Development of an Innovative Glass/Stainless Steel/Polyamide Commingled Yarn for Fiber–Metal Hybrid Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
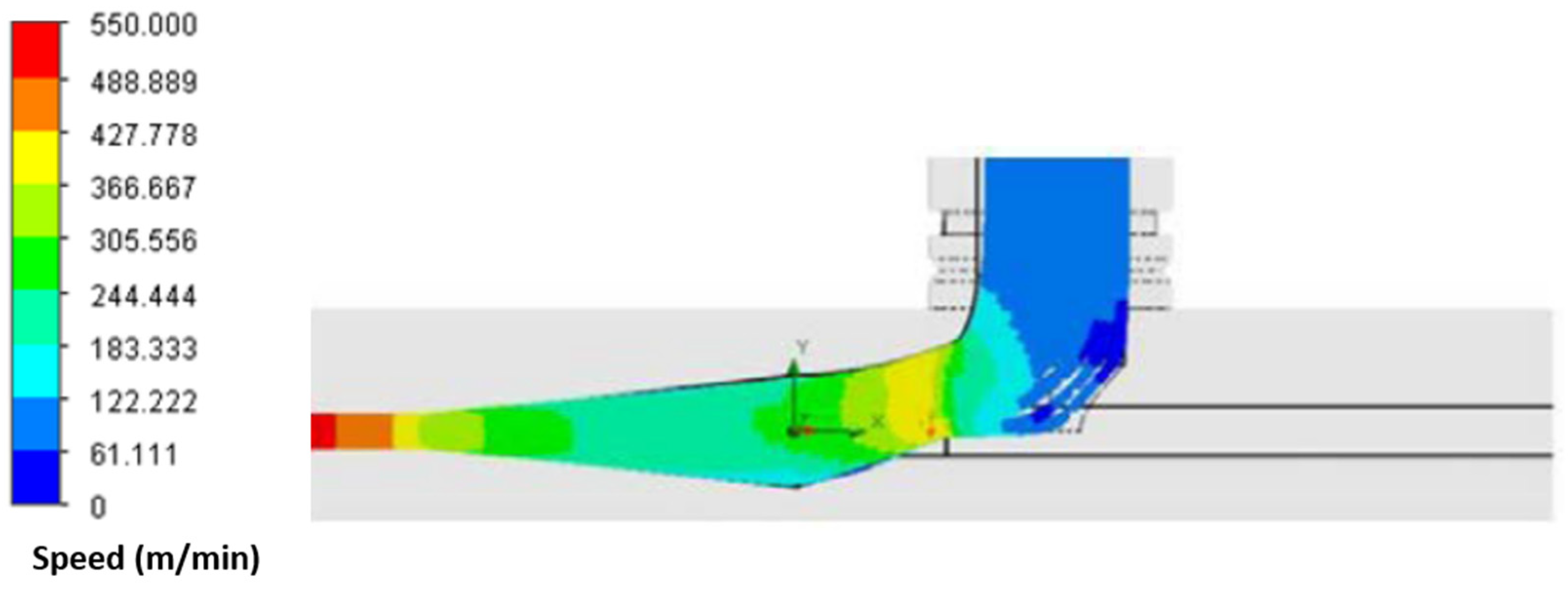
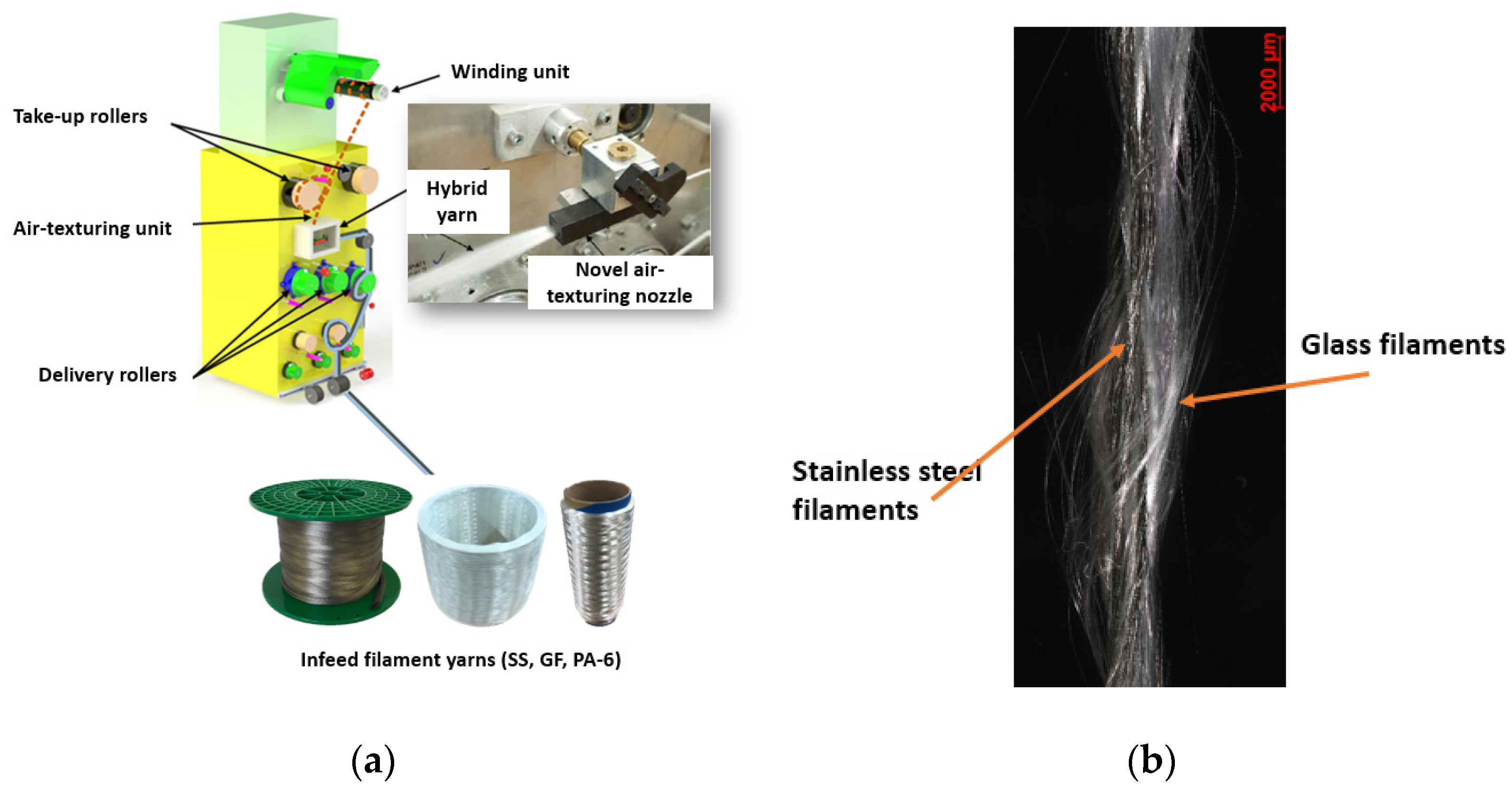
2.1. Development of Air-Texturing Nozzle for Processing Metal Filament Yarn
- In order to avoid turbulence or perpendicular flow in the compressed air against the fiber guiding direction, the flow generated by air pressure needed to be as parallel as possible to the fiber guiding direction at the first contact with the fibers.
- In order to overcome the high bending stiffness of the heavy metal filament yarn, the flow velocity needed to be at a maximum before reaching the outlet cross section of the nozzle unit. The decisive parameters for this were the angle and profile of the air channel as well as the profile of the yarn outlet in the nozzle design.
- ➢
- The filament feeding needed to not negatively influence the airflow.
- ➢
- The supersonic flow created by the Laval element needed to be guided along the airflow in such a way that the filaments were moved in a preferential direction.
- ➢
- The filaments needed to preferably be deflected with large radii transverse to the yarn direction. Furthermore, the filaments needed to be deflected in such a way that the different types of fibers were homogeneously distributed in the yarn cross-section.
2.2. Development of Innovative Hybrid Yarns
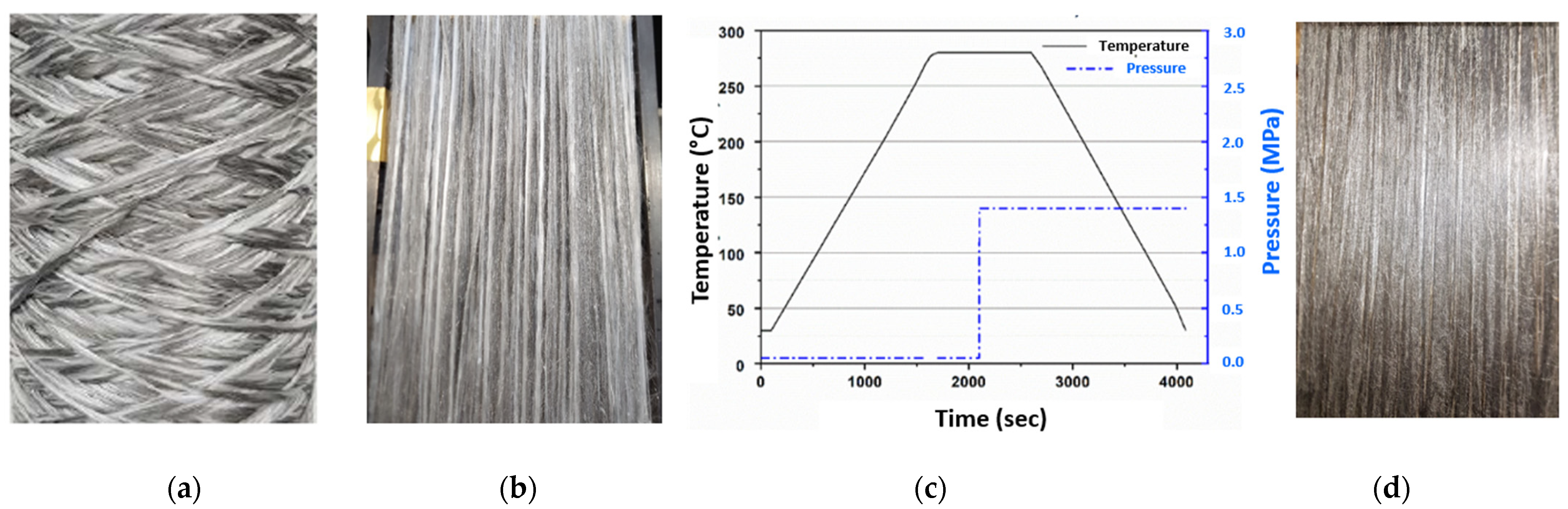
2.3. Development of Unidirectional Composites
2.4. Characterization of Fibers, Hybrid Yarns and Composites
3. Results and Discussion
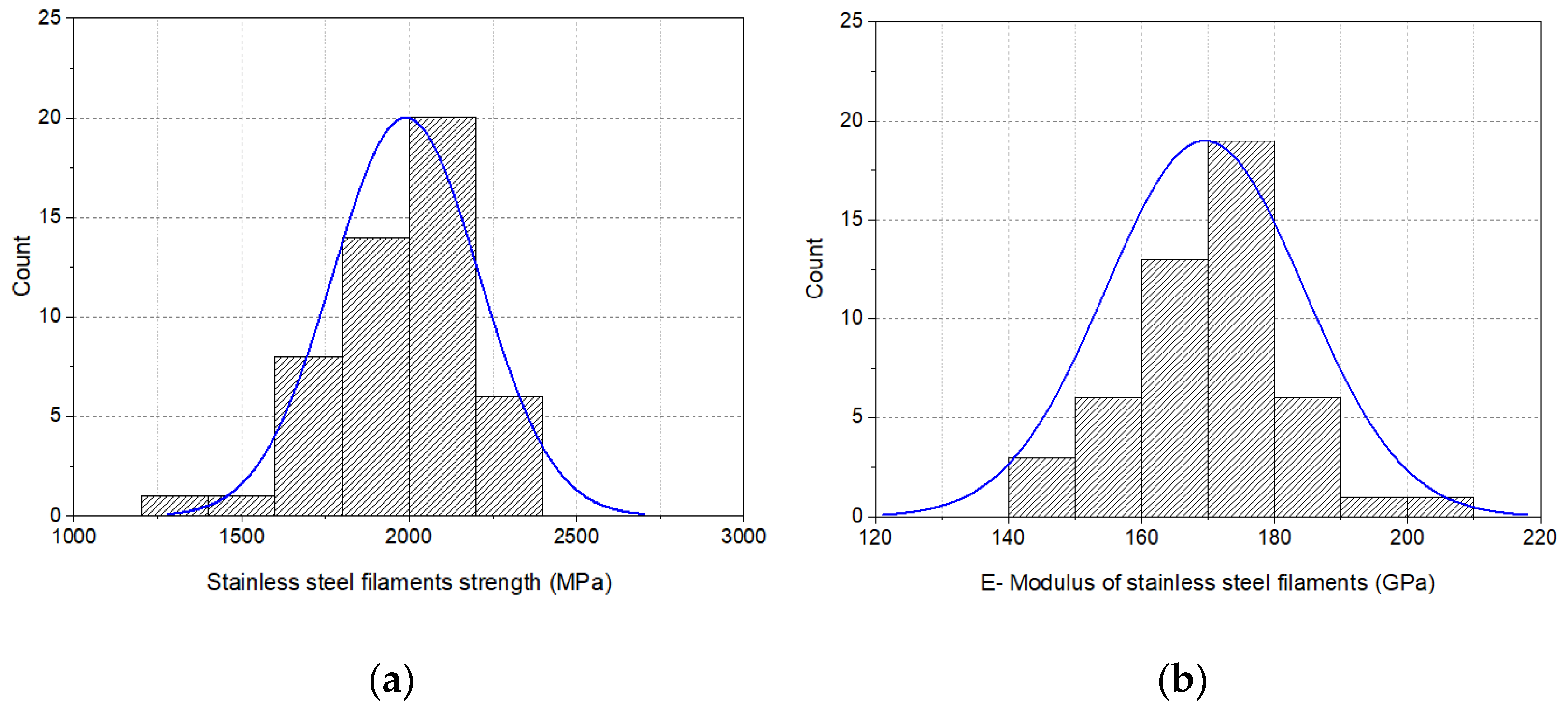
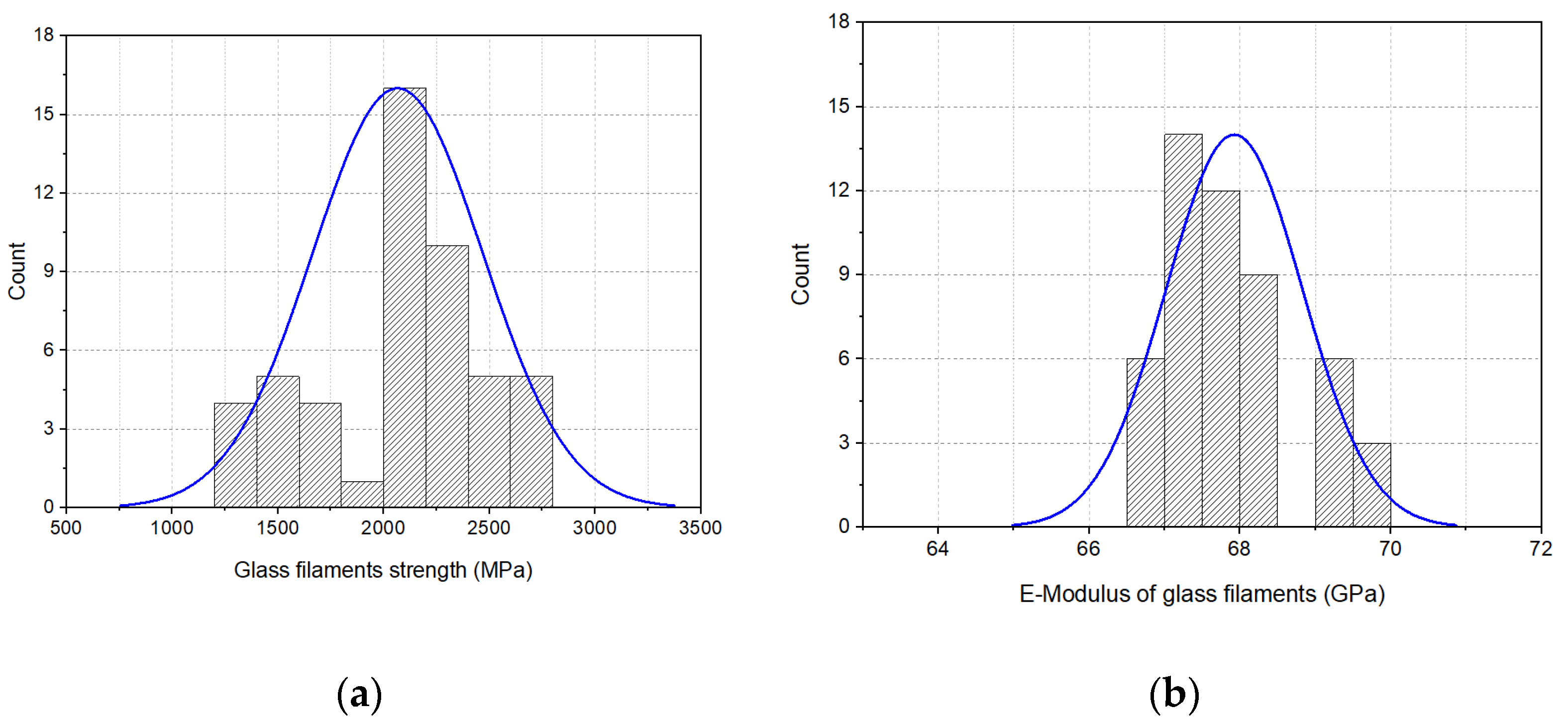
3.1. Properties of Metal and Glass Filaments
3.1.1. Surface Morphology and Topography
3.1.2. Tensile Properties
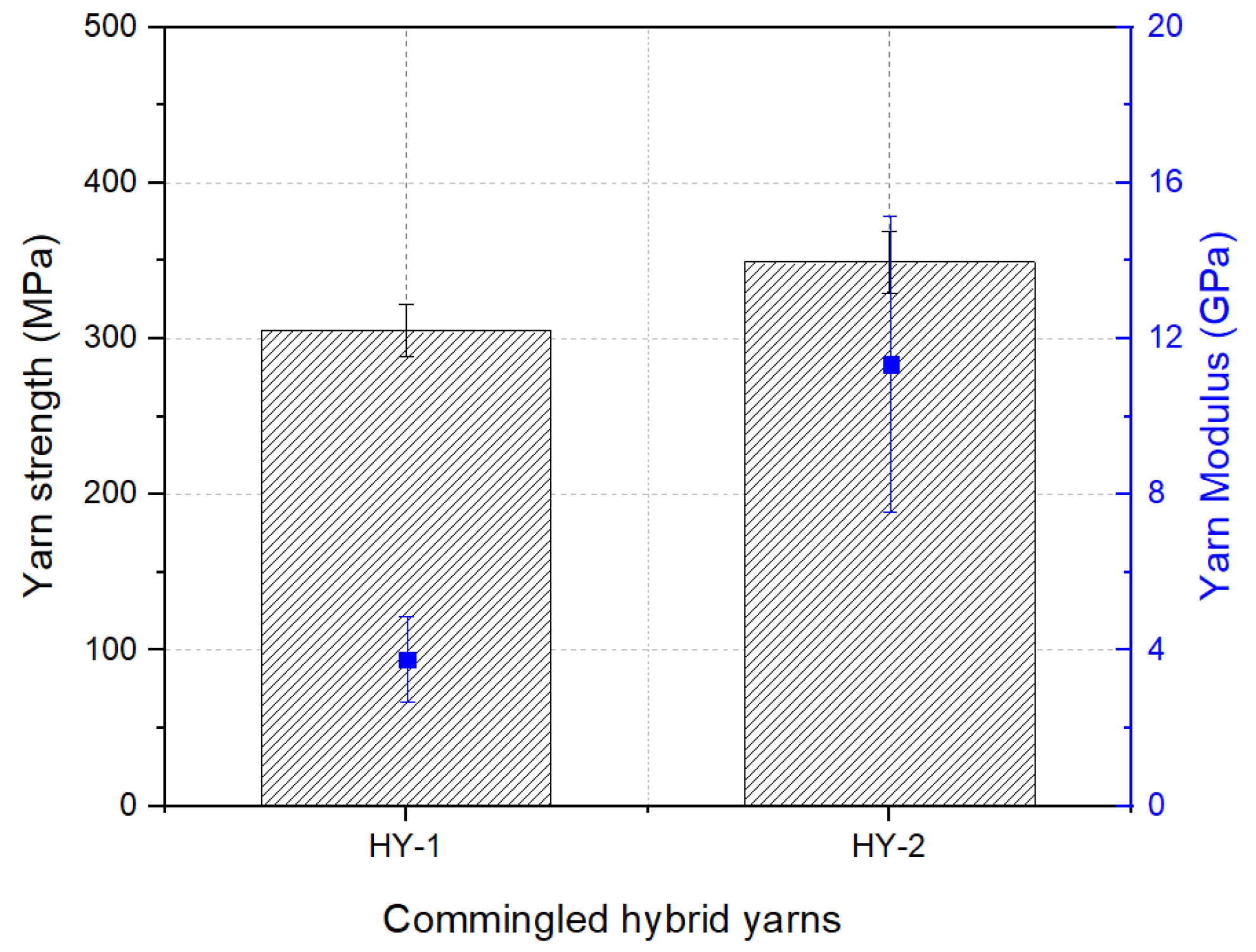
3.2. Properties of GF/Stainless-Steel/PA6 Hybrid Yarns
3.3. Properties of Composites Based on GF/Stainless-Steel/PA6 Commingled Yarn
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hannemann, B.; Backe, S.; Schmeer, S.; Balle, F.; Breuer, U.P. Metal fiber incorporation in carbon fiber reinforced polymers (CFRP) for improved electrical conductivity. Mater. Und Werkst. 2016, 47, 1015–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albracht, F. Metallfasern als Schallabsorbierende Strukturen und als Leitfähige Komponenten in Verbundwerkstoffen. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität Dresden, Dresden, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Offermann, R.; Mägel, M. Textile Verarbeitung von Stahlfasern und Stahlfäden für Technische Anwendungen; Verlag und Vertriebsgesellschaft GmbH: Düsseldorf, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Flemming, M.; Roth, S. Faserverbundbauweisen: Eigenschaften: Mechanische, Konstruktive, Thermische, Elektrische, Ökologische, Wirtschaftliche Aspekte; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2003; ISBN 9783540408253. [Google Scholar]
- Loy, W. Chemiefasern für Technische Textilprodukte: Standardtypen, Modifikationen, Ein-Satzgebiete, 2; Auflage, Dt. Fachverl.: Frankfurt, Germany, 2008; ISBN 3866411979. [Google Scholar]
- AVK—Industrievereinigung Verstärkte Kunststoffe e.V (Hrsg.). Handbuch Faserverbund-Kunststoffe. Grundlagen, Verarbeitung, Anwendungen, 3; Auflage, Vieweg & Teubner Verlag: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2010; ISBN 3834808814. [Google Scholar]
- Ganesh; Chavhan, R.; Lalit; Wankhade, N. Improvement of the mechanical properties of hybrid composites prepared by fibers, fiber-metals, and nano-filler particles—A review. Mater. Today: Proc. 2020, 27, 72–82. [Google Scholar]
- Cherif, C. Textile Materials for Lightweight Constructions-Technologies—Methods—Materials Properties; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Vlot Ad Gunnink, J.W. Fiber Metal Laminates an Introduction; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Antipov, V.; Senatorova, O.; Beumler, T.; Ijpma, M. Investigation of a new fibre metal lam-inate (FML) family on the base of Al-Li-Alloy with lower density. Mater. Und Werkst. 2012, 43, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marissen, R. Flight simulation behavior of aramid-reinforced aluminum laminates (ARALL). Eng. Fract. Mech. 1984, 19, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürger, A. Herstellung von Polymerfaser-Aluminium-Verbundwerkstoffen und deren thermische Volumen- und Formänderungen; VDI-Verl.: Düsseldorf, Germany, 1992; ISBN 9783181450055. [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbeek, M. Characterisation of Fibre Metal Laminates under Thermo-Mechanical Loadings. Ph.D. Thesis, TU Delft, Delft, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnakumar, S. Fiber Metal Laminates-The Synthesis of Metals and Composites. Mater. Manuf. Process. 1994, 9, 295–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gresham, J.; Cantwell, W. Drawing behavior of metal-composite sandwich structures. Compos. Struct. 2006, 75, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Wang, H.; Luo, J.; Li, N. A review on forming technologies of fibre metal laminates. Int. J. Lightweight Mater. Manuf. 2021, 4, 110–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekar, M.; Ishak, M.R.; Jawaid, M.; Leman, Z.; Sapuan, S.M. An experimental review on the mechanical properties and hygrothermal behaviour of fibre metal laminates. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2017, 36, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolnicki, M.; Lesiuk, G.; Duda, S.; de Jesus, A.M.P. A Review on Finite-Element Simulation of Fibre Metal Laminates. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2022, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlot, A. Impact loading on fibre metal laminates. Int. J. Impact Eng. 1996, 18, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderliesten, R. Fatigue and Fracture of Fibre Metal Laminates; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Karunagaran, N.; Bharathiraja, G.; Muniappan, A.; Yoganandam, K. Energy absorption and damage behaviour of surface treated glass fibre/stainless steel wire mesh reinforced hybrid composites. Mater. Today: Proc. 2020, 22, 1078–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, J.G.; Cantwell, W.J. Scaling effects in the tensile behavior of fiber-metal laminates. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 1684–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Yang, J.-M. The mechanical behavior of GLARE laminates for aircraft structures. JOM 2005, 57, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadigh, M.; Dariushi, S. An experimental study of the fiber orientation and laminate sequencing effects on mechanical properties of GLARE®. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part G (J. Aero-Space Eng.) 2008, 222, 1015–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudary, M.V.; Nagaraja, A.; Sai, K.O.C.; Balasubramanian, M. Characterization of laminate sandwiched with stainless steel and glass fibre. Mater. Today: Proc. 2020, 22, 847–852. [Google Scholar]
- Corradi, M.; Speranzini, E. Post-Cracking Capacity of Glass Beams Reinforced with Steel Fibers. Materials 2019, 12, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, M.; Morishita, M.; Tomura, S.; Takumida, K. Inelastic behavior and strength of fiber-metal hybrid composite: Glare. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 1998, 40, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, H.; Guo, H.; Zhuang, W. The Plastic Behavior in the Large Deflection Response of Fiber Metal Laminate Sandwich Beams under Transverse Loading. Materials 2022, 15, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baier, H.; Endler, S. Fiber-Metal-Composites for Synthesizing Electro-Magnetic and Mechanical Behavior. In Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Spacecraft Structures, Materials & Environmental Testing, Braunschweig, Germany, 1–4 April 2014; Volume 727, p. 122. [Google Scholar]
- Roh, J.S.; Chi, Y.S.; Kang, T.J.; Nam, S.W. Electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of multifunctional metal composite fabrics. Text. Res. J. 2008, 78, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, G.; Pradeep, P.V. Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Behavior of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Metal Laminates.
- Alderliesten, R.C.; Benedictus, R. Fiber/metal composite technology for future primary aircraft structures. J. Aircr. 2008, 45, 1182–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Ma, J.; Kang, L.; Sun, G.; Li, Q. An experimental study on fatigue characteristics of CFRP-steel hybrid laminates. Mater. Des. 2015, 88, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.F.; Li, Y.R. Deep Drawing Behavior of Metal-Composite Sandwich Plates. Materials 2022, 15, 6612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogelesang, L.B.; Vlot, A. Development of fibre metal laminates for advanced aerospace structures. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2000, 103, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botelho, E.C.; Silva, R.A.; Pardini, L.C.; Rezende, M.C. A review on the development and properties of continuous fiber/epoxy/aluminum hybrid composites for aircraft structures. Mater. Res. 2006, 9, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bourlegat, L.R.; Damato, C.A.; Da Silva, D.F.; Botelho, E.C.; Pardini, L.C. Processing and mechanical characterization of titanium-graphite hybrid laminates. J. Rein-Forced Plast. Compos. 2010, 29, 3392–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, S.; Specht, U.; Spieß, L.; Romanus, H.; Krischok, S.; Himmerlich, M.; Ihde, J. Improved adhesion at titanium surfaces via laser-induced surface oxidation and roughening. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 558, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinmazçelik, T.; Avcu, E.; Bora, M.Ö.; Çoban, O. A review: Fibre metal laminates, background, bonding types and applied test methods. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 3671–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, A.; Artzt, P.; Betz, D. Neues Verfahren zur Hybridgarnherstellung aus Filament und Stapelfasern. Technol. Text. 2004, 47, 72–75. [Google Scholar]
- Cherif, C.; Pfeifer, G.; Hoffmann, G.; Diestel, O.; Rödel, H.; Paul, C. Textile based thermoplastic composites in complex structure with integrated special functions. In Proceedings of the Aachen-Dresden International Textile Conference, Aachen, Germany, 29–30 November 2007; pp. 90–91. [Google Scholar]
- Hufenbach, W. Progress in textile-reinforce composite components for function integrated multi-materials design for complex lightweight applications. In Proceedings of the Aachen-Dresden International Textile Conference, Aachen, Germany, 29–30 November 2007; p. 48. [Google Scholar]
- Cherif, C. Textile Werkstoffe für den Leichtbau. In Techniken-Verfahren-Materialien-Eigenschaften; Springer: Dresden, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Manfred, N.; Mitschang, P.; Breuer, U. (Eds.) Handbuch Verbundwerkstoffe: Werkstoffe, Verarbeitung, Anwendung; Carl Hanser Verlag GmbH Co. KG: Munich, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, K.B.; Ramakrishna, S.; Lee, K.C. Electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of copper/glass fiber knitted fabric reinforced polypropylene composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2000, 31, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Lee, K.; Lin, J. Electromagnetic and electrostatic shielding properties of co-weaving-knitting fabrics reinforced composites. Compos. Part A: Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2004, 35, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.H.; Chiang, S.H.; Lou, C.W. Manufacturing and Mechanical Properties of Grids Braided from Stainless Steel/PP Functional Ply Yarn. J. Adv Mater-Covina 2006, 1, 82–86. [Google Scholar]
- DIN EN ISO 527-2; Plastics—Determination of Tensile Properties Part 2: Test Conditions for Moulding and Extrusion Plastics. DIN: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- Durai Prabhakaran, R.T.; Pillai, S.; Charca, S.; Oshkovr, S.A.; Knudsen, H.; Andersen, T.L.; Lilholt, H. Mechanical characterization and fractography of glass fiber/polyamide (PA6) composites. Polym. Compos. 2015, 36, 834–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan MM, B.; Nitsche, S.; Abdkader, A.; Cherif, C. Carbon fibre reinforced thermoplastic composites developed from innovative hybrid yarn structures consisting of staple carbon fibres and polyamide 6 fibres. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 167, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swolfs, Y.; Gorbatikh, L.; Verpoest, I. Fibre hybridisation in polymer composites: A review. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2014, 67, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Sankar, B.V. Mechanical properties of hybrid composites using finite element method-based micromechanics. Compos. Part B Eng. 2014, 58, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Properties | Unit | Commingled Yarn | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HY-1 | HY-2 | ||
| Glass filament yarn linear density/number of filament yarns | tex/No. | 200/1 | 200/1 |
| Stainless-steel filament yarn linear density/ number of filament yarns | tex/No. | 105/4 | 105/5 |
| Polyamide filament yarn linear density/ number of filament yarns | tex/No. | 47/4 | 47/5 |
| GF/SS volume fraction | % | 26/18 | 22/22 |
| PA-6 volume fraction | % | 56 | 56 |
| Commingled yarn linear density | tex | 835 | 1094 |
| Composite | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental | MRoHM | Error | Experimental | MRoHM | Error | |
| HCY-1 | 47 ± 6 | 49.9 | 6.17 | 640 ± 25 | 748.5 | 14.4 |
| HCY-2 | 55 ± 7 | 53.5 | 2.8 | 710 ± 39 | 802.5 | 12.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdkader, A.; Khurshid, M.F.; Cherif, F.; Hasan, M.M.B.; Cherif, C. Development of an Innovative Glass/Stainless Steel/Polyamide Commingled Yarn for Fiber–Metal Hybrid Composites. Materials 2023, 16, 1668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16041668
Abdkader A, Khurshid MF, Cherif F, Hasan MMB, Cherif C. Development of an Innovative Glass/Stainless Steel/Polyamide Commingled Yarn for Fiber–Metal Hybrid Composites. Materials. 2023; 16(4):1668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16041668
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdkader, Anwar, Muhammad Furqan Khurshid, Fathi Cherif, Mir Mohammad Badrul Hasan, and Chokri Cherif. 2023. "Development of an Innovative Glass/Stainless Steel/Polyamide Commingled Yarn for Fiber–Metal Hybrid Composites" Materials 16, no. 4: 1668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16041668
APA StyleAbdkader, A., Khurshid, M. F., Cherif, F., Hasan, M. M. B., & Cherif, C. (2023). Development of an Innovative Glass/Stainless Steel/Polyamide Commingled Yarn for Fiber–Metal Hybrid Composites. Materials, 16(4), 1668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16041668








