Predicting the Effect of Surface Waviness on Fatigue Life of a Wire + Arc Additive Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods

| Modulus (GPa) [4] | Yield Strength (MPa) [4] | Ultimate Tensile Strength (MPa) [4] | Elongation at Failure [4] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 116 | 872 ± 16 | 952 ± 9 | 17.5 ± 4 | 4.5 |
2.1. Characterisation of As-Built Surface
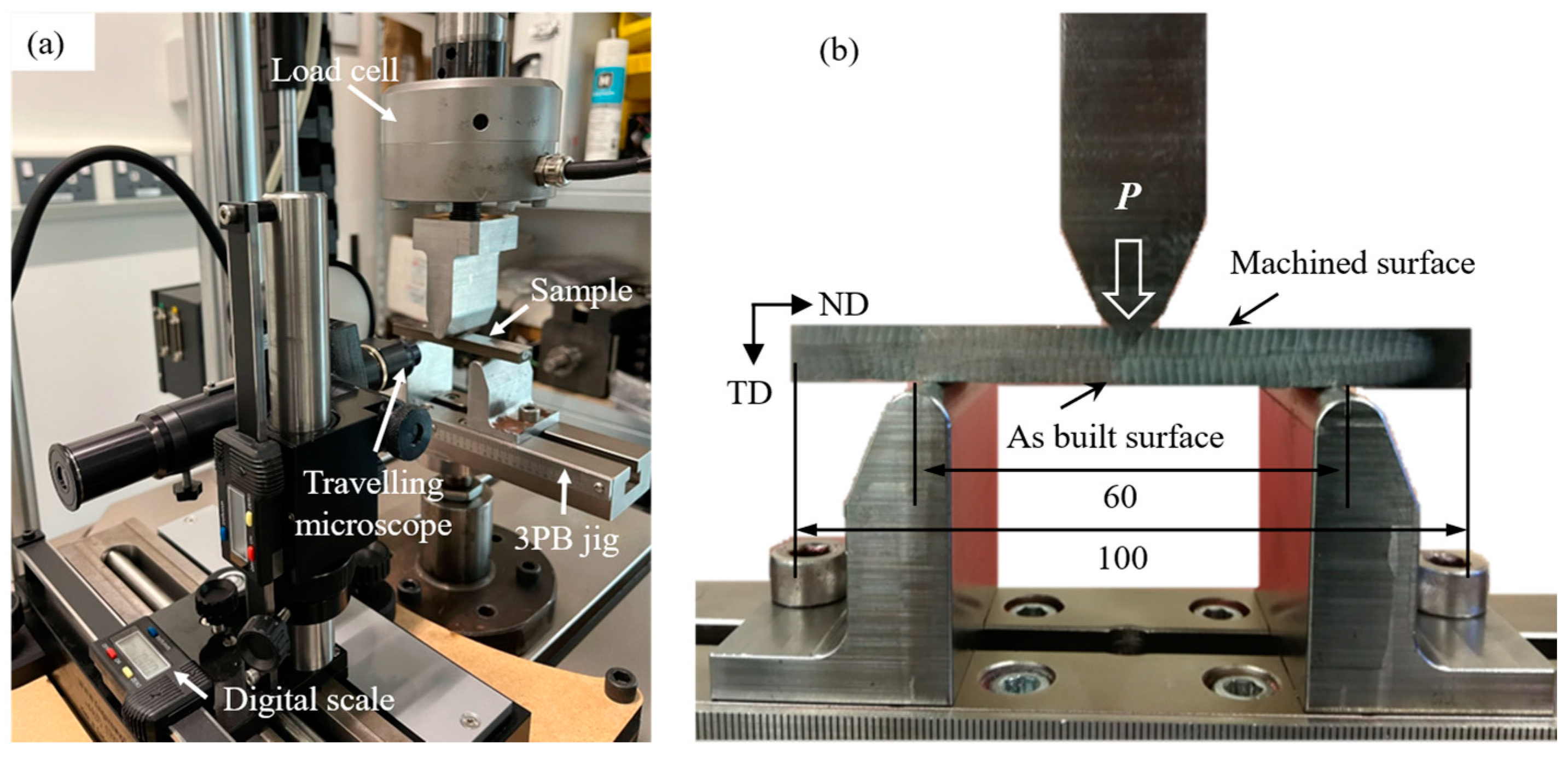
2.2. Fatigue Testing
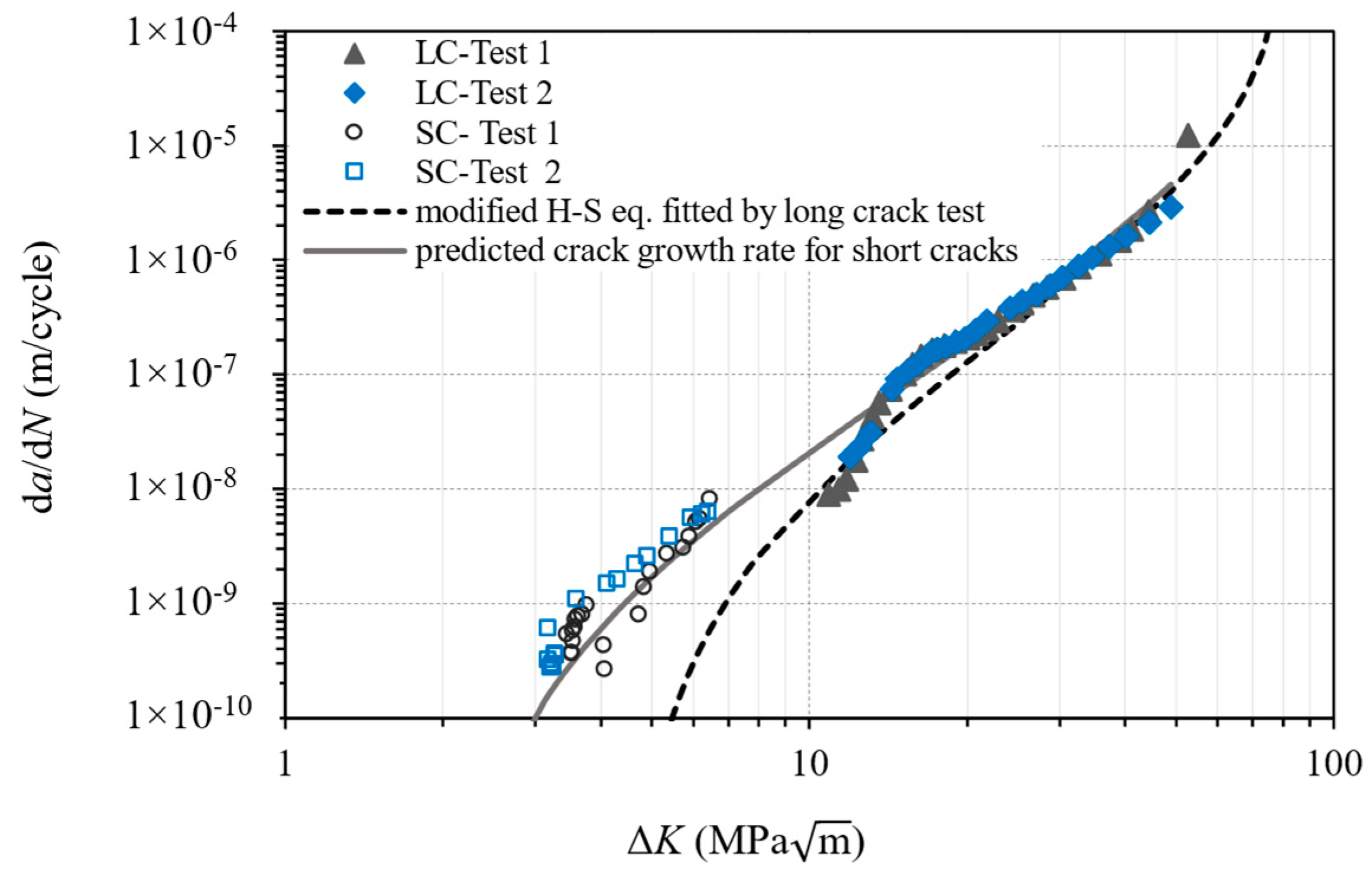
2.3. Life Prediction Methods
3. Finite Element Analysis of Stress Concentration Factor and Stress Intensity Factor
3.1. Stress Concentration Factor (Kt)
3.2. Stress Intensity Factor in Mode-I Loading (KI)
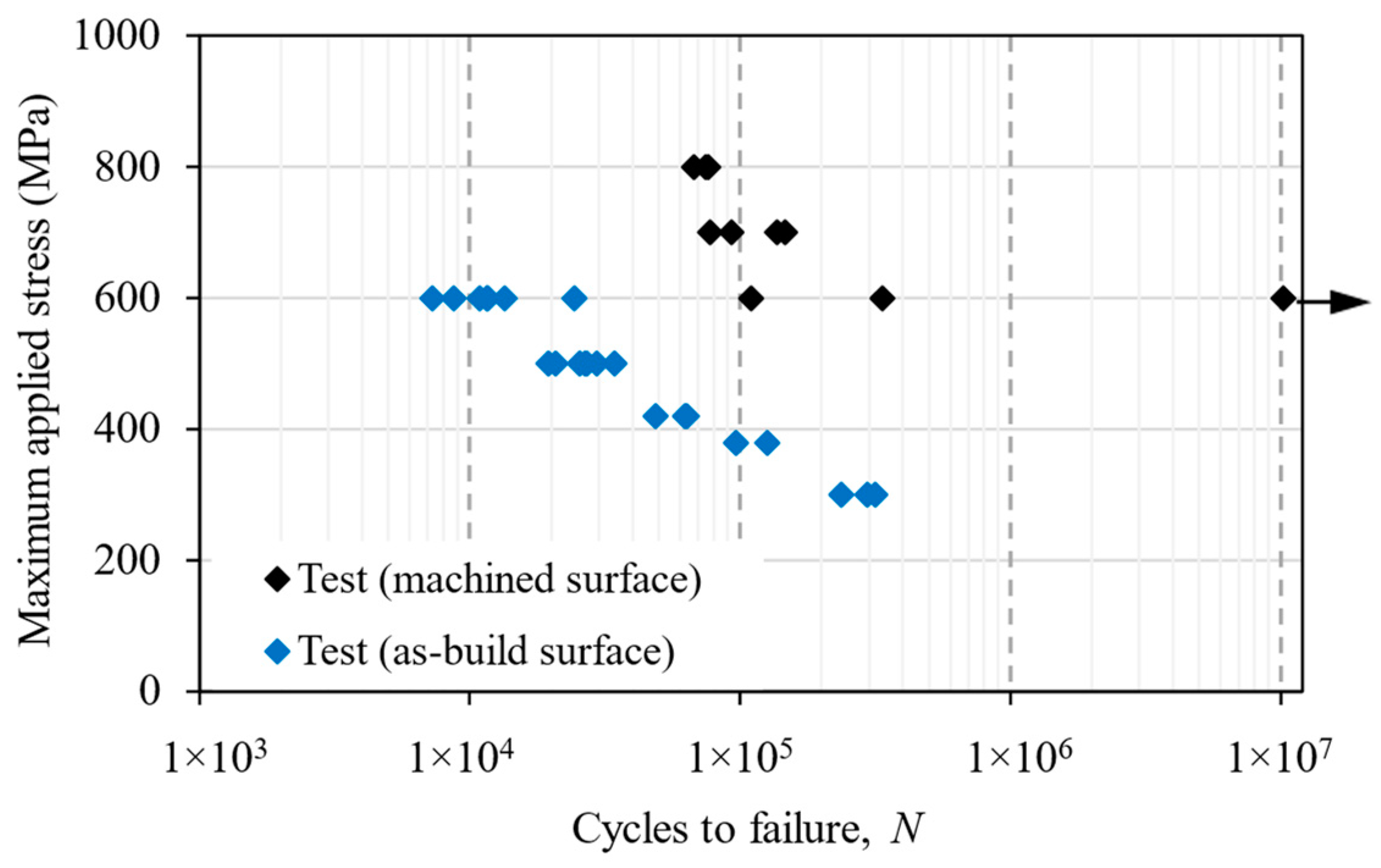
4. Experimental Test Results
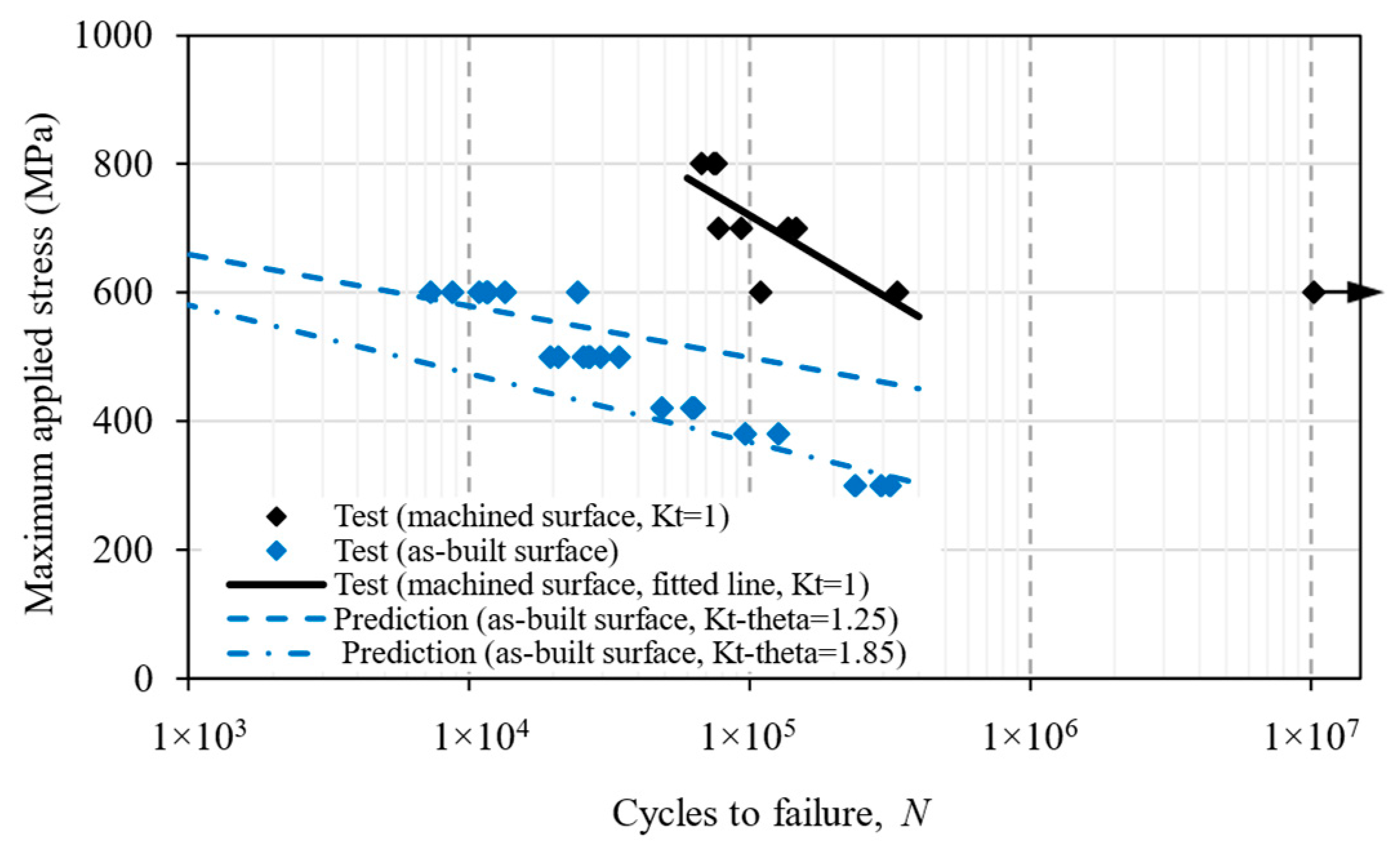
5. Fatigue Life Prediction
5.1. Notch Fatigue Approach
5.2. Fracture Mechanics Approach
6. Conclusions
- Troughs on the as-built surface of WAAM materials can be treated as a series of individual micro notches and can be characterised by three parameters: notch depth, notch base radius, and notch mouth opening angle.
- The traditional notch stress method cannot predict the correct S–N curve trend slop, which is attributed to the early crack initiation from the troughs and crack propagation as the dominant failure mechanism.
- The fracture mechanics approach has given good predictions by treating the troughs as small cracks. The predictive method can help with decision making as to whether surface machining is necessary, according to the service load level and fatigue strength target.
- The future perspective of this work is to use the short crack growth model as an engineering tool for the evaluation of the fatigue strength and for components with surface roughness or crack-like defects.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Williams, S.W.; Martina, F.; Addison, A.C.; Ding, J.; Pardal, G.; Colegrove, P. Wire + Arc additive manufacturing. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, D.; Vaneker, T.H.J.; Gibson, I. Wire and arc additive manufacturing : Opportunities and challenges to control the quality and accuracy of manufactured parts. Mater. Des. 2021, 202, 109471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Bhavsar, H.; Mahesh, P.V.S.; Srivastava, A.K.; Bora, B.J.; Saxena, A.; Dixit, A.R. Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing—A revolutionary method in additive manufacturing. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 285, 126144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, A.K.; Zhang, X.; Caballero, A.; Shamir, M.; Williams, S. Influence of deposition strategies on tensile and fatigue properties in a wire + arc additive manufactured Ti-6Al-4V. Int. J. Fatigue 2021, 149, 106268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arola, D.; Williams, C.L. Estimating the fatigue stress concentration factor of machined surfaces. Int. J. Fatigue 2002, 24, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegues, J.; Roach, M.; Scott Williamson, R.; Shamsaei, N. Surface roughness effects on the fatigue strength of additively manufactured Ti-6Al-4V. Int. J. Fatigue 2018, 116, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Fatemi, A. Surface roughness effect on multiaxial fatigue behavior of additive manufactured metals and its modeling. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2019, 103, 102260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ednie, L.; Lancaster, R.J.; Antonysamy, A.A.; Zelenka, F.; Scarpellini, A.; Parimi, L.; Maddalena, R.; Barnard, N.C.; Efthymiadis, P. The effects of surface finish on the fatigue performance of electron beam melted Ti–6Al–4V. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 857, 144050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greitemeier, D.; Dalle Donne, C.; Syassen, F.; Eufinger, J.; Melz, T. Effect of surface roughness on fatigue performance of additive manufactured Ti–6Al–4V. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gockel, J.; Sheridan, L.; Koerper, B.; Whip, B. The influence of additive manufacturing processing parameters on surface roughness and fatigue life. Int. J. Fatigue 2019, 124, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Ahmadi, Z.; Pegues, J.W.; Mahjouri-Samani, M.; Shamsaei, N. Laser polishing for improving fatigue performance of additive manufactured Ti-6Al-4V parts. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 134, 106639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greitemeier, D.; Palm, F.; Syassen, F.; Melz, T. Fatigue performance of additive manufactured TiAl6V4 using electron and laser beam melting. Int. J. Fatigue 2017, 94, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadi, H.; Jomaa, W.; Texier, D.; Brochu, M.; Bocher, P. Surface roughness effects on the fatigue behavior of as-Machined Inconel718. Solid State Phenom. 2016, 258, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanaei, N.; Fatemi, A. Progress in Materials Science Defects in additive manufactured metals and their effect on fatigue performance : A state-of-the-art review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2020, 117, 100724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlin, M.; Ansell, H.; Moverare, J.J. Fatigue behaviour of notched additive manufactured Ti6Al4V with as-built surfaces. Int. J. Fatigue 2017, 101, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ås, S.K.; Skallerud, B.; Tveiten, B.W. Surface roughness characterization for fatigue life predictions using finite element analysis. Int. J. Fatigue 2008, 30, 2200–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, T.D.; Vanwalleghem, J.; Xiang, H.; Erdelyi, H.; Craeghs, T.; Van Paepegem, W. A unified approach to model the effect of porosity and high surface roughness on the fatigue properties of additively manufactured Ti6-Al4-V alloys. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 33, 101139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Jones, R.; Ang, A.S.M.; Champagne, V.; Birt, A.; Michelson, A. A Numerical Study into the Effect of Machining on the Interaction between Surface Roughness and Surface Breaking Defects on the Durability of WAAM Ti-6Al-4V Parts. Metals 2022, 12, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Jones, R.; Ang, A.S.M.; Michelson, A.; Champagne, V.; Birt, A.; Pinches, S.; Kundu, S.; Alankar, A.; Singh, R.R.K. Computing the durability of WAAM 18Ni 250 maraging steel specimens. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2022, 45, 3535–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suraratchai, M.; Limido, J.; Mabru, C.; Chieragatti, R. Modelling the influence of machined surface roughness on the fatigue life of aluminium alloy. Int. J. Fatigue 2008, 30, 2119–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuo, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Morokoshi, S.; Yagura, H.; Uchida, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Murakami, Y. Influence of defects, surface roughness and HIP on the fatigue strength of Ti-6Al-4V manufactured by additive manufacturing. Int. J. Fatigue 2018, 117, 163–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vayssette, B.; Saintier, N.; Brugger, C.; El May, M.; Pessard, E. Numerical modelling of surface roughness effect on the fatigue behavior of Ti-6Al-4V obtained by additive manufacturing. Int. J. Fatigue 2019, 123, 180–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirisu, P.; Supriyo, G.; Martina, F.; Xu, X.; Williams, S. Wire plus arc additive manufactured functional steel surfaces enhanced by rolling. Int. J. Fatigue 2020, 130, 105237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Li, Y.-J.; Yin, Z.-Q.; Chen, H. Determination of surface roughness in wire and arc additive manufacturing based on laser vision sensing. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2018, 31, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM-E466; Standard Practice for Conducting Force Controlled Constant Amplitude Axial Fatigue Tests of Metallic Materials. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018.
- Shamir, M. Fatigue Crack Initiation and Small Crack Propagation in Additive Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V. Ph.D. Thesis, Coventry University, Coventry, UK, 2022. Available online: https://ethos.bl.uk/OrderDetails.do?uin=uk.bl.ethos.857446 (accessed on 26 May 2023).
- Formtracer SV-C3200/4500 Series Hybrid Measuring Instrument for Surface. 2016. Available online: https://www.mitutoyo.com/webfoo/wp-content/uploads/2073_SV-C3200-4500.pdf (accessed on 3 July 2023).
- Kline, M. Calculus: An intuitive and Physical Approach, 2nd ed.; Courier Corporation: Chelmsford, MA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Pilkey, W.D.; Pilkey, D.F. Peterson’s Stress Concentration Factors, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; ISBN 9780470048245. [Google Scholar]
- Shamir, M.; Zhang, X.; Syed, A.K. Characterising and representing small crack growth in an additive manufactured titanium alloy. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2021, 253, 107876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, S. Chapter 15: Small fatigue cracks. In Fatigue of Materials; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Gong, M.; Luo, Z.; Li, Q.; Gao, M.; Wang, F.; Zeng, X.; Wang, G. Effect of microstructure on short fatigue crack growth of wire arc additive manufactured Ti-6Al-4V. Mater. Charact. 2021, 177, 104743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molent, L.; Jones, R. The influence of cyclic stress intensity threshold on fatigue life scatter. Int. J. Fatigue 2016, 82, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.; Raman, R.K.S.; Iliopoulos, A.P.; Michopoulos, J.G.; Phan, N.; Peng, D. Additively manufactured Ti-6Al-4V replacement parts for military aircraft. Int. J. Fatigue 2019, 124, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliopoulos, A.; Jones, R.; Michopoulos, J.; Phan, N.; Singh Raman, R. Crack growth in a range of additively Manufactured aerospace structural materials. Aerospace 2018, 5, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.; Molent, L.; Walker, K. Fatigue crack growth in a diverse range of materials. Int. J. Fatigue 2012, 40, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E647; Standard Test Method for Measurement of Fatigue Crack Growth Rates. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015.
- Jones, R.; Michopoulos, J.G.; Iliopoulos, A.P.; Singh Raman, R.K.; Phan, N.; Nguyen, T. Representing crack growth in additively manufactured Ti-6Al-4V. Int. J. Fatigue 2018, 116, 610–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R. Fatigue crack growth and damage tolerance. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2014, 37, 463–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Champagne, V.K.; Ang, A.S.; Birt, A.; Michelson, A.; Pinches, S.; Jones, R. Computing the Durability of WAAM 18Ni-250 Maraging Steel Specimens with Surface Breaking Porosity. Crystals 2023, 13, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.; Rans, C.; Iliopoulos, A.P.; Michopoulos, J.G.; Phan, N.; Peng, D. Modelling the variability and the anisotropic behaviour of crack growth in slm ti-6al-4v. Materials 2021, 14, 1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iliopoulos, A.P.; Jones, R.; Michopoulos, J.G.; Phan, N.; Rans, C. Further studies into crack growth in additively manufactured materials. Materials 2020, 13, 2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caton, M.J.; John, R.; Porter, W.J.; Burba, M.E. Stress ratio effects on small fatigue crack growth in Ti-6Al-4V. Int. J. Fatigue 2012, 38, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, R.O.; Boyce, B.L.; Campbell, J.P.; Roder, O.; Thompson, A.W.; Milligan, W.W. Thresholds for high-cycle fatigue in a turbine engine Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Int. J. Fatigue 1999, 21, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broek, D.; Rice, J.R. Chapter 3: The elastic crack-tip stress field. In Elementary Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 3rd ed.; Martinus Nijhoff: Hague, The Netherlands, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM E1820; Standard Test Method for Measurement of Fracture Toughness 1. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 1–65.
- Schijve, J. (Ed.) Chapter 12-Fatigue and Scatter BT—Fatigue of Structures and Materials; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Dowling, N.E. Stress-based approach to fatigue: Notched members. In Mechanical Behaviour of Materials, 4th ed.; Pearson: Harlow, UK, 2013; pp. 491–541. ISBN 9780131395060. [Google Scholar]
- Schijve, J. (Ed.) Stress Concentration at Notches BT—Fatigue of Structures and Materials; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 59–88. [Google Scholar]








| Current (A) | 210 |
| Torch stand-off (mm) | 8 |
| Torch travel Speed (m/min) | 3.5 |
| Wire feed speed (m/min) | 2.2 |
| Shielding gas (L/min) | 200 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shamir, M.; Zhang, X.; Syed, A.K.; Sadler, W. Predicting the Effect of Surface Waviness on Fatigue Life of a Wire + Arc Additive Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V Alloy. Materials 2023, 16, 5355. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16155355
Shamir M, Zhang X, Syed AK, Sadler W. Predicting the Effect of Surface Waviness on Fatigue Life of a Wire + Arc Additive Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V Alloy. Materials. 2023; 16(15):5355. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16155355
Chicago/Turabian StyleShamir, Muhammad, Xiang Zhang, Abdul Khadar Syed, and Wayne Sadler. 2023. "Predicting the Effect of Surface Waviness on Fatigue Life of a Wire + Arc Additive Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V Alloy" Materials 16, no. 15: 5355. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16155355
APA StyleShamir, M., Zhang, X., Syed, A. K., & Sadler, W. (2023). Predicting the Effect of Surface Waviness on Fatigue Life of a Wire + Arc Additive Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V Alloy. Materials, 16(15), 5355. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16155355






