Effect of the Deposit Temperature of ZnO Doped with Ni by HFCVD
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
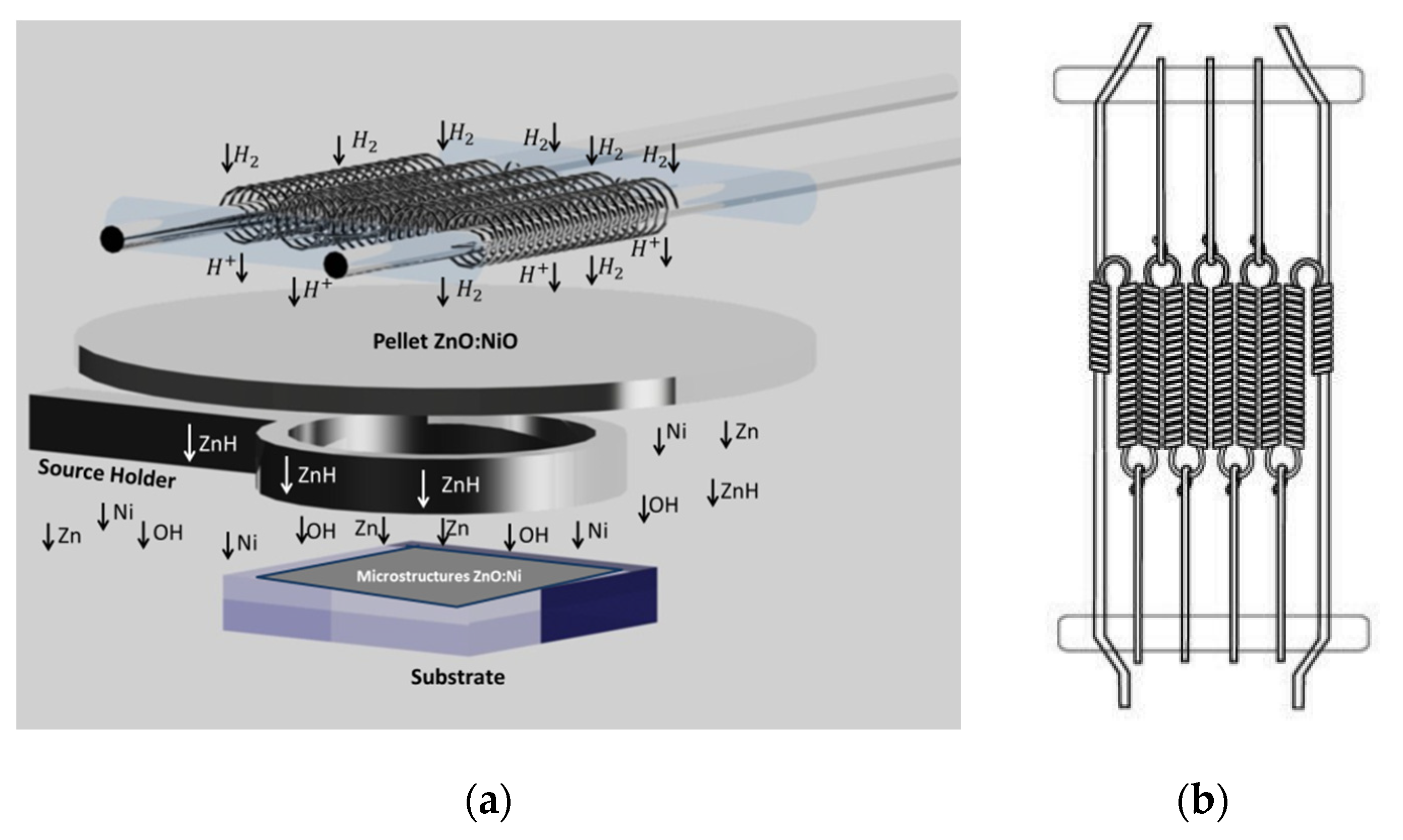
2.1. HFCVD Technique
2.2. Samples Preparation and Deposit
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Characterization
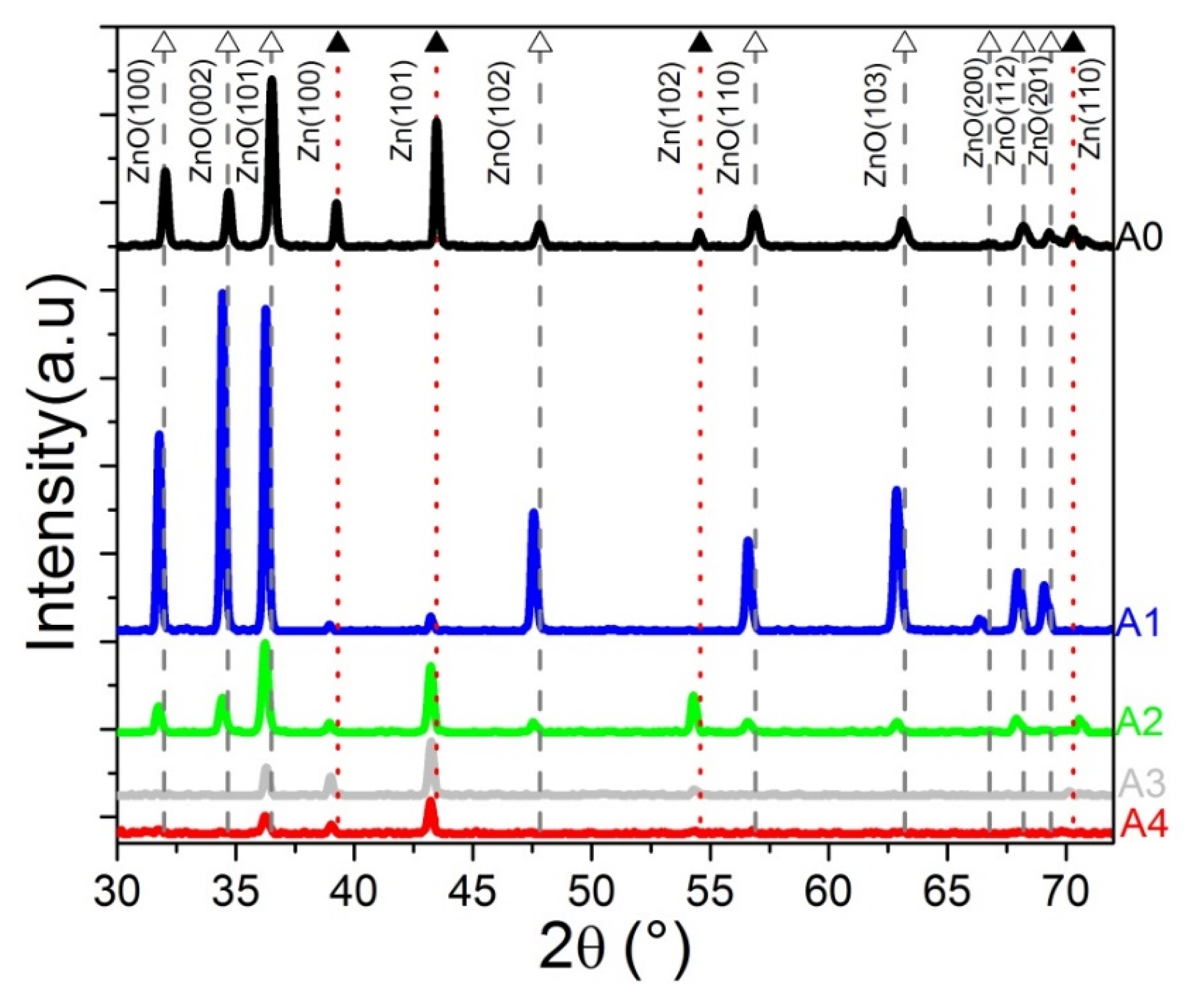
3.1.1. X-ray Diffraction
3.1.2. Micro-Raman Spectroscopy
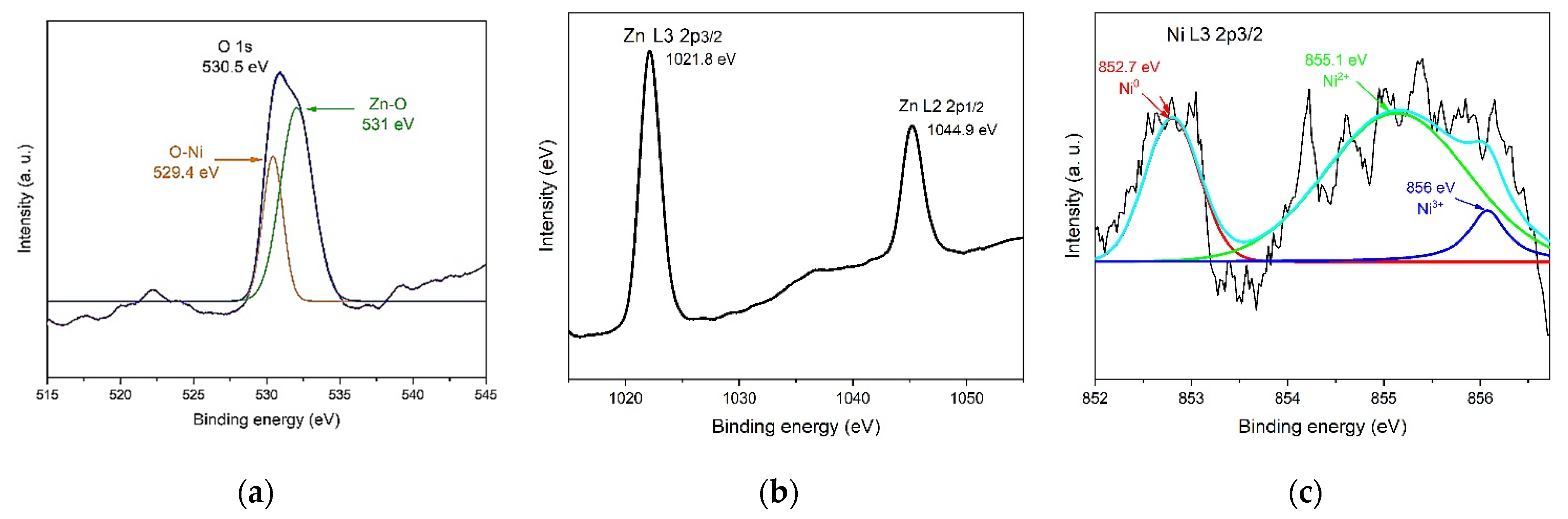
3.1.3. XPS
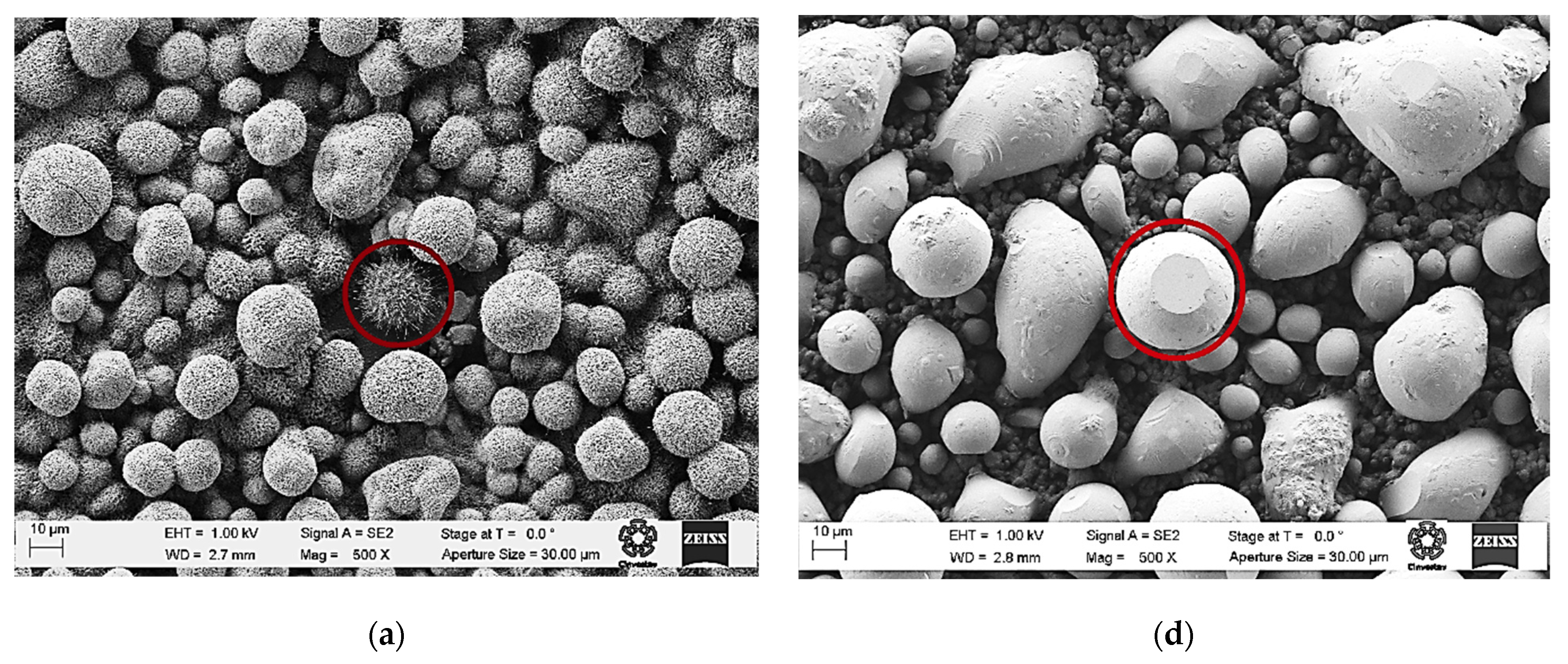
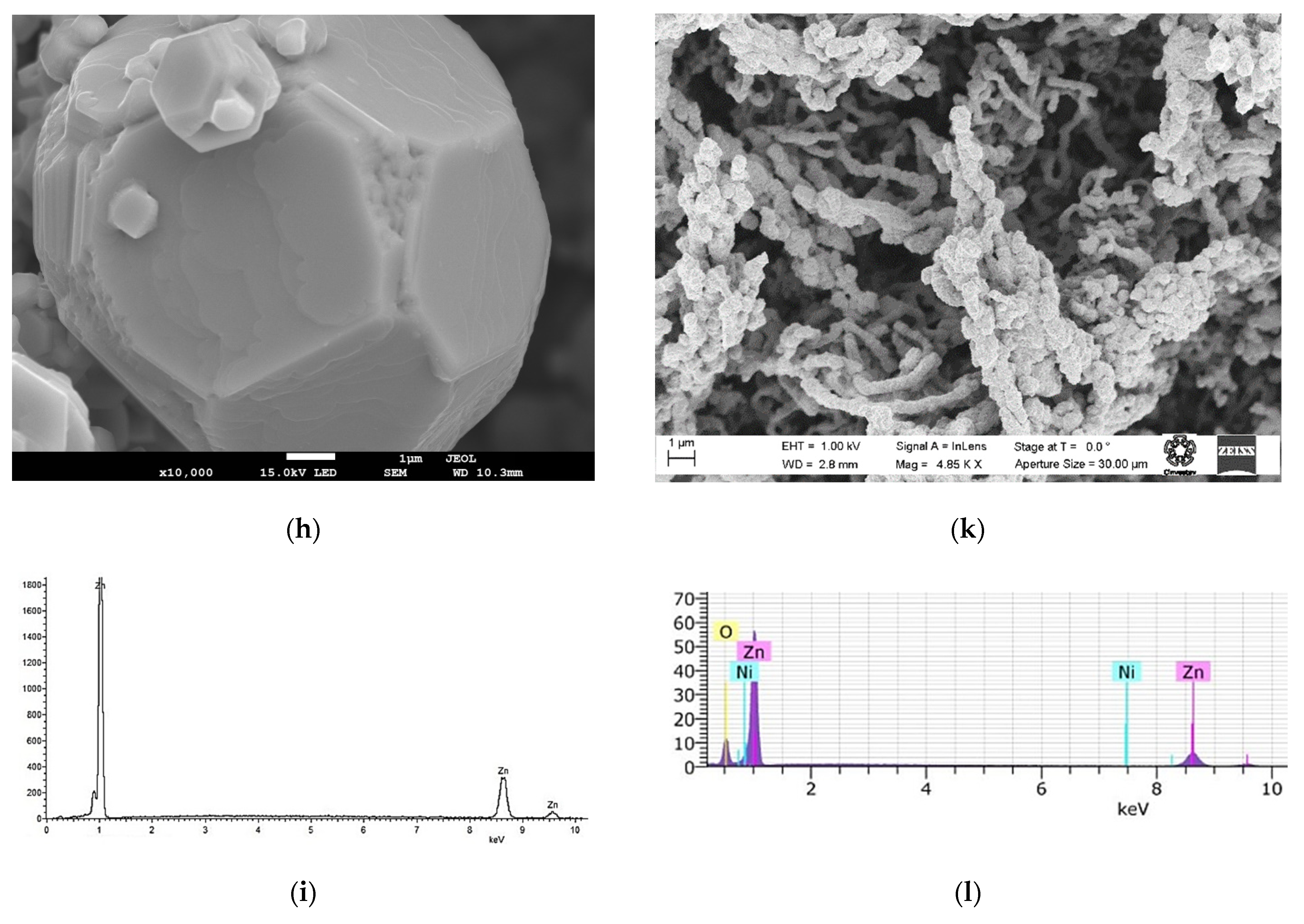
3.2. Morphological Characterization
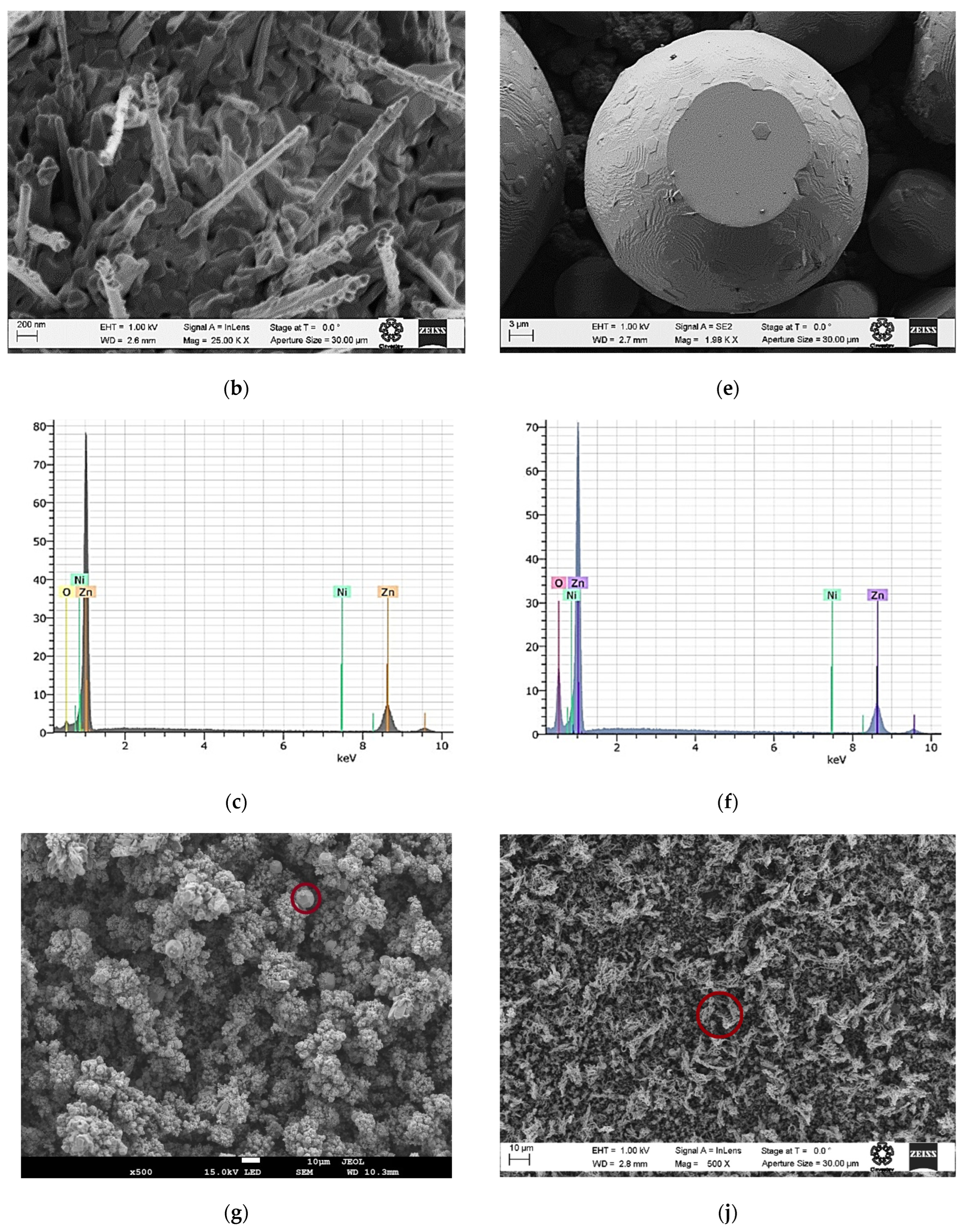
Scanning Electron Microscopy
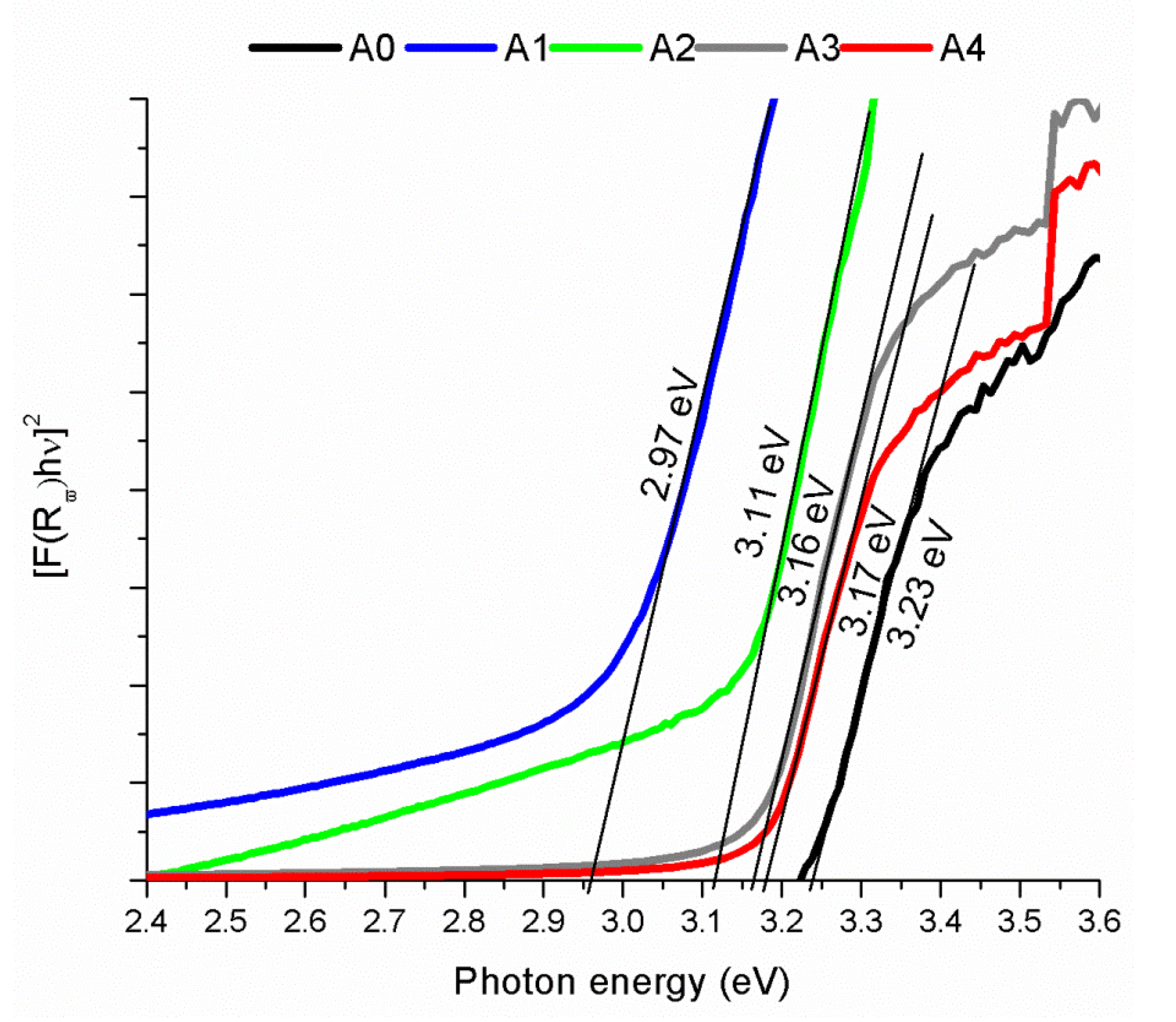
3.3. Optical Characterization
3.3.1. UV-Vis Spectroscopy
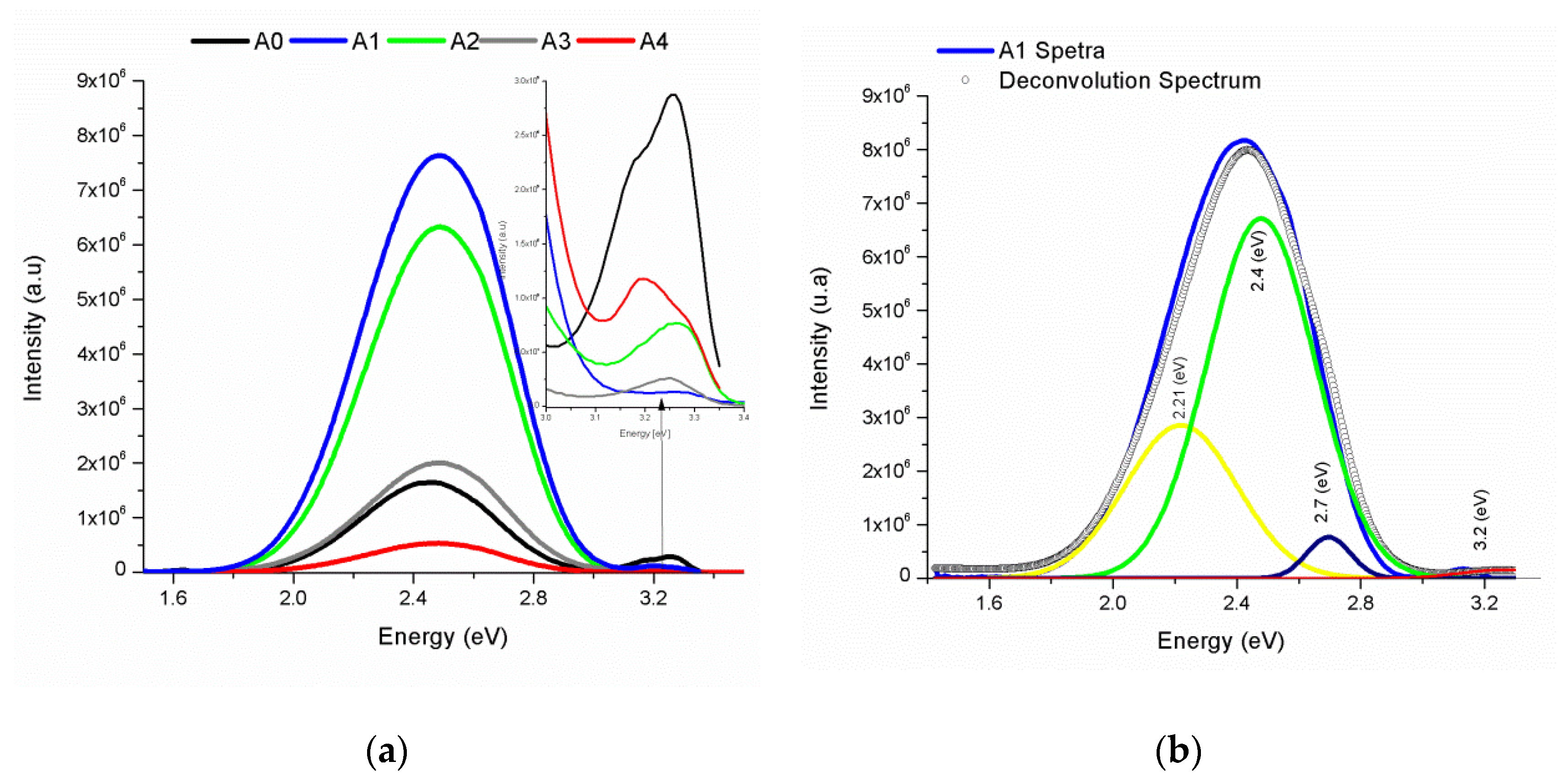
3.3.2. Photoluminescence
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Özgür, Ü.; Alivov, Y.I.; Liu, C.; Teke, A.; Reshchikov, M.A.; Doğan, S.; Avrutin, V.; Cho, S.-J.; Morkoç, H. A comprehensive review of ZnO materials and devices. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98, 041301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.S.; Kang, J.W.; Hwang, D.K.; Park, S.J. Recent advances in ZnO-based light-emitting diodes. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2010, 57, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faÿ, S.; Dubail, S.; Kroll, U.; Meier, J.; Ziegler, Y.; Shah, A. Light trapping enhancement for thin-film silicon solar cells by roughness improvement of the ZnO front TCO. In Proceedings of the 16th EC Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conference, Glasgow, UK, 1–5 May 2000; pp. 361–364. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zeng, H. ZnO-based transparent conductive thin films: Doping, performance, and processing. J. Nanomater. 2013, 2013, 196521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, S.; Hasnain Jameel, M.; Akhtar, N.; Nazir, N.; Ali, A.; Zaman, A.; Rehman, A.; Butt, S.; Sultana, F.; Mushtaq, M.; et al. Modification in structural, optical, morphological, and electrical properties of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles (NPs) by metal (Ni, Co) dopants for electronic device applications. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 15, 103518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, L.I.; El-Molla, S.A.; Ibrahim, M.M.; Mahmoud, H.R.; Naghmash, M.A. Effect of preparation methods and optical band gap of ZnO nanomaterials on photodegradation studies. Opt. Mater. 2016, 58, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, C.H.; Kim, Y.Y.; Kim, D.C.; Mohanta, S.K.; Cho, H.K. A comparative analysis of deep level emission in ZnO layers deposited by various methods. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105, 013502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanada, T. Basic properties of ZnO, GaN, and related materials. In Oxide and Nitride Semiconductors. Advances in Materials Research; Yao, T., Hong, S., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Y.; Han, L.; Zhang, J.; Asahina, S.; Huang, Z.; Shi, L.; Wang, B.; Cao, Y.; Yao, Y.; Ma, L.; et al. Optically active nanostructured ZnO films. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 15170–15175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurenti, M.; Stassi, S.; Canavese, G.; Cauda, V. Surface engineering of nanostructured ZnO surfaces. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 4, 1600758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitner, J.; Bartůněk, V.; Sedmidubský, D.; Jankovský, O. Thermodynamic properties of nanostructured ZnO. Appl. Mater. Today 2018, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purica, M. Optical and structural investigation of ZnO thin films prepared by chemical vapor deposition (CVD). Thin Solid Films 2002, 403–404, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krunks, M.; Mellikov, E. Zinc oxide thin films by the spray pyrolysis method. Thin Solid Films 1995, 270, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuri-Yakub, B.T.; Smits, J.G.; Barbee, T. Reactive magnetron sputtering of ZnO. J. Appl. Phys. 1981, 52, 4772–4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Fuge, G.M.; Ashfold, M.N.R. Growth of aligned ZnO nanorod arrays by catalyst-free pulsed laser deposition methods. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2004, 396, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Ko, K.H.; Park, B.O. Electrical and optical properties of ZnO transparent conducting films by the sol–gel method. J. Cryst. Growth 2003, 247, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, S.C.; Zhang, Y.; Lee, C.J.; Ruh, H.; Lee, H.J. Low-temperature growth of ZnO nanowire array by a simple physical vapor-deposition method. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 3294–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgueiredo, E.; Amaral, M.; Neto, M.A.; Fernandes, A.J.S.; Oliveira, F.J.; Silva, R.F. HFCVD diamond deposition parameters optimized by a Taguchi Matrix. Vacuum 2011, 85, 701–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, S.V.; Dupuiet, J.L.; Gulari, E. Filament-activated chemical vapour deposition of nitride thin films. Adv. Mater. Opt. Electron. 1996, 6, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.Y.; Zhou, X.T.; Wang, N.; Zheng, Y.F.; Liao, L.S.; Shi, W.S.; Lee, C.S.; Lee, S.T. Bulk-quantity GaN nanowires synthesized from hot filament chemical vapor deposition. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2000, 327, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.A.L.; López, J.C.; Valerdi, D.E.V.; Salgado, G.G.; Díaz-Becerril, T.; Pedraza, A.P.; Gracia, F.J.F. Morphological, compositional, structural, and optical properties of Si-nc embedded in SiOx films. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, H.Y.; Lo, S.Y.; Wuu, D.S.; Wu, B.R.; Ou, S.L.; Hsieh, H.Y.; Horng, R.H. Hot-wire chemical vapor deposition and characterization of p-type nanocrystalline Si films for thin film photovoltaic applications. Thin Solid Films 2012, 520, 5200–5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, F.; Limbu, T.B.; Weiner, B.R.; Morell, G. Large-area bilayer graphene synthesis in the hot filament chemical vapor deposition reactor. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2015, 51, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.B.; Zhu, M.K.; Ostrikov, K.; Shao, R.W.; Zheng, K. Structure and photoluminescence of molybdenum selenide nanomaterials grown by hot filament chemical vapor deposition. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 647, 734–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavi, S.H.; Ghorranneviss, M.; Dadashbaba, M.; Alipour, R. Synthesis and investigation of silicon carbide nanowires by HFCVD method. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2016, 39, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, J.R.; Morales, C.; García, G.; Díaz, T.; Rosendo, E.; Santoyo, J.; Oliva, A.I.; Galeazzi, R. Optical and structural analysis of ZnS core-shell type nanowires. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 736, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, D.R.; Díaz-Becerril, T.; García-Salgado, G.; Coyopol-Solís, A.; Rosendo-Andrés, E.; Galeazzi-Isasmendi, R.; Peña-Sierra, R.; Morales-Ruiz, C.; Romano-Trujillo, R.; Nieto-Caballero, F.G. Photoluminescent Enhancement by Effect of Incorporation Nickel in ZnO Films Grown. Eur. J. Eng. Technol. Res. 2021, 6, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, R.; Díaz, T.; García, G.; Galeazzi, R.; Rosendo, E.; Coyopol, A.; Pacio, M.; Juárez, H.; Oliva, A.I. Structural properties of Zn-ZnO core-shell microspheres grown by hot-filament CVD technique. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullity, B.D.; Stock, S.R. Elements of X-ray Diffraction; Prentice-Hall: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Elilarassi, R.; Chandrasekaran, G. Synthesis, structural and magnetic characterization of Ni-doped ZnO diluted magnetic semiconductor. Am. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 2, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.B.; Zhang, C.; Yang, F.J.; Duan, J.X.; Yang, C.P.; Xu, Y.M.; Zhou, M.J.; Li, Q. High resolution transmission electron microscopy and Raman scattering studies of room temperature ferromagnetic Ni-doped ZnO nanocrystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 052505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, B.; Sarkar, D.; Giri, P.K. Structural, optical, and magnetic properties of Ni doped ZnO nanoparticles: Correlation of magnetic moment with defect density. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 356, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Alsmadi, A.M.; Salameh, B.; Mathai, M.; Shatnawi, M.; Hadia, N.M.A.; Ibrahim, E.M.M. Influence of nickel doping on the energy band gap, luminescence, and magnetic order of spray deposited nanostructured ZnO thin films. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 816, 152538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquina, J.; Power, C.; González, J. Raman scattering on ZnO nanocrystals. Rev. Mex. Fis. 2007, 53, 170–173. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, M.; Li, Y.; Tariq, M.; Hu, Y.; Li, W.; Zhu, M.; Jin, H.; Li, Y. Effect of oxygen vacancy induced by pulsed magnetic field on the room-temperature ferromagnetic Ni-doped ZnO synthesized by hydrothermal method. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 675, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchkov, K.; Galluzzi, A.; Blagoev, B.; Paskaleva, A.; Terziyska, P.; Stanchev, T.; Mehandzhiev, V.; Tzvetkov, P.; Kovacheva, D.; Avramova, I.; et al. Magneto-optical characterization of ZnO / Ni nano-laminate obtained via Atomic Layer Deposition. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1762, 012041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankar, D.B.; Kanade, K.G.; Hawaldar, R.R.; Arbuj, S.S.; Shinde, M.D.; Takle, S.P.; Amalnerkar, D.P.; Shinde, S.T. Facile synthesis of nanostructured Ni-Co/ZnO material: An efficient and inexpensive catalyst for Heck reactions under ligand-free conditions. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 9005–9018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Džimbeg-Malčić, V.; Barbarić-Mikočević, Ž.; Itrić, K. Kubelka-Munk theory in describing optical properties of paper (I). Tech. Gaz. 2011, 18, 117–124. [Google Scholar]
- Srinet, G.; Kumar, R.; Sajal, V. Structural, optical, vibrational, and magnetic properties of sol-gel derived Ni doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 114, 033912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawale, J.S.; Kumar, A.; Swati, G.; Haranath, D.; Dhoble, S.J.; Srivastava, A.K. Microstructural evolution and photoluminescence performanance of nickel and chromium doped ZnO nanostructures. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 205, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.-M.; Shchukin, D.G.G.; Möhwald, H.; Xu, Y.; Xia, Y.-Y. Sonochemical synthesis of highly luminescent zinc oxide nanoparticles doped with magnesium(II). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 2727–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Shi, Z.; He, H.; Nan, C. Magnetic properties of ZnO-doped cobalt ferrite. J. Electroceramics 2008, 21, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janisch, R.; Gopal, P.; Spaldin, N.A. Transition metal-doped TiO2 and ZnO—Present status of the field. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2005, 17, R657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiter, F.H.; Alves, H.R.; Hofstaetter, A.; Hofmann, D.M.; Meyer, B.K. The oxygen vacancy as the origin of a green emission in undoped ZnO. Phys. Status Solidi 2001, 226, R4–R5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Fu, Z.; Jia, Y. Green luminescent center in undoped zinc oxide films deposited on silicon substrates. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 79, 943–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Cai, W.; Hu, J.; Duan, G.; Liu, P.; Li, Y. Violet photoluminescence from shell layer of Zn/ZnO core-shell nanoparticles induced by laser ablation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 171910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Cai, W.; Zeng, H. Temperature-dependent shifts of three emission bands for ZnO nanoneedle arrays. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 161101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample Label | ZnO:NiO Weight Ratio | Substrate Temperature (°C) | Source-Filament Distance (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A0 | 1:0 | 500 | 1 |
| A1 | 1:1 | 500 | 1 |
| A2 | 1:1 | 400 | 2 |
| A3 | 1:1 | 350 | 3 |
| A4 | 1:1 | 300 | 3.5 |
| Label | ZnO Lattice Parameters (Å) | Zn Lattice Parameters (Å) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | c | a | c | |
| A0 | 3.248 | 5.207 | 2.67 | 4.965 |
| A1 | 3.251 | 5.206 | 2.67 | 4.966 |
| A2 | 3.250 | 5.206 | 2.67 | 4.966 |
| A3 | - | - | 2.66 | 4.965 |
| A4 | - | - | 2.66 | 4.970 |
| Average Atomic Percentage of Elements | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Label | Zn | O | Ni |
| A1 | 80 | 19.66 | 0.29 |
| A2 | 80.11 | 19.66 | 0.23 |
| A3 | 80.13 | 19.66 | 0.21 |
| A4 | 80.21 | 19.66 | 0.13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gutiérrez, D.R.; García-Salgado, G.; Coyopol, A.; Rosendo-Andrés, E.; Romano, R.; Morales, C.; Benítez, A.; Severiano, F.; Herrera, A.M.; Ramírez-González, F. Effect of the Deposit Temperature of ZnO Doped with Ni by HFCVD. Materials 2023, 16, 1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16041526
Gutiérrez DR, García-Salgado G, Coyopol A, Rosendo-Andrés E, Romano R, Morales C, Benítez A, Severiano F, Herrera AM, Ramírez-González F. Effect of the Deposit Temperature of ZnO Doped with Ni by HFCVD. Materials. 2023; 16(4):1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16041526
Chicago/Turabian StyleGutiérrez, Delfino R., Godofredo García-Salgado, Antonio Coyopol, Enrique Rosendo-Andrés, Román Romano, Crisóforo Morales, Alfredo Benítez, Francisco Severiano, Ana María Herrera, and Francisco Ramírez-González. 2023. "Effect of the Deposit Temperature of ZnO Doped with Ni by HFCVD" Materials 16, no. 4: 1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16041526
APA StyleGutiérrez, D. R., García-Salgado, G., Coyopol, A., Rosendo-Andrés, E., Romano, R., Morales, C., Benítez, A., Severiano, F., Herrera, A. M., & Ramírez-González, F. (2023). Effect of the Deposit Temperature of ZnO Doped with Ni by HFCVD. Materials, 16(4), 1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16041526








