Properties of PBZTS Ferroelectric Ceramics Obtained Using Spark Plasma Sintering
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramana, M.V.; Kiran, S.R.; Reddy, N.R.; Kumar, K.V.S.; Murthy, V.R.K.; Murty, B.S. Investigation and characterization of Pb(Zr0.52Ti0.48)O3 nanocrystalline ferroelectric ceramics: By conventional and microwave sintering methods. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 126, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marakhovsky, M.A.; Panich, A.A.; Talanov, M.V.; Marakhovskiy, V.A. Comparative study of the hard and soft PZT-based ceramics sintered by various methods. Ferroelectrics 2021, 575, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.K.; Ounaies, Z.; Varadan, V.V.; Varadan, V.K. Dielectric and piezoelectric properties of microwave sintered PZT. Smart Mater. Struct. 2001, 10, 878–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.J.; Uekawa, N.; Kakegawa, K.; Sasaki, Y. Compositional fluctuation and dielectric properties of Pb(Zr0.3TiO0.7)O3 ceramics prepared by Spark Plasma Sintering. Mater. Lett. 2002, 57, 771–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudinepalli, V.R.; Leng, F. Dielectric and ferroelectric studies on high dense Pb(Zr0.52Ti0.48)O3 nanocrystalline ceramics by high energy ball milling and spark plasma sintering. Ceramics 2019, 2, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokita, M. Progress of spark plasma sintering (SPS) method, systems, ceramics applications and industrialization. Ceramics 2021, 4, 160–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Tsuji, K.; Randall, C.A.; Trolier-McKinstry, S. Model for the cold sintering of lead zirconate titanate ceramic composites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 103, 4894–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Wang, D.; Randall, C.A.; Trolier-McKinstry, S. Comparison of different sintering aids in cold sinter-assisted densification of lead zirconate titanate. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 104, 5479–5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Su, X.; Wu, Y.; Bai, G.; Wang, Z.; Yan, X.; Ai, T.; Zhao, P. Fabrication of lead zirconate titanate ceramics by reaction flash sintering of PbO-ZrO2-TiO2 mixed oxides. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 39, 3915–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laszkiewicz-Łukasik, J.; Putyra, P.; Klimczyk, P.; Podsiadło, M.; Bednarczyk, K. Spark plasma sintering/field assisted sintering technique as a universal method for the synthesis, densification and bonding processes for metal, ceramic and composite materials. J. Appl. Mater. Eng. 2020, 60, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisar, A.; Zhang, C.; Boesl, B.; Agarwal, A. Unconventional Materials Processing Using Spark Plasma Sintering. Ceramics 2021, 4, 20–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonenko, T.L.; Kalinina, M.V.; Simonenko, N.P.; Simonenko, E.P.; Glumov, O.V.; Mel’nikova, N.A.; Murin, I.V.; Shichalin, O.O.; Papynov, E.K.; Shilova, O.A. Spark plasma sintering of nanopowders in the CeO2-Y2O3 system as a promising approach to the creation of nanocrystalline intermediate-temperature solid electrolytes. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 19879–19884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Li, X.; Qu, S.; Li, Y. Effect of heating rate on densification and grain growth during spark plasma sintering of 93W-5.6Ni-1.4Fe heavy alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2013, 44, 4323–4336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, F.; Zhang, F.; Sajjadi, S.A.; Sabzevar, M.H.; Cavaliere, P. Spark Plasma Sintering of Materials: Advances in Processing and Applications; Springer Nature AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kosyanov, D.Y.; Yavetskiy, R.P.; Tolmachev, A.V.; Vornovskikh, A.A.; Pogodaev, A.V.; Gridasova, E.A.; Shichalin, O.O.; Kaidalova, T.A.; Kuryavyi, V.G. Fabrication of highly-doped Nd3+:YAG transparent ceramics by reactive SPS. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 23145–23149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaim, R.; Chevallier, G.; Weibel, A.; Estournès, C. Grain growth during spark plasma and flash sintering of ceramic nanoparticles: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 3087–3105. [Google Scholar]
- Antou, G.; Guyot, P.; Pradeilles, N.; Vandenhende, M.; Maître, A. Identification of densification mechanisms of pressure-assisted sintering: Application to hot pressing and spark plasma sintering of alumina. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 2327–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuer, M.; Bowen, P.; Zhao, Z. Spark plasma sintering of ceramics: From modeling to practice. Ceramics 2020, 3, 476–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noudem, J.G.; Xing, Y. Overview of Spark Plasma Texturing of functional ceramics. Ceramics 2021, 4, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Zhao, Z.; Jin, J.; Deng, L.; Gong, P.; Wang, X. Densification mechanism of Zr-based bulk metallic glass prepared by two-step spark plasma sintering. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 850, 156724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, Z.A.; Anselmi-Tamburini, U.; Ohyanagi, M. The effect of electric field and pressure on the synthesis and consolidation of materials: A review of the spark plasma sintering method. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 763–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, T.; Bétourné, E.; Tabuchi, M.; Kageyama, H.; Kobayashi, Y.; Coats, A.; Morrison, F.; Sinclair, D.C.; West, A.R. Dielectric properties of spark-plasma-sintered BaTiO3. J. Mater. Sci. 1999, 34, 917–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod, V.T. A review of electric impedance matching techniques for piezoelectric sensors, actuators and transducers. Electronics 2019, 8, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.G.; Jung, W.S.; Kang, C.Y.; Yoon, S.J. Recent progress on PZT based piezoelectric energy harvesting technologies. Actuators 2016, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, C.R.; Kim, H.A.; Weaver, P.M.; Dunn, S. Piezoelectric and ferroelectric materials and structures for energy harvesting applications. Energ. Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 25–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Cheng, L.-H.; Hong, R.-Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, C.-J.; Tian, C. Crystal structure and piezoelectric properties of xPb(Mn1/3Nb2/3)O3–(0.2−x)Pb(Zn1/3Nb2/3)O3–0.8Pb(Zr0.52Ti0.48)O3 ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2009, 35, 1719–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khacheba, M.; Abdessalem, N.; Hamdi, A.; Khemakhem, H. Effect of acceptor and donor dopants (Na, Y) on the microstructure and dielectric characteristics of high Curie point PZT-modified ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 61–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkuratov, S.I.; Lynch, C.S. A review of ferroelectric materials for high power devices. J. Mater. 2022, 8, 739–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Li, S.; Gong, Y.; Yu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Liu, P.; Jing, Q. Diversified electrical properties of Ba0.90Ca0.10Ti0.95Zr0.05O3−xRuO2 ceramics with defect electron complexes. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 204, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skulski, R. Gaussian-logarithmic distribution of relaxation times in relaxor materials. Phys. A 1999, 274, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skulski, R.; Niemiec, P.; Bochenek, D.; Chrobak, A. Dispersion of dielectric permittivity and magnetic properties of solid solution PZT–PFT. Mater. Sci.-Poland 2015, 33, 597–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yasuda, N.; Ohwa, H.; Asano, S. Dielectric properties and phase transitions of Ba(Ti1−xSnx)O3 solid solution. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1996, 35, 5099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzezińska, D.; Skulski, R.; Wawrzała, P.; Dercz, G. The properties of (Pb0.97Ba0.03)[(Zr0.98Ti0.02)1−zSnz]O3 ceramics with 0 < z < 0.08. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2013, 58, 1377–1380. [Google Scholar]
- Brzezińska, D.; Skulski, R.; Wawrzała, P. The properties of PBZTS ceramics near orthorhombic-rhombohedral morphotropic phase boundary. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2011, 56, 1243–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochenek, D.; Niemiec, P.; Skulski, R.; Adamczyk, M.; Brzezińska, D. Electrophysical properties of the multicomponent PBZT-type ceramics doped by Sn4+. J. Electroceram. 2019, 42, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fesenko, E.G.; Danziger, A.Y.; Rozumowskaya, O.N. Novye Pezokeramicheskie Materialy; RGU: Rostov-na-Donu, Russia, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Brzezińska, D. Properties of Pb1–xBax(Zr1–yTiy)1–zSnzO3 (x = 0.03, y = 0.02, z = 0 ÷ 0.08) ceramics. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2020, 65, 975–982. [Google Scholar]
- Kornphom, C.; Panich, C.; Bongkarn, T. Phase formation and piezoelectric properties of (Pb0.95Ba0.05)(Zr1−xTix)O3 ceramics fabricated by solid state reaction technique. Mater. Res. Innov. 2014, 18, S2-146–S2-150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Zhang, H.; Du, Z.; Liu, C. Structural insight into the optical and electro-optic properties of lead zirconate titanate for high-performance photonic devices. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 22324–22330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, B.; Cook, W.R.; Jaffe., H. Piezoelectric Ceramics; Academic Press: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Bongkarn, T.; Thiangchit, C. Preparation of PBZT ceramics via solid state reaction method. Ferroelectrics 2009, 383, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattanawikkam, C.; Chootin, S.; Bongkarn, T. Crystal structure and microstructure of (Pb1−xBax)(Zr1−yTiy)O3 ceramics prepared by the solid state reaction method. Ferroelectrics 2010, 403, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongtha, A.; Wattanawikkam, C.; Bongkarn, T. Phase formation and dielectric properties of (Pb0.925Ba0.075)(Zr1−xTix)O3 ceramics prepared by the solid-state reaction method. Phase Transit. 2011, 84, 952–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, S.; Badole, M.; Vasavan, H.N.; Kumar, S. Influence of annealing environments on the conduction behavior of KNN-based ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 18057–18066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagar, S.; Hooda, A.; Khasa, S.; Malik, M. Structural refinement, investigation of dielectric and magnetic properties of NBT doped BaFe12O19 novel composite system. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 826, 154214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osak, A. Hopping electrical conductivity in ferroelectric Pb[(Fe1/3Sb2/3)xTiyZrz]O3. Ferroelectrics 2011, 418, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonscher, A.K. The ‘uniwersal’ dielectric response. Nature 1977, 267, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonscher, A.K. Review a new understanding of the dielectric relaxation of solids. J. Mater. Sci. 1981, 16, 2037–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegab, N.A.; Afifi, M.A.; Atyia, H.E.; Ismael, M.I. Ac conductivity and dielectric properties of amorphous Ge15Se60X25 (X = As or Sn) films. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2011, 119, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osak, A.; Piwowarczyk, J. Studies of the dc and ac hopping electrical conductivity in ferroelectric Pb[(Fe1/3Sb2/3)xTiyZrz]O3. Technol. Trans. Fundam. Sci. 2011, 1-NP, 59–75. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.K.; Liu, J.F.; Nowick, A.S. Limiting behavior of ac conductivity in ionically conducting crystals and glasses: A new universality. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1994, 67, 1559–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Mallah, H.M.; Hegab, N.A. Studies on a.c. properties of Ca1−xSrxTiO3 perovskites. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dec, J. Real domain structure in orthorhombic phase of NaNbO3 crystals. Crystal. Res. Technol. 1983, 18, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handerek, J.; Ujma, Z.; Roleder, K. Phase transitions in PbZrxTi1−xO3 with up to 3% Ti content. Phase Transit. 1980, 1, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
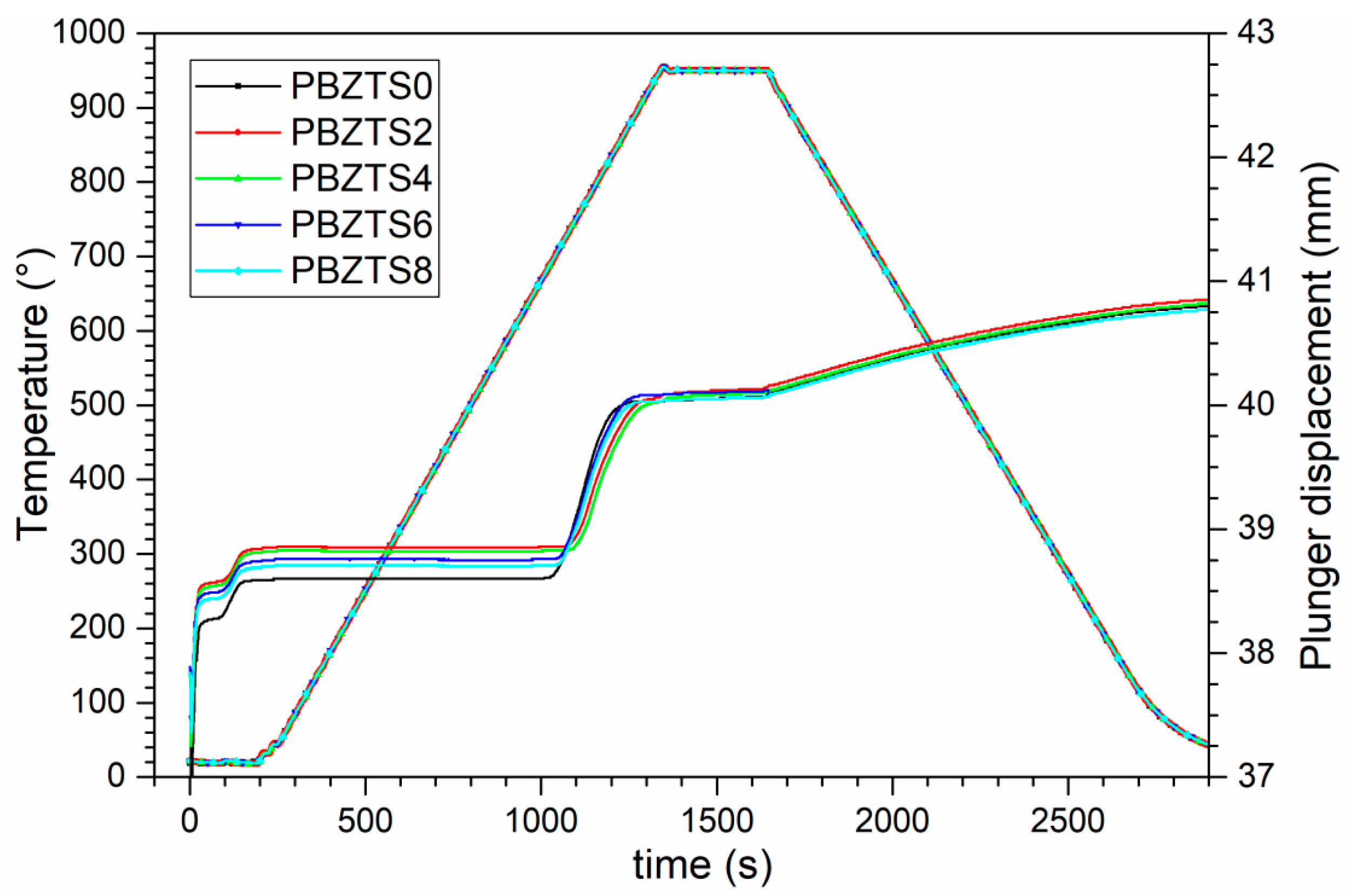
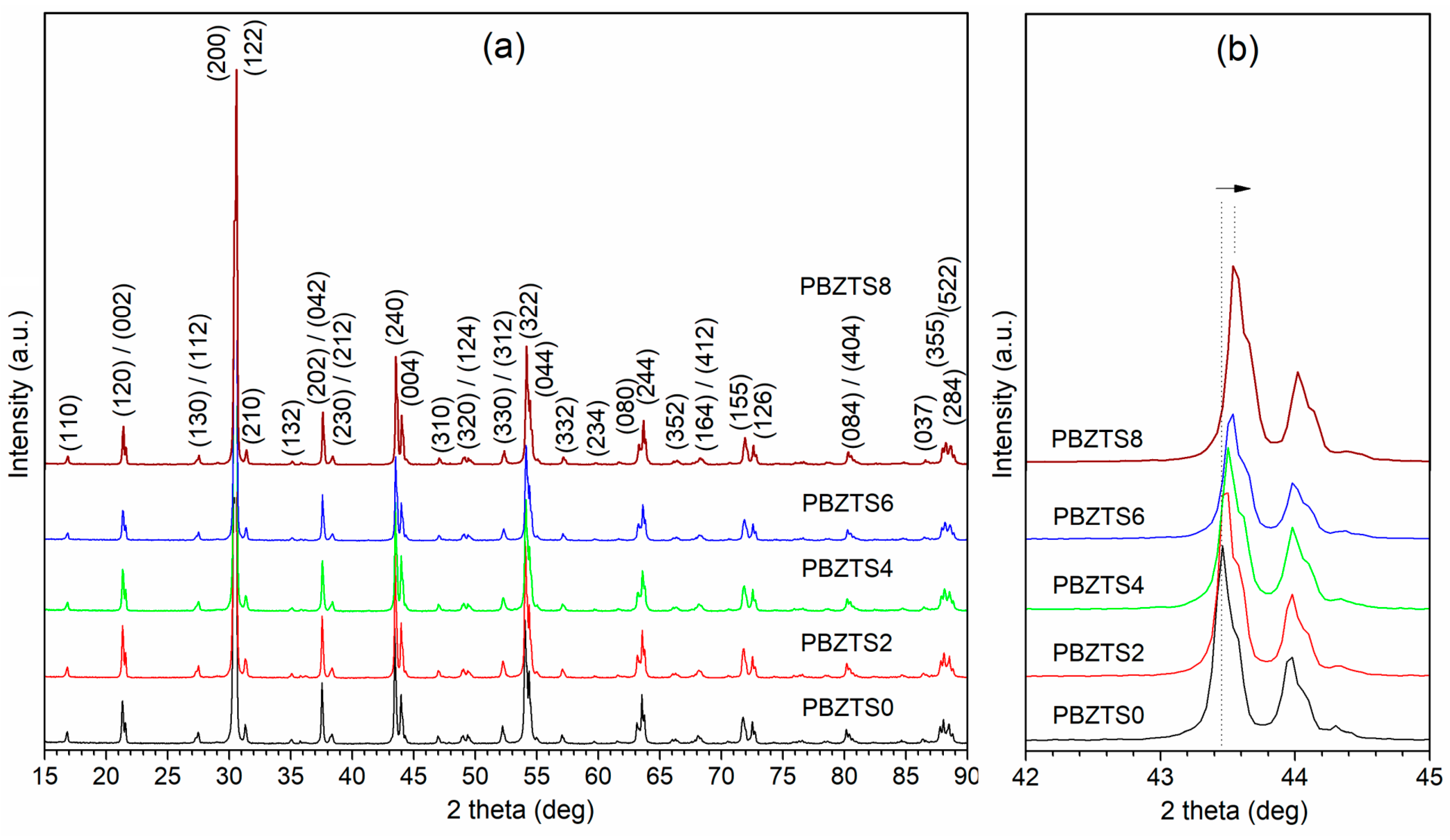

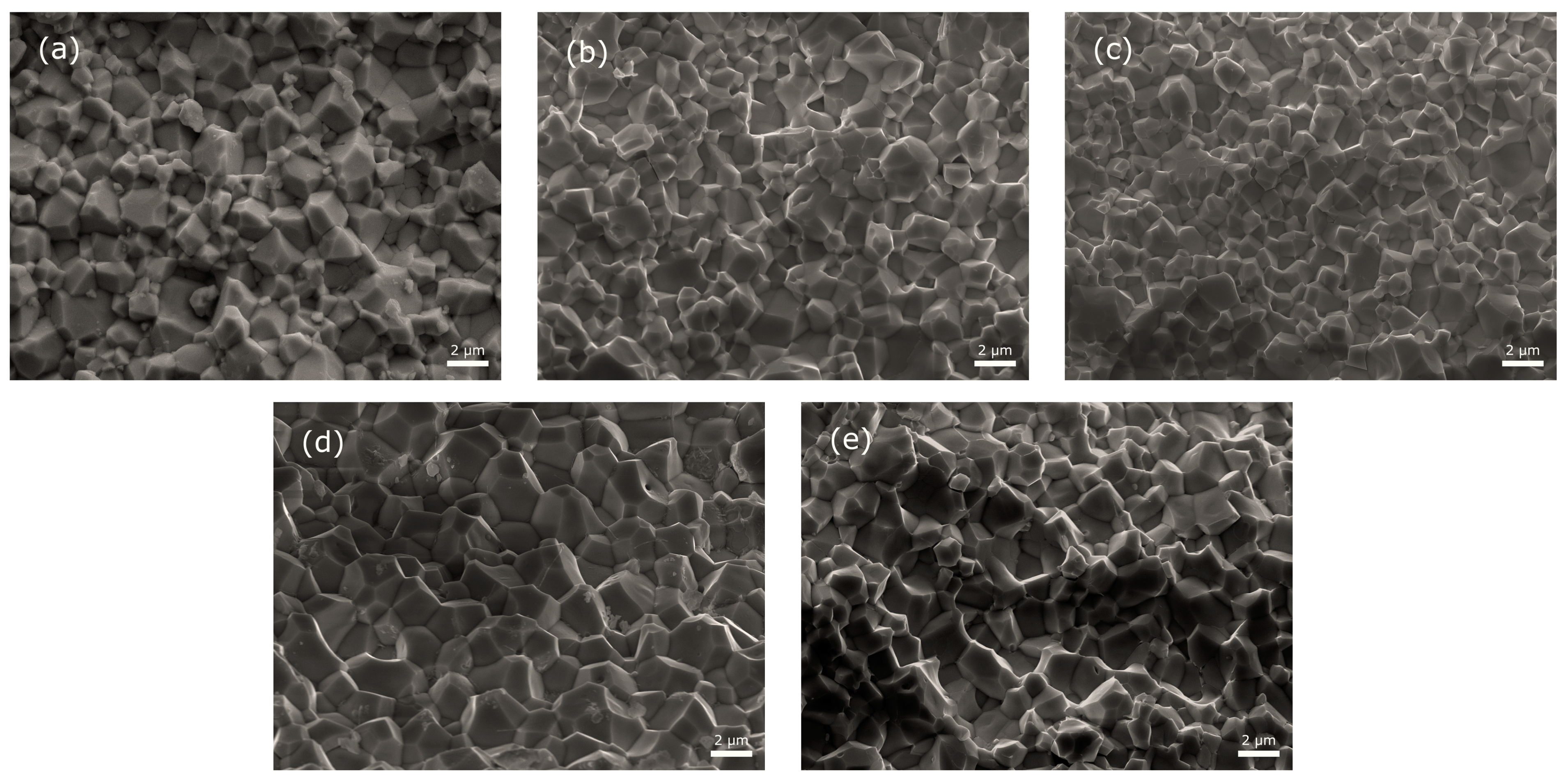
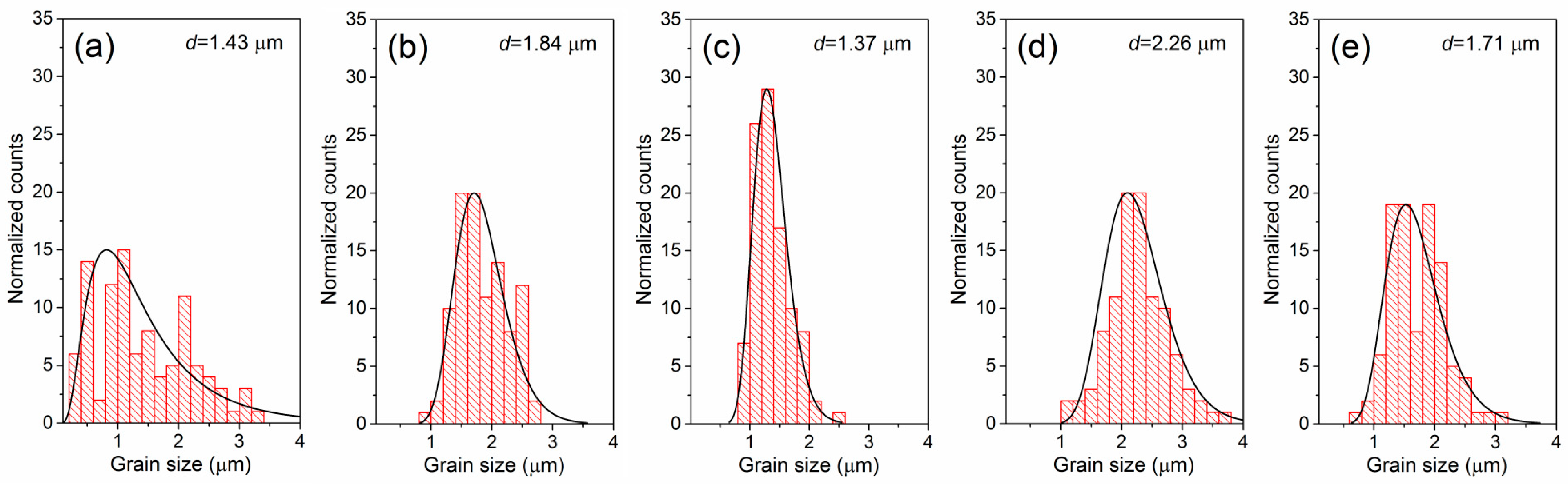



| Abbreviation | Basic Composition Mark | x (Sn Content) |
|---|---|---|
| PBZTS0 | Pb0.97Ba0.03(Zr0.98Ti0.02)O3 | 0 |
| PBZTS2 | Pb0.97Ba0.03(Zr0.98Ti0.02)0.98Sn0.02O3 | 0.02 |
| PBZTS4 | Pb0.97Ba0.03(Zr0.98Ti0.02)0.96Sn0.04O3 | 0.04 |
| PBZTS6 | Pb0.97Ba0.03(Zr0.98Ti0.02)0.94Sn0.06O3 | 0.06 |
| PBZTS8 | Pb0.97Ba0.03(Zr0.98Ti0.02)0.92Sn0.08O3 | 0.08 |
| Parameter | PBZTS0 | PBZTS2 | PBZTS4 | PBZTS6 | PBZTS8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| classical technology (fee sintering) | |||||
| ρ (g/cm3) | 6.76 | 6.52 | 5.76 | 6.24 | 7.01 |
| r (μm) | 1.79 | 2.84 | 2.05 | 2.02 | 1.91 |
| εr a,b | 134 | 146 | 156 | 161 | 166 |
| tan δ a,b | 0.036 | 0.014 | 0.027 | 0.047 | 0.011 |
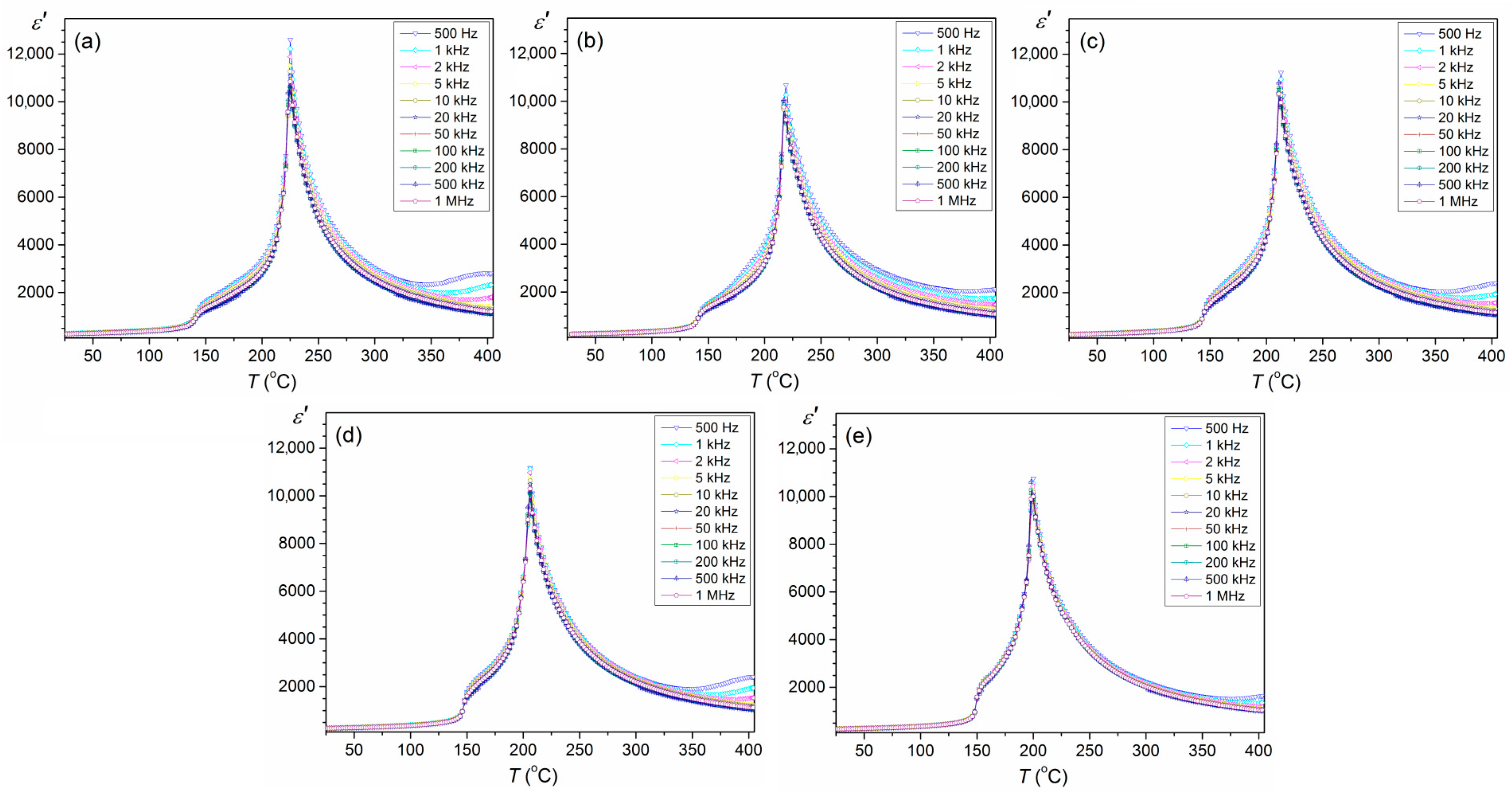
| Tm (°C) b | 225 | 218 | 211 | 203 | 199 |
| εm at Tm b | 663 | 1481 | 1168 | 1536 | 3264 |
| tan δ at Tm b | 0.139 | 0.284 | 0.110 | 0.063 | 0.273 |
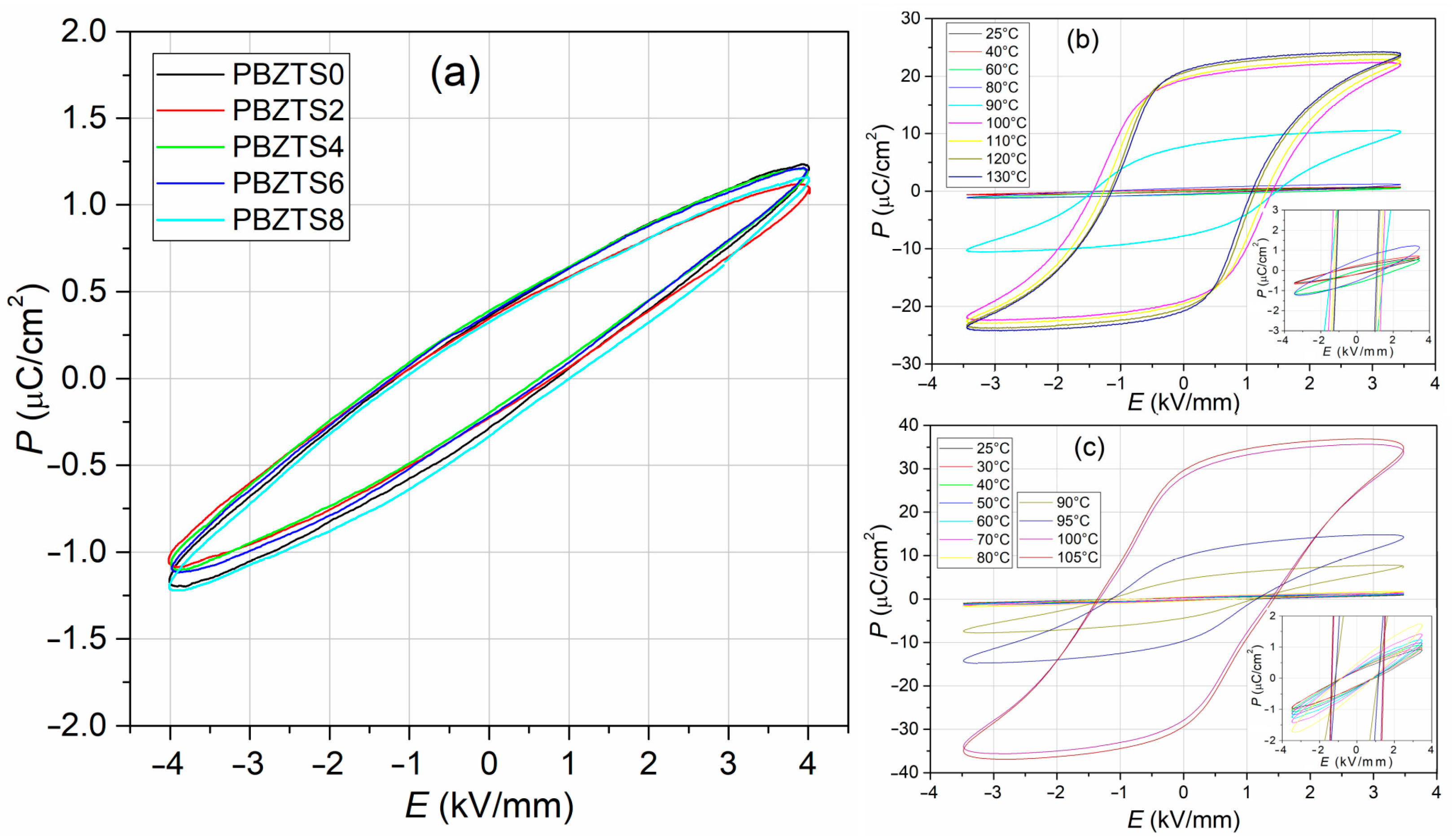
| Pr (μC/cm2) a | 0.19 | 0.24 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.29 |
| Ec (kV/mm) a | 1.27 | 1.30 | 0.76 | 1.05 | 1.35 |
| Pmax (μC/cm2) a | 0.49 | 0.65 | 0.79 | 0.63 | 0.71 |
| spark plasma sintering | |||||
| ρ (g/cm3) | 7.81 | 7.54 | 7.68 | 7.48 | 7.69 |
| r (μm) | 1.43 | 1.84 | 1.37 | 2.26 | 1.71 |
| εr a,b | 282 | 245 | 262 | 263 | 258 |
| tan δ a,b | 0.036 | 0.020 | 0.015 | 0.015 | 0.006 |
| Tm (°C) b | 225 | 219 | 213 | 206 | 200 |
| εm at Tm b | 12,221 | 10,259 | 10,946 | 11,122 | 10,563 |
| tan δ at Tm b | 0.049 | 0.070 | 0.033 | 0.018 | 0.020 |
| Pr (μC/cm2) a | 0.36 | 0.35 | 0.39 | 0.37 | 0.32 |
| Ec (kV/mm) a | 1.01 | 0.99 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 1.04 |
| Pmax (μC/cm2) a | 1.23 | 1.12 | 1.21 | 1.22 | 1.16 |
| Parameter | PBZTS0 | PBZTS2 | PBZTS4 | PBZTS6 | PBZTS8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ea in I (eV) | 0.09 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.06 |
| Ea in II (eV) | 0.48 | 0.36 | 0.24 | 0.36 | 0.74 |
| Ea in III (eV) | 0.53 | 0.48 | 0.46 | 0.43 | 0.21 |
| Ea in IV (eV) | 0.52 | 0.51 | 0.52 | 0.52 | 0.51 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brzezińska, D.; Bochenek, D.; Niemiec, P.; Dercz, G. Properties of PBZTS Ferroelectric Ceramics Obtained Using Spark Plasma Sintering. Materials 2023, 16, 5756. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16175756
Brzezińska D, Bochenek D, Niemiec P, Dercz G. Properties of PBZTS Ferroelectric Ceramics Obtained Using Spark Plasma Sintering. Materials. 2023; 16(17):5756. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16175756
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrzezińska, Dagmara, Dariusz Bochenek, Przemysław Niemiec, and Grzegorz Dercz. 2023. "Properties of PBZTS Ferroelectric Ceramics Obtained Using Spark Plasma Sintering" Materials 16, no. 17: 5756. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16175756
APA StyleBrzezińska, D., Bochenek, D., Niemiec, P., & Dercz, G. (2023). Properties of PBZTS Ferroelectric Ceramics Obtained Using Spark Plasma Sintering. Materials, 16(17), 5756. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16175756







