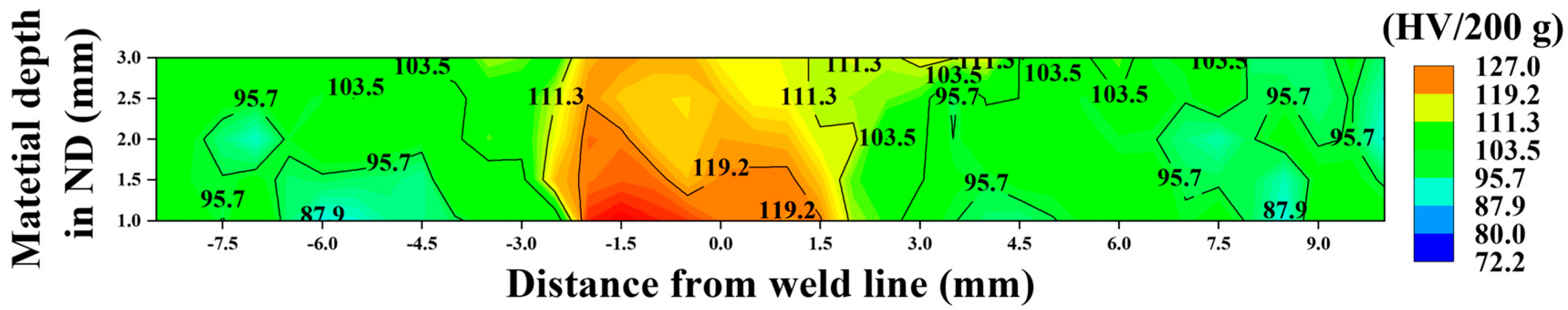
3.4. The Mechanical Properties of the Joint
4. Discussion
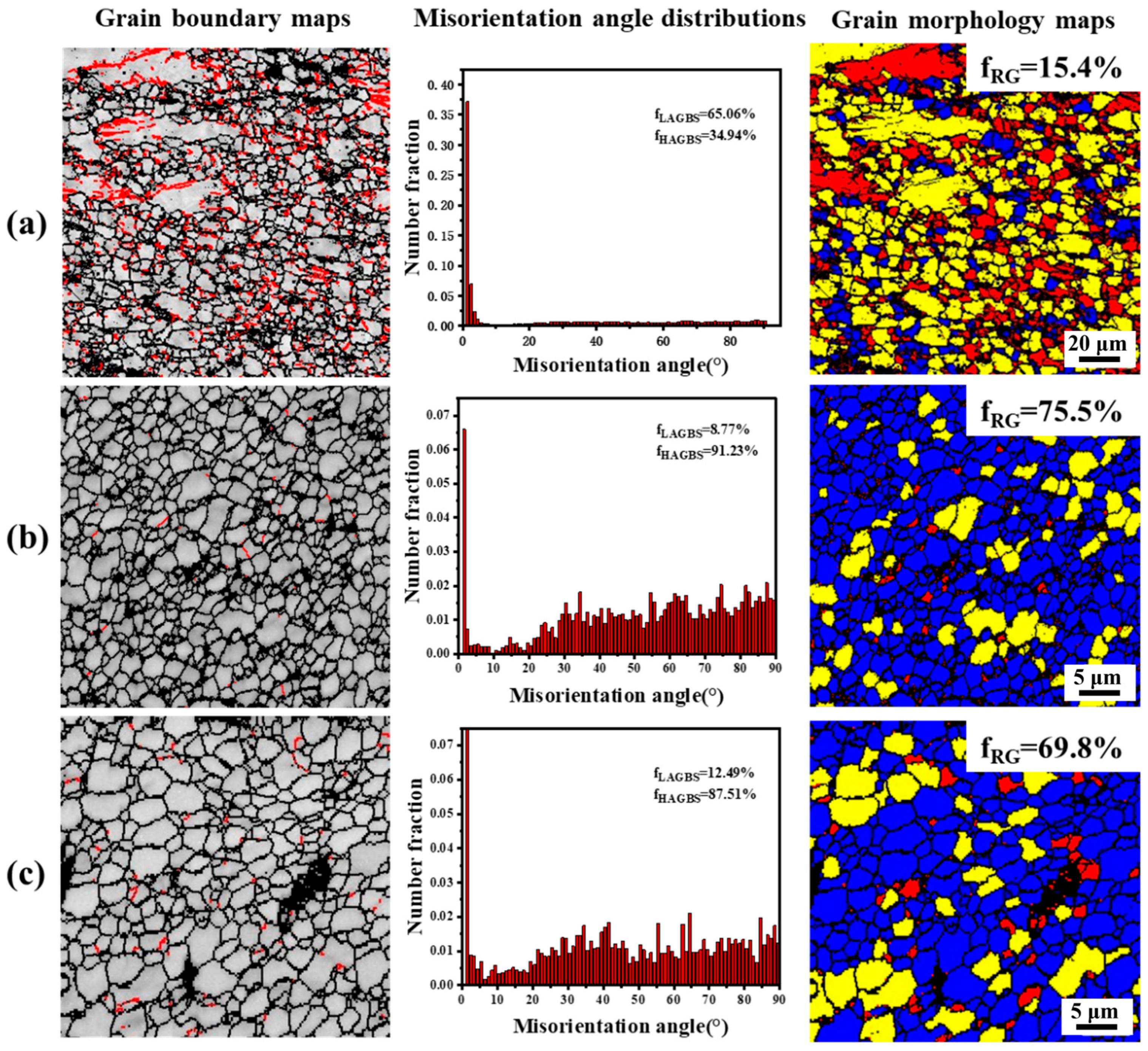
4.1. The Mechanisms of Grain Refinement
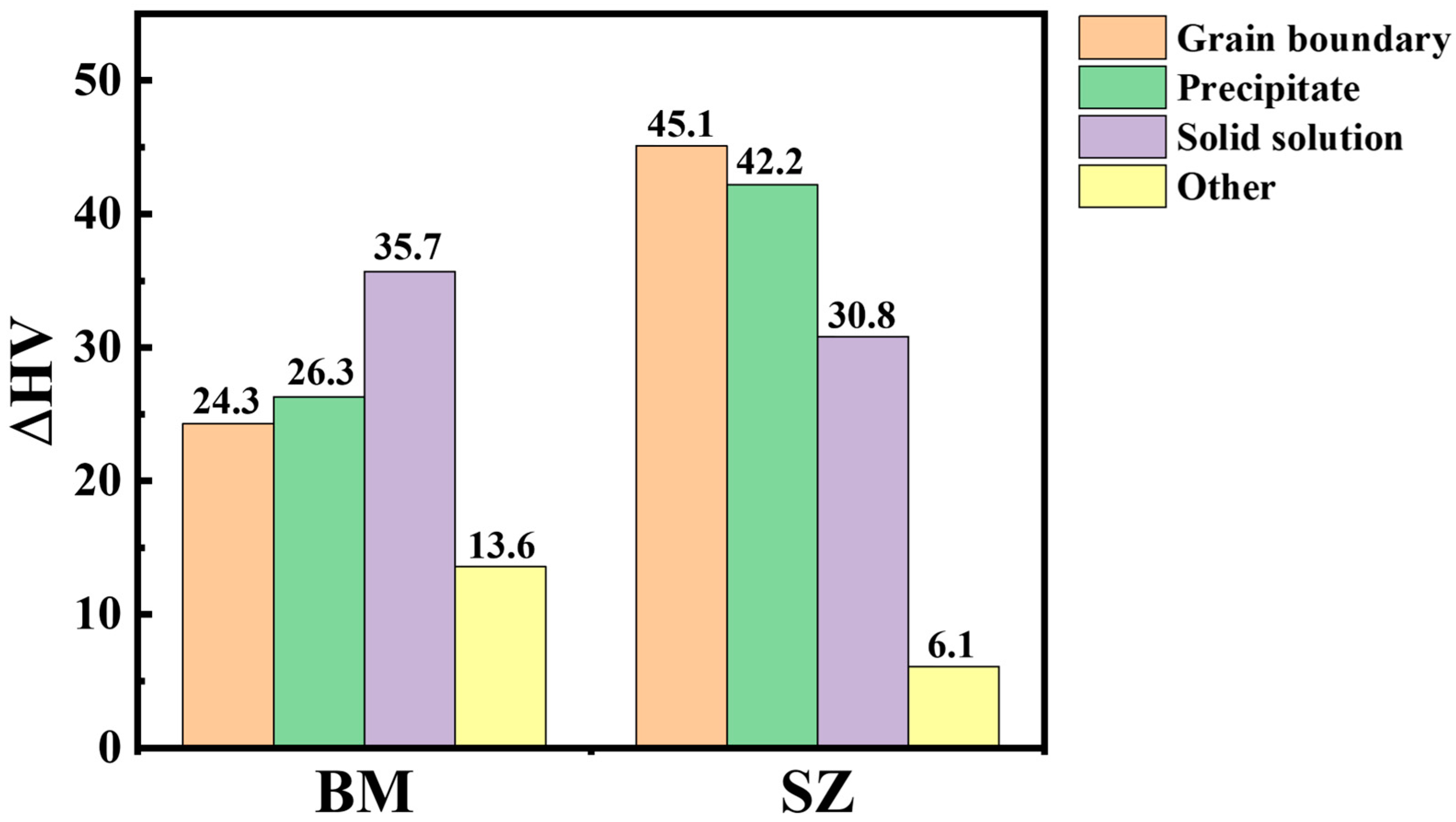
4.2. The Mechanisms of Joint Hardening
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The MVWZ842 alloy achieves high-quality connection after friction stir welding, the joint has no holes and cracks and the materials on both sides are fully mixed, with obvious onion ring characteristics.
- (2)
- The grain in the weld nugget zone is obviously refined. The LPSO at the interface of AS and RS is deformed and twisted, and there is an obvious transition of structure. The second phase in the weld nugget zone is not completely dissolved but is significantly broken and dispersed on the matrix. A large number of nanometer α-Mn elements are also distributed in the matrix, which has the effect of refining grains. In addition, stacking fault structures are precipitated in the grain.
- (3)
- Complete dynamic recrystallization occurs in the weld nugget zone, and the recrystallization fraction reaches 75%. The welding texture is formed in the weld nugget zone under the action of rotating shear, but the texture orientation is relatively discrete due to the large presence of Gd and Y elements.
- (4)
- The hardness of the micro-surface shows that the hardness of the weld nugget zone is significantly higher than that of the base, and the highest hardness is 123 HV on the AS of the stir zone. The hardness of all areas of the joint is not lower than that of the base, indicating that there is no area of performance weakening caused by welding.
- (5)
- There is no strain in the stir zone during the transverse tension, and the strain is mainly concentrated in the base at the edge of the thermo-mechanical affected zone. The existence of the transition zone makes the strain not concentrate directly on the edge of the weld nugget zone but change gradiently along the transition zone.
- (6)
- The strengthening mechanism of the joint is mainly fine crystal strengthening, second phase strengthening and solid solution strengthening. Through quantitative calculation, it is found that fine crystal strengthening and second phase strengthening contribute most to the strength.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bai, J.Y.; Yang, Y.; Wen, C.; Chen, J.; Zhou, G.; Jiang, B.; Peng, X.D.; Pan, F.S. Applications of magnesium alloys for aerospace: A review. J. Magnes. Alloys 2023, 11, 3609–3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Tabary, S.A.A.B.; Rahmatabadi, D.; Ebrahimi, M.S.; Abrinia, K.; Hashemi, R. Review of selective laser melting of magnesium alloys: Advantages, microstructure and mechanical characterizations, defects, challenges, and applications. J. Mater. Res. Technol.-JMR T 2022, 19, 1537–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmatabadi, D.; Tayyebi, M.; Najafizadeh, N.; Hashemi, R.; Rajabi, M. The influence of post-annealing and ultrasonic vibration on the formability of multilayered Al5052/MgAZ31B composite. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 37, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Liu, S.J.; Wu, R.Z.; Hou, L.G.; Zhang, M.L. Recent developments in high-strength Mg-RE-based alloys: Focusing on Mg-Gd and Mg-Y systems. J. Magnes. Alloys 2018, 6, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ju, J.; Yang, X.W.; Yan, J.L.; Song, D.; Jiang, J.H.; Ma, A.B. A two-step dynamic recrystallization induced by LPSO phases and its impact on mechanical property of severe plastic deformation processed Mg97Y2Zn1 alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 704, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Wang, F.L.; Zeng, J.; Zhao, C.Y.; Jin, L.; Dong, J. Effect of the interspacing of intragranular lamellar LPSO phase on dynamic recrystallization behaviors of Mg-Gd-Y-Zn-Zr alloys. Mater. Charact. 2022, 193, 112326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.M.; Morton, A.J.; Nie, J.F. The 18R and 14H long-period stacking ordered structures in Mg-Y-Zn alloys. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 2936–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, M.; Sasaki, M.; Nishijima, M.; Hiraga, K.; Kawamura, Y. Formation of 14H long period stacking ordered structure and profuse stacking faults in Mg-Zn-Gd alloys during isothermal aging at high temperature. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 6798–6805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.; Huang, Y.; Kainer, K.U.; Hort, N. Recent research and developments on wrought magnesium alloys. J. Magnes. Alloys 2017, 5, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, H.M.; Rodriguez, R.I.; Jordon, J.B.; Barkey, M.E.; Guo, Y.B.; Badarinarayan, H.; Yuan, W. Friction stir spot welding of rare-earth containing ZEK100 magnesium alloy sheets. Mater. Des. 2014, 56, 750–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, M.; Ii, S.; Kawamura, Y.; Ikuhara, Y.; Nishida, M. Interaction between long period stacking order phase and deformation twin in rapidly solidified Mg97Zn1Y2 alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2004, 386, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homma, T.; Kunito, N.; Kamado, S. Fabrication of extraordinary high-strength magnesium alloy by hot extrusion. Scr. Mater. 2009, 61, 644–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wang, J.F.; Hou, F.; Huang, X.H.; Pan, F.S. Effect of Gd and Y contents on the microstructural evolution of long period stacking ordered phase and the corresponding mechanical properties in Mg-Gd-Y-Zn-Mn alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2014, 612, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.J.; Wang, K.; Wang, J.F.; Huang, S.; Gao, S.Q.; Peng, X.; Hu, H.; Pan, F.S. Ageing behavior and mechanisms of strengthening and toughening of ultrahigh-strength Mg-Gd-Y-Zn-Mn alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2019, 758, 96–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Dou, X.X.; Wang, J.F.; Huang, Y.D.; Gavras, S.; Hort, N.; Liu, S.J.; Hu, H.; Wang, J.X.; Pan, F.S. Achieving enhanced mechanical properties in Mg-Gd-Y-Zn-Mn alloy by altering dynamic recrystallization behavior via pre-ageing treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2020, 790, 139635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Wu, Y.; Nie, Z.; Su, X.; Zuo, T. Effects of rare earth and alkaline earth on magnesium alloys and their applications status. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2006, 35, 1345–1349. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, H.; Ren, Y.; Fu, H.; Zhao, H.; Wang, L.; Meng, X.; Qin, G. Recent developments in rare-earth free wrought magnesium alloys having high strength: A review. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 663, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, D.; Ding, H.; Zhi, M.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, M. Research Progress on the Oxidation Behavior of Ignition-Proof Magnesium Alloy and Its Effect on Flame Retardancy with Multi-Element Rare Earth Additions: A Review. Materials 2024, 17, 3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.-Y.; Liu, F.; Yang, N.; Zhai, X.-B.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, B.; Li, J.; Ma, E.; Nie, J.-F.; et al. Large plasticity in magnesium mediated by pyramidal dislocations. Science 2019, 365, 73–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.S.; Ma, Z.Y. Friction stir welding and processing. Mater. Sci. Eng. R-Rep. 2005, 50, 1–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovid’ko, I.A.; Valiev, R.Z.; Zhu, Y.T. Review on superior strength and enhanced ductility of metallic nanomaterials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 94, 462–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Ma, T.; Yang, X.; Tao, J.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Vairis, A. In-situ investigation on dislocation slip concentrated fracture mechanism of linear friction welded dissimilar Ti17(α+β)/Ti17(β) titanium alloy joint. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 872, 144991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, P.H.C.P.d.; Lemos, G.V.B.; Bergmann, L.; Reguly, A.; Santos, J.F.d.; Marinho, R.R.; Paes, M.T.P. Effect of welding speed on friction stir welds of GL E36 shipbuilding steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidarzadeh, A.; Mironov, S.; Kaibyshev, R.; Cam, G.; Simar, A.; Gerlich, A.; Khodabakhshi, F.; Mostafaei, A.; Field, D.P.; Robson, J.D.; et al. Friction stir welding/processing of metals and alloys: A comprehensive review on microstructural evolution. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2021, 117, 100752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosayebi, M.; Zarei-Hanzaki, A.; Tahaghoghi, M.; Abedi, H.R.; Moshiri, A.; Ghaderi, A. Effect of second phase particles on the microstructure and texture of rare earth elements containing magnesium matrix surface-composite produced by friction stir processing. J. Mater. Res. Technol.-JMR T 2022, 18, 2428–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivashanmugam, N.; Harikrishna, K.L.; Rao, S.R.K.; Justin, S.J.S.; Wilson, P. Mechanical and corrosion characteristics of micro-arc oxidized magnesium alloy (ZE41) friction stir welds in modified SBF. Phys. Scr. 2023, 98, 105901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, E.P.; Oliveira, V.B.; Pereira, V.F.; Maluf, O.; Buzolin, R.H.; Pinto, H.C. Microstructure and Residual Stresses in a Friction Stir Welded Butt Joint of as-cast ZK60 Alloy Containing Rare Earths. Mater. Res.-Ibero-Am. J. Mater. 2017, 20, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, K.N. On the formation of onion rings in friction stir welds. Mater. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2002, 327, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, R.; Zheng, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, D.; Qiu, R.; Li, Z.; Liu, Q. Microstructure and texture evolution of an Mg-Gd-Y-Nd-Zr alloy during friction stir processing. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 659, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.C.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.F.; Xue, P.; Ni, D.R.; Wang, W.Z.; Ma, Z.Y.; Ye, H.Q.; Yang, Z.Q. Evolution of Quasicrystals and Long-Period Stacking Ordered Structures During Severe Plastic Deformation and Mixing of Dissimilar Mg Alloys Upon Friction Stir Welding. Acta Metall. Sin.-Engl. Lett. 2021, 34, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Xiao, B.L.; Wang, D.; Zheng, M.Y.; Ma, Z.Y. Study on distribution of long-period stacking ordered phase in Mg-Gd-Y-Zn-Zr alloy using friction stir processing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2015, 626, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.G.; Xu, C.; Yan, H.; Nakata, T.; Chen, Z.W.; Lao, C.S.; Chen, R.S.; Kamado, S.; Han, E.H. Quasi-in-situ observing the rare earth texture evolution in an extruded Mg-Zn-Gd alloy with bimodal microstructure. J. Magnes. Alloys 2021, 9, 1797–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.J.; Xin, R.L.; Sun, L.Y.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Q. Influence of sampling design on tensile properties and fracture behavior of friction stir welded magnesium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2013, 576, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, R.L.; Li, B.; Liao, A.L.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Q. Correlation Between Texture Variation and Transverse Tensile Behavior of Friction-Stir-Processed AZ31 Mg Alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A-Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2012, 43A, 2500–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.N.; Chang, C.I.; Lee, C.J.; Lin, H.K.; Huang, J.C. Texture and weak grain size dependence in friction stir processed Mg-Al-Zn alloy. Scr. Mater. 2006, 55, 637–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.T.; Liu, H.C.; Hsieh, P.Y.; Wei, C.Y.; Tsai, C.W.; Sato, Y.S.; Chen, S.C.; Yen, H.W.; Lu, N.H.; Chen, C.H. Heterogeneous structure-induced strength-ductility synergy by partial recrystallization during friction stir welding of a high-entropy alloy. Mater. Des. 2021, 197, 109238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Song, Q.N.; Bao, Y.F.; Fujii, H. Investigation on microstructure and mechanical properties of cold source assistant friction stir processed AZ31B magnesium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2019, 761, 138027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Li, S.X.; Zhang, Z.F. General relationship between strength and hardness. Mater. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2011, 529, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.T.; Qiao, X.G.; Zheng, M.Y.; Xu, C.; Kamado, S.; Zhao, X.J.; Chen, H.W.; Gao, N.; Starink, M.J. Altered ageing behaviour of a nanostructured Mg-8.2Gd-3.8Y-1.0Zn-0.4Zr alloy processed by high pressure torsion. Acta Mater. 2018, 151, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.F. Precipitation and Hardening in Magnesium Alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A-Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2012, 43A, 3891–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.F. Effects of precipitate shape and orientation on dispersion strengthening in magnesium alloys. Scr. Mater. 2003, 48, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Mg | Gd | Y | Zn | Mn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MVWZ842 | Bal. | 8.2167 | 3.9995 | 1.2922 | 0.9623 |
| Alloy | Tensile direction | Hardness (HV) | UTS (MPa) | YS (MPa) | EL (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MVWZ842 | ⊥ED | 95.7 | 328.4 | 229.5 | 10.7 |
| Position | Gd (at.%) | Y (at.%) | Zn (at.%) | Mn (at.%) | Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.2 | 4.1 | 5.4 | 0.6 | LPSO |
| 2 | 2.6 | 2.8 | 3.2 | 0.7 | LPSO |
| 3 | 6.6 | 17.5 | —— | —— | Mg5(RE) |
| 4 | 3.1 | 3.8 | 4.9 | 0.6 | LPSO |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Wan, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Zou, Y.; Wang, J.; Pan, F. Microstructure and Properties of Mg-Gd-Y-Zn-Mn High-Strength Alloy Welded by Friction Stir Welding. Materials 2024, 17, 4190. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174190
Wang J, Wan Z, Wang X, Wang J, Zou Y, Wang J, Pan F. Microstructure and Properties of Mg-Gd-Y-Zn-Mn High-Strength Alloy Welded by Friction Stir Welding. Materials. 2024; 17(17):4190. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174190
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jinxing, Zhicheng Wan, Xiyu Wang, Jiaxu Wang, Yi Zou, Jingfeng Wang, and Fusheng Pan. 2024. "Microstructure and Properties of Mg-Gd-Y-Zn-Mn High-Strength Alloy Welded by Friction Stir Welding" Materials 17, no. 17: 4190. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174190
APA StyleWang, J., Wan, Z., Wang, X., Wang, J., Zou, Y., Wang, J., & Pan, F. (2024). Microstructure and Properties of Mg-Gd-Y-Zn-Mn High-Strength Alloy Welded by Friction Stir Welding. Materials, 17(17), 4190. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174190







