Synthesis and Sintering Reaction Mechanism of High-Performance MgO-CaO-Fe2O3 Clinker
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Preparation of MgO-CaO-Fe2O3 Clinker
2.2. Characterization of the Prepared Specimens
3. Results and Discussion
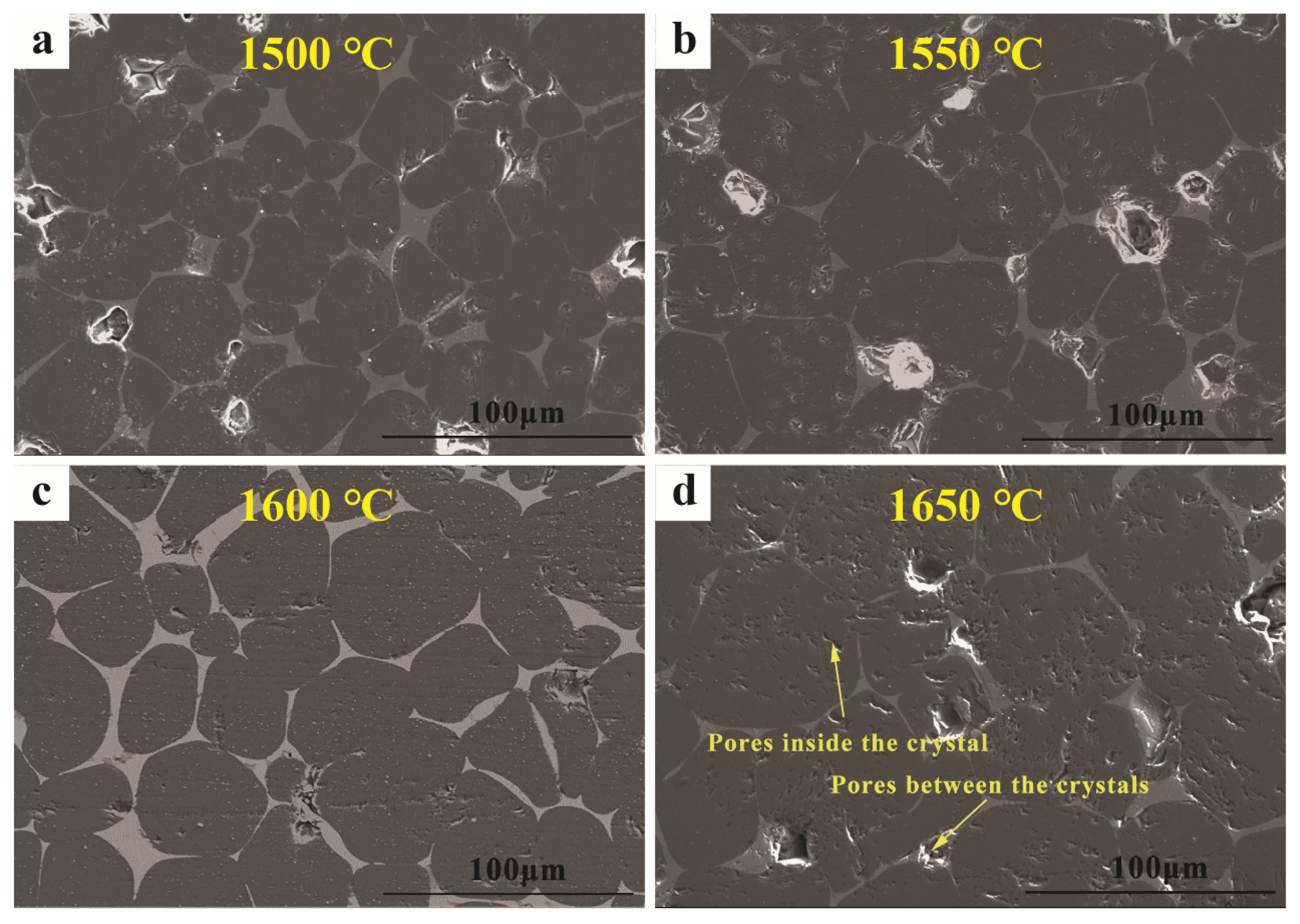
3.1. Performance of the Prepared MgO-CaO-Fe2O3 Clinker
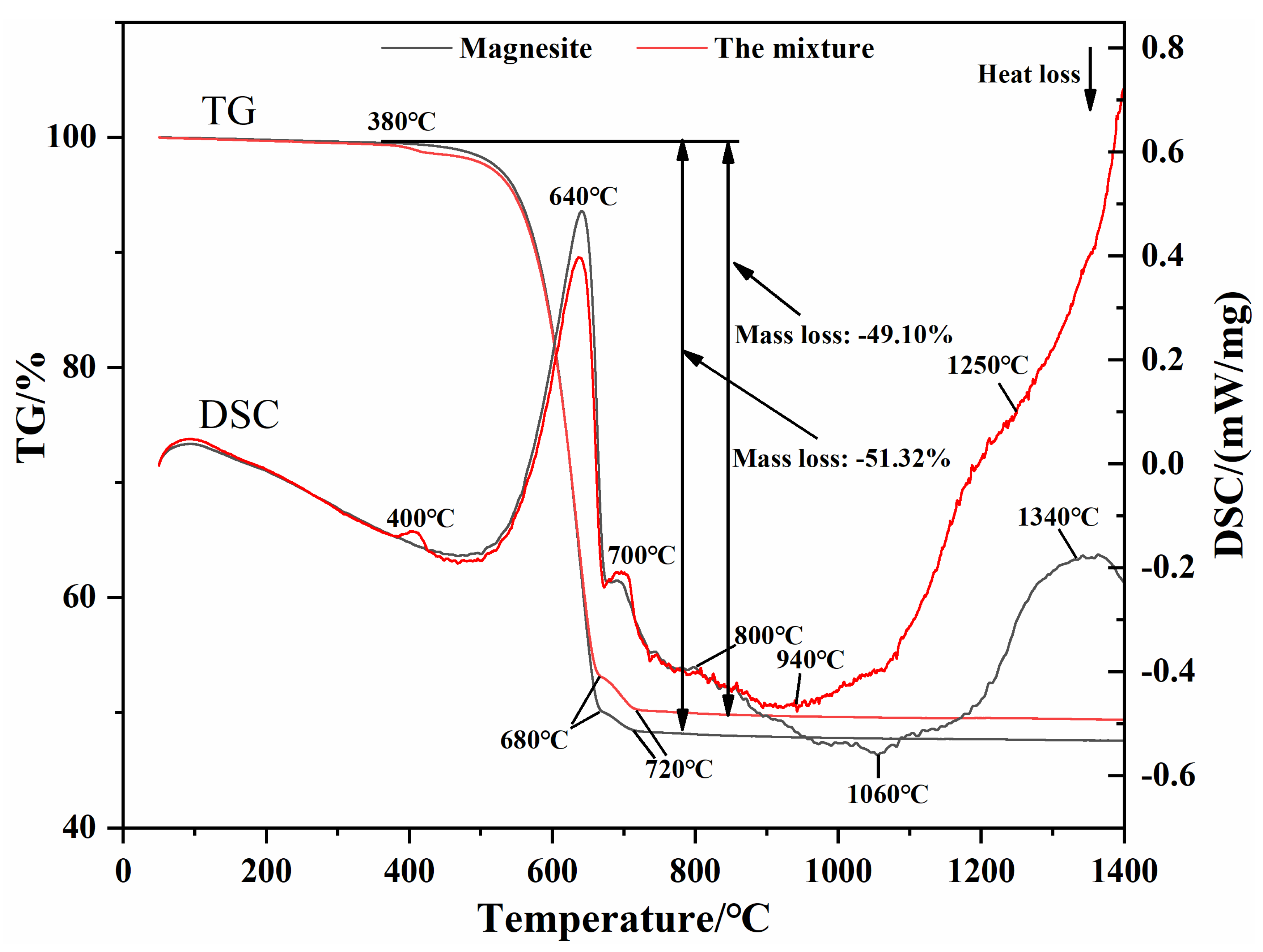
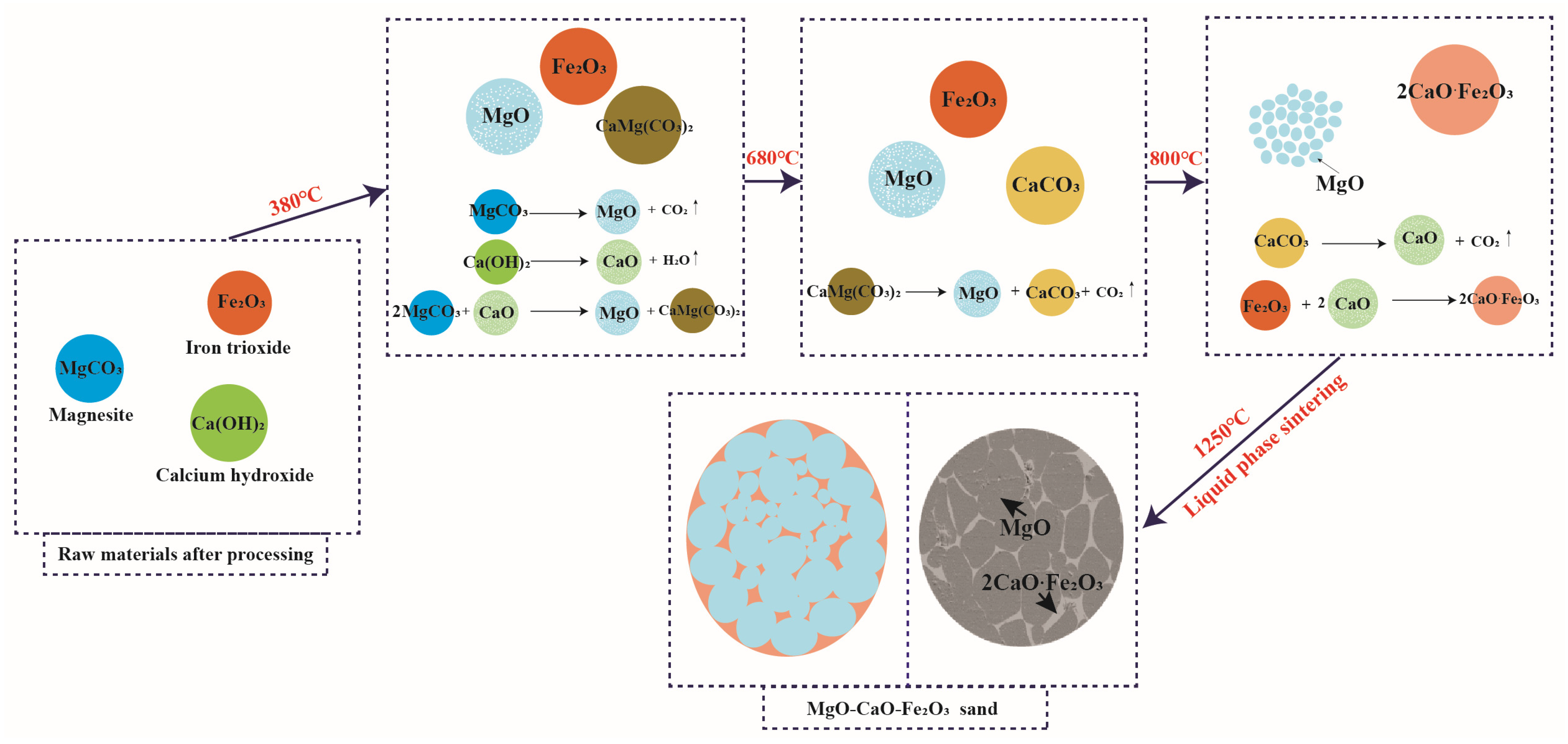
3.2. Synthesis Mechanism of MgO-CaO-Fe2O3 Clinker
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, G.; Yan, L.; Liu, D.; Jin, Y. Characterization and anticorrosion features of the MgO-CaO-Fe2O3 stamped packing used in the electrical arc furnaces for steelmaking. J. Northeast. Univ. 2001, 22, 91–94. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y. Application of dry ramming mix at electric arc furnace bottom. Shandong Yejin 1999, 21, 28–29. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, A. A Comparison of pre-cast bottom materials/designs at Dofasco Inc. Steelmaking Conference Proceedings. Chic. Iron Steel Soc. Am. 1999, 26, 287–297. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Fan, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, F.; Yuan, T. Properties and analysis of MgO-CaO-Fe2O3 dry ramming mix used in UHP-EAF. Met. Collect. 2012, 200, 6–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, Y. Alkaline Amorphous Refractory; Metallurgical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, N.; Guo, X.; Saito, N. Effect of MgO on formation and crystallization behaviors of calcium ferrite during heating and cooling processes. Isij Int. 2018, 58, 1406–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Refractories Handbook; Metallurgical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, Z.; Liu, Q.; Qin, J. Study on the Effect of Basicity on the Densification Behavior of Sinter. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2022, 75, 1545–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, C. MgO-CaO-Fe2O3 basic mix for EAF bottom. Refractory 2000, 34, 347–349. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wei, G.; Luo, M.; Liu, G.; Cao, Y. Application of magnesia calcium iron ramming compound in 150 t DC arc furnace. In Proceedings of the 2021 National Refractory Materials Academic Exchange Conference, Chongqing, China, 10–13 May 2021; pp. 162–166. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Liu, H. Application of furnace bottom ramming mass on 80 t electric furnace. Heavy Cast. Forg. 2008, 6, 29–30+32. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y. Optimization of bottom ramming material of MgO-CaO-Fe2O3 system for electric arc furnace. Spec. Steel 2002, 23, 46–48. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z. Application of bottom ramming material in a 90t shaft arc furnace at Runzhong steelworks. Spec. Steel 1999, 20, 46–47. [Google Scholar]
- Lothenbach, B.; Kulik, D.A.; Matschei, T.; Balonis, M.; Baquerizo, L.; Dilnesa, B.; Myers, R.J.; Miron, G.D. Cemdata18: A chemical thermodynamic database for hydrated Portland cements and alkali-activated materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 115, 472–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matschei, T.; Lothenbach, B.; Glasser, F.P. The role of calcium carbonate in cement hydration. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lothenbach, B.; Matschei, T.; Möschner, G.; Glasser, F.P. Thermodynamic modelling of the effect of temperature on the hydration and porosity of Portland cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cheng, S. Study on alkali capacity of alkali-bearing blast furnace slag based on thermodynamic calculation. Hebei Metallurge. 2023, 63, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, A.; Ren, Y.; Duan, F. Basic Science of Inorganic Nonmetallic Materials; Metallurgical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Qin, M. Synthesis of magnesia-calcia clinker from raw dolomite. Refractory 2012, 46, 107–110. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, B.; Ren, X. Effects of key factors on the densification and grain growth behaviour of sintered magnesia from magnesite. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 35525–35535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Ding, Q.; Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Luo, X.; Duan, F. Microstructural characteristics of refractory magnesia produced from macrocrystalline magnesite in China. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 22701–22708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
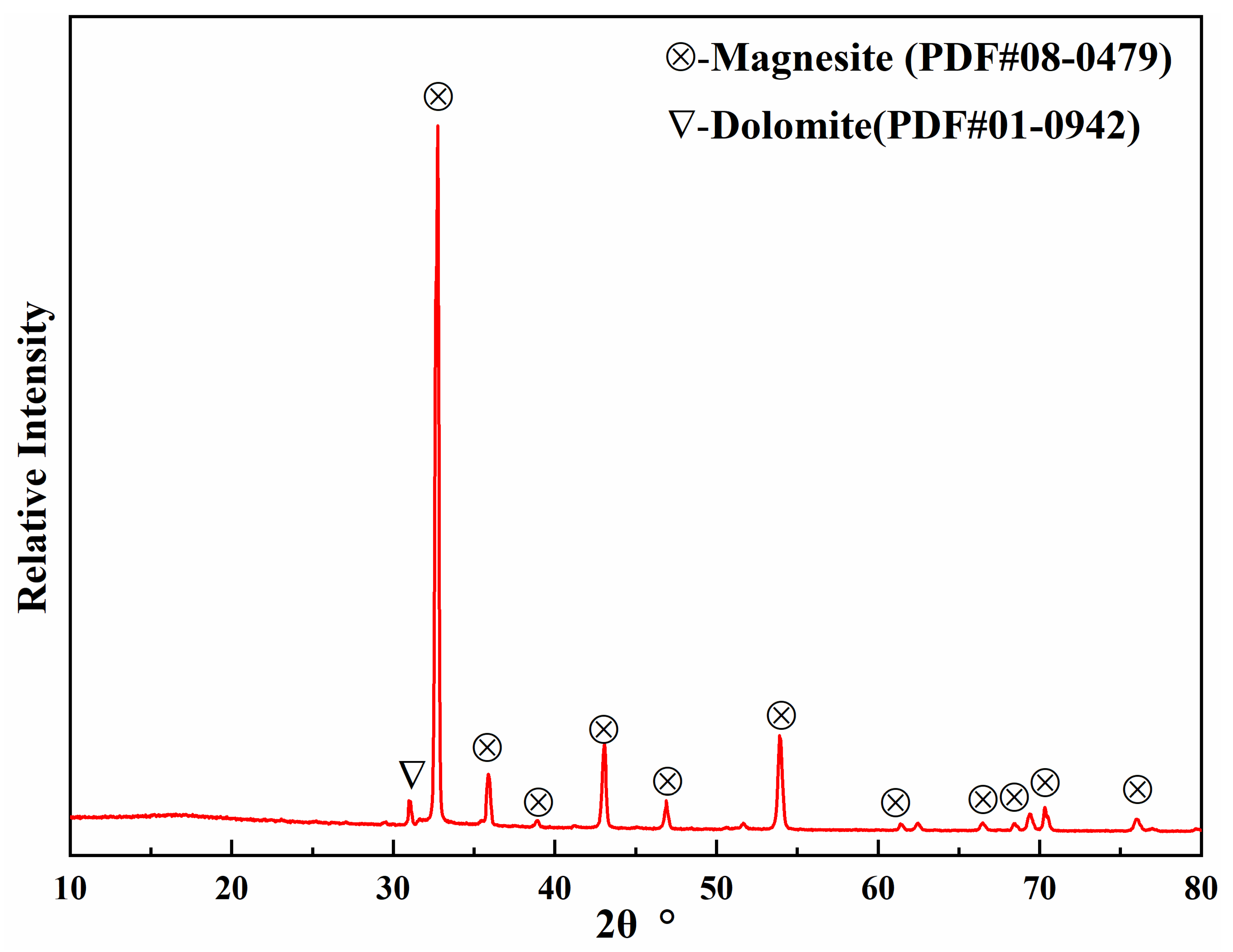
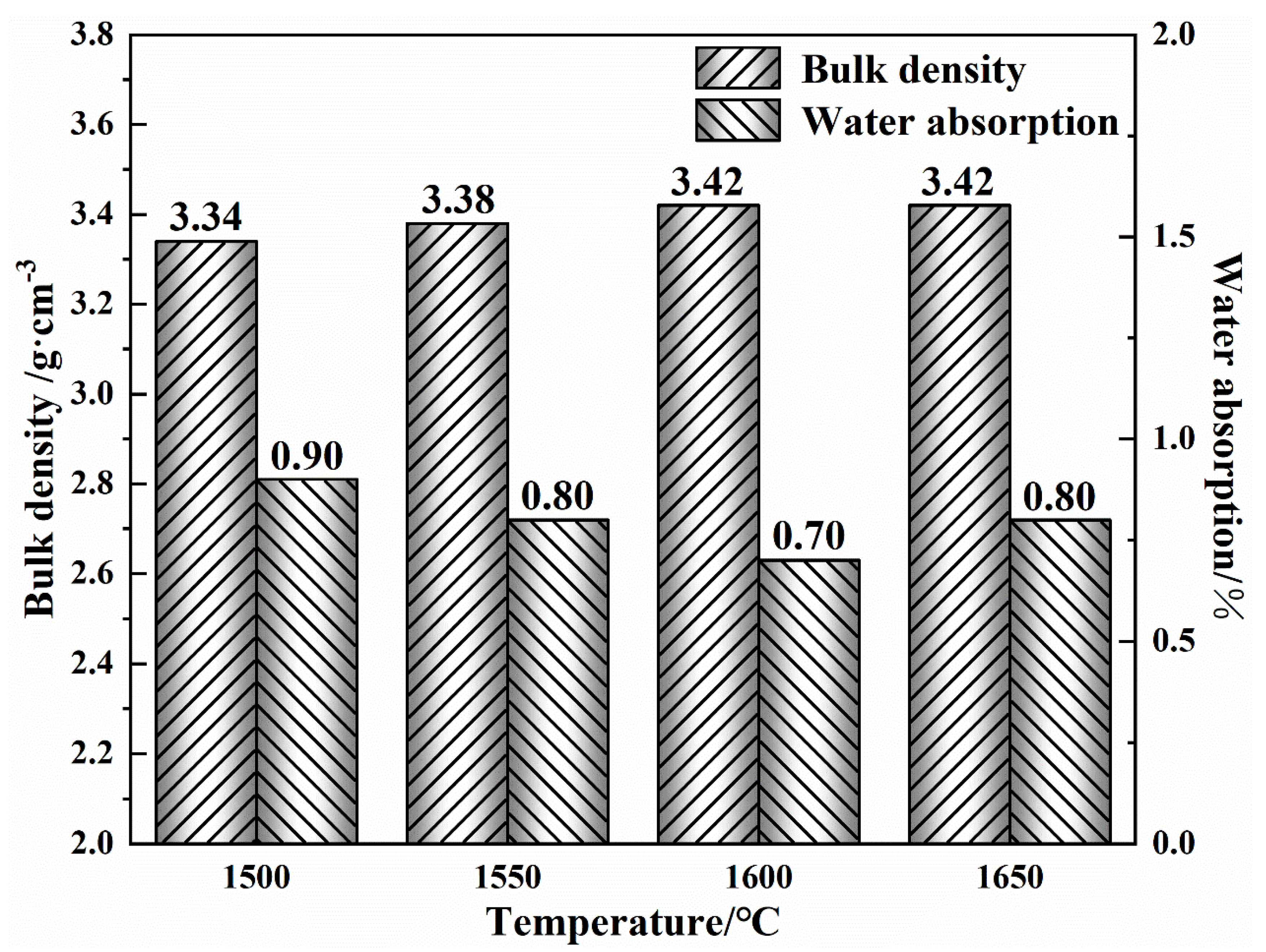
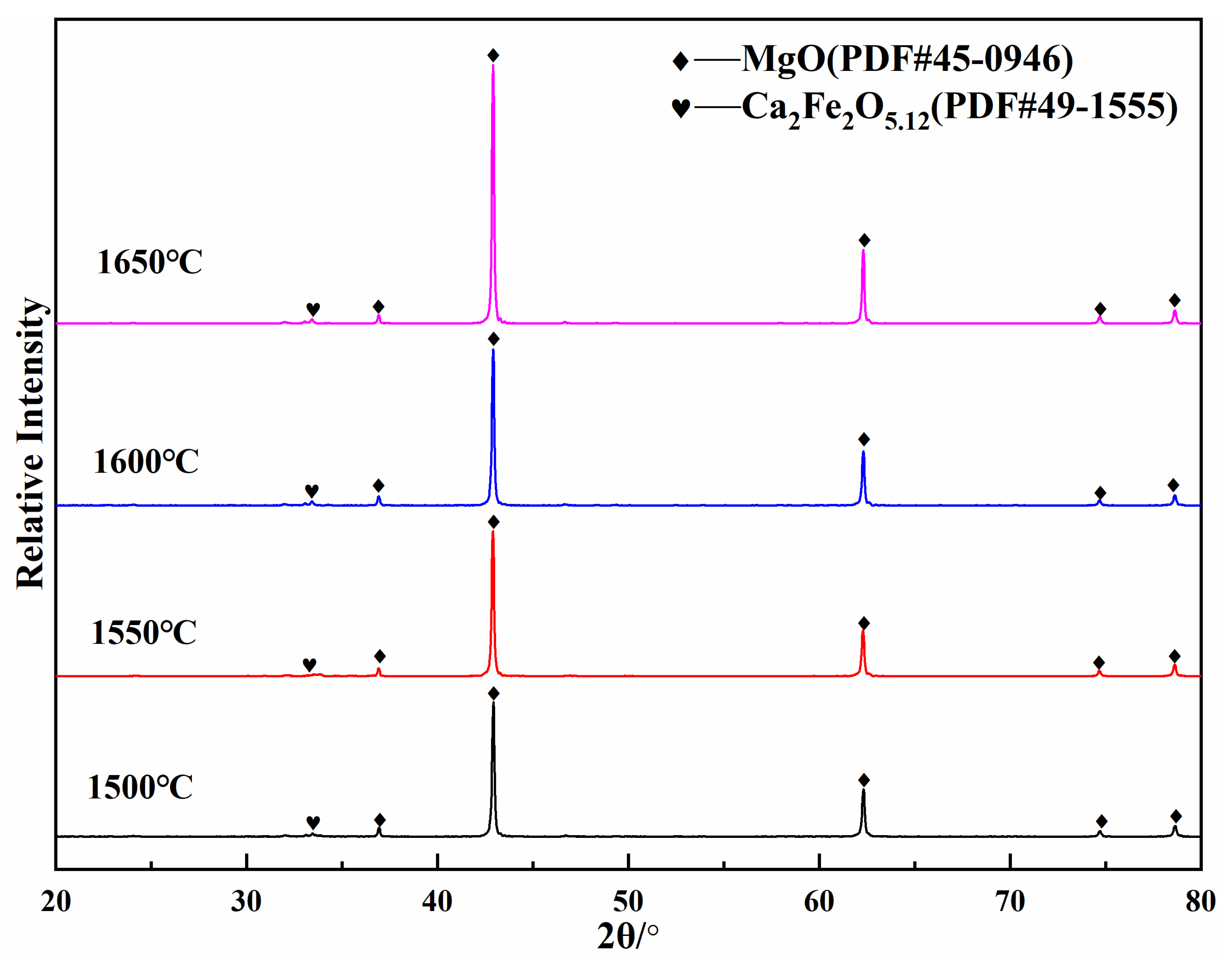
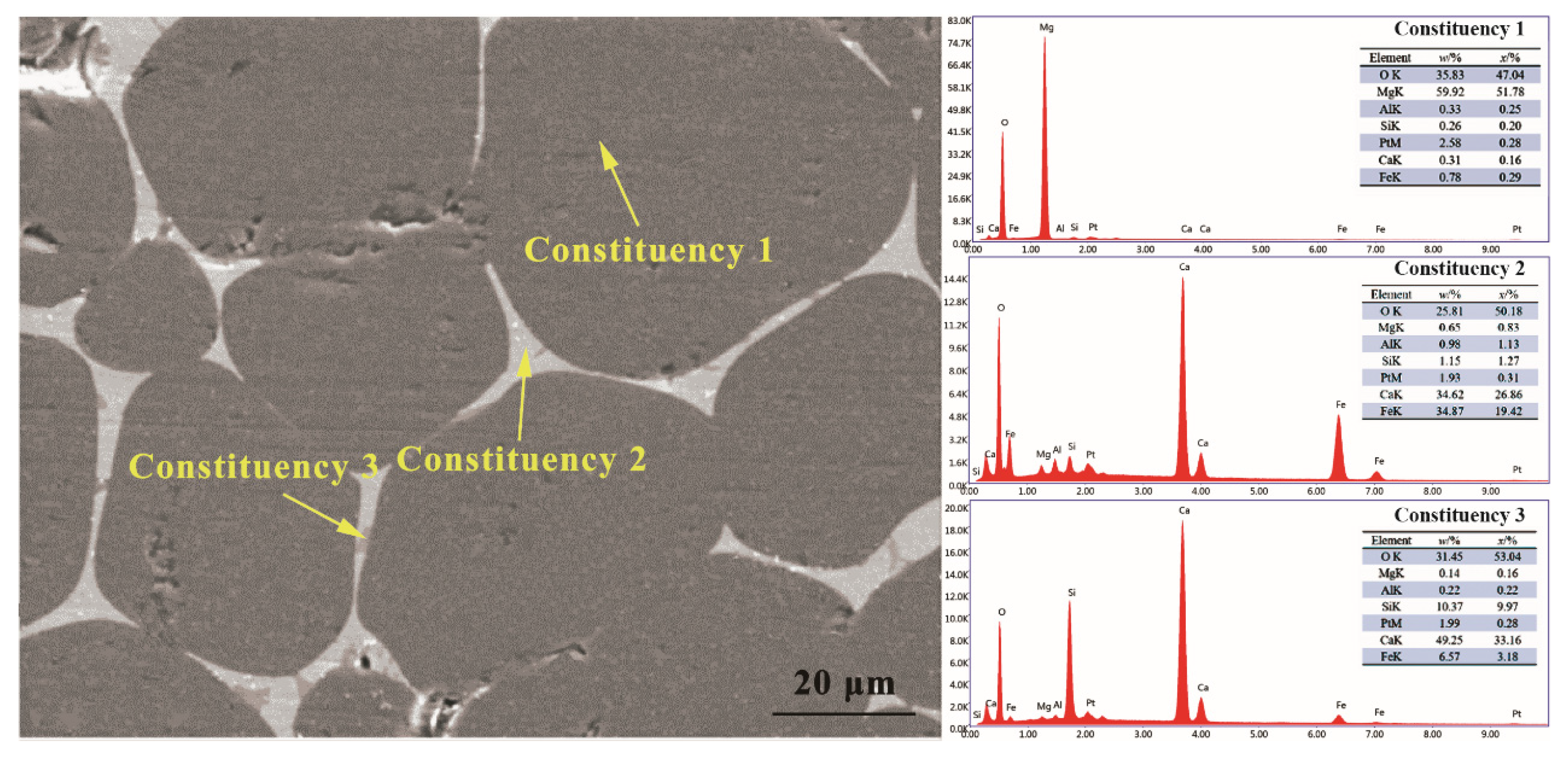

| MgO | CaO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | LoI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Magnesite | 44.97 | 1.99 | 0.43 | 0.13 | 0.58 | 51.95 |
| Bulk Density before Refiring /g·cm3 | Refiring Temperature /°C | Heating-Permanent Line Change after Refiring /% | Compressive Strength after Refiring /MPa | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MgO-CaO-Fe2O3 | 3.42 | 1300 | −0.5 | 17.9 |
| 1600 | −2.5 | 39.1 | ||
| DHL-81 | 3.25 | 1300 | −0.2~−0.5 | ≥10 |
| 1600 | −2.0~−3.0 | ≥30 |
| Temperatures /°C | Reaction (2) | Reaction (5) | Reaction (7) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔH /kJ·mol | ΔG /kJ·mol | ΔH /kJ·mol | ΔG /kJ·mol | ΔH /kJ·mol | ΔG /kJ·mol | |
| 200 | 100.004 | 17.989 | −102.077 | −107.386 | −40.330 | −52.972 |
| 300 | 98.986 | 0.744 | −103.502 | −108.377 | −40.405 | −55.644 |
| 400 | 97.583 | −16.291 | −105.406 | −109.077 | −40.907 | −58.269 |
| 500 | 95.773 | −33.088 | −107.764 | −109.461 | −41.980 | −60.781 |
| 600 | 93.530 | −49.624 | −110.566 | −109.511 | −43.895 | −63.106 |
| 700 | 90.828 | −65.877 | −113.812 | −109.215 | −46.860 | −65.143 |
| 800 | 87.649 | −81.829 | −117.507 | −108.563 | −47.118 | −67.001 |
| 900 | 83.970 | −97.461 | −121.656 | −107.545 | −47.009 | −68.859 |
| 1000 | 20.807 | −112.291 | −244.197 | −105.221 | −46.961 | −70.724 |
| 1100 | 16.795 | −122.592 | −247.847 | −94.159 | −47.025 | −72.590 |
| 1200 | 12.892 | −132.605 | −250.672 | −82.859 | −47.228 | −74.445 |
| 1300 | 9.089 | −142.356 | −252.678 | −71.396 | −47.578 | −76.282 |
| 1400 | 5.378 | −151.868 | −253.877 | −59.829 | −48.092 | −78.092 |
| 1500 | 1.754 | −161.160 | −254.277 | −48.215 | 105.501 | −84.387 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Y.; Wang, J.; Tian, X.; Yang, Y.; Hou, X. Synthesis and Sintering Reaction Mechanism of High-Performance MgO-CaO-Fe2O3 Clinker. Materials 2023, 16, 2086. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16052086
Gao Y, Wang J, Tian X, Yang Y, Hou X. Synthesis and Sintering Reaction Mechanism of High-Performance MgO-CaO-Fe2O3 Clinker. Materials. 2023; 16(5):2086. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16052086
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Yunqin, Jiawei Wang, Xiaoli Tian, Yanlong Yang, and Xing Hou. 2023. "Synthesis and Sintering Reaction Mechanism of High-Performance MgO-CaO-Fe2O3 Clinker" Materials 16, no. 5: 2086. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16052086
APA StyleGao, Y., Wang, J., Tian, X., Yang, Y., & Hou, X. (2023). Synthesis and Sintering Reaction Mechanism of High-Performance MgO-CaO-Fe2O3 Clinker. Materials, 16(5), 2086. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16052086




