Structural, Optical, Magnetic and Electrochemical Properties of CeXO2 (X: Fe, and Mn) Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
Characterization Techniques
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. XRD Analysis
3.2. TEM Analysis
3.3. UV-Vis Absorption Spectra
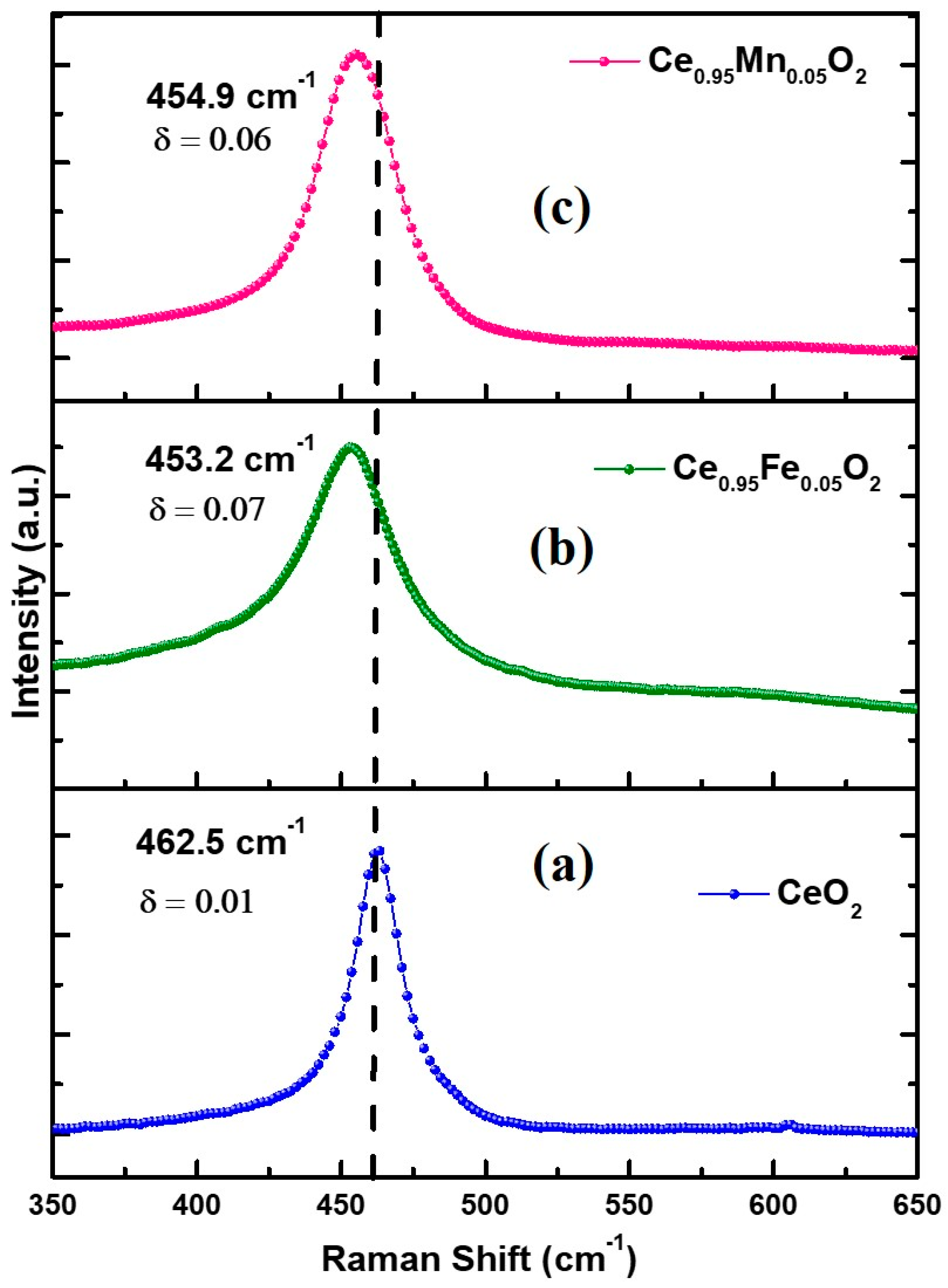
3.4. Raman Spectroscopy
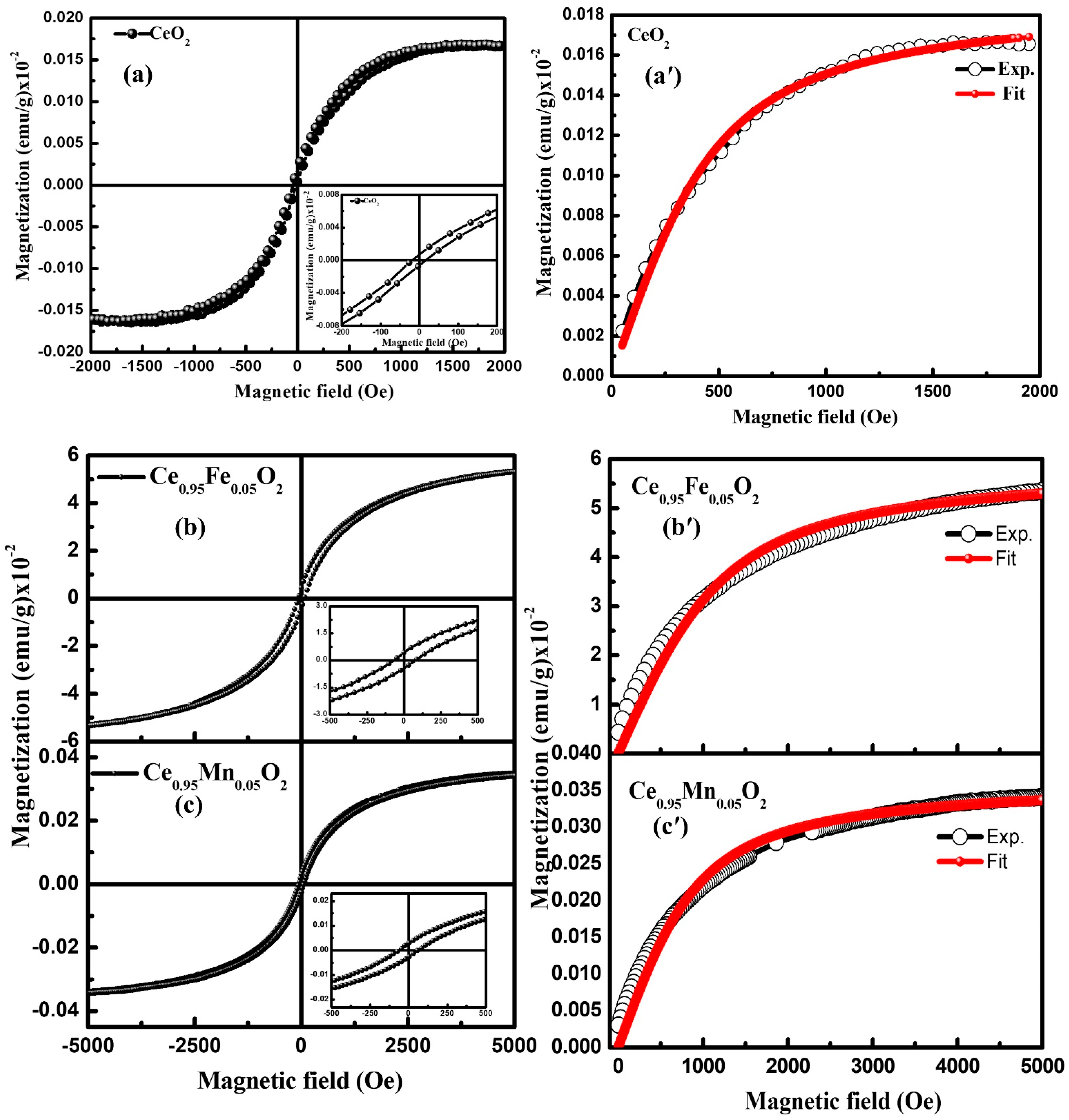
3.5. Magnetisation
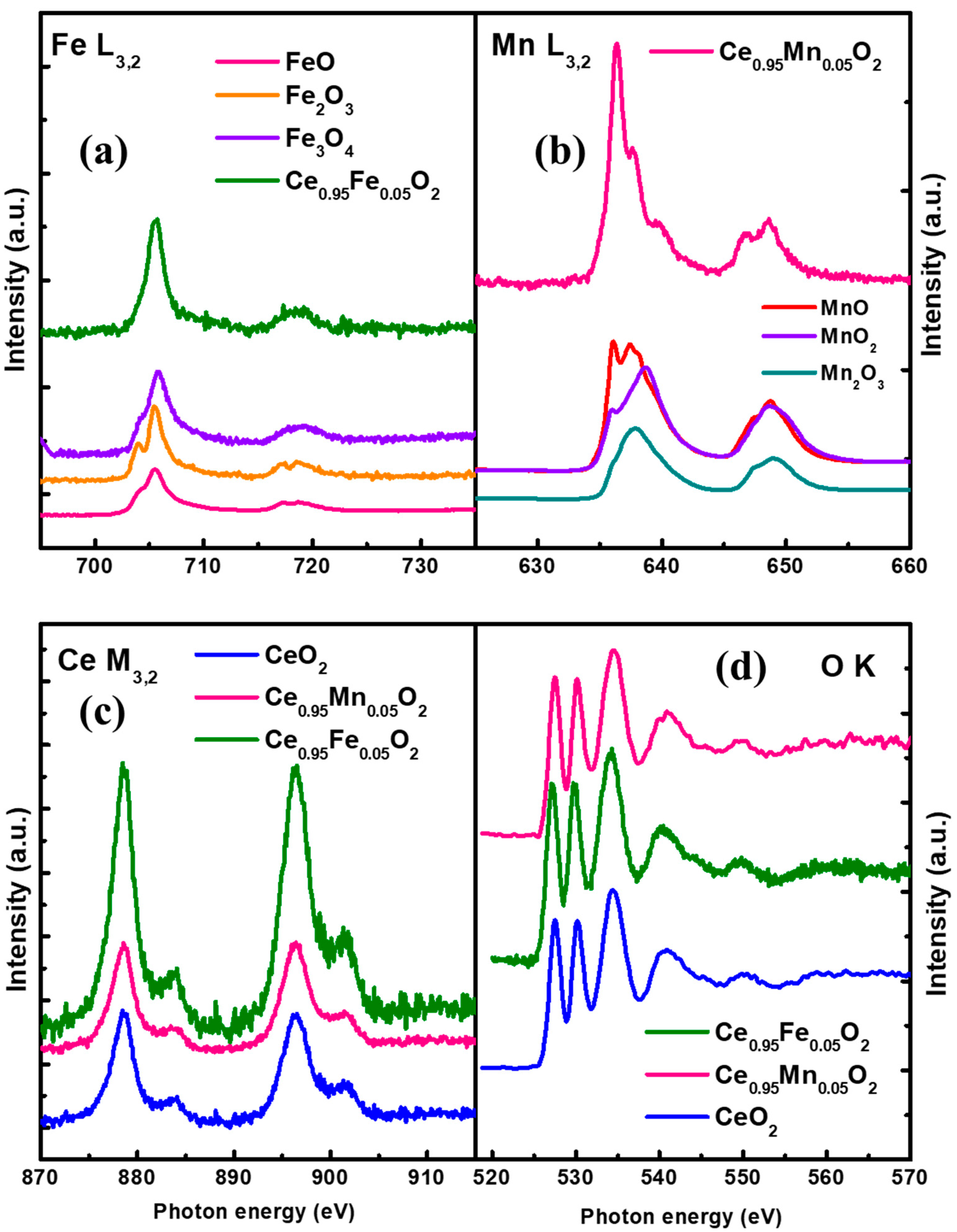
3.6. Near Edge X-ray Absorption Fine Spectroscopy (NEXAFS)
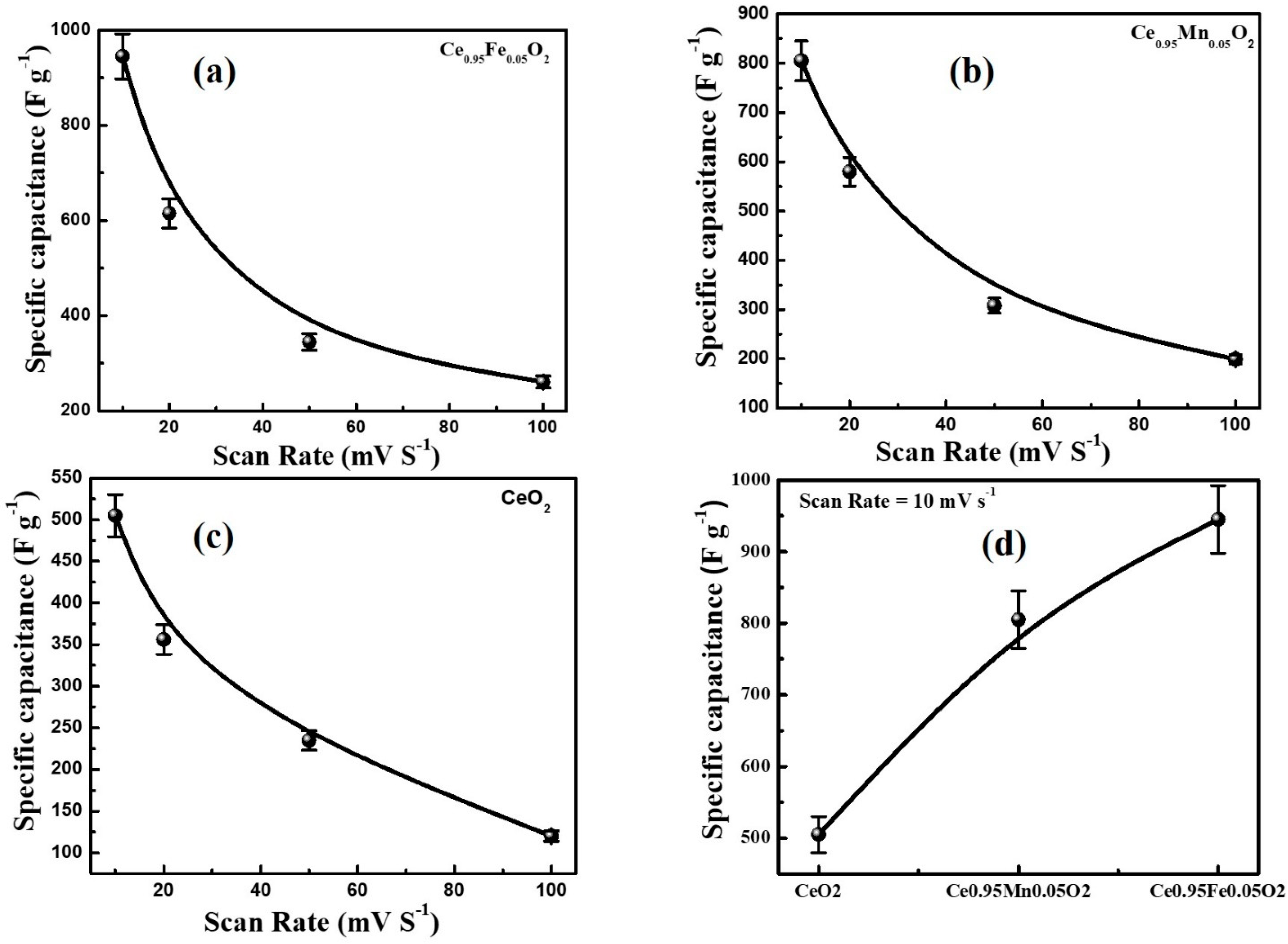
3.7. Electrochemical Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- An, C.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, H.; Wang, Y. Metal oxide-based supercapacitors: Progress and prospectives. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 4644–4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, Y.; El-Kady, M.F.; Sun, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, M.; Wang, H.; Dunn, B.; Kaner, R.B. Design and Mechanisms of Asymmetric Supercapacitors. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 9233–9280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, P.; Gogotsi, Y. Materials for electrochemical capacitors Gogotsi nmat2006. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Ahmed, F.; Shaalan, N.M.; Saber, O. Biosynthesis of CeO2 nanoparticles using egg white and their antibacterial and antibiofilm properties on clinical isolates. Crystals 2021, 11, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, S.; Kumar, S.; Dalela, B.; Kumar, S.; Alvi, P.A.; Dalela, S. Defects and oxygen vacancies tailored structural and optical properties in CeO2 nanoparticles doped with Sm3+ cation. J. Alloy. Compd. 2018, 752, 520–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakhal, H.R.; Kumar, S.; Dolia, S.N.; Dalela, B.; Vats, V.S.; Hashmi, S.Z.; Alvi, P.A.; Kumar, S.; Dalela, S. Oxygen vacancies and F+ centre tailored room temperature ferromagnetic properties of CeO2 nanoparticles with Pr doping concentrations and annealing in hydrogen environment. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 844, 156079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Alharthi, F.A.; El Marghany, A.; Ahmed, F.; Ahmad, N.; Chae, K.H.; Kumari, K. Role of Fe doping on surface morphology, electronic structure and magnetic properties of Fe doped CeO2 thin film. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 4012–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Koo, B.H.; Sharma, S.K.; Knobel, M.; Lee, C.G. Influence of Co Doping On Structural, Optical and Magnetic Studies of Co-Doped CeO2 Nanoparticles. Nano Br. Rep. Rev. 2010, 5, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, M.; Kumar, S.; Dalela, B.; Alvi, P.A.; Sharma, S.S.; Phase, D.M.; Gupta, M.; Kumar, S.; Dalela, S. Interplay of structural, optical, and magnetic properties of Ce1-xNdxO2-δ nanoparticles with electronic structure probed using X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Vacuum 2020, 180, 109537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezfuli, A.S.; Ganjali, M.R.; Naderi, H.R.; Norouzi, P. A high performance supercapacitor based on a ceria/graphene nanocomposite synthesized by a facile sonochemical method. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 46050–46058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Zhao, X.; Xu, H.; Yuan, C. CeO2 Spherical Crystallites: Synthesis, Formation Mechanism, Size Control, and Electrochemical Property Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 1651–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugrov, A.N.; Vorobiov, V.K.; Sokolova, M.P.; Kopitsa, G.P.; Bolshakov, S.A.; Smirnov, M.A. Hydrothermal synthesis of CeO2 nanostructures and their electrochemical properties. Nanosyst. Phys. Chem. Math. 2020, 11, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhu, B.; Yun, S.; Zhang, W.; Xia, C.; Afzal, M.; Cai, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H. Fast ionic conduction in semiconductor CeO2-δ electrolyte fuel cells. NPG Asia Mater. 2019, 11, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodrigues, M.A.; Catto, A.C.; Longo, E.; Nossol, E.; Lima, R.C. Characterization and electrochemical performance of CeO2 and Eu-doped CeO2 films as a manganese redox flow battery component. J. Rare Earths 2018, 36, 1074–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chueh, W.C.; Haile, S.M. Electrochemical studies of capacitance in cerium oxide thin films and its relationship to anionic and electronic defect densities. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2009, 11, 8144–8148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, S.; Mohsin, M.; Raza, A.H.; Anwar, R.; Ahmad, B.; Raza, R. Co-doped cerium oxide Fe0.25-xMnxCe0.75O2-δ as a composite cathode material for IT-SOFC. J. Alloy. Compd. 2022, 906, 164319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaran, C.; Baskaran, I.; Sathyaseelan, B.; Senthilnathan, K.; Manikandan, E.; Sambasivam, S. Effect of doping of iron on structural, optical and magnetic properties of CeO2 nanoparticles. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2022, 808, 140110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Han, Z.; Xu, L.; Baiker, A.; Li, G. Morphology effects in MnCeOx solid solution-catalyzed NO reduction with CO: Active sites, water tolerance, and reaction pathway. Nano Res. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, M.M.; Amin, F.; Ajaz-un-Nabi, M.; Khan, I.U.; Sabir, N. Synthesis and antimicrobial activities of Manganese (Mn) and iron (Fe) co-doped Cerium dioxide (CeO2) Nanoparticles. Phys. B 2021, 600, 412562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Wu, X.; Chen, Z.; Huang, Z.; Jing, G. Oxygen vacancy defect engineering in Mn-doped CeO2 nanostructures for nitrogen oxides emission abatement. Mol. Catal. 2019, 476, 110512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Shen, G.; Wang, Q.; Deng, K.; Liu, M.; Chen, Y.; Gong, Y.; Wang, Z. Roles of Oxygen Vacancies of CeO2 and Mn-Doped CeO2 with the Same Morphology in Benzene Catalytic Oxidation. Molecules 2021, 26, 6363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kainbayev, N.; Sriubas, M.; Virbukas, D.; Rutkuniene, Z.; Bockute, K.; Bolegenova, S.; Laukaitis, G. Raman Study of Nanocrystalline-Doped Ceria Oxide Thin Films. Coatings 2020, 10, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Kumar, A.; Sagdeo, A.; Sagdeo, P.R. Doping-Induced Combined Fano and Phonon Confinement Effect in La-Doped CeO2: Raman Spectroscopy Analysis. J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 2648–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraynis, O.; Lubomirsky, I.; Livneh, T. Resonant Raman Scattering in Undoped and Lanthanide-Doped CeO2. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 24111–24117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, T.; Singh, K.; Kolte, J. Effect of Intrinsic and Extrinsic Oxygen Vacancies on the Conductivity of Gd-Doped CeO2 Synthesized by a Sonochemical Route. J. Phys. Chem. C 2022, 126, 18018–18028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, H.T.; Balaji, E.; Dutta, S.; Das, N.; Das, P.; Mondal, A.; Imran, M. Recent trend of CeO2-based nanocomposites electrode in supercapacitor: A review on energy storage applications. J. Energy Storage 2022, 50, 104643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kumari, K.; Alvi, P.A.; Dalela, S. Study of the electronic structure of Ce0.95 Fe0.05 O2-δ thin film using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. J. Electron Spectros. Relat. Phenom. 2021, 250, 147073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, K.; Aljawfi, R.N.; Katharria, Y.S.; Dwivedi, S.; Chae, K.H.; Kumar, R.; Alshoaibi, A.; Alvi, P.A.; Dalela, S.; Kumar, S. Study the contribution of surface defects on the structural, electronic structural, magnetic, and photocatalyst properties of Fe: CeO2 nanoparticles. J. Electron Spectros. Relat. Phenom. 2019, 235, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, R.; Ravi, G.; Vijayaprasath, G.; Rajendran, S.; Thaiyan, M.; Nallappan, M.; Gopalan, M.; Hayakawa, Y. Ni-CeO2 spherical nanostructures for magnetic and electrochemical supercapacitor applications. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 4396–4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Li, Z.; Li, H.; Wu, Z.; Shen, W.; Fu, Y.Q. Mesoporous Zr-doped CeO2 nanostructures as superior supercapacitor electrode with significantly enhanced specific capacity and excellent cycling stability. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 331, 135366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, W.; Ali, F.; Raza, N.; Luo, Y.; Kim, K.H.; Yang, J.; Kumar, S.; Mehmood, A.; Kwon, E.E. Recent advancements in supercapacitor technology. Nano Energy 2018, 52, 441–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, K.; Santhoshkumar, P.; Jo, Y.N.; Sivagami, I.N.; Kang, S.H.; Joe, Y.C.; Lee, C.W. Highly porous CeO2 nanostructures prepared via combustion synthesis for supercapacitor applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 449, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyaranjan, A.; Sakthivel, T.S.; Molinari, M.; Sayle, D.C.; Seal, S. Morphology and Crystal Planes Effects on Supercapacitance of CeO2 Nanostructures: Electrochemical and Molecular Dynamics Studies. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2018, 35, 1800176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, M.S.; Kumar, S.; Arshi, N.; Ahmed, F.; Seo, Y.J.; Lee, C.G.; Koo, B.H. Structural and optical study of samarium doped cerium oxide thin films prepared by electron beam evaporation. J. Alloy. Compd. 2011, 509, 4525–4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, J.; Kumar, S.; Vats, V.S.; Alvi, P.A.; Dalela, B.; Phase, D.M. Role of defects and oxygen vacancy on structural, optical and electronic structure properties in Sm- substituted ZnO nanomaterials. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2022, 33, 21546–21568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, K.; Vij, A.; Chae, K.H.; Hashim, M.; Aljawfi, R.N.; Alvi, P.A.; Kumar, S. Near-edge X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy and structural properties of Ni-doped CeO2 nanoparticles. Radiat. Eff. Defects Solids 2017, 172, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, K.; Aljawfi, R.N.; Chawla, A.K.; Kumar, R.; Alvi, P.A.; Alshoaibi, A.; Vij, A.; Ahmed, F.; Abu-samak, M.; Kumar, S. Engineering the optical properties of Cu doped CeO2 NCs for application in white LED. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 7482–7488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Ahmed, F.; Anwar, M.S.; Choi, H.K.; Chung, H.; Koo, B.H. Signature of room temperature ferromagnetism in Mn doped CeO2 nanoparticles. Materials Research Bulletin 2012, 47, 2980–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kumari, K.; Alharthi, F.A.; Ahmed, F.; Naji, R.; Alvi, P.A.; Kumar, R.; Hashim, M.; Dalela, S. Investigations of TM (Ni, Co) doping on structural, optical and magnetic properties of CeO2 nanoparticles. Vacuum 2020, 181, 109717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akshay, V.R.; Arun, B.; Mandal, G.; Vasundhara, M. Structural, optical and magnetic behavior of sol–gel derived Ni-doped dilute magnetic semiconductor TiO2 nanocrystals for advanced functional applications. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 2519–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, P.; Chalotra, S.; Kaur, H.; Kandasami, A.; Singh, D.P. Role of Bound Magnetic Polaron Model in Sm Doped ZnO: Evidence from Magnetic and Electronic Structures. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2021, 5, 100100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherji, R.; Mathur, V.; Samariya, A.; Mukherji, M. Experimental and theoretical assessment of Fe-doped indium-oxide-based dilute magnetic semiconductors. Philos. Mag. 2019, 99, 2285–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.; Ravi, S. Magnetic properties of Sn1-xNixO2-based diluted magnetic semiconductors. Solid State Commun. 2010, 150, 1570–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvie, L.A.J.; Buseck, P.R. Determination of Ce4+/Ce3+ in electron-beam-damaged CeO2 by electron energy-loss spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1999, 60, 1943–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
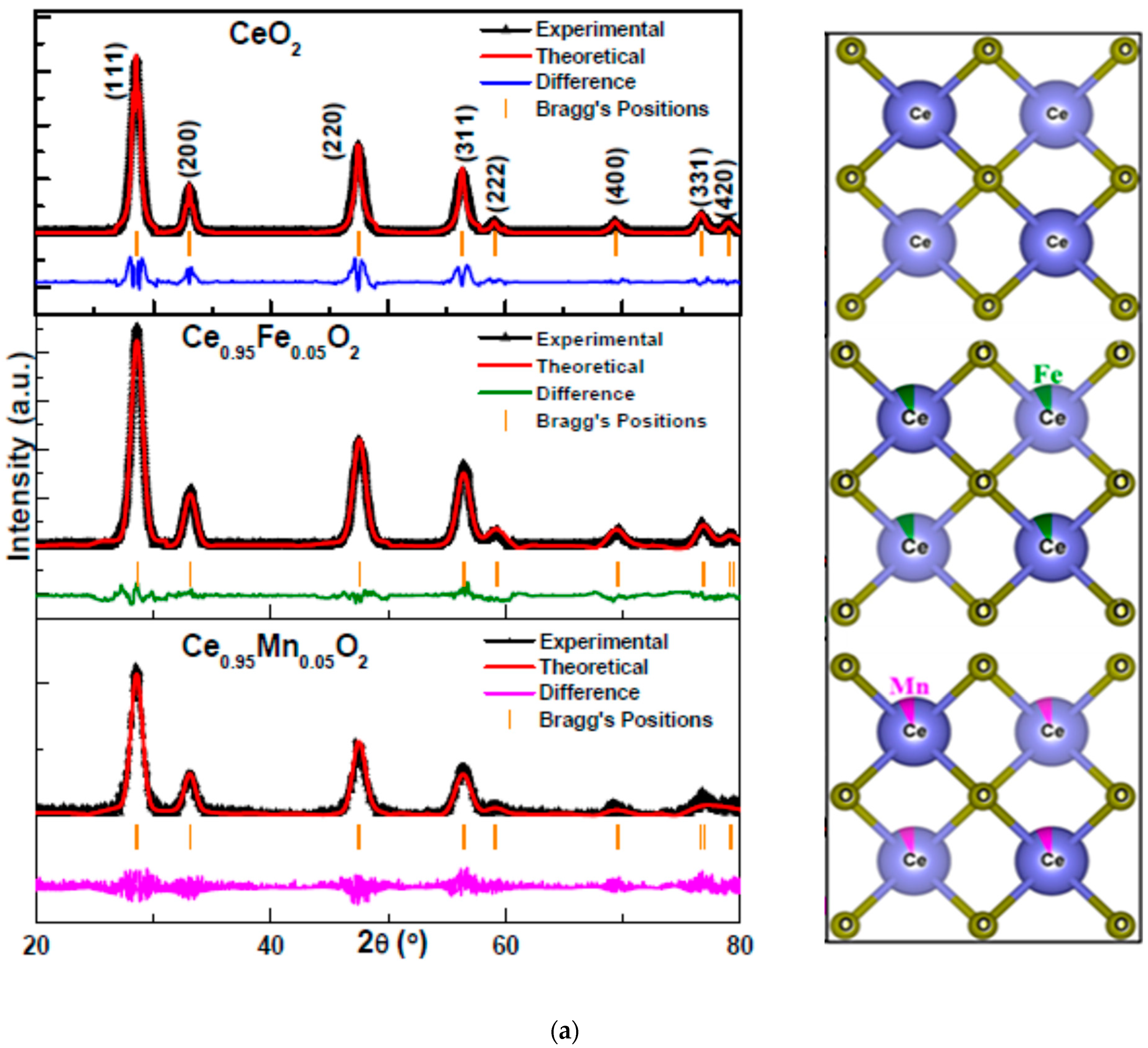
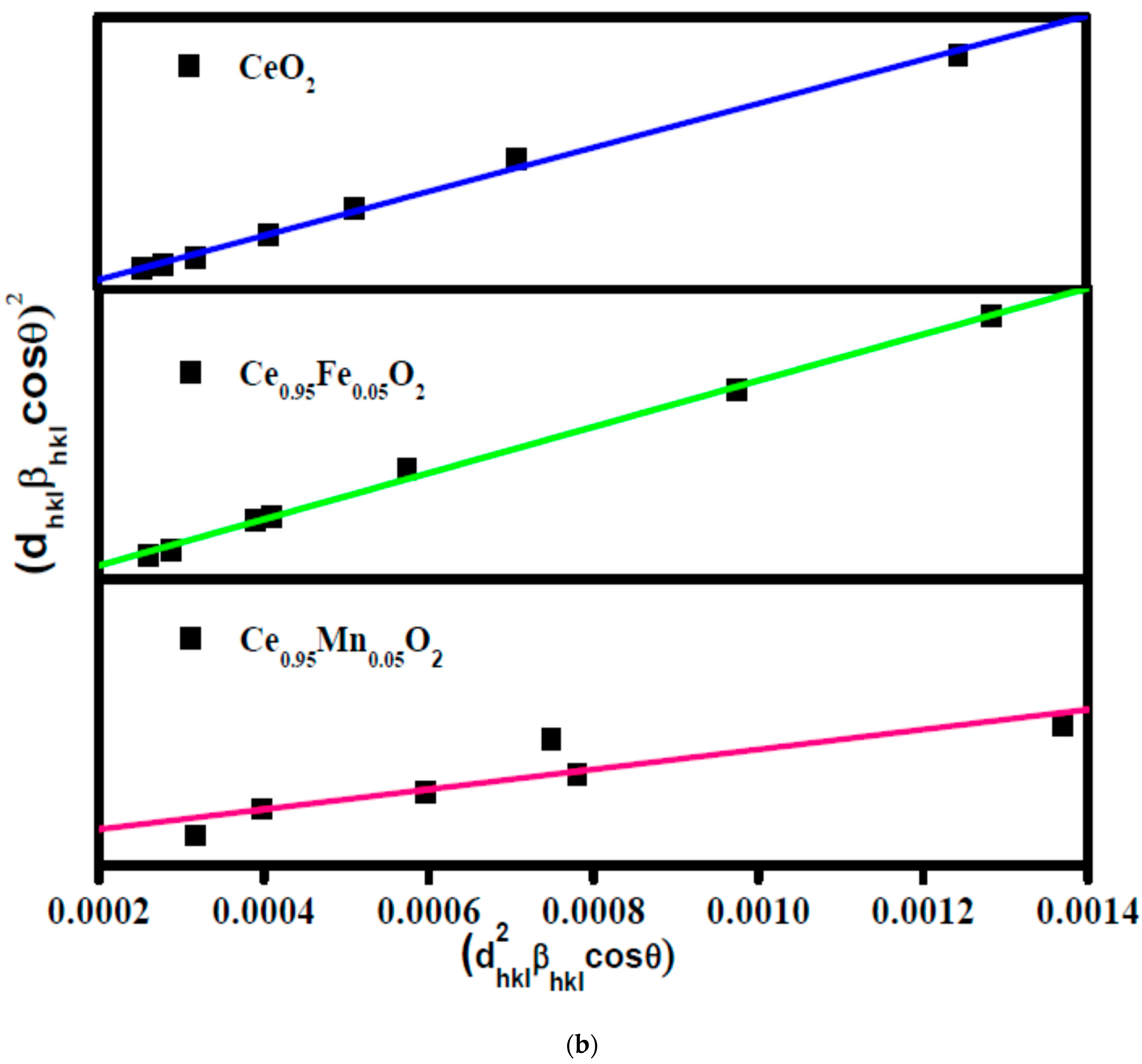
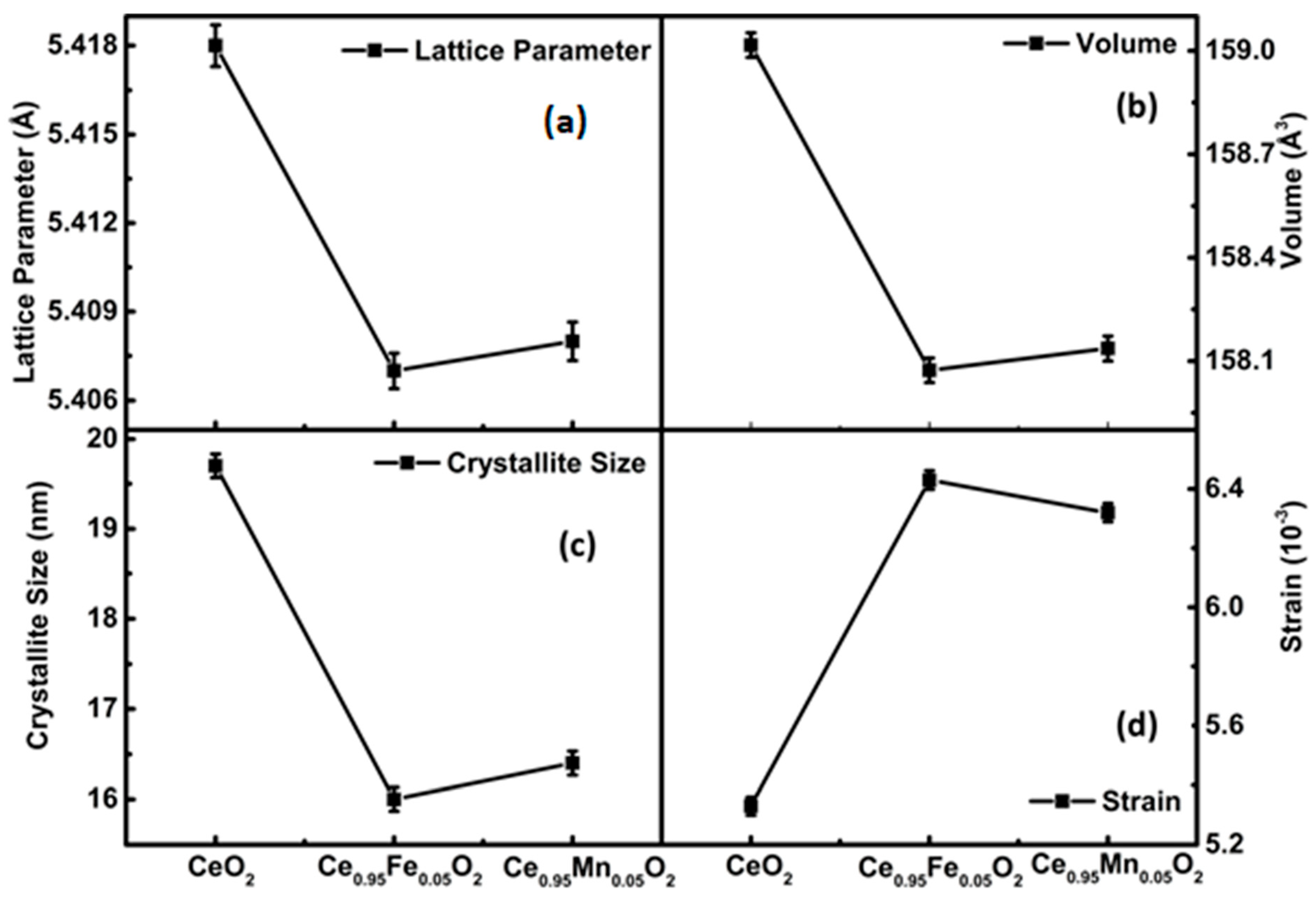
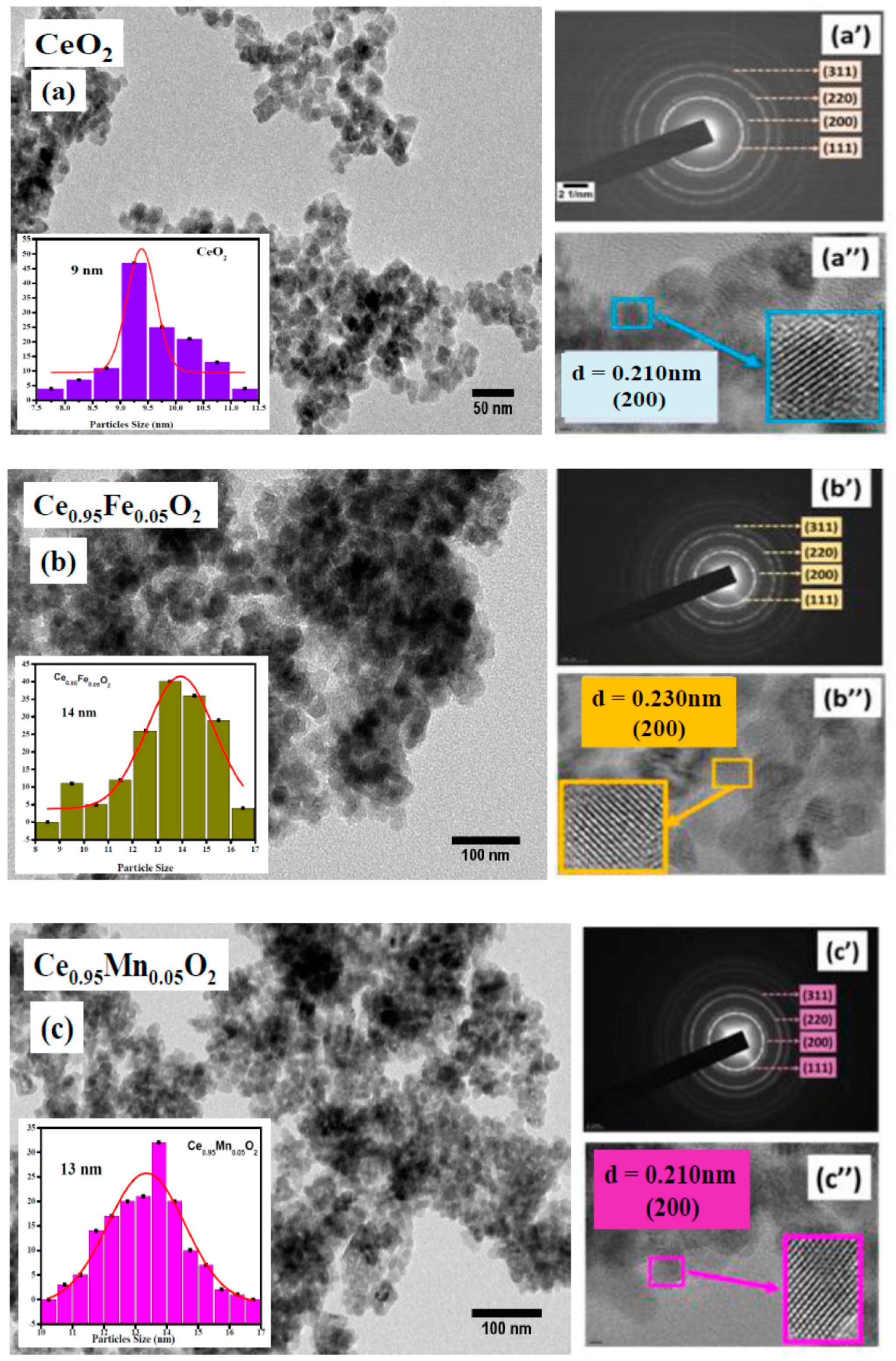


| Rp (%) | Rwp (%) | Rexp (%) | χ2 | Crystallite Size (nm) | Particle Size (nm) | Density ρ (g/cm3) | Occupancy | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | After Refinement | |||||||||
| Scherrer Method | SSP | TEM | Ce/X/O | Ce/X/O | ||||||
| CeO2 | 20.4 | 26.6 | 21.6 | 1.5 | 8.40 | 5.13 | 9 | 7.361 | 0.02083/ 0.04167 | 0.03336/ 0.08165 |
| Ce0.95Fe0.05O2 | 14.2 | 10.1 | 47.2 | 1.4 | 7.14 | 7.37 | 14 | 6.901 | 0.0197885/ 0.001042/ 0.04133 | 0.01956/ 0.00177/ 0.04148 |
| Ce0.95Mn0.05O2 | 31.2 | 40.5 | 35.4 | 1.3 | 6.34 | 7.05 | 13 | 7.350 | 0.0197885/ 0.001042/ 0.04133 | 0.01839/ 0.00142/ 0.04133 |
| Experimental Data | Fitting Parameters Extracted from BMP Model | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ms (emu/g) | Mr (emu/g) | Hc (Oe) | Mo (emu/g) | meff (μB) | N (cm−3) | χm (emu g Oe−1) | |
| CeO2 | 1.5 × 10−4 | 5.7 × 10−6 | 20.0 | 1.97 × 10−4 | 2.12 × 10−16 | 9.3 × 1011 | 5.8 × 10−9 |
| Ce0.95Fe0.05O2 | 3.5 × 10−4 | 3.2 × 10−5 | 60.0 | 0.058 | 0.77 × 10−16 | 7.4 × 1014 | 2.076 × 10−7 |
| Ce0.95Mn0.05O2 | 5.6 × 10−2 | 4.3 × 10−3 | 80.0 | 3.26 × 10−4 | 1.1 × 10−16 | 3.0 × 1014 | 6.02 × 10−9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumar, S.; Ahmed, F.; Shaalan, N.M.; Arshi, N.; Dalela, S.; Chae, K.H. Structural, Optical, Magnetic and Electrochemical Properties of CeXO2 (X: Fe, and Mn) Nanoparticles. Materials 2023, 16, 2290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16062290
Kumar S, Ahmed F, Shaalan NM, Arshi N, Dalela S, Chae KH. Structural, Optical, Magnetic and Electrochemical Properties of CeXO2 (X: Fe, and Mn) Nanoparticles. Materials. 2023; 16(6):2290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16062290
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumar, Shalendra, Faheem Ahmed, Nagih M. Shaalan, Nishat Arshi, Saurabh Dalela, and Keun H. Chae. 2023. "Structural, Optical, Magnetic and Electrochemical Properties of CeXO2 (X: Fe, and Mn) Nanoparticles" Materials 16, no. 6: 2290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16062290
APA StyleKumar, S., Ahmed, F., Shaalan, N. M., Arshi, N., Dalela, S., & Chae, K. H. (2023). Structural, Optical, Magnetic and Electrochemical Properties of CeXO2 (X: Fe, and Mn) Nanoparticles. Materials, 16(6), 2290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16062290











