Efficient Reduction in Methylene Blue Using Palladium Nanoparticles Supported by Melamine-Based Polymer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of PAN-NA
2.3. Synthesis of Pd@PAN-NA Catalyst by RDSA
2.4. Characterization
2.5. Methylene Blue Reduction
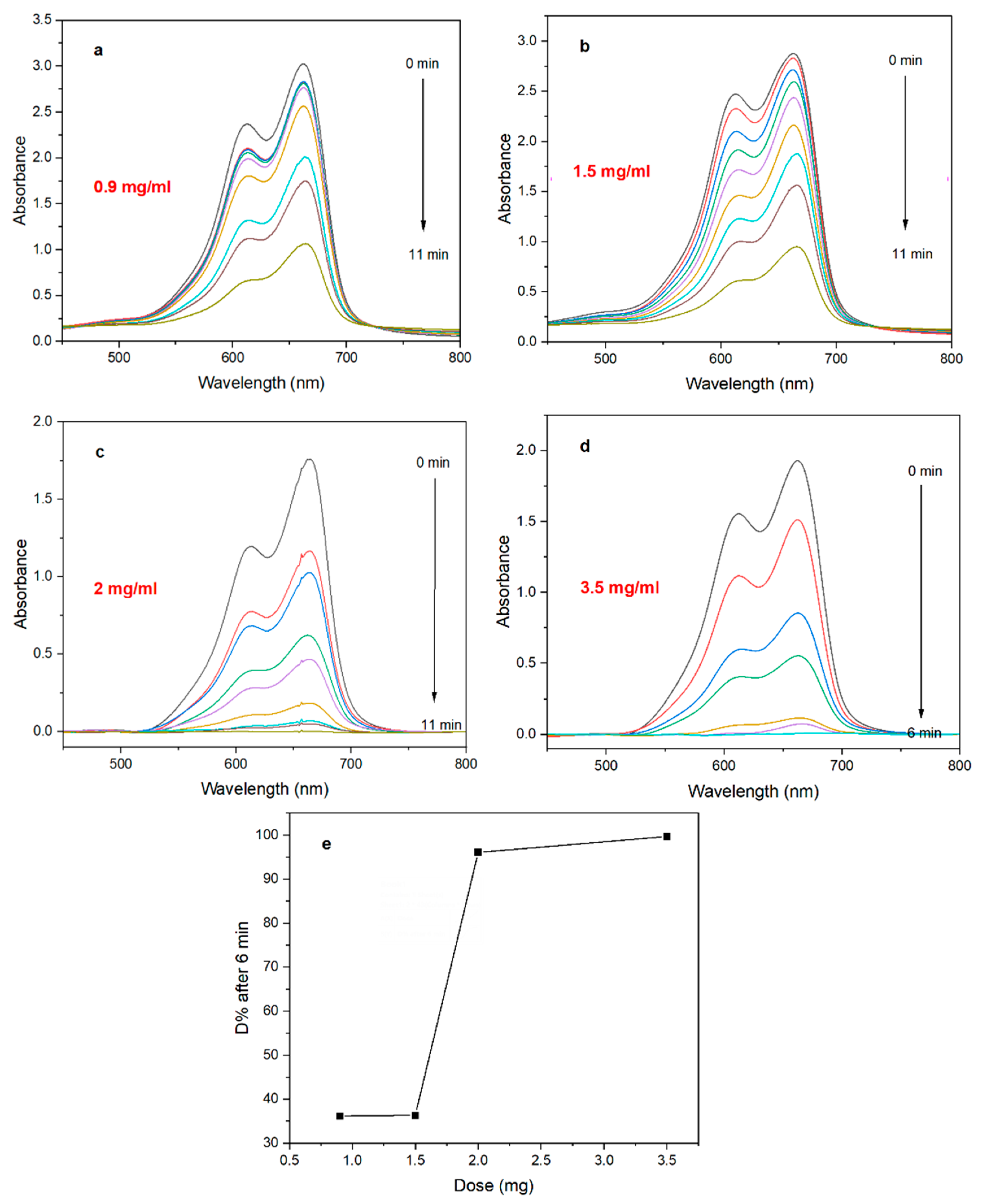
2.5.1. Effect of Catalyst Dose
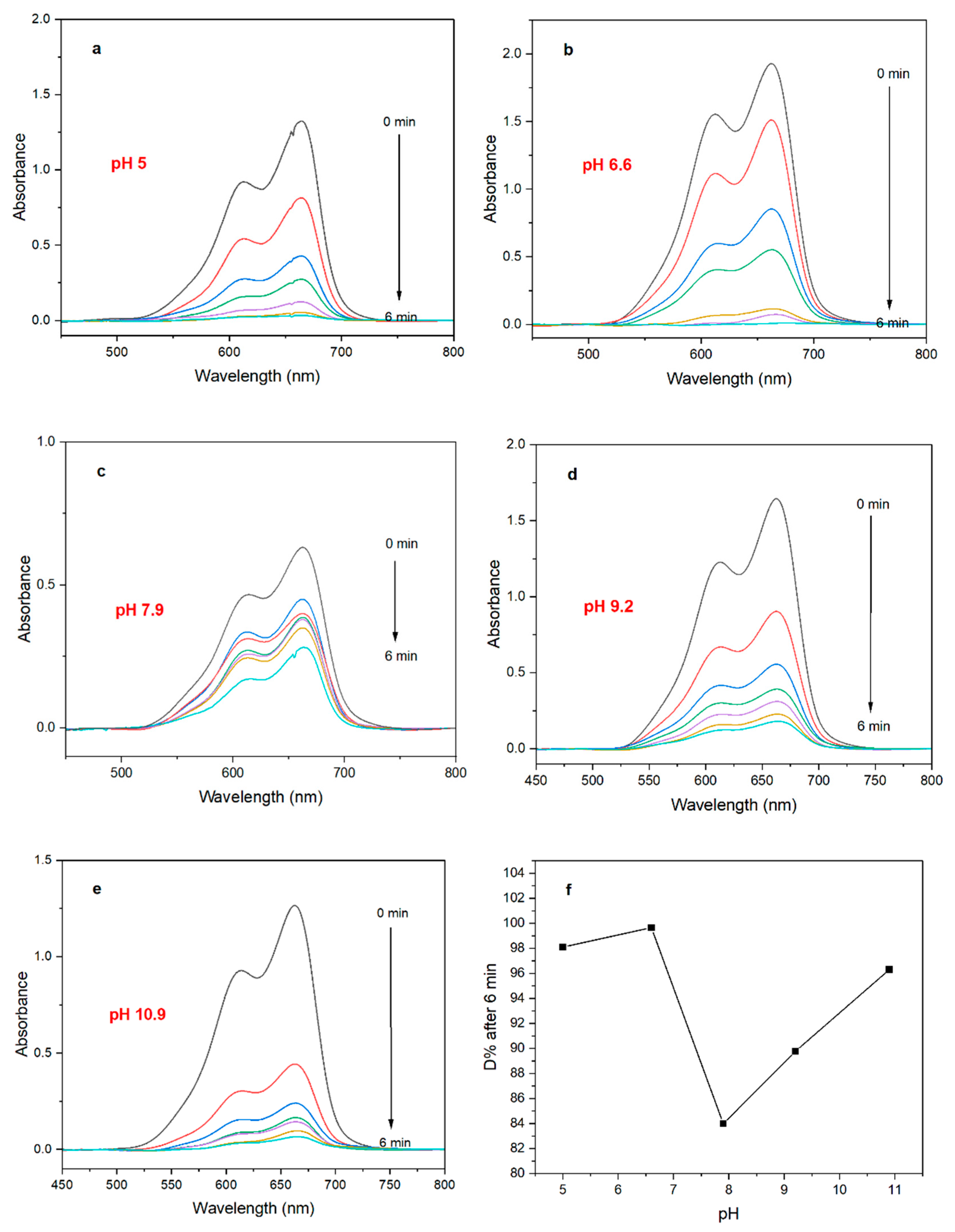
2.5.2. Effect of pH
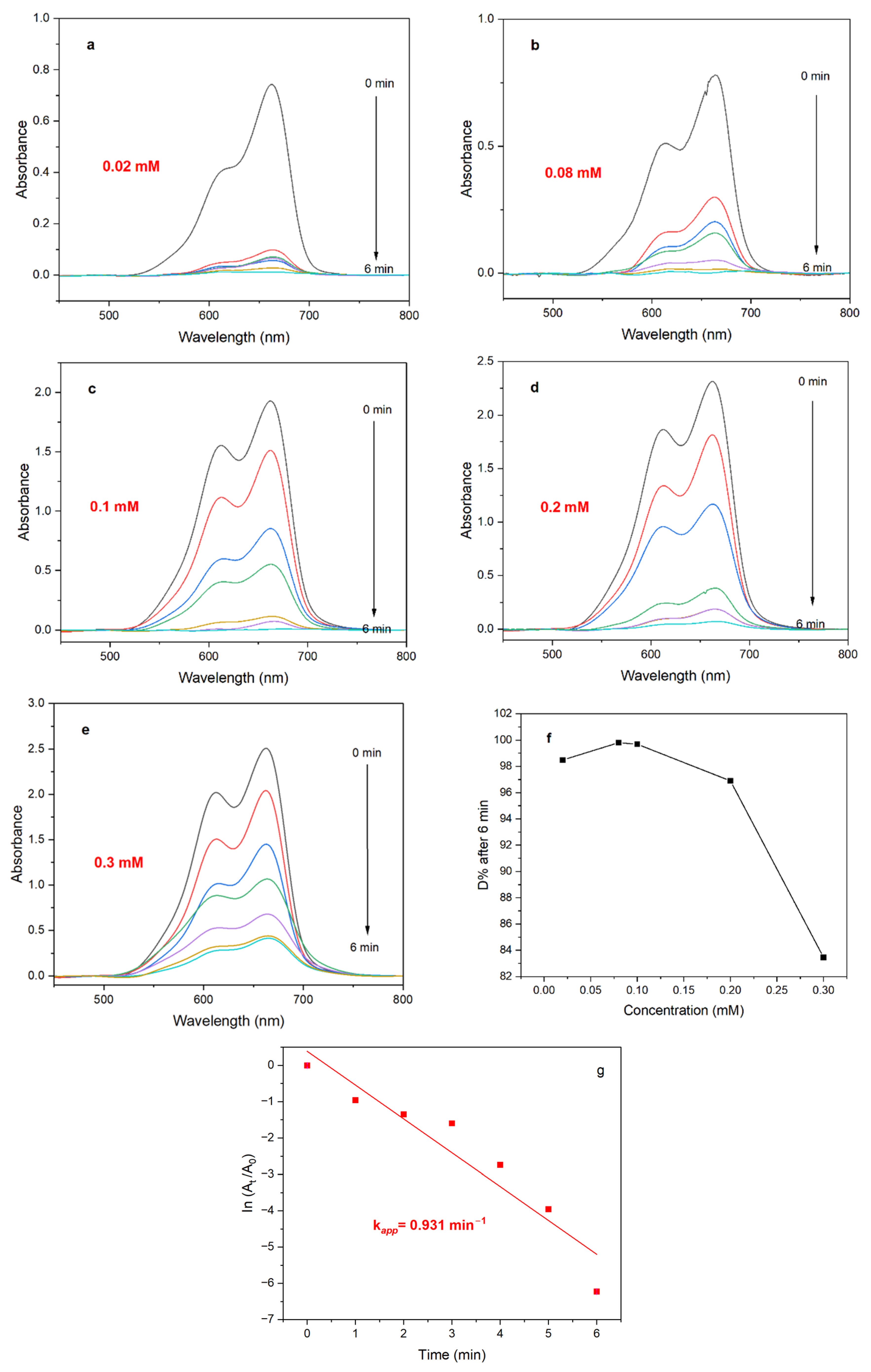
2.5.3. Effect of Dye Concentration
3. Results and Discussion
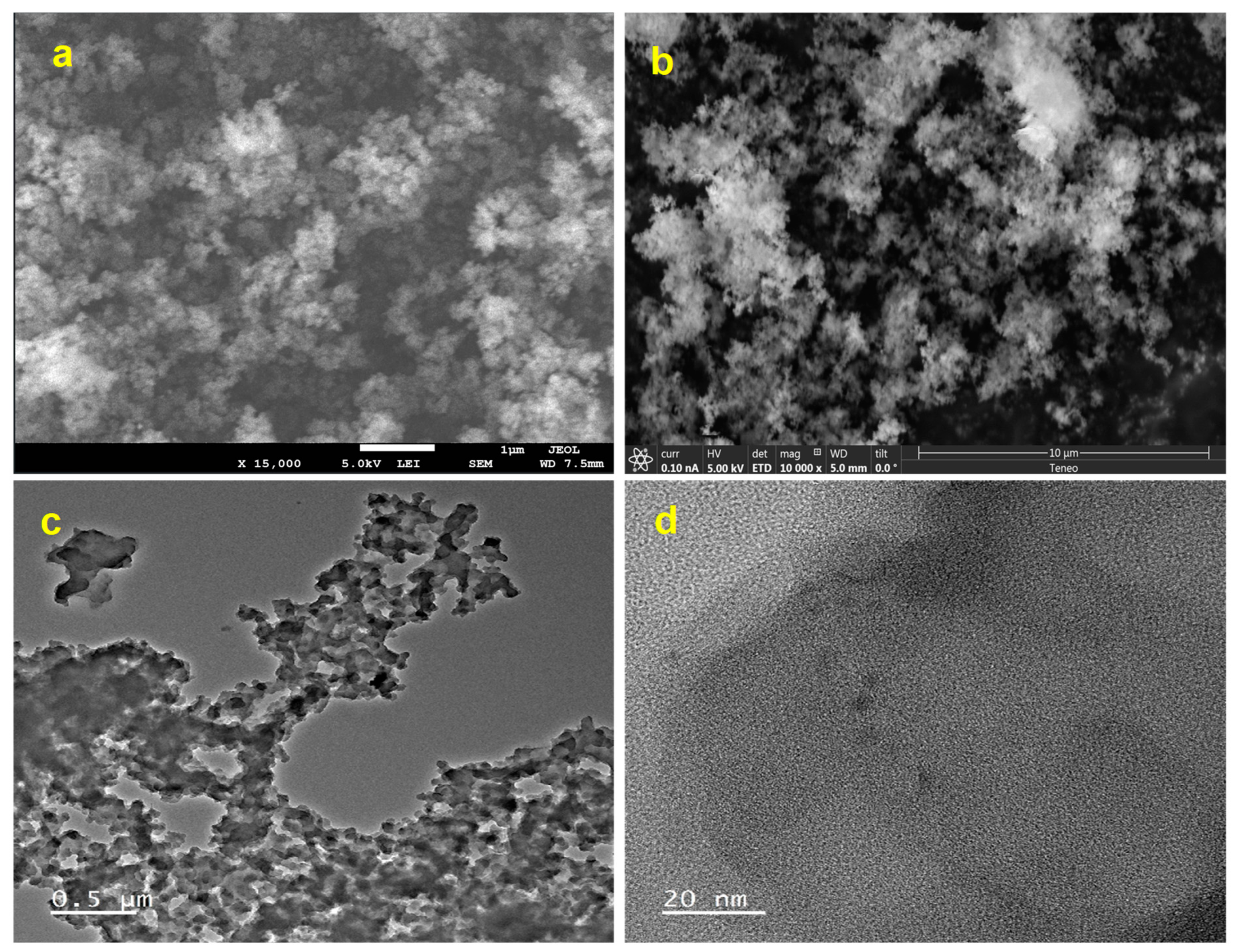
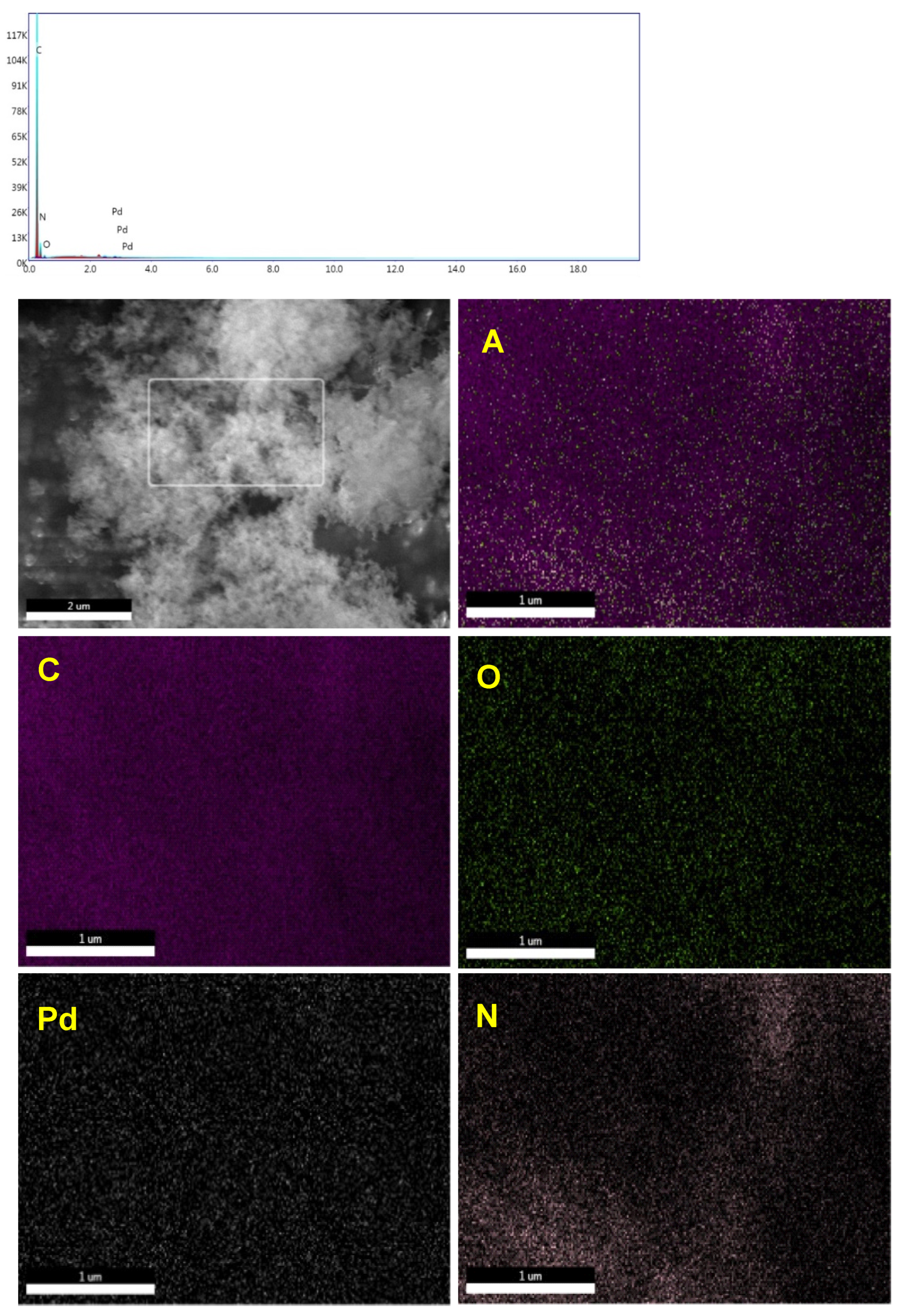
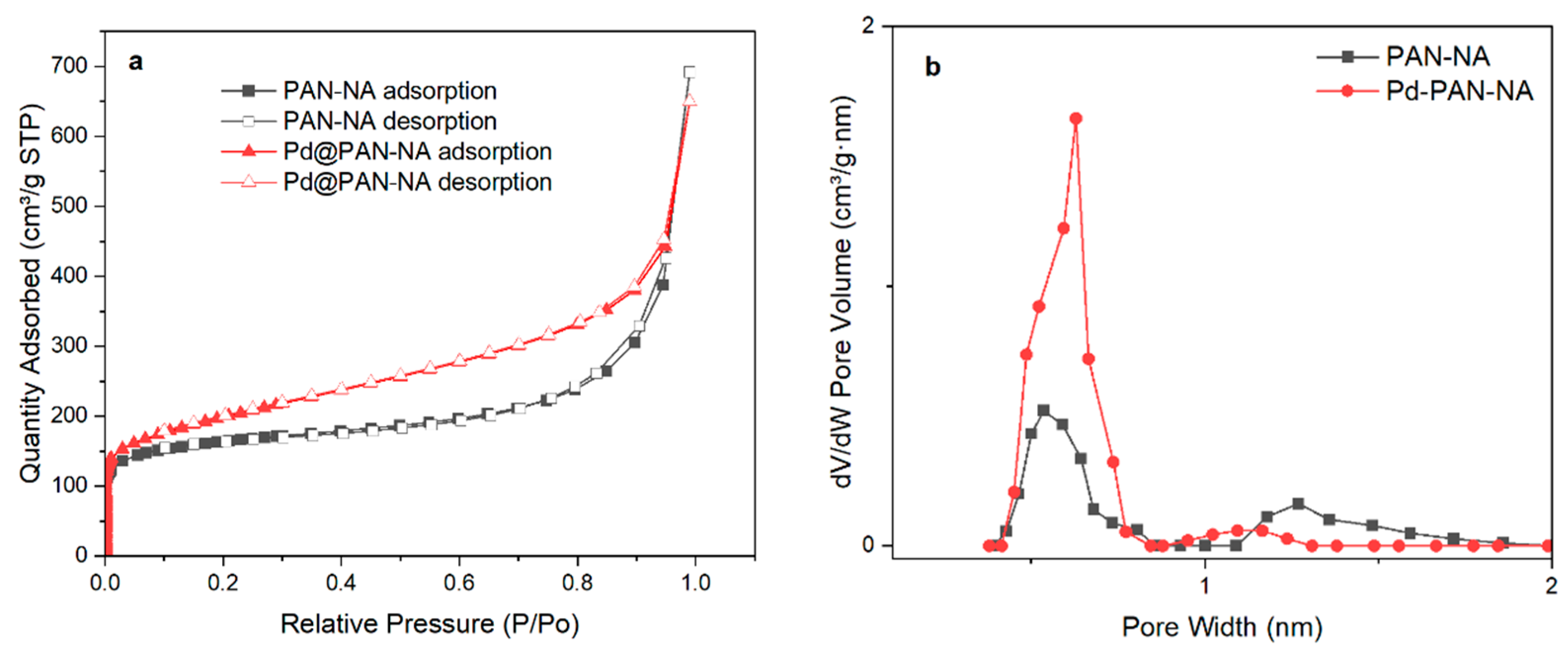
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Pd@PAN-NA Catalyst
3.2. Methylene Blue Reduction
3.2.1. Kinetic Study
3.2.2. Effect of Catalyst Dose
3.2.3. Effect of pH
3.2.4. Effect of Dye Concentration
3.2.5. Mechanism of Methylene Blue Reduction
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Panda, S.K.; Aggarwal, I.; Kumar, H.; Prasad, L.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, A.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Van Thuan, D.; Mishra, V. Magnetite nanoparticles as sorbents for dye removal: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 2487–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoso, E.; Ediati, R.; Kusumawati, Y.; Bahruji, H.; Sulistiono, D.O.; Prasetyoko, D. Review on recent advances of carbon based adsorbent for methylene blue removal from waste water. Mater. Today Chem. 2020, 16, 100233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, C.D.; Kanmani, S. Textile dye degradation using nano zero valent iron: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 177, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashkoor, F.; Nasar, A. Magsorbents: Potential candidates in wastewater treatment technology–A review on the removal of methylene blue dye. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 500, 166408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Ponce, N.T.; Banerjee, A.; Bandopadhyay, R.; Rajendran, S.; Lichtfouse, E. Green polymeric nanomaterials for the photocatalytic degradation of dyes: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 1569–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Chitkara, M.; Sandhu, I.S.; Mehta, D.; Kumar, S. Photocatalytic, optical and magnetic properties of Fe-doped ZnO nanoparticles prepared by chemical route. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 588, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Miao, J.; Wang, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhai, Z.; Dong, X.; Liu, Z. Nitrogen-rich melamine-based carbon nanosheets prepared via polyvinyl pyrrolidone/ammonia chloride-mediate strategy as an excellent adsorbent for methylene blue adsorption. Adv. Powder Technol. 2021, 32, 1774–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagub, M.T.; Sen, T.K.; Afroze, S.; Ang, H.M. Dye and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 209, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katheresan, V.; Kansedo, J.; Lau, S.Y. Efficiency of various recent wastewater dye removal methods: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4676–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkadokula, N.Y.; Kola, A.K.; Naz, I.; Saroj, D. A review on advanced physico-chemical and biological textile dye wastewater treatment techniques. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2020, 19, 543–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Mohd-Setapar, S.H.; Chuong, C.S.; Khatoon, A.; Wani, W.A.; Kumar, R.; Rafatullah, M. Recent advances in new generation dye removal technologies: Novel search for approaches to reprocess wastewater. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 30801–30818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadpoor, F.; Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Mohammad, M. Self-assembled lignosulfonate-inorganic hybrid nanoflowers and their application in catalytic reduction of methylene blue and 4-nitrophenol. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 272, 118864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, J.; Velusamy, P. Catalytic reduction of methylene blue using biogenic gold nanoparticles from Sesbania grandiflora L. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 2280–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, R.; Najeeb, J.; Sattar, A.; Naseem, K.; Irfan, A.; Al-Sehemi, A.G.; Farooqi, Z.H. Chemical reduction of methylene blue in the presence of nanocatalysts: A critical review. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2019, 36, 749–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajevardi, A.; Yaraki, M.T.; Masjedi, A.; Nouri, A.; Sadr, M.H. Green synthesis of MOF@Ag nanocomposites for catalytic reduction of methylene blue. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 276, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, K.; Farooqi, Z.H.; Begum, R.; Irfan, A. Removal of Congo red dye from aqueous medium by its catalytic reduction using sodium borohydride in the presence of various inorganic nano-catalysts: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 187, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Hu, Y.; Wan, S.; McCaffrey, R.; Jin, Y.; Gu, H.; Zhang, W. Synthesis of Ultrafine and Highly Dispersed Metal Nanoparticles Confined in a Thioether-Containing Covalent Organic Framework and Their Catalytic Applications. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 17082–17088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wu, J.; Chen, M.; Liu, X.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Feng, T.; Kang, S.; Wang, X. Recent advances in the biotoxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles: Impacts on plants, animals and microorganisms. Chemosphere 2019, 237, 124403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, R. Facile fabrication of a Cu@g-C3N4 nanocatalyst and its application for the aerobic oxidations of alkylaromatics and the reduction of 4-nitrophenol. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 90887–90896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-B.; Wang, Q.; Liang, J.; Wang, X.; Cao, R. Soluble Metal-Nanoparticle-Decorated Porous Coordination Polymers for the Homogenization of Heterogeneous Catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 10104–10107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Lyu, F.; Yin, Y. Encapsulated Metal Nanoparticles for Catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 834–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naz, M.; Rafiq, A.; Ikram, M.; Haider, A.; Ahmad, S.O.A.; Haider, J.; Naz, S. Elimination of dyes by catalytic reduction in the absence of light: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 15572–15608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Ma, X.; Wei, X.; Jin, Y.; Qiu, L.; Zhang, W. Porous organic polymer material supported palladium nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 17360–17391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, J.; Nath, I.; Song, S.; Mohamed, S.; Khan, A.; Heynderickx, P.M.; Verpoort, F. Porous organic polymer composites as surging catalysts for visible-light-driven chemical transformations and pollutant degradation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2019, 41, 100319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhao, H.; Wang, R. Tailorable Synthesis of Porous Organic Polymers Decorating Ultrafine Palladium Nanoparticles for Hydrogenation of Olefins. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 948–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilian, A.T.E.; Sivakumar, R.; Huh, Y.S.; Youk, J.H.; Han, Y.-K. Palladium Supported on an Amphiphilic Triazine–Urea-Functionalized Porous Organic Polymer as a Highly Efficient Electrocatalyst for Electrochemical Sensing of Rutin in Human Plasma. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 19554–19563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Fan, M.; Sun, X.; Wang, W.D.; Dong, Z. Ultrafine palladium nanoparticles confined in core–shell magnetic porous organic polymer nanospheres as highly efficient hydrogenation catalyst. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 554, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhao, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, R. Facile Fabrication of Ultrafine Palladium Nanoparticles with Size- and Location-Control in Click-Based Porous Organic Polymers. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 5352–5364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, F.; Dinari, M. Cu nanoparticles embedded in the porous organic polymer as highly effective catalysts for nitroaromatics reduction. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 325, 111339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xu, Q. Encapsulating Metal Nanocatalysts within Porous Organic Hosts. Trends Chem. 2020, 2, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Sun, J.-K.; Kitta, M.; Pang, H.; Xu, Q. Encapsulating highly catalytically active metal nanoclusters inside porous organic cages. Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Verma, P.; Samanta, D.; Dey, A.; Dey, J.; Maji, T.K. Stabilization of ultra-small gold nanoparticles in a photochromic organic cage: Modulating photocatalytic CO2 reduction by tuning light irradiation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 5780–5786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yuan, M.; Xu, D.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, Y.; Fan, M.; Zhang, F.; Dong, Z. Highly dispersed ultrafine palladium nanoparticles encapsulated in a triazinyl functionalized porous organic polymer as a highly efficient catalyst for transfer hydrogenation of aldehydes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 18242–18251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Yang, R.; Wei, S.; Hu, X.; Xu, D.; Yang, J.; Dong, Z. Ultra-fine Pd nanoparticles confined in a porous organic polymer: A leaching-and-aggregation-resistant catalyst for the efficient reduction of nitroarenes by NaBH4. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 538, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, M.; Tashkandi, N.; Hadjichristidis, N.; Alkayal, N.S. Synthesis of Naphthalene-Based Polyaminal-Linked Porous Polymers for Highly Effective Uptake of CO2 and Heavy Metals. Polymers 2022, 14, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Din, M.I.; Khalid, R.; Najeeb, J.; Hussain, Z. Fundamentals and photocatalysis of methylene blue dye using various nanocatalytic assemblies–A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 298, 126567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, J.; Begum, A.; Mukherjee, A.; Kumar, S. A novel green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their catalytic action in reduction of Methylene Blue dye. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2017, 27, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, M.; Kurtan, U.; Baykal, A. Rapid color degradation of organic dyes by Fe3O4@His@Ag recyclable magnetic nanocatalyst. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 27, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Cui, T.; Wang, H.; Xu, L.; Cui, F.; Wu, J. A simple way to prepare Au@polypyrrole/Fe3O4 hollow capsules with high stability and their application in catalytic reduction of methylene blue dye. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 7666–7674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedi, N.; Saidi, K.; Sheibani, H. Green Synthesis of Pd Nanoparticles Supported on Magnetic Graphene Oxide by Origanum vulgare Leaf Plant Extract: Catalytic Activity in the Reduction of Organic Dyes and Suzuki–Miyaura Cross-Coupling Reaction. Catal. Lett. 2018, 148, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, R.; Kumar, S.S.; Venkatesan, R. Efficient degradation of azo dyes using Ag and Au nanoparticles stabilized on graphene oxide functionalized with PAMAM dendrimers. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 1551–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, P.; Miah, A.T.; DAS, P.P. Highly efficient catalytic reductive degradation of various organic dyes by Au/CeO2-TiO2 nano-hybrid. J. Chem. Sci. 2017, 129, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Wu, T.; Hu, B.; Yang, Q.; Liu, L.; Yu, B.; Ding, Y.; Ye, S. Synthesis of thermo- and pH-responsive Ag nanoparticle-embedded hybrid microgels and their catalytic activity in methylene blue reduction. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 149–150, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Giordano, C.; Gradzielski, M.; Mehta, S.K. Microwave-assisted synthesis of small Ru nanoparticles and their role in degradation of congo red. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 411, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Khan, S.B.; Kamal, T.; Alamry, K.A.; Asiri, A.M.; Sobahi, T.R.A. Chitosan coated cotton cloth supported zero-valent nanoparticles: Simple but economically viable, efficient and easily retrievable catalysts. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, A.; Vellayan, K.; González, B.; Vicente, M.A.; Gil, A. Effective degradation of methylene blue in aqueous solution using Pd-supported Cu-doped Ti-pillared montmorillonite catalyst. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 168, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnia, N.; Kamaruddin, M.; Nawawi, M.; Ratim, S.; Azlina, H.; Ali, E. Green Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using ‘Polygonum Hydropiper’ and Study its Catalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue. Procedia Chem. 2016, 19, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.M.; Lee, J.; Cho, M.H. Au@TiO2 nanocomposites for the catalytic degradation of methyl orange and methylene blue: An electron relay effect. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 1584–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreeju, N.; Rufus, A.; Philip, D. Studies on catalytic degradation of organic pollutants and anti-bacterial property using biosynthesized CuO nanostructures. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 242, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucar, A.; Findik, M.; Gubbuk, I.H.; Kocak, N.; Bingol, H. Catalytic degradation of organic dye using reduced graphene oxide–polyoxometalate nanocomposite. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2017, 196, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimi, A.S.; Nohan, M.A.N.M.; Chin, S.X.; Zakaria, S.; Chia, C.H. Rapid Catalytic Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol and Clock Reaction of Methylene Blue using Copper Nanowires. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amir, M.; Kurtan, U.; Baykal, A. Synthesis and application of magnetically recyclable nanocatalyst Fe3O4@Nico@Cu in the reduction of azo dyes. Chin. J. Catal. 2015, 36, 1280–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Entry | Catalyst | Conditions | Time (min) | kapp (min−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pd@PAN-NA | [MB] = 0.08 mM [Catalyst] = 3.5 mg/mL | 6 | 0.931 | This work |
| 2 | Fe/CC-CH | [MB] = 0.05 mM [Catalyst] = 5 wt% | 9 | 0.280 | [45] |
| 3 | MTiCuPd500 | [MB] = 2 g/L [Catalyst] = 5 mg | 20 | - | [46] |
| 4 | AgNPs | [MB] = 0.001 M [Catalyst] = 0.01 M | 13 | - | [47] |
| 5 | Au@TiO2 | [MB] = 0.04 mM [Catalyst] = 2 mg | 12 | 0.156 | [48] |
| 6 | CuO | [MB] = 1 mM [Catalyst] = 1 mg | 12 | 0.419 | [49] |
| 7 | rGO-SiW | [MB] = 35 mg/L [Catalyst] = 0.1 mg/mL | 34 | 0.055 | [50] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alkayal, N.S.; Ibrahim, M.; Tashkandi, N.; Alotaibi, M.M. Efficient Reduction in Methylene Blue Using Palladium Nanoparticles Supported by Melamine-Based Polymer. Materials 2023, 16, 5887. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16175887
Alkayal NS, Ibrahim M, Tashkandi N, Alotaibi MM. Efficient Reduction in Methylene Blue Using Palladium Nanoparticles Supported by Melamine-Based Polymer. Materials. 2023; 16(17):5887. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16175887
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlkayal, Nazeeha S., Manal Ibrahim, Nada Tashkandi, and Maha M. Alotaibi. 2023. "Efficient Reduction in Methylene Blue Using Palladium Nanoparticles Supported by Melamine-Based Polymer" Materials 16, no. 17: 5887. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16175887
APA StyleAlkayal, N. S., Ibrahim, M., Tashkandi, N., & Alotaibi, M. M. (2023). Efficient Reduction in Methylene Blue Using Palladium Nanoparticles Supported by Melamine-Based Polymer. Materials, 16(17), 5887. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16175887






