Kinetics of Nickel Diffusion into Austenitic Stainless Steels AISI 304 and 316L and Calculation of Diffusion Coefficients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Experiment and Results
3.1. Determination of Mechanical Properties
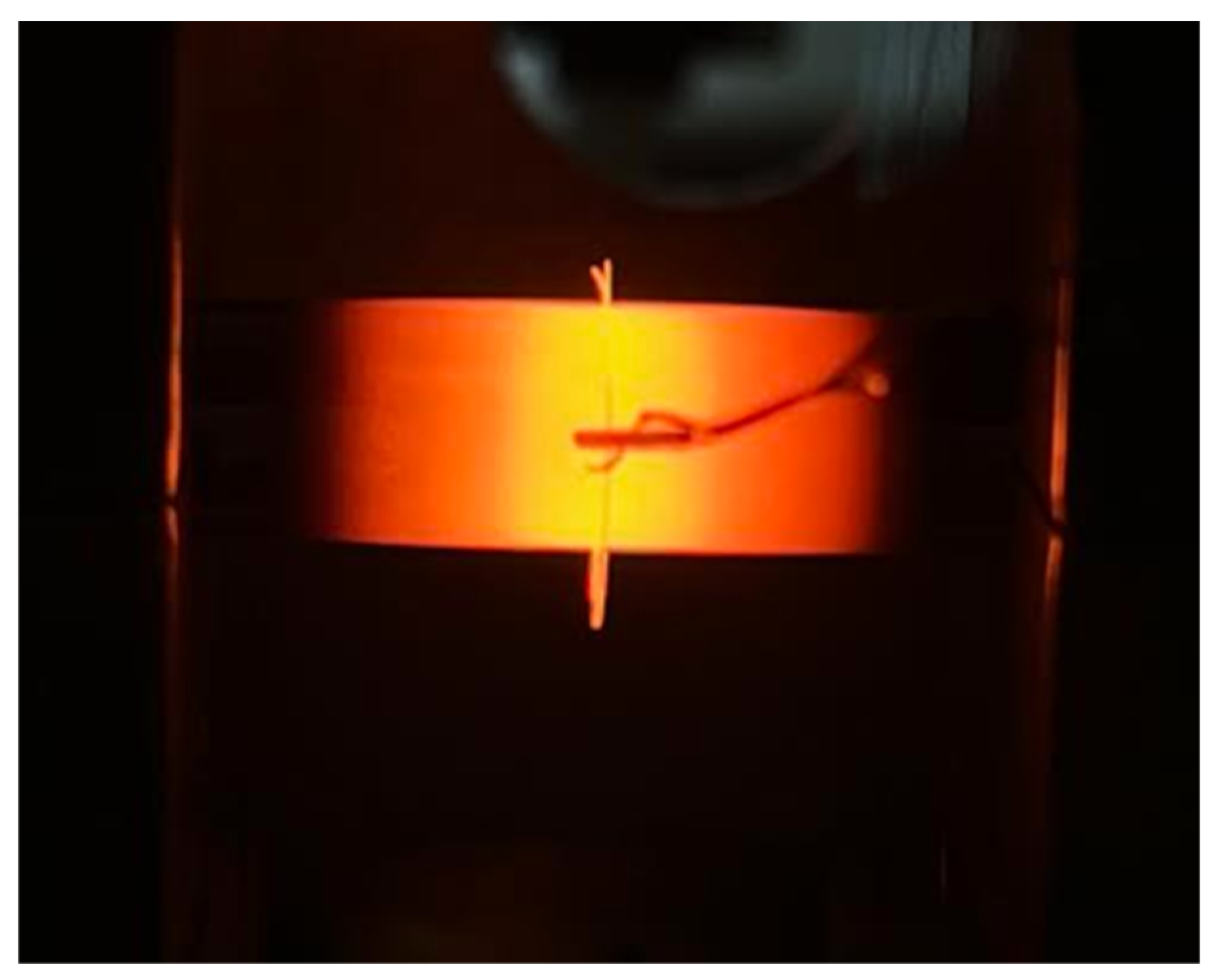
3.2. Diffusion Bonding in Gleeble 3500
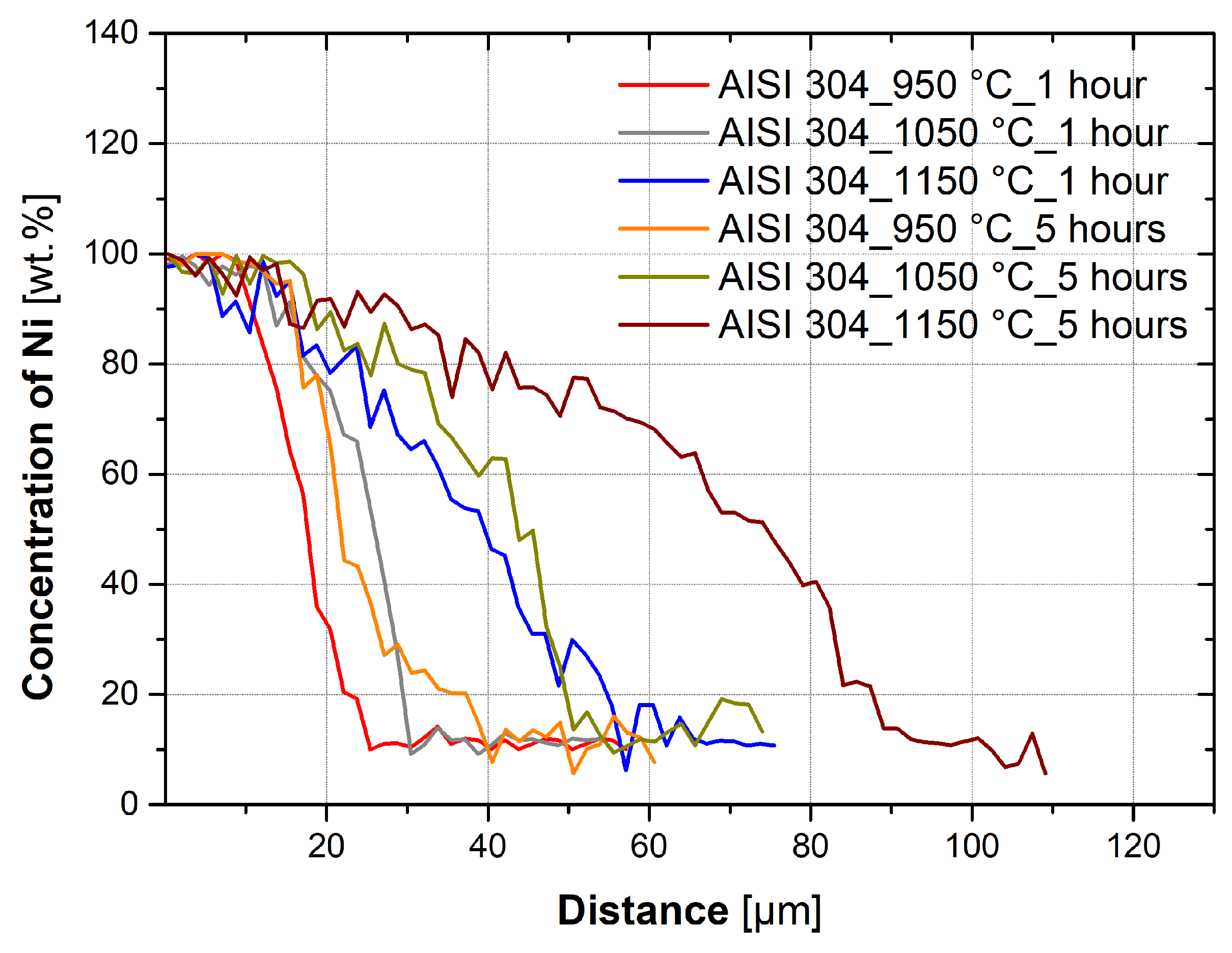
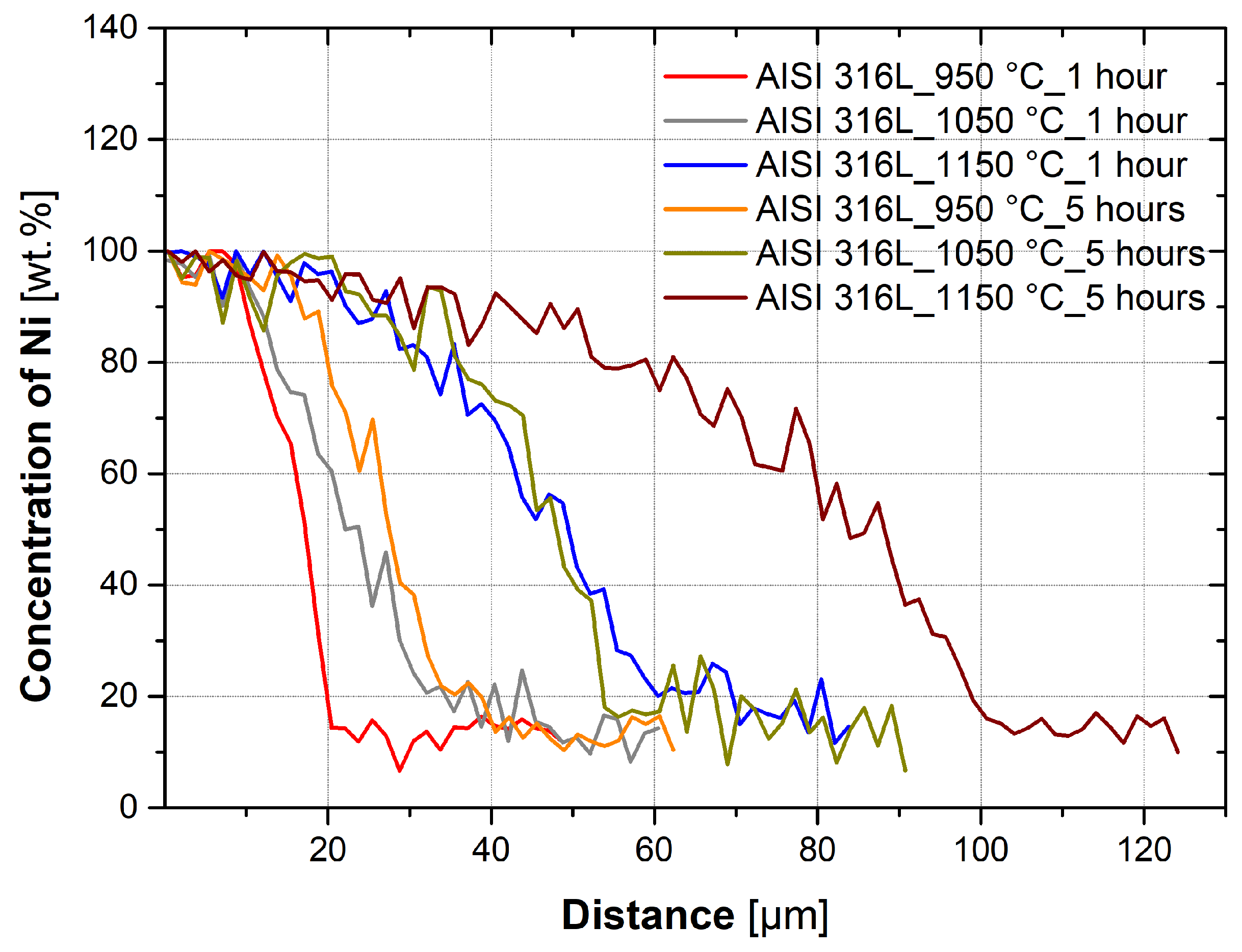
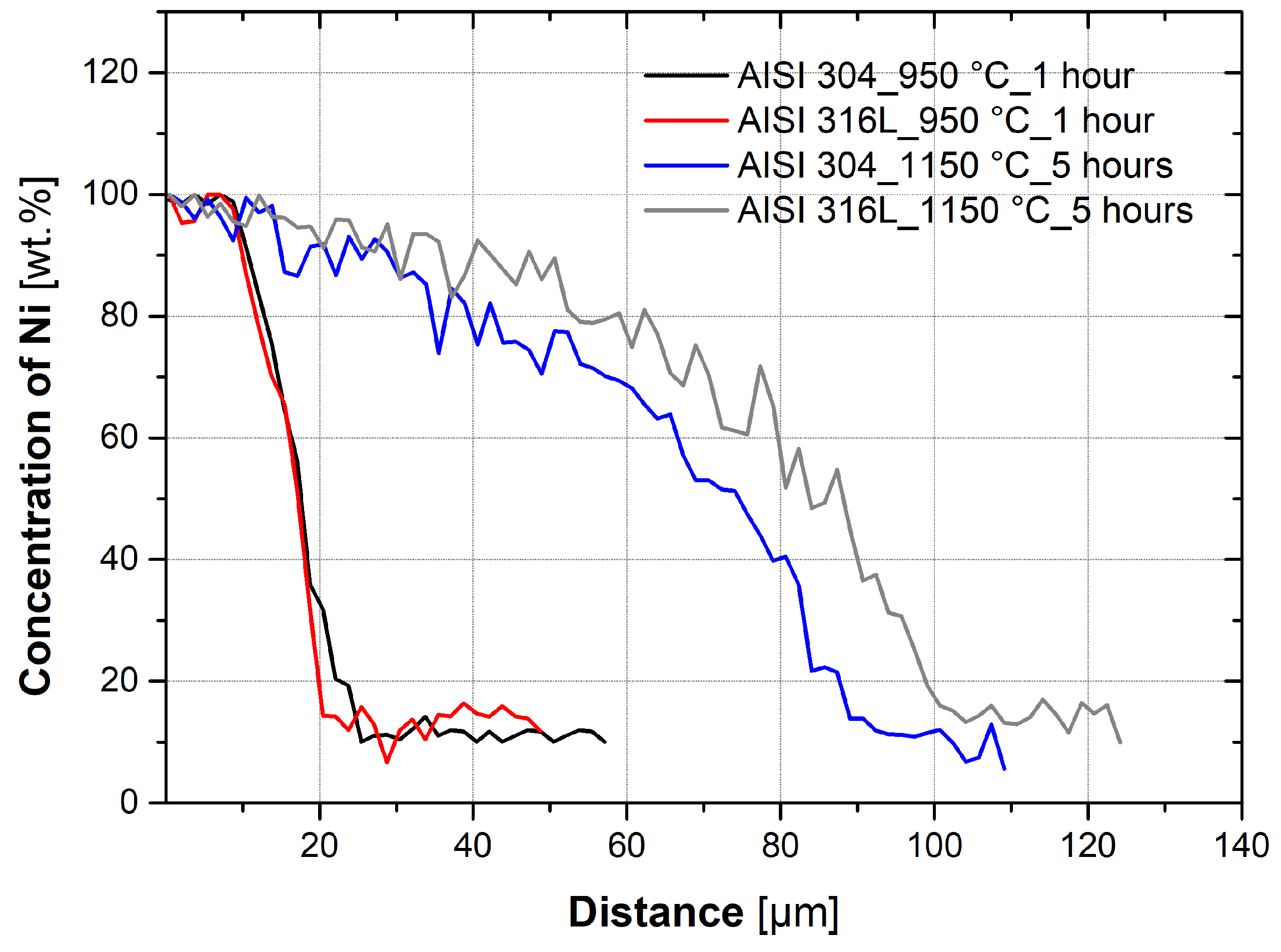
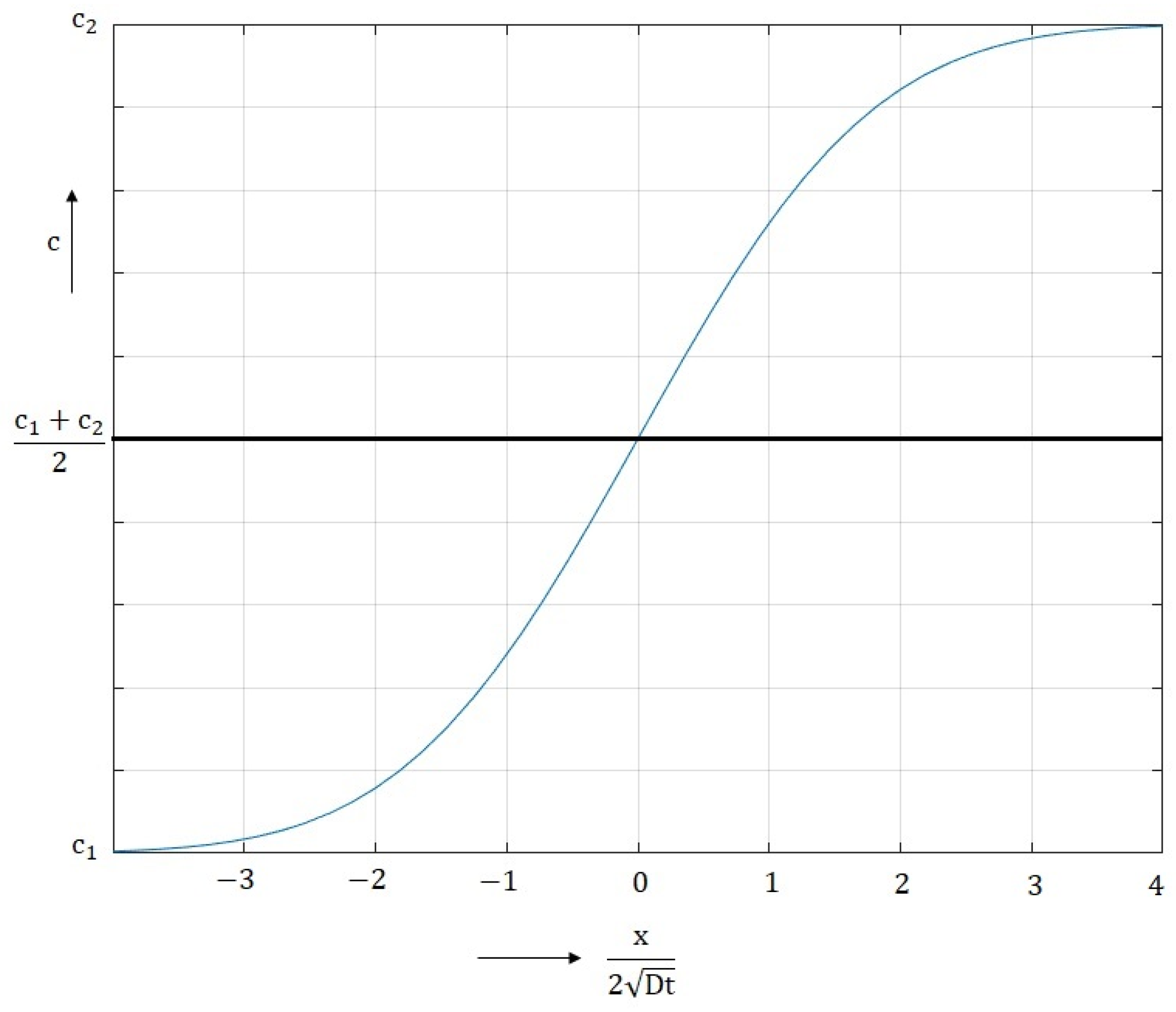
3.3. Evaluation of Diffusion Kinetics
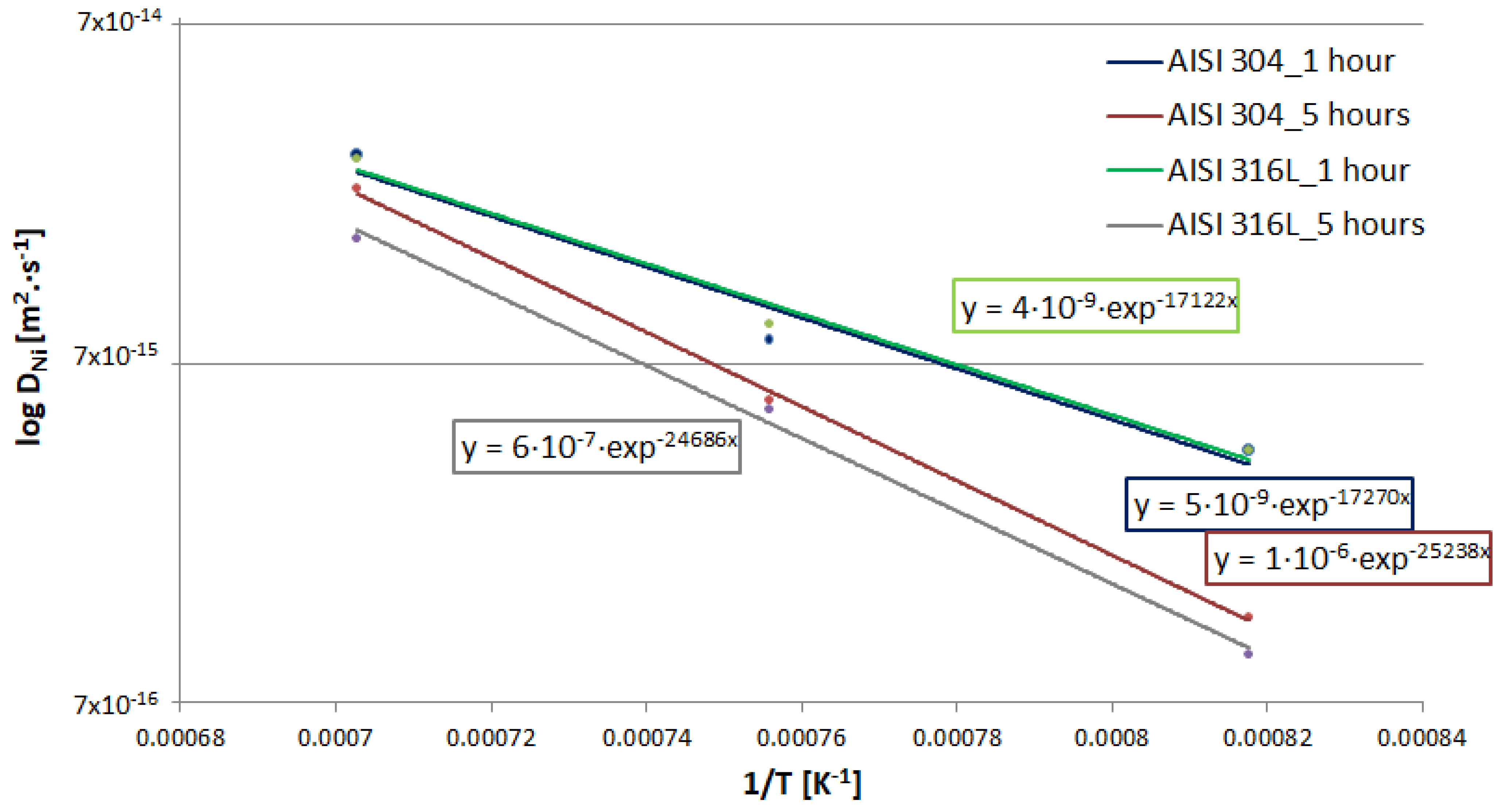
3.4. Calculation of Diffusion Coefficients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Temperature has a significant effect on the diffusion kinetics and, therefore, the depth of diffusion of nickel into the austenitic steel. It is also dependent on the holding time and temperature.
- (2)
- Nickel diffuses into both the austenitic steels, AISI 304 and AISI 316L, at approximately the same rate, although AISI 316L has approximately 5% more Ni and 2.2% more Mo.
- (3)
- Diffusion already occurs during the heating and subsequent cooling of the sample. In the case of a temperature of 950 °C for austenitic steels, it is between 5.6 and 7.3% of the total diffusion depth. At 1050 °C, it is 6.8–12.6%, and at 1150 °C, it is 11.7–23.8% of the total diffusion depths measured at holding times of 1 and 5 h.
- (4)
- To determine the diffusion coefficient of Ni into specific steels, generalized Equations (16) and (17) were formulated for a temperature range of 1223.15–1423.15 K, which can be used with sufficient accuracy to determine the widths of the diffusion zones at the interface between austenitic steel (AISI 316L/304) and the Ni interlayer.
- (5)
- The calculated diffusion depths were different from the real values in the range of 5% to 28.6%. The largest differences were at 950 °C. Although the deviation from the real value seems to be quite high, the real difference in diffusion zone width at 950 °C is a maximum of 6.7 µm.
- (6)
- The diffusion zone width, and therefore the basic information for optimizing the interlayer thickness, can be determined with sufficient accuracy for AISI 304 steel generally for temperatures (T) in the range 1223.15–1423.15 K and for times (t) in the range 1 to 5 h according to Equation (18) and for AISI 316L steel according to Equation (19).
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, P.; Li, C.; Dong, H.; Wu, B.; Ma, Y.; Zou, C.; Yang, Y. Vacuum Diffusion Bonding of TC4 Titanium Alloy to 316L Stainless Steel with AlCoCrCuNi2 High-Entropy Alloy Interlayer. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 909, 164698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.Q.; Wang, D.P.; Qi, F.G.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, Q.W.; Yang, Z.W. Joining of Titanium Diboride-Based Ultra High-Temperature Ceramics to Refractory Metal Tantalum Using Diffusion Bonding Technology. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2022, 42, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhan, N.; Khan, T.; Eroğlu, M. Diffusion Bonding of a Microduplex Stainless Steel to Ti–6Al–4V. Scr. Mater. 2001, 45, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, D.; Sun, D.; Li, H. Research Progress on Control Strategy of Intermetallic Compounds in Welding Process of Heterogeneous Materials. Steel Res. Int. 2022, 93, 2100427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Chatterjee, S. Interfacial Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Diffusion-Bonded Titanium–Stainless Steel Joints Using a Nickel Interlayer. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 425, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, M.; Bhanumurthy, K.; GB, K.; Krishnan, J.; Chatterjee, S. Strength of the Diffusion Bonded Joints between CP Ti and 304 Stainless Steel Processed below and above β-Transus. ISIJ Int. 2004, 44, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Negemiya, A.; Selvarajan, R.; Sonar, T. Effect of Diffusion Bonding Time on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Dissimilar Ti6Al4V Titanium Alloy and AISI 304 Austenitic Stainless Steel Joints. Mater. Test. 2023, 65, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Sam, S.; Chatterjee, S. Interfacial Reactions and Strength Properties in Dissimilar Titanium Alloy/Ni Alloy/Microduplex Stainless Steel Diffusion Bonded Joints. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 560, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabetghadam, H.; Hanzaki, A.Z.; Araee, A. Diffusion Bonding of 410 Stainless Steel to Copper Using a Nickel Interlayer. Mater. Charact. 2010, 61, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Gu, X.; Cui, M.; Gu, X.; Zhao, X. Laser Assisted Diffusion Bonding of TC4 Titanium Alloy to 301 Stainless Steel Using a Ni Interlayer. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 21, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheepu, M.; Che, W.-S. Characterization of Microstructure and Interface Reactions in Friction Welded Bimetallic Joints of Titanium to 304 Stainless Steel Using Nickel Interlayer. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2019, 72, 1597–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Balasubramanian, M. Analysis and Comparison of Diffusion Bonded and Friction Welded Ti-6Al-4V and Stainless Steel Joints with Copper as Interlayer. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 21, 1467–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, J.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, F.; Raza, S.H. Diffusion Bonding Titanium to Stainless Steel Using Nb/Cu/Ni Multi-Interlayer. Mater. Charact. 2012, 68, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, D.; Song, T.; Fang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Luo, C.Q.; Simpson, M.D.; Luo, Z. A Review on Diffusion Bonding between Titanium Alloys and Stainless Steels. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 2018, 8701890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Chatterjee, S. Characterization of Diffusion Bonded Joint between Titanium and 304 Stainless Steel Using a Ni Interlayer. Mater. Charact. 2008, 59, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, M.; Kundu, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Mishra, B. Influence of Interface Microstructure on the Strength of the Transition Joint between Ti-6Al-4V and Stainless Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2005, 36, 1891–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinotani, S.; Ohmori, Y. The Microstructure of Diffusion-Bonded Ti/Ni Interface. Trans. Jpn. Inst. Met. 1988, 29, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleman, B.; Gutiérrez, L.; Urcola, J. Interface Microstructures in Diffusion Bonding of Titanium Alloys to Stainless and Low Alloy Steels. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1993, 9, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolařík, L.; Kolaříková, M.; Vondrouš, P. Mechanical Properties of Interface of Heterogeneous Diffusion Welds of Titanium and Austenitic Steel. Trans. Tech. Publ. 2014, 586, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Ghosh, M.; Chatterjee, S. Reactive Diffusion Bonding between Commercially Pure Titanium and 304 Stainless Steel Using Nickel Interlayer. ISIJ Int. 2004, 44, 1882–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kundu, S.; Ghosh, M.; Laik, A.; Bhanumurthy, K.; Kale, G.; Chatterjee, S. Diffusion Bonding of Commercially Pure Titanium to 304 Stainless Steel Using Copper Interlayer. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 407, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigraman, T.; Ravindran, D.; Narayanasamy, R. Effect of Phase Transformation and Intermetallic Compounds on the Microstructure and Tensile Strength Properties of Diffusion-Bonded Joints between Ti–6Al–4V and AISI 304L. Mater. Des. (1980–2015) 2012, 36, 714–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, M. Development of Processing Windows for Diffusion Bonding of Ti–6Al–4V Titanium Alloy and 304 Stainless Steel with Silver as Intermediate Layer. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 2932–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.-L.; Sheng, G.-M.; Deng, Y.-Q. Impulse Pressuring Diffusion Bonding of Titanium to 304 Stainless Steel Using Pure Ni Interlayer. Rare Met. 2016, 35, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Jiang, X.; Shao, Z.; Fang, Y.; Mo, D.; Zhu, D.; Zhu, M. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Vacuum Diffusion Bonded Joints between Ti-6Al-4V Titanium Alloy and AISI316L Stainless Steel Using Cu/Nb Multi-Interlayer. Vacuum 2017, 145, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 10027-2:2015; Designation Systems for Steels—Part 2: Numerical System. ISO: Brussels, Belgium, 2015.
- ISO 10027-1:2016; Designation Systems for Steels—Part 1: Steel Names. ISO: Brussels, Belgium, 2016.
- EN 10088-1:2014; Stainless Steels—Part 1: List of Stainless Steels. European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2014.
- EN ISO 6892-1:2021; Metallic Materials—Tensile Testing—Part 1: Method of Test at Room Temperature. European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2021.



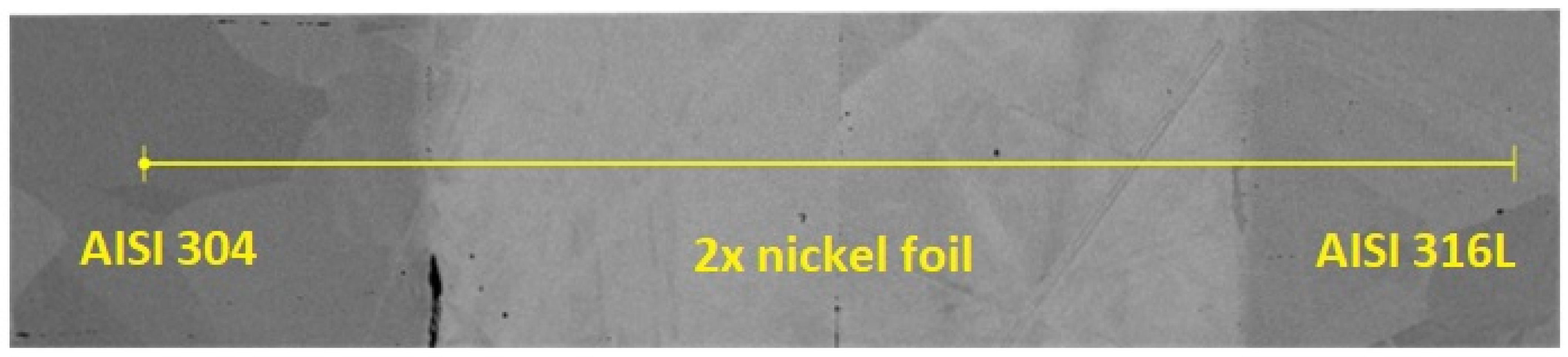
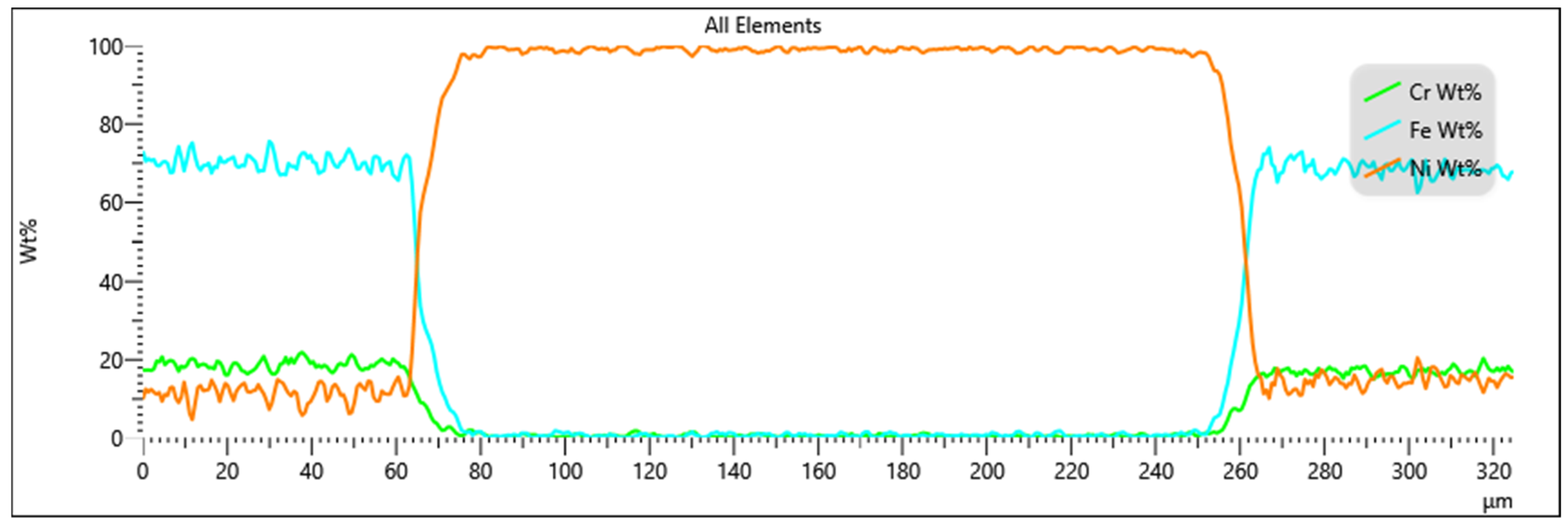

| AISI 304 | C | Cr | Mn | Ni | Si | S | P | N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EN 10088-1 | min. | - | 17.50 | - | 8.00 | - | - | - | - |
| max. | <0.07 | 19.50 | 2.00 | 10.50 | 1.00 | 0.015 | 0.045 | <0.11 | |
| Experiment | 0.045 | 18.37 | 1.66 | 8.11 | 0.23 | 0.013 | 0.077 |
| AISI 316L | C | Cr | Mn | Mo | Ni | Si | S | P | N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EN 10088-1 | min. | - | 16.50 | - | 2.00 | 10.00 | - | - | - | - |
| max. | <0.03 | 18.50 | 2.00 | 2.50 | 13.00 | 1.00 | 0.015 | 0.045 | <0.11 | |
| Experiment | 0.03 | 18.50 | 1.96 | 2.24 | 13.10 | 1.02 | 0.02 | 0.074 |
| Sample No. | Rp0.2 [MPa] | UTS [MPa] | Ag [%] | A40 [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AISI 304 | 445.5 ± 7.3 | 643.0 ± 3.2 | 33.60 ± 0.16 | 42.03 ± 0.09 |
| AISI 316L | 512.7 ± 5.2 | 662.5 ± 7.1 | 24.17 ± 0.61 | 39.47 ± 0.11 |
| Sample No. | Temperature [°C] | Time [Hours] |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 950 | 1 |
| 2 | 950 | 5 |
| 3 | 1050 | 1 |
| 4 | 1050 | 5 |
| 5 | 1150 | 1 |
| 6 | 1150 | 5 |
| DNi [m2·s−1] | 1 h | 5 h | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 | 316L | 304 | 316L | |
| 950 °C | 3.90 × 10−15 | 3.89 × 10−15 | 1.26 × 10−15 | 9.69 × 10−16 |
| 1050 °C | 8.28 × 10−15 | 9.15 × 10−15 | 5.47 × 10−15 | 5.18 × 10−15 |
| 1150 °C | 2.88 × 10−14 | 2.81 × 10−14 | 2.30 × 10−14 | 1.64 × 10−14 |
| Factor | AISI 304 | AISI 316L | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-Value | Evaluation | p-Value | Evaluation | |
| Time | 0.0014 | Has an effect | 1.62 × 10−5 | Has an effect |
| Temperature | 4.92 × 10−16 | Has an effect | 8.49 × 10−15 | Has an effect |
| h [µm] | 0 h | 1 h | 5 h | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 | 316L | 304 | 316L | 304 | 316L | |
| 950 °C | 1.46 | 1.31 | 19.89 | 20.04 | 25.08 | 23.41 |
| 1050 °C | 3.15 | 3.04 | 25.08 | 31.68 | 41.80 | 45.02 |
| 1150 °C | 10.72 | 9.41 | 45.09 | 44.96 | 71.90 | 80.26 |
| h [µm] | 1 h | 5 h | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 | 316L | 304 | 316L | |
| 950 °C | 14.99 | 14.97 | 19.03 | 16.71 |
| 1050 °C | 21.83 | 22.96 | 39.68 | 38.61 |
| 1150 °C | 40.73 | 40.24 | 81.30 | 68.73 |
| ∆h [µm] | 1 h | 5 h | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 | 316L | 304 | 316L | |
| 950 °C | 4.90 | 5.07 | 6.05 | 6.70 |
| 1050 °C | 3.25 | 8.72 | 2.12 | 6.41 |
| 1150 °C | 4.36 | 4.71 | 9.40 | 11.54 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bukovská, Š.; Moravec, J.; Švec, M. Kinetics of Nickel Diffusion into Austenitic Stainless Steels AISI 304 and 316L and Calculation of Diffusion Coefficients. Materials 2023, 16, 6783. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16206783
Bukovská Š, Moravec J, Švec M. Kinetics of Nickel Diffusion into Austenitic Stainless Steels AISI 304 and 316L and Calculation of Diffusion Coefficients. Materials. 2023; 16(20):6783. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16206783
Chicago/Turabian StyleBukovská, Šárka, Jaromír Moravec, and Martin Švec. 2023. "Kinetics of Nickel Diffusion into Austenitic Stainless Steels AISI 304 and 316L and Calculation of Diffusion Coefficients" Materials 16, no. 20: 6783. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16206783
APA StyleBukovská, Š., Moravec, J., & Švec, M. (2023). Kinetics of Nickel Diffusion into Austenitic Stainless Steels AISI 304 and 316L and Calculation of Diffusion Coefficients. Materials, 16(20), 6783. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16206783






